I’m trying to write a simple program to read a file and search for a word then print how many times that word is found in the file. Every time I type in «test.rtf» (which is the name of my document) I get this error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/AshleyStallings/Documents/School Work/Computer Programming/Side Projects/How many? (Python).py", line 9, in <module>
fileScan= open(fileName, 'r') #Opens file
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'test.rtf'
In class last semester, I remember my professor saying you have to save the file in a specific place? I’m not sure if he really said that though, but I’m running apple OSx if that helps.
Here’s the important part of my code:
fileName= input("Please enter the name of the file you'd like to use.")
fileScan= open(fileName, 'r') #Opens file
mkrieger1
18.4k4 gold badges53 silver badges64 bronze badges
asked Jul 15, 2013 at 16:13
1
If the user does not pass the full path to the file (on Unix type systems this means a path that starts with a slash), the path is interpreted relatively to the current working directory. The current working directory usually is the directory in which you started the program. In your case, the file test.rtf must be in the same directory in which you execute the program.
You are obviously performing programming tasks in Python under Mac OS. There, I recommend to work in the terminal (on the command line), i.e. start the terminal, cd to the directory where your input file is located and start the Python script there using the command
$ python script.py
In order to make this work, the directory containing the python executable must be in the PATH, a so-called environment variable that contains directories that are automatically used for searching executables when you enter a command. You should make use of this, because it simplifies daily work greatly. That way, you can simply cd to the directory containing your Python script file and run it.
In any case, if your Python script file and your data input file are not in the same directory, you always have to specify either a relative path between them or you have to use an absolute path for one of them.
wjandrea
27.2k9 gold badges59 silver badges80 bronze badges
answered Jul 15, 2013 at 16:17
0
Is test.rtf located in the same directory you’re in when you run this?
If not, you’ll need to provide the full path to that file.
Suppose it’s located in
/Users/AshleyStallings/Documents/School Work/Computer Programming/Side Projects/data
In that case you’d enter
data/test.rtf
as your file name
Or it could be in
/Users/AshleyStallings/Documents/School Work/Computer Programming/some_other_folder
In that case you’d enter
../some_other_folder/test.rtf
answered Jul 15, 2013 at 16:18
Jon KiparskyJon Kiparsky
7,4592 gold badges22 silver badges38 bronze badges
0
As noted above the problem is in specifying the path to your file.
The default path in OS X is your home directory (/Users/macbook represented by ~ in terminal …you can change or rename the home directory with the advanced options in System Preferences > Users & Groups).
Or you can specify the path from the drive to your file in the filename:
path = "/Users/macbook/Documents/MyPython/"
myFile = path + fileName
You can also catch the File Not Found Error and give another response using try:
try:
with open(filename) as f:
sequences = pick_lines(f)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File not found. Check the path variable and filename")
exit()
answered Sep 28, 2018 at 11:12
A good start would be validating the input. In other words, you can make sure that the user has indeed typed a correct path for a real existing file, like this:
import os
fileName = input("Please enter the name of the file you'd like to use.")
while not os.path.isfile(fileName):
fileName = input("Whoops! No such file! Please enter the name of the file you'd like to use.")
This is with a little help from the built in module os, That is a part of the Standard Python Library.
wjandrea
27.2k9 gold badges59 silver badges80 bronze badges
answered Jul 15, 2013 at 16:27
user1555863user1555863
2,5576 gold badges34 silver badges50 bronze badges
1
You might need to change your path by:
import os
path=os.chdir(str('Here_should_be_the_path_to_your_file')) #This command changes directory
This is what worked for me at least! Hope it works for you too!
answered Feb 19, 2021 at 7:55
RandML000RandML000
111 silver badge4 bronze badges
Difficult to give code examples in the comments.
To read the words in the file, you can read the contents of the file, which gets you a string — this is what you were doing before, with the read() method — and then use split() to get the individual words.
