One in a lifetime, Laravel developers face CSRF token mismatch error message in the Laravel. CSRF token is very useful to protect the HTTP requests.
Throughout this article, we will learn about how to solve CSRF token mismatch error, change the error message in a user-readable form, how to exclude your special route from the CSRF protection, etc.
Let’s start this article with a bang!
Why CSRF Token Mismatch Error Occurs
As per our real-life experience we found that this error occurs due to the following reasons:
- You might forget to include a hidden CSRF (cross-site request forgery) token field in the form.
- If you are submitting an AJAX-based request using
jQuery,JavaScript,Vue, etc then you might forget to include X-CSRF-TOKEN request header. - Your session might be expired and without refreshing a page, you are submitting a form or request.
These are the basic reasons for CSRF mismatch error occurs. Now, let’s see how to resolve the error.
Solution 01: Simple Form Submission
If you have the simple form and if you are not using any other mechanism to submit a form then you just need to include a hidden CSRF _token field in the form so that the CSRF protection middleware can validate the request.
To do that you can use @csrf blade directive that will generate hidden field automatically for you or you can write hidden field as below:
@csrf
// Or
<!-- Equivalent to... -->
<input type="hidden" name="_token" value="{{ csrf_token() }}" />
Both @csrf and <input type="hidden" ...> are equal as shown in the above code.
Solution 02: AJAX Based Requests
For the AJAX-based requests, you need to add the following meta tag in <head></head>
<meta name="csrf-token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}"> // Add in <head></head>
After that, include the following code before you request call
$.ajaxSetup({
headers: {
'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content')
}
});
You don’t need to repeat the above code for each request. But you need to include the above code on each page where the request is being fired of.
Exclude URIs From CSRF Protection
Sometimes you may wish to exclude the URLs from the CSRF protection. For example, if you are using any 3rd party services and in that you might need to submit a form from your website in that case, you don’t need to use CSRF token.
If you don’t exclude that specific URL then Laravel show you the error message. So to exclude URI follow the steps as below:
- Go to the
app/Http/Middlewaredirectory and open theVerifyCsrfToken.phpfile. - Now, in
protected $exceptarray, add your URIs like below and you are done.
<?php
namespace AppHttpMiddleware;
use IlluminateFoundationHttpMiddlewareVerifyCsrfToken as Middleware;
class VerifyCsrfToken extends Middleware
{
/**
* The URIs that should be excluded from CSRF verification.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $except = [
'stripe/*',
'http://example.com/foo/bar',
'http://example.com/foo/*',
];
}
Change CSRF Token Mismatch Error Message In Laravel
Recently, we were working on a Laravel + Vue based project. In that, we have added auto logout functionality if a user is inactive for more than 15 mins. But after the logout session is expired and due to that if the user re-try to login they were getting the “CSRF token mismatch” error so they have reported this issue to the site admin.
So due to that site admin wants to change that message in user-readable form like “Your session has expired. You will need to refresh the page and log in again to continue using the system.” This message is meaningful to users and they won’t see the error message again after refreshing the page. Let’s see how to change the CSRF Token Mismatch error message.
- First, go to the
app/Exceptionsdirectory and open theHandler.phpfile. - In
render()method add the following code.
if ($request->expectsJson()) {
if ($exception instanceof TokenMismatchException) {
return response()->json([
'message' => 'Your session has expired. You will need to refresh the page and login again to continue using the system.'], 419);
}
}
That’s it. You are done.
If you want to test the newly added message then open your site and open the developer tools by inspect element option.
Then, Delete the XSRF-TOKEN cookie and then try to submit your form or request again. You will see the newly added message.
