May 04, 2023
Nadia M.
7min Read
An HTTP status code is a response code sent between a browser and a web server every time the browser receives an HTTP request. For example, when you enter a URL to access a website.
When you make a request on your browser, it will send an If-Modified-Since request header to the web server. This request header is sent to know when the web page in question was last modified.
Then, the Last-Modified response header will specify when the web source was last modified. If there’s no change, the server will send the HTTP 304 response code.
The HTTP status code 304 means Not Modified – the web page you requested hasn’t changed since the last time you accessed it.
After that, your browser will retrieve the cached version of the web page in your local storage. That way, the browser doesn’t have to download the same information from the website’s server repeatedly.
This post will further discuss what is the HTTP 304 Not Modified status code and various methods to troubleshoot it.
What Are HTTP Status Codes?
HTTP status codes indicate information exchange. They let you know if the request you made was successful or if there was an error.
There are five categories of HTTP status codes, with each indicating a different type of issue:
- The 1xx status codes – informational requests
- The 2xx status codes – successful requests
- The 3xx status codes – redirects
- The 4xx status codes – client errors
- The 5xx status codes – server errors
However, there are only a few of these codes that you’ll likely encounter directly. If you ever come across any of these response status codes, it means you should take further action to solve the issue.
For example, response codes in the 400s indicate errors, such as the 403 Forbidden, which means you don’t have permission to access a resource.
Then there are the 200s responses like HTTP 200 OK, which communicates your request’s success.
Meanwhile, response codes in the 300s indicate redirection issues, such as the 301 and 302 redirects, used for permanent and temporary redirects.
HTTP 304 requests may improve user experience by speeding up resource page delivery, especially when you have a massive number of web pages.
It optimizes your user experience speed and minimizes the requests that the server has to handle. It also helps search engines crawl your pages more efficiently since they won’t waste their crawl budget on pages that haven’t been updated since their last visit.
However, it may also block the visitor’s access to your content.
What Causes the 304 Not Modified Status Code?
304 Not Modified status codes can happen either on the server or the client-side. However, if a user encounters a 304 Not Modified status code on your site, the error most likely occurred on their part and there isn’t much you can do to fix it.
Here are some of the causes why a user may receive a 304 Not Modified status code:
- Virus – The browser may be corrupted by viruses or malware, which affects its capability of communicating with web servers and caching web pages.
- Recent software installation – If a user just recently installed or uninstalled software on their computer, sometimes the registry can become corrupt. This condition also impacts the browser’s communication and caching function.
- Corrupt application – If a user has any application which has corrupt files related to their browser, it will impact its ability to save web pages and update information.
5 Methods to Fix the 304 Status Code
There are five ways to fix the 304 Not Modified status code. Even though you cannot solve the problem on the client-side, you will be able to recommend possible solutions.
1. Clear Your Browser Cache
You can start by deleting all your browsing data, cookies, and other cached information.
Clearing your browser’s cache will remove all data in your temporary storage. By clearing it once in a while, you’ll save plenty of disk space and enable it to work faster.
Outdated resources in your cache can also stop you from seeing the website’s updated content. Clearing them allows you to acquire a new copy of information from the site’s web server.
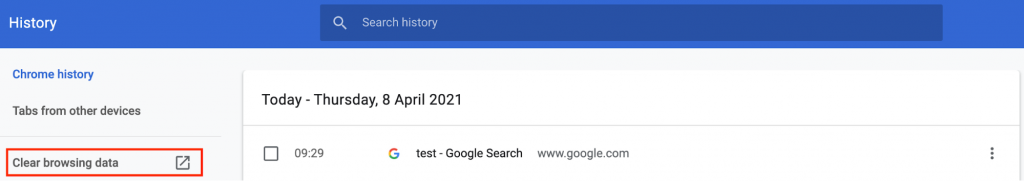
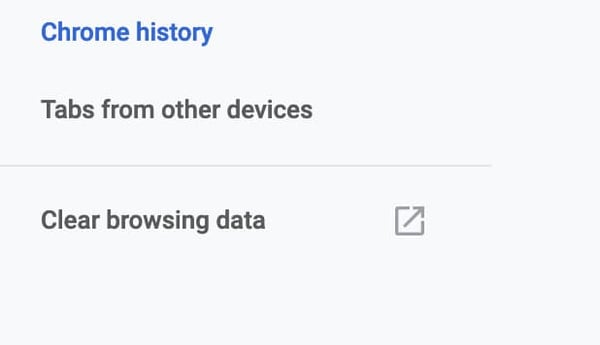
If you’re using Google Chrome, follow these steps to clear your browser’s cache:
- Click Customize and control Google Chrome – the three horizontal dots at the top-right corner of your window.
- Navigate to History -> History.
- Click Clear Browsing Data.
