С 0111 (может меняться в зависимости от рынка), иммобилайзер могут быть установлены в качестве опции на заводе или модернизированы при условии ввода автомобиля
оснащен координаторов и двигатель противоречивые единицу правильном поколения.
введите S6 или MS6.
1 ключ стартера с транспондером
Ключ стартера имеет традиционный механический
функционировать, но и имеет встроенный транспондер для шифрования электронных сигналов от координатора.
2 Блок приемопередатчика (E49)
Это действует в качестве связующего звена между координатором и транспондера. Он расположен вокруг замка стартер и включает в себя антенну и блок передатчика / приемника. Антенна катушка имеет индуктивную связь с транспондера, в то время как блок передатчика / приемника находится в последовательный контакт с координатором.
3 Выключатель стартера (S4)
Помимо обеспечения координатора напряжение через штифт 15, замок стартер также передает сигнал к координатору когда ключ зажигания вставлен в замок.
4 Сигнальная лампа (W33)
Эта лампа находится в панели управления и предоставляет водителю информацию о состоянии иммобилайзера. Он может постоянно гореть или мигать в зависимости от текущей ситуации.
5 координатор (E30)
Координатор содержит фактические мозги системы иммобилайзера. Автомобили с иммобилайзером всегда оснащены координатора по крайней мере 4 поколения.
6 Блок управления двигателем (E44 или E12)
Автомобили с иммобилайзером оснащены либо EDC S6 или EDC MS6 блока управления двигателем. Блок управления отключает подачу топлива, если условия устанавливаются системы иммобилайзера
не полностью выполнены.
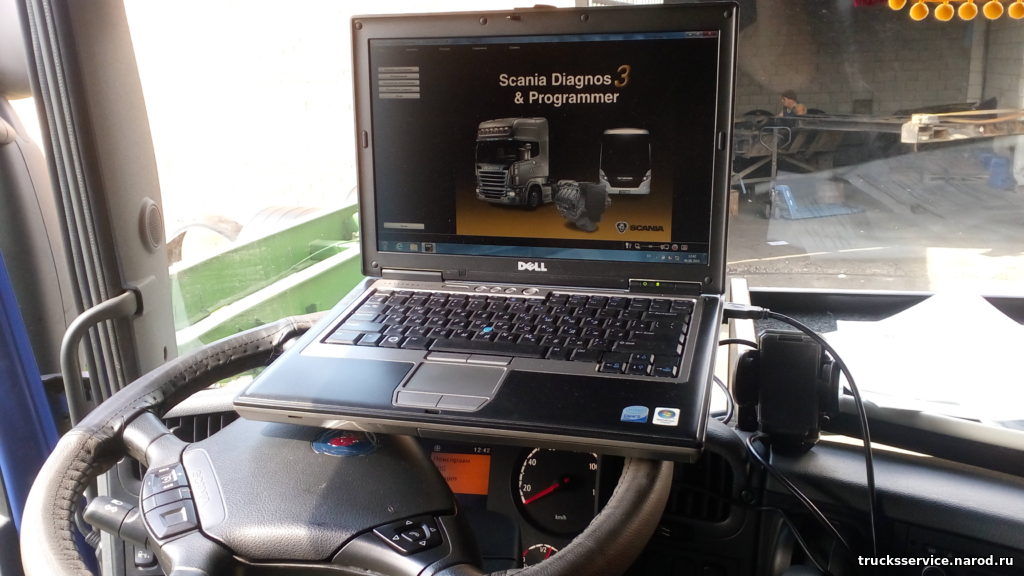
7 Диагностический разъем (К1)
Разъем для подключения VCI и Scania
Diagnos / программист находится на вершине
центральный электрический блок.
8 Производитель переключатель, встроенный в ускорителе
Датчик педали (B25)
Вместе с PIN система кода, это
делает возможным выполнять чрезвычайной ситуации
начать в случае, если проблема в
связи между транспондером и
трансивер (см. стр. 28). Переключатель открыт, когда педаль отпущена.
9 Реле стартера (R2)
Реле стартера регулирует управляющее напряжение на стартер штифт 50. Реле блокируется координатора, если условия, установленные системы иммобилайзера не полностью выполнены.
10 Контрольная лампа (W44)
Лампа находится в шельфовой панели крыши. Когда ключ стартера вынимается из замка стартер, лампа будет мигать, указывая, что иммобилайзер активен. Транспортные средства, оснащенные VPS и иммобилайзером не имеют W44 и только два VPS лампы используются.
Небольшое количество ранней серии автомобилей могут не иметь световой индикатор W44 вообще, независимо от того, или нет они оснащены VPS.
11 Жгут проводов
Существует специальный кабельный жгут для подключения трансивера. Кабели между блоками управления такие же, как на транспортных средствах без иммобилайзера, однако.
12 Разъем (C487)
Разъем C487 устанавливается только в небольшой серии автомобилей раннего производства, что делать
нет индикаторная лампа W44.
Компоненты 1, 2, 4, 10, 11 (и 12) являются уникальными для автомобилей, оснащенных иммобилайзером. Что касается Координатору и управления двигателем блок, это
возможно они присутствуют в других автомобилей с
же компонент обозначение. Это
программирования, который отличается.
Начиная процедуру
Когда водитель поворачивает ключ зажигания в положение питания 15, ток будет поступать на координатора, который в свою очередь поставляет 12 вольт в трансивера. Система использует 12 вольт
Ключ стартера, координатор и блок управления EDC впоследствии проверяется. Если все в согласии, реле стартера и подачи топлива будет
активирован. Предупреждение W33 лампа не покажет на, если есть что-то не так.
Весь этот процесс больше не принимает 200-300 мс и едва заметны для водителя.
Verifying the starter key
1 After powering up, the transceiver will seek inductive contact with the starter key
transponder.
2 After making contact, the transceiver will send confirmation to the coordinator.
3 The coordinator then sends a random number to the transponder via the transceiver unit.
4 The transponder encrypts the random number and sends back an encrypted response to the coordinator. Meanwhile, the coordinator has itself encrypted its own random number and now checks that the transponder’s response is the same as its own.
Fault codes
Fault codes related to the immobiliser are stored in the coordinator. The principle tool
used to check for any fault codes is Scania Diagnos. There are, however, other ways of reading and clearing codes using the diagnostic lamp and the diagnostic switch (S50) on the instrument panel.
The switch in question is marked «COO» (diagnostic switch panel pin 10) and is
connected to coordinator pin 12. The switch, which has a return spring, closes and earths pin 12 when it is depressed.
The coordinator interprets this as a request to show any fault codes and will flash them out by intermittently connecting pin 12 to ground in the required pulse sequence when the switch on the panel is released.
Reading fault codes
• Switch on the power supply.
• Depress the diagnostics switch marked
«COO» and keep it depressed for two seconds.
• The lamp will now flash if there are any fault codes present. A long flash indicates
tens and a short flash ones. Illustrated example: Fault code 26 is indicated with
two long flashes followed by six short ones.
• Depress the diagnostic switch once again to read the next fault code.
Erasing fault codes
Clear all fault codes as follows:
• Begin by switching off the current.
• Press the diagnostics switch and keep it depressed.
• Switch on the current again with the diagnostic switch depressed.
Limitations
Remember that reading fault codes is not always regarded as the perfect troubleshooting method. The software used is very advanced but, nonetheless, some types of faults may arise that cannot be registered with fault codes.
Likewise, situations may arise when a fault code is generated even though there is not
fault at present. Such an example may be temporary bad contact or that a cable splice has disconnected and then connected again while the power has been on.
Fault code 26
Fault
The starter key cannot be verified.
Cause
The starter key is interpreted as being invalid.
Either the key does not have a transponder at all or the transponder is faulty. However, it is also possible that the starter key has been programmed for another coordinator or other starter keys with transponders on the same key ring are interfering with the verification of the key.
A fault in the transceiver can also generate this
fault code.
Remarks
The immobiliser warning lamp, W33, will flash if this fault occurs.
For more information, select «Display of status» under the «Configuration…» button in
the system window.
Action
Make sure the correct starter key is in the starter lock. Make sure there are no more keys with transponders on the key ring. Check the transceiver and wiring.
Код ошибки 27
Координатор не может проверить контроль EDC
Блок управления EDC интерпретируется как
неисправен или не подходит для этого автомобиля. Оно не может быть
запрограммирован или имеет другой PIN кода, чем
координатор.
Это может быть связано с блок управления EDC не быть
заблокирован координатору после возобновления либо
координатор или блок управления EDC. Scania
Программист должен быть использован для блокировки единиц.
Замечания
Сигнальная лампа W33 придет на постоянно, если
автомобиль указана с иммобилайзером. Это
неисправность может возникнуть и на транспортных средствах, не
иммобилайзер, если они оснащены поколения
4 координатор. Эти транспортные средства не имеют
Предупреждение W33 лампа.
Двигатель не запустится, если происходит эта ошибка.
Более подробную информацию можно получить, прочитав
статус из блоков управления. Выберите «Отображение
Статус «под» кнопку Конфигурация … «в
оконная система.
Действие
Проверьте блок управления EDC, координатор и
проводки. Используйте Scania программист заблокировать EDC
блок управления к координатору.
Fault code 28
Fault
Short circuit on output from starter relay.
Cause
This fault code is generated when the output is short-circuited to ground.
Action
Check the starter relay and wiring.
Fault code 29
Fault
Invalid combination of signals to the coordinator.
Cause
This fault code is generated when the coordinator received a signal that the power is turned but there is no signal that the starter key is in the starter lock. The fault code will be generated if there is a fault for longer than 10 seconds.
Action
Check the starter lock and wiring.
Fault code 31
Fault
Start signal active continuously.
Cause
This fault code is generated when the coordinator receives a continuous signal that the engine has been started even though it is already running.
The fault code is generated when the signal has been active for over 5 minutes.
Action
Check the starter lock and wiring.
Codes
Besides a plastic pouch containing the mechanical code for the starter key, a plastic
pouch with three other codes is also delivered together with new vehicles with immobiliser.
These are the PIN code, encryption code and bar code.
IMPORTANT! The codes are required for programming control units and starter keys.
Scania does not keep a register of codes and it is important that the vehicle owner keeps them safe. Lost codes will lead to extra labour and increased costs.
1. PIN Code
The PIN code can be found concealed inside the sealed plastic pouch. It always comprises 6 digits.
Principally, both the associated control units must be unlocked before any work can be done on them. The PIN code then acts as a key.
Therefore, you must specify the PIN code in
order to carry out many of the actions in Scania
Programmer. The PIN code is generally
required:
• When renewing the coordinator.
• When renewing the EDC control unit.
• When removing any of the control units if they are to be used in another vehicle.
• When additional starter keys are used.
• When activating the immobiliser.
In addition, the PIN code is required if an emergency start has been necessary for some reason (see side 28).
2. Encryption code
The encryption code can be found concealed inside the sealed plastic pouch. It always
comprises 12 alphanumeric characters.
You could say that the encryption code is a key that is used to verify the transponder in the starter key. For this reason, the code must be used:
• When the coordinator has been renewed and you still want to use the same starter keys as before.
• When reactivating a system that has previously been deactivated.
3. Bar code
The bar code can be found outside the plastic pouch. It is read at the factory when the control units are initially programmed.
At that moment, the control units automatically learn the PIN code and encryption code that are associated with the bar code. This means that these codes need not be revealed at this time.
The bar code, however, may also have to be specified manually in Scania Programmer. In that case, enter the 16 alphanumeric characters printed underneath the bar code lines. This will be required:
• When using new starter keys.
• When renewing the coordinator with associated new starter keys.
Timed unlocking — if the codes have been mislaid
Scania Programmer has an emergency function called timed unlocking. Performing timed unlocking enables you to unlock and program the control units even though the PIN code and encryption code have been mislaid.
Timed unlocking activates a timer in the coordinator and requires 12 hours to complete, which is why it is regarded as an emergency function.
You can disconnect Scania Programmer during this time, but the power must be turned on.
Cutting off the power will interrupt the timed unlock.
After initiating timed unlocking, the program will display a lock code that must be given once the 12 hours are up. Entering this code manually will reset the coordinator to basic generation 3 and unlock the EDC control unit.
This means that new codes must be used for reprogramming once timed unlocking has been carried out. Starter keys (and possibly the starter lock) must be replaced with new ones. You will receive new codes with the new keys.
Coordinator serial number
The coordinator serial number must be given when initiating timed unlocking. The number is printed on a label affixed to the top of the coordinator (see illustration).
Functions in Scania Programmer
As Scania Programmer is required for most of the tasks that can be carried out on the
immobiliser system, this section contains an overview of the options listed under the
«Programming…» button.
An overview with brief descriptions of what each option is used for is given below. For more detailed instructions, refer to the program’s help
file.
Programming the coordinator
Choose this option to program the codes into an unprogrammed coordinator 4, for example when the coordinator has been replaced with a new one or when the old codes have been deleted from a used coordinator.
Note that all generation 4 coordinators must be programmed, even when the vehicle is not equipped with immobiliser.
You will be asked to select one of three
programming alternatives:
• To program new starter keys, which will
also entail new codes.
• To retain the vehicle’s previous keys and
codes.
• To program without immobiliser.
Once the codes have been programmed, the
coordinator must be locked to the EDC control
unit. Refer to «Locking the EDC control unit to
the coordinator» below.
Locking the EDC control unit
to the coordinator
Choose this option after renewing the
coordinator or the EDC control unit. You go
straight to this step after renewing the EDC
control unit. Refer to «Programming the
coordinator» above regarding the coordinator.
The program will first check the status of both
control units. Are they locked or unlocked?
Both units must be unlocked in order to be
reprogrammed.
This means that the control units can be locked
individually without being locked to any other
control unit. If any of them are locked, you will
be asked to unlock them using the PIN code.
What happens when the control units are
subsequently ready for locking to each other
naturally depends on the circumstances. Has
the coordinator been renewed and in that case
which options were selected under
«Programming the coordinator»? Or has the
EDC control unit been renewed?
The program will detect this information itself
and display it on the screen. In principle, the
control units will learn the same codes in order
to communicate with each other irrespective of
the circumstances. After learning it, they are
said to be locked with each other.
Resetting the coordinator
Choose this option if the coordinator is to be
removed from the vehicle and then reused in
another vehicle. This need not be done if the
coordinator is not programmed for an
immobiliser.
These measures can also be employed after
fitting a used and locked coordinator that is to
be reprogrammed. This presumes that you also
have access to the PIN code and encryption
code belonging to the coordinator in question.
Resetting the coordinator will delete its code
memory and it will retake the basic
programming of generation 3 or 4, which is the
equivalent of a new coordinator. Of course,
resetting also entails that the coordinator is no
longer locked to the EDC control unit.
If you remove the coordinator without resetting
it and still want to use it in a new connection,
you must make sure the PIN code and
encryption code accompany the coordinator.
Otherwise, it will remain locked and cannot be
reused.
Unlocking the EDC control
unit
The EDC control unit must be unlocked in
order to be reprogrammed. If it is removed from
a vehicle with immobiliser without doing this
first, its PIN code must accompany it so that the
control unit can be used together with another
coordinator. Otherwise, it will remain locked
and cannot be reused.
As soon as the EDC control unit is unlocked, it
will no longer contain any codes.
Additional starter keys
It is possible to add to the number of keys
available for a vehicle. The maximum number
of starter keys that can be programmed for one
and the same vehicle is 8.
The same encryption code programmed into the
coordinator is also used for the transponders in
the new keys. In this way, the original system
codes can be retained.
Replacing starter key
For security reasons, after purchasing a used
vehicle for instance, it may be necessary to
replace all the starter keys with new ones.
This measure entails first resetting the
coordinator to its basic programming (deleting
its codes). The new codes that come with the
new starter keys can then be programmed by
just entering the bar code. The old system codes
can then be discarded.
Finally, the control units must be locked to each
other again as described in «Locking the
coordinator to the EDC control unit» above.
The program will take you there automatically.
Activating immobiliser
To be able to activate the immobiliser using this
option, the vehicle must have previously had an
activated immobiliser that has been deactivated.
This option really does not involve anything
other than performing certain measures that
have been described earlier. The coordinator
must first be reset to a basic generation 4, after
which it must be programmed with codes again
(either with new ones or the old ones) and then
locked together with the EDC control unit.
Deactivating immobiliser
This option also gives only directions on which
earlier described measures are to be carried out
to deactivate the immobiliser.
Start by resetting the coordinator to a basic
generation 4. As all generation 4 coordinators
must be locked to the EDC control unit,
irrespective of whether the vehicle has an
immobiliser or not, you should now select
«Programming the coordinator».
You can then select «Without immobiliser» to
make the program lock the control units
together using the preset standard codes that
always apply when the immobiliser has been
deselected.
Upgrading the coordinator
If you have changed to a basic generation 3
coordinator in a vehicle that requires
coordinator 4, the program will be able to
upgrade the coordinator from 3 to 4.
If this is the case, you will not be able to access
the measures described above until the
coordinator has been upgraded. This is the only
selection that can be made at this stage.
Once the coordinator has been upgraded it will
be in its basic programmed form and at the
same initial position as described above.
«Programming the coordinator» is the next step.
Timed unlocking
This is an emergency function used to unlock
the control units if the codes have been mislaid.
This is described in the section «Codes» on
page 23.
Все ошибки SCANIA P, G, R, S, XT, V8
11 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
12 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
13 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
14 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
15 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
21 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
22 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
23 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
40 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
113 – Наружная температура – Температура наддувочного воздуха заметно выше наружной температуры, в то время как их значения должны быть одинаковыми
135 – Давление в системе питания топливом – Давление в топливной магистрали значительно ниже установленного значения
136 – Давление в системе питания топливом – Давление в топливной магистрали значительно превышает установленное значение
258 – Массовый расходомер – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
259 – Массовый расходомер – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
263 – Датчик давления наддува – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
264 – Датчик давления наддува – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
273 – Температура наддувочного воздуха – Температура наддувочного воздуха заметно ниже наружной температуры, в то время как их значения должны быть одинаковыми. Сигнал от датчика температуры наддувочного воздуха имеет недостоверное значение
274 – Датчик температуры наддувочного воздуха – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
275 – Датчик температуры наддувочного воздуха – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
279 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
280 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
386 – Датчик температуры топлива – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
387 – Датчик температуры топлива – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
396 – Датчик давления топлива – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
397 – Датчик давления топлива – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
535 – Защита от перегрева – Температура охлаждающей жидкости превысила 104°C
537 – Частота вращения двигателя – Частота вращения двигателя превышала допустимое значение
1025 – Состав EGR – Количество рециркулируемых отработавших газов (ОГ) слишком мало; невозможно увеличить количество рециркулируемых ОГ до установленного уровня
1026 – Состав EGR – Количество рециркулируемых отработавших газов (ОГ) слишком велико; невозможно уменьшить количество рециркулируемых ОГ до установленного уровня
1062 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Недостоверный сигнал от датчика. Постоянное значение сигнала
1063 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения
1064 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения
1068 – Датчик температуры после каталитического нейтрализатора SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения
1069 – Датчик температуры после каталитического нейтрализатора SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения
1138 – Датчик противодавления в системе выпуска – Напряжение в цепи было ниже допустимого уровня
1139 – Датчик противодавления в системе выпуска – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
1155 – Частота вращения вентилятора – Сигнал от датчика частоты вращения вентилятора был ниже нормального значения
1314 – Датчик давления масла – Напряжение в цепи упало ниже допустимого уровня
1315 – Датчик давления масла – Напряжение в цепи превышало допустимый уровень
1376 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Напряжение аккумулятора было выше допустимого значения. Оно было 47 В или больше в течение 0.5 секунд
1378 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Напряжение аккумулятора было ниже допустимого значения. В течение 5 секунд напряжение аккумуляторной батареи находилось в диапазоне 9…21,44 В.
1379 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Напряжение аккумулятора было выше допустимого значения. В течение 5 секунд напряжение аккумуляторной батареи было более 30,56 В.
2065 – Сцепление – Разница между частотой вращения коленчатого вала двигателя и скоростью колеса неправдоподобна с учетом передаточных чисел в коробке передач. Блок управления двигателем интерпретирует это как пробуксовку сцепления
4098 – SCR – Главный блок
4102 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Насос не поднимает давление в системе SCR в течение заданного времени
4103 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Давление в системе SCR не падает, как ожидается, при открывании электромагнитного клапана в возвратной магистрали
4104 – Обмен данными между датчиком NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора и блоком управления SCR. – Блок управления SCR получает несколько сообщений CAN от датчика NOx в слишком быстрой последовательности
4105 – Обмен данными между датчиком NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора и блоком управления SCR. – Блок управления SCR не получает сообщение CAN от датчика NOx
4106 – Связь с датчиком NOx – Блок управления двигателем не имеет никакого сообщения CAN от датчика NOx. Если автомобиль оснащен системой SCR, сообщение CAN передается через блок управления SCR
4107 – Связь с блоком управления SCR – Сообщение CAN MSG8 “NOx sensor data before catalytic converter” (Данные датчика NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором) не получено от датчика NOx. Если конфигурация автомобиля настроена на наличие системы SCR, это сообщение принимается через блок управления SCR
4108 – Связь с блоком управления SCR – Блок управления двигателем не получает сообщение по CAN от датчика NOx. Если автомобиль оснащен системой SCR, сообщение по CAN передается через блок управления SCR
4109 – Неправильная версия CAN – Блок управления двигателем и блок управления SCR не договариваются о том, какая версия CAN используется
4114 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Насос не поднимает давление в системе SCR в течение заданного времени
4115 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Давление в системе SCR не падает, как ожидается, когда открыт клапан впрыска
4116 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Слишком высокое давление воздуха в системе SCR
4118 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4119 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4120 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4121 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4122 – Экстренная остановка системы SCR – Система SCR была выключена
4123 – Подача напряжения к элементам в системе SCR – Напряжение в электрической цепи питания дозатора реагента было вне допустимого диапазона
4124 – Подача напряжения к элементам в системе SCR – Напряжение в электрической цепи питания дозатора реагента было вне допустимого диапазона
4128 – Давление реагента в системе SCR – Давление реагента при пуске падает больше чем на 0,5 бар
4129 – SCR – Клапан впрыска реагента – При впрыске давление в системе SCR не уменьшается, как предполагалось
4130 – Переключатель в системе SCR – Цифровые входные данные не регистрируются, когда зажигание включается ключом
4131 – Подача напряжения для блока управления SCR – Блок управления SCR выключается слишком рано. Подача питания от системы SCR была выключена раньше, чем было выполнено выключение системы
4132 – Подача напряжения для блока управления SCR – Блок управления SCR выключается слишком поздно
4133 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4134 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4135 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные
4143 – SCR – Давление реагента – Давление не увеличилось в достаточной степени после запуска насоса реагента с полной производительностью
4144 – SCR – Главный блок
4145 – SCR – Главный блок – Частота работы диафрагменного насоса в главном блоке была выше допустимого значения
4146 – SCR – Подача напряжения – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, выше установленного значения
4147 – SCR – Подача напряжения – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, ниже установленного значения.
4148 – SCR – Главный блок –
4149 – SCR – Главный блок –
4152 – SCR – Температура реагента – Температура реагента внутри главного блока была выше допустимого значения.
4157 – Давление в системе SCR – Давление в системе SCR неправдоподобно в сравнении с атмосферным давлением.
4160 – SCR – Давление реагента – Давление при запуске системы было выше допустимого значения.
4163 – SCR – Температура реагента – Датчик температуры в главном блоке показывает, что температура реагента ниже допустимой.