Additionally, read our guide:
- Laravel One To One Relationship Tutorial
- Best Way to Remove Public from URL in Laravel
- How To Print Or Debug Query In Laravel
- Specified Key Was Too Long Error In Laravel
- AJAX PHP Post Request With Example
- How To Use The Laravel Soft Delete
- How To Add Laravel Next Prev Pagination
- Laravel Remove Package With Example (Correct Way)
- Difference Between Factory And Seeders In Laravel
- Laravel: Increase Quantity If Product Already Exists In Cart
- How To Calculate Age From Birthdate
- How to Convert Base64 to Image in PHP
- Check If A String Contains A Specific Word In PHP
- How To Find Duplicate Records in Database
- How To Convert Word To PDF In Laravel
That’s it for now. We hope this article helped you to learn Laravel CSRF Token Mismatch Error Message related things.
Please let us know in the comments if everything worked as expected, your issues, or any questions. If you think this article saved your time & money, please do comment, share, like & subscribe. Thank you in advance. 🙂 Keep Smiling! Happy Coding!
Если вы столкнулись с ошибкой «истек CSRF-токен» — читайте нашу статью. Из неё вы узнаете, как работает CSRF-token защита, и что делать, если CSRF токен истек.
Что такое CSRF
CSRF (англ. cross-site request forgery) — это межсайтовая подделка запроса. Это атака, которой может подвергаться любой веб-ресурс или веб-приложение. В первую очередь это касается сайтов, которые используют cookies, сертификаты авторизации и браузерную аутентификацию. В результате атаки страдают клиенты и репутация ресурса.
Вредоносный скрипт прячется в коде сайта или обычной ссылке. С помощью него мошенник получает доступ к конфиденциальной информации: платежным реквизитам, логину и паролю, личной переписке. После того как данные “в кармане”, хакер может изменить пароль, указать свой номер телефона или email, перевести деньги на свой счёт и многое другое.
Как работает CSRF-атака
Злоумышленник может использовать фишинговую ссылку — это наиболее распространенный способ обмана. В этом случае атака работает по следующей схеме:
- Злоумышленник создаёт поддельную страницу, очень похожую на оригинальную, и встраивает её в сайт. В коде ссылка может выглядеть так: <a href=“вредоносная ссылка”>Unsubscribe here</a>.
- Пользователь переходит с одной страницы сайта на другую (например, на страницу оплаты) и вместо реальной страницы попадает на поддельную.
- Пользователь совершает действие на странице, например, оплачивает товар или вводит данные авторизации.
- Информация или денежные средства вместо оригинального сервера уходят на сервер мошенника.
CSRF-атаки случаются из-за того, что без специальных настроек сервер не может с точностью в 100% определить, кто именно выполняет действия со стороны пользователя. Он не может проверить, действительно ли на кнопку “оплатить” нажал тот пользователь, который изначально открыл страницу с оплатой. Хакеры активно используют этот люфт в безопасности HTTP-запросов и применяют вредоносные скрипты. Однако от атаки можно защититься с помощью CSRF-токенов.
Что такое CSRF-token и как он работает
В общем понимании токен — это механизм, который позволяет идентифицировать пользователя или конкретную сессию для безопасного обмена информацией и доступа к информационным ресурсам. Токены помогают проверить личность пользователя (например, клиента, который онлайн получает доступ к банковскому счёту). Их используют как вместо пароля, так и вместе с ним. Токен — это в каком-то смысле электронный ключ.
CSRF-token — это максимально простой и результативный способ защиты сайта от CSRF-мошенников. Он работает так: сервер создаёт случайный ключ (он же токен) и отправляет его браузеру клиента. Когда браузер запрашивает у сервера информацию, сервер, прежде чем дать ответ, требует показать ключ и проверяет его достоверность. Если токен совпадает, сессия продолжается, а если нет — прерывается. Токен действителен только одну сессию — с новой сессией он обновляется.
Чтобы получить ответ от сервера, используются разные методы запроса. Условно они делятся на две категории: те, которые не изменяют состояние сервера (GET, TRACE, HEAD), и те, которые изменяют (PUT, PATCH, POST и DELETE). Последние имеют большую CSRF-уязвимость и поэтому должны быть защищены в первую очередь.