Split breaks up a String on the delimiter provided, or on whitespace by default. For example,
"the quick brown fox".split()
produces
['the', 'quick', 'brown', 'fox']
Similarly,
fileScan.read().split()
will give you an array of Strings.
Hope that helps!
answered Jul 15, 2013 at 16:52
Jon KiparskyJon Kiparsky
7,4592 gold badges22 silver badges38 bronze badges
0
First check what’s your file format(e.g: .txt, .json, .csv etc ),
If your file present in PWD , then just give the name of the file along with the file format inside either single(»)or double(«») quote and the appropriate operation mode as your requirement
e.g:
with open('test.txt','r') as f: data=f.readlines() for i in data: print(i)
If your file present in other directory, then just give the full path name where is your file is present and file name along with file format of the file inside either single(»)or double(«») quote and the appropriate operation mode as your requirement.
If it showing unicode error just put either r before quote of file path or else put ‘/’ instead of »
with open(r'C:UserssomanDesktoptest.txt','r') as f: data=f.readlines() for i in data: print(i)
answered Nov 3, 2021 at 7:08
The mistake I did was
my code :
x = open('python.txt')
print(x)
But the problem was in file directory ,I saved it as python.txt instead of just python .
So my file path was
->C:UsersnoobDesktopPythonCourse 2python.txt.txt
That is why it was giving a error.
Name your file without .txt it will run.
Jamiu S.
8,0604 gold badges11 silver badges35 bronze badges
answered Aug 14, 2020 at 16:37
One of the most commonly occurring errors in C#, FileNotFoundException is raised when the developer tries to access a file in the program that either doesn’t exist or has been deleted. The following are some of the reasons the system is unable to locate the file:
- There might be a mismatch in the file name. For instance, instead of «demo.txt», the developer has written «Demo.txt».
- The file location may have changed.
- The file might have been deleted.
- The location or path the developer has passed might be wrong.
Syntax of FileNotFoundException
Similar to any class or a method, exceptions also have their own syntax.
Below is the syntax for FileNotFoundException:
public class FileNotFoundException :System.IO.IOExceptionThe FileNotFoundException comes under the class of IOExceptions, which is inherited from the SystemException. SystemException, which is inherited from the Exception class, which is in turn inherited from the Object class.
Object -> Exception -> SystemException -> IOException -> FileNotFoundExceptionAn Example of FileNotFoundException
In the below code, System.IO is imported, which is necessary for doing input and output operations on a file. Then within the main method, a try-catch block is placed to catch the exceptions, and within the try block we have our StreamReader class object.
The StreamReader class is used to read text files. An object of StreamReader, the path of file «demo.txt» is passed. This file doesn’t exist in its constructor. Then the ReadToEnd method is used to read the file till the end if it exists.
using System.IO;
using System;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
try {
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader("demo.txt")) {
reader.ReadToEnd();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
}An Output of FileNotFoundException Example
The output below is obtained on executing the above code. It includes a FileNotFoundException along with its stack trace, which we can later use for debugging the exception.
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Could not find file 'C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1binDebugdemo.txt'.
File name: 'C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1binDebugdemo.txt'
at System.IO.__Error.WinIOError(Int32 errorCode, String maybeFullPath)
at System.IO.FileStream.Init(String path, FileMode mode, FileAccess access, Int32 rights, Boolean useRights, FileShare share, Int32 bufferSize, FileOptions options, SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES secAttrs, String msgPath, Boolean bFromProxy, Boolean useLongPath, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.FileStream..ctor(String path, FileMode mode, FileAccess access, FileShare share, Int32 bufferSize, FileOptions options, String msgPath, Boolean bFromProxy, Boolean useLongPath, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.StreamReader..ctor(String path, Encoding encoding, Boolean detectEncodingFromByteOrderMarks, Int32 bufferSize, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.StreamReader..ctor(String path)
at ConsoleApp1.Program.Main(String[] args) in C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1Program.cs:line 17It is essential to handle exceptions when working with files in any programming language.
