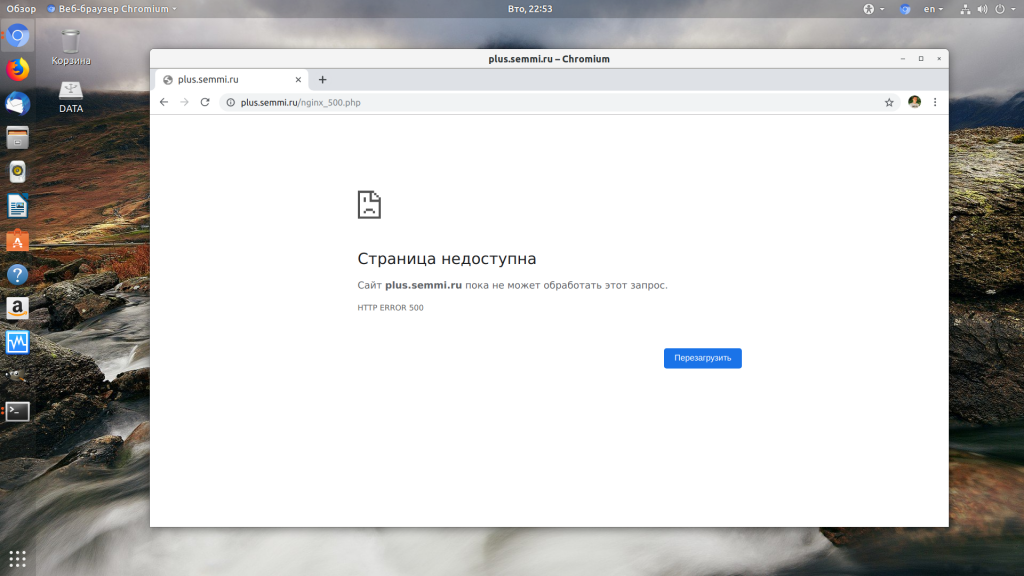
При разработке веб-сайтов и веб-приложений можно столкнуться с ошибкой 500 internal server error. Сначала она может испугать и ввести в заблуждение, поскольку обычно веб-сервер выдает более конкретные ошибки, в которых указана точная причина проблемы, например, превышено время ожидания, неверный запрос или файл не найден, а тут просто сказано что, обнаружена внутренняя ошибка.
Но не все так страшно и в большинстве случаев проблема вполне решаема и очень быстро. В этой статье мы разберем как исправить ошибку Internal server error в Nginx.
Дословно Internal server error означает внутренняя ошибка сервера. И вызвать её могут несколько проблем. Вот основные из них:
- Ошибки в скрипте на PHP — одна из самых частых причин;
- Превышено время выполнения PHP скрипта или лимит памяти;
- Неправильные права на файлы сайта;
- Неверная конфигурация Nginx.
А теперь рассмотрим каждую из причин более подробно и разберем варианты решения.
1. Ошибка в скрипте PHP
Мы привыкли к тому, что если в PHP скрипте есть ошибки, то сразу же видим их в браузере. Однако на производственных серверах отображение сообщений об ошибках в PHP отключено, чтобы предотвратить распространение информации о конфигурации сервера для посторонних. Nginx не может отобразить реальную причину ошибки, потому что не знает что за ошибка произошла, а поэтому выдает универсальное сообщение 500 internal server error.
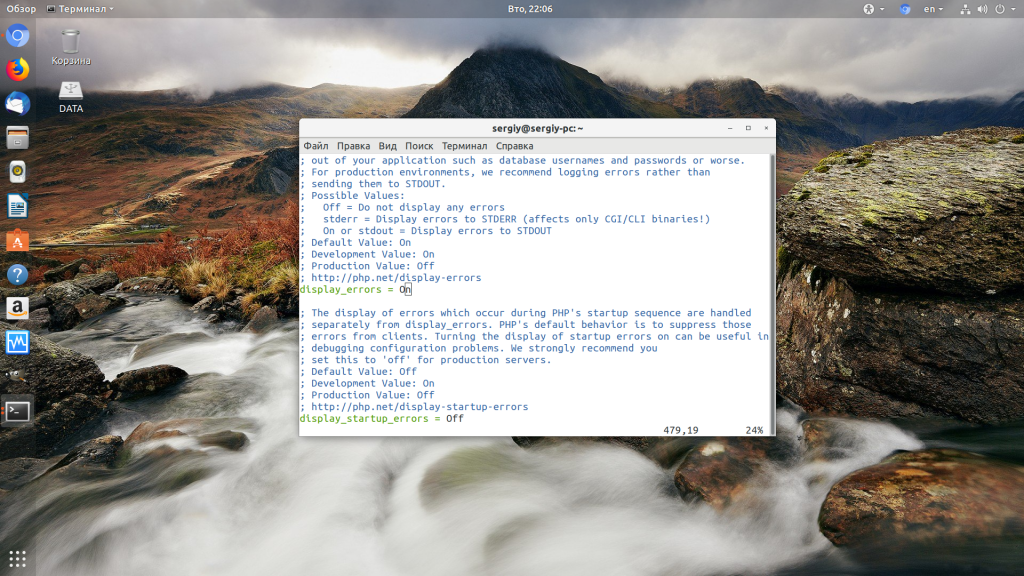
Чтобы исправить эту ошибку, нужно сначала понять где именно проблема. Вы можете включить отображение ошибок в конфигурационном файле php изменив значение строки display_errors с off на on. Рассмотрим на примере Ubuntu и PHP 7.2:
vi /etc/php/7.2/php.ini
display_errors = On
Перезапустите php-fpm:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
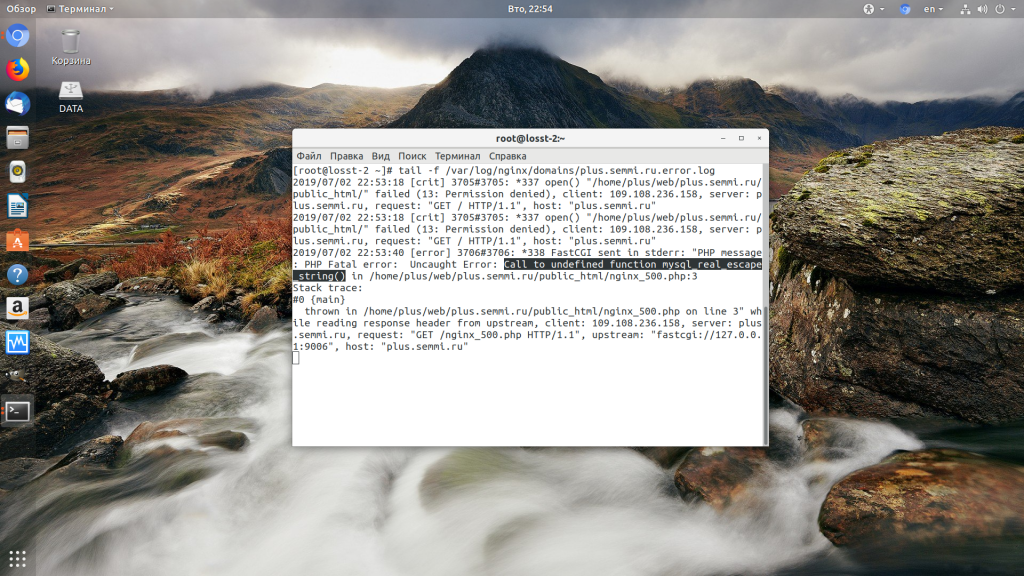
Затем обновите страницу и вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, из-за которого возникла проблема. Далее его можно исправить и отключить отображение ошибок, тогда все будет работать. Ещё можно посмотреть сообщения об ошибках PHP в логе ошибок Nginx. Обычно он находится по пути /var/log/nginx/error.log, но для виртуальных доменов может настраиваться отдельно. Например, смотрим последние 100 строк в логе:
tail -n 100 -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
Теперь аналогично, исправьте ошибку и страница будет загружаться нормально, без ошибки 500.