При создании и использовании токена должны соблюдаться следующие условия:
-
нахождение в скрытом параметре;
-
генерация с помощью генератора псевдослучайных чисел;
-
ограниченное время жизни (одна сессия);
-
уникальность для каждой транзакции;
-
устойчивый к подбору размер (в битах);
-
невозможно переиспользовать.
Типы токенов
Существует три основных типа токенов по способу генерации:
- Synchronizer Tokens или Anti-CSRF (токены синхронизации). В этом случае инициатором ключа выступает сервер — на нём хранится исходная шифровка. Когда браузер обращается к серверу и предъявляет ему ключ, сервер сравнивает его с исходником и в зависимости от результата продолжает или прерывает сессию.
- Double Submit Cookie (двойная отправка куки). При этом способе токен нигде не хранится. Когда браузер обращается к серверу впервые за сессию, сервер генерирует и передаёт ему ключ в двух формах: через куки и в одном из параметров ответа. При следующих обращениях браузера сервер дважды проверяет правильность ключа — в параметрах и в куках.
- Encrypted Token (зашифрованный токен). Этот способ предполагает, что ключом шифруется какая-то часть информации о клиенте, которая содержится в браузере. При первом запросе браузера сервер получает информацию о пользователе, зашифровывает её и передаёт браузеру токен. При следующем взаимодействии сервер расшифровывает токен и сверяет информацию.
Помимо токенов, для защиты используется флаг Same-Site (большинство браузеров его поддерживает). Он работает напрямую для cookies и позволяет помечать куки конкретного домена. Сервер проверяет, содержатся ли нужные пометки в куках страницы, с которых происходит оплата или вносятся изменения. Если пометок нет — сессия прекращается.
Также в качестве меры защиты на страницах сайта настраивают форму с капчей. Это особенно актуально для страниц смены пароля или совершения денежных транзакций.
«Истек срок действия токена» или «CSRF-значение недопустимо»: что это значит и что делать
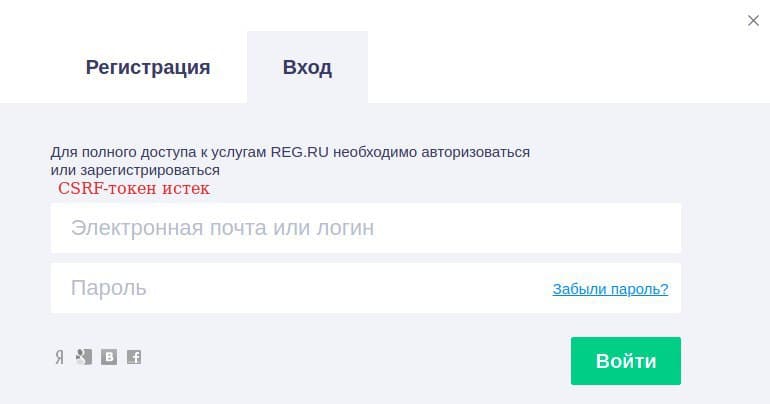
Даже при авторизации на сайтах, для которых настроена защита от атак, можно встретить следующие варианты сообщения об ошибке: «Недопустимое CSRF-значение»/«CSRF-токены не совпадают» или «Token expired» (в переводе — срок действия токена истек). Сообщение может отображаться как на английском, так и на русском. Пример ошибки при авторизации на сайте REG.RU:
Обычно ошибка возникает по двум основным причинам:
-
сервер некорректно сгенерировал токен;
-
срок токена истек — пользователь долго не совершал никаких действий на странице.
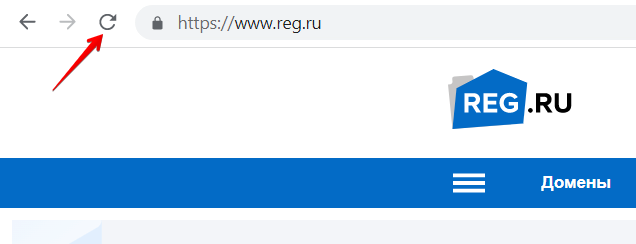
В обоих случаях исправить проблему поможет перезагрузка страницы — вы запустите новую сессию, а значит, сервер и браузер договорятся о новом рабочем токене. Для этого нажмите на значок обновления страницы:
Иногда ошибка возникает из-за расширений защиты конфиденциальности или плагинов блокировки рекламы (например, Ghostery, UBlock Origin, Blur), которые настроены у пользователя. В этом случае можно отключить расширение. Также можно добавить сайт, на котором появилось сообщение, в список доверенных сайтов.
