FTP server return codes always have three digits, and each digit has a special meaning.[1] The first digit denotes whether the response is good, bad or incomplete:
1xx
The requested action is being initiated; expect another reply before proceeding with a new command. (The user-process sending another command before the completion reply would be in violation of protocol; but server-FTP processes should queue any commands that arrive while a preceding command is in progress.) This type of reply can be used to indicate that the command was accepted and the user-process may now pay attention to the data connections, for implementations where simultaneous monitoring is difficult. The server-FTP process may send at most, one 1xx reply per command.
2xx
The requested action has been successfully completed. A new request may be initiated.
3xx
The command has been accepted, but the requested action is being held in abeyance, pending receipt of further information. The user should send another command specifying this information. This reply is used in command sequence groups.
4xx
The command was not accepted and the requested action did not take place, but the error condition is temporary and the action may be requested again. The user should return to the beginning of the command sequence, if any. It is difficult to assign a meaning to «transient», particularly when two distinct sites (Server- and User-processes) have to agree on the interpretation. Each reply in the 4xx category might have a slightly different time value, but the intent is that the user-process is encouraged to try again. A rule of thumb in determining if a reply fits into the 4xx or the 5xx (Permanent Negative) category is that replies are 4xx if the commands can be repeated without any change in command form or in properties of the User or Server (e.g., the command is spelled the same with the same arguments used; the user does not change his file access or user name; the server does not put up a new implementation.)
5xx
The command was not accepted and the requested action did not take place. The User-process is discouraged from repeating the exact request (in the same sequence). Even some «permanent» error conditions can be corrected, so the human user may want to direct his User-process to reinitiate the command sequence by direct action at some point in the future (e.g., after the spelling has been changed, or the user has altered his directory status.)
6xx
RFC 2228 introduced the concept of protected replies to increase security over FTP communications. The 6xx replies are Base64 encoded protected messages that serves as responses to secure commands. When properly decoded, these replies fall into the above categories.
Below is a list of all known return codes that may be issued by an FTP server.
100 Series
110
MARK yyyy = mmmm where yyyy is User-process data stream marker, and mmmm server’s equivalent marker (note the spaces between markers and «=»).
120
125
150
200 Series
202
211
212
213
214
215
220
221
225
226
227
228
229
230
232
234
235
250
257
300 Series
331
332
334
335
336
350
400 Series
421
425
426
430
431
434
450
451
452
500 Series
501
502
503
504
530
532
533
534
535
536
537
550
551
552
553
600 Series
631
632
633
10000 Series
10054
10060
10061
10065
10066
10068
THE INFORMATION IN THIS ARTICLE APPLIES TO:
- EFT Server all versions
- CuteFTP® all versions
DISCUSSION
During FTP sessions, servers send and receive various numbered codes to/from FTP clients. Some codes represent errors, most others simply communicate the status of the connection. Below are brief explanations for the most common status and error codes.
When determining a course of action, review the entire log; some codes are informational only, others indicate that you have entered the wrong information, and others indicate what the information is that you need to provide before continuing.
For troubleshooting CuteFTP connection problems, also refer to Troubleshooting CuteFTP Connection Problems.
The table below is provided so that you have some idea whether you can solve the issue on your own (e.g., code 331=you need to provide a password) or you need to call your ISP for assistance (e.g., code 426=you are unable to connect to the remote server). These codes are used by most FTP servers/clients.
NOTE: The information below is only offered as a courtesy to assist you in telling your Internet Service Provider what the error is so that they can help solve your issue. For example, if you get a code 426, the transfer was aborted and the connection closed. The solution to this error is to «try logging back in; contact your hosting provider to check if you need to increase your hosting account; try disabling the firewall on your PC to see if that solves the problem. If not, contact your hosting provider or ISP.»
The list below contains standard FTP codes. Numbers outside this list are proprietary to the Server or Client that you are using.
Click the code number in the left-most column of the table, if it’s linked (blue), to read a more-specific reason for the code.
| Code | Description | Discussion |
| 100 Series | The requested action was initiated; expect another reply before proceeding with a new command. | |
| 110 | Restart marker reply. |
The text is exact and not left to the particular implementation; it must read «MARK yyyy = mmmm» where yyyy is User-process data stream marker, and mmmm server’s equivalent marker (note the spaces between markers and «=»). |
| 120 | Service ready in nn minutes. | (Informational) |
| 125 | Data Connection already open; transfer starting. | (Informational) |
| 150 | File status okay; about to open data connection. | FTP uses two ports: 21 for sending commands, and 20 for sending data. A status code of 150 indicates that the server is about to open a new connection on port 20 to send some data. |
| 200 Series |
The requested action has been successfully completed. |
|
| 200 | Command okay. | (Informational) |
| 202 | Command not implemented, superfluous at this site. | (Informational) |
| 211 | System status, or system help reply. | (Informational) |
| 212 | Directory status. | (Informational) |
| 213 | File status. | (Informational) |
| 214 | Help message. | (Informational) |
| 215 | NAME system type. | Where NAME is an official system name from the list in the Assigned Numbers document. |
| 220 | Service ready for new user. | (Informational) |
| 221 | Service closing control connection. | Logged out if appropriate. |
| 225 | Data connection open; no transfer in progress. | (Informational) |
| 226 | Closing data connection. | Requested file action successful (for example; file transfer or file abort). The command opens a data connection on port 20 to perform an action, such as transferring a file. This action successfully completes, and the data connection is closed. |
| 227 | Entering Passive Mode. | (h1,h2,h3,h4,p1,p2) |
| 230 | User logged in, proceed. This status code appears after the client sends the correct password. It indicates that the user has successfully logged on. | (Informational) |
| 250 | Requested file action okay, completed. | (Informational) |
| 257 | «PATHNAME» created. | (Informational) |
| 300 Series | The command has been accepted, but the requested action is on hold, pending receipt of further information. | |
| 331 | User name okay, need password. | You see this status code after the client sends a user name, regardless of whether the user name that is provided is a valid account on the system. |
| 332 | Need account for login. | Provide login credentials |
| 350 | Requested file action pending further information. | (Informational) |
| 400 Series | The command was not accepted and the requested action did not take place, but the error condition is temporary and the action may be requested again. | |
| 421 |
Error 421 Service not available, closing control connection. Error 421 User limit reached Error 421 You are not authorized to make the connection Error 421 Max connections reached Error 421 Max connections exceeded |
This can be a reply to any command if the service knows it must shut down. Try logging in later. |
| 425 | Cannot open data connection. | Change from PASV to PORT mode, check your firewall settings, or try to connect via HTTP. |
| 426 | Connection closed; transfer aborted. |
The command opens a data connection to perform an action, but that action is canceled, and the data connection is closed. Try logging back in; contact your hosting provider to check if you need to increase your hosting account; try disabling the firewall on your PC to see if that solves the problem. If not, contact your hosting provider or ISP. |
| 450 | Requested file action not taken. | File unavailable (e.g., file busy). Try again later. |
| 451 | Requested action aborted: local error in processing. | Ensure command and parameters were typed correctly. |
| 452 | Requested action not taken. Insufficient storage space in system. | Ask FTP administrator to increase allotted storage space, or archive/delete remote files. |
|
500 Series |
The command was not accepted and the requested action did not take place. |
|
| 500 | Syntax error, command unrecognized, command line too long. | Try switching to passive mode. |
| 501 | Syntax error in parameters or arguments. | Verify your input; e.g., make sure there are no erroneous characters, spaces, etc. |
| 502 | Command not implemented. | The server does not support this command. |
| 503 | Bad sequence of commands. | Verify command sequence. |
| 504 | Command not implemented for that parameter. | Ensure entered parameters are correct. |
| 530 | User not logged in. | Ensure that you typed the correct user name and password combination. Some servers use this code instead of 421 when the user limit is reached |
| 532 | Need account for storing files. | Logged in user does not have permission to store files on remote server. |
| 550 | Requested action not taken. File unavailable, not found, not accessible | Verify that you are attempting to connect to the correct server/location. The administrator of the remote server must provide you with permission to connect via FTP. |
| 552 | Requested file action aborted. | Possible causes: Client aborted the action; EFT Site not running; storage allocation exceeded. |
| 553 | Requested action not taken. File name not allowed. | Change the file name or delete spaces/special characters in the file name. |
| 10,000 series | Common Winsock Error Codes (complete list of Winsock error codes) | |
| 10054 | Connection reset by peer. The connection was forcibly closed by the remote host. | (Informational) |
| 10060 | Cannot connect to remote server. | Generally a time-out error. Try switching from PASV to PORT mode, or try increasing the time-out value. |
| 10061 | Cannot connect to remote server. The connection is actively refused by the server. | Try switching the connection port. |
| 10066 | Directory not empty. |
The server will not delete this directory while there are files/folders in it. If you want to remove the directory, first archive or delete the files in it. |
| 10068 | Too many users, server is full. | Try logging in at another time. |
Share Article
On a scale of 1-5, please rate the helpfulness of this article
Optionally provide additional feedback to help us improve this article…
Thank you for your feedback!