4164 – SCR – Температура в бачке реагента – Температура в бачке ниже допустимой.
4165 – Подача сжатого воздуха для системы SCR – Подача сжатого воздуха для системы SCR не достаточна для запуска системы SCR.
4166 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Разница в давлении воздуха перед сужением и после него при дозировании меньше ожидаемой.
4167 – Напряжение в системе SCR – Блок управления SCR обнаруживает, что напряжение аккумулятора ниже значения, измеренного блоком управления двигателем.
4168 – Выделение оксидов азота (NOx) – Измеренный уровень оксидов азота (NOx) выше допустимого.
– – Высокий уровень токсичности выхлопа. Возникает риск превышения предписанного предельного уровня выделения NOx. Уменьшение крутящего момента не активировано.
4169 – Выделение оксидов азота (NOx) – Измеренный уровень оксидов азота (NOx) выше допустимого.
– – Чрезмерно высокий уровень токсичности выхлопа. В автомобиле происходит превышение предписанного предельного уровня выделения NOx. Активировано уменьшение крутящего момента.
4170 – SCR – Оксиды азота (NOx) после каталитического нейтрализатора – Измеренное количество оксидов азота отличается от того, которое должно быть.
4171 – SCR – Оксиды азота (NOx) после каталитического нейтрализатора – Измеренное количество оксидов азота отличается от того, которое должно быть.
4172 – Датчик NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора – Измеренное количество оксидов азота отличается от того, которое должно быть.
4175 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Недостоверный сигнал от датчика. Температура ниже ожидаемой блоком управления.
4177 – Выделение оксидов азота (NOx) – Измеренный уровень оксидов азота (NOx) выше допустимого.
4178 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Недостоверный сигнал от датчика. Температура ниже ожидаемой блоком управления.
4180 – SCR – Температура в бачке – Температура реагента в бачке была выше допустимого значения.
4209 – Наружная температура – Сигнал датчика температуры наружного воздуха, поступающий от координатора, является недействительным. Значение ниже допустимого.
4210 – Наружная температура – Неправильный сигнал от датчика наружной температуры, который подсоединен к блоку управления BCS, был получен по шине CAN.
4352 – Датчик давления наддувочного воздуха – Давление наддувочного воздуха и атмосферное давление отличаются, когда двигатель работает в режиме холостого хода.
4369 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 1 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4370 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 2 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4371 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 3 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4372 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 4 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4373 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 5 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4374 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 6 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4375 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 7 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4376 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 8 – Был достигнуто самое низкое значение, до которого блок управления может регулировать объем топлива для цилиндра
4385 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 1 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4386 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 2 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4387 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 3 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4388 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 4 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4389 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 5 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4390 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 6 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4391 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 7 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4392 – Обеспечение баланса цилиндров, цилиндр 8 – Достигнуто максимальное значение цикловой подачи для данного цилиндра двигателя, которое разрешено блоком управления.
4400 – Температура охлаждающей жидкости – Сигнал датчика температуры охлаждающей жидкости недостоверен по отношению к текущим условиям работы. Значение ниже ожидаемого.
4416 – Атмосферное давление – Показываемое на дисплее давление наддувочного воздуха неправдоподобно в сравнении с атмосферным давлением.
4417 – Атмосферное давление – Показываемое на дисплее давление наддувочного воздуха неправдоподобно в сравнении с атмосферным давлением.
4624 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4625 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4626 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4627 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4628 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4629 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4630 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 1 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4640 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4641 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4642 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4643 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4644 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4645 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4646 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 2 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4656 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4657 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4658 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4659 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4660 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4661 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4662 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 3 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4672 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4673 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4674 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4675 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4676 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4677 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4678 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 4 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4688 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4689 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4690 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4691 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4692 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4693 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4694 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 5 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4704 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4705 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4706 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4707 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4708 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4709 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4710 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 6 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4720 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4721 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4722 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4723 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Драйвер электромагнитного клапана предупреждает о неисправности.
4724 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4725 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4726 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 7 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4736 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4737 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Слишком быстрое нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4738 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Слишком медленное нарастание тока в обмотке электромагнитного клапана. Время нарастания тока определяется блоком управления в зависимости от напряжения аккумуляторной батареи и температуры охлаждающей жидкости.
4739 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Эта неисправность может быть вызвана коротким замыканием проводки, коротким замыканием электромагнитного клапана или коротким замыканием внутри блока управления.
4740 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Нет сигнала закрытия электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки.
4741 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Слишком раннее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более ранний, чем требуется.
4742 – Насос-форсунка цилиндра 8 – Слишком позднее закрытие электромагнитного клапана насос-форсунки. Угол опережения впрыскивания более поздний, чем требуется.
4745 – Давление в системе питания топливом – Давление подачи на некоторый период превысило допустимое значение.
4752 – Клапан отсечки топлива – На выводы электромагнитного клапана прекращения подачи топлива постоянно подаётся высокое напряжение.
4753 – Клапан отсечки топлива – Не работает электромагнитный клапан прекращения подачи топлива.
4754 – Клапан отсечки топлива –
– – Во время останова двигателя выключением клапана прекращения подачи топлива давление топлива в линии низкого давления понижается очень медленно.
4757 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Крутящий момент, развиваемый передней группой цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3), значительно превышает крутящий момент, развиваемый задней группой цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6).
4759 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Крутящий момент, развиваемый задней группой цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6), значительно превышает крутящий момент, развиваемый передней группой цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3).
4762 – Параметр блока управления – В блоке управления двигателем есть параметр, который показывает, имеется ли сцепление на автомобиле.
– – Блок управления двигателем также получает информацию о статусе сцепления от координатора по шине CAN.
– – Этот код неисправности генерируется, если настройка в блоке управления двигателем полностью не соответствует информации, которая поступает по шине CAN.
4768 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана количества топлива для переднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4769 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана количества топлива для переднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4770 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Нет сигнала управления подачей топлива передней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3).
4771 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Параметры сигнала электромагнитного клапана управления подачей топлива передней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) сильно отличаются от параметров сигналов других электромагнитных клапанов.
4772 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – На электромагнитный клапан управления подачей топлива передней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) подаётся слишком низкое напряжение.
4784 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана количества топлива для заднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4785 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана количества топлива для заднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4786 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Нет сигнала управления подачей топлива задней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6).
4787 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Параметры сигнала электромагнитного клапана управления подачей топлива задней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) сильно отличаются от параметров сигналов других электромагнитных клапанов.
4788 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – На электромагнитный клапан управления подачей топлива задней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) подаётся слишком низкое напряжение.
4800 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана опережения впрыска для переднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4801 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана опережения впрыска для переднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4802 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Нет сигнала управления углом опережения впрыскивания передней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3).
4803 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Параметры сигнала электромагнитного клапана управления углом опережения впрыскивания передней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) сильно отличаются от параметров сигналов других электромагнитных клапанов.
4804 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – На электромагнитный клапан управления углом опережения впрыскивания передней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 1-3) подаётся слишком низкое напряжение.
4816 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана опережения впрыска для заднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4817 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Напряжение в электрической цепи для электромагнитного клапана опережения впрыска для заднего ряда цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) было вне допустимого диапазона.
4818 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Нет сигнала управления углом опережения впрыскивания задней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6).
4819 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – Параметры сигнала электромагнитного клапана управления углом опережения впрыскивания задней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) сильно отличаются от параметров сигналов других электромагнитных клапанов.
4820 – Подача топлива в цилиндры – На электромагнитный клапан управления углом опережения впрыскивания задней группы цилиндров (цилиндры 4-6) подаётся слишком низкое напряжение.
4864 – Частота вращения двигателя – Частота вращения двигателя превышала допустимое значение.
4865 – Сигналы частоты вращения коленчатого вала – Во время работы двигателя сигналы двух датчиков частоты вращения не соответствуют друг другу.
4866 – Сигналы частоты вращения коленчатого вала – Уровень сигнала от датчика 1 частоты вращения коленчатого вала ниже, чем должен быть для текущего значения частоты вращения коленчатого вала.
4867 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 1 – Частота вращения двигателя, определённая по сигналу датчика частоты вращения, ниже установленного минимального значения.
4868 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 1 – Частота вращения двигателя, определённая по сигналу датчика частоты вращения, ниже установленного минимального значения.
4869 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 1 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя показывает слишком большое увеличение частоты вращения двигателя за период времени между двумя последовательными импульсами.
4870 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 1 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя показывает слишком большое уменьшение частоты вращения двигателя за период времени между двумя последовательными импульсами.
4871 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 1 – Сигнал от датчика частоты вращения коленчатого вала был неправильным с самого начала.
4872 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 1 – Нет сигнала от датчика частоты вращения коленчатого вала.
4881 – Сигналы частоты вращения коленчатого вала – Во время работы двигателя сигналы двух датчиков частоты вращения не соответствуют друг другу.
4882 – Сигналы частоты вращения коленчатого вала – Уровень сигнала от датчика 2 частоты вращения коленчатого вала ниже, чем должен быть для текущего значения частоты вращения коленчатого вала.
4883 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2 – Частота вращения двигателя, определённая по сигналу датчика частоты вращения, ниже установленного минимального значения.
4884 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2 – Частота вращения двигателя, определённая по сигналу датчика частоты вращения, ниже установленного минимального значения.
4885 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя показывает слишком большое увеличение частоты вращения двигателя за период времени между двумя последовательными импульсами.
4886 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя показывает слишком большое уменьшение частоты вращения двигателя за период времени между двумя последовательными импульсами.
4887 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2
4888 – Датчик частоты вращения двигателя 2 – Нет сигнала от датчика частоты вращения коленчатого вала.
4896 – Защита двигателя при запуске – Частота вращения двигателя во время запуска превысила разрешённое значение в течение установленного интервала времени (обычно 1 секунда).
4912 – Частота вращения двигателя – Частота вращения коленчатого вала на некоторый период превысила допустимое значение.
4913 – Частота вращения двигателя – Частота вращения коленчатого вала на некоторый период превысила допустимое значение.
4928 – Сигналы частоты вращения коленчатого вала – Нет сигналов от обоих датчиков частоты вращения коленчатого вала.
5122 – Калибровка массового расходомера – Во время калибровки датчика массового расхода получено минимально допустимое значение.
5123 – Калибровка массового расходомера – Во время калибровки датчика массового расхода получено максимально допустимое значение.
5124 – Диффузор – Диффузор не может правильно управляться.
5125 – Калибровка массового расходомера – Отключена калибровка массового расходомера.
5126 – EGR – Блок управления двигателем отключил систему рециркуляции ОГ.
5127 – Состав EGR – Количество рециркулируемых отработавших газов слишком мало; невозможно увеличить количество рециркулируемых отработавших газов до установленного уровня.
5129 – Охладитель EGR –
5139 – Противодавление в системе выпуска – Противодавление в системе выпуска слишком высокое, когда подача топлива выключена.
5141 – Противодавление в системе выпуска – Противодавление в системе выпуска слишком низкое при задействованном моторном тормозе.
5168 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Недостоверный сигнал от датчика. Температура ниже ожидаемой блоком управления.
5169 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Недостоверный сигнал от датчика. Температура выше ожидаемой блоком управления.
5170 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Недостоверный сигнал от датчика. Постоянное значение сигнала.
5171 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Неправдоподобный сигнал от датчика температуры отработавших газов, установленного на каталитическом нейтрализаторе SCR.
5376 – Электрическое питание – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, выше установленного значения.
5377 – Электрическое питание – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, ниже установленного значения.
5392 – Электрическое питание – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, выше установленного значения.
5393 – Электрическое питание – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, ниже установленного значения.
5408 – Датчик давления масла – Сигнал датчика давления масла в системе смазки двигателя превышает нормальное значение. Это означает, что давление масла, измеренное на определённой скорости, выше нормального.
5409 – Датчик давления масла – Сигнал датчика давления масла в системе смазки двигателя ниже нормального значения. Это означает, что давление масла, измеренное на определённой скорости, ниже нормального.
5476 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Напряжение аккумулятора было ниже допустимого значения. Оно было 9 В или меньше в течение 0.5 секунд.
5635 – Вентилятор радиатора – Частота вращения вентилятора радиатора отклоняется от значения, запрашиваемого блоком управления.
5648 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5649 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5650 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5651 – Конфигурация системы управления двигателем – Система управления двигателем получает от OPC сигнал о том, что автомобиль имеет автоматическое сцепление, хотя конфигурация системы управления двигателем не была настроена соответствующим образом.
5652 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5653 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5654 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5655 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5656 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5657 – Отключение системы – Неправильная процедура выключения блока управления двигателем. Линия питания 30 была отключена от блока управления раньше, чем линия 15, то есть питание от аккумуляторной батареи было прервано до выключения зажигания.
5658 – Блок управления – Передача данных в память блока управления была прервана.
5659 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5660 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5661 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5662 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5663 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5664 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5666 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5667 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5668 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5669 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5670 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5680 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5681 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5682 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5683 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5684 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5685 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5686 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5687 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5688 – Блок управления – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
5696 – Блок управления – Ненадёжные данные.
5697 – Управление вентилятором – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5698 – Управление вентилятором – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5699 – Управление клапаном обхода турбины – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5700 – Управление клапаном обхода турбины – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5701 – Управление стартером – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5702 – Управление стартером – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5703 – Генератор 1 – При работающем двигателе ток не подаётся в обмотку возбуждения генератора.
5704 – Генератор 1 – Ток подаётся в обмотку возбуждения генератора при остановленном двигателе.
5705 – Генератор 1 – При работающем двигателе ток не подаётся в обмотку возбуждения генератора.
5706 – Генератор 1 – Ток подаётся в обмотку возбуждения генератора при остановленном двигателе.
5707 – Управление системой кондиционирования – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5708 – Управление системой кондиционирования – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5709 – Клапан включения/выключения диффузора – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5710 – Клапан включения/выключения диффузора – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5713 – Напряжение питания массового расходомера – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
5714 – Электромагнитный клапан моторного тормоза-замедлителя. – Напряжение продолжает поступать на электромагнитный клапан моторного тормоза-замедлителя после его выключения.
5715 – Электромагнитный клапан моторного тормоза-замедлителя. – Напряжение на электромагнитном клапане моторного тормоза-замедлителя значительно ниже требуемого уровня.
5716 – Моторный тормоз-замедлитель – Широтно-модулированный сигнал на модулятор моторного тормоза-замедлителя отклоняется от ожидаемого значения.
5728 – Следящий клапан EGR – Блок управления регистрирует ток в цепи, хотя блок управления питания в цепь не подаёт.
5729 – Следящий клапан EGR – Блок управления обнаружил, что ток в цепи меньше установленного значения.
5744 – Стартер. – Блок управления двигателем не читает сигнал датчика частоты вращения коленчатого вала.
5745 – Стартер. – Автомобиль слишком долго перемещался с помощью стартера.
8234 – SCR – Водяной клапан нагрева реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8236 – SCR – Водяной клапан нагрева реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8237 – SCR – Давление реагента – В периоды, когда реагент не впрыскивается, давление в системе SCR уменьшается больше, чем это должно быть.
8247 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Давление воздуха в системе SCR было вне допустимого диапазона.
8249 – SCR – Главный блок –
8252 – SCR – Датчик уровня в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8253 – SCR – Датчик уровня в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8255 – SCR – Уровень в бачке реагента – Количество реагента в бачке ниже допустимого значения.
8256 – SCR – Главный блок –
8260 – SCR – Главный блок –
8261 – SCR – Главный блок –
8263 – SCR – Дозатор реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8265 – SCR – Дозатор реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8267 – SCR – Давление реагента – Давление в системе при нормальной работе было выше допустимого значения.
8268 – SCR – Главный блок –
8269 – SCR – Главный блок –
8284 – SCR – Датчик температуры в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8285 – SCR – Датчик температуры в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
8291 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Блок управления SCR указал, что напряжение аккумулятора было ниже допустимого значения.
– – Оно было ниже 8.6 В.
8292 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Блок управления SCR указал, что напряжение аккумулятора было выше допустимого значения.
– – Оно было выше 64.6 В.
8348 – SCR – Главный блок –
8349 – SCR – Главный блок –
8352 – SCR – Главный блок –
8355 – SCR – Главный блок –
8358 – SCR – Главный блок –
8361 – SCR – Главный блок –
8381 – SCR – Главный блок –
8384 – SCR – Главный блок –
8385 – SCR – Главный блок –
8388 – SCR – Главный блок –
8394 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Давление воздуха при текущих рабочих условиях ниже ожидаемого.
8704 – SCR – датчик NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора – Блок управления SCR получил от датчика NOx сообщение о том, что имеется разрыв в электрической цепи.
8705 – Датчик NOx – Сигнал от датчика NOx не изменяется, как предписано.
8706 – SCR – датчик NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора – Блок управления SCR получил от датчика NOx сообщение о том, что в электрической цепи имеется короткое замыкание.
8723 – SCR – датчик NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором – Блок управления SCR получил от датчика NOx сообщение о том, что имеется разрыв в электрической цепи.
8725 – SCR – датчик NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором – Блок управления SCR получил от датчика NOx сообщение о том, что имеется разрыв в электрической цепи.
9299 – Сажевый фильтр – Разница давления на входе и выходе сажевого фильтра показывает значение ниже нормы.
9300 – Датчик дифференциального давления для сажевого фильтра – Сигнал от датчика дифференциального давления показал значение, которое ниже значения 0,1 В.
9301 – Датчик дифференциального давления для сажевого фильтра – Сигнал от датчика дифференциального давления показал значение, которое превышает значение 4,9 В.
11175 – Информационный код для контроля NOx – не может быть удален – Этот код неисправности не указывает на наличие какой-либо неисправности. Он предназначен только для того, чтобы информировать полномочные органы, и не должен использоваться для поиска неисправностей.
11176 – Информационный код для контроля NOx – не может быть удален – Этот код неисправности не указывает на наличие какой-либо неисправности. Он предназначен только для того, чтобы информировать полномочные органы, и не должен использоваться для поиска неисправностей.
11180 – Информационный код для контроля NOx – не может быть удален – Этот код неисправности не указывает на наличие какой-либо неисправности. Он предназначен только для того, чтобы информировать полномочные органы, и не должен использоваться для поиска неисправностей.
11181 – Информационный код для контроля NOx – не может быть удален – Этот код неисправности не указывает на наличие какой-либо неисправности. Он предназначен только для того, чтобы информировать полномочные органы, и не должен использоваться для поиска неисправностей.
11182 – Информационный код для контроля NOx – не может быть удален – Этот код неисправности не указывает на наличие какой-либо неисправности. Он предназначен только для того, чтобы информировать полномочные органы, и не должен использоваться для поиска неисправностей.
40961 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
40964 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
40965 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
40976 – SCR – Главный блок –
40977 – SCR – Главный блок –
40992 – SCR – Датчик температуры в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
40993 – SCR – Датчик температуры в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
40999 – SCR – Температура в бачке – Температура реагента в бачке была выше допустимого значения.
41008 – SCR – Главный блок –
41009 – SCR – Главный блок –
41015 – SCR – Температура реагента – Температура реагента внутри главного блока была выше допустимого значения.
41024 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Блок управления SCR указал, что напряжение аккумулятора было выше допустимого значения.
– – Оно было выше 64.6 В.
41025 – Напряжение аккумуляторной батареи – Блок управления SCR указал, что напряжение аккумулятора было ниже допустимого значения.
– – Оно было ниже 8.6 В.
41056 – SCR – Главный блок –
41057 – SCR – Главный блок –
41072 – SCR – Датчик уровня в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41073 – SCR – Датчик уровня в бачке – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41075 – SCR – Уровень в бачке реагента – Количество реагента в бачке ниже допустимого значения.
41077 – SCR – Расход реагента – Слишком высокий расход реагента. Расход в бачке больше расчетного количества реагента, которое может быть впрыснуто.
41078 – SCR – Расход реагента – Слишком низкий расход реагента. Расход в бачке ниже, чем впрыснутое количество реагента.
41080 – SCR – Температура в бачке реагента – Температура в бачке ниже допустимой.
41081 – SCR – Температура реагента – Датчик температуры в главном блоке показывает, что температура реагента ниже допустимой.
41088 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41089 – Датчик температуры отработавших газов перед каталитическим нейтрализатором SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41104 – Датчик температуры после каталитического нейтрализатора SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41105 – Датчик температуры после каталитического нейтрализатора SCR – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41218 – SCR – Дозатор реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41219 – SCR – Дозатор реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41235 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Давление воздуха в системе SCR было вне допустимого диапазона.
41236 – Подача сжатого воздуха для системы SCR – Подача сжатого воздуха для системы SCR не достаточна для запуска системы SCR.
41251 – SCR – Давление реагента – Давление при запуске системы было выше допустимого значения.
41267 – SCR – Давление реагента – Давление не увеличилось в достаточной степени после запуска насоса с полной производительностью.
41283 – SCR – Давление реагента – Давление в системе при нормальной работе было выше допустимого значения.
41362 – SCR – Главный блок –
41363 – SCR – Главный блок –
41474 – SCR – Водяной клапан нагрева реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41475 – SCR – Водяной клапан нагрева реагента – Напряжение в цепи выходило за установленные ограничения.
41490 – SCR – Главный блок –
41491 – SCR – Главный блок –
41776 – Подача напряжения для блока управления SCR – Блок управления SCR выключается слишком рано. Подача питания от системы SCR была выключена раньше, чем было выполнено выключение системы.
41777 – Подача напряжения для блока управления SCR – Блок управления SCR выключается слишком поздно.
41808 – SCR – Главный блок – Частота работы диафрагменного насоса в главном блоке была выше допустимого значения.
41809 – SCR – Главный блок –
42048 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Насос не поднимает давление в системе SCR в течение заданного времени.
42049 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Давление в системе SCR не падает, как ожидается, когда открыт клапан впрыска.
42050 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Насос не поднимает давление в системе SCR в течение заданного времени.
42051 – Размораживание реагента в системе SCR – Давление в системе SCR не падает, как ожидается, при открывании электромагнитного клапана в возвратной магистрали.
42240 – SCR – Подача напряжения – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, выше установленного значения.
42241 – SCR – Подача напряжения – Напряжение одного из датчиков, имеющих общее питание, выше установленного значения.
42242 – SCR – Главный блок –
42243 – SCR – Главный блок –
42244 – Обмен данными между датчиком NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора и блоком управления SCR. – Блок управления SCR не получает сообщение CAN от датчика NOx.
42245 – Обмен данными между датчиком NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора и блоком управления SCR. – Блок управления SCR получает несколько сообщений CAN от датчика NOx в слишком быстрой последовательности.
42248 – SCR – Клапан впрыска реагента – При впрыске давление в системе SCR не уменьшается, как предполагалось.
42249 – SCR – Давление реагента – В периоды, когда реагент не впрыскивается, давление в системе SCR уменьшается больше, чем это должно быть.
42251 – SCR – Главный блок –
42252 – SCR – Главный блок –
42255 – Давление в системе SCR – Давление в системе SCR неправдоподобно в сравнении с атмосферным давлением.
42256 – Экстренная остановка системы SCR – Система SCR была выключена.
42258 – SCR – Главный блок –
42261 – SCR – Главный блок –
42262 – SCR – Главный блок –
42264 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Давление воздуха при текущих рабочих условиях ниже ожидаемого.
42265 – SCR – Главный блок –
42266 – SCR – Главный блок –
43329 – Неправильная версия CAN – Блок управления двигателем и блок управления SCR не договариваются о том, какая версия CAN используется.