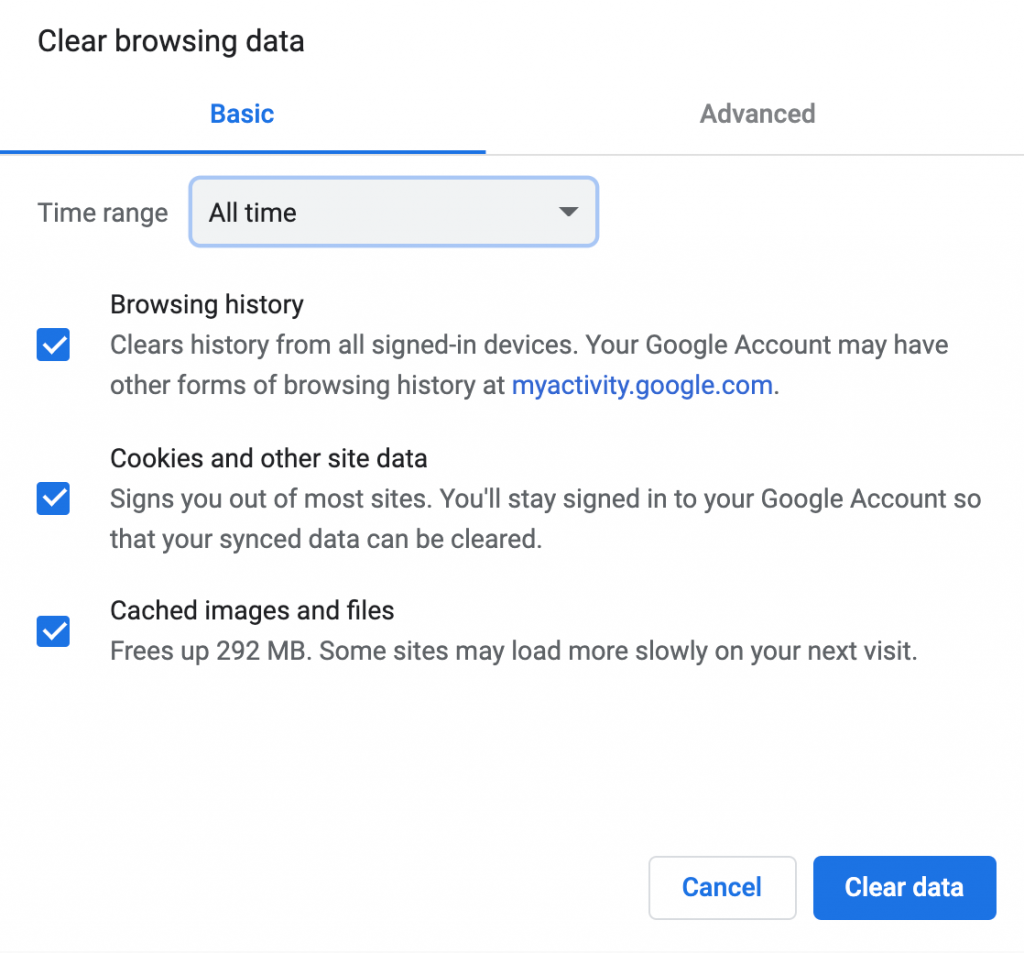
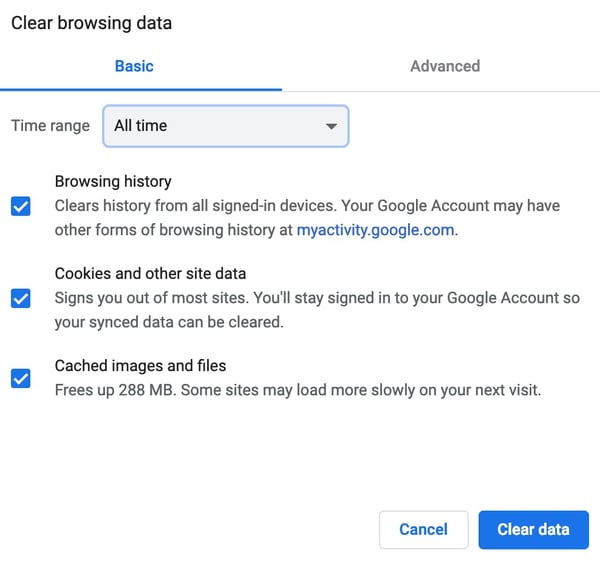
- A new window will pop up. Select the Time range – if you want to clear up everything, choose All Time.
- Choose what you want to clear – browsing history, cookies and other site data, cached images and files.
- Click the Clear Data button.
If you use another browser, the steps to clear the browser cache will vary, but we provide a step-by-step guide for different desktop and mobile platforms.
2. Flush the DNS
Similar to web browsers, operating systems also store cache files, but in the Domain Name System (DNS) cache. It contains information about your browsing data, including hostnames, IP addresses, and resource records.
DNS caching helps load web pages faster when you visit them again, lessening the DNS server’s burden when traffic is high.
The cache files have a validity period, which is determined by the Time to Live (TTL) value. Valid DNS caches can answer any content request without going through a DNS server, but they can cause errors or security issues if they’re outdated or corrupted.
Regularly flushing your DNS can improve your operating system’s security and prevent search behavior tracking, making it hard for hackers to predict your browsing history.
It can also solve technical problems, such as connection issues or the HTTP 304 Not Modified response codes.
If you use Google Chrome, flush your DNS by entering chrome://net-internals/#dns into the address bar.
A menu page will open. Click the Clear host cache button.
Google Chrome keeps a separate DNS cache, so it is necessary to flush DNS on your computer as well.