На примере сайта reg.ru покажем, что для этого нужно:
в Google Chrome
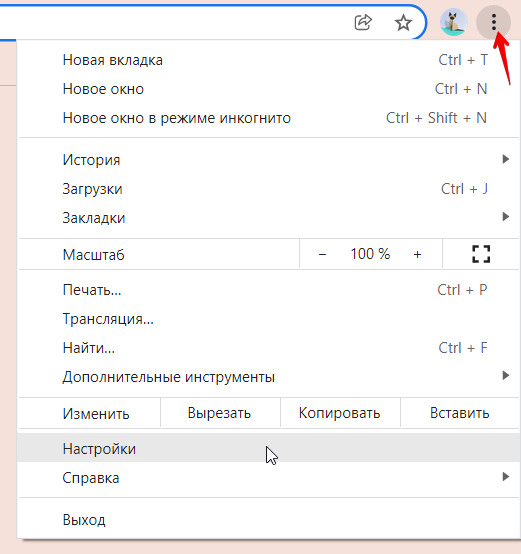
- Откройте настройки Chrome:
- В списке слева выберите Конфиденциальность и безопасность, а затем Файлы cookie и другие данные сайтов.
- Внизу страницы откройте Сайты, которые всегда могут использовать файлы cookie и кликните Добавить.
- Введите «[*.]www.reg.ru» и нажмите Добавить.
- Нажмите Все файлы cookie и данные сайта и удалите все записи, которые связаны с сайтом reg.ru.
- Перезагрузите браузер и выполните операцию повторно.
в Яндекс.Браузер
-
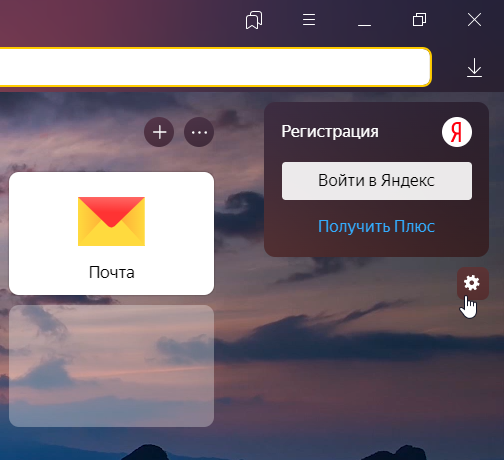
Откройте настройки браузера Яндекс:
- Перейдите на Сайты — Расширенные.
- Кликните Настройки… для первого параметра в списке. Затем на вкладке «Разрешена» введите www.reg.ru и кликните Добавить.
- Добавьте адрес сайта для всех параметров списка по аналогии.
в Safari
- Откройте настройки Safari комбинацией Cmd + , (⌘,).
- Перейдите на вкладку Конфиденциальность и проверьте, что в пункте «Файлы cookie и данные веб-сайтов» не выбрано «Блокировать все файлы cookie». Если это так, снимите настройки.
- Кликните Управление данными веб-сайтов и удалите все записи, которые относятся к www.reg.ru.
- Перезагрузите браузер и выполните операцию повторно.
В некоторых случаях сгенерировать верный токен мешают локальные настройки куки в браузере. Чтобы сессия прошла успешно, достаточно вернуть дефолтные настройки.
Заключение
Успешная атака CSRF позволяет хакеру действовать на сайте от имени другого зарегистрированного посетителя. Чтобы мошенник не добрался до конфиденциальных данных, для сайта нужно настроить один из типов CSRF-токенов. Токены позволяют серверу и браузеру безопасно обмениваться информацией в течение сессии. Однако даже на безопасных сайтах можно столкнуться с ошибкой «токен CSRF истек». В этом нет ничего страшного. Чтобы возобновить подключение, достаточно обновить страницу браузера.