43345 – Связь с блоком управления SCR – Блок управления двигателем не получает сообщение по CAN от датчика NOx. Если автомобиль оснащен системой SCR, сообщение по CAN передается через блок управления SCR.
43361 – Связь с датчиком NOx – Блок управления двигателем не имеет никакого сообщения CAN от датчика NOx. Если автомобиль оснащен системой SCR, сообщение CAN передается через блок управления SCR.
43362 – Связь с датчиком NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором – Блок управления двигателем не имеет никакого сообщения CAN MSG8 “NOx sensor data before catalytic converter” (Данные датчика NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором) от датчика NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором. Если автомобиль оснащен системой SCR, сообщение CAN передается через блок управления SCR.
43376 – SCR – датчик NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора – Блок управления SCR получил от датчика NOx сообщение о том, что имеется разрыв в электрической цепи.
43377 – SCR – датчик NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора – Блок управления SCR получил от датчика NOx сообщение о том, что в электрической цепи имеется короткое замыкание.
43378 – SCR – датчик NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором – Датчик NOx зарегистрировал разрыв в электрической цепи и посылает сообщение к блоку управления SCR.
43379 – SCR – датчик NOx перед каталитическим нейтрализатором – Датчик NOx зарегистрировал короткое замыкание в электрической цепи и посылает сообщение к блоку управления SCR.
43520 – SCR – Оксиды азота (NOx) после каталитического нейтрализатора – Измеренное количество оксидов азота отличается от того, которое должно быть.
43521 – SCR – Оксиды азота (NOx) после каталитического нейтрализатора – Измеренный уровень оксидов азота (NOx) выше допустимого.
43525 – Неисправность в каталитическом нейтрализаторе SCR – Температура после каталитического нейтрализатора SCR отличается от той, которая должна быть.
43526 – Уровень NOx – Измеренный уровень оксидов азота (NOx) выше допустимого.
– – Высокий уровень токсичности выхлопа. Возникает риск превышения предписанного предельного уровня выделения NOx. Уменьшение крутящего момента не активировано.
43527 – Уровень NOx – Измеренный уровень оксидов азота (NOx) выше допустимого.
– – Чрезмерно высокий уровень токсичности выхлопа. В автомобиле происходит превышение предписанного предельного уровня выделения NOx. Активировано уменьшение крутящего момента.
43552 – Датчик NOx после каталитического нейтрализатора – Измеренное количество оксидов азота отличается от того, которое должно быть.
43584 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
43585 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
43586 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
43587 – Блок управления SCR – Неправильные или недостоверные данные.
43590 – Подача напряжения к элементам в системе SCR – Напряжение в электрической цепи питания дозатора реагента было вне допустимого диапазона.
43591 – Подача напряжения к элементам в системе SCR – Прерывание в электрической цепи питания дозатора реагента.
43592 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Разница в давлении воздуха перед сужением и после него слишком мала.
43593 – Давление воздуха в системе SCR – Слишком высокое давление воздуха в системе SCR.
43673 – Напряжение в системе SCR – Блок управления SCR обнаруживает, что напряжение аккумулятора ниже значения, измеренного блоком управления двигателем.
49920 – Неправильная версия CAN – Блок управления двигателем и координатор не договариваются о том, какая версия CAN используется.
53504 – Связь с координатором – Блок управления двигателем не получает от блока-координатора сообщений о текущем положении педали акселератора, о работе тормозной системы, о включении стартера и кондиционера, о работе системы ограничения крутящего момента и других системах.
53505 – Связь с координатором – Блок управления двигателем не получает сведений от координатора относительно тахографа.
53506 – Связь с координатором – Блок управления двигателем не получает от блока-координатора никаких сообщений о работе тормозной системы, круиз-контроля, сцепления и других систем.
53507 – Связь с координатором – Блок управления двигателем не имеет сообщения CAN от координатора на штырях B1/9 и B1/10.
53508 – Связь с координатором – Блок управления двигателем не имеет сообщения CAN от координатора на штырях B1/9 и B1/10.
43517 – Сигнал от блока управления Opticruise, OPC. – Блок управления двигателем утратил связь с блоком управления OPC или получил запрос на выключение от блока управления OPC.
54292 – Сигнал от датчика положения педали акселератора – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о том, что текущее положение педали акселератора превышает 100%. Датчик положения педали акселератора подключен к блоку-координатору.
54294 – Неправильный сигнал для атмосферного давления – Блок управления двигателем получил по шине CAN сообщение по поводу неправильного сигнала от датчика атмосферного давления, который соединен с координатором.
54295 – Неправильный сигнал для наружной температуры – Блок управления двигателем получил по шине CAN сообщение по поводу неправильного сигнала от датчика наружной температуры, который соединен с координатором.
54296 – Положения педали – В блок управления двигателем и в координатор поступают несовпадающие данные о положении педали акселератора.
54297 – Положения педали – Постоянно включён выключатель “кикдауна” (педаль акселератора не находится в крайнем положении).
65424 – Неправильный сигнал на остановку двигателя от координатора –
65425 – Неправильный сигнал на остановку двигателя от блока управления изготовителя дополнительного оборудования – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о неисправности дистанционного пульта останова двигателя, подключённого к блоку управления для изготовителя дополнительного оборудования.
65426 – Неправильный сигнал запроса частоты вращения холостого хода. –
65427 – Неправильный сигнал для стояночного тормоза –
65428 – Неправильный сигнал для стартера –
65429 – Неправильный сигнал для поддержания скорости спуска с помощью моторного тормоза-замедлителя – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сигнал о неисправности выключателя системы управления скоростью при спуске, подключённого к блоку-координатору.
65430 – Неправильный сигнал для ограничителя крутящего момента –
65431 – Неправильный сигнал для ограничителя скорости 2 –
65433 – Неправильный сигнал для педали тормоза – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о неисправности датчика педали тормоза, подключённого к блоку-координатору или к блоку управления тормозной системы.
65434 – Неправильный сигнал для педали сцепления – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сигнал о неисправности датчика педали сцепления, подключённого к блоку-координатору.
65435 – Неправильный сигнал для выключателя кик-дауна – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сигнал о неисправности выключателя “кикдауна”, подключённого к блоку-координатору.
65436 – Неправильный сигнал для круиз-контроля –
65437 – Неправильный сигнал для компрессора системы кондиционирования –
65438 – Неправильный сигнал для круиз-контроля – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сигнал о неисправности системы круиз-контроля, подключённой к блоку-координатору.
65439 – Неправильный сигнал для моторного тормоза-замедлителя –
65440 – Неправильный сигнал на режим быстрого прогрева –
65441 – Неправильный сигнал от коробки отбора мощности. –
65442 – Неправильный сигнал от коробки отбора мощности. –
65443 – Неправильный сигнал скорости автомобиля – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о неисправности датчика скорости автомобиля, установленного на вторичном валу коробки передач и подключённого к блоку-координатору или к тахографу.
65444 – Неправильный сигнал скорости движения автомобиля – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о неисправности датчика скорости автомобиля, подключённого к блоку-координатору или к тахометру.
65445 – Неправильный сигнал для атмосферного давления – Блок управления двигателем получил по шине CAN сообщение по поводу неправильного сигнала от датчика атмосферного давления, который соединен с координатором.
65446 – Неправильный сигнал для наружной температуры – Блок управления двигателем получил по шине CAN сообщение по поводу неправильного сигнала от датчика наружной температуры, который соединен с координатором.
65456 – Сигнал от датчика положения педали акселератора – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о том, что текущее положение педали акселератора превышает 100%. Датчик положения педали акселератора подключен к блоку-координатору.
65457 – Выключатель режима холостого хода – Блок управления двигателем по шине CAN получил сообщение о неисправности датчика-выключателя холостого хода. Датчик-выключатель холостого хода подключен к блоку-координатору.
65520 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не была завершена за предписанный промежуток времени.
65521 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не была завершена за предписанный промежуток времени.
65522 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не прошла.
65523 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не прошла.
65524 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не прошла.
65525 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не прошла.
– Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не была завершена за предписанный промежуток времени.
65527 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Неправильное последнее выключение блока управления двигателем.
65532 – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором – Взаимопроверка между блоком управления двигателем и координатором не прошла.
С 0111 (может меняться в зависимости от рынка), иммобилайзер могут быть установлены в качестве опции на заводе или модернизированы при условии ввода автомобиля
оснащен координаторов и двигатель противоречивые единицу правильном поколения.
введите S6 или MS6.
1 ключ стартера с транспондером
Ключ стартера имеет традиционный механический
функционировать, но и имеет встроенный транспондер для шифрования электронных сигналов от координатора.
2 Блок приемопередатчика (E49)
Это действует в качестве связующего звена между координатором и транспондера. Он расположен вокруг замка стартер и включает в себя антенну и блок передатчика / приемника. Антенна катушка имеет индуктивную связь с транспондера, в то время как блок передатчика / приемника находится в последовательный контакт с координатором.
3 Выключатель стартера (S4)
Помимо обеспечения координатора напряжение через штифт 15, замок стартер также передает сигнал к координатору когда ключ зажигания вставлен в замок.
4 Сигнальная лампа (W33)
Эта лампа находится в панели управления и предоставляет водителю информацию о состоянии иммобилайзера. Он может постоянно гореть или мигать в зависимости от текущей ситуации.
5 координатор (E30)
Координатор содержит фактические мозги системы иммобилайзера. Автомобили с иммобилайзером всегда оснащены координатора по крайней мере 4 поколения.
6 Блок управления двигателем (E44 или E12)
Автомобили с иммобилайзером оснащены либо EDC S6 или EDC MS6 блока управления двигателем. Блок управления отключает подачу топлива, если условия устанавливаются системы иммобилайзера
не полностью выполнены.
7 Диагностический разъем (К1)
Разъем для подключения VCI и Scania
Diagnos / программист находится на вершине
центральный электрический блок.
8 Производитель переключатель, встроенный в ускорителе
Датчик педали (B25)
Вместе с PIN система кода, это
делает возможным выполнять чрезвычайной ситуации
начать в случае, если проблема в
связи между транспондером и
трансивер (см. стр. 28). Переключатель открыт, когда педаль отпущена.
9 Реле стартера (R2)
Реле стартера регулирует управляющее напряжение на стартер штифт 50. Реле блокируется координатора, если условия, установленные системы иммобилайзера не полностью выполнены.
10 Контрольная лампа (W44)
Лампа находится в шельфовой панели крыши. Когда ключ стартера вынимается из замка стартер, лампа будет мигать, указывая, что иммобилайзер активен. Транспортные средства, оснащенные VPS и иммобилайзером не имеют W44 и только два VPS лампы используются.
Небольшое количество ранней серии автомобилей могут не иметь световой индикатор W44 вообще, независимо от того, или нет они оснащены VPS.
11 Жгут проводов
Существует специальный кабельный жгут для подключения трансивера. Кабели между блоками управления такие же, как на транспортных средствах без иммобилайзера, однако.
12 Разъем (C487)
Разъем C487 устанавливается только в небольшой серии автомобилей раннего производства, что делать
нет индикаторная лампа W44.
Компоненты 1, 2, 4, 10, 11 (и 12) являются уникальными для автомобилей, оснащенных иммобилайзером. Что касается Координатору и управления двигателем блок, это
возможно они присутствуют в других автомобилей с
же компонент обозначение. Это
программирования, который отличается.
Начиная процедуру
Когда водитель поворачивает ключ зажигания в положение питания 15, ток будет поступать на координатора, который в свою очередь поставляет 12 вольт в трансивера. Система использует 12 вольт
Ключ стартера, координатор и блок управления EDC впоследствии проверяется. Если все в согласии, реле стартера и подачи топлива будет
активирован. Предупреждение W33 лампа не покажет на, если есть что-то не так.
Весь этот процесс больше не принимает 200-300 мс и едва заметны для водителя.
Verifying the starter key
1 After powering up, the transceiver will seek inductive contact with the starter key
transponder.
2 After making contact, the transceiver will send confirmation to the coordinator.
3 The coordinator then sends a random number to the transponder via the transceiver unit.
4 The transponder encrypts the random number and sends back an encrypted response to the coordinator. Meanwhile, the coordinator has itself encrypted its own random number and now checks that the transponder’s response is the same as its own.
Fault codes
Fault codes related to the immobiliser are stored in the coordinator. The principle tool
used to check for any fault codes is Scania Diagnos. There are, however, other ways of reading and clearing codes using the diagnostic lamp and the diagnostic switch (S50) on the instrument panel.
The switch in question is marked «COO» (diagnostic switch panel pin 10) and is
connected to coordinator pin 12. The switch, which has a return spring, closes and earths pin 12 when it is depressed.
The coordinator interprets this as a request to show any fault codes and will flash them out by intermittently connecting pin 12 to ground in the required pulse sequence when the switch on the panel is released.
Reading fault codes
• Switch on the power supply.
• Depress the diagnostics switch marked
«COO» and keep it depressed for two seconds.
• The lamp will now flash if there are any fault codes present. A long flash indicates
tens and a short flash ones. Illustrated example: Fault code 26 is indicated with
two long flashes followed by six short ones.
• Depress the diagnostic switch once again to read the next fault code.
Erasing fault codes
Clear all fault codes as follows:
• Begin by switching off the current.
• Press the diagnostics switch and keep it depressed.
• Switch on the current again with the diagnostic switch depressed.
Limitations
Remember that reading fault codes is not always regarded as the perfect troubleshooting method. The software used is very advanced but, nonetheless, some types of faults may arise that cannot be registered with fault codes.
Likewise, situations may arise when a fault code is generated even though there is not
fault at present. Such an example may be temporary bad contact or that a cable splice has disconnected and then connected again while the power has been on.
Fault code 26
Fault
The starter key cannot be verified.
Cause
The starter key is interpreted as being invalid.
Either the key does not have a transponder at all or the transponder is faulty. However, it is also possible that the starter key has been programmed for another coordinator or other starter keys with transponders on the same key ring are interfering with the verification of the key.
A fault in the transceiver can also generate this
fault code.
Remarks
The immobiliser warning lamp, W33, will flash if this fault occurs.
For more information, select «Display of status» under the «Configuration…» button in
the system window.
Action
Make sure the correct starter key is in the starter lock. Make sure there are no more keys with transponders on the key ring. Check the transceiver and wiring.
Код ошибки 27
Координатор не может проверить контроль EDC
Блок управления EDC интерпретируется как
неисправен или не подходит для этого автомобиля. Оно не может быть
запрограммирован или имеет другой PIN кода, чем
координатор.
Это может быть связано с блок управления EDC не быть
заблокирован координатору после возобновления либо
координатор или блок управления EDC. Scania
Программист должен быть использован для блокировки единиц.
Замечания
Сигнальная лампа W33 придет на постоянно, если
автомобиль указана с иммобилайзером. Это
неисправность может возникнуть и на транспортных средствах, не
иммобилайзер, если они оснащены поколения
4 координатор. Эти транспортные средства не имеют
Предупреждение W33 лампа.
Двигатель не запустится, если происходит эта ошибка.
Более подробную информацию можно получить, прочитав
статус из блоков управления. Выберите «Отображение
Статус «под» кнопку Конфигурация … «в
оконная система.
Действие
Проверьте блок управления EDC, координатор и
проводки. Используйте Scania программист заблокировать EDC
блок управления к координатору.
Fault code 28
Fault
Short circuit on output from starter relay.
Cause
This fault code is generated when the output is short-circuited to ground.
Action
Check the starter relay and wiring.
Fault code 29
Fault
Invalid combination of signals to the coordinator.
Cause
This fault code is generated when the coordinator received a signal that the power is turned but there is no signal that the starter key is in the starter lock. The fault code will be generated if there is a fault for longer than 10 seconds.
Action
Check the starter lock and wiring.
Fault code 31
Fault
Start signal active continuously.
Cause
This fault code is generated when the coordinator receives a continuous signal that the engine has been started even though it is already running.
The fault code is generated when the signal has been active for over 5 minutes.
Action
Check the starter lock and wiring.
Codes
Besides a plastic pouch containing the mechanical code for the starter key, a plastic
pouch with three other codes is also delivered together with new vehicles with immobiliser.
These are the PIN code, encryption code and bar code.
IMPORTANT! The codes are required for programming control units and starter keys.
Scania does not keep a register of codes and it is important that the vehicle owner keeps them safe. Lost codes will lead to extra labour and increased costs.
1. PIN Code
The PIN code can be found concealed inside the sealed plastic pouch. It always comprises 6 digits.
Principally, both the associated control units must be unlocked before any work can be done on them. The PIN code then acts as a key.
Therefore, you must specify the PIN code in
order to carry out many of the actions in Scania
Programmer. The PIN code is generally
required:
• When renewing the coordinator.
• When renewing the EDC control unit.
• When removing any of the control units if they are to be used in another vehicle.
• When additional starter keys are used.
• When activating the immobiliser.
In addition, the PIN code is required if an emergency start has been necessary for some reason (see side 28).
2. Encryption code
The encryption code can be found concealed inside the sealed plastic pouch. It always
comprises 12 alphanumeric characters.
You could say that the encryption code is a key that is used to verify the transponder in the starter key. For this reason, the code must be used:
• When the coordinator has been renewed and you still want to use the same starter keys as before.
• When reactivating a system that has previously been deactivated.
3. Bar code
The bar code can be found outside the plastic pouch. It is read at the factory when the control units are initially programmed.
At that moment, the control units automatically learn the PIN code and encryption code that are associated with the bar code. This means that these codes need not be revealed at this time.
The bar code, however, may also have to be specified manually in Scania Programmer. In that case, enter the 16 alphanumeric characters printed underneath the bar code lines. This will be required:
• When using new starter keys.
• When renewing the coordinator with associated new starter keys.
Timed unlocking — if the codes have been mislaid
Scania Programmer has an emergency function called timed unlocking. Performing timed unlocking enables you to unlock and program the control units even though the PIN code and encryption code have been mislaid.
Timed unlocking activates a timer in the coordinator and requires 12 hours to complete, which is why it is regarded as an emergency function.
You can disconnect Scania Programmer during this time, but the power must be turned on.
Cutting off the power will interrupt the timed unlock.
After initiating timed unlocking, the program will display a lock code that must be given once the 12 hours are up. Entering this code manually will reset the coordinator to basic generation 3 and unlock the EDC control unit.
This means that new codes must be used for reprogramming once timed unlocking has been carried out. Starter keys (and possibly the starter lock) must be replaced with new ones. You will receive new codes with the new keys.
Coordinator serial number
The coordinator serial number must be given when initiating timed unlocking. The number is printed on a label affixed to the top of the coordinator (see illustration).
Functions in Scania Programmer
As Scania Programmer is required for most of the tasks that can be carried out on the
immobiliser system, this section contains an overview of the options listed under the
«Programming…» button.
An overview with brief descriptions of what each option is used for is given below. For more detailed instructions, refer to the program’s help
file.
Programming the coordinator
Choose this option to program the codes into an unprogrammed coordinator 4, for example when the coordinator has been replaced with a new one or when the old codes have been deleted from a used coordinator.
Note that all generation 4 coordinators must be programmed, even when the vehicle is not equipped with immobiliser.
You will be asked to select one of three
programming alternatives:
• To program new starter keys, which will
also entail new codes.
• To retain the vehicle’s previous keys and
codes.
• To program without immobiliser.
Once the codes have been programmed, the
coordinator must be locked to the EDC control
unit. Refer to «Locking the EDC control unit to
the coordinator» below.
Locking the EDC control unit
to the coordinator
Choose this option after renewing the
coordinator or the EDC control unit. You go
straight to this step after renewing the EDC
control unit. Refer to «Programming the
coordinator» above regarding the coordinator.
The program will first check the status of both
control units. Are they locked or unlocked?
Both units must be unlocked in order to be
reprogrammed.
This means that the control units can be locked
individually without being locked to any other
control unit. If any of them are locked, you will
be asked to unlock them using the PIN code.
What happens when the control units are
subsequently ready for locking to each other
naturally depends on the circumstances. Has
the coordinator been renewed and in that case
which options were selected under
«Programming the coordinator»? Or has the
EDC control unit been renewed?
The program will detect this information itself
and display it on the screen. In principle, the
control units will learn the same codes in order
to communicate with each other irrespective of
the circumstances. After learning it, they are
said to be locked with each other.
Resetting the coordinator
Choose this option if the coordinator is to be
removed from the vehicle and then reused in
another vehicle. This need not be done if the
coordinator is not programmed for an
immobiliser.
These measures can also be employed after
fitting a used and locked coordinator that is to
be reprogrammed. This presumes that you also
have access to the PIN code and encryption
code belonging to the coordinator in question.
Resetting the coordinator will delete its code
memory and it will retake the basic
programming of generation 3 or 4, which is the
equivalent of a new coordinator. Of course,
resetting also entails that the coordinator is no
longer locked to the EDC control unit.
If you remove the coordinator without resetting
it and still want to use it in a new connection,
you must make sure the PIN code and
encryption code accompany the coordinator.
Otherwise, it will remain locked and cannot be
reused.
Unlocking the EDC control
unit
The EDC control unit must be unlocked in
order to be reprogrammed. If it is removed from
a vehicle with immobiliser without doing this
first, its PIN code must accompany it so that the
control unit can be used together with another
coordinator. Otherwise, it will remain locked
and cannot be reused.
As soon as the EDC control unit is unlocked, it
will no longer contain any codes.
Additional starter keys
It is possible to add to the number of keys
available for a vehicle. The maximum number
of starter keys that can be programmed for one
and the same vehicle is 8.
The same encryption code programmed into the
coordinator is also used for the transponders in
the new keys. In this way, the original system
codes can be retained.
Replacing starter key
For security reasons, after purchasing a used
vehicle for instance, it may be necessary to
replace all the starter keys with new ones.
This measure entails first resetting the
coordinator to its basic programming (deleting
its codes). The new codes that come with the
new starter keys can then be programmed by
just entering the bar code. The old system codes
can then be discarded.
Finally, the control units must be locked to each
other again as described in «Locking the
coordinator to the EDC control unit» above.
The program will take you there automatically.
Activating immobiliser
To be able to activate the immobiliser using this
option, the vehicle must have previously had an
activated immobiliser that has been deactivated.
This option really does not involve anything
other than performing certain measures that
have been described earlier. The coordinator
must first be reset to a basic generation 4, after
which it must be programmed with codes again
(either with new ones or the old ones) and then
locked together with the EDC control unit.
Deactivating immobiliser
This option also gives only directions on which
earlier described measures are to be carried out
to deactivate the immobiliser.
Start by resetting the coordinator to a basic
generation 4. As all generation 4 coordinators
must be locked to the EDC control unit,
irrespective of whether the vehicle has an
immobiliser or not, you should now select
«Programming the coordinator».
You can then select «Without immobiliser» to
make the program lock the control units
together using the preset standard codes that
always apply when the immobiliser has been
deselected.
Upgrading the coordinator
If you have changed to a basic generation 3
coordinator in a vehicle that requires
coordinator 4, the program will be able to
upgrade the coordinator from 3 to 4.
If this is the case, you will not be able to access
the measures described above until the
coordinator has been upgraded. This is the only
selection that can be made at this stage.
Once the coordinator has been upgraded it will
be in its basic programmed form and at the
same initial position as described above.
«Programming the coordinator» is the next step.
Timed unlocking
This is an emergency function used to unlock
the control units if the codes have been mislaid.
This is described in the section «Codes» on
page 23.