Last Modified: 2 Months Ago
Last Modified By: kmarsh
Type: ERRMSG
Rated 2 stars based on 1189 votes.
Article has been viewed 897K times.
FTP server response codes are helpful for system administrators in charge of their company’s FTP server. Oftentimes, users might see these response codes listed in their favorite FTP client, such as FileZilla.
When troubleshooting a file transfer problem, it’s often helpful to identify the FTP response code that is being thrown around. It’s also important to ask what time of connection they’re using (ie FTP, SFTP or FTPS).
This guide will help you understand each element of the FTP server response code so you can get a better feel of what’s happening. It will also give you a full listing of each error code.
Shortcuts
1st Digit in the FTP Server Code 2nd Digit in the FTP Server Code 3rd Digit in the FTP Server Code Complete FTP Server Code Listing
FTP Server Response Codes: The First Digit
The first digit in the FTP server code lets you know whether or not the that step was successful. They also tell you what you should expect next. For instance, a 100 level code tells you that the process has started and to expect another code shortly.
| Range | Purpose |
|---|---|
1xx |
Positive Preliminary ReplyThe request is being initiated and you should expect another reply before proceeding with a new command. If a user sends another command before the reply completion the server-FTP process should queue the commands while this is in progress. This type of reply can indicate that the command was accepted and the user-process may now pay attention to the data connections, for implementations where simultaneous monitoring is difficult. The server-FTP process may send, at most, one 1xx reply per command. |
2xx |
Positive Completion ReplyThe request was successful. A new request may now be sent. |
3xx |
Positive Intermediate ReplyThe command was accepted but the request is being held in abeyance, pending the receipt of more information. The user should send another command with this information. This reply is used in command sequence groups. |
4xx |
Transient Negative Completion ReplyThe command wasn’t accepted and the request didn’t occur, but the error condition is temporary and the action may be resent. The user should return to the beginning of the command sequence, if any. A rule of thumb in determining if this reply belongs to the 4xx (Temporary Negative) or the 5xx (Permanent Negative) category is that replies are 4xx if the commands can be repeated without any change in command form or in properties of the User or Server. |
5xx |
Permanent Negative Completion ReplyThe command wasn’t accepted and the requested action didn’t occur. The User-process shouldn’t repeat the exact same request (in the same sequence). Some “permanent” error conditions can be fixed, so the human user may want to direct his User-process to reinitiate the command sequence by direct action (e.g., the user has changed his directory status.) |
6xx |
Protected ReplyThe RFC 2228 introduced the concept of protected replies to increase security over the FTP communications. The 6xx replies are Base64 encoded protected messages that serves as responses to secure commands. When decoded, these replies fall into the above categories. |
FTP Response Codes: The Second Digit
The second digit in the FTP server code lets you know what group or category the request belongs too. For instance, it tells you if it’s regarding connections or if it’s regarding authentication.
| Range | Purpose |
|---|---|
x0x |
SyntaxThese replies refer to syntax errors, syntactically correct commands that don’t fit any functional category, unimplemented or superfluous commands. |
x1x |
InformationReplies to requests for information, like help or support. |
x2x |
ConnectionsReplies regarding the control and data connections. |
x3x |
Authentication and accountingReplies for the login process and accounting procedures. |
x4x |
Unspecified as of RFC 959. |
x5x |
File systemIndicates the status of the Server file system vis-a-vis the requested transfer or other file system action. |
FTP Server Codes: The Third Digit
The third digit in the FTP serve code gives further explanation on what exactly is causing this code. Usually it’s the final piece of the puzzle.
Looking For a User-Friendly FTP Alternative?
Get our guide to a more secure and easier-to-use FTP replacement:
Get the Guide
FTP Server Codes: List of Error Codes
Here is a full list of known FTP server error codes:
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
100 Series |
The request has started, expect another reply before proceeding with a new command. |
110 |
Restart marker replay. In this case, the text is exact and not left to the particular implementation; it must read: MARK yyyy = mmmm where yyyy is User-process data stream marker, and mmmm server’s equivalent marker (note the spaces between markers and “=”). |
120 |
Service ready in xx minutes. |
125 |
Data connection is already open and the transfer is starting. |
150 |
File status is okay and about to open data connection. |
200 Series |
The request was successfully completed. |
202 |
Command was not implemented, superfluous at this site. |
211 |
System status, or system help reply. |
212 |
Directory status. |
213 |
File status. |
214 |
Help message. On how to use the server or the meaning of a particular non-standard command. |
215 |
NAME system type. Where NAME is an official system name from the registry kept by IANA. |
220 |
Service is ready for new user. |
221 |
Service closing control connection. |
225 |
Data connection is open and no transfer is in progress. |
226 |
Closing the data connection. Requested file action successful (for example, file transfer or file abort). |
227 |
Entering Passive Mode (h1, h2, h3, h4, p1, p2). |
228 |
Entering Long Passive Mode (long address, port). |
229 |
Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||port|). |
230 |
User has logged in, proceed. Logged out if appropriate. |
231 |
User has logged out and the service is terminated. |
232 |
Logout command noted, will complete when the transfer done. |
234 |
Specifies that the server accepts the authentication mechanism specified by the client, and the exchange of security data is complete. A higher level nonstandard code created by Microsoft. |
250 |
Requested file action okay and completed. |
257 |
“PATHNAME” created. |
300 Series |
The command was accepted, but the request is on hold, pending receipt of further information. |
331 |
User name okay, need password. |
332 |
Need account for login. |
350 |
Requested file action pending further information |
400 Series |
The command wasn’t accepted and the requested action didn’t occur, but the error condition is temporary and the action may be requested again. |
421 |
Service not available, closing control connection. This may be a reply to any command if the service knows it must shut down. |
425 |
Can’t open data connection. |
426 |
Connection closed; transfer aborted. |
430 |
Invalid username or password. |
434 |
Requested host unavailable. |
450 |
Requested file action not taken. |
451 |
Requested action aborted. Local error in processing. |
452 |
Requested action not taken. Insufficient storage space in system.File unavailable (e.g., file busy). |
500 Series |
Syntax error, command unrecognized and the request did not take place. This may include errors such as command line too long. |
501 |
Syntax error in parameters or arguments. |
502 |
Command not implemented. |
503 |
Bad sequence of commands. |
504 |
Command not implemented for that parameter. |
530 |
Not logged in. |
532 |
Need account for storing files. |
550 |
Request not taken. File unavailable (e.g., file not found, no access). |
551 |
Request aborted. Page type unknown. |
552 |
Requested file action aborted. Exceeded storage allocation (for current directory or dataset). |
553 |
Requested action not taken. File name not allowed. |
600 Series |
Replies regarding confidentiality and integrity |
631 |
Integrity protected reply. |
632 |
Confidentiality and integrity protected reply. |
633 |
Confidentiality protected reply. |
10000 Series |
Common Winsock Error Codes |
10054 |
Connection reset by peer. The connection was forcibly closed by the remote host. |
10060 |
Cannot connect to remote server. |
10061 |
Cannot connect to remote server. The connection is actively refused by the server. |
10066 |
Directory not empty. |
10068 |
Too many users, server is full. |
Looking for an FTP Alternative? Get Our Full Guide!

Learn the 5 Ways FTP Fails You (Security, Scripting, etc…)
Identify Things to Look for in an FTP Alternative (Accessibility, Scalability, etc…)
Discover Available Alternatives that Make Your Job Easier
Sources: SmartFile’s I.T. Personnel, Wikipedia
Иногда случаются проблемы с подключением по FTP. Для того, чтобы оперативно решить такую задачу, необходимо выполнить диагностические меры, описанные ниже.
