Синтаксическая ошибка:JSON.parse:плохой парсинг
Исключения JavaScript, создаваемые JSON.parse() возникают, когда строку не удалось проанализировать как JSON.
Message
SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad control character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad Unicode escape SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad escape character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string SyntaxError: JSON.parse: no number after minus sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-digit SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after decimal point SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated fractional number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent indicator SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: exponent part is missing a number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected end of data SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected keyword SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data while reading object contents SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when property name was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected double-quoted property name SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property name when SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property value in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: property names must be double-quoted strings SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-whitespace character after JSON data
Error type
Что пошло не так?
JSON.parse() анализирует строку как JSON. Эта строка должна быть действительным JSON и вызовет эту ошибку, если будет обнаружен неправильный синтаксис.
Examples
JSON.parse()не позволяет использовать запятые в конце текста
Обе линии бросят синтаксическую ошибку:
JSON.parse('[1, 2, 3, 4,]'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1,}');
Опустите запятые,чтобы правильно разобрать JSON:
JSON.parse('[1, 2, 3, 4]'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
Имена объектов недвижимости должны быть двузначно процитированными.
Нельзя использовать одиночные кавычки вокруг свойств,например,’foo’.
JSON.parse("{'foo': 1}");
Вместо этого напишите «фу»:
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
Ведущие нули и десятичные знаки
Нельзя использовать опережающие нули,например 01,а за десятичными точками должен следовать хотя бы один знак.
JSON.parse('{"foo": 01}'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1.}');
Вместо этого запишите только 1 без нуля и используйте по крайней мере одну цифру после запятой:
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1.0}');
See also
JSONJSON.parse()JSON.stringify()
JavaScript
-
TypeError: недопустимый операнд «экземпляр» «х»
Исключение JavaScript «недопустимый операнд экземпляра» возникает, когда оператор правых операндов не используется с объектом конструктора, т.е.
-
TypeError: ‘x’ не повторяется
Исключение JavaScript «не является итерируемым» возникает, когда значение, заданное правой частью for…of, функции аргумента, такой как Promise.all TypedArray.from,
-
Синтаксическая ошибка:Некорректный формальный параметр
Исключение JavaScript «искаженный формальный параметр» возникает, когда список аргументов вызова конструктора Function() каким-то образом недействителен.
-
URIError:некорректная последовательность URI
Исключение JavaScript «неверная последовательность URI» возникает, когда декодирование кодирования не было успешным.

A refresher on the purpose and syntax of JSON, as well as a detailed exploration of the JSON Parse SyntaxError in JavaScript.
Traveling deftly through to the next item in our JavaScript Error Handling series, today we’re taking a hard look at the JSON Parse error. The JSON Parse error, as the name implies, surfaces when using the JSON.parse() method that fails to pass valid JSON as an argument.
In this article, we’ll dig deeper into where JSON Parse errors sit in the JavaScript error hierarchy, as well as when it might appear and how to handle it when it does. Let’s get started!
The Technical Rundown
- All JavaScript error objects are descendants of the
Errorobject, or an inherited object therein. - The
SyntaxErrorobject is inherited from theErrorobject. - The
JSON Parseerror is a specific type ofSyntaxErrorobject.
When Should You Use It?
While most developers are probably intimately familiar with JSON and the proper formatting syntax it requires, it doesn’t hurt to briefly review it ourselves, to better understand some common causes of the JSON Parse error in JavaScript.
JavaScript Object Notation, better known as JSON, is a human-readable text format, commonly used to transfer data across the web. The basic structure of JSON consists of objects, which are sets of string: value pairs surrounded by curly braces:
{
"first": "Jane",
"last": "Doe"
}
An array is a set of values, surrounded by brackets:
[
"Jane",
"Doe"
]
A value can be a string, number, object, array, boolean, or null.
That’s really all there is to the JSON syntax. Since values can be other objects or arrays, JSON can be infinitely nested (theoretically).
In JavaScript, when passing JSON to the JSON.parse() method, the method expects properly formatted JSON as the first argument. When it detects invalid JSON, it throws a JSON Parse error.