ошибки скания
Ошибки SCANIA
Если Вы не нашли какой-то код неисправности, напишите, пожалуйста, об этом в WhatsApp на номер +79313424546
EMS Scania Engine Control Unit Fault codes list 5120-6149
See also: Scania trucks service repair manuals PDF
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
EGR valve with a pneumatic cylinder control
Fault:
When an EGR valve receives a request to go to the closed position, the EGR valve position sensor T124 indicates an open position (> 8%) affecting engine performance (power and emissions).
The reasons:
- The EGR valve could not close completely.
- Spring return fault on the EGR valve control cylinder.
- A problem with the operation of the valve block, V107.
- The EGR Position Sensor T124 is faulty or disconnected from the circuit.
Notes:
After starting the engine, the engine control unit performs an active check on the EGR valve if the following conditions are met:
The engine runs at idle.
Engine temperature above 60 ° C.
There is no request to turn on the EGR system (0%).
Motor brake is not included.
EGR has been adapted.
The air pressure in the parking brake circuit is at a normal level (above 7.5 bar).
In the case of a DTC, the EGR system remains active and the engine power does not decrease.
A fault code can be cleared even if it is active.
Elimination:
Check:
- EGR valve control cylinder by activating the EGR valve using SDP3. Set the set point to 0% and make sure that the EGR position sensor T124 reports a position close to zero. If an EGR adaptation was performed, the position should be below 1%. If the position does not fall below 8%, a fault code is generated. If the position is close to 8% or above this value, this is the cause of the DTC.
- EGR valve control cylinder, connectors and wiring to EGR valve position sensor circuit T124.
- Functioning valve block V107.
- If the EGR valve position sensor T124 is faulty or disconnected from the circuit.
- After replacing the control cylinder, EGR valve, or T124 EGR valve position sensor, be sure to perform basic setup and adaptation of the EGR system using SDP3.
EMS 5122
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Mass Flow Calibration
Fault:
During the calibration of the mass flow sensor, the minimum acceptable value was obtained.
The reasons:
Possible causes of the DTC may be as follows:
- Incorrect mass flow sensor, boost pressure sensor, or air temperature sensor in the intake manifold.
- Leaks in the EGR system or in the intake tract after the turbocharger.
- If the engine is not gaining momentum well, then a pressure sensor is likely to malfunction.
Notes:
The engine control unit switches off the exhaust gas recirculation system.
Elimination:
- Check sensors and wiring.
- Check for leaks in the EGR system or in the charge-air system.
- After the repair work with SDP3, it is necessary to restore the original parameters of the EGR system in the memory of the control unit.
EMS 5123
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Mass Flow Calibration
Fault:
During the calibration of the mass flow sensor, the maximum allowable value was obtained.
The reasons:
Possible causes of the DTC may be as follows:
- Incorrect mass flow sensor, boost pressure sensor, or air temperature sensor in the intake manifold.
- Leaks in the EGR system or in the intake tract after the turbocharger.
- If the engine is not gaining momentum well, then a pressure sensor is likely to malfunction.
Notes:
The engine control unit switches off the exhaust gas recirculation system.
Elimination:
- Check sensors and wiring.
- Check for leaks in the EGR system or in the charge-air system.
- After the repair work with SDP3, it is necessary to restore the original parameters of the EGR system in the memory of the control unit.
EMS 5124
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Diffuser
Fault:
Diffuser can not be properly controlled.
The reasons:
Jamming in the diffuser due to mechanical failure or due to insufficient pressure in the cavity of the executive cylinder. This can also be due to a blockage in the pressure relief valve channel in the valve block.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts down the EGR system and calibrates the mass flow sensor.
If the diffuser remains in the closed position, then at high loads and high speeds, the resistance of the diffuser increases significantly. As a result, the boost pressure and engine power will decrease, and black smoke may appear in the exhaust gases.
Elimination:
- Check diffuser and actuator cylinder.
- Check the tightness of the on-off valve.
- Check for pressure relief through the valve block.
EMS 5125
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Mass Flow Calibration
Fault:
Mass flow meter calibration disabled.
The reasons:
This DTC was recorded due to a fault in the EGR system during the current operating cycle (that is, since the on-board voltage was turned on). In this case, the sensor calibration is disabled.
Notes:
Mass flow meter calibration disabled. The malfunction code is automatically cleared when the ignition key supplies voltage.
Elimination:
Check other EGR codes (active and inactive). Turn on and off the onboard power supply with the ignition key.
EMS 5126
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
EGR
Fault:
The engine control unit has turned off the exhaust gas recirculation system.
The reasons:
The EGR system is disabled due to a system malfunction during the current cycle of operation (that is, since the on-board voltage is turned on).
Notes:
The engine control unit switches off the exhaust gas recirculation system. The malfunction code is automatically cleared when the ignition key supplies voltage.
Elimination:
Check other EGR codes (active and inactive). Turn on and off the onboard power supply with the ignition key.
EMS 5127
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
EGR composition
Fault:
Exhaust gas recirculated too little; It is not possible to increase the amount of recycled exhaust gas to a fixed level.
The reasons:
Possible causes of the DTC may be as follows:
- The EGR valve shut-off element does not open. This can be caused by sticking of the valve itself, insufficient pressure of compressed air supplied to the executive cylinder or leakage of compressed air from the executive cylinder.
- Track valve may be faulty.
- The movable element of the diffuser stuck in the open position.
- EGR gas leakage.
- The mass flow sensor may indicate a too high value, as a result forcing the engine control unit to conclude that the engine is receiving too few EGR gases.
Notes:
The fault affects the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by the car, and a warning lamp lights up in the instrument cluster, warning of a high level of pollutants. On vehicles with NOx control, a text message is also displayed.
Cars with NOx control
An active DTC cannot be deleted from the control unit. When the malfunction is resolved so that the malfunction code becomes inactive, the control unit must ensure that the malfunction has been eliminated.
Elimination:
- Check the throttle in the EGR valve, control cylinder and follow valve by activating the elements with SDP3.
- Check wedge diffuser.
- Check for leaks in the EGR system.
- Check the air flow sensor.
- After elimination of malfunction with the help of SDP3, it is necessary to restore the initial parameters of the EGR system in the control unit.
- Continue as follows to ensure that the problem is resolved:
- Drive the car for at least 10 minutes to get the EGR system running. The EGR system must be running so that the control unit can verify the repair.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. In this case, delete the fault code.
- To turn off the alarm, turn off and turn on the ignition with the ignition key three times in a row at 10-second intervals.
EMS 5129
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
EGR cooler
Fault:
No description
The reasons:
The EGR cooler is locked.
Notes:
The engine control unit reduces the amount of EGR gases.
Elimination:
Remove and clean the EGR cooler.
EMS 5138
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Back pressure in exhaust system
Fault:
The back pressure in the exhaust system is too high when the engine brake is applied.
The reasons:
The exhaust manifold is plugged or the engine retarder damper is faulty, for example, it is stuck in the maximum braking position. A malfunction may also be the result of a malfunction in the backpressure sensor in the exhaust system or in the atmospheric pressure sensor.
Notes:
The check is performed only during operation of the engine brake. The engine brake works with increased braking force. This fault may cause engine damage.
Elimination:
- Check the proper operation of the follower valve.
- Check the engine brake valve for binding.
- Check back pressure sensor in exhaust system and atmospheric pressure sensor, as well as their electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5139
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 2110163, 2110160, 2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Back pressure in exhaust system
Fault:
The back pressure in the exhaust system is too high when the fuel supply is turned off.
The reasons:
The exhaust system is blocked or the engine retarder damper is faulty, such as stuck in the closed position. A malfunction may also be the result of a malfunction in the backpressure sensor in the exhaust system or in the atmospheric pressure sensor.
Notes:
Perform this check only when the fuel supply is turned off and the engine retarder is not activated. The engine brake moderator helps to increase braking force. This fault may cause engine damage.
Elimination:
- Make sure that the engine brake retarder valve is not stuck in the closed position and the exhaust system is not blocked.
- Check back pressure sensor in exhaust system and atmospheric pressure sensor.
- Check the connectors and wiring.
EMS 5140
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Back pressure in exhaust system
Fault:
The back pressure in the exhaust system is too high when the fuel supply is normal.
The reasons:
The variable nozzle of the turbocharger with variable geometry stuck in the closed position. A malfunction may also be the result of a malfunction in the backpressure sensor in the exhaust system or in the atmospheric pressure sensor.
Notes:
Perform this check only when the fuel supply is normal.
Engine torque is reduced to prevent engine damage.
The engine brake moderator helps to increase braking force. This fault may cause engine damage.
Elimination:
- Perform a lag check for a variable geometry turbocharger to ensure that the annular nozzle is stuck in the closed position.
- Make sure the EGR valve and the EGR cooler are not blocked. Make sure that in the turbocharger the compressor shaft and the wheel of the turbine wheel rotate with the creation of proper friction.
- Check back pressure sensor in exhaust system and atmospheric pressure sensor.
- Check the connectors and wiring.
EMS 5141
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 2110163, 2110160, 2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Back pressure in exhaust system
Fault:
The back pressure in the exhaust system is too low when the engine brake is applied.
The reasons:
Leakage in the exhaust manifold. Leaks in the engine brake valve or in the EGR valve or in the connections between the cylinder block and the engine brake valve and the EGR valve.
Notes:
The engine brake works with reduced braking force.
Elimination:
Check:
- for leaks in the exhaust manifold
- EGR valve for leaks using the EGR check for leaks
- work of the watching valve and valve of the motor brake
- back pressure sensor in exhaust system and atmospheric pressure sensor
- electrical connectors and wiring
EMS 5142
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Back pressure in exhaust system
Fault:
One or more faults in the backpressure sensor in the exhaust system.
The reasons:
- In the back pressure sensor in the exhaust system, several faults may occur.
- The DTC may also be caused by a fault in the atmospheric pressure sensor.
Notes:
The engine brake does not develop proper braking force.
Elimination:
Check:
- no leaks in exhaust manifold
- the operation of the follower valve and valve motor retarder.
- back pressure sensor in exhaust system and atmospheric pressure sensor
- electrical connectors and wiring
EMS 5145
Blocks:
9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Atmosphere pressure
Fault:
The atmospheric pressure sensor is generating an incorrect signal.
The reasons:
Atmospheric pressure sensor defective.
Notes:
Depending on the vehicle configuration, a reduction in torque is possible.
Elimination:
The atmospheric pressure sensor is built into the optional gas engine control unit; its separate replacement is not allowed.
EMS 5152
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Pressure sensor charge air.
Fault:
The value of the charge air pressure sensor is outside the acceptable range.
The reasons:
- The value of the charge air pressure sensor is too high or too low compared to signals from other pressure sensors.
- Possible reasons:
- Faulty charge air pressure sensor connector.
- The electrical wires of the charge air pressure sensor are faulty.
Notes:
The amount of fuel cannot be adjusted correctly.
This may adversely affect engine performance.
Elimination:
- Compare the values from the charge air pressure sensor, atmospheric pressure sensor and backpressure sensor in the exhaust system with the ignition on without starting the engine (power is supplied via terminal U15). All sensors must display atmospheric pressure.
- Replace the charge air pressure sensor if its reading deviates from other sensors by more than 0.35 bar.
- Verify that the repair was successful as follows:
- Run the engine until it reaches normal operating temperature.
- Turn off the engine, but leave the ignition key in the powering position via terminal U15.
- Wait 30 seconds and verify that the DTC has been deactivated.
EMS 5153
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Backpressure sensor in exhaust system
Fault:
The value of the backpressure sensor in the exhaust system is outside the acceptable range.
The reasons:
- The value from the pressure sensor in the exhaust manifold is too low compared to the values from other sensors.
- Possible reasons:
- Defective counter pressure sensor connector in the exhaust system.
- Defective back pressure sensor wires in exhaust system.
Notes:
The amount of fuel cannot be adjusted correctly.
This may adversely affect engine performance.
Elimination:
- Compare the values from the charge air pressure sensor, atmospheric pressure sensor and backpressure sensor in the exhaust system with the ignition on without starting the engine (power is supplied via terminal U15). All sensors must display atmospheric pressure.
- Replace the backpressure sensor in the exhaust system, if its reading is more than 0.35 bar deviating from that of the other sensors.
- Verify that the repair was successful as follows:
- Run the engine until it reaches normal operating temperature.
- Turn off the engine, but leave the ignition key in the powering position via terminal U15.
- Wait 30 seconds and verify that the DTC has been deactivated.
EMS 5154
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Air filter
Fault:
Air pressure after the filter is too low.
The reasons:
Air filter clogged.
Notes:
The air filter warning light comes on. Leads to increased fuel consumption, degradation and black smoke.
May damage the turbocharger.
Elimination:
Replace the air filter.
EMS 5155
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Sensor air filter.
Fault:
The air filter sensor generates a signal voltage that is too high.
The reasons:
Malfunction of the T157 air filter sensor, its wiring or connector.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on.
Air filter monitoring is deactivated.
Elimination:
Check T157 air filter sensor, wiring harness and connector.
EMS 5156
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
EGR valve
Fault:
The EGR valve reacts too slowly when closing.
The reasons:
Malfunction of the tracking valve V107 or EGR valve.
Notes:
Engine performance is deteriorating. Increased release of soot particles; smoke may be present.
Elimination:
- Using SDP3, check the function of the EGR valve. Make sure the valve moves gently. Check wiring and connectors.
- After replacing the control cylinder, EGR valve, or position sensor T124, be sure to perform basic setup and adaptation of the EGR system using SDP3.
EMS 5157
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Turbine Bypass Valve
Fault:
Short circuit to + battery or ground or open circuit of the servo valve controlling the turbine bypass valve.
The reasons:
Electrical wiring or monitor follower connector is damaged or not connected.
Notes:
A fault code can only be deleted when it is inactive.
Elimination:
Check the follow valve, wiring and connector.
EMS 5158
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Turbine Bypass Valve
Fault:
Short circuit to + battery tracking valve control valve bypass the turbine.
The reasons:
Short to + pin 8 battery in connector A3.
Notes:
A fault code can only be deleted when it is inactive.
Elimination:
Check the follow valve, wiring and connector.
EMS 5168
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
Invalid signal from the sensor. The temperature is lower than expected by the control unit.
The reasons:
- Defective exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter.
- In addition, a malfunction may occur if the design of the exhaust system has been changed.
Notes:
Faults lead to a lack of reagent supply or the addition of a very small amount of reagent.
Elimination:
- Check exhaust gas temperature sensor and wiring.
- Check exhaust system.
- To check if the malfunction has been fixed and if the malfunction code does not occur again, you can click on the malfunction code monitoring function and view the malfunction code. This DTC is not generated immediately. In order for the control unit to generate an active fault code, the fault causing the code generation must occur in four consecutive cycles, that is, the ignition must be turned off and on four times. To see if the DTC is in the process of being considered, that is, whether a DTC is generated, you can use the DTC Monitoring feature.
EMS 5169
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
Invalid signal from the sensor. The temperature is higher than expected by the control unit.
The reasons:
- Defective exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter.
- In addition, a malfunction may occur if the design of the exhaust system has been changed.
Notes:
As a result of this fault, too much reagent is added. This means that the unused reagent will pass through the SCR catalytic converter.
Elimination:
- Check exhaust gas temperature sensor and wiring.
- Check exhaust system.
EMS 5170
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
Invalid signal from the sensor. The constant value of the signal.
The reasons:
The temperature sensor in front of the catalytic converter SCR is faulty.
Notes:
Faults lead to a lack of reagent supply or the addition of a very small amount of reagent.
Elimination:
- Check exhaust gas temperature sensor and wiring.
- To check if the malfunction has been fixed and if the malfunction code does not occur again, you can click on the malfunction code monitoring function and view the malfunction code. This DTC is not generated immediately. In order for the control unit to generate an active fault code, the fault causing the code generation must occur in four consecutive cycles, that is, the ignition must be turned off and on four times. To see if the DTC is in the process of being considered, that is, whether a DTC is generated, you can use the DTC Monitoring feature.
EMS 5171
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
An improbable signal from an exhaust gas temperature sensor mounted on an SCR catalytic converter.
The reasons:
The exhaust gas temperature sensor gives an incorrect indication. The sensor is most likely to show a lower temperature than is typical for the respective operating conditions. In addition, this malfunction may occur if the design of the exhaust pipe has been changed.
Notes:
Reagent injection does not work properly when this DTC is activated.
Elimination:
- Check for signal from the sensor.
- Check exhaust system.
- Cars with NOx control
- This DTC will reduce torque on vehicles with control over NOx emissions.
- This fault code can be made inactive by traveling on a vehicle if the fault has been rectified.
EMS 5376
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Power supply
Fault:
The voltage of one of the sensors having a common power is higher than the set value.
The reasons:
Short circuit on the “+” battery of one of the sensors with common power. This may be one of the following sensors: Oil pressure sensor, mass flow sensor for exhaust gases or fuel temperature sensor.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
Elimination:
Check sensors, connectors and wiring.
EMS 5377
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Power supply
Fault:
The voltage of one of the sensors having a common power is below the set value.
The reasons:
Short circuit to ground of one of the sensors with common power. This may be one of the following sensors: Oil pressure sensor, mass flow sensor for exhaust gases or fuel temperature sensor.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
Elimination:
Check sensors, connectors and wiring.
EMS 5380
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Turbocharger, speed sensor 1
Fault:
Invalid speed value. The value is lower than expected.
The reasons:
- Malfunction in the turbine speed sensor.
- Malfunction of one of the other sensors related to the calculation of the engine load: charge air pressure sensor, mass flow sensor, charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check the turbine speed sensor, wiring harnesses and electrical connector.
- Check the charge air pressure sensor, mass flow sensor, charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5381
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Turbocharger, speed sensor 1
Fault:
Turbine speed too high.
The reasons:
- There may be a malfunction in the turbocharger speed sensor.
- The engine must produce too high a turbine speed.
Notes:
As long as the DTC is present, the engine power is reduced.
Elimination:
- Check the turbocharger speed sensor, electrical connectors and wiring.
- Check the mass flow sensor, charge air pressure sensor, charge air temperature sensor and atmospheric pressure sensor.
- Be sure to perform the basic adjustment of the mass flow sensor adaptation values after replacing the mass flow sensor or after repairing a leak in the engine intake system.
EMS 5382
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Turbocharger, speed sensor 1
Fault:
Invalid speed value. Value is higher than expected.
The reasons:
- Malfunction in the turbine speed sensor.
- Malfunction of one of the other sensors related to the calculation of the engine load: charge air pressure sensor, mass flow sensor, charge air temperature sensor.
- Air filter or intercooler closure. Leak in the intake system.
- The throttle valve does not open.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check the turbine speed sensor, wiring harnesses and electrical connector.
- Check the charge air pressure sensor, mass flow sensor, charge air temperature sensor.
- Check the air filter, intercooler and throttle valve.
- Check the intake system for leaks.
EMS 5383
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Supply voltage 1, engine control unit
Fault:
The power supply to the engine control unit was below acceptable levels.
The reasons:
The engine control unit has two parallel circuits for supplying voltage. A single-circuit voltage supply was insufficient, which could be due to a faulty fuse or a damaged electrical wiring harness.
Notes:
If the fuse is OK, the system is operating normally, but a fault code is generated. If the fuses of both circuits are faulty, the engine control unit does not receive voltage and the engine stalls.
Elimination:
Check the engine power supply fuses. Replace fuses if necessary. If the fault persists, check the wiring and connectors.
EMS 5385
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Power supply 2, engine control unit
Fault:
The power supply to the engine control unit was below acceptable levels.
The reasons:
The engine control unit has two parallel circuits for supplying voltage. A single-circuit voltage supply was insufficient, which could be due to a faulty fuse or a damaged electrical wiring harness.
Notes:
If the fuse is OK, the system is operating normally, but a fault code is generated. If the fuses of both circuits are faulty, the engine control unit does not receive voltage and the engine stalls.
Elimination:
Check the engine power supply fuses. Replace fuses if necessary. If the fault persists, check the wiring and connectors.
EMS 5392
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Power supply
Fault:
The voltage of one of the sensors having a common power is higher than the set value.
The reasons:
One of the common-power sensors has a short to battery. This may be one of the following sensors: Coolant temperature sensor, charge air temperature sensor, charge air pressure sensor, fuel line pressure sensor, or fan speed sensor.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
Elimination:
Check sensors, connectors and wiring.
EMS 5393
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Power supply
Fault:
The voltage of one of the sensors having a common power is below the set value.
The reasons:
One of the sensors with a common power supply has a short circuit between the power supply circuit of the sensor and the mass point of the sensor. This may be one of the following sensors: Coolant temperature sensor, charge air temperature sensor, charge air pressure sensor, fuel line pressure sensor, or fan speed sensor.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
Elimination:
Check sensors, connectors and wiring.
EMS 5408
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200, 2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Oil pressure sensor
Fault:
The signal of the oil pressure sensor in the engine lubrication system exceeds the normal value. This means that the oil pressure, measured at a certain speed, is higher than normal.
The reasons:
- The fault may be either electrical or mechanical.
- Electrical faults may be caused by a sensor or wiring fault.
- Mechanical faults that can lead to high oil pressure is a malfunction in the oil pump, safety valve or piston cooling valve.
- In addition, a malfunction may be caused by a blockage of the oil filter, a blockage of the lubrication system, or an incorrect viscosity of the oil.
- Due to the fact that the oil pressure sensor, fuel temperature sensor and mass flow sensor have a common power supply, the fault can also be caused by a fault in the electrical circuits of the fuel temperature sensor or mass flow sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check oil level and oil filter.
- Check the oil pressure sensor, fuel temperature sensor and mass flow sensor with connectors and electrical wiring.
- Check the oil and other elements in the lubrication system.
- To check if the malfunction has been fixed and if the malfunction code does not occur again, you can click on the malfunction code monitoring function and view the malfunction code. To allow the control unit to check the DTC, the coolant temperature must be in the range of 70 – 90 ° C, and the engine speed must be in the range of 500 – 2400 rpm. To see if the above conditions are satisfied, you can use the DTC function.
EMS 5409
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Oil pressure sensor
Fault:
The signal from the oil pressure sensor in the engine lubrication system is below the normal value. This means that the oil pressure, measured at a certain speed, is lower than normal.
The reasons:
- The fault may be either electrical or mechanical.
- Electrical faults can be caused by faulty sensors, electrical connectors, or electrical wiring.
- Mechanical faults that can lead to low oil pressure are faults in the oil pump, safety valve or piston cooling valve.
- In addition, a malfunction may be caused by leaks in the lubrication system, a blockage of the oil filter or suction pipe, the presence of fuel in the oil, a low oil level, or improper viscosity of the oil.
Notes:
Excessively low oil pressure can adversely affect many engine components and cause damage to them.
Elimination:
- Check oil level and oil filter.
- Check other parts of the lubrication system.
- Ensure that the oil pressure sensor shows the correct value.
EMS 5409
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Oil pressure sensor
Fault:
The signal from the oil pressure sensor in the engine lubrication system is below the normal value. This means that the oil pressure, measured at a certain speed, is lower than normal.
The reasons:
- The fault may be either electrical or mechanical.
- Electrical faults may be caused by a sensor or wiring fault.
- Mechanical faults that can lead to low oil pressure are faults in the oil pump, safety valve or piston cooling valve.
- In addition, a malfunction may be caused by leaks in the lubrication system, a blockage of the oil filter or suction nozzle, the presence of fuel in the oil, a low oil level or improper viscosity of the oil.
- Due to the fact that the oil pressure sensor, fuel temperature sensor and mass flow sensor have a common power supply, the fault can also be caused by a fault in the electrical circuits of the fuel temperature sensor or mass flow sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check oil level and oil filter.