Flushing your operating system’s DNS is also relatively simple. Follow the steps below if you use Windows – it’s applicable for Windows XP, 7, Vista, 8, 8.1, or 10:
- Click the Start button, then navigate to Windows Systems -> Command Prompt.
- The command-line interface will open. Type this command line:
ipconfig /flushdns
- A confirmation message will appear once the process is successful.
It’s also possible to flush your DNS on other operating systems, such as Mac and Linux.
3. Check Your Redirect Instructions In .htaccess
If none of the previous methods corrected the error message, the issue may be on your server configuration file. For example, your redirect instructions may be incorrect.
To check your server configuration file, you need to know whether your server is running on Nginx or Apache.
If you use Nginx, you don’t have access to the .htaccess file. Check the error logs to see what you need to troubleshoot.
With Apache, check the .htaccess file in your site’s root directory. Log into your hosting account’s File Manager, then navigate to the public_html folder.
Disable the .htaccess by renaming it to .htaccess_disabled. Check the site’s availability and the 304 Not Modified status code while the .htaccess is disabled. Rename it back to .htaccess to enable it again.
If this method resolves the error code, check the code in the .htaccess with your developer. Also, look for incorrect redirect settings, which differ on each website.
4. Run a Malware Scan
Another possible cause of the HTTP 304 Not Modified status is a browser corrupted by a virus or malware infection.
Those threats may interrupt or interfere with your system, including the header request. To identify and remove the threats from your system, run a malware scan.
If you use Google Chrome on Windows, perform it by running the built-in Malware Scanner and Cleanup Tool.
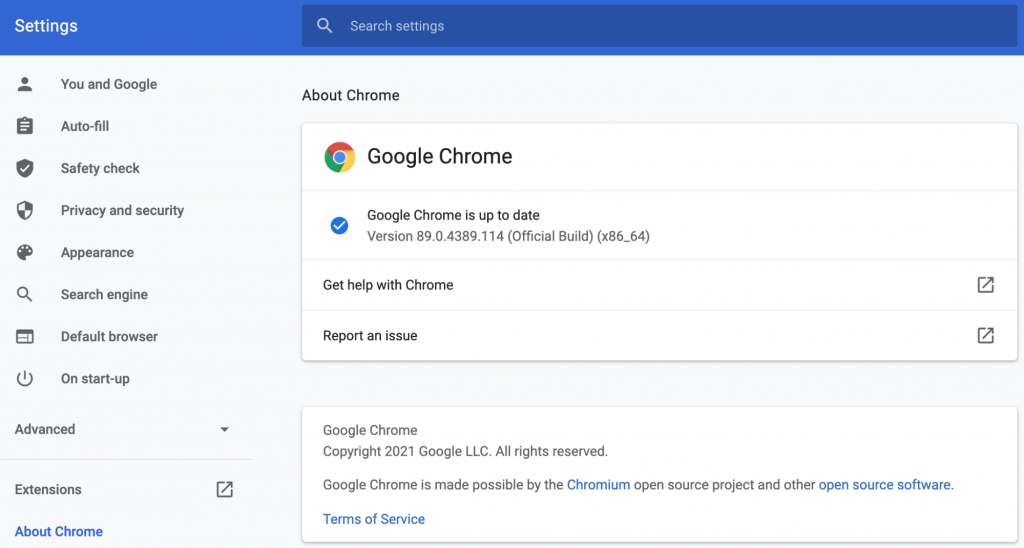
First, check if your Chrome is up to date. Click on the three vertical dots on the top-right of Chrome’s window, then navigate to Settings -> About Chrome.
If you’re not using Chrome’s current version, update it by clicking the Relaunch button.
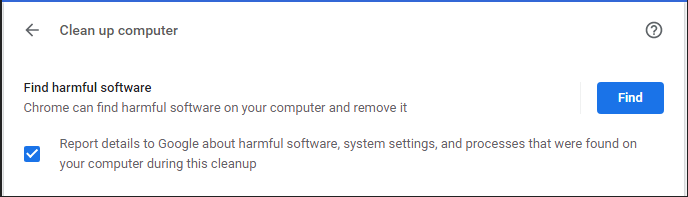
Now that you’ve updated Chrome, open a new tab and enter chrome://settings/cleanup on the URL bar. Click Find.
It will immediately scan your computer, then provide you with the result report.
Other browsers such as Mozilla Firefox and Microsoft Edge don’t have a built-in malware scanner. The same goes for other operating systems like Mac and Linux.
If you use these browsers or operating systems, run the malware scan with the antivirus software on your computer.
5. Disable Browser Extensions
Infected browser extensions can also interfere with requests and server communication, causing the HTTP 304 Not Modified status code.
Disable your browser’s extensions to solve this issue. The steps vary for each browser, so here is a guide for four major browsers – Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge.