How Does FileNotFoundException Work in C# ?
The FileNotFoundException class implements HRESULT COR_E_FILENOTFOUND, which contains 0x80070002 value. When the code is executed and the file is not found by the system it creates a new instance of FileNotFoundException() along with a string which contains a system defined message for the error.
Types of FileNotFoundException errors:
The Message property of FileNotFoundException class gives the error message that explains the reason for the occurrence of the exception. This helps you to find out what kind of file not found error it is.
1. Could not find file error:
Let’s look at a block of code to observe this error. Instead of using StreamReader, let’s directly use the method ReadAllText of the File class to read the text file.
using System.IO;
using System;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
try {
File.ReadAllText("demo.txt");
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
}Output: Could not find file error
In the following output the error message is of the format Could not find file 'filename'. As discussed previously this happens because the developer is trying to load a file that doesn’t exist in the file system. The exception message gives a useful description of the error along with the absolute path to the missing file.
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Could not find file 'C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1binDebugdemo.txt'.
File name: 'C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1binDebugdemo.txt'2. Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070002
This error generally occurs when the developer tries to load a non-existing Assembly into the system.
using System.IO;
using System;
using System.Reflection;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
try {
Assembly.LoadFile("C:\non_existing_dll_file.dll");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}Output of Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070002
In this scenario as well the same FileNotFoundExceptionis raised but the error message is different. Unlike the previous output, the error message from System.Reflection is quite hard to comprehend. Going through a stack trace can help pinpoint that the error is occurring during Assembly.LoadFile.
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: The system cannot find the file specified. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070002)
at System.Reflection.RuntimeAssembly.nLoadFile(String path, Evidence evidence)
at System.Reflection.Assembly.LoadFile(String path)
at ConsoleApp1.Program.Main(String[] args) in C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1Program.cs:line 17Another thing to keep in mind is that neither the filename nor the file path are provided in the message. This is because no name is printed in the output as the Filename attribute on FileNotFoundException is null.
How to debug FileNotFoundException
Let’s look at debugging the code, using the stack trace generated in the first example.
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Could not find file 'C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1binDebugdemo.txt'.
File name: 'C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1binDebugdemo.txt'
at System.IO.__Error.WinIOError(Int32 errorCode, String maybeFullPath)
at System.IO.FileStream.Init(String path, FileMode mode, FileAccess access, Int32 rights, Boolean useRights, FileShare share, Int32 bufferSize, FileOptions options, SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES secAttrs, String msgPath, Boolean bFromProxy, Boolean useLongPath, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.FileStream..ctor(String path, FileMode mode, FileAccess access, FileShare share, Int32 bufferSize, FileOptions options, String msgPath, Boolean bFromProxy, Boolean useLongPath, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.StreamReader..ctor(String path, Encoding encoding, Boolean detectEncodingFromByteOrderMarks, Int32 bufferSize, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.StreamReader..ctor(String path)
at ConsoleApp1.Program.Main(String[] args) in C:ConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1Program.cs:line 17As we scan the stack trace from bottom to top, the StreamReader object we have created to read the file to end with the path of the “demo.txt” file is creating an issue. This happens as the reader.ReadToEnd() is trying to read the file which doesn’t exist. To resolve this create the file using a File class method File.Create() within the catch block.
Code after debugging:
using System.IO;
using System;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
try {
using(StreamReader reader = new StreamReader("demo.txt")) {
reader.ReadToEnd();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Console.WriteLine("File doesn't exists so we created the file");
File.Create(e.FileName);
}
}
}When the above code is executed we get the following output:
File doesn't exists so we created the fileHow to Avoid FileNotFoundException in C#
Ultimately, it is better to avoid this exception rather than try to analyze or debug it, which could be time-consuming for extensive projects. You should use the File.Exists() method to determine whether or not a file exists before referring to it. This method returns true if the file exists, else it returns false.