- Check the oil pressure sensor, fuel temperature sensor and mass flow sensor with connectors and electrical wiring.
- Check the oil and other elements in the lubrication system.
- To check if the malfunction has been fixed and if the malfunction code does not occur again, you can click on the malfunction code monitoring function and view the malfunction code. To allow the control unit to check the DTC, the coolant temperature must be in the range of 70 – 90 ° C, and the engine speed must be in the range of 500 – 2400 rpm. To see if the above conditions are satisfied, you can use the DTC function.
EMS 5456
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Accelerator pedal position sensor, downshift signal (“kick-down”)
Fault:
The signal from the accelerator pedal is missing or incorrect.
The reasons:
Failure CAN signal or a signal failure “kickdown” of the accelerator pedal
Notes:
Activated increased idling speed.
Elimination:
Check for the presence of the coordinator generated by the fault codes that relate to the position of the accelerator pedal.
EMS 5476
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200, 2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Battery voltage
Fault:
Battery voltage was below acceptable value. It was 9 volts or less for 0.5 seconds.
The reasons:
The fault may occur during a cold start, if the battery is in poor condition.
Notes:
Under reduced voltage can be observed difficult start the engine.
Elimination:
- Check the battery and alternator.
- Check the connectors and wiring.
EMS 5477
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Battery voltage
Fault:
The battery voltage was above the allowable value.
The reasons:
This may be caused by the work start-charger.
Notes:
The engine is controlled and safely shut down.
Elimination:
- Check the battery and alternator.
- Check the connectors and wiring.
EMS 5479
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Atmospheric pressure sensor
Fault:
The atmospheric pressure sensor outputs a value that is higher or lower than expected. Differences in values issued by the atmospheric pressure sensor, a pressure in the exhaust system and a charge air pressure sensor, is too large.
The reasons:
The atmospheric pressure sensor may be dirty or defective and thus indicates an incorrect value.
Notes:
The engine control unit cannot compensate for differences in atmospheric pressure. As long as the fault code is present, the engine power can be reduced.
Elimination:
- Check the atmospheric pressure sensor, connectors and wiring.
- The engine is off, the voltage is turned on by the ignition key.
- Ensure that the atmospheric pressure sensor, backpressure sensor in the exhaust system and the charge air pressure sensor are the same. Otherwise, replace the sensor.
- Deactivate the trouble code by warming up the engine. Turn off the engine and turn on the power. Start the engine. The DTC will deactivate within 30 seconds.
EMS 5632
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Coil Electromagnetic Clutch Air Conditioning Compressor
Fault:
Malfunction in the air conditioning compressor.
The reasons:
The coil winding may be faulty or limited in operability. An open circuit in the wiring or connectors.
Notes:
The air conditioning system does not work.
Elimination:
Follow the general procedure for troubleshooting the air conditioning system, for example, in the coil winding and in its wiring.
EMS 5633
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Additional cooler fan
Fault:
Malfunction in the fan for additional cooler.
The reasons:
The solenoid valve may be faulty or limited in operability. An open circuit in the wiring or connectors.
Notes:
The additional cooler fan is not working satisfactorily.
Elimination:
Follow the general troubleshooting procedure for the optional cooler fan, for example, in a solenoid valve and its wiring.
EMS 5634
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Fan control
Fault:
Faulty fan.
The reasons:
The solenoid valve may be faulty or limited in operability. An open circuit in the wiring or connectors. In addition, it may be that in the element at the same time manifest several different faults.
Notes:
The fan does not work satisfactorily.
Elimination:
Perform a general procedure for troubleshooting a fan, for example, in a solenoid valve and its wiring.
EMS 5635
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 2110163, 2110160, 2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Radiator fan clutch unit
Fault:
The fan speed of the radiator deviates from the value requested by the control unit.
The reasons:
- Incorrect fan clutch.
- Too little or no oil in the fan clutch.
- The viscosity of the oil contained in the fan clutch has been changed.
Notes:
Fan clutch does not work properly and therefore cooling performance is reduced. It will not be possible to drive with high power output for extended periods of time.
Elimination:
- Check fan clutch.
- When manually turning the fan, a certain resistance should be felt. If the fan can be turned without resistance, the fan clutch is faulty.
- Also check the fan clutch for oil leaks. An oil leak from the fan clutch indicates that it is faulty.
EMS 5636
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Hardware check
Fault:
Malfunction in the electrical circuit to check the hardware.
The reasons:
A hardware check indicates a malfunction with regard to the stated specifications.
Notes:
Battery pressure may be difficult to verify.
The engine is off and it will not be possible to start it until the DTC is cleared.
Elimination:
- Clear the fault code. Restart the engine control unit by turning the ignition on with the ignition key. Wait a minute and turn off the ignition with the key.
- Clear trouble codes. Turn off the ignition and wait one minute. Turn the ignition ON and verify that the DTCs are cleared.
- If the DTC becomes active again, replace the engine control unit.
EMS 5637
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Engine management system
Fault:
The control unit has lost data or detected a malfunction in the system memory.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- A new software was programmed into the engine management system just before the relevant data was saved.
- A malfunction has occurred in the system data memory.
Notes:
The system is unreliable.
Elimination:
- Clear the fault code. Restart the engine control unit by turning off the ignition with the ignition key. Wait a minute and turn on the ignition with the key.
- Allow the engine to run for approximately 10 minutes. If the DTC appears again, replace the engine control unit.
EMS 5638
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
The engine control unit
Fault:
Fault memory engine control unit.
The reasons:
Faulty control unit or software changed.
Notes:
While there is a malfunction, the engine only works with increased idling speed.
Elimination:
- Clear the fault code. Restart the engine control unit by turning off the ignition with the ignition key. Wait a minute and turn on the ignition with the key.
- Allow the engine to run for approximately 10 minutes. If the DTC appears again, replace the engine control unit.
EMS 5639
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
The engine control unit
Fault:
Failure of the control unit.
The reasons:
The engine control unit is faulty or has been exposed to an electromagnetic field (EMC).
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving. The control system shuts off the fuel supply to the injectors.
Elimination:
- Clear the fault memory and turn off the ignition with the ignition key.
- Wait one minute.
- Turn on the ignition with the ignition key.
- Repeat this five times. Replace the control unit if this DTC is generated again.
EMS 5640
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
EOL data
Fault:
Vehicle data is lost.
The reasons:
This may be due to reprogramming the engine control unit using new software immediately before storing the relevant data or a malfunction in the system data memory.
Notes:
While there is a malfunction, the engine only works with increased idling speed.
Elimination:
Install the correct software in the engine control unit. Erase the DTC and turn off the ignition with the ignition key. Wait a minute and turn on the ignition with the key.
EMS 5641
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Error code
Fault:
Nozzle settings were lost from the block memory.
The reasons:
This may be due to reprogramming the engine control unit using new software immediately before storing the relevant data or a malfunction in the system data memory.
Notes:
As long as the DTC is present, the engine power is reduced.
Elimination:
The engine control unit must be reprogrammed.
EMS 5642
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Software Verification
Fault:
The engine control unit received an internal fault message.
The reasons:
For information about the current software version, refer to the technical information (TI).
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
For information about the current software version, refer to the technical information (TI).
EMS 5643
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Generator 2
Fault:
Failure in alternator charge power 2.
The reasons:
Short circuit or open circuit generator.
Notes:
The poor state of the power supply system. The battery discharge indicator located on the instrument panel lights up. Equipment that consumes significant current is turned off. Examples of disconnecting equipment: seat heating and heated exterior mirrors.
The EGR system is turned off. In accordance with current legal requirements, engine power is reduced on vehicles that are equipped with NOx exhaust control.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
- Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5644
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Starter control
Fault:
Starter malfunction.
The reasons:
A possible cause may be a malfunction in the starter or an element in which there are several different malfunctions at the same time.
Notes:
Starter is unreliable.
Elimination:
Perform a general procedure for troubleshooting a starter, such as a starter relay and its wiring.
EMS 5645
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Starter control
Fault:
Inadvertent inclusion of a starter.
The reasons:
Incorrect inside information in engine control unit.
Notes:
When the starter is activated while the engine is running, abnormal noise coming from the engine can be heard.
The starter is activated when the engine is off.
Elimination:
- Move the mode selector to neutral.
- Erase the DTC and turn off the ignition with the ignition key. Wait a minute and turn on the ignition with the key. Repeat this five times and make sure that the starter is not activated.
- Start the engine. If the starter does not work satisfactorily, it should be checked.
- Allow the engine to idle for approximately 10 minutes. If this DTC is generated again, a short to ground may be the cause. If this is the case, check the connectors and wiring.
- If there is no fault in the connectors and wiring: Replace the engine control unit and perform the test again.
EMS 5647
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
The engine control unit
Fault:
Failure of the control unit.
The reasons:
The engine control unit is faulty or has been exposed to an electromagnetic field (EMC).
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving. The control system shuts off the fuel supply to the injectors.
Elimination:
- Clear the memory of the trouble codes and:
- turn off the ignition using the ignition key
- wait one minute
- Switch on the ignition with the ignition key.
- repeat five times. If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5648
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
The engine control unit
Fault:
Internal malfunction of the engine control unit.
The reasons:
It may be due to malfunctioning equipment or unauthorized modification of the software.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Clear the fault memory and turn off the ignition with the ignition key. Start the engine and let it run for 10 minutes. If the fault code reappears, the control unit should be reprogrammed or, as a last resort, replaced.
EMS 5648
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving.
Elimination:
Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5649
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving.
Elimination:
Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5650
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving.
Elimination:
Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5651
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 2110163, 2110160, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Engine management system configuration
Fault:
The engine management system receives from the OPC a signal that the vehicle has an automatic clutch, although the configuration of the engine management system has not been properly configured.
The reasons:
Engine management system configuration is incorrect.
Notes:
A request for an emergency stop from OCR will not work.
Elimination:
If necessary, contact Helpdesk for the correct SOPS file.
EMS 5652
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
This DTC will also generate DTC 5656.
Elimination:
Use SDP3 to restore the original values of the configuration parameters to the control unit. Erase the trouble codes from the memory, then turn off the ignition with the ignition key, and then turn it on again. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5653
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
This DTC will also generate DTC 5656.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble code memory. Turn on and off the onboard power supply with the ignition key. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5654
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving.
Elimination:
Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5655
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
While there is a fault, the car cannot start moving.
Elimination:
Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5656
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed). During the entire time interval when the detected fault appears, the following functions are disabled:
Engine power takeoff
Clutch protection
Engine torque limit on some gears
Vehicle mass rating
Cruise control and cruise control will operate with a noticeable delay.
The engine fan speed control system will operate abnormally.
Elimination:
Use SDP3 to restore the original values of the configuration parameters to the control unit. Erase the trouble codes from the memory, then turn off the ignition with the ignition key, and then turn it on again. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5657
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
System shutdown
Fault:
Incorrect procedure to turn off the engine control unit. Power line 30 was disconnected from the control unit earlier than line 15, that is, the power from the battery was interrupted before the ignition was turned off.
The reasons:
- The power to the engine control unit was turned off prematurely.
- This could be due to an incorrect engine stopping procedure with the ignition key or the engine being stopped using the ground switch.
- The supply voltage can be interrupted if additional equipment is connected to the consumer.
Notes:
When checking in engine kill mode, the control unit performs a functional check of the components after the ignition is turned off.
If the car is equipped with the SCR system, then at a stop, the system hoses are cleaned. It is important that the SCR system can be stopped without interrupting the power supply. Otherwise, the SCR system may be damaged: the reducing agent in the hoses will freeze and the nozzles will be clogged.
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
This fault also leads to a longer engine start.
It is assumed that the malfunction is resolved as soon as the engine control unit successfully completes a kill test.
An active DTC cannot be cleared until successful testing in the kill mode.
Elimination:
- Always turn off the engine with the ignition key.
- If the car has an SCR system, the main battery switch should not be turned off until at least 1.5 minutes have passed after turning off the key.
- Make sure that there is no additional equipment that interferes with the power supply.
EMS 5658
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Data transfer to the control unit has been interrupted.
The reasons:
- This malfunction may occur if the control unit supply voltage is too low or if the control unit itself malfunctions.
- If the car has a battery mass switch in the cab (used in buses and ADR cars), a fault code can be generated if the battery mass switch is used immediately after the ignition is turned off.
Notes:
A malfunction code may lead to a longer engine start.
This DTC may also generate DTC 65527.
Elimination:
- Check the battery and alternator.
- Clear the memory of trouble codes, and then turn off and turn on the ignition with the key.
- If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5659
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
A malfunction code may lead to a longer engine start.
Elimination:
Erase the trouble codes from the memory, then turn off the ignition with the ignition key and turn it on again. If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5660
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
If several fault codes are stored in the memory at once, then you should check whether this trouble code has also been recorded in the memory. As a result of this fault, the control unit cannot convert signals from pressure and temperature sensors, as well as other sensors, as a result of which fault codes of all these elements are recorded.
If the control unit starts working normally again, then in order for this code not to be considered as active, it is necessary to perform a check in the engine stop mode. When checking in engine kill mode, the control unit performs a functional check of the components after the ignition is turned off.
Elimination:
- If this DTC has been recorded into the memory of the control unit only once, erase the DTC from the memory, then turn off the ignition with the ignition key and then turn it on again. If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
- If this DTC has been generated several times, replace the control unit.
EMS 5661
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
If several fault codes are stored in the memory at once, then you should check whether this trouble code has also been recorded in the memory. As a result of this fault, the control unit cannot convert the signals from the pressure and temperature sensors and the battery voltage, as well as the signals from other sensors, as a result of which the fault codes for all these elements are recorded.
If the control unit starts working normally again, then in order for this code not to be considered as active, it is necessary to perform a check in the engine stop mode. When checking in engine kill mode, the control unit performs a functional check of the components after the ignition is turned off.
The fault affects the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by the car, and a warning lamp lights up in the instrument cluster, warning of a high level of pollutants. On vehicles with NOx control, a text message is also displayed.
Cars with NOx control
An active DTC cannot be deleted from the control unit. When the malfunction is resolved so that the malfunction code becomes inactive, the control unit must ensure that the malfunction has been eliminated.
Elimination:
- If the fault code was generated only once. Clear the memory of trouble codes, and then turn off and turn on the ignition with the key. If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
- If this DTC has been generated several times, replace the control unit.
- Continue as follows to ensure that the problem is resolved:
- Turn off and turn on the ignition with the ignition key.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Clear the fault code.
- To turn off the alarm, turn off and turn on the ignition with the ignition key three times in a row at 10-second intervals.
EMS 5662
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts off the fuel supply to the engine using solenoid valves. As a result, it is difficult to start the engine (the engine may not start at all).
Elimination:
Erase the trouble codes from the memory, then turn off the ignition with the ignition key and turn it on again. If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5663
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
- Internal malfunction in the control unit. A malfunction code can be generated by generating one of malfunction codes 1376, 5680-5686, 58880, or 58881.
- This DTC will also generate DTC 5665.
Notes:
While there is a malfunction, the engine control unit shuts off the fuel supply using solenoid valves. This often leads to short-term disruptions of the engine or, when the malfunction is present for a long period of time, to stop the engine.
Elimination:
Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5664
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
- The cause of the malfunction may be:
- Internal malfunction in the control unit.
- When starting, terminal U15 (ignition voltage) has an external current consumer.
- Power supply via terminal U15 from the control unit when disconnected, or through additional equipment or another control unit.
Notes:
Depending on the fault described above, the following will occur:
If a fault code is stored in memory, the engine control unit, despite repeated attempts, cannot turn off the EGR system.
Starting the control unit takes considerable time.
If a fault code is stored in memory, the engine control unit, despite repeated attempts, cannot turn off the EGR system.
Elimination:
- Check if there is a high current consumer at terminal U15.
- Check if the control unit is receiving power from the optional equipment.
- Check electrical wiring.
- Clear the DTC memory and perform a vehicle road test within 10 minutes. Check whether the malfunction code has been generated again. If this DTC was generated again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5666
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
As a result, engine unevenness may occur.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble code memory. Start the engine and increase the speed several times. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5667
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
As a result, engine unevenness may occur.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble code memory. Start the engine and increase the speed several times. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5668
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
As a result, engine unevenness may occur.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble code memory. Start the engine and increase the speed several times. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5669
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
As a result, engine unevenness may occur.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble code memory. Start the engine and increase the speed several times. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5670
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
With this fault, the maximum torque of the engine is reduced by 30%.
As a result, engine unevenness may occur.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble code memory. Start the engine and increase the speed several times. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5680
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
Wrong signal transmitted by the control unit to the solenoid valve controlling the fuel supply to the front group of cylinders.
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5681
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
Wrong signal transmitted by the control unit to the solenoid valve controlling the fuel supply to the rear cylinder group
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5682
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5683
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
One of the engine speed sensors is faulty.
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5684
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
One of the engine speed sensors is faulty.
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5685
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5686
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
During the entire time when the detected fault appears, the fuel supply to the engine stops. If the fault period is sufficiently long, the engine may stop.
As a result, other trouble codes can be recorded in the memory of the control unit.
Elimination:
Clear the trouble codes and test drive the car for 10 minutes. The fault code remains active? If the code is written to memory again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5687
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
If this DTC is stored in the memory, the control unit ignores pressing the accelerator pedal. The set engine speed of 750 rpm allows the vehicle to continue driving at minimum speed. At the same time, engine speed, coolant temperature and oil pressure are not displayed on the instrument panel.
In case of this fault, the engine cannot be started.
If the control unit starts working normally again, then in order for this code not to be considered as active, it is necessary to perform a check in the engine stop mode. When checking in engine kill mode, the control unit performs a functional check of the components after the ignition is turned off.
Elimination:
Erase the trouble codes from the memory, then turn off the ignition with the ignition key and turn it on again. If this DTC is generated again, replace the control unit.
EMS 5688
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Incorrect or unreliable data.
The reasons:
Internal malfunction in the control unit.
Notes:
Due to a fault, there is no communication with the SCR control unit.
If the control unit starts up again normally, in order for this code not to be considered as active, you must first perform a stop engine check.
Elimination:
- Clear the trouble code memory. Turn off and turn on the ignition with the ignition key. Check whether the malfunction code has been generated again. If this DTC was generated again, replace the control unit.
- Continue as follows to ensure that the problem is resolved:
- Turn off and turn on the ignition with the ignition key.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Clear the fault code.
EMS 5696
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Control block
Fault:
Unreliable data.
The reasons:
The software in the control unit was changed incorrectly.
Notes:
The fault leads to activation of the fuel supply at the level of 0% and, as long as the fault is present, the engine speed is limited to the nominal idling speed.
Elimination:
Replace the control unit.
EMS 5697
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Fan control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Open or short circuit in the electric circuit of the solenoid valve of the fan.
Notes:
The fan of the cooling system is not controlled. In this case, the motor fan may spontaneously turn on. May affect engine temperature.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5698
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Fan control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Short circuit in the fan solenoid valve circuit.
Notes:
The fan of the cooling system is not controlled. May affect engine temperature.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5699
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Turbine Bypass Valve Control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
An open or short in the solenoid circuit for the control valve for bypassing the turbine.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5700
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Turbine Bypass Valve Control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Short circuit in the electrical circuit of the solenoid valve for the turbine bypass valve.
Notes:
With this fault, the engine torque is reduced by 30% while the fault code is active (confirmed).
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5701
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Starter control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was out of range.
The reasons:
Short to battery + in the starter circuit.
Notes:
A short to battery can cause the starter to inadvertently turn on.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
Measure the resistance of the electric circuit of the traction electromagnet.
EMS 5702
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Starter control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
A short to ground in the electrical circuit of the starter.
Notes:
Starter cannot be turned on.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
Measure the resistance of the electric circuit of the traction electromagnet.
EMS 5703
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Generator 1
Fault:
When the engine is running, no current is supplied to the excitation winding of the generator.
The reasons:
Short circuit or open circuit in the generator power supply.
Notes:
The poor state of the power supply system. The battery discharge indicator located on the instrument panel lights up. Equipment that consumes significant current is turned off. Examples of disconnecting equipment: seat heating and heated exterior mirrors.
Elimination:
- Check the settings for the Number of Generators parameter.
- Make sure that the charging performed by the generator is directly controlled by the engine control unit.
- Check wiring and generator.
EMS 5704
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Generator 1
Fault:
The current is fed into the excitation winding of the generator when the engine is stopped.
The reasons:
Short to +24 V in the generator circuit.
Notes:
The poor state of the power supply system. The battery discharge indicator located on the instrument panel lights up. Equipment that consumes significant current is turned off. Examples of disconnecting equipment: seat heating and heated exterior mirrors.
Elimination:
- Check the settings for the Number of Generators parameter.
- Make sure that the charging performed by the generator is directly controlled by the engine control unit.
- Check wiring and generator.
EMS 5705
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Generator 1
Fault:
When the engine is running, no current is supplied to the excitation winding of the generator.
The reasons:
Short circuit or open circuit in the generator power supply.
Notes:
The poor state of the power supply system. The battery discharge indicator located on the instrument panel lights up. Equipment that consumes significant current is turned off. Examples of disconnecting equipment: seat heating and heated exterior mirrors.
Elimination:
- Check the settings for the Number of Generators parameter.
- Make sure that the charging performed by the generator is directly controlled by the engine control unit.
- Check wiring and generator.
EMS 5706
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Generator 1
Fault:
The current is fed into the excitation winding of the generator when the engine is stopped.
The reasons:
Short to +24 V in the generator circuit.
Notes:
The poor state of the power supply system. The battery discharge indicator located on the instrument panel lights up. Equipment that consumes significant current is turned off. Examples of disconnecting equipment: seat heating and heated exterior mirrors.
Elimination:
- Check the settings for the Number of Generators parameter.
- Make sure that the charging performed by the generator is directly controlled by the engine control unit.
- Check wiring and generator.
EMS 5707
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Air Conditioning Control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Open or short to +24 V in the solenoid circuit.
Notes:
The air conditioning compressor is not controlled. In this case, it is possible spontaneous activation of the air conditioning compressor.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5708
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Air Conditioning Control
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Short circuit in the air conditioning solenoid valve circuit.
Notes:
The air conditioning compressor is not controlled.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5709
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Diffuser On / Off Valve
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Open or short to +24 V in the on / off valve circuit.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts down the EGR system and calibrates the mass flow sensor.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5710
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Diffuser On / Off Valve
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Short circuit in the on / off valve circuit.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts down the EGR system and calibrates the mass flow sensor.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5713
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Power Supply Voltage
Fault:
The voltage in the circuit was outside the limits.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- A short to ground in the mass flow sensor circuit.
- Malfunction of the electrical circuit of the fuel temperature sensor or electrical circuit of the oil pressure sensor.
Notes:
The mass flow sensor, oil pressure sensor and fuel temperature sensor have a common power supply. In the event of a fault in one of the sensors, it may affect the electrical circuits of the other sensors.
A malfunction occurs because the mass flow sensor is not working. The engine will work with EGR, but without feedback on the signal of the mass flow sensor. Therefore, the control unit will only control the composition of EGR gases roughly, “roughly”, using predefined values to set the position of the EGR valve.
Calibration of the mass flow sensor is turned off.
Malfunction affects vehicle emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx); on the instrument cluster a warning lamp lights up, warning of a high level of pollutants. Vehicles with a NOx control system also display a text message.
Cars with NOx control system
An active DTC limits the maximum engine torque to approximately 40% after the engine has been running for 50 hours.