Проверка режима FTP
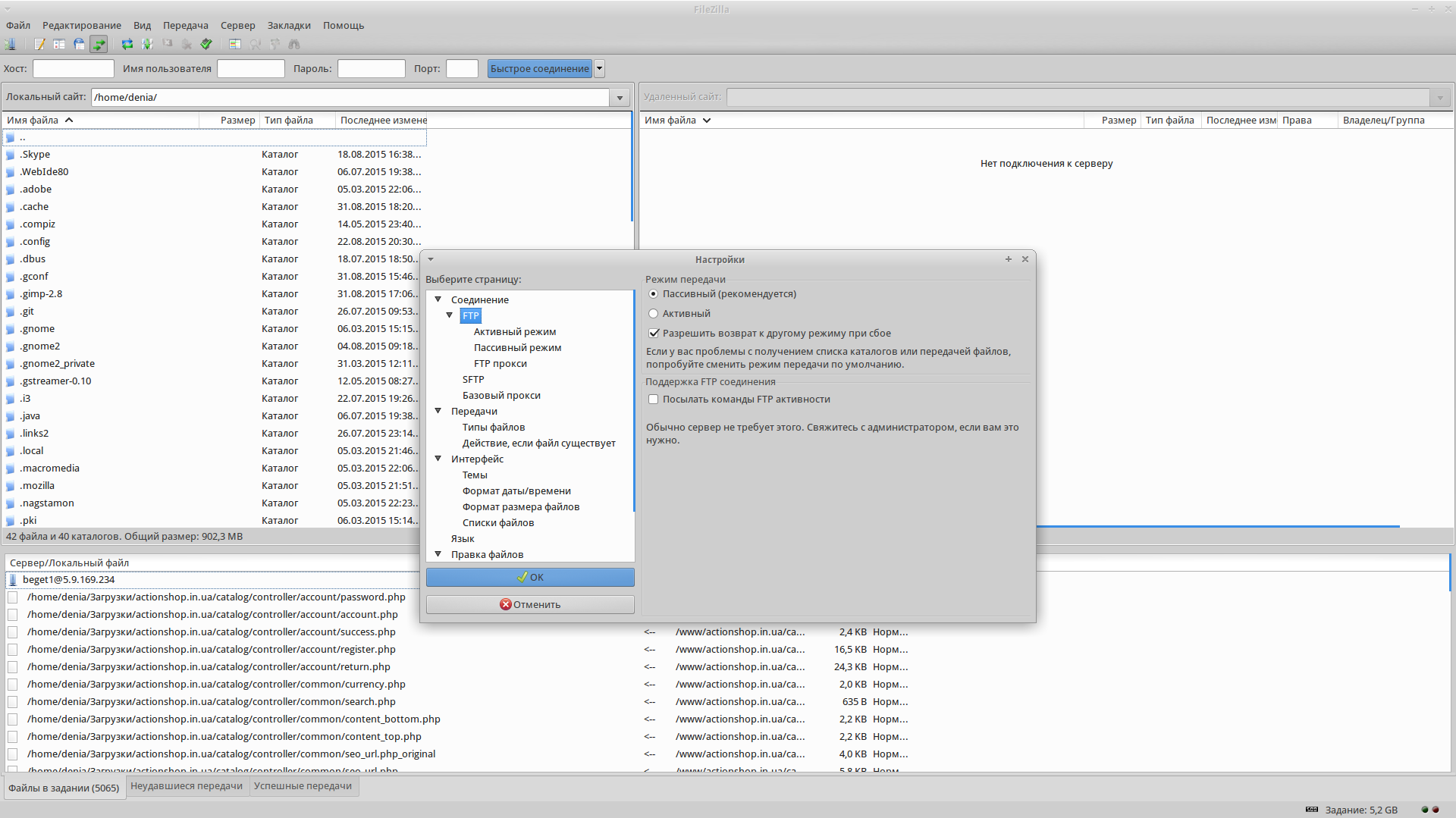
Первым делом стоит проверить, какой режим FTP используется. Рекомендуется использовать Пассивный, к примеру в клиенте Filezilla это настраивается во вкладке Редактирование -> Настройки -> FTP
Если изначально режим используется пассивный, то стоит проверить, не блокирует ли соединение локальный брендмауер (фаервол) или антивирус. Для этого банально отключаем поочередно брендмауер и антивирус и подключаемся еще раз. Если проблема осталась актуальной, то проведём диагностику подключения.
Для начала, проверим подключение к серверу через утилиту telnet, в качестве имени сервера указываем название, которое можно посмотреть в личном кабинете в разделе FTP (в нашем случае — это matrix.beget.com).
telnet matrix.beget.com 21Если все в порядке, то должно будет появиться приглашение сервера, что-то вроде этого:
Connected to matrix.beget.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 Welcome to LTD Beget FTP Server 'matrix'Ошибка Unable to connect to remote host: Connection refused
Означает, что FTP-клиент не может соединиться с сервером. Обычно ошибка выглядит примерно так:
Trying 81.222.215.42...
telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection refusedКак правило, здесь имеют место быть три причины:
- блокировка ftp-подключения брандмауэром (файерволом) или антивирусом Вашего компьютера;
- блокировка вашего внешнего ip-адреса на нашем сервере;
- проблемы на стороне промежуточных узлов (между нашим сервером и вашим компьютером).
Чтобы попробовать определить на каком узле происходит обрыв, нужно сделать трассировку маршрута командой traceroute:
В Mac OS X команда будет выглядеть так:
traceroute matrix.beget.comДолжно появиться примерно следующее:
1 192.168.2.1 (192.168.2.1) 0.253 ms 0.245 ms 0.231 ms
2 beget-i.cust.smartspb.net (80.79.241.141) 0.516 ms 0.511 ms 0.504 ms
3 k12-lak.ra.smartspb.net (185.42.63.18) 0.756 ms 0.753 ms 0.747 ms
4 beget.spb.cloud-ix.net (31.28.18.90) 1.386 ms 1.366 ms 1.371 ms
5 m1.matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64) 1.367 ms 1.357 ms 1.362 msТакже стоит пропинговать хост утилитой ping:
ping matrix.beget.com -n 10Должно появиться примерно следующее:
PING matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from m1.matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64): icmp_seq=1 ttl=60 time=1.44 ms
64 bytes from m1.matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64): icmp_seq=2 ttl=60 time=1.44 ms
64 bytes from m1.matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64): icmp_seq=3 ttl=60 time=1.52 ms
64 bytes from m1.matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64): icmp_seq=4 ttl=60 time=1.23 ms
64 bytes from m1.matrix.beget.com (5.101.156.64): icmp_seq=5 ttl=60 time=1.56 ms
--- matrix.beget.com ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4006ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 1.231/1.441/1.562/0.124 msВозможно проблема связана с тем, что Ваш внешний IP-адрес заблокирован на сервере, для проверки идем на сайт http://myip.ru/, он отобразит Ваш внешний IP-адрес. Его нужно сообщить технической поддержке, чтобы специалисты проверили, не заблокирован ли указанный IP-адрес на сервере, к которому идет подключение. Лучше всего обратиться, написав тикет из Личного кабинета (раздел «Связь» или «Помощь и поддержка»). В тикете необходимо предоставить вывод команд ping, tracert (traceroute) и внешний IP-адрес, который Вы узнали на сайте http://myip.ru/. Не лишним будет указать также данные, с которыми Вы пытаетесь подключиться, так как зачастую ошибка в подключении кроется в неверно вводимых данных: логин, пароль, имя сервера.
Ошибка 530 Login incorrect
Очень распространённая ошибка «Login incorrect«. В журнале FTP-клиентов она выглядит примерно так:
220 Welcome to LTD Beget FTP Server 'matrix'
USER username
331 Please specify the password.
PASS *******
530 Login incorrect.Означает эта ошибка то, что передаваемые логин, пароль или сервер ошибочные. В этом случае перепроверьте правильность введённых данных и исправьте ошибку.
Удачной работы! Если возникнут вопросы — напишите нам, пожалуйста, тикет из Панели управления аккаунта, раздел «Помощь и поддержка».
Table Of Contents
FTP Server Messages
FTP Server Messages
121 Bye noted, will logout when transfer completes
125 Transfer started
150 Dataset opened; data connection starting.
150- Data transfer type is type. Structure is struct. Mode is mode.
