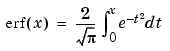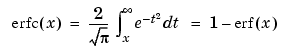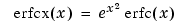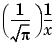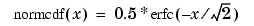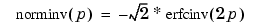Main Content
Syntax
Description
Examples
collapse all
Find Error Function
Find the error function of a value.
Find the error function of the elements of a vector.
V = [-0.5 0 1 0.72]; erf(V)
ans = 1×4
-0.5205 0 0.8427 0.6914
Find the error function of the elements of a matrix.
M = [0.29 -0.11; 3.1 -2.9]; erf(M)
ans = 2×2
0.3183 -0.1236
1.0000 -1.0000
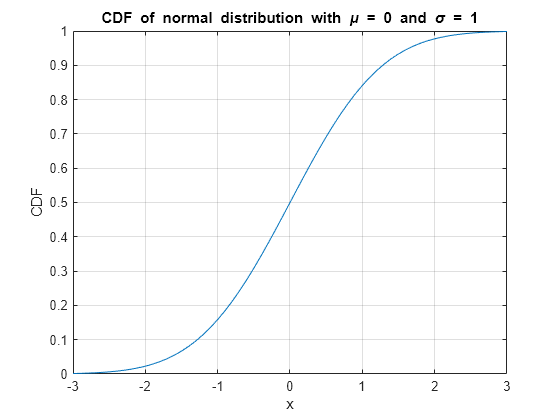
Find Cumulative Distribution Function of Normal Distribution
The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the normal, or Gaussian, distribution with standard deviation σ and mean μ is
ϕ(x)=12(1+erf(x-μσ2)).
Note that for increased computational accuracy, you can rewrite the formula in terms of erfc . For details, see Tips.
Plot the CDF of the normal distribution with μ=0 and σ=1.
x = -3:0.1:3; y = (1/2)*(1+erf(x/sqrt(2))); plot(x,y) grid on title('CDF of normal distribution with mu = 0 and sigma = 1') xlabel('x') ylabel('CDF')
Calculate Solution of Heat Equation with Initial Condition
Where u(x,t) represents the temperature at position x and time t, the heat equation is
∂u∂t=c∂2u∂x2,
where c is a constant.
For a material with heat coefficient k, and for the initial condition u(x,0)=a for x>b and u(x,0)=0 elsewhere, the solution to the heat equation is
u(x,t)=a2(erf(x-b4kt)).
For k = 2, a = 5, and b = 1, plot the solution of the heat equation at times t = 0.1, 5, and 100.
x = -4:0.01:6; t = [0.1 5 100]; a = 5; k = 2; b = 1; figure(1) hold on for i = 1:3 u(i,:) = (a/2)*(erf((x-b)/sqrt(4*k*t(i)))); plot(x,u(i,:)) end grid on xlabel('x') ylabel('Temperature') legend('t = 0.1','t = 5','t = 100','Location','best') title('Temperatures across material at t = 0.1, t = 5, and t = 100')
Input Arguments
collapse all
x — Input
real number | vector of real numbers | matrix of real numbers | multidimensional array of real numbers
Input, specified as a real number, or a vector, matrix, or multidimensional
array of real numbers. x cannot be sparse.
Data Types: single | double
More About
collapse all
Error Function
The error function erf of x is
Tips
-
You can also find the standard normal probability
distribution using the functionnormcdf(Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox). The relationship between the error
functionerfandnormcdfis -
For expressions of the form
1 - erf(x),
use the complementary error functionerfcinstead.
This substitution maintains accuracy. Whenerf(x)is
close to1, then1 - erf(x)is
a small number and might be rounded down to0.
Instead, replace1 - erf(x)witherfc(x).
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
This function fully supports tall arrays. For
more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Usage notes and limitations:
-
Strict single-precision calculations are not supported. In the
generated code, single-precision inputs produce single-precision
outputs. However, variables inside the function might be
double-precision.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For
more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports distributed arrays. For more
information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
- Trial Software
- Trial Software
- Product Updates
- Product Updates
Main Content
Syntax
Description
example
erf( representsX)
the error function of X.