An active DTC cannot be deleted from the control unit. When the malfunction is resolved so that the malfunction code becomes inactive, the control unit must ensure that the malfunction has been eliminated.
Elimination:
- Check the mass flow sensor, oil pressure sensor and fuel temperature sensor with connectors and electrical wiring.
- Continue as follows to ensure that the problem is resolved:
- Start the engine and let it run at idle for at least 15 seconds.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Clear the fault code.
- Using the ignition key, turn off and turn on the power three times in a row at intervals of 10 seconds to deactivate the test lamp.
EMS 5714
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Solenoid valve of the motor retarder.
Fault:
Voltage continues to flow to the solenoid valve of the motor brakes after it is turned off.
The reasons:
Short to +24 V in the solenoid circuit.
Notes:
The engine retarder is off while the DTC is present.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5715
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Solenoid valve of the motor retarder.
Fault:
The voltage on the motor solenoid valve of the retarder is significantly lower than the required level.
The reasons:
Short circuit in the solenoid valve circuit.
Notes:
The engine retarder is off while the DTC is present.
Elimination:
Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5716
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
Engine brakes
Fault:
The latitude-modulated signal to the modulator of the motor retarder deviates from the expected value.
The reasons:
This malfunction may occur as a result of the wear of the shut-off element of the engine retarder solenoid valve. There are also possible leakage of compressed air from the air tubes or from the actuating cylinder.
Notes:
The effectiveness of the motor brakes is lower than expected.
Elimination:
Ensure that there are no air leaks. Check the solenoid valve.
EMS 5728
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
EGR valve tracking
Fault:
The control unit registers the current in the circuit, although the control unit does not supply power to the circuit.
The reasons:
Short to +24 V in the follower circuit.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts down the EGR system and calibrates the mass flow sensor.
The fault affects the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by the car, and a warning lamp lights up in the instrument cluster, warning of a high level of pollutants. On vehicles with NOx control, a text message is also displayed.
Cars with NOx control
An active DTC cannot be deleted from the control unit. When the malfunction is resolved so that the malfunction code becomes inactive, the control unit must ensure that the malfunction has been eliminated.
Elimination:
- Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
- Continue as follows to ensure that the problem is resolved:
- Start the engine and let it run at idle for at least 15 seconds.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Clear the fault code.
- Using the ignition key, turn off and turn on the power three times in a row at intervals of 10 seconds to deactivate the test lamp.
EMS 5729
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116
Title:
EGR valve tracking
Fault:
The control unit has detected that the current in the circuit is less than the set value.
The reasons:
Short in the follower circuit.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts down the EGR system and calibrates the mass flow sensor.
The fault affects the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by the car, and a warning lamp lights up in the instrument cluster, warning of a high level of pollutants. On vehicles with NOx control, a text message is also displayed.
Cars with NOx control
An active DTC cannot be deleted from the control unit. When the malfunction is resolved so that the malfunction code becomes inactive, the control unit must ensure that the malfunction has been eliminated.
Elimination:
- Check the electrical components, electrical connectors and wiring.
- Continue as follows to ensure that the problem is resolved:
- Turn on the onboard power with the ignition key.
- Activate the EGR check valve (part of the V107 valve block) by supplying 100% using SDP3.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Clear the fault code.
- Using the ignition key, turn off and turn on the power three times in a row at intervals of 10 seconds to deactivate the test lamp.
EMS 5744
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Starter.
Fault:
The engine control unit does not read the crankshaft speed sensor signal.
The reasons:
- This malfunction may occur if the starter drive gear cannot engage with the flywheel ring gear while the engine is starting.
- This DTC also appears if the engine control unit does not receive an engine speed signal (a speed sensor or electrical wiring is faulty).
Notes:
If within a few seconds after turning on the starter, the engine control unit does not receive a signal from the speed sensor, the starter will automatically shut down.
Elimination:
- Clear the DTC and restart the engine.
- It may be necessary to rotate the crankshaft at an angle.
- In order to accurately determine the cause of the malfunction, check that there are no malfunction codes related to the speed sensors in the memory.
- Check the speed sensors and their wiring.
EMS 5745
Blocks:
2110164, 2110165, 2110166, 2110162, 2110116, 2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Starter.
Fault:
The starter has been active for too long.
The reasons:
For some reason, the starter cannot start the engine.
Notes:
This feature is designed to protect the starter from overheating.
Starter start is ignored.
Elimination:
- The starter can be restarted immediately after shutdown.
- Cold weather conditions may require a longer start time.
- Check for air in the fuel system or other problems with the engine.
EMS 5746
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Engine crankshaft speed sensor
Fault:
No signal from engine speed sensors
The reasons:
The cause of the malfunction may be:
- lack of connection or malfunction of the engine speed sensors
- starter malfunction
- A fault code can also be generated if the battery is weakly charged and the starter does not work properly.
Notes:
As long as the DTC is active, the fuel supply stops.
Elimination:
- If the engine crankshaft rotates when attempting to start, check the engine speed sensors, electrical connectors and wiring.
- If the crankshaft does not rotate when the engine is started, check the starter motor.
EMS 5762
Blocks:
9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, mechanical failure
Fault:
The engine control unit has detected that the mechanism is not moving properly, with the result that the correct charge air pressure cannot be achieved.
The reasons:
Sticking of mechanical elements in a variable geometry turbocharger. This may be due, for example, to the presence of deposits, icing or damage to the guide vanes.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
The time for confirming the DTC is 1 s, the time for invalidation is 1 s.
Elimination:
Check the mechanical components of the turbocharger by checking the state of the variable geometry turbocharger in SDP3. Mechanical damage can be detected already at room temperature. Jamming due to mechanical tolerances or deposits can be detected when the turbocharger has a high operating temperature. Therefore, it is also necessary to perform a check on a heated turbocharger. The heated turbocharger has a temperature above 300 ° C (the exhaust gas temperature in the turbocharger can reach 600 ° C). Measure the temperature of the turbine housing using a non-contact infrared thermometer.
If the result of the status check is unsatisfactory:
- Remove the actuator. Make sure that the lever with the toothed segment can move freely between its extreme positions when moved by hand.
- If the lever with the toothed segment can move freely: Replace the actuator. Reinstall the actuator using SDP3 and perform a turbocharger status check with variable geometry.
- If the reset or status check fails, replace the actuator.
- If the status check is successful, it is possible that the previous adaptation of the actuator was incorrect. No replacement is required.
- If the lever with the toothed segment cannot move freely: replace the turbocharger with a variable geometry.
- If the status check is successfully passed for both the warm-up and the cold turbocharger, the cause of the DTC is a temporary malfunction, for example, as a result of icing when starting in low temperature conditions.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5763
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, danger of overspeeding
Fault:
Indication of exceeding the allowable rotational speed of a variable geometry turbocharger.
The reasons:
- Excessive speeds could be caused by a combination of a number of factors: for example, the width of the annular gap in the nozzle of a turbocharger with variable geometry, the position of the EGR valve and the amount of fuel supplied. The annular gap of the nozzle and the EGR valve is likely to be fully or partially closed at the same time, since there is a high engine load at the time of the malfunction.
- Turbine speed is measured by a turbine speed sensor. However, at the same time, the charge air pressure sensor checks the accuracy of the rotational speed. A fault code is generated if the difference between the actual and the estimated speed is too large. The fault may be present either in the turbine speed sensor or in the charge air pressure sensor.
Notes:
To reduce the turbine speed, the engine control unit immediately reduces engine power. Engine power will remain low until the turbine speed is sufficiently reduced.
The time for confirming the malfunction code is 30 s, the acknowledgment time is 5 s.
Elimination:
- Check the installation and operation of the turbine speed sensor T120.
- Measure the resistance at the turbocharger T120 speed sensor at room temperature. The resistance between pins 1 and 2 should be 850 ohms ± 50 ohms.
- Make sure the air filter is not blocked.
- Ensure that the charge air lines are not clogged and do not leak.
- Check the installation and operation of the charge air pressure sensor.
- Check if any other DTCs are generated. Take the necessary actions to eliminate the causes of other fault codes for the EGR system, fuel system or variable geometry turbocharger that were active.
EMS 5764
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, temperature
Fault:
The temperature in the turbocharger with variable geometry is too high.
The reasons:
The turbocharger does not cool well due to the fact that the cooling channels are blocked, or because the engine has been working for a long time with a high load.
Notes:
The power output of the turbocharger is reduced to prevent damage to the turbocharging system.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
Check:
- turbocharger and related items
- correct circulation of coolant in a turbocharger motor
- Disassemble the turbocharger and the electric motor and make sure that their mechanical components are working properly.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5765
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, temperature
Fault:
Abnormally high temperature in a variable geometry turbocharger.
The reasons:
The turbocharger does not cool well due to the fact that the cooling channels are blocked, or because the engine has been working for a long time with a high load.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Clean the cooling channels of the turbocharger with variable geometry.
EMS 5766
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, supply voltage
Fault:
An open circuit voltage supply to the actuator of a variable geometry turbocharger or supply voltage is too low.
The reasons:
An open circuit in the wiring harness or connectors or actuator supply voltage is too low.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases. The actuator warns of a malfunction when the supply voltage is below 20 V, which can occur when the starter is operating, at low temperature and when the battery is weak.
The time for confirming the malfunction code is 1–10 s, the acknowledgment time is 1 s.
Elimination:
- Check the operation of the F9 actuator fuse on the RP25.
- Make sure that the engine control unit receives the correct voltage (24 V) and supplies the correct voltage to the actuator of the turbocharger.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5769
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, several faults in the variable geometry turbocharger system.
Fault:
Several faults were detected in the variable geometry turbocharger system.
The reasons:
The variable geometry turbocharger actuator detected several faults and signaled them.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
- Eliminate other passive fault codes for variable geometry turbochargers.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5771
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, mechanical failure
Fault:
The actuator registered a mechanical fault in a variable geometry turbocharger.
The reasons:
Sticking of mechanical elements in a variable geometry turbocharger. This may be due, for example, to the presence of deposits, icing or damage to the guide vanes.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The time to confirm the fault code is 4-600 s. The acknowledgment time of the fault code is 10-20 s.
Elimination:
Check the mechanical components of the turbocharger by checking the state of the variable geometry turbocharger in SDP3. Mechanical damage can be detected already at room temperature. Jamming due to mechanical tolerances or deposits can be detected when the turbocharger has a high operating temperature. Therefore, it is also necessary to perform a check on a heated turbocharger. The heated turbocharger has a temperature above 300 ° C (the exhaust gas temperature in the turbocharger can reach 600 ° C). Measure the temperature of the turbine housing using a non-contact infrared thermometer.
If the result of the status check is unsatisfactory:
- Remove the actuator. Make sure that the lever with the toothed segment can move freely between its extreme positions when moved by hand.
- If the lever with the toothed segment can move freely: Replace the actuator. Reinstall the actuator using SDP3 and perform a turbocharger status check with variable geometry.
- If the reset or status check fails, replace the actuator.
- If the status check is successful, it is possible that the previous adaptation of the actuator was incorrect. No replacement is required.
- If the lever with the toothed segment cannot move freely: replace the turbocharger with a variable geometry.
- If the status check is successfully passed for both the warm-up and the cold turbocharger, the cause of the DTC is a temporary malfunction, for example, as a result of icing when starting in low temperature conditions.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5772
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, electric motor
Fault:
Too much movement of the ring nozzle in a variable geometry turbocharger.
The reasons:
Moving the ring nozzle incorrectly due to damage to the element or improper installation of the electric motor.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
- Make sure the variable geometry turbocharger is installed correctly.
- Reinstall software using SDP3.
- Check the turbocharger system with variable geometry, its elements, wiring and connectors.
- Check motor drive mechanism for damage and wear.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5773
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, electric motor
Fault:
Incorrect end position of the annular nozzle in a variable geometry turbocharger.
The reasons:
The shortened movement of the ring nozzle may be due to deposits in the turbocharger.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
- Check the turbocharger system with variable geometry and its elements.
- Check the nozzle for damage or deposits.
EMS 5774
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, actuator
Fault:
The actuator is turned off, which means that the turbocharger cannot provide the correct charge air pressure.
The reasons:
The cause of the malfunction is that the actuator failed in two consecutive attempts to properly register its own internal magnet.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
DTC is instantaneous.
Elimination:
- Try to recognize the invalidity of the malfunction code by turning off the ignition with the ignition key. Wait 10 seconds and then start the engine. If the DTC continues to be active:
- Remove the actuator. Make sure that the lever with the toothed segment can move freely between its extreme positions when moved by hand.
- If the lever with the toothed segment can move freely: Replace the actuator. Reinstall the actuator using SDP3 and perform a turbocharger status check with variable geometry.
- If the reset or status check fails, replace the actuator.
- If the status check is successful, it is possible that the previous adaptation of the actuator was incorrect. No replacement is required.
- If the lever with the toothed segment cannot move freely: replace the turbocharger with a variable geometry.
- Clear the DTC by turning off the key with the key and wait 10 seconds. Start the engine.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5775
Blocks:
9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, electric motor
Fault:
Too slow response time for nozzle ring.
The reasons:
A malfunction can be caused by carbon in the electric motor or damage to the turbocharger.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts off the EGR system and reduces engine power.
Elimination:
- Check the turbocharger system with variable geometry and its elements.
- Check the nozzle for damage or deposits.
EMS 5776
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable Geometry Turbocharger, timeout in the CAN bus
Fault:
The rupture of the communication circuit between the engine control unit and the turbocharger actuator with variable geometry. DTC, if not received a certain number of consecutive CAN messages.
The reasons:
Constant or repeated gap in the CAN circuits between the engine control unit and the actuator. Permanent faults are often caused by faults in the electrical wiring harness, connector or engine control unit. Repeated malfunctions are often caused by scratching the wires on the connector.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
The time for confirming the DTC is 0.005 s, the time for acknowledgment is 0.005 s.
Elimination:
Check whether DTC 1686 has also been generated. If so, run diagnostics for this DTC. If not, see instructions below.
- Ensure that the connector on the actuator harness is healthy and clean and that there is no moisture in it. Replace the connector if it is damaged.
- Disconnect the connector between the actuator and the engine wiring harness.
- Measure the resistance between pin 3 and pin 4 in the actuator connector at room temperature. Resistance should be either 120 ohms ± 10 ohms or 2,600 ohms ± 50 ohms. If the resistance does not match the specified values, replace the actuator.
- Measure the resistance between pin 3 and pin 4 in the engine wiring harness connector at room temperature. Resistance should be 120 ohms ± 10 ohms.
If the resistance does not match the stipulated values:
Disconnect the connector from the engine control unit. Measure the resistance in the cable harness between pin 3 and pin A4_6 at room temperature. Resistance should be 5 ohms ± 4 ohms. Repeat the measurement for pin 4 and pin A4_7. Measure between the individual wires of the wiring harness to eliminate any short circuit in the wiring harness. Measure the resistance between the A4_6 pin and A4_7 pin in the engine control unit at room temperature. Resistance should be 120 ohms ± 10 ohms.
If all of the above measurements gave the correct values, the waiting time on the CAN bus is probably due to friction between the pin and the cylindrical contact in the connector. This type of rubbing is difficult to detect without advanced electronic equipment. Replace the actuator and the connector and the opposite connector in the engine wiring harness. Securely fasten the wiring harness and its connectors.
If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5777
Blocks:
9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, mechanical failure
Fault:
The actuator registered a mechanical fault in a variable geometry turbocharger.
The reasons:
Sticking of mechanical elements in a variable geometry turbocharger. This may be due, for example, to the presence of deposits, icing or damage to the guide vanes.
Notes:
The engine control unit shuts off the EGR system and reduces engine power.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
The time to confirm the fault code is 4-300 s. The time of invalidation of the malfunction code is 5-10 s.
Elimination:
Check the mechanical components of the turbocharger by checking the state of the variable geometry turbocharger in SDP3. Mechanical damage can be detected already at room temperature. Jamming due to mechanical tolerances or deposits can be detected when the turbocharger has a high operating temperature. Therefore, it is also necessary to perform a check on a heated turbocharger. The heated turbocharger has a temperature above 300 ° C (the exhaust gas temperature in the turbocharger can reach 600 ° C). Measure the temperature of the turbine housing using a non-contact infrared thermometer.
If the result of the status check is unsatisfactory:
- Remove the actuator. Make sure that the lever with the toothed segment can move freely between its extreme positions when moved by hand.
- If the lever with the toothed segment can move freely: Replace the actuator. Reinstall the actuator using SDP3 and perform a turbocharger status check with variable geometry.
- If the reset or status check fails, replace the actuator.
- If the status check is successful, it is possible that the previous adaptation of the actuator was incorrect. No replacement is required.
- If the lever with the toothed segment cannot move freely: replace the turbocharger with a variable geometry.
- If the status check is successfully passed for both the warm-up and the cold turbocharger, the cause of the DTC is a temporary malfunction, for example, as a result of icing when starting in low temperature conditions.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5778
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Injector supply voltage
Fault:
Incorrect voltage supply to the injectors.
The reasons:
Possible cause is a faulty engine control unit.
Notes:
The engine control unit turns off the EGR system and the engine power decreases.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
- Clear the DTC and start the engine again. If this DTC is still active, replace the engine control unit.
- If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5779
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger, actuator
Fault:
Internal malfunction of the actuator, which means the inability to control the turbocharger with variable geometry.
The reasons:
The variable geometry turbocharger actuator has an internal electrical or mechanical fault that cannot be repaired.
Notes:
To protect the engine, the engine torque is reduced and the EGR system shuts down.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
DTC is instantaneous.
Elimination:
Replace the actuator following the instructions in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-30.
If the operating time since the generation of the fault code exceeds 10 hours, empty the EGR cooler, as there is a danger of condensation in the air-cooled EGR cooler after the EGR system is turned off. Empty the EGR cooler following the instructions given in the manual for service stations, subgroup 01-65.
EMS 5780
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
Too high pressure drop in the particulate filter.
The reasons:
The particulate filter is clogged with soot. This is probably due to the fact that the car was operated with a small load for a long time.
Notes:
If soot is present in the particulate filter, fuel consumption increases.
A large amount of soot causes an increase in engine noise, a deterioration in acceleration at high loads, and an increase in the risk of engine failure.
Elimination:
Clean the filter by driving the vehicle at high speed and with a high load for 15 minutes – 1 hour. If the DTC persists, the filter should be replaced.
EMS 5783
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Engine management system, EMS
Fault:
Malfunction in engine management software.
The reasons:
The control system memory may be full or damaged.
Notes:
The system may behave unpredictably.
In the event of a malfunction, fuel injection could be inadvertently stopped.
Elimination:
- Save the demo file.
- Contact Scania helpdesk and tell them what happened.
- Clear the DTC and see if it reappears.
EMS 5801
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Gas engine, ME7
Fault:
Internal malfunction in ME7.
The reasons:
Internal sensor malfunction or memory malfunction.
Notes:
Engine performance is deteriorating. The system can go into fail-safe mode.
Elimination:
- Check battery voltage.
- Replace the ME7 unit.
EMS 5802
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
SCR main unit
Fault:
Internal malfunction in the main unit.
The reasons:
The cause may be an external electrical fault (for example, a power or ground fault) of the level sensor and temperature in the reagent tank, or an internal hardware fault.
Notes:
The fault affects the level of emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by the engine.
Elimination:
- Check for any other DTCs indicating electrical faults in the system and correct these faults.
- If no other fault is found, replace the SCR main unit.
EMS 5803
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
High levels of soot in the particulate filter, automatic and manual regeneration blocked.
The differential pressure in the particulate filter exceeds the pre-set level.
The reasons:
- Manual regeneration was not performed.
- Malfunction of the differential pressure sensor T141.
Notes:
Automatic and manual regeneration blocked.
Maximum engine torque limit.
Elimination:
- Check the trouble codes and troubleshoot the corresponding faults in the EMS and EEC regarding faults in the sensors.
- Using SDP3, perform regeneration at a service station to clean the particulate filter.
EMS 5804
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
High level of soot in the black filter. All types of regeneration (automatic, manual and at the service station) are blocked.
The differential pressure in the particulate filter exceeds the pre-set level.
The reasons:
- Manual regeneration was not performed. Maximum soot level exceeded for safe regeneration.
- Malfunction of the differential pressure sensor T141.
Notes:
All types of regeneration (automatic, manual and at the service station) are blocked.
Maximum engine torque limit.
Elimination:
- Check the trouble codes and troubleshoot the corresponding faults in the EMS and EEC regarding faults in the sensors.
- The particulate filter is full and must be replaced.
- After installing a new filter, adjust the particulate filter load to the base value using SDP3.
EMS 5809
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
Excessive temperature drop in the oxidation catalytic converter.
Too short time delay for the temperature to change before or after the oxidation catalytic converter. Installed in case of load changes of less than 60 minutes.
The reasons:
- The oxidative catalytic converter is defective or missing.
- Malfunction in exhaust gas temperature sensors T158.
- Malfunction in other sensors.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on, automatic and manual regeneration is blocked.
Elimination:
- Check the trouble codes and troubleshoot the corresponding faults in the EMS and EEC regarding faults in the sensors.
- Do a search for damage that could lead to leaks in the exhaust system between the engine and the silencer.
- Ensure that the oxidation catalytic converter is in place and not damaged, see method “Removing and installing diesel particulate filter”.
- To confirm the repair, complete the journey on a car with various loads for 60 minutes.
EMS 5812
Blocks:
9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
Particulate filter cracks
Fault:
No description
The reasons:
No description
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Replace the particulate filter.
EMS 5813
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901, 9000000, 2089202, 2089201, 2089200
Title:
VGT, variable geometry turbocharger, internal temperature sensor
Fault:
Short circuit to ground U31.
The reasons:
Short circuit sensor circuit.
Notes:
This DTC can only be deleted when it is inactive. The NOx control system causes delayed torque limits.
Elimination:
Due to the fact that the sensor is installed on the PCB of the VGT actuator, the entire actuator must be replaced.
EMS 5822
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Torque reduction
Fault:
A malfunction has occurred, resulting in a reduction in torque. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the nature of the fault.
The reasons:
A malfunction has occurred, resulting in a reduction in torque. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the cause of the fault.
Notes:
The fault code is deactivated after the fault has been rectified.
Elimination:
Check for other DTCs and correct the corresponding problems.
EMS 5823
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Engine shutdown
Fault:
A malfunction has occurred, causing the engine to shut down. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the nature of the fault.
The reasons:
A malfunction has occurred, causing the engine to shut down. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the cause of the fault.
Notes:
The fault code is deactivated after the fault has been rectified.
Elimination:
Check for other DTCs and correct the corresponding problems.
EMS 5824
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Feature request ignored
Fault:
A malfunction has occurred, causing the engine control unit to ignore the function request. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the nature of the fault.
The reasons:
A malfunction has occurred, causing the engine control unit to ignore the function request. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the cause of the fault.
Notes:
The fault code is deactivated after the fault has been rectified.
Elimination:
Check for other DTCs and correct the corresponding problems.
EMS 5825
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Engine idle speed
Fault:
A malfunction has occurred, causing an increase in the idling speed. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the nature of the fault.
The reasons:
A malfunction has occurred, causing an increase in the idling speed. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the cause of the fault.
Notes:
The fault code is deactivated after the fault has been rectified.
Elimination:
Check for other DTCs and correct the corresponding problems.
EMS 5826
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Engine speed
Fault:
There was a malfunction that caused the engine speed to be fixed at the level of the idling speed. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the nature of the fault.