150- Dataset name: dsname Dataset attributes: Dsorg=dsorg Recfm=recfm
150- Lrecl=lrecl Blksize=blksize Volser=volser Unit=unit
150- Primary allocation is tracks1 tracks. Secondary allocation is tracks2 tracks.
150- Network data which exceeds LRECL will be wrapped to the next record.
200 Note: Ignored, overridden by site space
200 OK, Ready
200- % Free Free Largest Free
202 ACCT not needed, ignored
211 —Status—
211 <End of Status>
214 —HELP—
214 <end of HELP>
215 MVS is the operating system of this server
220 Enter USER command with userid operand
220 Logged out, parms reset, enter USER command and ID
220 Logged out, parms retained, enter USER command
220 sitename FTP Server, Enter command or HELP
221 Session terminated
226 Abort command completed
226 Empty file transfer complete — 0 (zero) data bytes sent
226 Transfer complete
226- Transfer complete. number bytes sent/received in secs seconds (rate bytes/s)
226 Transfer complete (unique file name: filename)
230- Logged in — User=user Working directory «dir»
250 Deleted OK
250 Renamed OK
250 File action OK
250 Data will be written to NULLFILE
250 dsname deleted.
257 prefix
257 No prefix defined
257 «‘pathname'» partitioned dataset is current directory
257 «‘pathname'» partitioned dataset created with attributes:
331 Enter PASS command
331 Logged out, parms retained, enter PASS command
331 Logged out, parms reset, enter PASS command
332 Enter ACCT command
350 Requested file action pending further information
421 Operator forced logout
422 Host network software error, incomplete
425 Unable to open connection
426 Data connection closed. Transfer incomplete
426 Data transfer aborted
426 Data transfer aborted. Ready
426 Data transfer timeout, aborted
426 Invalid RDW length detected on input file. Transfer incomplete
450 All access paths to volume busy
450 Data set tied up by another user
450 No path to volume
450 OBTAIN FAILED FOR oper PROCESSING
450 function FUNCTION FAILED RETURN CODE = nn =QNAME = qname
RNAME = dsname[_membername] LEN = lll function FAILED FOR oper PROCESSING
451 Aborting transfer, network block header invalid
451 Aborting transfer, network block header invalid
451 Character translation failed, transfer incomplete
451 Data set cannot be opened
451 Host software error
451 HSM recall wait time expired, request cancelled
451 I/O error detected in data set
451 I/O error in data set, transfer incomplete
451 Magnetic tape volume cannot be mounted
451 Network interface module not available
451 Open/mount of tape data set failed; rtn=rrrrrrrr
451 Request cancelled by operator
451 Requested magnetic tape unit(s) not available
451 Tape mount wait time expired; request cancelled
451 Transfer aborted. Error during I/O processing. System code is xxx-rc
451 Transfer aborted. I/O error detected. SYNAD data is
jobname, stepname, unit, type, ddname, operation, error, address, BSAM.
451 Transfer completed abnormally. Completion code is Sxxx
451 Transfer completed abnormally, Completion code is Uxxxx
451 I/O error while updating PDS directory. Directory is possible full
451 Transfer incomplete due to system error
451 VTOC full
451 System error in locating data set, R1=xxxxxxxx
451 Transfer aborted. Transport error detected,
RTNCD=XXYYZZZZ. See Messages and Codes Reference for API Return Codes.
452 No core to execute operation now
452 No core to interpret command now
500 Command exceeds 82 characters, ignored
500 Command unrecognized
500 Empty line, ignored
500 Excessive operands or ending parenthesis not found
500 Ending quote not found
500 Invalid delimiter syntax
500- Unable to recall DCBDSN dcbdsn_name.
500- Unable to locate DCBDSN dcbdsn_name.
500- DCBDSN data set dcbdsn_name is not on DASD.
500- The DCBDSN data set name is too long.
500- parameter parameter is unrecognized.
500- parameter keyword has an invalid subparameter value.
500- EXPDT cannot be specified with RETPD
500- RETPD cannot be specified with EXPDT
500- The maximum length of the parameter parameter is length characters.
500- The keyword keyword requires at least one subparameter.
500 SITE command was accepted with errors.
501 Invalid or conflicting parameters, command ignored
501 Invalid value on RECFM keyword
501 MOUNT waittime set to system configured maximum
501 Padding value should be Z (zeroes), O (ones), or B (blanks)
501 Parameter value not in correct numerical range
501 Requested tape label option is not permitted by system.
501 Required operand or keyword value not found
501 SITE CHARSET/DECSSET command failed to load table. Command not implemented
501 SITE RECALL command specified an invalid value of 0 for HSM wait time
501 Wildcard characters are not permitted within a partitioned dataset name
501 Member name not permitted; MVS does not support subdirectories
501 Wildcard characters (* and %) may only be specified in last qualifier in directory mode
502 Command not implemented
502 Data set list functions not implemented, use TSO command LISTCAT or LISTDS
502 HSM is not configured to system. Command not implemented
502 Tape processing is not configured. Command not implemented.
502 Unimplemented MODE type C, command ignored
503 Abort ignored, no data transfer in progress
503 APPE/REST not implemented for Magnetic Tape datasets.
503 Command conflicts with previous commands
503 Command unexpected after ALLO, ignored
503 Command unexpected at this point, refused
503 Expected RNTO, RNFR ignored
503 Expected STOR, APPE, or RETR, REST ignored
503 Login required, enter USER
503 Unable to logout until data transfer completes
503 SUBMIT requires STOR command, ignored
504 Not implemented for that parameter, ignored
504 Option not implemented
504 Unsupported combination of TYPE and STRU
504 Restart requires BLOCK mode
520 Network connection open error
520 Storage shortage, causes TOPEN Failure
521 «‘pathname'» already exists
530 Invalid userid or password, try again
530 Login required, enter USER
530 Password expired, next time try: PASS current-password/new-password
530 Invalid new password, next time try: PASS current-password/new-password
530 FAILED ACCOUNTING EXIT
530 Bad system security option
530 No external security system is active
530 Password is not authorized for this userid
530 Password was omitted
530 User access has been revoked
530 User access to the group has been revoked
530 User logon rejected by installation exit routine
530 User is not authorized to this application
530 User is not authorized to this terminal
530 Userid is not defined to the security system
530 User is not defined to the group
530 Userid matches userid of TCP address space
550 Bad member name or generation index specified
550 Catalog structure invalid or user lacks authority to catalog
550 Data set not found
550 Dataset medium is tape; request cannot be performed.
550 Error occurred during directory update, directory NOT updated
550 File access denied
550 File cannot be accessed. HSM SVC is not supported by installation.
550 File cannot be deleted. SCRATCH failed or expiration date not reached.
550 File not accessed. A volume must be mounted, and mount is not permitted.
550 File not accessed. Migrated file requires SITE RECALL command
550 New member name bad, format — DSN(OLDMEM) (NEWMEM)
550 No multi-volume data sets
550 Rename failed (New name already exists in directory)
550 Rename failed (PDS DIRECTORY IS FULL)
550 Rename failed (RNTO base name is invalid)
550 Rename failed (RNTO name CANNOT contain member name)
550 Rename failed (RNFR data set not found)
550 Rename failed (RNTO data set exists in catalog already)
550 Rename failed (RNFR data set OBTAIN error)
550 Rename failed (RNTO/RNFR CATLG error)
550 Rename failed (RNTO name contained an invalid generation)
550 Not a partitioned dataset. Use DELE to delete
550 Partitioned dataset contains members
550 No matching datasets or members were found
550 MKD failed. DCBDSN data set dcbdsn_name is invalid for a PDS.
550 Unable to create unique data set name for STOU
550 No matching entries were found entries
552 Insufficient space on volume. Transfer terminated
552 Unable to continue data transfer, data set full
553 Bad data set name syntax
553 Operation failed — data set cataloged on another volume
553 Operation failed — SITE command implies DISP=NEW — data set already exists
554 Illegal RECFM in data set
554 LRECL or BLKSIZE invalid or inconsistent
554 Old data set not replaced, DSORG different
554 SITE LRECL, BLKSIZE, or RECFM do not match those of existing data set
554 RETRieve of a whole PDS is not permitted
FTP Server Messages
This chapter explains the causes of the messages issued by the FTP Server and suggests appropriate responses.
FTP Server Messages
Messages are presented in numerical order.