Example of File.Exists() method:
using System.IO;
using System;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
if (File.Exists("demos.txt")) {
using(StreamReader reader = new StreamReader("check.txt")) {
reader.ReadToEnd();
}
} else {
Console.WriteLine("File doesn't exist please create it");
}
}
}An Output of File.Exists() method:
File doesn't exist please create itTrack, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyse, and manage errors in real-time can help you proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing C# errors are easier than ever. Sign Up Today!
java.io.FileNotFoundException which is a common exception which occurs while we try to access a file. FileNotFoundExcetion is thrown by constructors RandomAccessFile, FileInputStream, and FileOutputStream. FileNotFoundException occurs at runtime so it is a checked exception, we can handle this exception by java code, and we have to take care of the code so that this exception doesn’t occur.
Declaration :
public class FileNotFoundException
extends IOException
implements ObjectInput, ObjectStreamConstants
Constructors :
- FileNotFoundException() : It gives FileNotFoundException with null message.
- FileNotFoundException(String s) : It gives FileNotFoundException with detail message.
It doesn’t have any methods. Now let’s understand the hierarchy of this class i.e FileNotFoundException extends IOException which further extends the Exception class which extends the Throwable class and further the Object class.
Hierarchy Diagram:
Why this Exception occurs?
There are mainly 2 scenarios when FileNotFoundException occurs. Now let’s see them with examples provided:
- If the given file is not available in the given location then this error will occur.
- If the given file is inaccessible, for example, if it is read-only then you can read the file but not modify the file, if we try to modify it, an error will occur or if the file that you are trying to access for the read/write operation is opened by another program then this error will occur.
Scenario 1:
If the given file is not available in the given location then this error will occur.
Example:
Java
import java.io.*;
public class Example1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FileReader reader = new FileReader("file.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
String data =null;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null)
{
System.out.println(data);
}
br.close();
}
}
Output
prog.java:14: error: unreported exception FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
FileReader reader = new FileReader("file.txt");
^
prog.java:25: error: unreported exception IOException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null)
^
prog.java:31: error: unreported exception IOException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
br.close();
^
3 errors
Scenario 2:
If the given file is inaccessible, for example, if it is read-only then you can read the file but not modify the file if we try to modify it, an error will occur or if the file that you are trying to access for the read/write operation is opened by another program then this error will occur.
Example:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Example2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File f=new File("file.txt");
PrintWriter p1=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(f), true);
p1.println("Hello world");
p1.close();
f.setReadOnly();
PrintWriter p2=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("file.txt"), true);
p2.println("Hello World");
}
catch(Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output
java.security.AccessControlException: access denied ("java.io.FilePermission" "file.txt" "write")
at java.base/java.security.AccessControlContext.checkPermission(AccessControlContext.java:472)
at java.base/java.security.AccessController.checkPermission(AccessController.java:897)
at java.base/java.lang.SecurityManager.checkPermission(SecurityManager.java:322)
at java.base/java.lang.SecurityManager.checkWrite(SecurityManager.java:752)
at java.base/java.io.FileOutputStream.<init>(FileOutputStream.java:225)
at java.base/java.io.FileOutputStream.<init>(FileOutputStream.java:187)
at java.base/java.io.FileWriter.<init>(FileWriter.java:96)
at Example2.main(File.java:19)
Handling Exception:
Firstly we have to use the try-catch block if we know whether the error will occur. Inside try block all the lines should be there if there are chances of errors. There are other remedies to handle the exception:
- If the message of the exception tells that there is no such file or directory, then you re-verify whether you mentioned the wrong file name in the program or file exists in that directory or not.
- If the message of the exception tells us that access is denied then we have to check the permissions of the file (read, write, both read and write) and also check whether that file is in use by another program.
- If the message of the exception tells us that the specified file is a directory then you must either delete the existing directory(if the directory not in use) or change the name of the file.