For example, one of the most common typos or syntax errors in JSON is adding an extra comma separator at the end of an array or object value set. Notice in the first few examples above, we only use a comma to literally separate values from one another. Here we’ll try adding an extra, or «hanging», comma after our final value:
var printError = function(error, explicit) {
console.log(`[${explicit ? 'EXPLICIT' : 'INEXPLICIT'}] ${error.name}: ${error.message}`);
}
try {
var json = `
{
«first»: «Jane»,
«last»: «Doe»,
}
`
console.log(JSON.parse(json));
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof SyntaxError) {
printError(e, true);
} else {
printError(e, false);
}
}
Note: We’re using the backtick (`) string syntax to initialize our JSON, which just allows us to present it in a more readable form. Functionally, this is identical to a string that is contained on a single line.
As expected, our extraneous comma at the end throws a JSON Parse error:
[EXPLICIT] SyntaxError: Unexpected token } in JSON at position 107
In this case, it’s telling us the } token is unexpected, because the comma at the end informs JSON that there should be a third value to follow.
Another common syntax issue is neglecting to surround string values within string: value pairs with quotations ("). Many other language syntaxes use similar key: value pairings to indicate named arguments and the like, so developers may find it easy to forget that JSON requires the string to be explicitly indicated using quotation marks:
var printError = function(error, explicit) {
console.log(`[${explicit ? 'EXPLICIT' : 'INEXPLICIT'}] ${error.name}: ${error.message}`);
}
try {
var json = `
{
«first»: «Jane»,
last: «Doe»,
}
`
console.log(JSON.parse(json));
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof SyntaxError) {
printError(e, true);
} else {
printError(e, false);
}
}
Here we forgot quotations around the "last" key string, so we get another JSON Parse error:
[EXPLICIT] SyntaxError: Unexpected token l in JSON at position 76
A few examples are probably sufficient to see how the JSON Parse error comes about, but as it so happens, there are dozens of possible versions of this error, depending on how JSON was improperly formatted. Here’s the full list:
| JSON Parse Error Messages |
|---|
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string literal |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad control character in string literal |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad character in string literal |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad Unicode escape |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad escape character |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: no number after minus sign |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-digit |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after decimal point |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated fractional number |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent indicator |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent sign |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: exponent part is missing a number |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected end of data |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected keyword |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data while reading object contents |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or ‘}’ |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when ‘,’ or ‘]’ was expected |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘,’ or ‘]’ after array element |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when property name was expected |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected double-quoted property name |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property name when ‘:’ was expected |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘:’ after property name in object |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property value in object |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘,’ or ‘}’ after property value in object |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘,’ or ‘}’ after property-value pair in object literal |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: property names must be double-quoted strings |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or ‘}’ |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character |
| SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-whitespace character after JSON data |
To dive even deeper into understanding how your applications deal with JavaScript Errors, check out the revolutionary Airbrake JavaScript error tracking tool for real-time alerts and instantaneous insight into what went wrong with your JavaScript code.
An Easier Way to Find JavaScript Errors
The first way to find a JSON Parse error is to go through your logs, but when you’re dealing with hundreds, if not thousands, of lines of code, it can be difficult to find that one line of broken code. With Airbrake Error and Performance Monitoring, you can skip the logs and go straight to the line of broken code resulting in the JSON Parse error.
Don’t have Airbrake? Create your free Airbrake dev account today!
Note: We published this post in February 2017 and recently updated it in April 2022.
JSON ( JavaScript Object Notation), is widely used format for asynchronous communication between webpage or mobile application to back-end servers. Due to increasing trend in Single Page Application or Mobile Application, popularity of the JSON is extreme.
Why do we get JSON parse error?
Parsing JSON is a very common task in JavaScript. JSON.parse() is a built-in method in JavaScript which is used to parse a JSON string and convert it into a JavaScript object. If the JSON string is invalid, it will throw a SyntaxError.
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
How to handle JSON parse error?