Chrome
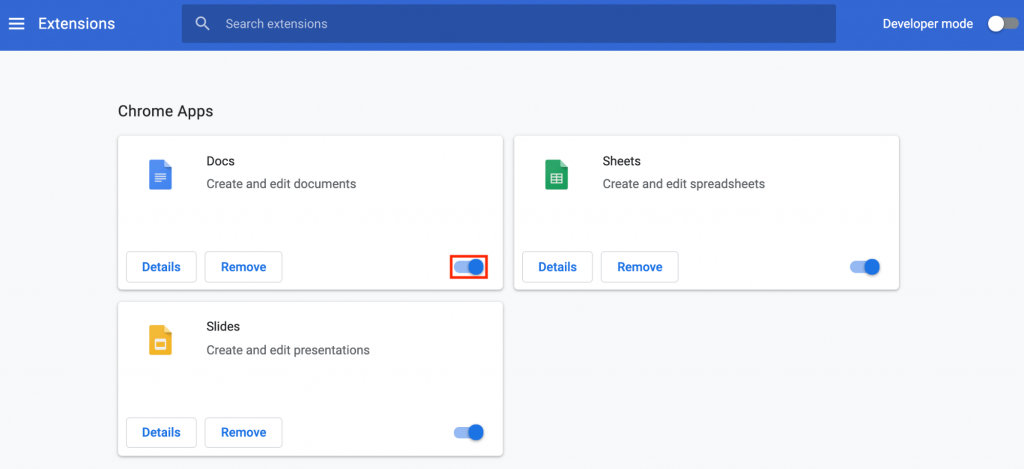
Navigate to Settings -> Extensions. On the Extensions page, disable each extension by clicking on their toggle switches.
Click the Remove button if you want to delete unused or outdated extensions.
Mozilla Firefox
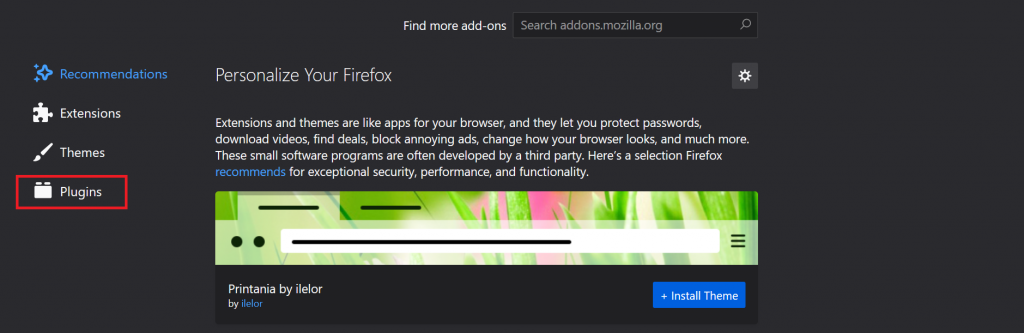
- Click the Open menu icon on the top-right of your Mozilla Firefox window, then select Add-ons.
- On the Add-ons Manager tab, select Plugins.
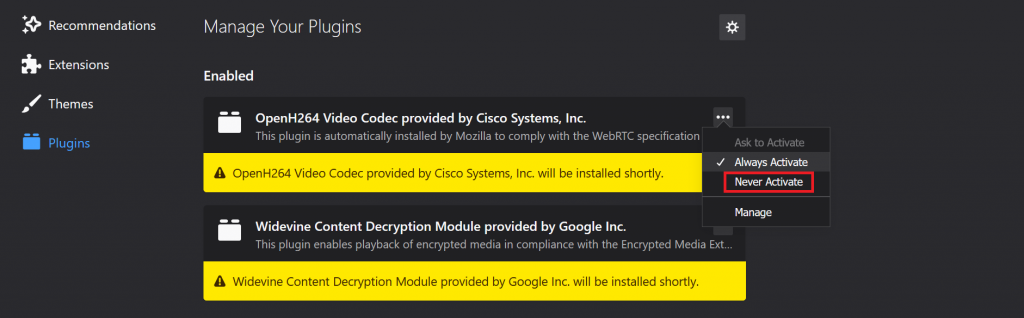
- Choose the plugins that you want to disable by selecting Never Activate on the drop-down menu.
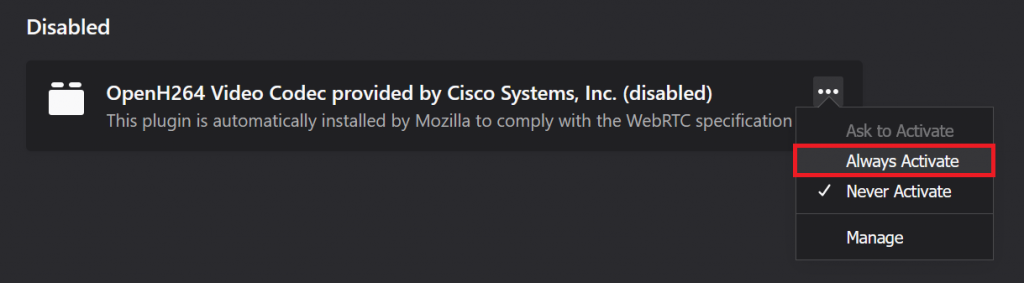
- If you want to re-enable the plugin, check the Disabled plugins list and select Always Activate on the drop-down menu.
