400 — Bad Request (Некорректный запрос)
«Плохой запрос». Этот ответ означает, что сервер не понимает… Читать далее
Подробнее
401 — Unauthorized (Не авторизован)
«Неавторизовано». Для получения запрашиваемого ответа нужна … Читать далее
Подробнее
402 — Payment Required (Необходима оплата)
«Необходима оплата». Этот код ответа зарезервирован для буду… Читать далее
Подробнее
403 — Forbidden (Запрещено)
«Запрещено». У клиента нет прав доступа к содержимому, поэто… Читать далее
Подробнее
404 — Not Found (Не найдено)
«Не найден». Сервер не может найти запрашиваемый ресурс. Код… Читать далее
Подробнее
405 — Method Not Allowed (Метод не поддерживается)
«Метод не разрешен». Сервер знает о запрашиваемом методе, но… Читать далее
Подробнее
406 — Not Acceptable (Неприемлемо)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда веб сервер после выполнения ser… Читать далее
Подробнее
407 — Proxy Authentication Required (Необходима аутентификация прокси)
Этот код ответа аналогичен коду 401, только аутентификация т… Читать далее
Подробнее
408 — Request Timeout (Истекло время ожидания)
Ответ с таким кодом может прийти, даже без предшествующего з… Читать далее
Подробнее
409 — Conflict (Конфликт)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда запрос конфликтует с текущим со… Читать далее
Подробнее
410 — Gone (Удалён)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда запрашиваемый контент удален с … Читать далее
Подробнее
411 — Length Required (Необходима длина)
Запрос отклонен, потому что сервер требует указание заголовк… Читать далее
Подробнее
412 — Precondition Failed (Условие ложно)
Клиент указал в своих заголовках условия, которые сервер не … Читать далее
Подробнее
413 — Request Entity Too Large (Полезная нагрузка слишком велика)
Размер запроса превышает лимит, объявленный сервером. Сервер… Читать далее
Подробнее
414 — Request-URI Too Long (URI слишком длинный)
URI запрашиваемый клиентом слишком длинный для того, чтобы с… Читать далее
Подробнее
415 — Unsupported Media Type (Неподдерживаемый тип данных)
Медиа формат запрашиваемых данных не поддерживается сервером… Читать далее
Подробнее
416 — Requested Range Not Satisfiable (Диапазон не достижим)
Диапозон указанный заголовком запроса Range не может бы… Читать далее
Подробнее
417 — Expectation Failed (Ожидание не удалось)
Этот код ответа означает, что ожидание, полученное из заголо… Читать далее
Подробнее
418 — I’m a teapot (Я — чайник)
I’m a teapot — Этот код был введен в 1998 году как одна из т… Читать далее
Подробнее
419 — Authentication Timeout (not in RFC 2616) (Обычно ошибка проверки CSRF)
Authentication Timeout (not in RFC 2616) — Этого кода нет в … Читать далее
Подробнее
420 — Enhance Your Calm (Twitter) (Подождите немного (Твиттер))
Возвращается Twitter Search и Trends API, когда клиент отпра… Читать далее
Подробнее
421 — Misdirected Request (Неверный запрос)
Misdirected Request — запрос был перенаправлен на сервер, не… Читать далее
Подробнее
422 — Unprocessable Entity (Необрабатываемый экземпляр)
Запрос имел правильный формат, но его нельзя обработать из-з… Читать далее
Подробнее
423 — Locked (Заблокировано)
Целевой ресурс из запроса заблокирован от применения к нему … Читать далее
Подробнее
424 — Failed Dependency (Невыполненная зависимость)
Не удалось завершить запрос из-за ошибок к предыдущем запрос… Читать далее
Подробнее
425 — Too Early (Слишком рано)
Too Early — сервер не готов принять риски обработки «ранней … Читать далее
Подробнее
426 — Upgrade Required (Необходимо обновление)
Указание сервера, клиенту, обновить протокол. Заголовок отве… Читать далее
Подробнее
428 — Precondition Required (Необходимо предусловие)
Precondition Required — сервер указывает клиенту на необходи… Читать далее
Подробнее
429 — Too Many Requests (Слишком много запросов)
Too Many Requests — клиент попытался отправить слишком много… Читать далее
Подробнее
430 — Would Block (Будет заблокировано)
Код состояния 430 would Block — это код, который сервер мог … Читать далее
Подробнее
431 — Request Header Fields Too Large (Поля заголовка запроса слишком большие)
Request Header Fields Too Large — Превышена допустимая длина… Читать далее
Подробнее
434 — Requested host unavailable (Запрашиваемый адрес недоступен)
Сервер к которому вы обратились недоступен… Читать далее
Подробнее
444 — No Response (Nginx) (Нет ответа (Nginx))
Код ответа Nginx. Сервер не вернул информацию и закрыл соеди… Читать далее
Подробнее
449 — Retry With (Повторить с…)
Retry With — возвращается сервером, если для обработки запро… Читать далее
Подробнее
450 — Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft) (Заблокировано родительским контролем Windows (Microsoft))
Расширение Microsoft. Эта ошибка возникает, когда родительск… Читать далее
Подробнее
451 — Unavailable For Legal Reasons (Недоступно по юридическим причинам)
Unavailable For Legal Reasons — доступ к ресурсу закрыт по ю… Читать далее
Подробнее
499 — Client Closed Request (Клиент закрыл соединение)
Нестандартный код состояния, представленный nginx для случая… Читать далее
Подробнее
HTTP response status code 208 Already Reported is returned by the server in cases where a HTTP response has already been given with regard to a specific resource. A server opts for this to avoid repeating information about a resource, sometimes caused by multiple bindings. Constant reiteration is not only less efficient in terms of bandwidth, but if a resource loops back onto itself then it may cause an infinite loop error.
Usage
When the 208 Already Reported status code is received, the client will understand that it can refer to data that was previously supplied. Essentially, it is a shortcut taken to mean that the same resource with the same binding was already reported, so additional details will not be given a subsequent time.
Note
The 208 Already Reported status code is used by WebDAV to handle Binding Extensions. It will only occur in cases where the Depth: infinity request was made.