The reasons:
There was a malfunction that caused the engine speed to be fixed at the level of the idling speed. A fault code appears in combination with another fault code describing the cause of the fault.
Notes:
The fault code is deactivated after the fault has been rectified.
Elimination:
Check for other DTCs and correct the corresponding problems.
EMS 5827
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature
Fault:
The charge air temperature is too high.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- The cooling efficiency of the charge air cooler is too low due to pollution, low air consumption or a similar reason.
- Leakage in the charge air system or in the exhaust pipe in front of the turbine of the turbocompressor.
- Bypass valve stuck.
- The solenoid valve hose of the bypass valve is torn.
- The diaphragm of the bypass valve solenoid valve flows.
- The turbocharger impeller is dirty or broken.
- Turbine wheel of turbocharger broken.
Notes:
The yellow indicator lamp in the instrument panel is on.
Elimination:
Proceed as follows:
- Clean the charge air cooler.
- Check fan and fan clutch.
- Ensure that the intake air entering the intercooler is not too hot.
- Make sure that there is no leakage in the charge air system and in the exhaust pipe in front of the turbine of the turbocompressor.
- Check the bypass valve.
- Clean the turbocharger.
EMS 5829
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Additional accelerator pedal
Fault:
The voltage in the electrical circuit of the additional accelerator pedal was too low.
The reasons:
Short to ground.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Check out the optional accelerator pedal, as well as electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5830
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Additional accelerator pedal
Fault:
The voltage in the electrical circuit of the additional accelerator pedal was too high.
The reasons:
Short circuit to + battery or open circuit.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Check out the optional accelerator pedal, as well as electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5832
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Fuel drive
Fault:
Malfunction in the fuel supply drive or CAN connection timeout.
The reasons:
The signal from the fuel supply actuator from the coordinator indicates a malfunction, unavailable or gives an implausible value.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
No description
EMS 5833
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Accelerator pedal
Fault:
The control unit received a signal from the coordinator, indicating an accelerator pedal fault.
The reasons:
Accelerator pedal fault.
Notes:
Instead of the usual accelerator pedal will be used extra.
Elimination:
No description
EMS 5835
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air pressure sensor
Fault:
The charge air pressure sensor shows a static value even when the engine is running at varying speeds.
This DTC can only be deleted when it is inactive.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air pressure sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Make sure the sensor value is static.
- Check sensor connectors and wiring.
- Replace the charge air pressure sensor.
- To clear the DTC, let the engine run under load. If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive and can be erased.
EMS 5836
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Exhaust pressure sensor
Fault:
The pressure sensor in the exhaust system shows a static value even when the engine is running at varying speeds.
The reasons:
Malfunction of the pressure sensor in the exhaust system.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Make sure the sensor value is static.
- Check sensor connectors and wiring.
- Replace the pressure sensor in the exhaust system.
EMS 5837
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the catalytic converter
Fault:
The pressure sensor in the exhaust system in front of the catalytic converter shows a static value.
The reasons:
Malfunctioning exhaust gas temperature sensor in front of the catalytic converter.
Notes:
If the specified value is lower than the actual value, this may result in too small an amount of injected reagent and, thus, an increase in engine emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx).
If the specified value is higher than the actual value, this may result in too much injected reagent or injecting reagent into a cold catalytic converter.
Elimination:
- Check sensor signal. Check sensor connectors and wiring for visible damage.
- In the case of engines with a NOx monitoring system, the control unit must verify that the malfunction has been rectified. Verify that the exhaust temperature sensor is working. Using SDP3, execute “Invalidation of DTCs for the NOx Control System”. This will take about 30 minutes and should be performed outdoors. Alternatively, four times in a row for 12 minutes, allow the engine to run at a speed of 1000 rpm and an exhaust gas temperature above 200 ° C with the ignition off between the segments. If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive and can be erased.
EMS 5838
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor after SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The NOx sensor after the catalytic converter shows a static value. Typically, the value should vary in accordance with the engine speed and load.
The reasons:
Malfunction or incorrect installation of the NOx sensor.
Notes:
The fault affects the emissions of nitrogen oxides by the engine. NOx warning lamp is on.
Engine torque is reduced by approximately 40% after the engine has completed 36 hours.
Elimination:
- Check if the NOx sensor indicates a static value. Check the sensor connectors and wires and make sure the sensor is installed correctly.
- If no other problems are found, replace the sensor.
- To verify that the problem is resolved, follow these steps:
- Switch off the onboard power using the ignition key. Wait at least 90 seconds and then turn on the power again.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Then clear the fault code.
- To turn off the test lamp, turn off and turn on the power with the ignition key three times. Pause 10 seconds between each cycle.
EMS 5839
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The NOx sensor in front of the catalytic converter shows a static value. Typically, the value should vary in accordance with the engine speed and load.
The reasons:
Malfunction or incorrect installation of the NOx sensor.
Notes:
Malfunction affects engine emissions of NOx. NOx warning lamp is on.
An active DTC cannot be deleted using SDP3. The following repair operations with the control unit must confirm the repair of the fault.
Elimination:
- Check if the NOx sensor indicates a static value. Check the sensor connectors and wires and make sure the sensor is installed correctly. If no other problems are found, replace the sensor.
- To verify that the problem is resolved, follow these steps:
- Switch off the onboard power using the ignition key. Wait at least 90 seconds and then turn on the power again.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Then clear the fault code.
- Turn off and turn on the power three times at intervals of 10 seconds to deactivate the test lamp.
EMS 5845
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
The value of the differential pressure sensor is more than permissible differs from 0 when the engine is off and the power is on. Without the exhaust gas flow rate, the pressure drop must be close to 0. The fault is set for one minute while the power is on.
The reasons:
Malfunction of the differential pressure sensor T141. Fault in the wiring harness or connectors. Faulty outdoor temperature sensor.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on.
Elimination:
- Check the outdoor temperature sensor fault code and correct the corresponding fault.
- Check the differential pressure sensor T141 with the power on and the engine off. The differential pressure should be close to 0. Start the engine and make sure that the value is different from 0 at high idle speed.
- Check the wiring harness between the differential pressure sensor and the control unit. Inspect the exhaust system for damage related to the sensor.
- If the sensor does not respond as described, replace it.
- To confirm the repair:
- If the engine is hot, leave it off for at least one hour and then turn on the power for at least one minute.
- If the engine is cold, turn on the power for at least one minute.
EMS 5846
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
Poor fit between measured pressure drop and engine exhaust gas flow.
The reasons:
- Malfunction of the differential pressure sensor T141. Fault in the wiring harness or sensor connector.
- Malfunction in other sensors.
- Leaks in the exhaust system between the engine and silencers.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on.
Elimination:
- Check the differential pressure sensor T141 with the power on and the engine off. The differential pressure should be close to 0. Start the engine and make sure that the value is different from 0 at high idle speed.
- Check wiring harness and sensor connector.
- Verify that there is no physical damage to the exhaust system and muffler.
- Check the malfunction codes and correct the relevant malfunctions related to the mass flow sensor, charge air pressure sensor and outdoor temperature sensor.
- Check for leaks in the exhaust system between the engine and mufflers.
- If the sensor does not respond as described, replace it.
- To check the quality of repair, allow the engine to work with a variable load up to 20 minutes.
EMS 5847
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Camshaft sensor
Fault:
No description
The reasons:
The engine control unit has an internal software error or hardware malfunction.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Clear the fault code.
- If this DTC is re-generated, follow these steps:
- Make sure the sensor is properly connected to the engine control unit.
- Check the sensor electrical wires.
- Replace sensor.
- Reinstall the software in the engine control unit.
- Replace engine control unit.
EMS 5848
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter indicates a too low value.
The reasons:
Possible causes may be a failure of the NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter or the incorrect installation of the NOx sensor in front of the catalytic converter.
Notes:
The fault does not affect engine emissions. NOx warning lamp is on.
On engines with a NOx control system, torque is reduced by 40% after the engine has been running for 36 hours.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
- Check that the NOx sensor is installed correctly. Check sensor connectors and wiring. Perform an SCR system check using SDP3. If no other problems are found, replace the sensor.
- To verify that the problem is resolved, follow these steps:
- Switch off the onboard power using the ignition key. Wait at least 90 seconds and then turn on the power again with the ignition key.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Then clear the fault code.
- Turn off and turn on the power three times at intervals of 10 seconds to deactivate the test lamp.
EMS 5849
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor after SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter shows too low a value.
The reasons:
The cause of the malfunction may be an old or incorrectly installed NOx sensor, the formation of reagent crystals in the SCR system or a damaged SCR catalytic converter.
Notes:
The fault does not affect engine emissions. NOx warning lamp is on.
Engine torque is reduced by approximately 40% after the engine has completed 36 hours.
Elimination:
- Check for the presence of reagent crystals in the SCR catalytic converter and the presence of visible damage to the SCR catalytic converter.
- Check the connectors and wires of the NOx sensor and make sure the sensor is installed correctly. Perform an SCR system check using SDP3. If no other problems are found, replace the sensor.
- To verify that the problem is resolved, follow these steps:
- Switch off the onboard power using the ignition key. Wait at least 90 seconds and then turn on the power again with the ignition key.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Then clear the fault code.
- Turn off and turn on the power three times at intervals of 10 seconds to deactivate the test lamp.
EMS 5850
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Atmospheric pressure sensor
Fault:
The voltage in the electrical circuit of the atmospheric pressure sensor was too low.
The reasons:
Short to ground or open circuit.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Check the atmospheric pressure sensor, as well as electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5851
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Atmospheric pressure sensor
Fault:
The voltage in the electrical circuit of the atmospheric pressure sensor was too high.
The reasons:
Short to battery +.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Check the atmospheric pressure sensor, as well as electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5853
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
SCR system
Fault:
The SCR adaptation values have reached the maximum end position.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- Poor quality reagent.
- Corked reagent dispenser.
- Faulty NOx sensors.
- Failure to measure exhaust gas flow.
- Malfunction of the charge air pressure sensor T122.
- Exhaust gas leaks.
Notes:
For information only.
Elimination:
- Check the quality of the reagent.
- Check reagent dispenser.
- Check the NOx sensors.
- Check for large exhaust leaks.
- Check the charge air pressure sensor T122.
EMS 5854
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
SCR system
Fault:
The SCR adaptation values have reached the minimum end position.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- Poor quality reagent.
- Corked reagent dispenser.
- Faulty NOx sensors.
- Failure to measure exhaust gas flow.
- Malfunction of the charge air pressure sensor T122.
- Exhaust gas leaks.
Notes:
For information only.
Elimination:
- Check the quality of the reagent.
- Check reagent dispenser.
- Check the NOx sensors.
- Check for large exhaust leaks.
- Check the charge air pressure sensor T122.
EMS 5855
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Variable Geometry Turbocharger, VGT
Fault:
Installation of a variable geometry turbocharger was not completed.
The reasons:
During installation, the engine was started or SDP3 disconnected.
Notes:
Actuator does not respond to control signals.
Elimination:
Perform the installation again and make sure the programming and adaptation is complete.
EMS 5856
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Oxidizing Catalytic Converter
Fault:
The temperature sensor in front of the oxidative catalytic converter shows a constant value despite the fact that the engine operates at different speeds and loads.
The reasons:
Temperature sensor malfunction or incorrect positioning of the sensor in the exhaust gas stream.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Check the temperature sensor, its connector and wiring.
If the measured value remains constant and there are no other faults, replace the sensor and erase the DTCs.
EMS 5859
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
The pressure drop in the particulate filter is less than expected. Possible suspicion of the complete lack of functioning of the filter.
It is installed when driving with a load for less than 30 minutes.
The reasons:
- Particulate filter missing or damaged.
- Malfunction of differential pressure sensor.
- Malfunction in other sensors.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on and filter regeneration is blocked.
Elimination:
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the corresponding malfunctions associated with the T141 differential pressure sensors.
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the corresponding malfunctions associated with the T158 temperature sensors.
- Check the malfunction codes and troubleshoot the associated mass flow sensor malfunctions, such as the outside temperature sensor and the charge air pressure sensor.
- Search for leaks in the exhaust pipe between the engine and the muffler or in the muffler itself.
- Ensure that the access door on the muffler is properly installed and sealed.
- Search for signs of a damaged filter: Soot in the exhaust pipe after the diesel particulate filter is one of the signs of a damaged filter. If soot is present in the outlet of the exhaust pipe, check the outlet of the filter through the inspection hatch. Black soot spots on the filter outlet indicate a damaged filter unit.
- Damage to the filter may be caused by fuel or oil leakage or a too high particulate load in the diesel particulate filter. Check the fuel system using SDP3, for example, for injector faults. Low engine oil may be a sign of oil leakage.
- To confirm the repair, drive the vehicle under load for 30 minutes.
EMS 5860
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
The pressure drop in the particulate filter is less than expected. This may indicate a poor functioning of the filter.
The reasons:
- Particulate filter is damaged or missing.
- Malfunction of differential pressure sensor T141 or other sensors.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on, filter regeneration is not allowed.
Elimination:
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the corresponding malfunctions related to the T141 differential pressure sensor.
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the relevant malfunctions related to the T158 temperature sensor.
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the relevant malfunctions related to the mass flow sensor, outdoor temperature sensor and charge air pressure sensor.
- Check for leaks in the exhaust system between the engine and the muffler, or in the muffler.
- Ensure that the inspection hatch in the silencer is fitted with a properly installed seal.
- Search for signs of filter damage. Soot in the exhaust system after the diesel particulate filter indicates a damaged filter. If soot is present in the exhaust pipe, remove the inspection hatch and check the filter outlet. Black spots of soot on the outlet of the filter indicate a damaged filter element. Damage to the filter may be caused by a leak of oil or fuel or a too high particulate load in the diesel particulate filter.
- Check nozzles with SDP3.
- A low engine oil level may indicate an oil leak.
- To check the quality of repair, allow the engine to work with a load of up to 30 minutes.
EMS 5861
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
The temperature sensor after the oxidative catalytic converter shows a constant value despite the fact that the engine operates at different speeds and loads.
The reasons:
Temperature sensor malfunction or incorrect positioning of the sensor in the exhaust gas stream.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check the temperature sensor, its connector and wiring.
- If the measured value remains constant and there are no other faults, replace the sensor and erase the DTCs.
EMS 5863
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Variable geometry turbocharger
Fault:
The temperature sensor of the turbocharger with variable geometry is blocked at one value.
The reasons:
Malfunction of the temperature sensor of the turbocharger with variable geometry.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check the connectors and wiring of the turbocharger motor with variable geometry.
- If there are no faults in the connectors and wiring, replace the motor with a variable geometry turbocharger. The entire motor should be replaced due to the fact that the temperature sensor is located on the printed circuit board inside the motor.
EMS 5866
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The charge air temperature sensor indicates a too high value.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check wiring and connectors.
- Replace sensor.
EMS 5867
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The charge air temperature sensor indicates a too low value.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Check wiring and connectors.
Replace sensor.
EMS 5868
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The temperature of the charge air is higher than expected.
The reasons:
The efficiency of the intercooler is low or the value from the charge-air temperature sensor is too high.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Restore the efficiency of the intercooler by cleaning it, check the air flow and the fan.
Check the intake and exhaust manifolds for leaks. Check the turbine bypass valve and clean the turbocharger.
Check wiring harness and charge air temperature sensor connector.
Replace the charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5869
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The temperature of the charge air is lower than expected.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check wiring and connectors.
- Replace the charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5870
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The temperature of the charge air is higher than expected.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check wiring and connectors.
- Replace the charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5871
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The temperature of the charge air is lower than expected.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check wiring and connectors.
- Replace the charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5872
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The temperature of the charge air is higher than expected.
The reasons:
- Low efficiency of the intercooler and / or EGR cooler.
- Too high value from the charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Clean and test the intercooler and the EGR cooler.
- Check wiring and connectors.
- Replace the charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5873
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Charge air temperature sensor
Fault:
The temperature of the charge air is lower than expected.
The reasons:
Faulty charge air temperature sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check wiring and connectors.
- Replace the charge air temperature sensor.
EMS 5874
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor after SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The signal from the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter is lower than expected.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- NOx sensor malfunction after SCR catalytic converter.
- Reagent crystals are present in the SCR system.
- The NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter is not installed correctly.
- Malfunction in the SCR catalytic converter.
Notes:
The level of toxic vehicle emissions is increasing. NOx warning lamp is on.
After the engine has been running for 36 hours from the time the malfunction has been detected, the engine torque will be reduced by approximately 40%.
Elimination:
Check out the following:
- SCR catalytic converter for damage or an SCR system for the presence of reagent crystals.
- The correct installation of the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter.
- NOx sensor, connectors and wiring for a fault.
- If the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter is installed correctly and the SCR catalytic converter is working, perform a SDP3 System Check. If the sensitivity of the NOx sensor then remains low, replace the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter.
- To verify that the problem is resolved, follow these steps:
- Turn off the onboard power with the ignition key and wait at least 90 seconds. Then turn on the ignition again.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Then clear the fault code.
- Extinguish the test lamp by turning the ignition key off and on three times. Pause 10 seconds between each cycle.
EMS 5876
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The NOx sensor signal value before the SCR catalytic converter is lower than expected.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- NOx sensor malfunction in front of the SCR catalytic converter.
- NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter is not installed correctly.
Notes:
The level of toxic vehicle emissions is increasing. The control lamp for the NOx control system lights up and a text message is displayed.
The fault code cannot be cleared while the fault is present.
Elimination:
Check out the following:
- Proper installation of the NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter.
- NOx sensor, connectors and wiring for a fault.
- If the NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter is installed correctly, perform a system check using SDP3. If the sensitivity of the NOx sensor then remains low, replace the NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter.
- To verify that the problem is resolved, follow these steps:
- Turn off the onboard power with the ignition key and wait at least 90 seconds. Then turn on the ignition again.
- If the fault is resolved, the fault code becomes inactive. Then clear the fault code.
- Extinguish the test lamp by turning the ignition key off and on three times. Pause 10 seconds between each cycle.
EMS 5877
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Upper NOx sensor shows implausible value.
Fault:
General DTC for implausible NOx sensor value.
If this DTC is active, DTC 16CE, 16D8, 16F4 and / or 16FA (which describes the fault in more detail) is also active.
The reasons:
See the cause of another active DTC or DTC for the same fault.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Troubleshoot problems indicated by other active DTCs or DTCs related to the same fault.
EMS 5878
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Lower NOx sensor indicates an implausible value.
Fault:
General DTC for implausible NOx sensor value.
If this DTC is active, DTC 16CE, 16D9, 16F2 and / or 16FB (which describes the fault in more detail) is also active.
The reasons:
See the cause of another active DTC or DTC for the same fault.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
Troubleshoot with another active fault code or fault codes for the same fault.
EMS 5881
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Fan speed sensor
Fault:
Short circuit to + fan speed sensor battery.
The reasons:
Electrical connectors or electrical leads to the fan speed sensor were damaged.
Notes:
The fan will operate at maximum speed until the fault is eliminated.
Elimination:
Check fan speed sensor, electrical connectors and wiring.
EMS 5882
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter shows an incorrect value.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- NOx sensor malfunction in front of the SCR catalytic converter.
- Crystallization of the reagent in the SCR system
Notes:
The level of toxic vehicle emissions is increasing. NOx warning lamp is on.
Elimination:
- Replace the NOx sensor in front of the SCR catalytic converter. Clear the fault code.
- Extinguish the test lamp by turning the ignition key off and on three times at 10-second intervals three times.
EMS 5883
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
NOx sensor after SCR catalytic converter
Fault:
The NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter shows an incorrect value.
The reasons:
Possible reasons:
- NOx sensor malfunction after SCR catalytic converter.
- Crystallization of the reagent in the SCR system
Notes:
The level of toxic vehicle emissions is increasing. NOx warning lamp is on.
Engine torque is reduced by approximately 40% after the engine has completed 36 hours.
Elimination:
- Check the SCR system for reagent crystals.
- If there are crystals in the SCR system, do the following:
- Remove the crystals.
- Get two new NOx sensors. Replace the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter.
- Start the engine and let it run for 10 seconds. Then stop the engine.
- Replace the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter. Repeat step 3.
- Install the original NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter. Repeat step 3.
- If the DTC has become inactive: Clear the DTC.
- Extinguish the test lamp by turning the ignition key off and on three times at 10-second intervals three times.
- If there are no crystals in the SCR system, replace the NOx sensor after the SCR catalytic converter. Clear the fault code. Extinguish the test lamp by turning the ignition key off and on three times at 10-second intervals three times.
EMS 5884
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
temperature sensor
Fault:
Temperature sensors before and after the oxidative catalytic converter and after the diesel particulate filter show mutually improbable values when compared to pairs. It is installed during 60 minutes of driving under load, not in idle mode.
The reasons:
- Malfunction in temperature sensors T158.
- Leakage of oil or fuel in the muffler.
- Malfunction in other sensors.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on, regeneration is completely blocked.
Elimination:
- Compare with SDP3 the values of the temperature sensors (T158) taken from the muffler or at high idle, PTO 1000 1 / min. After the end of the stabilization period, all three sensors should produce similar values. If not, replace the appropriate item.
- Check for signs of leakage of oil and fuel in the exhaust manifold between the engine and the muffler. Check with SDP3 the condition of the fuel system, in particular, possible injector malfunctions. A low engine oil level may indicate an oil leak.
- Remove the flexible pipe coming from the muffler and check if black or white smoke is released when the throttle is opened. White smoke indicates the presence of excess fuel, which may result in the registration of this DTC.
- To check the quality of the repair, let the engine run under load for 60 minutes.
EMS 5885
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
temperature sensor
Fault:
A temperature sensor located in front of the oxidizing catalytic converter produces an incompatible value when pairwise matching the three sensors. The test is carried out for 60 minutes while driving under load, but not during idling.
The reasons:
- Malfunction of temperature sensors T158.
- Oil or fuel leak in a silencer.
- Malfunction of other sensors.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on, regeneration is completely blocked.
Elimination:
- Compare with SDP3 the values of the temperature sensors (T158) taken from the muffler or at high idle, PTO 1000 1 / min. After the end of the stabilization period, all three sensors should produce similar values. If not, replace the appropriate item.
- Check for signs of leakage of oil and fuel in the exhaust pipe, between the engine and the muffler. Check with SDP3 the condition of the fuel system, in particular, possible injector malfunctions. A low engine oil level may indicate an oil leak.
- Remove the flexible pipe coming from the muffler and check if black or white smoke is released when the throttle is opened. White smoke indicates the presence of excess fuel, which may result in the registration of this DTC.
- To check the quality of the repair, let the engine run under load for 60 minutes.
EMS 5887
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
temperature sensor
Fault:
CAN fault from the EEC control unit for T158 temperature sensors.
The reasons:
Sensor incorrectly connected or faulty.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check the trouble codes in the EEC control unit.
- Check the wiring harness and the connector between the sensor and the EEC control unit.
- Replace sensor.
EMS 5888
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
temperature sensor
Fault:
An improbably high temperature in front of an oxidative catalytic converter.
The reasons:
- Sensor malfunction before oxidative catalytic converter.
- In addition, a fault code may appear if the design of the exhaust system has been changed.
Notes:
A malfunction may result in too much injected reagent or injecting reagent into a cold catalytic converter.
Elimination:
Check the sensor in front of the oxidation catalytic converter and its connector and wiring.
EMS 5889
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
temperature sensor
Fault:
An unbelievably low temperature in front of an oxidative catalytic converter.
The reasons:
- Sensor malfunction before oxidative catalytic converter.