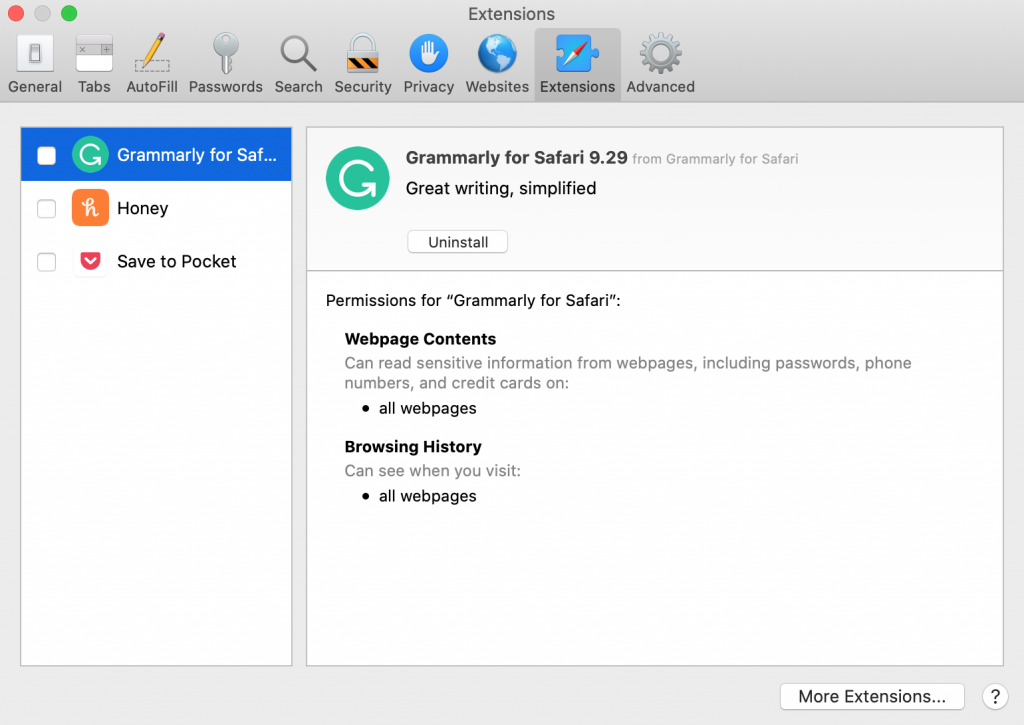
Safari
- On Safari, open the menu and select Preferences.
- Click the Extensions icon.
- Deselect an extension’s checkbox to turn it off.
- If you no longer need an extension, it’s better to uninstall it. Click the Uninstall button to do so.
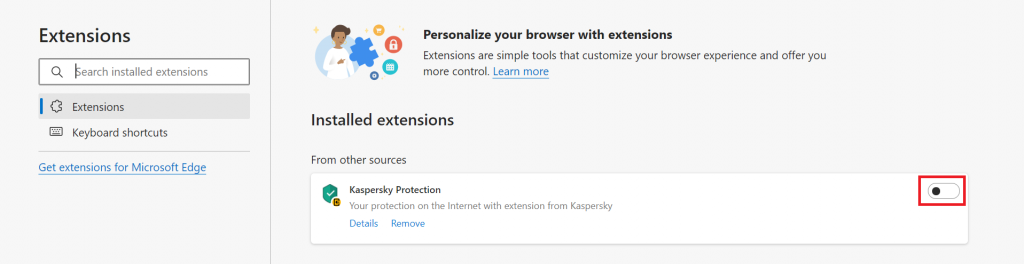
Microsoft Edge
Navigate to Settings and more on the top-right corner of the Microsoft Edge window. Select Extensions.
Click on the extension’s toggle switch to disable it. It will erase the extension icon next to the address bar.
We recommend relaunching your browser once you finish disabling the extensions to get the best results. After that, check the URL that you initially wanted to visit. See if it still has the HTTP 304 Not Modified status code.
If it resolves the issue, it’s safe to re-enable your extensions one by one.
Conclusion
If you come across the HTTP 304 Not Modified status code when accessing a website, it means your browser and the web server experienced a communication issue.
This status code can appear on both your side or your site visitors’ and might block access to your content.
The HTTP 304 Not Modified status code indicates that there is no need to retransmit the resources you request – it will redirect you to cached content instead.
However, the 304 status code may also indicate that your browser or server is not configured correctly, causing issues in the communication between the two.
There are five methods you can follow to fix this issue:
- Clearing your browser cache
- Flushing the DNS
- Checking your redirect instructions in .htaccess
- Running malware scan
- Disabling the browser extensions
After performing each method, make sure to recheck everything by relaunching your browser.
Keep in mind that it is not possible to solve the 304 not modified status code on your visitor’s side, but you’ll be able to provide them with a resource to fix the error codes.
304 Status Code FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the 304 status code.
Is the 304 Status Code Bad?
No, a 304 status code is not bad. It is a response status code that indicates that the requested resource has not been modified since the last time it was accessed and can be used to help reduce bandwidth usage and improve page loading times by allowing cached resources to be reused.
How Can I Avoid Getting a 304 Status Code Error?
You cannot avoid getting a 304 status code error as it is not an error but a response indicating that the requested resource has not been modified. However, you can optimize your website’s caching policies to minimize unnecessary requests and reduce the likelihood of receiving a 304 response.
Maya is a website development and digital marketing enthusiast, and she’s keen to share her knowledge so people can thrive online. When she’s not writing, you can find her watching sci-fi movies while eating ramen.