There are many ways to handle JSON parse error. In this post, I will show you how to handle JSON parse error in JavaScript.
1. Using try-catch block
The most common way to handle JSON parse error is using try-catch block. If the JSON string is valid, it will return a JavaScript object. If the JSON string is invalid, it will throw a SyntaxError.
try {
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
// expected output: SyntaxError: Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1
}
2. Using if-else block
Another way to handle JSON parse error is using if-else block.
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json);
if (obj instanceof SyntaxError) {
console.log(obj);
// expected output: SyntaxError: Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1
} else {
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
}
3. Using try-catch block with JSON.parse()
The third way to handle JSON parse error is using try-catch block with JSON.parse().
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
try {
return JSON.parse(value);
} catch (e) {
return value;
}
});
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
4. Using try-catch block with JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify()
The fourth way to handle JSON parse error is using try-catch block with JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify(). If the JSON string is valid, it will return a JavaScript object. If the JSON string is invalid, it will return a SyntaxError.
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
try {
return JSON.parse(value);
} catch (e) {
return value;
}
});
const str = JSON.stringify(obj);
console.log(str);
// expected output: {"result":true,"count":42}
Сообщение
SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad control character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad Unicode escape SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad escape character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string SyntaxError: JSON.parse: no number after minus sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-digit SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after decimal point SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated fractional number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent indicator SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: exponent part is missing a number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected end of data SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected keyword SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data while reading object contents SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or '}' SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when ',' or ']' was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ',' or ']' after array element SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when property name was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected double-quoted property name SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property name when ':' was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ':' after property name in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property value in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ',' or '}' after property value in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ',' or '}' after property-value pair in object literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: property names must be double-quoted strings SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or '}' SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-whitespace character after JSON data
Тип ошибки
Что пошло не так?
JSON.parse() обрабатывает (парсит) строку в формате JSON. Это строка должна соответствовать формату, иначе будет выведена ошибка, что был нарушен синтаксис.
Examples
JSON.parse() не допускает запятые
Метод JSON.parse() не разрешает использование, так называемых, trailling запятых.
Обе строки выдадут ошибку типа SyntaxError:
JSON.parse('[1, 2, 3, 4,]');
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1,}');
// SyntaxError JSON.parse: unexpected character
// at line 1 column 14 of the JSON data
Необходимо убрать последние запятые в строках и тогда ошибки не будет:
JSON.parse('[1, 2, 3, 4]');
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
Названия свойств должны быть в двойных кавычках
Вы не можете использовать одинарные кавычки в именах свойств. Например, ‘foo’.
JSON.parse("{'foo': 1}");
// SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or '}'
// at line 1 column 2 of the JSON data
Вместо этого необходимо написать «foo»:
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
Незначащие нули или плавающая точка без последующей цифры
Вы не можете использовать незначащие нули, например, 01. Плавающая точка должна всегда сопровождаться хотя бы одной цифрой после неё.
JSON.parse('{"foo": 01}');
// SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ',' or '}' after property value
// in object at line 1 column 2 of the JSON data
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1.}');
// SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated fractional number
// at line 1 column 2 of the JSON data
Вместо этого напишите просто 1 без нуля и используйте хотя бы одну цифру после точки:
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1.0}');
Смотрите также
Deeksha Agarwal
Posted On: April 5, 2018
26533 Views
3 Min Read
JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is a ubiquitous data format used by all sorts of mobile and web apps for asynchronous browser-server communication. JSON is an extremely popular data format, very easy to work with, compatible with every major programming language, and is supported by every major browser. However just like any programming language, it throws a lot of errors when it decide that today is not going to be your day.
JSON.Parse Syntax Errors
In most web applications, nearly all data transferred from web server is transmitted in a string format. To convert that string into JSON, we use JSON.parse() function, and this the main function that throws errors. Nearly all JSON.parse errors are a subset of SyntaxError error type. Debugging console throws around 32 different errors messages when you mess up your JSON data. And some of them are very tricky to debug; and yes I am talking about you unexpected non-whitespace character after JSON data.
Why the SyntaxError Horror?