121 Bye noted, will logout when transfer completes
Explanation The user requests logoff from the host, and when the current file transfer completes, the logoff is processed.
125 Transfer started
Explanation The file transfer is started.
150 Dataset opened; data connection starting.
150- Data transfer type is type. Structure is struct. Mode is mode.
150- Dataset name: dsname Dataset attributes: Dsorg=dsorg Recfm=recfm
150- Lrecl=lrecl Blksize=blksize Volser=volser Unit=unit
150- Primary allocation is tracks1 tracks. Secondary allocation is tracks2 tracks.
150- Network data which exceeds LRECL will be wrapped to the next record.
Explanation This is a multi-line server message produced during data transfer. The 150 message provides information about the file being transferred and about the settings associated with the data transfer.
This table shows the fields in this 150 message:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
type |
Describe the settings associated with the data transfer. Read the FTP chapters of the Cisco IOS for S/390 User’s Guide for details about these settings. |
|
dsname |
Indicates the data set being transferred. |
|
lrecl |
Indicates the value for each field. These fields relate to the data set being transferred in the dsname field. |
200 Note: Ignored, overridden by site space
Explanation The space allocation information supplied by the user is ignored because the space allocation was previously specified in a SITE command.
200 OK, Ready
Explanation FTP is ready for command processing.
200- % Free Free Largest Free
Explanation This reply is issued by the FTP server in response to the SITE QDISK command. It provides information on DASD devices.
202 ACCT not needed, ignored
Explanation The accounting information supplied by the user is unnecessary and is ignored.
211 —Status—
Explanation This message marks the beginning of the listing from the STAT command.
211 <End of Status>
Explanation This message marks the end of the listing from the STAT command.
214 —HELP—
Explanation This message marks the beginning of the listing from the HELP command.
214 <end of HELP>
Explanation This message marks the end of the listing from the HELP command.
215 MVS is the operating system of this server
Explanation This reply is issued by the FTP server in response to the SYST command. It identifies the operating system on which the server resides.
220 Enter USER command with userid operand
Explanation This message directs the user to supply a user command and user ID.
220 Logged out, parms reset, enter USER command and ID
Explanation The user ID for logon to either Host A or Host B is logged off the host. The values for BYTE, ALLO, TYPE, STRU, and MODE parameters are reset to the defaults.
220 Logged out, parms retained, enter USER command
Explanation The user ID for logon to either Host A or Host B is logged off the host. The values for BYTE, ALLO, TYPE, STRU, and MODE parameters are saved.
220 sitename FTP Server, Enter command or HELP
Explanation The FTP server process at site sitename is ready to accept commands.
221 Session terminated
Explanation The command connection either to Host A or to Host B is closed.
226 Abort command completed
Explanation The abort command issued successfully aborted the file transfer.
226 Empty file transfer complete — 0 (zero) data bytes sent
Explanation The file transfer completes successfully, and the disk file of the retrieving host is closed. However, the file contains zero data bytes.
226 Transfer complete
Explanation The file transfer completes successfully, and the disk file of the receiving host is closed.
226- Transfer complete. number bytes sent/received in secs seconds (rate bytes/s)
Explanation The FTP server produces a multi-line 226 response after a successful data transfer. Within the 226 response, statistics about the data transfer are reported back to the user. The following multi-line 226 response read data from an MVS data set and sent it across the network.
Transfer complete. 3439 bytes sent in 2.49 seconds (1381 bytes/s) Path FILE.NAME User UID Data bytes sent 6480 Disk tracks read 1 226
These are the fields in this 226 message:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
numbers |
Statistics about bytes transferred across the network and the rate of transfer per second. |
|
dsname |
Name of the data set read from disk and transferred over the network. |
|
user |
Indicates that user ID UID initiated the file transfer. |
|
numwritten |
Total number of data bytes read from disk for dsname. |
|
tracks |
Total number of disk tracks read. |
If the file transfer had been read from the network and written to a file on MVS, a multi-line 226 response might look like this:
226-Transfer complete 19 bytes received in 8.00 seconds (2 bytes/s) Dataset name: MVS.TEMP.DATA User UID Data bytes received 17 Disk tracks written 1 Records padded 1 226
This message is similar to the previous multi-line 226 response, except the data transfer is from the network to be stored on an MVS data set.
Depending on the file attributes of the file being written to, certain events will happen to records as they are placed into a file. Some messages that might appear in this 226 response are:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Records padded n |
Indicates the total number of records that had pad characters inserted at the end to accommodate the file structure. |
|
Records truncated n |
Indicates the total number of records truncated because the record sent was larger than the record size for the file. |
|
Records folded n |
Indicates the total number of records broken into multiple records because the record sent was larger than the record size for the file. |
|
Records suspect n |
Indicates total number of records shipped in block mode by the sending side that may contain suspect data (i.e., the data sent is suspected of errors and is not reliable). |
226 Transfer complete (unique file name: filename)
Explanation If SUNIQUE filename was specified, this message reflects the remote host’s unique file name.
230- Logged in — User=user Working directory «dir»
Explanation The user user is logged in with working directory dir. The IP address of the FTP server is address.
250 Deleted OK
Explanation The specified file is deleted successfully.
250 Renamed OK
Explanation The specified file is renamed successfully.
250 File action OK
Explanation The file action is performed successfully.
250 Data will be written to NULLFILE
Explanation This reply is issued by the FTP server when a change directory (CD/CWD) command is received with a path name of *DEV.NULL. Subsequent data transfers which cause data to be written to the file system by the FTP server will be written to a dummy data set (NULLFILE). To reverse this, enter another change directory command, specifying a different path name.
250 dsname deleted.
Explanation This reply is issued by the FTP server in response to the DELE command. It identifies the data set which has been successfully deleted.
257 prefix
Explanation prefix is the current default prefix for the user.
257 No prefix defined
Explanation There is no default prefix defined.
257 «‘pathname‘» partitioned dataset is current directory
Explanation The partitioned data set ‘pathname‘ is the working directory.
257 «‘pathname‘» partitioned dataset created with attributes:
Explanation A partitioned data set was created in response to a MKD command. The file attributes follow.
331 Enter PASS command
Explanation The user is directed to enter a password command and password.
331 Logged out, parms retained, enter PASS command
Explanation The user is logged out, and the values for BYTE, ALLO, TYPE, STRU, and MODE parameters are saved.
331 Logged out, parms reset, enter PASS command
Explanation The user is logged out, and the values for BYTE, ALLO, TYPE, STRU, and MODE parameters are not saved.
332 Enter ACCT command
Explanation The user is directed to enter an accounting command and accounting information.
350 Requested file action pending further information
Explanation This is an interim reply indicating the completion of a part of a multi-part request. For instance, a RNFR (ReName FRom) command has been received, and the server is awaiting a RNTO (ReName TO) command.
421 Operator forced logout
Explanation A privileged user in DDNMVSOP mode (the operator control mode of OPEN-Link for IBM/MVS) cancels the FTP session.
422 Host network software error, incomplete
Explanation FTP processing is incomplete because a software error was encountered in the host network’s software.
425 Unable to open connection
Explanation The connection could not be opened.
426 Data connection closed. Transfer incomplete
Explanation File transfer is incomplete because the data connection between hosts is lost.
426 Data transfer aborted
Explanation The file transfer operation aborts.
426 Data transfer aborted. Ready
Explanation The file transfer aborts and FTP is ready for further user commands.
426 Data transfer timeout, aborted
Explanation The DATAIDLE time specified for FTP expired before the last receive request completed. The transfer aborts.
426 Invalid RDW length detected on input file. Transfer incomplete
Explanation File transfer is incomplete because input file is variable blocked and an invalid record descriptor word (RDW) length value was detected.
450 All access paths to volume busy
Explanation No access paths are available to write a file to or read a file from the device (volume).
450 Data set tied up by another user
Explanation Another user has exclusive control of the data set to be processed by FTP. Generally, the other user issued a PUT command to the data set causing an enqueue for exclusive control. Cisco IOS for S/390 provides resource serialization on the data set level, which has certain consequences for partitioned data sets. In particular, only one user at a time can access a data set for the purpose of storing data. If one FTP user is attempting to store a member into a partitioned data set, other users are prevented from accessing the same data set, even if the access is for a different member. However, multiple users can simultaneously retrieve members from the same partitioned data set because retrieve operations do not require exclusive control.