If you are using template files, than you can put your meta tag in the head section (or whatever you name it) which contain your meta tags.
@section('head')
<meta name="csrf_token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}" />
@endsection
Next thing, you need to put the headers attribute to your ajax(in my example, I am using datatable with server-side processing:
"headers": {'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf_token"]').attr('content')}
Here is the full datatable ajax example:
$('#datatable_users').DataTable({
"responsive": true,
"serverSide": true,
"processing": true,
"paging": true,
"searching": { "regex": true },
"lengthMenu": [ [10, 25, 50, 100, -1], [10, 25, 50, 100, "All"] ],
"pageLength": 10,
"ajax": {
"type": "POST",
"headers": {'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf_token"]').attr('content')},
"url": "/getUsers",
"dataType": "json",
"contentType": 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
"data": function (data) {
console.log(data);
},
"complete": function(response) {
console.log(response);
}
}
});
After doing this, you should get 200 status for your ajax request.
Hi All,
So I’ve been spending some time with the issue and I’ve gotten a little bit closer to solving it.
Updated CORS Library
First, I updated my CORS library to be the BarryVDH (which is now fruitcake/laravel-cors). I did this because it was mentioned by Taylor that it will be integrated in Laravel 7.0 (https://twitter.com/taylorotwell/status/1216198072319037440?s=20) and I figured, the best way to test would be to use the package.
Current CORS Config
The changes to the default config are as follows:
'paths' => [
'airlock/csrf-cookie',
'login',
'api/*'
],
and
'allowed_origins' => ['http://localhost:3000'],
I explicitly set the allowed_origins to my local host and NOT the *. I read about this within the Axios GitHub (sorry I lost the link), but it mentioned that for any POST, we had to explicitly set the origin.
Airlock Config
I also set the airlock config to explicitly be my Nuxt domain as well:
'stateful' => [
'http://localhost:3000',
],
Nuxt Login Call
Since I’m working within Nuxt, I wanted to limit the amount of variables and use their Auth package. The call I make for authentication is as follows:
this.$axios.get('https://API/airlock/csrf-cookie', {
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
},
withCredentials: true
}).then(function( response ){
this.$auth.loginWith('local', {
data: {
email: this.email,
password: this.password
},
withCredentials: true,
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
},
});
}.bind(this));
I ensure that the withCredentials is set to true so it passes the cookies correctly.
Now when I inspect my request, I see that under the cookies sent with the request, the XSRF-TOKEN is being sent along to the POST /login route. @robertotcestari I had the same issue where these weren’t being sent, but the current config I have set up, sends the cookies.
This is great! However, I’m still getting a 419 response.
Current Questions
Diving into the VerifyCsrfToken.php middleware, it looks for the header X-CSRF-TOKEN or X-XSRF-TOKEN. Since these are not headers in my request (they are in the cookies), do I have to set up Axios to send as a header? If so, is there any instructions on how to send as a header vs a cookie?
Thanks a ton!
UPDATE
So it’s definitely Axios needing to send the cookie as a header. The IlluminateFoundationHttpMiddlewareVerifyCsrfToken.php checks the header of the request for the X-XSRF-TOKEN and currently axios is passing it as the XSRF-TOKEN cookie.
In my testing environment, with the same variables I have listed above, I forked and modified the middleware to read the cookie, and it worked!
CSRF is an attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application where they are currently authenticated. Laravel’s CSRF protection works by adding a CSRF token to all form submissions, which ensures that the request comes from an authenticated user and prevents malicious attacks. In this article, we will discuss how to fix the Laravel CSRF token mismatch error from AJAX requests.

What is CSRF Token Mismatch Error?
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is a type of web attack that forces an authenticated user to perform unwanted actions on a web application. In a CSRF attack, the attacker tricks the victim into performing an action that they did not intend to perform, such as transferring money or changing their account password.