SyntaxError is an inherited object of the main error object The main reason behind the error is usually a mistake in the JSON file syntax. You mess up and put a “ instead of a ‘ and you invite to face the SyntaxError JSON.parse: unexpected character.
Just like every programming language, a JSON file has a fixed syntax. Small syntax errors throws errors. For example, in the following code, i forgot to remove a trailing comma
|
JSON.parse(‘[a,b, c, d, e, f,]’); |
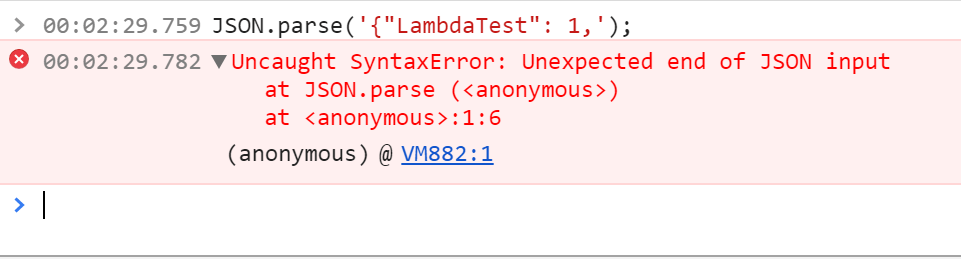
Similarly, in this example I forgot to add }
|
JSON.parse(‘{«LambdaTest»: 1,’); |
How to Catch The Error Before Hand?
The problem with debugging JSON errors are that you get to know about one error at a time. Debuggers throw the first error they find and then stop. It would be upto you to regression find the bugs. Usually it’s not as difficult as it sounds.
The first step is to make sure that your JSON file is perfect from the get go. Here you can take help from JSON linting tools like cleverly named jsonlint.com
If you don’t have any control over the receiving JSON file, then the next step is to add catch exceptions around your JSON.parse.
|
function validatingJSON (json) { var checkedjson try { checkedjson = JSON.parse(json) } catch (e) { } return checkedjson } |
Also, here are the main errors related to JSON.parse that I very painstakingly collected from a very single source [https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Errors/JSON_bad_parse] 😛
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad control character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad Unicode escape SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad escape character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string SyntaxError: JSON.parse: no number after minus sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non—digit SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after decimal point SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated fractional number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent indicator SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: exponent part is missing a number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected end of data SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected keyword SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data while reading object contents SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or ‘}’ SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when ‘,’ or ‘]’ was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘,’ or ‘]’ after array element SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when property name was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected double—quoted property name SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property name when ‘:’ was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘:’ after property name in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property value in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘,’ or ‘}’ after property value in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected ‘,’ or ‘}’ after property—value pair in object literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: property names must be double—quoted strings SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or ‘}’ SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non—whitespace character after JSON data |
If this doesn’t help, then you are in for one long debugging session. Leave a comment below with your issue. I can help.
Deeksha Agarwal
Deeksha Agarwal is in Product Growth at LambdaTest and is also a passionate tech blogger and product evangelist.
Author’s Profile
Deeksha Agarwal
Deeksha Agarwal is in Product Growth at LambdaTest and is also a passionate tech blogger and product evangelist.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now
Test your websites, web-apps or mobile apps seamlessly with LambdaTest.
- Selenium, Cypress, Playwright & Puppeteer Testing
- Real Devices Cloud
- Native App Testing
- Appium Testing
- Live Interactive Testing
- Smart Visual UI Testing
Book a Demo
JSON ( JavaScript Object Notation), is widely used format for asynchronous communication between webpage or mobile application to back-end servers. Due to increasing trend in Single Page Application or Mobile Application, popularity of the JSON is extreme.
Why do we get JSON parse error?
Parsing JSON is a very common task in JavaScript. JSON.parse() is a built-in method in JavaScript which is used to parse a JSON string and convert it into a JavaScript object. If the JSON string is invalid, it will throw a SyntaxError.
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
How to handle JSON parse error?
There are many ways to handle JSON parse error. In this post, I will show you how to handle JSON parse error in JavaScript.