- The sensor is not installed in the exhaust system.
- In addition, a fault code may appear if the design of the exhaust system has been changed.
Notes:
A malfunction may result in too little injected reagent, as a result of which the NOx emission may become too large.
Elimination:
- Check the sensor before the oxidation catalytic converter. Make sure it is installed in the exhaust system.
- Check its wiring and connectors.
EMS 6146
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
Particulate filter does not cause the expected temperature change. It may be suspected that the filter is not functioning.
The reasons:
- Malfunction of temperature sensor T158 or other sensors.
- Particulate filter damaged or removed.
Notes:
The engine warning light comes on.
Regeneration of the filter is not allowed.
Elimination:
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the relevant malfunctions related to the T158 temperature sensor.
- Check the malfunction codes and eliminate the relevant malfunctions related to the mass flow sensor, outdoor temperature sensor and charge air pressure sensor.
- Check for leaks in the exhaust system between the engine and the muffler, or in the muffler.
- Search for signs of filter damage. Soot in the exhaust system after the diesel particulate filter indicates a damaged filter. If soot is present in the exhaust pipe, remove the inspection hatch and check the filter outlet. Black spots of soot on the outlet of the filter indicate a damaged filter element. Damage to the filter may be caused by a leak of oil or fuel or a too high particulate load in the diesel particulate filter.
- Check nozzles with SDP3.
- A low engine oil level may indicate an oil leak.
- To check the quality of repair, let the engine run at variable speed up to 30 minutes.
EMS 6147
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
temperature sensor
Fault:
Temperature too high after oxidation catalytic converter.
The reasons:
- Oil or fuel leakage in the exhaust gas stream before the oxidation catalytic converter.
- Temperature sensor malfunction.
Notes:
The red engine indicator light comes on.
Elimination:
- Using SDP3, compare temperature sensors T158 removed from the muffler. After a short time, all sensors show almost the same temperature. If not, replace the appropriate item.
- Check for leakage of oil or fuel in the exhaust gas stream before the oxidation catalytic converter. See “Internal leakage” and “Cylinder pressure balance” methods in SDP3. A low engine oil level may indicate an oil leak.
- A malfunction in the differential pressure sensor can cause a high particulate load, which leads to an increase in temperature. Check the differential pressure sensor for reading when the engine is off and the ignition is on. The value should be close to zero. Start the engine and make sure that at high idle speeds the value is different from zero. Otherwise, replace the differential pressure sensor. Check the connector and wiring harness and check for damage to the exhaust pipe between the engine and the muffler or the muffler.
EMS 6148
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
Hydrocarbon injection off.
The reasons:
Failure of sensor signals.
Notes:
Regeneration of the filter is not allowed.
Elimination:
- Check the active fault codes and correct the corresponding faults for the sensors in the EMS engine management system and in the EEC3 exhaust gas after-treatment system.
- To confirm the repair, turn on the ignition for 10 seconds.
EMS 6149
Blocks:
2098547, 2098546, 2098545, 2096902, 2096901
Title:
Particulate filter
Fault:
Regeneration of the diesel particulate filter is not allowed.
The reasons:
Weak signal from EGR valve position sensor.
Notes:
No description
Elimination:
- Check active EGR fault codes and correct relevant faults.
- To confirm the repair, turn on the ignition for 10 seconds.
Опубликовано: 06.06.2023
Просходит что то непонятное с ems скамья R420 5 — серия ⇐ Техобслуживание и ремонт Scania
авто SCANIA R420 5-й серии на трассе ехала и заглохла пишет красным двиган неисправен и соо координатор не исправен начинаешь запускать стартёр раз крутанёт и желтым пишет двигатель не исправен и отключение массы пробовали 1-й раз завести с толкача загорелось красным двиган не исправен и в EMS пишет нет контакта фишки передёрнули на C100 , Е44В и серую фишку у ног пассажира . Попробовали 2-й раз с толкача загорелось красным двиган неисправен и координатор неисправен пишет ошибки в EMS 4871 , 4886 , 4887 а в BMS 24142 по координатору ошибок нету . С этой машиной была аналогичная ситуация год назад но там серую фишку у ног пассажира передёрнули и авто запустилось приехали в сервис ничего не показало . Двиган после капиталки 700 км прошёл . Подскажите в чём проблема заранее благодарю . Или может кто электрика знает толкового стоим в карпачево трасса м5 до уфы 130 км со стороны екатеринбурга
Последний раз редактировалось: артемий (Вс Фев 26, 2012 7:36 am), всего редактировалось 1 раз
_________________
volvo! это круто! но очень больно.
подскажите номер датчика и где он стоит если не трудно vin 5186280
_________________
volvo! это круто! но очень больно.
нашли благодарю т74 и т75 . может ли быть координатор неисправен и по нему не выдавать никаких ошибок и могут выскочить ошибки по датчикам вращения при буксировке на 2 — й пониженной с толкача из-за неправильной буксировки ?
_________________
volvo! это круто! но очень больно.
фишки передёрнули не Е44А советовался с электриком скания говорит что ошибки датчика показали потому что плавного движения авто не было гдето авто проскользило на гололёде гдето зацепилось резко за асфальт будем сейчас пробовать буксировать и смотреть какие ошибки по EMS покажет во время буксировки
_________________
volvo! это круто! но очень больно.
когда колёса не едут а идут юзом я так понимаю и маховик не крутится и датчик вращения это видит или я не прав . я думаю что датчикам не понравилось что маховик дёргается .
_________________
volvo! это круто! но очень больно.
нашёл ошибки нету связи координатора с блоком управления двиганом подскажите где искать причину фишки с100 и е44в передёргивали где ещё может быть обрыв
Можно и так воспринимать ситуацию, но в данном случае — только сервис вам поможет! нужно искать грамотного электрика, который сможет провести диагностику и определить виновного, а это может быть и проводка и блоки и .
_________________
Удачного ремонта
у меня предыдущие неактивные ошибки есть хочется знать что предшевствовало такому исходу что двиган заглох может есть у кого полный справочник кодов неисправности по СОО и EMS на 5-ю серию скиньте буду благодарен
ИНСТРУКЦИИ ДЛЯ РЕМОНТА И ЭКСПЛУАТАЦИИ ГРУЗОВОЙ СПЕЦТЕХНИКИ.
Страницы
Cамые просматриваемые
Сразу попрошу прощения за несколько корявый перевод (переводил документ через программу),но суть неисправности понять можно.
Начиная процедуру
Когда водитель поворачивает ключ зажигания в положение питания 15, ток будет поступать на координатора, который в свою очередь поставляет 12 вольт в трансивера. Система использует 12 вольт
Ключ стартера, координатор и блок управления EDC впоследствии проверяется. Если все в согласии, реле стартера и подачи топлива будет
активирован. Предупреждение W33 лампа не покажет на, если есть что-то не так.
Весь этот процесс больше не принимает 200-300 мс и едва заметны для водителя.
Fault codes
Fault codes related to the immobiliser are stored in the coordinator. The principle tool
used to check for any fault codes is Scania Diagnos. There are, however, other ways of reading and clearing codes using the diagnostic lamp and the diagnostic switch (S50) on the instrument panel.
The switch in question is marked «COO» (diagnostic switch panel pin 10) and is
connected to coordinator pin 12. The switch, which has a return spring, closes and earths pin 12 when it is depressed.
The coordinator interprets this as a request to show any fault codes and will flash them out by intermittently connecting pin 12 to ground in the required pulse sequence when the switch on the panel is released.
Reading fault codes
• Switch on the power supply.
• Depress the diagnostics switch marked
«COO» and keep it depressed for two seconds.
• The lamp will now flash if there are any fault codes present. A long flash indicates
tens and a short flash ones. Illustrated example: Fault code 26 is indicated with
two long flashes followed by six short ones.
• Depress the diagnostic switch once again to read the next fault code.
Erasing fault codes
Clear all fault codes as follows:
• Begin by switching off the current.
• Press the diagnostics switch and keep it depressed.
• Switch on the current again with the diagnostic switch depressed.
Limitations
Remember that reading fault codes is not always regarded as the perfect troubleshooting method. The software used is very advanced but, nonetheless, some types of faults may arise that cannot be registered with fault codes.
Likewise, situations may arise when a fault code is generated even though there is not
fault at present. Such an example may be temporary bad contact or that a cable splice has disconnected and then connected again while the power has been on.
Fault code 26
Fault
The starter key cannot be verified.
Cause
The starter key is interpreted as being invalid.
Either the key does not have a transponder at all or the transponder is faulty. However, it is also possible that the starter key has been programmed for another coordinator or other starter keys with transponders on the same key ring are interfering with the verification of the key.
A fault in the transceiver can also generate this
fault code.
Remarks
The immobiliser warning lamp, W33, will flash if this fault occurs.
For more information, select «Display of status» under the «Configuration…» button in
the system window.
Action
Make sure the correct starter key is in the starter lock. Make sure there are no more keys with transponders on the key ring. Check the transceiver and wiring.
Ещё много причин о неисправности систем автомобиля Scania мог бы подсказать координатор Но случается такое что сам координатор неисправен или как любят говорить глюкнул координатор В этом случае необходим ремонт координатора COO7 Скания, repair coordinator COO7 SCANIA
Симптомы неисправности координатора, машина не заводится, на щитке приборов горят все ошибки, экран горит красным и на нем надпись ( COORDINATOR MALFUNCTION )
Основные признаки выхода из строя Координатора:
- машина не заводится
- на панели приборов горят все значки ошибок
- начинают пропадать ряды передач
- выкидывает ошибку тахограф
- экран горит красным цветом
- на экране горит надпись COORDINATOR MALFUNCTION или НЕИСПРАВНОСТЬ КООРДИНАТОРА
- при включенном зажигании горят стопы
Прошивка Координатора на автомобиль Скания
Прошивка координатора – необходимый момент, если имеющееся в наличии ПО такого оборудования устарело и не соответствует современным требованиям безопасности. Применяют эту меру еще и в качестве экстренного способа устранения возникших в транспортном средстве неисправностей. Если такое воздействие не помогло, применяется замена вышедшей из строя детали. После переустановки производится программирование координатора, позволяющее обеспечить необходимую синхронизацию всех систем между собой.
Вне зависимости от того, есть в транспортном средстве иммобилайзер или он отсутствует, необходимо позаботиться о правильном соблюдении последовательности установки нового электронного оборудования. Крайне важно проконтролировать момент запуска двигателя. Он может проводиться только после того, как блок управления EDC и координатор будут заблокированы соответствующим образом. Синхронизация потребуется и в том случае, если любой из элементов этой цепи будет заменен.
Диагностика координатора Scania
Если же ошибки не уходят или автомобиль перестал заводиться, то отключение массы и стирание ошибок не поможет, скорее всего вышел из строя микропроцессор на плате блока координатора. Простая замена одного блока на другой не поможет и может привести к еще большим проблемам, т.к. блок координатора содержит в своей памяти конфигурационный файл настроек автомобиля (сокращенно SOPS).
Наши специалисты могут проводить все вышеперечисленные работы. Мы проводим восстановление работы автомобиля на месте поломки и Вам не надо тратиться на эвакуацию автомобиля до сервиса. Наш специалист приедет на место с рабочим блоком, подключит диагностику, пропишет новый блок под ваш автомобиль, после очистит в памяти ошибки вызванные выходом из строя старого блока и после этого Ваш автомобиль может дальше выполнять свой рейс.
Случаи из жизни
Все дело произошло в Чебоксарах на новенькой Скания, огненно красным цветом на панели загорелась ошибка координатора. Сканер не подключается к блоку, разбираем на столе, контроллер не работает. Выпаяли поставили другой и малышка завелась. Все отремонтировали все довольны
Для записи на ремонт или ответ на интересующие вопросы обращайтесь по телефону:
РАБОТАЕМ СО ВСЕЙ РОССИЕЙ, УСЛУГИ ТРАНСПОРТНОЙ КОМПАНИИ НЕ ТАКИЕ ДОРОГИЕ
Для заявки на ремонт ЭЛЕКТРОНИКИ пользуйтесь формой
- При повороте ключа в замке зажигания, стартер прокручивает двигатель экскаватора
- Стартер не включается и не крутит двигатель
Постараюсь более подробно рассказать про каждый из вариантов неисправности техники.
Не крутит стартер SCANIA
Если система управления вышеуказанной техники при повороте ключа зажигания на старт, не включает стартер, то причина поломки заключается в электрическом оборудовании или электронных системах грузовика. Причины могут быть следующие:
- Неисправность блока реле и предохранителей
- Отсутствие контактов в разъемах электропроводки
- Неисправность главного реле грузового автомобиля
- Выход из строя замка зажигания Выход из строя стартера
- Обрыв или замыкание шины КАН
- Отсутствие “массы”
- Отсутствие напряжения питания на блоке управления двигателем
- Обрыв или замыкание жгута проводки
- Неисправность втягивающего реле стартера
- Выход из строя замка зажигания
- Выход из строя блока управления двигателем
Если стартер описываемой техники при повороте ключа в замке зажигания крутится, но при этом мотор не подает никаких признаков. Причина неисправности может заключаться как в электрооборудовании автомобиля, так и в механике. Неисправности автоэлектрики могут быть как описанные выше, кроме неисправностей связанных со стартером и его цепями, плюс следующие причины:
- Неисправность топливного насоса высокого давления (ТНВД)
- Механическая поломка двигателя
- “Завоздушивание“ топливной аппаратуры
- Неисправность иммобилайзера
- Отсутствие солярки в баке
- Засорение топливного фильтра
- Неисправность чипа в ключе
- Засорение топливопроводов
- Поломка обратного клапана
- Механические неисправности форсунок
Запуск двигателя на выезде
Специалистами нашего предприятия накоплен огромный опыт оказания услуг по запуску двигателя SCANIA, когда техника заглоха при выполнении работ. У нас имеются автомобили техпомощи, опытные мастера готовые в любой момент приехать на помощь. Специализированное диагностическое оборудование.
10 Comments
В общем у меня такая проблема.заглох на сканиа.кончилась солярка.так как подъемник кабины не работает пробовал закачать стартером крутил.после этого он видимо нагрелся и машина не заводится с ключа.сделал следующее.залез под машину замкнул на прямую стартер.после прыгнул в кабину и завелась с ключа.сейчас проделал такую же операцию не выходит.щелкает реле в кабине а стартер крутит только на прямую.помогите подскажите как быть.
Чем проблемма разрешилась?
День добрый скания r 440 2011г xpi заводится работает проезжает 150-300 км глохнит в ходу и потом не запускается стартер не реагирует. Контактная группа в норме по ошибкам неисправность двигателя, координатора, подвески ,коробка,осушитель.стоит час запускается и нет ошибка.на 2,3 реле при выключенном зажигание есть 9в потом
Здравствуйте. Скорее всего проблема в реле. Но чтобы получить точный ответ, надо сделать диагностику
Подскажи что делать , замкнула проводка на стопы погорели провода , заглушил , разобрался в проводах , включаю зажигание горят ошибки (тапогроф, ссо, активная работа эмобилайзера ) на топограф подал плюс в ручную , топограф загорелся работает , координатор ошибка пропала , горит эмобилайзер, стартер на прямую подцепили крутим но нет не каких признаков , как отключить эмобилайзер без чипа на севере?
Здравствуйте. Проверяйте жгут, возможно не все нашли
Всем доброго времени суток . Скания . 86й год . Соседская . Стоит эбу и тд . Возможно модернизирована была перед попаданием в снг . Пропало питание на ЭБУ . Как слышал в эбу должно зайти 3 плюса , но есть только 1 . Грешу на релюхи , допускаю надлом в косе . Машина просто была заглушена и не стала заводиться . Правда во время последних 400 км глючил уровень пола . Поможет кто советом , какие пины должны давать плюс ? Связано ли отказ запуска с предыдущим глюком пола ?
Нет сервисов рядом . Просто хочу помочь соседу , человек он дюже хороший .
Здравствуйте, подскажите заглохла скания на ключ не реагирует, с толкача пробовал тоже не как что может быть?
Привет Все, ситуация такая, скания P230 коробка автомат, проработал на ней весь день, приехал, припарковал, пришел с утра, не заводится, хотя стартер крутит, ошибок нет, подскажите, что посмотреть
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Наши специалисты с многолетним опытом
Точные диагносты по грузовым автомобилям и спецтехнике
Высококвалифицированные инженеры-электронщики по ремонту блоков управления
Грамотные и трудолюбивые автоэлектрики по ремонту электрооборудования
Оперативный выезд
Выезд специалиста осуществляем срочно с момента принятия заказа не более 15 минут
Сеть Станций Технического Обслуживания
Наши сервисы находятся на Западе Москвы и в Московской области в городе Электросталь
Заменяемые агрегаты
Техническая информация относится к замене блока управления EDC или блока сопряжения (СОО) в автотранспортных средствах с блоком сопряжения.
Причина изменения:
Как стало известно, иногда при замене блоков управления в автотранспортных средствах с блоком сопряжения возникают проблемы. Трудности появляются прежде всего в связи с происшествиями, по причине которых замена кабины или двигателя обусловливает замену блока управления двигателем или блока сопряжения.
Проблемы могут быть также вызваны ошибочным использованием не предназначенных для данных АТС блоков управления, например, в процессе испытания различных АТС, в связи с поиском неисправностей или при
проверке технических показателей.
По этой причине ниже предлагаются некоторые уточнения, которые разъяснят аспекты, связанные с возможными трудностями, и покажут, как избежать этих проблем.
Совместимость
Взаимная функциональная связь между блоками управления делает
невозможным применение блоков управления различных версий в произвольных сочетаниях в одном автотранспортном средстве. Выполнение определённых исходных условий должно быть обеспечено с помощью программирующего устройства Scania Programmer 2 (SP2). В некоторых сочетаниях блоки управления вообще не могут работать.
В настоящий момент имеются блоки сопряжения COO 3 и COO 4. Блоки управления EDC создаются для работы с соответствующим блоком сопряжения.
Блок сопряжения обладает совместимостью сверху вниз, т. е. COO 4 можно программировать и использовать как блок COO 3. В противоположность этому блок COO 3 не может заменить COO 4. Блоки управления EDC могут работать только вместе с определённым блоком сопряжения. Это означет, что новый блок управления EDC не может взаимодействовать с COO 3. С другой стороны, более ранний блок управления EDC может работать вместе с COO 4, который можно запрограммировать как COO 3. Автотранспортное средство с иммобилайзером всегда имеет COO 4 и EDC для COO 4. Иммобилайзер представляет собой одну из функций COO 4.
Запасные части
В качестве запасной части COO 4 программируется для работы как COO 3.
Новая кабина всегда оснащается блоком
COO 4, запрграммированным как COO 4. В качестве запасной части блок управления EDC должен заказываться для соответствующего блока сопряжения: для COO 3 или COO 4. Заменяющие двигатели всегда оснащены блоком EDC для COO 4.
Блокирование блоков управления
Вместе с COO 4 внедряется иммобилайзер в качестве защиты от угона. Это обусловливает необходимость в целях безопасности иметь блокирующую связь между блоком управления EDC и блоком сопряжения. Это означает, однако, что
даже в автотранспортном средстве с COO 4, в котором иммобилайзер не включён, требуется иметь блокировку с блоком управления EDC.
Существует два типа блокирования:
• В автотранспортных средствах с иммобилайзером: использование PIN-кода, который означает взаимное блокирование ключей и блоков управления.
• В автотранспортных средствах без иммобилайзера: блокирование между блоком сопряжения и блоком EDC происходит без выдачи PIN-кода.
На автотранспортных средствах с COO 3 блоки управления заблокированы быть
не могут. Также нет необходимости в каком-либо программировании.
Иммобилайзер.
АТС с иммобилайзером Надёжное хранение кодов имеет исключительно важное значение, поскольку завод-изготовитель не может заменить потерянные коды.
Однажды запрограммированные ключи всегда сохраняют коды неизменными.
Код, программируемый в блоке сопряжения и блоке EDC, связан с ключами и будет всегда сохранять эту связь.
Когда SP2 запрашивает PIN-код, требуется сообщить тот код, который был запрограммирован в блоке управления ранее (код ключей). Таким образом, если в автотранспортном средстве устанавливается неизвестный (уже заблокированный) блок управления, он не может быть разблокирован кодом этих ключей.
Коды можно удалить из блока сопряжения и блока управления EDC, ключи же всегда сохраняют свой код.
АТС без иммобилайзера
В автотранспортных средствах без иммобилайзера не используется никаких
кодов. Если SP2 запрашивает коды, это указывает на то, что какой-то из блоков
управления системы EDC или блок сопряжения использовался в автотранспортном средстве с иммобилайзером. В этом случае разблокирование блока управления можно осуществить только с помощью кодов из автотранспортного средства, в
котором он был смонтирован ранее.
Известные проблемы
Имели место случаи перестановки блока сопряжения с одного автотранспортного средства на другое без предварительного перевода его в исходное состояние.
Другими словами, новое программирование производилось без предшествующего удаления старых кодов из блока сопряжения. Это вызывало взаимное несоответствие ключей и блока сопряжения. Имели место попытки заблокировать блоки управления EDC с COO 3 с помощью COO 4, что лишало SP2 возможности разблокировать блок управления EDC. SP2 будет утверждать, что используется неправильный PIN-код, хотя введён был правильный код (с
иммобилайзером), или что вообще нет никакого кода для ввода (без
иммобилайзера). Эта проблема устранена, начиная с SP2 17.
Незавершённое программирование
Если начатое программирование с SP2 по какой-либо причине будет прервано и
блок управления оставлен лишь частично запрограммированным, потребуется произвести повторное программирование. См. текстовые указания в SP2, где есть точная информация о том, как выполнить программирование.
О чём следует подумать перед заменой блока управления
Замена блока сопряжения в автотранспортных средствах без иммобилайзера
Перед заменой
В автотранспортных средствах без иммобилайзера каких-либо подготовительных операций не требуется за исключением идентификации блока сопряжения для
считывания конфигурации.
После замены
При замене блока сопряжения требуется произвести его программирование.
После этого блок управления EDC должен быть заблокирован через блок
сопряжения.
Замена блока сопряжения в автотранспортных средствах с иммобилайзером
Перед заменой
Если блок сопряжения будет передан в рекламацию, его PIN-код и криптокод должны быть удалены. Это осуществляется посредством службы Восстановление блока сопряжения в SP2. Это означает, что блок сопряжения разблокирован и может быть программирован вновь.
После замены
При замене блока сопряжения сначала требуется запрограммировать в нём коды ключей. Вслед за тем необходимо заблокировать блок EDC через блок сопряжения.
Замена блока управления EDC в автотранспортных средствах без иммобилайзера
Перед заменой
В автотранспортных средствах без иммобилайзера каких-либо подготовительных операций не требуется за исключением идентификации блока сопряжения для считывания конфигурации.
После замены
После замены блок управления EDC должен быть заблокирован через блок сопряжения.
Замена блока управления EDC в автотранспортных средствах с иммобилайзером
Перез заменой
Если блок управления EDC будет передан в рекламацию, его PIN-код должен быть удалён. Это осуществляется посредством службы Разблокирование блока управления EDC в SP2. Это означает, что система EDC разблокирована и может быть программирована вновь.
После замены
После замены блок управления EDC должен быть заблокирован через блок сопряжения.
Читайте также:
- Сила тяги уменьшена на 36 часов вольво ошибка
- Ошибка чтения контейнера описателей настроек starline
- Ошибка c1490 00 jeep
- Ваз 2103 не горит фара ближнего света
- Ошибка p1652 фольксваген б6