Last Updated :
16 Nov, 2021
Like Article
Save Article
This is the third part in the series named Debugging common .NET exceptions. Today, I want to help you track down and fix a very common and very well-known exception, System.IO.FileNotFoundException. Admitted! In all instances this error is caused by trying to access a file that isn’t there. But, there are actually multiple scenarios that can trigger this exception. You may think you know everything there is to know about this exception, but I bet there is something left for you to learn. At least I did while digging down into the details for this post. Stay tuned to get the full story.
Types of file not found errors
Let’s dig into the different causes of this error. The Message property on FileNotFoundException gives a hint about what is going on.
Could not find file ‘filename’
As the message says, you are trying to load a file that couldn’t be found. This type of error can be re-created using a single line of code:
try
{
File.ReadAllText("non-existing.file");
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
line 3 is the important one here. I’m trying to load a file that doesn’t exist on the file system (non-existing.file). In the example above, the program will print output to the console looking similar to this:
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Could not find file 'APP_PATHbinDebugnon-existing.file'.
File name: 'APP_PATHbinDebugnon-existing.file'
at System.IO.__Error.WinIOError(Int32 errorCode, String maybeFullPath)
at System.IO.FileStream.Init(String path, FileMode mode, FileAccess access, Int32 rights, Boolean useRights, FileShare share, Int32 bufferSize, FileOptions options, SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES secAttrs, String msgPath, Boolean bFromProxy, Boolean useLongPath, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.FileStream..ctor(String path, FileMode mode, FileAccess access, FileShare share, Int32 bufferSize, FileOptions options, String msgPath, Boolean bFromProxy, Boolean useLongPath, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.StreamReader..ctor(String path, Encoding encoding, Boolean detectEncodingFromByteOrderMarks, Int32 bufferSize, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.File.InternalReadAllText(String path, Encoding encoding, Boolean checkHost)
at System.IO.File.ReadAllText(String path)
at ConsoleApp.Program.Main(String[] args) in APP_PATHProgram.cs:line 19
APP_PATH will be the absolute path to the file that cannot be found. This type of FileNotFoundException actually contains all the information needed to debug the problem. The exception message contains a nice error description, as well as an absolute path to the missing file. If you want to present the user with the path or maybe create the file when not found, there is a nifty property available on FileNotFoundException:
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
File.Create(e.FileName);
}
In the example I simply create the missing file by using the Filename property. I’ve seen code parsing the exception message to get the name of the missing file, which is kind of a downer when the absolute path is available right there on the exception 
The system cannot find the file specified. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070002)
This error is typically thrown when trying to load an assembly that doesn’t exist. The error can be re-created like this:
try
{
Assembly.LoadFile("c:\Nonexisting.dll");
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
In this scenario, the program still throws a FileNotFoundException. But the exception message is different:
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: The system cannot find the file specified. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070002)
at System.Reflection.RuntimeAssembly.nLoadFile(String path, Evidence evidence)
at System.Reflection.Assembly.LoadFile(String path)
at ConsoleApp.Program.Main(String[] args) in APP_PATHProgram.cs:line 20
Unlike the error thrown on reading the missing file, messages from the System.Reflection namespace are harder to understand. To find the cause of this error you will need to look through the stack trace, which hints that this is during Assembly.LoadFile. Notice that no filename is present in the exception message and in this case, the Filename property on FileNotFoundException is null.
Could not load file or assembly ‘assembly’ or one of its dependencies. The system cannot find the file specified.
An error similar to the one above is the Could not load file or assembly 'assembly' or one of its dependencies. The system cannot find the file specified. error. This also means that the program is trying to load an assembly that could not be found. The error can be re-created by creating a program that uses another assembly. Build the program, remove the references assembly (the .dll file) from the binDebug folder and run the program. In this case, the program fails during startup:
Unhandled Exception: System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Could not load file or assembly 'Lib, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null' or one of its dependencies. The system cannot find the file specified.
at ConsoleApp.Program.Main(String[] args)
In this example, I’m referencing an assembly named Lib, which doesn’t exist on the disk or in the Global Assembly Cache (GAC).