To prevent CSRF attacks, Laravel uses a built-in mechanism called CSRF protection. CSRF protection adds a unique token to every form submitted to the application. The token is checked on the server-side to ensure that the form submission comes from a legitimate source, i.e., the form is submitted by the authenticated user and not by an attacker.
The CSRF token mismatch error occurs when the token value in the request does not match the token value stored in the user’s session. This error indicates that the request has been tampered with or that the token has expired.
Steps to Fix CSRF Token Mismatch Error from AJAX Request
When making AJAX requests to a Laravel application, you may encounter a CSRF token mismatch error. This error occurs because the CSRF token is not sent with the AJAX request, and Laravel is expecting it to be present. Follow the below steps to fix them:
Step 1: Add CSRF Token to AJAX Request Headers
To fix the CSRF token mismatch error, we need to add the CSRF token to the headers of our AJAX request. Laravel provides a convenient way to obtain the CSRF token using the csrf_token() function. This function returns the current CSRF token value, which we can use to add the CSRF token to the headers of our AJAX request.
Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to add the CSRF token to the headers of an AJAX request using jQuery:
$.ajaxSetup({
headers:
{
'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content')
}
});
In the above code snippet, we use the ajaxSetup() function provided by jQuery to set the headers for all AJAX requests. The X-CSRF-TOKEN header is set to the value of the CSRF token, which is obtained from the meta tag in the HTML document using the attr() function.
Step 2: Verify CSRF Token in Laravel Controller
After adding the CSRF token to the headers of our AJAX request, we need to verify the token in our Laravel controller. Laravel provides a middleware called VerifyCsrfToken that handles the CSRF token verification for all incoming requests, including AJAX requests.
However, when making AJAX requests to a Laravel application, we need to ensure that the X-CSRF-TOKEN header matches the CSRF token value stored in the user’s session. To do this, we can add the web middleware group to our AJAX route in the routes/web.php file, which enables CSRF protection for AJAX requests.
Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to enable CSRF protection for an AJAX route:
Route::group(['middleware' => ['web']], function ()
{
Route::post('/example', 'ExampleController@store');
});
In the above code snippet, we wrap our AJAX route in a web middleware group, which enables CSRF protection for AJAX requests. Now, when an AJAX request is made to the /example route, Laravel will verify that the X-CSRF-TOKEN header matches the CSRF token value stored in the user’s session.
Step 3: Refresh CSRF Token on Session Timeout
In some cases, the CSRF token may expire before the user completes the form submission. This can happen if the user takes a long time to fill out the form, and their session times out. To prevent this issue, we can refresh the CSRF token on session timeout using JavaScript.
Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to refresh the CSRF token using JavaScript:
setInterval(function()
{
$.get('/refresh-csrf').done(function(data)
{
$('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content', data);
});
}, 1800000); // 30 minutes
In the above code snippet, we use the setInterval() function to refresh the CSRF token every 30 minutes. We make an AJAX request to the `/refresh-csrf endpoint, which returns a new CSRF token value, and update the meta tag in the HTML document with the new token value.
Step 4: Display CSRF Token in View
Finally, to ensure that the CSRF token is available in all views, we need to include the token value in the HTML document. Laravel provides a convenient way to do this using the csrf_token() function.
Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to include the CSRF token value in a hidden form field:
<form method="POST" action="/example">
@csrf
<input type="text" name="name">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
In the above code snippet, we use the @csrf directive provided by Laravel to include the CSRF token value in a hidden form field. This ensures that the token is submitted with the form data and verified in the Laravel controller.
Conclusion
We discussed how to fix the Laravel CSRF token mismatch error from AJAX requests. We learned how to add the CSRF token to the headers of our AJAX request, verify the token in our Laravel controller, refresh the CSRF token on session timeout, and display the CSRF token in the view. By following these steps, you can ensure that your Laravel application is secure from CSRF attacks and that your AJAX requests are properly authenticated.