Example
In the example, the client received a 207 Multi-Status HTTP response status code from the server. This is in response to a PROPFIND request that was processed, where the resources are not fully independent. The /main/ resource has an element, /dependent, that uses the same resource as /main itself. The result is an infinite loop because the Depth: infinity specifier was part of the request. The loop is broken because the server recognizes that it has already been enumerated and when it comes across it the second time, does not delve into it and returns the 208 Already Reported status code.
Request
PROPFIND /main/ HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.ai
Depth: infinity
DAV: bind
Content-Type: application/xml; charset="utf-8"
Content-Length: 139
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<d:propfind xmlns:d="DAV:">
<d:prop>
<d:name/>
<d:link/>
</d:prop>
</d:propfind>
Response
HTTP/1.1 207 Multi-Status
Content-Type: application/xml; charset="utf-8"
Content-Length: 568
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<d:multistatus xmlns:d="DAV:">
<d:response>
<d:href>http://www.example.ai/main/</d:href>
<d:propstat>
<d:prop>
<d:name>Main Resource</d:name>
<d:resource-id>
<href>urn:uuid: 1234 … 0000</href>
</d:resource-id>
<d:status>HTTP/1.1 200 OK</d:status>
</d:prop>
</d:propstat>
</d:response>
<d:multistatus xmlns:d="DAV:">
<d:response>
<d:href>http://www.example.ai/main/dependent</d:href>
<d:propstat>
<d:prop>
<d:name>Main Resource</d:name>
<d:resource-id>
<href>urn:uuid: 1234 … 0000</href>
</d:resource-id>
<d:status>HTTP/1.1 208 Already Reported</d:status>
</d:prop>
</d:propstat>
</d:response>
</d:multistatus>
Code references
.NET
HttpStatusCode.AlreadyReported
Rust
http::StatusCode::ALREADY_REPORTED
Rails
:already_reported
Go
http.StatusAlreadyReported
Symfony
Response::HTTP_ALREADY_REPORTED
Python3.5+
http.HTTPStatus.ALREADY_REPORTED
Apache HttpComponents Core
org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpStatus.SC_ALREADY_REPORTED
Angular
@angular/common/http/HttpStatusCode.AlreadyReported
Takeaway
HTTP response status code 208 Already Reported is sent by a server to indicate that the specified resource has already been mentioned and that it will not be done a second time. This is to conserve bandwidth and to break infinite loops in some circumstances.
See also
- 207 Multi-Status
- RFC 5842
Last updated: June 29, 2022
400 — Bad Request (Некорректный запрос)
«Плохой запрос». Этот ответ означает, что сервер не понимает… Читать далее
Подробнее
401 — Unauthorized (Не авторизован)
«Неавторизовано». Для получения запрашиваемого ответа нужна … Читать далее
Подробнее
402 — Payment Required (Необходима оплата)
«Необходима оплата». Этот код ответа зарезервирован для буду… Читать далее
Подробнее
403 — Forbidden (Запрещено)
«Запрещено». У клиента нет прав доступа к содержимому, поэто… Читать далее
Подробнее
404 — Not Found (Не найдено)
«Не найден». Сервер не может найти запрашиваемый ресурс. Код… Читать далее
Подробнее
405 — Method Not Allowed (Метод не поддерживается)
«Метод не разрешен». Сервер знает о запрашиваемом методе, но… Читать далее
Подробнее
406 — Not Acceptable (Неприемлемо)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда веб сервер после выполнения ser… Читать далее
407 — Proxy Authentication Required (Необходима аутентификация прокси)
Этот код ответа аналогичен коду 401, только аутентификация т… Читать далее
Подробнее
408 — Request Timeout (Истекло время ожидания)
Ответ с таким кодом может прийти, даже без предшествующего з… Читать далее
Подробнее
409 — Conflict (Конфликт)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда запрос конфликтует с текущим со… Читать далее
Подробнее
410 — Gone (Удалён)
Этот ответ отсылается, когда запрашиваемый контент удален с … Читать далее
Подробнее
411 — Length Required (Необходима длина)
Запрос отклонен, потому что сервер требует указание заголовк… Читать далее
Подробнее
412 — Precondition Failed (Условие ложно)
Клиент указал в своих заголовках условия, которые сервер не … Читать далее
Подробнее
413 — Request Entity Too Large (Полезная нагрузка слишком велика)
Размер запроса превышает лимит, объявленный сервером. Сервер… Читать далее
414 — Request-URI Too Long (URI слишком длинный)
URI запрашиваемый клиентом слишком длинный для того, чтобы с… Читать далее
Подробнее
415 — Unsupported Media Type (Неподдерживаемый тип данных)
Медиа формат запрашиваемых данных не поддерживается сервером… Читать далее
Подробнее
416 — Requested Range Not Satisfiable (Диапазон не достижим)
Диапозон указанный заголовком запроса Range не может бы… Читать далее
Подробнее
417 — Expectation Failed (Ожидание не удалось)
Этот код ответа означает, что ожидание, полученное из заголо… Читать далее
Подробнее
418 — I’m a teapot (Я — чайник)
I’m a teapot — Этот код был введен в 1998 году как одна из т… Читать далее
Подробнее
419 — Authentication Timeout (not in RFC 2616) (Обычно ошибка проверки CSRF)
Authentication Timeout (not in RFC 2616) — Этого кода нет в … Читать далее
Подробнее
420 — Enhance Your Calm (Twitter) (Подождите немного (Твиттер))
Возвращается Twitter Search и Trends API, когда клиент отпра… Читать далее
421 — Misdirected Request (Неверный запрос)
Misdirected Request — запрос был перенаправлен на сервер, не… Читать далее
Подробнее
422 — Unprocessable Entity (Необрабатываемый экземпляр)
Запрос имел правильный формат, но его нельзя обработать из-з… Читать далее
Подробнее
423 — Locked (Заблокировано)
Целевой ресурс из запроса заблокирован от применения к нему … Читать далее
Подробнее
424 — Failed Dependency (Невыполненная зависимость)
Не удалось завершить запрос из-за ошибок к предыдущем запрос… Читать далее
Подробнее
425 — Too Early (Слишком рано)
Too Early — сервер не готов принять риски обработки «ранней … Читать далее
Подробнее
426 — Upgrade Required (Необходимо обновление)