The typical cause of this error is that the referenced assembly isn’t on the file system. There can be multiple causes of this. To help you debug this, here are some things to check:
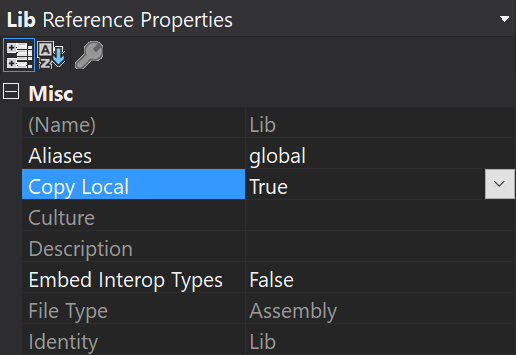
- If you are deploying using a system like Azure DevOps or Octopus Deploy, make sure all the files from the build output are copied to the destination.
- Right-click the referenced assembly in Visual Studio, click Properties and make sure that Copy Local is set to
true:
Access errors when running on IIS
Until now all instances of this error have been a missing file from the disk. I want to round off this post with a quick comment about security. In some cases, the FileNotFoundException can be caused by the user account trying to access the file, and simply don’t have the necessary access. Under optimal circumstances, the framework should throw a System.UnauthorizedAccessException when this happens. But I have seen the issue in the past when hosting websites on IIS. Make sure that the ASP.NET worker process account (or NETWORK SERVICE depending on which user you are using) has access to all files and folders needed to run the application.
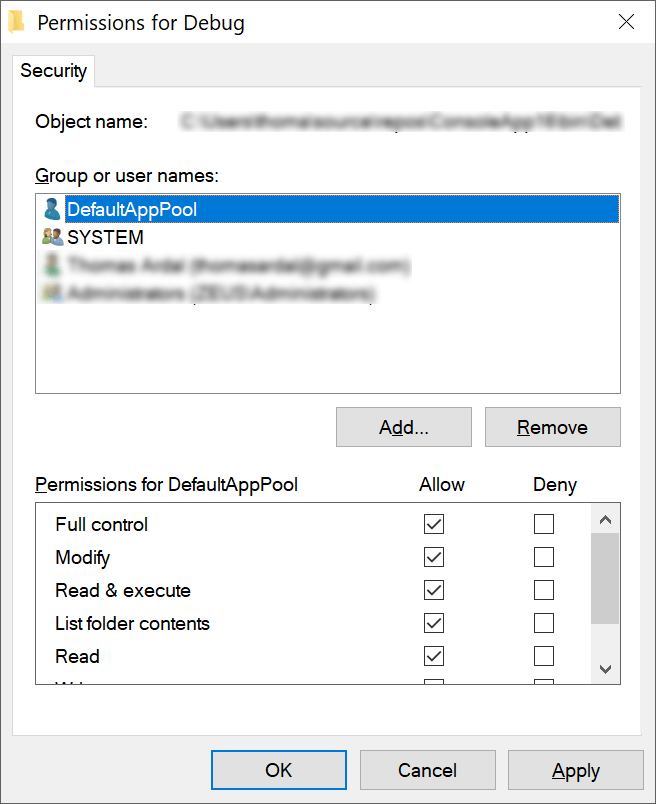
To make sure that the app pool user has access:
- Right-click the folder containing your web application
- Click Properties
- Select the Security tab
- Click Edit…
- Click Add…
- Input IIS AppPoolDefaultAppPool in the text area
- Click Check Names and verify that the user is resolved
- Click OK
- Assign Full control to the new user and save
Also make sure to read the other posts in this series: Debugging common .NET exception.
elmah.io: Error logging and Uptime Monitoring for your web apps
This blog post is brought to you by elmah.io. elmah.io is error logging, uptime monitoring, deployment tracking, and service heartbeats for your .NET and JavaScript applications. Stop relying on your users to notify you when something is wrong or dig through hundreds of megabytes of log files spread across servers. With elmah.io, we store all of your log messages, notify you through popular channels like email, Slack, and Microsoft Teams, and help you fix errors fast.