2. Превышено время выполнения или лимит памяти
Это продолжение предыдущего пункта, так тоже относится к ошибкам PHP, но так, как проблема встречается довольно часто я решил вынести её в отдельный пункт. В файле php.ini установлены ограничения на время выполнения скрипта и количество оперативной памяти, которую он может потребить. Если скрипт потребляет больше, интерпретатор PHP его убивает и возвращает сообщение об ошибке.
Также подобная ошибка может возникать, если на сервере закончилась свободная оперативная память.
Если же отображение ошибок отключено, мы получаем error 500. Обратите внимание, что если время ожидания было ограничено в конфигурационном файле Nginx, то вы получите ошибку 504, а не HTTP ERROR 500, так что проблема именно в php.ini.
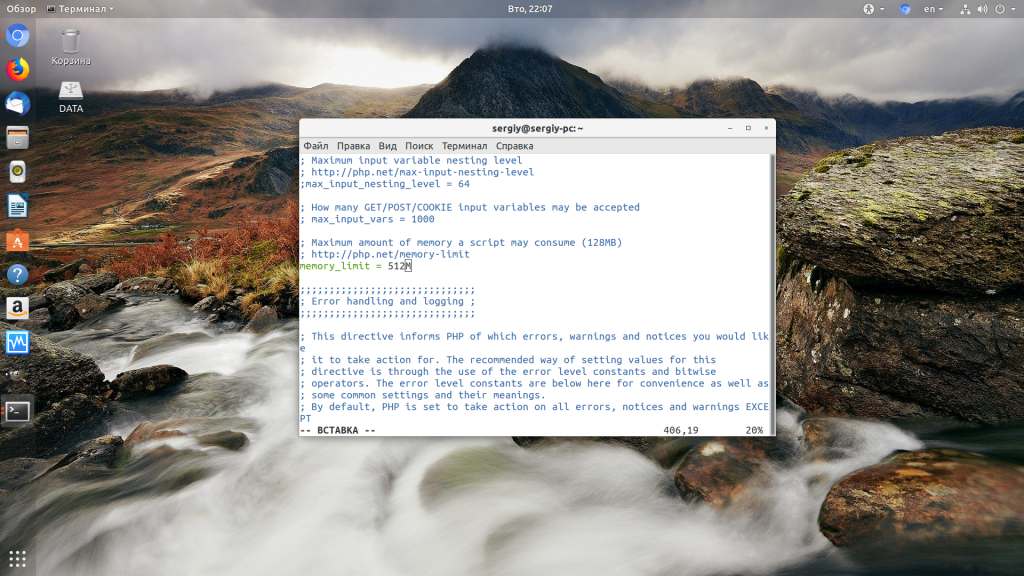
Чтобы решить проблему увеличьте значения параметров max_execution_time и memory_limit в php.ini:
sudo vi /etc/php/7.2/php.ini
max_execution_time 300
memory_limit 512M
Также проблема может быть вызвана превышением других лимитов установленных для скрипта php. Смотрите ошибки php, как описано в первом пункте. После внесения изменений в файл перезапустите php-fpm:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
3. Неверные права на файлы
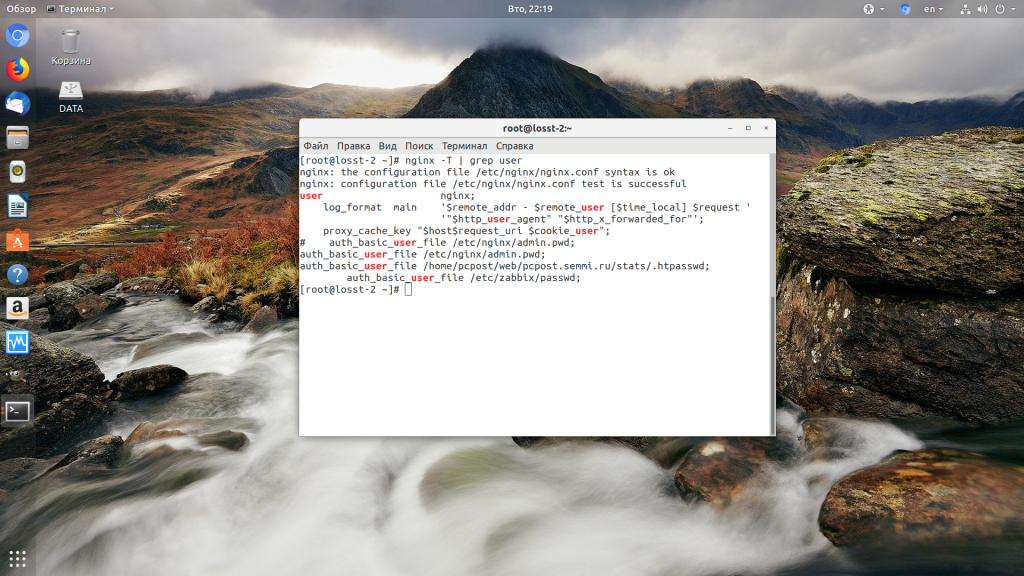
Такая ошибка может возникать, если права на файлы, к которым обращается Nginx установлены на правильно. Сервисы Nginx и php-fpm должны быть запущены от имени одного и того же пользователя, а все файлы сайтов должны принадлежать этому же пользователю. Посмотреть от имени какого пользователя запущен Nginx можно командой:
nginx -T | grep user
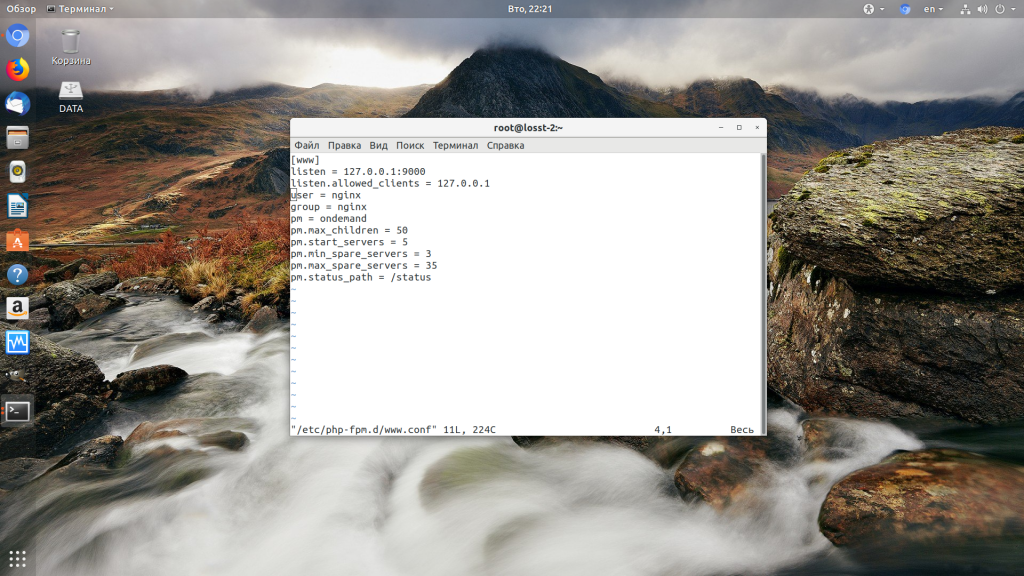
Чтобы узнать от какого пользователя запущен php-fpm посмотрите содержимое конфигурационного файла используемого пула, например www.conf:
sudo vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
В моем случае это пользователь nginx. Теперь надо убедится, что файлы сайта, к которым вы пытаетесь обратиться принадлежат именно этому пользователю. Для этого используйте команду namei:
namei -l /var/www/site
Файлы сайта должны принадлежать пользователю, от имени которого запущены сервисы, а по пути к каталогу с файлами должен быть доступ на чтение для всех пользователей. Если файлы принадлежат не тому пользователю, то вы можете все очень просто исправить:
sudo chown nginx:nginx -R /var/www/site
Этой командой мы меняем владельца и группу всех файлов в папке на nginx:nginx. Добавить права на чтение для всех пользователей для каталога можно командой chmod. Например:
sudo chmod o+r /var/www/
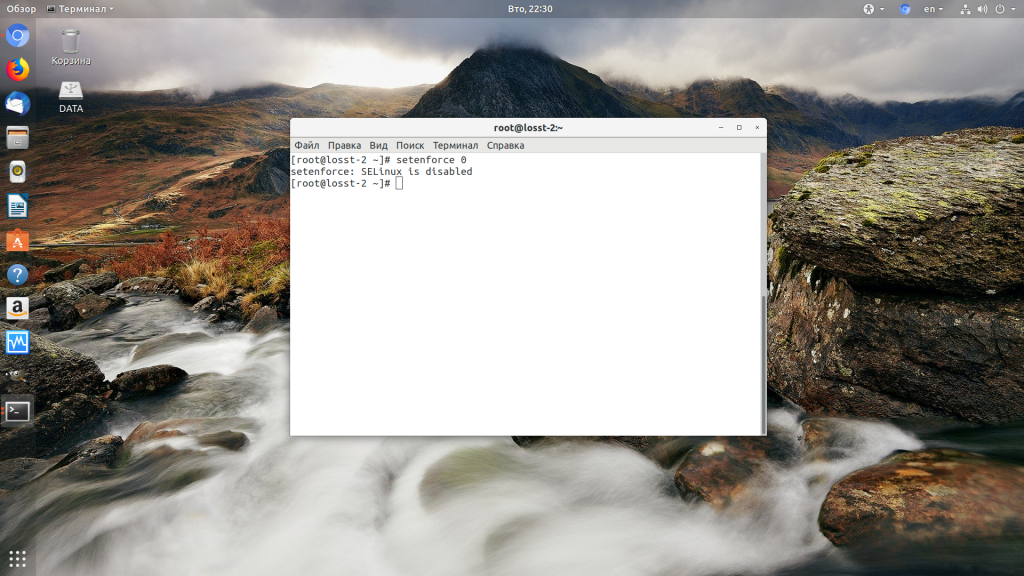
Далее все должно работать. Также, проблемы с правами может вызывать SELinux. Настройте его правильно или отключите:
setenforce 0
Выводы
В этой статье мы разобрали что делать если на вашем сайте встретилась ошибка 500 internal server error nginx. Как видите проблема вполне решаема и в большинстве случаев вам помогут действия описанные в статье. А если не помогут, напишите свое решение в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
This is an Ancient answer from 2013, back when PHP was new and security wasn’t an issue:
Here in the future it’s a security risk to dump errors to screen like this. You better not be doing this in any production setting.
Why are the 500 Internal Server Errors not being logged into your apache error logs?
The errors that cause your 500 Internal Server Error are coming from a PHP module. By default, PHP does NOT log these errors. Reason being you want web requests go as fast as physically possible and it’s a security hazard to log errors to screen where attackers can observe them.
These instructions to enable Internal Server Error Logging are for Ubuntu 12.10 with PHP 5.3.10 and Apache/2.2.22.
Make sure PHP logging is turned on:
-
Locate your php.ini file:
el@apollo:~$ locate php.ini /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini -
Edit that file as root:
sudo vi /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini -
Find this line in php.ini:
display_errors = Off -
Change the above line to this:
display_errors = On -
Lower down in the file you’ll see this:
;display_startup_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ;error_reporting ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE ; Development Value: E_ALL | E_STRICT ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED -
The semicolons are comments, that means the lines don’t take effect. Change those lines so they look like this:
display_startup_errors = On ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off error_reporting = E_ALL ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE ; Development Value: E_ALL | E_STRICT ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATEDWhat this communicates to PHP is that we want to log all these errors. Warning, there will be a large performance hit, so you don’t want this enabled on production because logging takes work and work takes time, time costs money.
-
Restarting PHP and Apache should apply the change.