450 No path to volume
Explanation The operating system cannot access the device (volume) from which a file is to be read or to which a file is to be written.
450 OBTAIN FAILED FOR oper PROCESSING
Explanation This message is sent when the VTOC information cannot be retrieved.
The type of operation being processed to the PDS (oper) can be one of the following:
|
DELETE |
Delete a member. |
|
RENAME |
Rename a member. |
450 function FUNCTION FAILED RETURN CODE = nn =QNAME = qname
RNAME = dsname[_membername] LEN = lll function FAILED FOR oper PROCESSING
Explanation The type of MVS function being attempted for this operation (oper), where function can be one of the following:
|
ENQUEUE |
Enqueue a resource to the MVS system. |
|
DEQUEUE |
Dequeue a resource from the MVS system. |
|
RESERVE |
Reserve the disk volume where the PDS resides. |
The return code generated by the above MVS function (nn) is in hexadecimal. The return codes for the MVS function are described in the IBM Application Development Reference documentation set.
The name of the queue (queue) can be one of these:
|
SPFEDIT |
Used for text, source, or object data set. |
|
SYSIEWLP |
Used for load module data set. |
The DSNAME of the PDS is represented by (dsname); The name of the PDS member to be processed is represented by membername; the length of the RNAME field, in decimal, is represented by lll. The length of dsname is 44; if membername is included, the length of the RNAME field will be 52.
The type of operation being processed to the PDS (oper) can be one of the following:
|
DELETE |
Delete a member. |
|
RENAME |
Rename member. |
|
STOR |
Store a member. |
This message is sent when the PDS member is tied up by another user.
451 Aborting transfer, network block header invalid
Explanation A block mode (Mode B) file transfer was in progress and a block header received contained invalid data in the flag field of the header.
451 Aborting transfer, network block header invalid
Explanation A block mode (Mode B) file transfer was in progress and a block header received contained invalid data in the flag field of the header. This may be caused by the sender not being in Mode B.
451 Character translation failed, transfer incomplete
Explanation An attempt to load a single or double byte character set translation table failed.
451 Data set cannot be opened
Explanation The file to be processed by FTP cannot be opened for reading or writing.
451 Host software error
Explanation A host software error occurs, causing abnormal termination of the requested action.
451 HSM recall wait time expired, request cancelled
Explanation An HSM recall of a migrated file does not occur within a specified amount of time. The request is cancelled.
Recommended Action Verify system default parameters with system programmer or issue a SITE RECALL command to increase default wait time.
451 I/O error detected in data set
Explanation The file being read or written contains an I/O error.
451 I/O error in data set, transfer incomplete
Explanation The file being written at the receiving host or read from the sending host contains an I/O error. The file transfer terminates abnormally.
451 Magnetic tape volume cannot be mounted
Explanation The requested data set is currently allocated to another user, or otherwise cannot be mounted at this time.
Recommended Action Retry the FTP transfer later, or contact the tape librarian or operator for an explanation, as appropriate.
451 Network interface module not available
Explanation One of the modules required to initiate or complete the file transfer was missing at the time of execution of the command.
451 Open/mount of tape data set failed; rtn=rrrrrrrr
Explanation An attempt to mount and open a data set on magnetic tape failed. The return code is rrrrrrrr.
451 Request cancelled by operator
Explanation A request to mount a tape was cancelled by the operator. The request is cancelled.
Recommended Action Retry the FTP transfer later, or contact the tape librarian or operator for an explanation, as appropriate.
451 Requested magnetic tape unit(s) not available
Explanation Either all tape units of the type requested are currently off-line or allocated to other users, or a PARALLELMOUNT or UNITCOUNT parameter has requested more units than are currently available.
Recommended Action Retry the FTP transfer when device(s) are available.
451 Tape mount wait time expired; request cancelled
Explanation The wait time specified in the configuration or on a SITE command for a tape mount has expired. The request is cancelled.
Recommended Action Retry the FTP transfer later, or contact the tape librarian or operator for an explanation, as appropriate.
451 Transfer aborted. Error during I/O processing. System code is xxx—rc
Explanation During either End-of-Volume (EOV) or close processing, the data management DCB ABEND exit was driven. An ABEND would have occurred had the exit not suppressed the ABEND. The file transfer is terminated. The system code of the suppressed ABEND is represented by xxx; The reason code of the suppressed ABEND is represented by rc.
Recommended Action Check the appropriate MVS manuals to identify the cause of the ABEND using the ABEND code xxx and the reason code rc. If the ABEND is issued during EOV processing due to insufficient space in the data set, make sure sufficient space exists in the data set or on the volume before restarting the file transfer. Certain close ABENDs such as the B14 occur when there is insufficient room in either the PDS directory or PDS data areas. After correcting the condition causing the ABEND, restart the file transfer.
451 Transfer aborted. I/O error detected. SYNAD data is
jobname, stepname, unit, type, ddname, operation, error, address, BSAM.
Explanation During the CHECK of either a READ or WRITE macro, the synchronous error exit was driven. This exit extracted the error data listed in line two of the error via the SYNADF macro. The file transfer was terminated.
Recommended Action Attempt to diagnose the error using data provided by SYNADF. If possible, correct it and restart the data transfer. If the error is a wrong length record condition, it is likely that there is a record in the data set that exceeds the data set’s block size. If this is the case, either delete the record or PDS member or change the attributes of the data set to have a larger block size.
451 Transfer completed abnormally. Completion code is Sxxx
Explanation An ABEND with the specified system ABEND code (xxx) occurred during the file transfer. The file transfer did not complete.
Recommended Action If the ABEND is due to an I/O error condition such as end of volume or data set close, correct the data management problem that caused the error and retry the file transfer. If the ABEND is of a programmatic nature, contact Customer Support.
451 Transfer completed abnormally, Completion code is Uxxxx
Explanation Either the data transfer PTASK PABENDed with the specified user code (xxx) or the data transfer task PEXITed with the specified return code (xxx). Module FTPSFTDR could not match the code with a list of known exit codes and cannot determine whether the file transfer was successful. It is assumed that the file transfer failed.
Recommended Action Contact your Customer Support for assistance in diagnosing the cause of this message.
451 I/O error while updating PDS directory. Directory is possible full
Explanation A CLOSE macro was issued after writing a member of a partitioned data set and an ABEND SB14 occurred indicating an I/O error occurred while updating the PDS directory. This condition is accompanied by MVS system message IEC217 B14-xx which explains in detail the reason IOS issued the SB14 ABEND. This error usually occurs when there is no room left in a PDS directory.
451 Transfer incomplete due to system error
Explanation A host system error occurred during file transfer. The file transfer halts abnormally before completion.
451 VTOC full
Explanation The table of contents on the volume (VTOC) to which a file is to be written is full and can accept no more entries.
451 System error in locating data set, R1=xxxxxxxx
Explanation The host system had a problem with the allocation. Other IBM SVC99 messages may follow if SMS is coded on the GLOBAL statement in the APPCFGxx member. These messages are in the IBM documentation, MVS/ESA Vx System Messages Volume 1-5, GC28-1656 through GC28-1660. The value xxxxxxxx is the dynamic allocation (SVC99) return code.
451 Transfer aborted. Transport error detected,
RTNCD=XXYYZZZZ. See Messages and Codes Reference for API Return Codes.
Explanation This message indicates that the FTP transfer has aborted. The XX of RTNCD is the recovery action codes; YY is the specific error code; ZZZZ is the diagnostic and Sense codes.
Recommended Action Refer to the API Return Codes for a complete explanation of RTNCD.
452 No core to execute operation now
Explanation No memory is available on the host attempting to execute the FTP command.
452 No core to interpret command now
Explanation No memory is available on the host attempting to interpret the FTP command.
500 Command exceeds 82 characters, ignored
Explanation The entered command exceeds the maximum length of 82 characters.
500 Command unrecognized
Explanation The FTP software does not recognize the entered command.
500 Empty line, ignored
Explanation An empty command line is entered and FTP ignored it.
500 Excessive operands or ending parenthesis not found
Explanation Excessive operands found for a valid keyword or a parenthesis is missing from the command line.
500 Ending quote not found
Explanation The ending quote expected at the end of the FTP command is not entered.
500 Invalid delimiter syntax
Explanation Delimiter entered is unrecognizable or invalid.
500- Unable to recall DCBDSN dcbdsn_name.