See how we can help you monitor your website for crashes
Monitor your website
Автор оригинала: baeldung.
1. введение
В этой статье мы поговорим об очень распространенном исключении в Java – исключении FileNotFoundException .
Мы рассмотрим случаи, когда это может произойти, возможные способы лечения и некоторые примеры.
2. Когда Возникает исключение?
Как указано в документации API Java, это исключение может быть вызвано, когда:
- Файл с указанным именем пути не существует не существует
- Файл с указанным именем пути существует , но недоступен по какой-либо причине (запрошена запись для файла только для чтения или разрешения не позволяют получить доступ к файлу)
3. Как с Этим справиться?
Прежде всего, принимая во внимание, что он расширяет java.io.IOException , который расширяет java.lang.Исключение , вам нужно будет справиться с ним с помощью блока try-catch , как и с любым другим проверенным E xception .
Затем, что делать (связано с бизнесом/логикой) внутри блока try-catch на самом деле зависит от того, что вам нужно сделать.
Возможно, вам это понадобится:
- Создание исключения для конкретного бизнеса: это может быть ошибка stopexecutionerror, но вы оставите решение в верхних слоях приложения (не забудьте включить исходное исключение)
- Предупредите пользователя диалогом или сообщением об ошибке: это не ошибка stopexecutionerror, поэтому достаточно просто уведомить
- Создание файла: чтение необязательного файла конфигурации, его поиск и создание нового файла со значениями по умолчанию
- Создайте файл по другому пути: вам нужно что-то написать, и если первый путь недоступен, попробуйте использовать отказоустойчивый
- Просто зарегистрируйте ошибку: эта ошибка не должна останавливать выполнение, но вы регистрируете ее для дальнейшего анализа
4. Примеры
Теперь мы рассмотрим несколько примеров, все из которых будут основаны на следующем тестовом классе:
public class FileNotFoundExceptionTest {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(FileNotFoundExceptionTest.class);
private String fileName = Double.toString(Math.random());
protected void readFailingFile() throws IOException {
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(fileName)));
rd.readLine();
// no need to close file
}
class BusinessException extends RuntimeException {
public BusinessException(String string, FileNotFoundException ex) {
super(string, ex);
}
}
}
4.1. Регистрация исключения
Если вы запустите следующий код, он “зарегистрирует” ошибку в консоли:
@Test
public void logError() throws IOException {
try {
readFailingFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
LOG.error("Optional file " + fileName + " was not found.", ex);
}
}
4.2. Создание исключения для конкретного бизнеса
Далее приведен пример создания исключения для конкретного бизнеса, чтобы ошибка могла быть обработана на верхних уровнях:
@Test(expected = BusinessException.class)
public void raiseBusinessSpecificException() throws IOException {
try {
readFailingFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BusinessException(
"BusinessException: necessary file was not present.", ex);
}
}
4.3. Создание файла
Наконец, мы попытаемся создать файл, чтобы его можно было прочитать (возможно, для потока, который непрерывно читает файл), но снова поймаем исключение и обработаем возможную вторую ошибку:
@Test
public void createFile() throws IOException {
try {
readFailingFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
try {
new File(fileName).createNewFile();
readFailingFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"BusinessException: even creation is not possible.", ioe);
}
}
}
5. Заключение
В этой быстрой записи мы видели, когда может возникнуть исключение FileNotFoundException и несколько вариантов его обработки.
Как всегда, полные примеры находятся на Github .
By Lenin Mishra
in
python
—
Jan 22, 2022
Learn to handle FileNotFound error in Python using try-except block.
The FileNotFoundError Exception in Python is raised when you are trying to access a file or a directory that doesn’t exist.