-
Do what you did to cause the 500 Internal Server error again, and check the log:
tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log -
You should see the 500 error at the end, something like this:
[Wed Dec 11 01:00:40 2013] [error] [client 192.168.11.11] PHP Fatal error: Call to undefined function Foobar\byob\penguin\alert() in /yourproject/ your_src/symfony/Controller/MessedUpController.php on line 249
I am trying to update my system to PHP7-FPM and nginx, have done all the steps required to have this setup working according to what I found on the web (mostly https://ungeek.be/2016/08/php7-fpm-nginx-debian/, in french), but to no avail: nginx keeps throwing an error 500 page at me and without specific errors / info in the log files.
Nginx version: nginx/1.10.3 (package nginx-full)
PHP-FPM version: PHP 7.0.15-1 (dotdeb)
Here are the steps I follow:
- echo «deb http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie all» >>
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/dotdeb.list wget -O- - https://www.dotdeb.org/dotdeb.gpg | apt-key add —
- apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
- apt-get install nginx-full
- apt-get install php7.0 php7.0-bcmath php7.0-bz2 php7.0-cli php7.0-common php7.0-curl php7.0-dev php7.0-enchant php7.0-fpm php7.0-gd php7.0-geoip php7.0-imagick php7.0-intl php7.0-json php7.0-mbstring php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-mysql php7.0-opcache php7.0-pspell php7.0-readline php7.0-sqlite3 php7.0-tidy php7.0-xml php7.0-xmlrpc php7.0-zip
- configured /etc/php/7.0/fpm/pool.d/bookworm.conf (see configuration below)
- created and filled /etc/nginx/sites-available/bookworm (see configuration below)
- ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/bookworm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
- service nginx restart && service php7.0-fpm restart
I have tried to debug this, but no error logged neither in /var/logs/nginx/* nor in /var/logs/php7.0-fpm.log (well, nothing regarding the error 500 I get).
The only message generated is the following:
127.0.0.1 — — [03/Feb/2017:00:39:53 +0100] «GET /app.php HTTP/1.1» 500 507 «-» «Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:45.0) Gecko/20100101
Firefox/45.0»
bookworm site file (some parts are taken from a Symfony recipe available on Nginx’ website):
server {
listen 80 default_server; # with or without, doesn't matter
server_name some.hostname; # actually set to a resolvable server
root /opt/git/Bookworm/web/;
index index.php app.php;
location / {
# try to serve file directly, fallback to app.php
try_files $uri /app.php$is_args$args;
}
# DEV
location ~ ^/(app_dev|config).php(/|$) {
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7-fpm-pool_bookworm.sock; # the socket file exists
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(/.*)$;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $realpath_root;
}
# PROD
location ~ ^/app.php(/|$) {
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7-fpm-pool_bookworm.sock; # the socket file exists
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(/.*)$;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $realpath_root;
# Prevents URIs that include the front controller. This will 404:
# http://domain.tld/app.php/some-path
# Remove the internal directive to allow URIs like this
# internal; # with or without, doesn't matter
}
# return 404 for all other php files not matching the front controller
# this prevents access to other php files you don't want to be accessible.
#location ~ .php$ {
# return 404;
# }
error_log /var/log/nginx/bookworm_error.log;
access_log /var/log/nginx/bookworm_access.log;
location ~ /.ht {
deny all;
}
}
The pool (bookworm.conf) file:
[bookworm]
user = naeikindus
group = naeikindus
listen = /run/php/php7-fpm-pool_$pool.sock
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-data
process.priority = 0
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 50
pm.start_servers = 2
pm.min_spare_servers = 1
pm.max_spare_servers = 3
pm.status_path = /fpm-status-$pool
catch_workers_output = yes
php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/php-fpm/pool_$pool.log
php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on
env[PATH] = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
A sample of the files’ permissions:
ls -lah /opt/git/Bookworm/web
total 64K
drwxr-xr-x 3 naeikindus naeikindus 4.0K Jan 12 22:50 .
drwxr-xr-x 10 naeikindus naeikindus 4.0K Feb 2 22:08 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 1.2K Jan 12 22:48 app_dev.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 2.1K Jan 12 22:48 apple-touch-icon.png
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 631 Jan 12 22:48 app.php
drwxr-xr-x 2 naeikindus naeikindus 4.0K Jan 12 22:50 bundles
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 21K Jan 12 22:50 config.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 6.4K Jan 12 22:48 favicon.ico
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 3.3K Jan 12 22:48 .htaccess
-rw-r--r-- 1 naeikindus naeikindus 116 Jan 12 22:48 robots.txt
l /run/php/php7*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5 Feb 3 01:01 /run/php/php7.0-fpm.pid
srw-rw---- 1 www-data www-data 0 Feb 3 01:01 /run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock
srw-rw---- 1 www-data www-data 0 Feb 3 01:01 /run/php/php7-fpm-pool_bookworm.sock
The user I’m trying to use (naeikindus) is also a member of the www-data group, just in case.
And finally, php.ini (all the ones I could find, to be honest) declare a correct timezone (you can’t be sure enough :-/ ), along with all the display errors I could find. I also tried with cgi.fix_pathinfo=0 / 1, no luck.
Both nginx and php-fpm are started.
I also tried with another «dummy» site (no fancy PHP framework, just an old
If anyone here has a solution or ideas, that would help me a great deal. Thanks a lot !
—-EDIT—-
Full output of nginx -V:
nginx version: nginx/1.10.3 built with OpenSSL 1.0.1t 3 May 2016 TLS
SNI support enabled configure arguments: —with-cc-opt=’-g -O2
-fstack-protector-strong -Wformat -Werror=format-security -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2′ —with-ld-opt=’-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now’ —prefix=/usr/share/nginx —conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf —http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log —error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log —lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock —pid-path=/run/nginx.pid —modules-path=/usr/lib/nginx/modules —http-client-body-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/body —http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/fastcgi —http-proxy-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/proxy —http-scgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/scgi —http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/uwsgi —with-debug —with-pcre-jit —with-ipv6 —with-http_ssl_module —with-http_stub_status_module —with-http_realip_module —with-http_auth_request_module —with-http_v2_module —with-http_dav_module —with-file-aio —with-threads —with-http_addition_module —with-http_geoip_module=dynamic —with-http_gunzip_module —with-http_gzip_static_module —with-http_image_filter_module=dynamic —with-http_secure_link_module —with-http_sub_module —with-http_xslt_module=dynamic —with-stream=dynamic —with-stream_ssl_module —with-mail=dynamic —with-mail_ssl_module —add-dynamic-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/nginx-auth-pam —add-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/nginx-dav-ext-module —add-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/nginx-echo —add-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/nginx-upstream-fair —add-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/ngx_http_substitutions_filter_module —add-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/nginx-cache-purge —add-module=/usr/src/builddir/debian/modules/nginx-x-rid-header —with-ld-opt=-lossp-uuid
Processes information:
ps axuf:
www-data 3798 0.0 0.0 106428 3596 ? S 14:55 0:00 _ nginx: worker process
naeikin+ 3811 0.0 0.1 405828 22680 ? S 14:55 0:00 _ php-fpm: pool bookworm
Calling directly PHP from the CLI works as intended. No SELinux seems to be available (only the library is installed).