Диалог клиентской программы (браузера, робота поисковой системы и других) с сервером, отличаясь только деталями, ведется по одним и тем же принципам: запрос клиента — ответ сервера в виде кода. Он состоит из трехзначного числа (первая цифра в котором указывает на класс состояния HTTP) и фразы-пояснения на английском языке. Прочитав первичную инструкцию, программа понимает, как вести дальнейшую работу с запрашиваемым документом или страницей. В каждом классе может быть несколько кодовых вариаций. Далее разберемся, что представляет собой ошибка 304, какие причины приводят к её возникновению и какие методы исправления существуют.
Если поисковый бот уже видел документ/страницу в том виде, в каком они представлены на данный момент, сервер выдает код 304 Not Modified (Не изменен). Это означает, что кэш, сгенерированный во время предыдущего визита, актуален (If-Modified-Since или If-Match не изменились). То есть роботу нет необходимости ещё раз полностью исследовать часть сайта, достаточно будет получить http-заголовки и двигаться дальше, существенно сэкономив время на индексировании.
При этом снижается нагрузка на сервер, которому нужно передавать автору запроса только измененные документы или страницы. Соответственно, увеличивается скорость работы: если пользователю требуется попасть на страницу, с момента предыдущего визита оставшуюся неизменной, то документ повторно не пересылается, браузер выдает локальную копию, ранее уже сохраненную в кэше.
В ответе сервера содержатся следующие поля заголовков (они всегда завершаются пустой строкой):
-
Date;
-
ETag или Content-Location;
-
Expires, Cache-Control или Vary.
Ошибка Not Modified может появляться в любых из нижеперечисленных операционных систем:
-
Windows 2000;
-
Windows ME;
-
Windows XP;
-
Windows Vista;
-
Windows 7;
-
Windows 8;
-
Windows 10.
Признаки наличия ошибки HTTP 304
-
Окно активной программы закрывается после демонстрации сообщения «Ошибка HTTP 304».
-
Используемый браузер постоянно сообщает об ошибке HTTP 304 на одном или нескольких веб-ресурсах.
-
Отображается «Not Modified».
-
Медленная работа Windows, отсроченная реакция на ввод с мыши или клавиатуры.
-
Компьютер подвисает на некоторое время (случается периодически).

Не всегда сообщения браузера об ошибке отражают истинное положение дел. Так, «Страница не найдена» (HTTP 404) может выдаваться и при посещении нормально функционирующей страницы. То же с ошибкой 304, которая далеко не всегда указывает на действительно не измененную с даты последнего сканирования страницу. Ошибка может стать следствием целого ряда причин, которые мы рассмотрим в следующем разделе.
Причины возникновения ошибки HTTP 304
-
Интернет-браузер может быть поврежден вирусом или вредоносной инфекцией, которые перехватывают контроль и действуют в своих корыстных целях.
-
Если недавно производились установка или удаление Windows, реестр операционной системы может быть поврежден.
-
Файлы браузера могут быть инфицированы внешней вредоносной программой.
Очевидно, ответ на вопрос: «304 ошибка — что это?» не может ограничиться только описанием ответа сервера, который предлагает использовать сохраненную версию неизмененной страницы.

Так, ошибка 304 вполне может быть результатом заражения браузера вирусными инфекциями, которые негативно отражаются и на реестре Windows. Сообщения об ошибках будут появляться всё чаще, тормозя работу и, мягко говоря, раздражая. Чтобы устранить проблемы, нужно последовательно выполнить ряд действий.
Как исправить ошибку 304: пошаговое руководство
Приведенная инструкция составлена таким образом, чтобы избежать ненужных усилий и временных затрат. Двигаясь от простого к сложному, можно с наименьшими потерями исправить ошибку через устранение причин, следствием которых она является.

Шаг 1. Восстановление записей реестра, связанных с ошибкой 304
Если вы опытный мастер, то вполне можете вручную внести редакторские правки в реестр. В противном случае лучше довериться надежным инструментам, например разработанной Microsoft Gold Certified Partner утилите Reimage, которая поможет оптимизировать операционку, избавив её от накопившегося мусора.
Реестр — это иерархически выстроенная текстовая база, хранящая практически все системные настройки. Даже малейшая неточность (поставленная не в том месте запятая, удаленный символ и другие) может нанести серьезный ущерб системе и компьютеру в целом вплоть до его полной неработоспособности. Риск велик, поэтому для исправления ошибки 304 лучше всего привлекать автоматическую чистку.
Перед каждым сканированием программа создает резервную копию, защищая тем самым компьютер от возможного повреждения. Если были внесены ненужные изменения, их можно отменить одним щелчком мыши. В процессе работы программа находит поврежденные записи, нерабочие ссылки и ссылки на несуществующие файлы (которые, к примеру, вызывают ошибку 304). После проведения автоматической чистки вы можете в буквальном смысле не узнать свой ПК, который начнет работать значительно быстрее.
Важно: ручное редактирование реестра Windows НЕ рекомендовано неопытным пользователям. Если «Редактор реестра» используется некорректно, это может стать причиной серьезных проблем в работе компьютера и привести к необходимости переустановки системы. Нет гарантии устранения неполадок, ставших следствием неправильного использования «Редактора реестра». Принимая решение о редактировании вручную, вы пользуетесь «Редактором реестра» на свой страх и риск.