Указание сервера, клиенту, обновить протокол. Заголовок отве… Читать далее
Подробнее
428 — Precondition Required (Необходимо предусловие)
Precondition Required — сервер указывает клиенту на необходи… Читать далее
429 — Too Many Requests (Слишком много запросов)
Too Many Requests — клиент попытался отправить слишком много… Читать далее
Подробнее
430 — Would Block (Будет заблокировано)
Код состояния 430 would Block — это код, который сервер мог … Читать далее
Подробнее
431 — Request Header Fields Too Large (Поля заголовка запроса слишком большие)
Request Header Fields Too Large — Превышена допустимая длина… Читать далее
Подробнее
434 — Requested host unavailable (Запрашиваемый адрес недоступен)
Сервер к которому вы обратились недоступен… Читать далее
Подробнее
444 — No Response (Nginx) (Нет ответа (Nginx))
Код ответа Nginx. Сервер не вернул информацию и закрыл соеди… Читать далее
Подробнее
449 — Retry With (Повторить с…)
Retry With — возвращается сервером, если для обработки запро… Читать далее
Подробнее
450 — Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft) (Заблокировано родительским контролем Windows (Microsoft))
Расширение Microsoft. Эта ошибка возникает, когда родительск… Читать далее
451 — Unavailable For Legal Reasons (Недоступно по юридическим причинам)
Unavailable For Legal Reasons — доступ к ресурсу закрыт по ю… Читать далее
Подробнее
499 — Client Closed Request (Клиент закрыл соединение)
Нестандартный код состояния, представленный nginx для случая… Читать далее
Подробнее
Skip to content
Тарков ошибка 208. Как исправить?
Escape from Tarkov — Ошибка 208. Что это значит и как исправить?
Код ошибки 208 — Не верный регион
Ошибка происходит из-за того, что игра запускается из региона, для которого она не предназначена. Т.е. если вы купили игру, например в СНГ, вы можете использовать ее только в этих рамках.
Всего для игры доступно 3 региона:
- Регион СНГ — разрешает запускать игру только в рамках СНГ
- Европа — разрешает запускать игру из любой точки мира. Можно улучшить свою версию предзаказа до Европейского региона на странице предзаказов, для этого нужно залогинится, после чего под вашим предзаказом появится кнопка, чтобы улучшить региона
- Другой регион — разрешает запускать игру везде, кроме Европейского региона. Также может называться как «США»
Как исправить ошибку 208 в Таркове?
- Проверьте, что у вас отключен VPN
- Если появляется ошибка 208, можно свой предзаказ улучшить до требуемого региона
В общем если вы путешественник, то вам нужно приобрести игру для Европейского региона, чтобы играть где вы хотите)
Related Posts
Page load link
Как исправить время выполнения Ошибка 208 Код ошибки Crystal Reports 208
В этой статье представлена ошибка с номером Ошибка 208, известная как Код ошибки Crystal Reports 208, описанная как Ошибка 208: Возникла ошибка в приложении Crystal Reports. Приложение будет закрыто. Приносим свои извинения за неудобства.
О программе Runtime Ошибка 208
Время выполнения Ошибка 208 происходит, когда Crystal Reports дает сбой или падает во время запуска, отсюда и название. Это не обязательно означает, что код был каким-то образом поврежден, просто он не сработал во время выполнения. Такая ошибка появляется на экране в виде раздражающего уведомления, если ее не устранить. Вот симптомы, причины и способы устранения проблемы.
Определения (Бета)
Здесь мы приводим некоторые определения слов, содержащихся в вашей ошибке, в попытке помочь вам понять вашу проблему. Эта работа продолжается, поэтому иногда мы можем неправильно определить слово, так что не стесняйтесь пропустить этот раздел!
- Crystal reports . Crystal Reports — это средство записи отчетов, которое работает как автономный дизайнер отчетов, интегрированная часть Visual Studio или часть пакета SAP Business Objects Enterprise.
- Код ошибки . Код ошибки — это значение, возвращаемое для предоставления контекста о причине возникновения ошибки.
- Отчеты — отчет содержит обобщенные информация из источника данных, обычно в удобном для конечного пользователя формате, таком как PDF или Excel, хотя также существуют проприетарные инструменты отчетности, обычно со встроенными инструментами проектирования.
- Crystal — Crystal Reports — это средство записи отчетов, которое работает как автономный дизайнер отчетов, интегрированная часть Visual Studio или часть пакета SAP Business Objects Enterprise.
Симптомы Ошибка 208 — Код ошибки Crystal Reports 208
Ошибки времени выполнения происходят без предупреждения. Сообщение об ошибке может появиться на экране при любом запуске %программы%. Фактически, сообщение об ошибке или другое диалоговое окно может появляться снова и снова, если не принять меры на ранней стадии.
Возможны случаи удаления файлов или появления новых файлов. Хотя этот симптом в основном связан с заражением вирусом, его можно отнести к симптомам ошибки времени выполнения, поскольку заражение вирусом является одной из причин ошибки времени выполнения. Пользователь также может столкнуться с внезапным падением скорости интернет-соединения, но, опять же, это не всегда так.
(Только для примера)
Причины Код ошибки Crystal Reports 208 — Ошибка 208
При разработке программного обеспечения программисты составляют код, предвидя возникновение ошибок. Однако идеальных проектов не бывает, поскольку ошибки можно ожидать даже при самом лучшем дизайне программы. Глюки могут произойти во время выполнения программы, если определенная ошибка не была обнаружена и устранена во время проектирования и тестирования.
Ошибки во время выполнения обычно вызваны несовместимостью программ, запущенных в одно и то же время. Они также могут возникать из-за проблем с памятью, плохого графического драйвера или заражения вирусом. Каким бы ни был случай, проблему необходимо решить немедленно, чтобы избежать дальнейших проблем. Ниже приведены способы устранения ошибки.