Nginx is a very popular web server these days. This article will show you some common errors when running an Nginx web server and possible solutions. This is not a complete list. If you still can’t fix the error after trying the advised solutions, please check your Nginx server logs under /var/log/nginx/ directory and search on Google to debug the problem.
Unable to connect/Refused to Connect
If you see the following error when trying to access your website:
Firefox can’t establish a connection to the server at www.example.com
or
www.example.com refused to connect
or
The site can't be reached, www.example.com unexpectedly closed the connection.
It could be that
- Nginx isn’t running. You can check Nginx status with
sudo systemctl status nginx. Start Nginx withsudo systemctl start nginx. If Nginx fails to start, runsudo nginx -tto find if there is anything wrong with your configuration file. And check the journal (sudo journalctl -eu nginx) to find out why it fails to start. - Firewall blocking ports 80 and 443. If you use the UFW firewall on Debian/Ubuntu, run
sudo ufw allow 80,443/tcpto open TCP ports 80 and 443. If you use Firewalld on RHEL/CentOS/Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux, runsudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}, thensudo systemctl reload firewalldto open TCP ports 80 and 443. - Fail2ban. If your server uses fail2ban to block malicious requests, it could be that fail2ban banned your IP address. Run
sudo journalctl -eu fail2banto check if your IP address is banned. You can add your IP address to the fail2banignoreiplist, so it won’t be banned again. - Nginx isn’t listening on the right network interface. For example, Nginx isn’t listening on the server’s public IP address.
If systemctl status nginx shows Nginx is running, but sudo ss -lnpt | grep nginx shows Nginx is not listening on TCP port 80/443, it could be that you deleted the following lines in the /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*;
So Nginx doesn’t use the virtual host files in /etc/nginx/conf.d/ directory. Add this line back.
The Connection Has Timed Out
This could mean that your server is offline, or Nginx isn’t working properly. I once had an out-of-memory problem, which caused Nginx to fail to spawn the worker processes. If you can see the following error message in /var/log/nginx/error.log file, your server is short of memory.
fork() failed while spawning "worker process" (12: Cannot allocate memory)
404 Not Found
404 not found means Nginx can’t find the resources your web browser asks for. The reason could be:
- The web root directory doesn’t exist on your server. In Nginx, the web roor directory is configured using the
rootdirective, like this:root /usr/share/nginx/linuxbabe.com/;. Make sure your website files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP) are stored in the correct directory. - PHP-FPM isn’t running. You can check PHP-FPM status with
sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm(Debian/Ubuntu) orsudo systemctl status php-fpm. - You forgot to include the
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;directive in your Nginx server config file. This directive is needed to process PHP code. - Your server has no free disk space. Try to free up some disk space. You can use the
ncduutility (sudo apt install ncduorsudo dnf install ncdu) to find out which directories are taking up huge amount of disk space.
403 Forbidden
This error means that you are not allowed to access the request resources. Possible scenario includes:
- The website administrator blocks public access to the requested resources with an IP whitelist or other methods.
- The website could be using a web application firewall like ModSecurity, which detected an intrusion attack, so it blocked the request.
Some web applications may show a different error message when 403 forbidden happens. It might tell you that “secure connection failed”, while the cause is the same.
500 Internal Server Error
This means there is some error in the web application. It could be that
- The database server is down. Check MySQL/MariaDB status with
sudo systemctl status mysql. Start it withsudo systemctl start mysql. Runsudo journalctl -eu mysqlto find out why it fails to start. MySQL/MariaDB process could be killed due to out-of-memory issue. - You didn’t configure Nginx to use PHP-FPM, so Nginx doesn’t know how to execute PHP code.
- If your web application has a built-in cache, you can try flushing the app cache to fix this error.
- Your web application may produce its own error log. Check this log file to debug this error.
- Your web application may have a debugging mode. Turn it on and you will see more detailed error messages on the web page. For example, you can turn on debugging mode in the Modoboa mail server hosting platform by setting
DEBUG = Truein the/srv/modoboa/instance/instance/settings.pyfile. - PHP-FPM could be overloaded. Check your PHP-FPM log (such as
/var/log/php7.4-fpm.log). If you can find the[pool www] seems busy (you may need to increase pm.start_servers, or pm.min/max_spare_servers)warning message, you need to allocate more resources to PHP-FPM. - Sometimes reloading PHP-FPM (
sudo systemctl reload php7.4-fpm) can fix the error. - It also might be that you didn’t install the database module for PHP, so PHP can’t connect to the database. For MySQL/MariaDB, install it with
sudo apt install php7.4-mysql. For PostgreSQL, install it withsudo apt install php7.4-pgsql.
Nginx Shows the default page
If you try to set up an Nginx virtual host and when you type the domain name in your web browser, the default Nginx page shows up, it might be
- Your Nginx virtual host file doesn’t have the
server_namedirective. - You didn’t use a real domain name for the
server_namedirective in your Nginx virtual host. - You forgot to reload Nginx.
- You can try deleting the default virtual host file in Nginx (
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default).
The page isn’t redirecting properly
Firefox displays this error as The page isn’t redirecting properly. Google Chrome shows this error as www.example.com redirected you too many times.
This means you have configured Nginx redirection too many times. For example, you may have added an unnecessary return 301 directive in the https server block to redirect HTTP to HTTPS connection.
If you have set up a page cache such as Nginx FastCGI cache, you need to clear your server page cache.
504 Gateway time-out
This means the upstream like PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB isn’t able to process the request fast enough. You can try restarting PHP-FPM to fix the error temporarily, but it’s better to start tuning PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB for faster performance.
Optimize MySQL/MariaDB Performance
Here is the InnoDB configuration in my /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf file. This is a very simple performance tunning.
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1024M innodb_buffer_pool_dump_at_shutdown = ON innodb_buffer_pool_load_at_startup = ON innodb_log_file_size = 512M innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M #Improving disk I/O performance innodb_file_per_table = 1 innodb_open_files = 400 innodb_io_capacity = 400 innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT innodb_read_io_threads = 64 innodb_write_io_threads = 64 innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 3
Where:
- The InnoDB buffer pool size needs to be at least half of your RAM. ( For VPS with small amount of RAM, I recommend setting the buffer pool size to a smaller value, like 400M, or your VPS would run out of RAM.)