1. Using try-catch block
The most common way to handle JSON parse error is using try-catch block. If the JSON string is valid, it will return a JavaScript object. If the JSON string is invalid, it will throw a SyntaxError.
try {
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
// expected output: SyntaxError: Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1
}
2. Using if-else block
Another way to handle JSON parse error is using if-else block.
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json);
if (obj instanceof SyntaxError) {
console.log(obj);
// expected output: SyntaxError: Unexpected token o in JSON at position 1
} else {
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
}
3. Using try-catch block with JSON.parse()
The third way to handle JSON parse error is using try-catch block with JSON.parse().
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
try {
return JSON.parse(value);
} catch (e) {
return value;
}
});
console.log(obj.count);
// expected output: 42
console.log(obj.result);
// expected output: true
4. Using try-catch block with JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify()
The fourth way to handle JSON parse error is using try-catch block with JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify(). If the JSON string is valid, it will return a JavaScript object. If the JSON string is invalid, it will return a SyntaxError.
const json = '{"result":true, "count":42}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
try {
return JSON.parse(value);
} catch (e) {
return value;
}
});
const str = JSON.stringify(obj);
console.log(str);
// expected output: {"result":true,"count":42}
Синтаксическая ошибка:JSON.parse:плохой парсинг
Исключения JavaScript, создаваемые JSON.parse() возникают, когда строку не удалось проанализировать как JSON.
Message
SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad control character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad character in string literal SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad Unicode escape SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad escape character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated string SyntaxError: JSON.parse: no number after minus sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-digit SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after decimal point SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unterminated fractional number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent indicator SyntaxError: JSON.parse: missing digits after exponent sign SyntaxError: JSON.parse: exponent part is missing a number SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected end of data SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected keyword SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data while reading object contents SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data when property name was expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected double-quoted property name SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property name when SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: end of data after property value in object SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected SyntaxError: JSON.parse: property names must be double-quoted strings SyntaxError: JSON.parse: expected property name or SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected character SyntaxError: JSON.parse: unexpected non-whitespace character after JSON data
Error type
Что пошло не так?
JSON.parse() анализирует строку как JSON. Эта строка должна быть действительным JSON и вызовет эту ошибку, если будет обнаружен неправильный синтаксис.
Examples
JSON.parse()не позволяет использовать запятые в конце текста
Обе линии бросят синтаксическую ошибку:
JSON.parse('[1, 2, 3, 4,]'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1,}');
Опустите запятые,чтобы правильно разобрать JSON:
JSON.parse('[1, 2, 3, 4]'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
Имена объектов недвижимости должны быть двузначно процитированными.
Нельзя использовать одиночные кавычки вокруг свойств,например,’foo’.
JSON.parse("{'foo': 1}");
Вместо этого напишите «фу»:
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}');
Ведущие нули и десятичные знаки
Нельзя использовать опережающие нули,например 01,а за десятичными точками должен следовать хотя бы один знак.
JSON.parse('{"foo": 01}'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1.}');
Вместо этого запишите только 1 без нуля и используйте по крайней мере одну цифру после запятой:
JSON.parse('{"foo": 1}'); JSON.parse('{"foo": 1.0}');
See also
JSONJSON.parse()JSON.stringify()
JavaScript
- TypeError: недопустимый операнд «экземпляр» «х»
- Исключение JavaScript «недопустимый операнд экземпляра» возникает, когда оператор правых операндов не используется с объектом конструктора, т.е.
- TypeError: ‘x’ не повторяется
- Исключение JavaScript «не является итерируемым» возникает, когда значение, заданное правой частью for…of, функции аргумента, такой как Promise.all TypedArray.from,
- Синтаксическая ошибка:Некорректный формальный параметр
- Исключение JavaScript «искаженный формальный параметр» возникает, когда список аргументов вызова конструктора Function() каким-то образом недействителен.
- URIError:некорректная последовательность URI
- Исключение JavaScript «неверная последовательность URI» возникает, когда декодирование кодирования не было успешным.