Методы исправления
Ошибки времени выполнения могут быть раздражающими и постоянными, но это не совсем безнадежно, существует возможность ремонта. Вот способы сделать это.
Если метод ремонта вам подошел, пожалуйста, нажмите кнопку upvote слева от ответа, это позволит другим пользователям узнать, какой метод ремонта на данный момент работает лучше всего.
Обратите внимание: ни ErrorVault.com, ни его авторы не несут ответственности за результаты действий, предпринятых при использовании любого из методов ремонта, перечисленных на этой странице — вы выполняете эти шаги на свой страх и риск.
Метод 1 — Закройте конфликтующие программы
Когда вы получаете ошибку во время выполнения, имейте в виду, что это происходит из-за программ, которые конфликтуют друг с другом. Первое, что вы можете сделать, чтобы решить проблему, — это остановить эти конфликтующие программы.
- Откройте диспетчер задач, одновременно нажав Ctrl-Alt-Del. Это позволит вам увидеть список запущенных в данный момент программ.
- Перейдите на вкладку «Процессы» и остановите программы одну за другой, выделив каждую программу и нажав кнопку «Завершить процесс».
- Вам нужно будет следить за тем, будет ли сообщение об ошибке появляться каждый раз при остановке процесса.
- Как только вы определите, какая программа вызывает ошибку, вы можете перейти к следующему этапу устранения неполадок, переустановив приложение.
Метод 2 — Обновите / переустановите конфликтующие программы
Использование панели управления
- В Windows 7 нажмите кнопку «Пуск», затем нажмите «Панель управления», затем «Удалить программу».
- В Windows 8 нажмите кнопку «Пуск», затем прокрутите вниз и нажмите «Дополнительные настройки», затем нажмите «Панель управления»> «Удалить программу».
- Для Windows 10 просто введите «Панель управления» в поле поиска и щелкните результат, затем нажмите «Удалить программу».
- В разделе «Программы и компоненты» щелкните проблемную программу и нажмите «Обновить» или «Удалить».
- Если вы выбрали обновление, вам просто нужно будет следовать подсказке, чтобы завершить процесс, однако, если вы выбрали «Удалить», вы будете следовать подсказке, чтобы удалить, а затем повторно загрузить или использовать установочный диск приложения для переустановки. программа.
Использование других методов
- В Windows 7 список всех установленных программ можно найти, нажав кнопку «Пуск» и наведя указатель мыши на список, отображаемый на вкладке. Вы можете увидеть в этом списке утилиту для удаления программы. Вы можете продолжить и удалить с помощью утилит, доступных на этой вкладке.
- В Windows 10 вы можете нажать «Пуск», затем «Настройка», а затем — «Приложения».
- Прокрутите вниз, чтобы увидеть список приложений и функций, установленных на вашем компьютере.
- Щелкните программу, которая вызывает ошибку времени выполнения, затем вы можете удалить ее или щелкнуть Дополнительные параметры, чтобы сбросить приложение.
Метод 3 — Обновите программу защиты от вирусов или загрузите и установите последнюю версию Центра обновления Windows.
Заражение вирусом, вызывающее ошибку выполнения на вашем компьютере, необходимо немедленно предотвратить, поместить в карантин или удалить. Убедитесь, что вы обновили свою антивирусную программу и выполнили тщательное сканирование компьютера или запустите Центр обновления Windows, чтобы получить последние определения вирусов и исправить их.
Метод 4 — Переустановите библиотеки времени выполнения
Вы можете получить сообщение об ошибке из-за обновления, такого как пакет MS Visual C ++, который может быть установлен неправильно или полностью. Что вы можете сделать, так это удалить текущий пакет и установить новую копию.
- Удалите пакет, выбрав «Программы и компоненты», найдите и выделите распространяемый пакет Microsoft Visual C ++.
- Нажмите «Удалить» в верхней части списка и, когда это будет сделано, перезагрузите компьютер.
- Загрузите последний распространяемый пакет от Microsoft и установите его.
Метод 5 — Запустить очистку диска
Вы также можете столкнуться с ошибкой выполнения из-за очень нехватки свободного места на вашем компьютере.
- Вам следует подумать о резервном копировании файлов и освобождении места на жестком диске.
- Вы также можете очистить кеш и перезагрузить компьютер.
- Вы также можете запустить очистку диска, открыть окно проводника и щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по основному каталогу (обычно это C
- Щелкните «Свойства», а затем — «Очистка диска».
Метод 6 — Переустановите графический драйвер
Если ошибка связана с плохим графическим драйвером, вы можете сделать следующее:
- Откройте диспетчер устройств и найдите драйвер видеокарты.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши драйвер видеокарты, затем нажмите «Удалить», затем перезагрузите компьютер.
Метод 7 — Ошибка выполнения, связанная с IE
Если полученная ошибка связана с Internet Explorer, вы можете сделать следующее:
- Сбросьте настройки браузера.
- В Windows 7 вы можете нажать «Пуск», перейти в «Панель управления» и нажать «Свойства обозревателя» слева. Затем вы можете перейти на вкладку «Дополнительно» и нажать кнопку «Сброс».
- Для Windows 8 и 10 вы можете нажать «Поиск» и ввести «Свойства обозревателя», затем перейти на вкладку «Дополнительно» и нажать «Сброс».
- Отключить отладку скриптов и уведомления об ошибках.
- В том же окне «Свойства обозревателя» можно перейти на вкладку «Дополнительно» и найти пункт «Отключить отладку сценария».
- Установите флажок в переключателе.
- Одновременно снимите флажок «Отображать уведомление о каждой ошибке сценария», затем нажмите «Применить» и «ОК», затем перезагрузите компьютер.
Если эти быстрые исправления не работают, вы всегда можете сделать резервную копию файлов и запустить восстановление на вашем компьютере. Однако вы можете сделать это позже, когда перечисленные здесь решения не сработают.