- InnoDB log file size needs to be 25% of the buffer pool size.
- Set the read IO threads and write IO thread to the maximum (64) and
- Make MariaDB use 3 instances of InnoDB buffer pool. The number of instances needs to be the same number of CPU cores on your system.
After saving the changes, restart MariaDB.
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
Recommended reading: MySQL/MariaDB Database Performance Monitoring with Percona on Ubuntu Server
Find Out Which PHP Script Caused 504 Error
You can check the web server access log to see if there are any bad requests. For example, some folks might find the following lines in the Nextcloud access log file (/var/log/nginx/nextcloud.access).
"GET /apps/richdocumentscode/proxy.php?req=/hosting/capabilities HTTP/1.1" 499 0 "-" "Nextcloud Server Crawler" "GET /apps/richdocumentscode/proxy.php?req=/hosting/capabilities HTTP/1.1" 499 0 "-" "Nextcloud Server Crawler" "GET /apps/richdocumentscode/proxy.php?req=/hosting/capabilities HTTP/1.1" 499 0 "-" "Nextcloud Server Crawler"
Notice the HTTP status code 499, which means the HTTP client quit the connection before the server gives back an answer. Successful HTTP code should be 2xx or 3xx. If you can find HTTP code 4xx, it means there’s a problem with this HTTP request. In this example, the Nextcloud richdocumentscode app isn’t working.
Increase Timeout Settings
You can also set a longer timeout value in Nginx to reduce the chance of gateway timeout. Edit your Nginx virtual host file and add the following lines in the server {...} block.
proxy_connect_timeout 600; proxy_send_timeout 600; proxy_read_timeout 600; send_timeout 600;
If you use Nginx with PHP-FPM, then set the fastcgi_read_timeout to a bigger value like 300 seconds. Default is 60 seconds.
location ~ .php$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
Then reload Nginx.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
PHP-FPM also has a max execution time for each script. Edit the php.ini file.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
You can increase the value to 300 seconds.
max_execution_time = 300
Then restart PHP-FPM
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Memory Size Exhausted
If you see the following line in your Nginx error log, it means PHP reached the 128MB memory limit.
PHP Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 57134520 bytes)
You can edit the php.ini file (/etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini) and increase the PHP memory limit.
memory_limit = 512M
Then restart PHP7.4-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
If the error still exists, it’s likely there’s bad PHP code in your web application that eats lots of RAM.
PR_END_OF_FILE_ERROR
- You configured Nginx to rediect HTTP request to HTTPS, but there’s no server block in Nginx serving HTTPS request.
- Maybe Nginx isn’t running?
- Sometimes, the main Nginx binary is running, but a worker process can fail and exit due to various reasons. Check the Nginx error log (
/var/log/nginx/error.log) to debug.
PHP-FPM Upstream Time Out
Some folks can find the following error in Nginx error log file ( under /var/log/nginx/).
[error] 7553#7553: *2234677 upstream timed out (110: Connection timed out) while reading response header from upstream
Possible solutions:
- Restart PHP-FPM.
- Upgrade RAM.
- Optimize database performance. Because PHP-FPM needs to fetch data from the database, if the database is slow to process requests, PHP-FPM will time out.
502 Bad Gateway
This error could be caused by:
- PHP-FPM isn’t running. Check its status:
sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm. - PHP-FPM is running, but Nginx isn’t able to connect to PHP-FPM (Resource temporarily unavailable), see how to fix this error below.
- PHP-FPM is running, but Nginx doesn’t have permission to connect to PHP-FPM socket (Permission denied). It might be that Nginx is running as nginx user, but the socket file
/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sockis owned by thewww-datauser. You should configure Nginx to run as thewww-datauser.
Resource temporarily unavailable
Some folks can find the following error in Nginx error log file ( under /var/log/nginx/).
connect() to unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock failed (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
This usually means your website has lots of visitors and PHP-FPM is unable to process the huge amounts of requests. You can adjust the number of PHP-FPM child process, so it can process more requests.
Edit your PHP-FPM www.conf file. (The file path varies depending on your Linux distribution.)
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
The default child process config is as follows:
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 5 pm.start_servers = 2 pm.min_spare_servers = 1 pm.max_spare_servers = 3
The above configuration means
- PHP-FPM dynamically create child processes. No fixed number of child processes.
- It creates at most 5 child processes.
- Start 2 child processes when PHP-FPM starts.
- There’s at least 1 idle process.
- There’s at most 3 idle processes.
The defaults are based on a server without much resources, like a server with only 1GB RAM. If you have a high traffic website, you probably want to increase the number of child processes, so it can serve more requests. (Make sure you have enough RAM to run more child processes.)
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 20 pm.start_servers = 8 pm.min_spare_servers = 4 pm.max_spare_servers = 12
Save and close the file. Then we also increase the PHP memory limit.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
Find the following line.
memory_limit = 128M
By default, a script can use at most 128M memory. It’s recommended to set this number to at lest 512M.
memory_limit = 512M
Save and close the file. Restart PHP-FPM. (You might need to change the version number.)
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
To monitor the health of PHP-FPM, you can enable the status page. Find the following line in the PHP-FPM www.conf file.
;pm.status_path = /status
Remove the semicolon to enable PHP-FPM status page. Then restart PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Then edit your Nginx virtual host file. Add the following lines. The allow and deny directives are used to restrict access. Only the whitelisted IP addresses can access the status page.
location ~ ^/(status|ping)$ {
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow your_other_IP_Address;
deny all;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}
Save and close the file. Then test Nginx configurations.
sudo nginx -t
If the test is successful, reload Nginx for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Sample PHP-FPM status page.
The PHP-FPM www.conf file gives you a good explanation of what each parameter means.
If PHP-FPM is very busy and unable to serve a request immediately, it will queue this request. By default, there can be at most 511 pending requests, determined by the listen.backlog parameter.
listen.backlog = 511
If you see the following value on the PHP-FPM status page, it means there has never been a request put in the queue, i.e. your PHP-FPM can process requests quickly.
listen queue: 0 max listen queue: 0
If there are 511 pending requests in the queue, it means your PHP-FPM is very busy, so you should increase the number of child processes.
You may also need to change the Linux kernel net.core.somaxconn setting, which defines max number of connections allowed to a socket file on Linux, such as the PHP-FPM Unix socket file. By default, its value is 128 before kernel 5.4 and 4096 starting with kernel 5.4.
[email protected]:~$ sysctl net.core.somaxconn net.core.somaxconn = 128
If you run a high traffic website, you can use a big value. Edit /etc/sysctl.conf file.