If X is a vector or a matrix, erf(X) computes
the error function of each element of X.
Examples
Error Function for Floating-Point and Symbolic Numbers
Depending on its arguments, erf can
return floating-point or exact symbolic results.
Compute the error function for these numbers. Because these
numbers are not symbolic objects, you get the floating-point results:
A = [erf(1/2), erf(1.41), erf(sqrt(2))]
Compute the error function for the same numbers converted to
symbolic objects. For most symbolic (exact) numbers, erf returns
unresolved symbolic calls:
symA = [erf(sym(1/2)), erf(sym(1.41)), erf(sqrt(sym(2)))]
symA = [ erf(1/2), erf(141/100), erf(2^(1/2))]
Use vpa to approximate symbolic results
with the required number of digits:
d = digits(10); vpa(symA) digits(d)
ans = [ 0.5204998778, 0.9538524394, 0.9544997361]
Error Function for Variables and Expressions
For most symbolic variables and expressions, erf returns
unresolved symbolic calls.
Compute the error function for x and sin(x):
+ x*exp(x)
syms x f = sin(x) + x*exp(x); erf(x) erf(f)
ans = erf(x) ans = erf(sin(x) + x*exp(x))
Error Function for Vectors and Matrices
If the input argument is a vector or a matrix, erf returns
the error function for each element of that vector or matrix.
Compute the error function for elements of matrix M and
vector V:
M = sym([0 inf; 1/3 -inf]); V = sym([1; -i*inf]); erf(M) erf(V)
ans = [ 0, 1] [ erf(1/3), -1] ans = erf(1) -Inf*1i
Special Values of Error Function
erf returns special values
for particular parameters.
Compute the error function for x =
0, x =
∞, and x =
–∞. Use sym to convert 0 and
infinities to symbolic objects. The error function has special values
for these parameters:
[erf(sym(0)), erf(sym(Inf)), erf(sym(-Inf))]
Compute the error function for complex infinities. Use sym to
convert complex infinities to symbolic objects:
[erf(sym(i*Inf)), erf(sym(-i*Inf))]
Handling Expressions That Contain Error Function
Many functions, such as diff and int,
can handle expressions containing erf.
Compute the first and second derivatives of the error function:
syms x diff(erf(x), x) diff(erf(x), x, 2)
ans = (2*exp(-x^2))/pi^(1/2) ans = -(4*x*exp(-x^2))/pi^(1/2)
Compute the integrals of these expressions:
int(erf(x), x) int(erf(log(x)), x)
ans = exp(-x^2)/pi^(1/2) + x*erf(x) ans = x*erf(log(x)) - int((2*exp(-log(x)^2))/pi^(1/2), x)
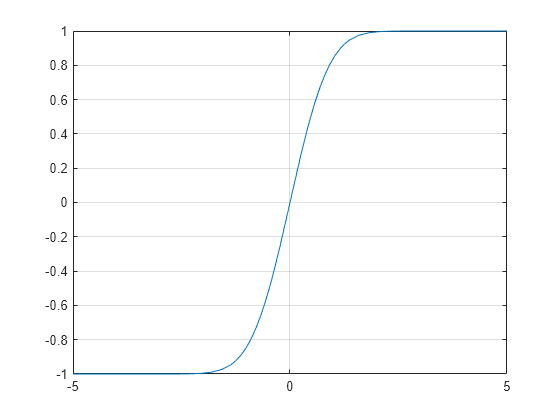
Plot Error Function
Plot the error function on the interval from -5 to 5.
syms x fplot(erf(x),[-5 5]) grid on
Input Arguments
collapse all
X — Input
symbolic number | symbolic variable | symbolic expression | symbolic function | symbolic vector | symbolic matrix
Input, specified as a symbolic number, variable, expression,
or function, or as a vector or matrix of symbolic numbers, variables,
expressions, or functions.
More About
collapse all
Error Function
The following integral defines the error function:
Tips
-
Calling
erffor a number that
is not a symbolic object invokes the MATLAB®erffunction. This function accepts real
arguments only. If you want to compute the error function for a complex
number, usesymto convert
that number to a symbolic object, and then callerffor
that symbolic object. -
For most symbolic (exact) numbers,
erfreturns
unresolved symbolic calls. You can approximate such results with floating-point
numbers usingvpa.