Другие языки:
How to fix Error 208 (Crystal Reports Error Code 208) — Error 208: Crystal Reports has encountered a problem and needs to close. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
Wie beheben Fehler 208 (Crystal Reports-Fehlercode 208) — Fehler 208: Crystal Reports hat ein Problem festgestellt und muss geschlossen werden. Wir entschuldigen uns für die Unannehmlichkeiten.
Come fissare Errore 208 (Crystal Reports Codice di errore 208) — Errore 208: Crystal Reports ha riscontrato un problema e deve essere chiuso. Ci scusiamo per l’inconveniente.
Hoe maak je Fout 208 (Crystal meldt foutcode 208) — Fout 208: Crystal Reports heeft een probleem ondervonden en moet worden afgesloten. Excuses voor het ongemak.
Comment réparer Erreur 208 (Crystal rapporte le code d’erreur 208) — Erreur 208 : Crystal Reports a rencontré un problème et doit fermer. Nous sommes désolés du dérangement.
어떻게 고치는 지 오류 208 (Crystal Reports 오류 코드 208) — 오류 208: Crystal Reports에 문제가 발생해 닫아야 합니다. 불편을 끼쳐드려 죄송합니다.
Como corrigir o Erro 208 (Crystal Reports Código de erro 208) — Erro 208: O Crystal Reports encontrou um problema e precisa fechar. Lamentamos o inconveniente.
Hur man åtgärdar Fel 208 (Crystal Reports Error Code 208) — Fel 208: Crystal Reports har stött på ett problem och måste avslutas. Vi är ledsna för besväret.
Jak naprawić Błąd 208 (Kod błędu raportów Crystal 208) — Błąd 208: Crystal Reports napotkał problem i musi zostać zamknięty. Przepraszamy za niedogodności.
Cómo arreglar Error 208 (Código de error 208 de Crystal Reports) — Error 208: Crystal Reports ha detectado un problema y debe cerrarse. Lamentamos las molestias.
Об авторе: Фил Харт является участником сообщества Microsoft с 2010 года. С текущим количеством баллов более 100 000 он внес более 3000 ответов на форумах Microsoft Support и создал почти 200 новых справочных статей в Technet Wiki.
Следуйте за нами:
Рекомендуемый инструмент для ремонта:
Этот инструмент восстановления может устранить такие распространенные проблемы компьютера, как синие экраны, сбои и замораживание, отсутствующие DLL-файлы, а также устранить повреждения от вредоносных программ/вирусов и многое другое путем замены поврежденных и отсутствующих системных файлов.
ШАГ 1:
Нажмите здесь, чтобы скачать и установите средство восстановления Windows.
ШАГ 2:
Нажмите на Start Scan и позвольте ему проанализировать ваше устройство.
ШАГ 3:
Нажмите на Repair All, чтобы устранить все обнаруженные проблемы.
СКАЧАТЬ СЕЙЧАС
Совместимость
Требования
1 Ghz CPU, 512 MB RAM, 40 GB HDD
Эта загрузка предлагает неограниченное бесплатное сканирование ПК с Windows. Полное восстановление системы начинается от $19,95.
ID статьи: ACX03527RU
Применяется к: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000
Совет по увеличению скорости #52
Преобразование диска FAT в NTFS:
Воспользуйтесь преимуществами мощной файловой системы NTFS, преобразовав FAT-диск вашего компьютера с Windows XP или Vista. Конвертировать легко, поскольку для этого не нужно форматировать диск. Помимо высокой производительности и улучшенных функций согласованности файлов, файловая система NTFS также выделяет надежную систему безопасности.
Нажмите здесь, чтобы узнать о другом способе ускорения работы ПК под управлением Windows
by Radu Tyrsina
Radu Tyrsina has been a Windows fan ever since he got his first PC, a Pentium III (a monster at that time). For most of the kids of… read more
Updated on March 14, 2022
- Many Windows 10 users reported that the SteamVR error 208 on HTC Vive prevents them from enjoying the VR experience.
- The error is triggered by outdated drivers, so be sure to update your graphics driver.
- You should reinstall your SteamVR USB devices, and check the HDMI connection.
- Enable a specific mode on your SteamVR by following our step-by-step guide below.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
This software will repair common computer errors, protect you from file loss, malware, hardware failure and optimize your PC for maximum performance. Fix PC issues and remove viruses now in 3 easy steps:
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
Some less fortunate HTC users have been having a harsh time trying to deal with a strange error that involves uninstalling VR drivers each time they give SteamVR a new boot.
Otherwise, they get a message on Windows 10 that says their HDMI is detected, but the monitor isn’t found.
Here’s how one user describes this issue:
Ok, so I recently purchased the HTC Vive and I did a complete reformat to make sure I get the best performance out of my rig. I went ahead and did all of my windows updates and NVidia updates to make sure I was up to date before resintalling steam. I got steam installed and updated, I installed VIVE for the first time and it seems to say the headset is not connected, I am getting the 208 error code […]
Why do I get the SteamVR error 108?
SteamVR is a virtual reality hardware and software platform developed by Valve for use with its Steam video game console. It is a tool for interacting with virtual reality material on the hardware of your choosing.
It is compatible with a wide range of virtual reality headsets, including the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, Valve Index, and Windows Mixed Reality headsets, amongst other models. Unfortunately, some users have reported that they have got the SteamVR error 108 while using the software.
You should have noticed the Vive Link Box, which is a critical component. A female HDMI port and a USB Type-A port are included, and it serves as the connection between your PC and the Vive VR headset.
As a result, in order to resolve HTC Vive problem 108, you should first ensure that the USB port on your PC is operational. You can also try connecting it to a different 2.0 USB port to see if it helps. This is due to the fact that some 3.0 and 3.1 USB ports are incompatible with the headset.
Once you have done that, move on to the following steps in order to put an end to the errors you are experiencing and enjoy the best possible VR experience on your Windows 10 PC.
How can I fix the HTC Vive error 208 on Windows 10?
- Update your graphics drivers
- Enable Direct Mode on SteamVR
- Select the beta version of SteamVR
- Reinstall your SteamVR USB devices
- Fresh Install SteamVR
- Push the HDMI all the way in
- Other general fixes
1. Update your graphics drivers
- Depending on your GPU, go to AMD or NVIDIA’s website and download the latest drivers.