Explanation A SITE DCBDSN command was received, but the model data set is migrated and cannot be recalled (possibly because NORECALL was specified in the FTP configuration, or by a previous SITE command).
Recommended Action If possible, recall the data set. Otherwise, change the DCBDSN data set name.
500- Unable to locate DCBDSN dcbdsn_name.
Explanation A SITE DCBDSN command was received, but the model data set cannot be found.
Recommended Action Change the DCBDSN data set name to the name of a cataloged data set.
500- DCBDSN data set dcbdsn_name is not on DASD.
Explanation A SITE DCBDSN command was received, but the model data set does not reside on a direct access device.
Recommended Action Change the DCBDSN data set name to the name of a cataloged data set on a DASD device.
500- The DCBDSN data set name is too long.
Explanation A SITE command was received which specified the DCBDSN parameter, but the data set name specified (when appended to the current prefix) exceeds 44 characters.
Recommended Action Check the data set name specified. If it is a fully-qualified data set name, enclose it in single quotes.
500- parameter parameter is unrecognized.
Explanation A SITE command was received which specified an unknown parameter.
Recommended Action Read the Cisco IOS for S/390 User’s Guide for a list of SITE parameters and syntax.
500- parameter keyword has an invalid subparameter value.
Explanation A SITE command was received which contained a keyword parameter specifying an invalid value for one or more subparameters.
Recommended Action Read the Cisco IOS for S/390 User’s Guide for a list of SITE parameters and syntax.
500- EXPDT cannot be specified with RETPD
Explanation A SITE command was received which contained the EXPDT parameter, but the RETPD had been previously specified. EXPDT and RETPD are mutually exclusive. The EXPDT parameter is ignored.
Recommended Action Use SITE RESET to remove the RETPD value before specifying EXPDT.
500- RETPD cannot be specified with EXPDT
Explanation A SITE command was received which contained the RETPD parameter, but the EXPDT had been previously specified. EXPDT and RETPD are mutually exclusive. The RETPD parameter is ignored.
Recommended Action Use SITE RESET to remove the EXPDT value before specifying RETPD.
500- The maximum length of the parameter parameter is length characters.
Recommended Action A SITE command was received that contained a keyword parameter which specified an over-long subparameter
Recommended Action Read the Cisco IOS for S/390 User’s Guide for a list of SITE parameters and syntax.
500- The keyword keyword requires at least one subparameter.
Explanation A SITE command was received that contained a keyword parameter which requires a subparameter, but no subparameter was specified.
Recommended Action Read the Cisco IOS for S/390 User’s Guide for a list of SITE parameters and syntax.
500 SITE command was accepted with errors.
Explanation Indicates that one or more errors were detected in the SITE command.
This message is preceded by one or more 500 replies. Refer to accompanying messages to determine appropriate action.
501 Invalid or conflicting parameters, command ignored
Explanation Invalid or conflicting parameters are specified in the command.
501 Invalid value on RECFM keyword
Explanation The record format value entered in the SITE RECFM record format is invalid.
501 MOUNT waittime set to system configured maximum
Explanation A MOUNT request specified a greater value than the maximum wait time allowed by the system configuration.
501 Padding value should be Z (zeroes), O (ones), or B (blanks)
Explanation A char value other than Z, O, or B is specified in the SITE PAD char command.
501 Parameter value not in correct numerical range
Explanation A parameter value specified in the command line has a value outside its valid numeric range.
501 Requested tape label option is not permitted by system.
Explanation A SITE command specified BLP or NL where that LABEL option is not allowed by the system configuration.
501 Required operand or keyword value not found
Explanation A required operand or keyword is omitted from the command.
501 SITE CHARSET/DECSSET command failed to load table. Command not implemented
Explanation An attempt to load a single or double byte character set translation table failed.
501 SITE RECALL command specified an invalid value of 0 for HSM wait time
Explanation An invalid value of zero (0) is specified on the SITE RECALL command.
Recommended Action Reissue SITE RECALL command with a value of 1-1439.
501 Wildcard characters are not permitted within a partitioned dataset name
Explanation Wildcard characters (‘*’) are not permitted within the data set name of a partitioned data set.
501 Member name not permitted; MVS does not support subdirectories
Explanation An MKD command was received specifying a directory name within the current PDS directory.
501 Wildcard characters (* and %) may only be specified in last qualifier in directory mode
Explanation A LIST or NLST command was received in directory mode and the path name specified a wildcard pattern character (* or %) in a qualifier other than the last qualifier. In directory mode, only the final qualifier can contain wildcard characters.
Recommended Action Change the path name or enter data set mode.
502 Command not implemented
Explanation The requested facility is not implemented on the host, and the command cannot be performed.
502 Data set list functions not implemented, use TSO command LISTCAT or LISTDS
Explanation The FTP functions that list data set information have not been implemented on the host. The user should use the LISTCAT and LISTDS TSO commands.
502 HSM is not configured to system. Command not implemented
Explanation A SITE RECALL command is issued, but HSM is not defined to the system.
Recommended Action Verify ACFSFTP macro parameter HSM is not NORECALL. Edit APPCFGxx with HSM defined to FTP.
502 Tape processing is not configured. Command not implemented.
Explanation A SITE command was received to modify a parameter for tape, but tape processing has been disallowed by the system administrator.
502 Unimplemented MODE type C, command ignored
Explanation Mode type compress (C) is not supported by the FTP Server.
503 Abort ignored, no data transfer in progress
Explanation The ABORT command is ignored because no file transfer was in progress when it was issued.
503 APPE/REST not implemented for Magnetic Tape datasets.
Explanation A RESTART or APPEND was attempted for a data set on magnetic tape. These commands are not supported for magnetic tape.
503 Command conflicts with previous commands
Explanation The entered command does not logically follow previous commands and cannot be processed.
503 Command unexpected after ALLO, ignored
Explanation The entered command is unacceptable because it is entered after the ALLO function for the specified file.
503 Command unexpected at this point, refused
Explanation The entered command is unacceptable at this time and is refused.
503 Expected RNTO, RNFR ignored
Explanation The entered RENAME command is invalid.
503 Expected STOR, APPE, or RETR, REST ignored
Explanation The RESTART command is ignored because the STORE, RETRIEVE, or APPEND command was expected.
503 Login required, enter USER
Explanation The message directs the user to supply user ID information to the host system.
503 Unable to logout until data transfer completes
Explanation Logoff from the host cannot be processed until the current file transfer completes.
503 SUBMIT requires STOR command, ignored
Explanation The command entered is not acceptable because a PUT command cannot be accepted after a SITE SUBMIT.
504 Not implemented for that parameter, ignored
Explanation A parameter used on the preceding command is not implemented on the specified host system.
504 Option not implemented
Explanation The requested processing option is not implemented on the specified host.
504 Unsupported combination of TYPE and STRU
Explanation The specified file TYPE/STRUcture combination is not supported by FTP.
504 Restart requires BLOCK mode
Explanation BLOCK mode must be specified for a restart.
520 Network connection open error
Explanation The CONN command request cannot be completed successfully; the open for the remote host connection fails.
520 Storage shortage, causes TOPEN Failure
Explanation Server FTP cannot create a data connection due to an SOS failure during the TOPEN for the data connection session.
Recommended Action Ensure that sufficient storage is available for the Cisco IOS for S/390 address space.
521 «‘pathname‘» already exists
Explanation A MKD command attempted to create a partitioned data set ‘pathname’, but a cataloged data set already exists by that name.
530 Invalid userid or password, try again
Explanation An invalid user ID or password has been entered.
530 Login required, enter USER
Explanation The user is directed to supply a user ID to the host system.
530 Password expired, next time try: PASS current-password/new-password
Explanation The user’s password has expired. The user should update the password as shown.
530 Invalid new password, next time try: PASS current-password/new-password
Explanation The user’s new password is invalid. Re-enter a new password as shown.
530 FAILED ACCOUNTING EXIT
Explanation Accounting exit ACEXIT00 rejected the sign-on attempt. ACEXIT00 is a local exit under control of the Cisco IOS for S/390 System Administrator. Read the Cisco IOS for S/390 Customization Guide for more information about ACEXIT00. The account was probably entered incorrectly.
Recommended Action Retry the sign-on with a valid user ID/password/account combination. Contact your local Cisco IOS for S/390 System Administrator if the problem persists.