Подготовка к редактуре включает обязательный этап — создание резервной копии. Исправляя ошибку 304, необходимо экспортировать ту часть реестра, которая связана с пояснением кода «Не изменен» (например, Windows Operating System):
-
Нажать кнопку «Начать».
-
Ввести «command» в строке поиска… ENTER НЕ НАЖИМАТЬ!
-
Зажав CTRL-Shiftна клавиатуре, нажать ENTER.
-
Появляется диалоговое окно доступа.
-
Нажать «Да».
-
Черный ящик открыть мигающим курсором.
-
Ввести «regedit», затем нажатьENTER.
-
В «Редакторе реестра» выбрать ключ, связанный с ошибкой 304 (например, Windows Operating System), для которого требуется создать резервную копию.
-
В меню «Файл»выбрать «Экспорт».
-
В списке «Сохранить в»выбрать папку, куда отправится резервная копия ключа Windows Operating System.
-
В поле «Имя файла»ввести название файла резервной копии (например, «Windows Operating System резервная копия»).
-
Убедиться, что в поле «Диапазон экспорта»выбрано значение «Выбранная ветвь».
-
Нажать «Сохранить». Файл будет сохранен с расширением .reg.
Резервная копия записи реестра, связанная с ошибкой 304 (Not Modified), готова.
Шаг 2. Полное сканирование компьютера на предмет вредоносного программного обеспечения
Ошибка Not Modified может возникать вследствие заражения компьютера вредоносным ПО, которое повреждает или даже удаляет файлы, связанные с кодами состояний браузера. Не исключена вероятность связи ошибки 304 с компонентом самой вредоносной программы.

Шаг 3. Очистка системы от мусора (временных файлов и папок) с помощью очистки диска (cleanmgr)
Утилита позволяет освободить жесткий диск от хлама, который неизбежно появляется со временем. Ненужные файлы не только перегружают память, снижают работоспособность компьютера, но могут ещё и стать причиной ошибки с кодом 304.
Совет: cleanmgr — отличный встроенный инструмент, однако ему не под силу вычистить абсолютно все временные файлы с компьютера. Даже некоторые майкрософтовские программы не поддаются его очистке, не говоря уже о Chrome, Firefox, LiveMessenger и сотнях других.
Поэтому для качественной «уборки» следует применять специализированное программное обеспечение очистки жесткого диска / защиты конфиденциальности, например продукт от Microsoft Gold Partner — WinSweeper, проводящий очистку всего компьютера. Если раз в день запускать автоматическое сканирование WinSweeper, можно гарантировать чистоту устройства, высокую скорость его работы и отсутствие ошибок Not Modified, поскольку будет устранена их причина — временные файлы, мешающие нормальному функционированию системы.

Алгоритм запуска cleanmgr (очистка диска) на Windows 7, 8, 10, XP, Vista:
-
Нажать кнопку «Начать».
-
Ввести «command» в строке поиска… ENTER НЕ НАЖИМАТЬ!
-
Зажав CTRL-Shiftна клавиатуре, нажать ENTER.
-
Появляется диалоговое окно доступа.
-
Нажать «Да».
-
Черный ящик открыть мигающим курсором.
-
Ввести «cleanmgr» и нажать ENTER.
-
Программа подсчитает, сколько дискового пространства можно освободить от ненужных файлов.
-
Откроется диалоговое окно «Очистка диска», где нужно выбрать флажки, отметив категории для «уборки». Чаще всего большую часть диска занимают «Временные файлы».
-
Установив флажки, нажать «OK».
Кейс: VT-metall
Узнай как мы снизили стоимость привлечения заявки в 13 раз для металлообрабатывающей компании в Москве
Узнать как
Шаг 4. Обновление драйверов устройств компьютера
Ещё одной причиной возникновения ошибки Not Modified может являться устаревание или повреждение драйверов. Кажется, ещё вчера всё было прекрасно, все устройства работали без сбоев, а сегодня драйверы уже вышли из строя. Оптимально решить эту проблему с помощью утилиты обновления драйверов (например, DriverDoc от разработчика Microsoft Gold Partner). Обновление драйверов — процесс сложный и длительный, не стоит отказываться от прекрасной возможности его автоматизировать.
Ошибка 304 может быть устранена, может остаться, поскольку её причиной не являются проблемы в драйверах. Но в любом случае четвертый шаг алгоритма будет полезен. Чтобы компьютер работал быстро и без сбоев, нужно убедиться, что в управлении устройствами операционной системе помогают новейшие программы.
Шаг 5. Восстановление системы Windows для отмены последних изменений
Данный шаг помогает откатиться к тому моменту, когда компьютер работал без сбоев и навязчивой ошибки Not Modified. Порой отмена внесенных изменений может стать средством устранения причин, приведших к появлению ошибки 304.
Важно помнить, что восстановление системы не оказывает влияния на данные (документы, изображения, музыку).

Алгоритм восстановления системы для Windows 7, 8, 10, XP, Vista:
-
Нажать кнопку «Начать».
-
Ввести в строке поиска «Восстановление системы»и нажать ENTER.
-
В окне результатов выбрать «Восстановление системы».
-
Появится запрос пароля, ввести пароль администратора.
-
Для выбора точки восстановления следовать предлагаемым «Мастером» инструкциям.
-
Восстановить компьютер.