- Restart your PC, and launch SteamVR to see if the problem persists.
Keeping your drivers updated is important if you want to ensure the maximum performance of your PC. We recommend you to install the latest drivers for your graphics card.
To make sure you don’t make any mistakes by choosing the wrong drivers for your needs, then you can use software that automatically does this for you.
This is where DriverFix comes into play. It is light and easy to use and provides all driver management features a PC user may need.
It can scan and update all your drivers in bulk, but you can also select any specific driver you want to take care of. You can set it up to regularly scan and update your drivers so you won’t have to worry about this issue in the future.
⇒ Get DriverFix
2. Enable Direct Mode on SteamVR
- Go to the Start menu, and launch Steam.
- Start SteamVR by clicking the VR button.
- Click the dropdown arrow, go to Settings, and select Developer.
- Make sure that Direct Mode is enabled, and restart your PC.
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to corrupted repositories or missing Windows files. If you are having troubles fixing an error, your system may be partially broken.
We recommend installing Restoro, a tool that will scan your machine and identify what the fault is.
Click here to download and start repairing.
Some users have reported that by enabling Direct Mode on SteamVR they no longer get the HTC Vive 208 error on Windows 10, so be sure to try it out.
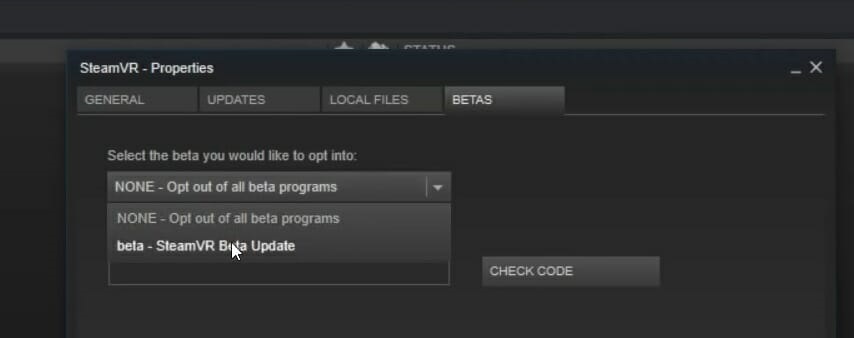
3. Select the beta version of SteamVR
- Launch Steam, go to Library, and select Tools.
- Right-click on SteamVR, and go to Properties.
- Click on the Betas tab, and navigate to Select the beta you would like to opt into.
- Select None, close the menu, and restart your PC.
Sometimes if you select the beta version of SteamVR, HTC Vive error 208 in Windows 10 also disappears, so follow the steps above to make sure you enjoy the VR experience.
Also, read our complete guide if SteamVR Home has stopped working and fix the error in no time.
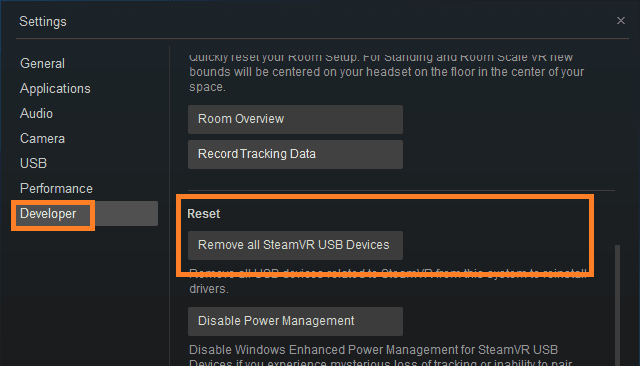
4. Reinstall your SteamVR USB devices
- Unplug all cables from your PC, and launch Steam.
- Open SteamVR, go to Settings, and select Developer.
- Click on Remove all SteamVR USB Device.
- Select Yes, and Continue.
- Restart your PC.
After the restart, you should plug the cables back in, but be sure to use a different port for your HDMI. Launch SteamVR and set up the device if required. Check for any improvements.
- Perform a SteamVR upgrade of the graphics driver in 3 steps
- Fix SteamVR error 306 in easy steps
- Full Fix: SteamVR error 436 Display connection trouble
5. Fresh install SteamVR
- Launch Steam, go to Library, and select Tools.
- Right–click on SteamVR, select Uninstall, and click Delete.
- Restart your PC, and follow the above steps again, but this time select Install.
Many WIndows 10 users have reported that uninstalling and reinstalling SteamVR helped them get rid of the HTC Vive 208 error.
Also, if you’re experiencing problems with the hybrid reality technology from Windows Mixed Reality, check out our detailed guide and get them fixed in no time.
6. Push the HDMI all the way in
- Unplug your HTC Vive‘s power source.
- Remove the cover of your headset.
- When you see the HDMI, easily push it until you feel it go all the way in.
- Plug in your Vive, and reconnect it to the PC.
Many HTC Vive users have this issue. It seems like some of them stumbled upon a solution that has a very good chance of success. Try it yourself by following the above steps.
It’s that simple. It seems like over time, while you play Steam VR games and move a lot, the HDMI cable can be only half-way plugged in, and you need to connect it properly.
7. Other general fixes
If HTC Vive error 208 on Windows 10 annoys you, and you still can’t seem to deal with it, then you need to know other general solutions that can help you in similar situations.
- Don’t keep your Vive connected to your Windows 10 PC. Plug in the headsets main power plug only after the computer starts.
- When the error appears, unplug the main power source of the Vive, wait a couple of seconds, and then re-plug it in.
- Plug the headset directly into your GPU, change the USB port, and then restart your computer.
Although the issue was addressed through some beta updates from SteamVR, it still persists on some systems. Try out some of our quick solutions to fix the problem in no time.
Also, check out our comprehensive guide if you’re having problems with VR on Windows 10 to quickly get rid of them with the best solutions.
If you’re aware of another workaround that solves the problem, please share your steps along with any other questions you may have in the comments section below.