530 Bad system security option
Explanation A bad parameter list was passed to the external security system (ACF2, RACF, or Top Secret). The signon fails.
Recommended Action Contact your Cisco IOS for S/390 support personnel.
530 No external security system is active
Explanation A signon was attempted and the external security system (ACF2, RACF, or Top Secret) has become inactive.
Recommended Action Contact your local external security System Administrator.
530 Password is not authorized for this userid
Explanation A signon was attempted with an invalid password. The password was probably entered incorrectly.
Recommended Action Retry the signon with a valid user ID/password combination.
530 Password was omitted
Explanation A signon was attempted without a password.
Recommended Action Retry the signon with a valid user ID/password combination.
530 User access has been revoked
Explanation A signon attempt was rejected because your external security system (ACF2, RACF, or Top secret) has revoked your user ID.
Recommended Action Contact your local external security Cisco IOS for S/390 System Administrator.
530 User access to the group has been revoked
Explanation A signon attempt was rejected because your external security system (ACF2, RACF, or Top Secret) has revoked your user ID access to the group you are attempting to sign on with.
Recommended Action Contact your local external security System Administrator.
530 User logon rejected by installation exit routine
Explanation A signon attempt was rejected by a local installation security exit.
Recommended Action Contact your local external security System Administrator.
530 User is not authorized to this application
Explanation A signon attempt failed due to application security by your external security system (ACF2, RACF, or Top Secret).
Recommended Action Contact your local external security System Administrator.
530 User is not authorized to this terminal
Explanation A signon attempt failed due to terminal security by your external security system (ACF2, RACF, or Top Secret).
Recommended Action Contact your local external security System Administrator.
530 Userid is not defined to the security system
Explanation A signon was attempted using an unknown user ID. The user ID was probably entered incorrectly.
Recommended Action Retry the signon with a valid user ID/password combination.
530 User is not defined to the group
Explanation A signon was attempted using a group that the user ID is not connected to.
Recommended Action Contact your local external security System Administrator.
530 Userid matches userid of TCP address space
Explanation A sign-on was attempted using the user ID of the Cisco IOS for S/390 address space. As a security precaution, Cisco IOS for S/390 will not accept its own user ID for a sign-on attempt.
550 Bad member name or generation index specified
Explanation The name supplied for the member of a partitioned data set is incorrect.
550 Catalog structure invalid or user lacks authority to catalog
Explanation Dynamic allocation returned an information reason code of 5708. The attempted operation did not complete due to security reasons or an invalid catalog structure.
Recommended Action Determine if the catalog is password protected or whether the catalog structure is invalid.
550 Data set not found
Explanation The file specified for processing cannot be located on the host system.
550 Dataset medium is tape; request cannot be performed.
Explanation A RENAME has been requested but the data set is on magnetic tape.
550 Error occurred during directory update, directory NOT updated
Explanation A serious error occurs during ACDYNAL processing of the PDS directory.
550 File access denied
Explanation Access to the specified file is denied by the security (access control) system of the host.
550 File cannot be accessed. HSM SVC is not supported by installation.
Explanation File has been migrated and HSM recall abnormally terminates with an x’16D’.
Recommended Action Verify HSM is supported by the host operating system or HSM uses SVC 109 (x’6D’). Contact your local Cisco IOS for S/390 support personnel.
550 File cannot be deleted. SCRATCH failed or expiration date not reached.
Explanation A DELETE for a data set failed, either because the SCRATCH routine returned an error code, or because the expiration date has not occurred.
550 File not accessed. A volume must be mounted, and mount is not permitted.
Explanation A data set on a tape volume has been requested, but tape processing has been disallowed by the system administrator.
550 File not accessed. Migrated file requires SITE RECALL command
Explanation File has been migrated and HSM recall ability is not enabled for the user.
Recommended Action Issue a SITE RECALL command to enable HSM for file transfer.
550 New member name bad, format — DSN(OLDMEM) (NEWMEM)
Explanation The new member name must be enclosed in parentheses () and must not be qualified (i.e., no quotes).
550 No multi-volume data sets
Explanation FTP does not support multi-volume data sets.
550 Rename failed (New name already exists in directory)
Explanation The new member name given in the RNTO command already exists as a member in the PDS.
550 Rename failed (PDS DIRECTORY IS FULL)
Explanation The STOW system command returned with an error indicating there were not enough directory blocks available to complete the rename.
550 Rename failed (RNTO base name is invalid)
Explanation A RENAME for a data set failed because the GDG base name was invalid.
550 Rename failed (RNTO name CANNOT contain member name)
Explanation A RENAME for a data set is issued but the new data set name specified a member name in addition to the data set name.
550 Rename failed (RNFR data set not found)
Explanation A RENAME for a data set is issued but the data set was not found.
550 Rename failed (RNTO data set exists in catalog already)
Explanation A RENAME for a data set failed because a data set by that name already exists in the catalog.
550 Rename failed (RNFR data set OBTAIN error)
Explanation A RENAME for a data set failed due to an OBTAIN error.
550 Rename failed (RNTO/RNFR CATLG error)
Explanation A RENAME for a data set failed due to a catalog error.
550 Rename failed (RNTO name contained an invalid generation)
Explanation A RENAME failed because the name contained an invalid generation.
550 Not a partitioned dataset. Use DELE to delete
Explanation A RMD command was received specifying a non-partitioned data set.
550 Partitioned dataset contains members
Explanation A RMD command was received for a partitioned data set that contains members. Delete the members first, or use DELE to delete the PDS.
550 No matching datasets or members were found
Explanation The file specified for processing cannot be located or no matching directory entries are found on the host system.
550 MKD failed. DCBDSN data set dcbdsn_name is invalid for a PDS.
Explanation A SITE DCBDSN command was received, but the model data set has a record format (RECFM) or data set organization (DSORG) that is invalid for a PDS.
Recommended Action Change the DCBDSN data set name, or issue SITE RESET to reset SITE parameters.

Note The following replies will be prefixed with the number sequence 200- (rather than 500-), if the FTP configuration option SITEREPLY(200) is specified.
550 Unable to create unique data set name for STOU
Explanation A store unique (STOU) command was received. The server attempts to generate a unique name by appending 1-999 to the last qualifier of the data set name. It has exhausted the set of unique names.
Recommended Action Change the file name
550 No matching entries were found entries
Explanation A directory command (LIST/NLST) was received, but no entries were found to match the request. entries is one of the following:
|
members |
if the current working directory is a partitioned data set. |
|
volumes |
if the filetype is VTOC. |
|
data sets |
in all other cases. |
Recommended Action Change the file name
552 Insufficient space on volume. Transfer terminated
Explanation The device to which the transferred file is being written has run out of storage space. The file transfer is incomplete.
552 Unable to continue data transfer, data set full
Explanation The receiving host does not have sufficient storage space for the data being transferred to it. The file transfer cannot continue.
553 Bad data set name syntax
Explanation The file name specified is incorrect, or it violates the syntax or naming conventions defined by the remote host.
553 Operation failed — data set cataloged on another volume
Explanation The file transfer completes unsuccessfully. A SITE command probably was issued to a specific VOLUME or UNIT and the file (data set) exists as a cataloged entry on another volume.
553 Operation failed — SITE command implies DISP=NEW — data set already exists
Explanation One of the SITE commands (i.e., SPACE, TRACK, CYLINDER, BLOCKS) implies that the data set is to be created, but the data set already is defined.
554 Illegal RECFM in data set
Explanation This message indicates one of these conditions:
•One of these record formats is specified as an unblocked print format: FA, FSA, VA, VSA, UA. The FTP Server can read from, but not write to, these files.
•The print format A is specified when the TYPE parameter specifies binary data. A print data set can be created or retrieved only as text, not as binary data.
554 LRECL or BLKSIZE invalid or inconsistent
Explanation The logical record length and blocksize specified are either invalid or inconsistent.
554 Old data set not replaced, DSORG different
Explanation Data transferred from the sending host does not replace the existing data set on the receiving host because the data set organizations conflict.
554 SITE LRECL, BLKSIZE, or RECFM do not match those of existing data set
Explanation The logical record length, blocksize, and/or record format specified in the preceding SITE command(s) are not consistent with the characteristics of the existing file on the receiving host.
554 RETRieve of a whole PDS is not permitted
Explanation A RETR command was received specifying a partitioned data set as the pathname. A member name must be supplied.