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
Add the following two lines.
net.core.somaxconn = 20000 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 65535
Save and close the file. Then apply the settings.
sudo sysctl -p
Note: If your server has enough RAM, you can allocate a fixed number of child processes for PHP-FPM like below. In my experience, this fixed the 500 internal error for a Joomla + Virtuemart website.
pm = static pm.max_children = 50
Two Virtual Host files For the Same Website
If you run sudo nginx -t and see the following warning.
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "example.com" on [::]:443, ignored nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "example.com" on 0.0.0.0:443, ignored
It means there are two virtual host files that contain the same server_name configuration. Don’t create two virtual host files for one website.
PHP-FPM Connection reset by peer
Nginx error log file shows the following message.
recv() failed (104: Connection reset by peer) while reading response header from upstream
This may be caused by a restart of PHP-FPM. If it’s retarted manually by yourself, then you can ignore this error.
Nginx Socket Leaks
If you find the following error message in the /var/log/nginx/error.log file, your Nginx has a socket leaks problem.
2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120606 open socket #16 left in connection 163 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120629 open socket #34 left in connection 188 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120622 open socket #9 left in connection 213 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120628 open socket #25 left in connection 217 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120605 open socket #15 left in connection 244 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120614 open socket #41 left in connection 245 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120631 open socket #24 left in connection 255 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120616 open socket #23 left in connection 258 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120615 open socket #42 left in connection 269 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: aborting
You can restart the OS to solve this problem. If it doesn’t work, you need to compile a debug version of Nginx, which will show you debug info in the log.
invalid PID number “” in “/run/nginx.pid”
You need to restart your web server.
sudo pkill nginx sudo systemctl restart nginx
Cloudflare Errors
Here are some common errors and solutions if your website runs behind Cloudflare CDN (Content Delivery Network).
521 Web Server is Down
- Nginx isn’t running.
- You didn’t open TCP ports 80 and 443 in the firewall.
- You changed the server IP address, but forgot to update DNS record in Cloudflare.
The page isn’t redirecting properly
If your SSL setting on the SSL/TLS app is set to Flexible, but your origin server is configured to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS, Your Nginx server sends reponse back to Cloudflare in encrypted connection. Since Cloudflare is expecting HTTP traffic, it keeps resending the same request, resulting in a redirect loop. In this case, you need to use the Full (strict) SSL/TLS option in your Cloudflare settings.
Wrapping Up
I hope this article helped you to fix common Nginx web server errors. As always, if you found this post useful, then subscribe to our free newsletter to get more tips and tricks 🙂
You may want to check out:
- How to Fix Common Let’s Encrypt/Certbot Errors
If you’ve ever encountered the 500 internal server error Nginx on your website, we know how frustrating and stressful it can be. You may have spent hours or even days creating and designing your website, and the thought of visitors being unable to access it can be disheartening.
But you do not need to worry, we’re here to help you to fix this Nginx server error with the best possible troubleshooting methods!
In this Guide, we’ll walk you through the main causes that trigger 500 internal server error Nginx, How to prevent it, and the steps to fix the Nginx 500 error and get your website back up and running.
![How to Fix 500 Internal Server Error Nginx? [9 Solutions] 3 500 Internal Server Error Message Nginx](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/500_internal_server_error_Nginx_1.png.webp)
Let us get started then!
Read: 🚩 How to fix HTTP 500 Internal Server Error in WordPress?
What does the 500 internal server error Nginx mean?
The 500 internal server error Nginx simply means that something has gone wrong on the server side of things. It is a generally comprehensive response that indicates the server could not able to determine the exact error code in response.
This could be due to a variety of factors, including faulty scripts, misconfigured servers, incompatible plugins, or inadequate file permissions.
Whatever the cause may be, the 500 Internal Server Error Nginx is a sign that something is preventing the server from functioning as it should.
One of the most common reasons for this error is an issue with one of the web servers that NGINX is working with, such as Apache. If the web server encounters an issue and returns a 500 error response to NGINX, this error message can then be returned to the client’s browser and displayed on the screen as 500 Internal Server Error Nginx.
What Are The Causes Of 500 Internal Server Errors Nginx?
The Nginx 500 Internal Server Error can be a real headache for website owners, causing frustration and anxiety. Below are some of the most common reasons that cause 500 internal server errors in Nginx.
- Misconfigured Server
- Incompatible Plugins
- A faulty script
- Inadequate File Permissions
1. A misconfigured server
A misconfigured server can lead to an error, causing a conflict between the server and the browser, leading to a disruption in the communication between the two. This can be due to server mismanagement, which can be caused by human error, a lack of expertise, or outdated software.
2. Incompatible plugins
Sometimes the WordPress plugins that you have installed can be the possible cause of the 500 internal server error Nginx. These plugins may have compatibility issues with the website, leading to the error. This can be due to plugin updates, which can cause compatibility issues with other plugins or website software.
3. A faulty script
A faulty script is another possible cause of the Nginx 500 Internal Server Error. Scripts can become corrupted, causing issues with the website’s functionality, and leading to the error. This can be due to programming errors, file corruption, or compatibility issues.
4. Inadequate file permissions
Insufficient file permissions can prevent the server from accessing or modifying files, leading to errors. This can be due to user error, misconfigured file permissions, or file corruption.
By understanding and identifying the root cause of the 500 Internal Server Error in Nginx, you can take the necessary steps to resolve the issue and ensure that the website runs smoothly and efficiently.
Let us check out them in detail.
1. Force Refresh or Reload your Webpage
The 500 Internal Server Error in Nginx can sometimes appear on your screen due to a temporary issue with your server. The server may be restarting or may be overburdened with too many requests to handle, resulting in insufficient resources to process them.
If it is the case, then Force refreshing or reloading the webpage can do the job. To do this,
- Press the Windows + R key simultaneously or Press the F5 key in windows.
- For Mac, Press Apple + R or Cmd+shift+ R key simultaneously
- For Linux, Press F5 Key
2. Clear Browser Cookies and Cache memory
If the Nginx 500 internal server error is triggered due to a cache-related issue, clearing your browser’s cookies and cache memory can help. Here are the steps you can follow:
Note: Since Chrome has a major Browser market share, here we will be using Chrome for this tutorial.
Step 1: Depending on your browser, navigate to the settings menu. In Google Chrome, you can click on the three vertical dots in the upper right corner of the window.
Step 2: Select “More tools” and Click on “Clear browsing data“.
Step 3: A pop-up window will open on which, you can select all three options under the “Basic” section as shown in the picture below. These options are “Browsing history“, “Cookies and other site data“, and “Cached images and files“.
Step 4: Click on “Clear data” to initiate the process.
Quick tip: Alternatively you can try to access the website in Private or Incognito mode, in which the browser doesn’t store any cookies/cache of the website you visit.