Still having issues? Fix them with this tool:
SPONSORED
If the advices above haven’t solved your issue, your PC may experience deeper Windows problems. We recommend downloading this PC Repair tool (rated Great on TrustPilot.com) to easily address them. After installation, simply click the Start Scan button and then press on Repair All.
Newsletter
by Radu Tyrsina
Radu Tyrsina has been a Windows fan ever since he got his first PC, a Pentium III (a monster at that time). For most of the kids of… read more
Updated on March 14, 2022
- Many Windows 10 users reported that the SteamVR error 208 on HTC Vive prevents them from enjoying the VR experience.
- The error is triggered by outdated drivers, so be sure to update your graphics driver.
- You should reinstall your SteamVR USB devices, and check the HDMI connection.
- Enable a specific mode on your SteamVR by following our step-by-step guide below.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
This software will repair common computer errors, protect you from file loss, malware, hardware failure and optimize your PC for maximum performance. Fix PC issues and remove viruses now in 3 easy steps:
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
Some less fortunate HTC users have been having a harsh time trying to deal with a strange error that involves uninstalling VR drivers each time they give SteamVR a new boot.
Otherwise, they get a message on Windows 10 that says their HDMI is detected, but the monitor isn’t found.
Here’s how one user describes this issue:
Ok, so I recently purchased the HTC Vive and I did a complete reformat to make sure I get the best performance out of my rig. I went ahead and did all of my windows updates and NVidia updates to make sure I was up to date before resintalling steam. I got steam installed and updated, I installed VIVE for the first time and it seems to say the headset is not connected, I am getting the 208 error code […]
Why do I get the SteamVR error 108?
SteamVR is a virtual reality hardware and software platform developed by Valve for use with its Steam video game console. It is a tool for interacting with virtual reality material on the hardware of your choosing.
It is compatible with a wide range of virtual reality headsets, including the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, Valve Index, and Windows Mixed Reality headsets, amongst other models. Unfortunately, some users have reported that they have got the SteamVR error 108 while using the software.
You should have noticed the Vive Link Box, which is a critical component. A female HDMI port and a USB Type-A port are included, and it serves as the connection between your PC and the Vive VR headset.
As a result, in order to resolve HTC Vive problem 108, you should first ensure that the USB port on your PC is operational. You can also try connecting it to a different 2.0 USB port to see if it helps. This is due to the fact that some 3.0 and 3.1 USB ports are incompatible with the headset.
Once you have done that, move on to the following steps in order to put an end to the errors you are experiencing and enjoy the best possible VR experience on your Windows 10 PC.
How can I fix the HTC Vive error 208 on Windows 10?
- Update your graphics drivers
- Enable Direct Mode on SteamVR
- Select the beta version of SteamVR
- Reinstall your SteamVR USB devices
- Fresh Install SteamVR
- Push the HDMI all the way in
- Other general fixes
1. Update your graphics drivers
- Depending on your GPU, go to AMD or NVIDIA’s website and download the latest drivers.
- Restart your PC, and launch SteamVR to see if the problem persists.
Keeping your drivers updated is important if you want to ensure the maximum performance of your PC. We recommend you to install the latest drivers for your graphics card.
To make sure you don’t make any mistakes by choosing the wrong drivers for your needs, then you can use software that automatically does this for you.
This is where DriverFix comes into play. It is light and easy to use and provides all driver management features a PC user may need.
It can scan and update all your drivers in bulk, but you can also select any specific driver you want to take care of. You can set it up to regularly scan and update your drivers so you won’t have to worry about this issue in the future.
⇒ Get DriverFix
2. Enable Direct Mode on SteamVR
- Go to the Start menu, and launch Steam.
- Start SteamVR by clicking the VR button.
- Click the dropdown arrow, go to Settings, and select Developer.
- Make sure that Direct Mode is enabled, and restart your PC.
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to corrupted repositories or missing Windows files. If you are having troubles fixing an error, your system may be partially broken.
We recommend installing Restoro, a tool that will scan your machine and identify what the fault is.
Click here to download and start repairing.
Some users have reported that by enabling Direct Mode on SteamVR they no longer get the HTC Vive 208 error on Windows 10, so be sure to try it out.
3. Select the beta version of SteamVR
- Launch Steam, go to Library, and select Tools.
- Right-click on SteamVR, and go to Properties.
- Click on the Betas tab, and navigate to Select the beta you would like to opt into.
- Select None, close the menu, and restart your PC.
Sometimes if you select the beta version of SteamVR, HTC Vive error 208 in Windows 10 also disappears, so follow the steps above to make sure you enjoy the VR experience.
Also, read our complete guide if SteamVR Home has stopped working and fix the error in no time.
4. Reinstall your SteamVR USB devices
- Unplug all cables from your PC, and launch Steam.
- Open SteamVR, go to Settings, and select Developer.
- Click on Remove all SteamVR USB Device.
- Select Yes, and Continue.
- Restart your PC.
After the restart, you should plug the cables back in, but be sure to use a different port for your HDMI. Launch SteamVR and set up the device if required. Check for any improvements.
- Perform a SteamVR upgrade of the graphics driver in 3 steps
- Fix SteamVR error 306 in easy steps
- Full Fix: SteamVR error 436 Display connection trouble
5. Fresh install SteamVR
- Launch Steam, go to Library, and select Tools.
- Right–click on SteamVR, select Uninstall, and click Delete.
- Restart your PC, and follow the above steps again, but this time select Install.
Many WIndows 10 users have reported that uninstalling and reinstalling SteamVR helped them get rid of the HTC Vive 208 error.
Also, if you’re experiencing problems with the hybrid reality technology from Windows Mixed Reality, check out our detailed guide and get them fixed in no time.
6. Push the HDMI all the way in
- Unplug your HTC Vive‘s power source.
- Remove the cover of your headset.
- When you see the HDMI, easily push it until you feel it go all the way in.
- Plug in your Vive, and reconnect it to the PC.
Many HTC Vive users have this issue. It seems like some of them stumbled upon a solution that has a very good chance of success. Try it yourself by following the above steps.
It’s that simple. It seems like over time, while you play Steam VR games and move a lot, the HDMI cable can be only half-way plugged in, and you need to connect it properly.