Algorithms
The toolbox can simplify expressions that contain error functions
and their inverses. For real values x, the toolbox
applies these simplification rules:
-
erfinv(erf(x)) = erfinv(1 - erfc(x)) = erfcinv(1
- erf(x)) = erfcinv(erfc(x)) = x -
erfinv(-erf(x)) = erfinv(erfc(x) - 1) = erfcinv(1
+ erf(x)) = erfcinv(2 - erfc(x)) = -x
For any value x, the system applies these
simplification rules:
-
erfcinv(x) = erfinv(1 - x) -
erfinv(-x) = -erfinv(x) -
erfcinv(2 - x) = -erfcinv(x) -
erf(erfinv(x)) = erfc(erfcinv(x)) = x -
erf(erfcinv(x)) = erfc(erfinv(x)) = 1 - x
References
[1] Gautschi, W. “Error Function and Fresnel Integrals.” Handbook
of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical
Tables. (M. Abramowitz and I. A. Stegun, eds.). New York:
Dover, 1972.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
- Trial Software
- Trial Software
- Product Updates
- Product Updates
Указания и ограничения по применению:
-
Строгие вычисления с одинарной точностью не поддерживаются. В сгенерированном коде входные параметры с одинарной точностью производят выходные параметры с одинарной точностью. Однако переменные в функциональной силе быть с двойной точностью.
Эта функция полностью поддерживает основанные на потоке среды. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска в Основанной на потоке Среде.
Эта функция полностью поддерживает массивы графического процессора. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска на графическом процессоре (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Эта функция полностью поддерживает распределенные массивы. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска с Распределенными Массивами (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
erf, erfc, erfcx, erfinv, erfcinv
Error functions
Syntax
-
Y = erf(X) Error function Y = erfc(X) Complementary error function Y = erfcx(X) Scaled complementary error function X = erfinv(Y) Inverse error function X = erfcinv(Y) Inverse complementary error function
Definition
The error function erf(X) is twice the integral of the Gaussian distribution with 0 mean and variance of 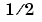
The complementary error function erfc(X) is defined as
The scaled complementary error function erfcx(X) is defined as
For large X, erfcx(X) is approximately
Description
Y = erf(X) returns the value of the error function for each element of real array
X.
Y = erfc(X) computes the value of the complementary error function.
Y = erfcx(X) computes the value of the scaled complementary error function.
X = erfinv(Y) returns the value of the inverse error function for each element of
Y. Elements of Y must be in the interval [-1 1]. The function erfinv satisfies 
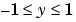
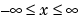
X = erfcinv(Y) returns the value of the inverse of the complementary error function for each element of
Y. Elements of Y must be in the interval [0 2]. The function erfcinv satisfies 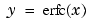
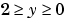
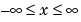
Remarks
The relationship between the complementary error function erfc and the standard normal probability distribution returned by the Statistics Toolbox function normcdf is
The relationship between the inverse complementary error function erfcinv and the inverse standard normal probability distribution returned by the Statistics Toolbox function norminv is
Examples
erfinv(1) is Inf
erfinv(-1) is -Inf.
For abs(Y) > 1, erfinv(Y) is NaN.
Algorithms
For the error functions, the MATLAB code is a translation of a Fortran program by W. J. Cody, Argonne National Laboratory, NETLIB/SPECFUN, March 19, 1990. The main computation evaluates near-minimax rational approximations from [1].
For the inverse of the error function, rational approximations accurate to approximately six significant digits are used to generate an initial approximation, which is then improved to full accuracy by one step of Halley’s method.
References
[1] Cody, W. J., «Rational Chebyshev Approximations for the Error Function,»
Math. Comp., pgs. 631-638, 1969
 |
eps | error |  |
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
This function fully supports tall arrays. For
more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Usage notes and limitations:
-
Strict single-precision calculations are not supported. In the generated code,
single-precision inputs produce single-precision outputs. However, variables inside the
function might be double-precision.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).