3. Deactivate or Disable VPN
Sometimes, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can be at fault. You can add a VPN or use a VPN client to access the website again.
However, if you have already used VPN, try to deactivate it and then access the website. To do this,
Press the Windows Key + I simultaneously to open the settings interface.
Go to the Network and Internet
Click on VPN, located on the right pane, select your VPN and click on the Remove button.
If you are using any VPN client, do not forget to disconnect it from the VPN.
![How to Fix 500 Internal Server Error Nginx? [9 Solutions] 4 Removing VPN from Windows PC](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/disable_vpn.png.webp)
After completing all the steps, restart your device and check whether the 500 internal server error in Nginx has been resolved or not.
4. Remove Unwanted Browser Extensions
If you have installed a lot of plugins or extensions on your browsers, try to delete or remove the unwanted ones. Sometimes, extensions can also create issues that can trigger such types of errors.
5. Check Server Logs
You can also check out your error logs and find out the possible causes that trigger 500 internal server errors Nginx. All you need to do is log in to the FTP client and then navigate to the Error log Directory and either download it or directly open it in an editor.
This will help you to narrow down the issue so that you easily figure out the exact problem and you can immediately fix it.
You can also read our complete guide on How to access and set up WordPress error logs?
6. Check out the Scripts
- Check Nginx error logs: The first step is to look at the error logs for Nginx, which are usually located in the /var/log/nginx/error.log file (or a similar location depending on your configuration). Look for any error messages related to the 500 error, such as “upstream timed out” or “connect() failed”.
- Check PHP error logs: If you’re running PHP scripts, check the PHP error logs as well. These logs may provide more specific information about the cause of the error, such as syntax errors or runtime issues.
- Check permissions: Make sure that the script and any files it accesses have the correct permissions. Check the owner and group of the script and files and make sure they match the user running the Nginx process.
- Check syntax: If the script is written in a scripting language like PHP, make sure that the syntax is correct. You can do this by running the script from the command line and checking for any syntax errors.
- Check for infinite loops: If the script is in a loop that never ends, it can cause Nginx to timeout and return a 500 error. Look for any infinite loops in the script and fix them.
- Check resource limits: Check the resource limits for the server, such as the maximum memory or CPU usage. If the script is using too many resources, it can cause Nginx to timeout and return a 500 error. Increase the limits if necessary.
- Check for database errors: If the script is accessing a database, check the database logs for any errors or connection issues.
Read: 🚩 How to Fix HTTP 504 Gateway Timeout Error?
7. Check whether adequate permission is granted to folders and files.
To make the WordPress website work perfectly fine, it is essential to have all the directory and file permissions correctly configured. The recommended file permission settings are as follows:
- 755 for all folders and sub-folders.
- 644 for all files.
Incorrect permission settings will lead to the blocking of some plugins, themes, and scripts to work.
At WPOven you can use the “Fix Permissions” tool for fixing file permissions in Sites->Tools in the dashboard.
8. Check all your redirections
Sometimes misconfigured or incorrect redirections in web servers can show 500 internal server error Nginx. Make sure to check that files like mod_rewrite or .htaccess are properly configured and working as they should be.
9. Increase Script timeout value
Sometimes, web servers take longer time than usual to send a request, and if the response time exceeds the timeout value, the web server may time out on the request without waiting for Nginx to respond. This can result in a 500 internal server error Nginx.
To avoid this situation, it is recommended that you increase your web server’s timeout value. This will give your server more time to connect with Nginx and receive a valid response.
10. Contact your Web hosting provider or Developer
If none of the above-mentioned methods can help you fix the 500 Internal Server Error Nginx, the last option left is to contact the support team of your web hosting provider or seek assistance from a developer for further help
Best Practices For Preventing 500 Internal Server Error Nginx
- Regularly update server software and plugins
- Monitor server logs
- Use a content delivery network (CDN)
- Optimize website performance and reduce resource usage
- Use a backup system
Regular Update Server Software and plugins: Regularly updating server software and plugins with their latest version available is crucial to ensure that your website is running on the latest and most secure version of your server and plugins. Outdated software can be vulnerable to security threats, which can cause internal server errors.
Monitor server logs: Monitoring server logs is also important, as it can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems. Checking server logs regularly can help you detect unusual activity or errors, allowing you to take quick action before it causes an internal server error.
Use CDN: CDN or Content Delivery Network can help improve website performance and reduce server load, reducing the risk of internal server errors. CDNs help distribute website content across multiple servers, reducing the load on any single server and improving website speed.
Optimizing website performance and reducing resource usage: It is another important step in preventing internal server errors. This can involve techniques like image compression, minification of code, and reducing the number of HTTP requests.
Use a backup system: It is crucial for ensuring that your website can quickly recover from any internal server errors or other issues. Regular backups can help you restore your website to a previous version quickly and easily, reducing downtime and minimizing the impact of any errors or issues. Check out this dedicated blog on “How to Backup WordPress Site in 5 minutes“.
Conclusion
Tackling the 500 internal server error Nginx can be stressful and frustrating for any individual, but with the proper troubleshooting steps outlined that we have mentioned in this guide, you can easily figure out the issue and fix it.
In addition to that, also do not forget to implement the best practices that we have mentioned to prevent to prevent this error to happen in the future.
Always remember, a well-functioning website is essential for the success of your business, and we’re here to assist you in achieving that. If you have any queries or would like to add any valuable points to it, please do let us know in the comment section below.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix NGINX 500 internal server error?
Here are some best troubleshooting methods you can try to fix 500 internal server errors Nginx on Ubuntu, PHP, WordPress, or other platforms.
1. Force Refresh or Reload your Webpage
2. Clear Browser Cookies and Cache memory
3. Deactivate or Disable VPN
4. Remove Unwanted Browser Extensions
5. Check Server Logs
6. Check out the Scripts
7. Check whether adequate permission is granted to folders and files.
8. Check all your redirections
9. Increase Script timeout value
What causes 500 internal server error?
Here are some of the most common issues due to which your WordPress website has an HTTP 500 Internal Server Error.
1. Corrupt .htaccess file
2. Exceeding PHP Memory Limit
3. Faulty Plugin or theme Issue
4. Corrupted Core Files
5. Check File Permissions
6. Unsupported PHP Version
7. Incorrect DNS entries
8. Problem with the Server itself
9. Inode Limitation Reached
Is a 500 error my fault?
If you are getting 500 internal server error Nginx message, it means there is something went wrong on the server side. There is nothing wrong, with the client side, i.e browser, your computer, or the internet connectivity. It is simply a problem with your website.














![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 7 Clear browsing data on Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/7.png)
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 8 Clearing data in Google Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/8.png)