7. Other general fixes
If HTC Vive error 208 on Windows 10 annoys you, and you still can’t seem to deal with it, then you need to know other general solutions that can help you in similar situations.
- Don’t keep your Vive connected to your Windows 10 PC. Plug in the headsets main power plug only after the computer starts.
- When the error appears, unplug the main power source of the Vive, wait a couple of seconds, and then re-plug it in.
- Plug the headset directly into your GPU, change the USB port, and then restart your computer.
Although the issue was addressed through some beta updates from SteamVR, it still persists on some systems. Try out some of our quick solutions to fix the problem in no time.
Also, check out our comprehensive guide if you’re having problems with VR on Windows 10 to quickly get rid of them with the best solutions.
If you’re aware of another workaround that solves the problem, please share your steps along with any other questions you may have in the comments section below.
Still having issues? Fix them with this tool:
SPONSORED
If the advices above haven’t solved your issue, your PC may experience deeper Windows problems. We recommend downloading this PC Repair tool (rated Great on TrustPilot.com) to easily address them. After installation, simply click the Start Scan button and then press on Repair All.
Newsletter

Как устранить 208?
Сброс ошибки для осуществляется следующим образом. Котлы Аристон в целом являются отличным вариантом, когда необходимо качество и по нормальной цене. Однако даже на таких устройствах бывают типичные неисправности. Во-первых в большинстве случаев это связано с перегревом оборудования. Для устранения необходимо убедиться в опытности мастера, устанавливающего дымоход и сам котел. Также следует хотя бы 1 раз в год проводить обслуживание. Во-вторых выход из строя контуров отопления, системы ГВС и розжига. Возникает по причине опять же неправильной установки. В третьих это выход из строя датчиков и плат управления. Причина в перепадах напряжения в сети или временных сбоях в прошивке.
Одна из самых разрекламированных игр 2022 года, Overwatch 2, наконец-то вышла. Однако запуск игры вызвал недовольство игроков, поскольку при ее выпуске они столкнулись с рядом проблем с сетью.
LC-208 — один из самых популярных кодов ошибок в названии. Пользователи сообщают, что они отключаются в середине игры с кодом ошибки LC-208, отображаемым на их экране после отключения.
Overwatch 2 – это игра-шутер от Blizzard Entertainment, которая является преемницей чрезвычайно популярной и любимой игры. Овервотч (2016). Это бесплатная игра с двумя командами по пять игроков в каждой, которые выбирают «Героев» с особыми способностями и способностями. Эти Герои разделены на классы — Поддержка, Танк и Боец — где каждый класс играет свою роль в игре.
В этой статье более подробно рассматривается код ошибки LC-208 и некоторые возможные исправления для него.
Все, что нужно знать игрокам о коде ошибки LC-208 в Overwatch 2
Ошибка LC-208 код не ограничивается конкретной системой. Это также может беспокоить владельцев игр на ПК, Xbox, PlayStation и Nintendo Switch. Эта ошибка возникает, когда игроки находятся в середине матча и внезапно отключаются, не имея возможности снова присоединиться к матчу.
Существует множество причин, по которым может возникнуть эта ошибка. Чаще всего это вообще проблема с игровыми серверами. Серверы Overwatch 2 подверглись массивной DDoS-атаке при запуске, в результате чего многие игроки не смогли получить доступ к игре или застряли в длинных очередях на несколько часов.
Более того, многие пользователи пытались получить доступ к игре в день ее запуска, что привело к серверы перегружены и запрещают вход игрокам.
Прежде чем приступить к возможным исправлениям, геймеров просят проверить, подключены ли игровые серверы к сети. К сожалению, если серверы отключены, пользователи не могут исправить это со своей стороны и должны будут ждать, пока они не заработают.
Возможные исправления ошибки LC-208 в Overwatch 2:
1) Обеспечьте что вы подключены к Интернету. Если вы используете Wi-Fi, убедитесь, что у вас хороший уровень сигнала. Рекомендуется использовать проводное соединение с помощью кабеля Ethernet или приблизиться к маршрутизатору, если уровень сигнала слабый. В крайнем случае попробуйте перезагрузить маршрутизатор/модем.
2) Если вы работаете именно на консоли, убедитесь, что ваш тип NAT не Strict/3/C. Это может сильно ограничить вас от игры с другими игроками. Если у вас строгий (Xbox), 3 (Playstation) или C (Switch) тип NAT, рекомендуется связаться с вашим интернет-провайдером и изменить тип NAT на Moderate/2/B, так как это безопасно и также позволяют подключаться к различным игровым серверам.
3) Это для игроков на ПК. На своем ПК откройте клиент Battle.net и перейдите на вкладку Overwatch 2. Здесь, рядом с кнопкой «Играть», будет значок «глобус». Нажмите на него и измените регион сервера на другой, отличный от выбранного в данный момент. Хотя это может не дать вам наилучшего игрового опыта, это должно позволить вам получить доступ к игре.
4) Пользователи PS5 могут в качестве альтернативы попробовать установить версии игры для PS4 и PS5 на свою систему. Наличие разных версий Overwatch 2 на консоли позволяет пользователям легко переключаться между ними. Игроки могут переключиться на другую, если одна версия игры не работает. Это обеспечит доступ к игре и позволит избежать ошибок при входе.
5) Наконец, убедитесь, что ваша учетная запись Battle.net подключена к консоли. Если нет, перейдите на страницу подключений на Battle.net и свяжите свои учетные записи. Если это уже сделано, попробуйте отменить связь, а затем снова связать их.
Хотя приведенные выше методы, вероятно, исправят ошибку LC-208, следует отметить, что это только возможные исправления, которые могут не работать на 100 % время. Игрокам следует рассмотреть возможность обращения в службу поддержки Blizzard за дополнительной помощью, если это не сработает.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet. [3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[34]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[35] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[36]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[37]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[38]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[38]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[39]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[40]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[41]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[42]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[43]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[44]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[45] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[46]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[47] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[48][49]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[50] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[51]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[52]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[53]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[54]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[55]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[55]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[55]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org