Example 1
Code/Output
x = open("random_file.txt")
>>> FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'random_file.txt'You can deal with such errors by using the FileNotFoundError Exception class.
Example 2
Code
try:
x = open('random.txt')
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(f"FileNotFoundError successfully handledn"
f"{e}")Output
FileNotFoundError successfully handled
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'random.txt'The above code uses f-strings. Check out that article and other string formatting techniques.
Check out other Python Built-in Exception classes in Python.
built-in-exception-classes — Pylenin
A programmer who aims to democratize education in the programming world and help his peers achieve the career of their dreams.
FileNotFoundException в Java
1. Вступление
В этой статье мы поговорим об очень распространенном исключении в Java —FileNotFoundException.
Мы рассмотрим случаи, когда это может произойти, возможные способы лечения и несколько примеров.
**2. Когда выбрасывается исключение?
Как указано в документации API Java, это исключение может быть создано, когда:
-
Файл с указанным путемdoesnot существует
-
Файл с указанным путемdoes существуетbutis inaccessible по какой-то причине (запрошена запись для файла, доступного только для чтения, или разрешения не позволяют получить доступ к файлу)
3. Как с этим справиться?
Прежде всего, учитывая, что он расширяетjava.io.IOException, который расширяетjava.lang.Exception, вам нужно будет иметь дело с ним с блокомtry-catch, как с любым другим проверенным Exception.
Затем, что делать (связанное с бизнесом / логикой) внутри блокаtry-catch, на самом деле зависит от того, что вам нужно делать.
Вам может понадобиться:
-
Создание исключения для бизнеса: это может быть ошибка остановки выполнения, но вы оставите решение на верхних уровнях приложения (не забудьте включить исходное исключение)
-
Предупредить пользователя диалоговым окном или сообщением об ошибке: это не ошибка остановки выполнения, поэтому достаточно простого уведомления
-
Создайте файл: прочитав необязательный файл конфигурации, не найдя его и создав новый файл со значениями по умолчанию
-
Создайте файл по другому пути: вам нужно что-то написать, а если первый путь недоступен, попробуйте найти отказоустойчивый
-
Просто зарегистрируйте ошибку: эта ошибка не должна останавливать выполнение, но вы регистрируете ее для дальнейшего анализа
4. Примеры
Теперь мы рассмотрим несколько примеров, все из которых будут основаны на следующем тестовом классе:
public class FileNotFoundExceptionTest {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(FileNotFoundExceptionTest.class);
private String fileName = Double.toString(Math.random());
protected void readFailingFile() throws IOException {
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(fileName)));
rd.readLine();
// no need to close file
}
class BusinessException extends RuntimeException {
public BusinessException(String string, FileNotFoundException ex) {
super(string, ex);
}
}
}4.1. Регистрация исключения
Если вы запустите следующий код, он «зарегистрирует» ошибку в консоли:
@Test
public void logError() throws IOException {
try {
readFailingFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
LOG.error("Optional file " + fileName + " was not found.", ex);
}
}4.2. Создание исключения для бизнеса
Далее приведен пример создания бизнес-исключения, чтобы ошибка могла быть обработана на верхних уровнях:
@Test(expected = BusinessException.class)
public void raiseBusinessSpecificException() throws IOException {
try {
readFailingFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BusinessException(
"BusinessException: necessary file was not present.", ex);
}
}4.3. Создание файла
Наконец, мы попытаемся создать файл, чтобы его можно было прочитать (возможно, для потока, который постоянно читает файл), но снова перехватим исключение и обработаем возможную вторую ошибку:
@Test
public void createFile() throws IOException {
try {
readFailingFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
try {
new File(fileName).createNewFile();
readFailingFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"BusinessException: even creation is not possible.", ioe);
}
}
}5. Заключение
В этой быстрой записи мы увидели, когда может произойтиFileNotFoundException, и несколько вариантов решения этой проблемы.