Шаг 6. Удаление и восстановление связанной с ошибкой Not Modified программы Windows Operating System
Алгоритм для Windows 7 и Vista:
-
Нажать кнопку «Пуск», найти «Программы и компоненты», открыть.
-
В меню справа нажать на «Панель управления».
-
Выбрать «Программы».
-
Выбрать «Программы и компоненты».
-
В столбце«Имя» найти «Windows Operating System», нажать.
-
В верхней ленте меню нажать кнопку «Удалить».
-
Для завершения удаления Windows Operating System нужно следовать инструкциям, которые появятся на экране.

Алгоритм для Windows XP:
-
Нажать кнопку «Пуск», найти «Программы и компоненты», открыть.
-
Нажать на «Панель управления».
-
Нажать на «Установка и удаление программ».
-
В списке «Установленные программы» найти Windows Operating System, нажать.
-
Справа нажать на кнопку «Удалить».
-
Чтобы завершить удаление Windows Operating System, необходимо следовать инструкциям на экране.
Алгоритм для Windows 8:
-
Курсор мыши установить в левой нижней части экранадля показа изображения меню «Пуск».
-
Щелкнуть правой кнопкой мышидля вызова контекстного меню «Пуск».
-
Нажать «Программы и компоненты».
-
В столбце«Имя» найти и нажать на Windows Operating System.
-
В верхней ленте меню нажать «Удалить/изменить».
-
Для завершения удаления Windows Operating System нужно следовать инструкциям на экране.

Когда удаление будет успешно завершено, необходимо заново установить программу (в рассмотренном примере — Windows Operating System). В этом поможет инструкция Microsoft Corporation.
Обратите внимание: шаг 6 решит проблему, если причиной ошибки Not Modified является определенная программа Microsoft Corporation. Удалив и повторно установив её, вы, скорее всего, избавитесь от ошибки 304.
Шаг 7. Запуск проверки системных файлов Windows («sfc /scannow»)
Поврежденные системные файлы нередко могут приводить к ошибке 304. Чтобы узнать, есть ли такие в Windows, нужно просканировать систему, а потом восстановить элементы с выявленными повреждениями. Для этого в состав операционной системы включен очень удобный инструмент проверки.
Алгоритм проведения проверки файлов системы для Windows 7, 8, 10, XP, Vista:
-
Нажать кнопку «Начать».
-
Ввести «command» в строке поиска… ENTER НЕ НАЖИМАТЬ!
-
Зажав CTRL-Shiftна клавиатуре, нажать ENTER.
-
Появляется диалоговое окно доступа.
-
Нажать «Да».
-
Черный ящик открыть мигающим курсором.
-
Ввести «sfc /scannow» и нажать ENTER.
-
Программа проверки начнет сканирование системы, в том числе на предмет ошибки 304. Процесс может быть небыстрым, нужно запастись терпением, чтобы в итоге получить полную и объективную картину.
-
Необходимо следовать командам на экране.
Шаг 8. Установка обновлений операционной системы
В некоторых случаях для решения проблемы с возникновением ошибки Not Modified достаточно обновить Windows. Разработчики постоянно улучшают системные файлы, формируют пакеты обновлений и различные патчи, которые становятся ценными помощниками для реализации шага 8. Найдите обновления, установите их и устраните ошибку 304 — иногда именно так и будет выглядеть резюме процесса.
Для проверки наличия обновлений Windows 7, 8, 10, XP, Vista, необходимо:
-
Нажать кнопку «Начать».
-
В строке поиска ввести «update» и нажать ENTER.
-
Появится диалоговое окно «Обновление Windows».
-
В случае если доступные обновления есть, нужно нажать кнопку «Установить обновления».

Шаг 9. Чистая установка Windows
Порой 304 ошибка сервера — проблема, которая может быть решена только через переустановку операционной системы. Принципиально важно тщательно подготовиться к сложному процессу. Необходимо создать резервные копии всех важных данных, которые нельзя потерять. Это могут быть изображения, документы, программы установки ПО и прочее.
Существуют рекомендованные инструменты для резервного копирования, которые выполняют столь ценную работу по сохранению данных. Важность создаваемых копий можно недооценивать, когда компьютер работает в штатном режиме. Но как только возникают проблемы, значимость резервного копирования сразу становится очевидной.
Важно! Если переустановка Windows не привела к устранению ошибки 304, это говорит об ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНОЙ связи проблемы с аппаратным обеспечением. Причину следует искать в оборудовании, которое с большой долей вероятности необходимо будет заменить.
Коротко о других основных кодах-ошибках по протоколу HTTP

Информационные (Informational 1xx)
Числовые коды от 100 до 199 указывают на принятие, понимание и обработку клиентского запроса.
-
100=»Continue»
Ответ «Продолжить» означает: первая часть запроса сервером успешно принята, можно продолжать запрашивать.
-
101=»SwitchingProtocols»
«Переключение протокола». Сервер переключается на определенный протокол, указание на который дано в заголовке Upgrade клиентского запроса.
Успешные (Successful 2xx)
Коды от 200 до 299 входят в класс «Успешных» и означают принятие запроса и отправку запрашиваемого документа.
-
200=»OK»
Успешная обработка запроса, ответ включает данные, затребованные клиентом.
-
201=»Created»
«Создан». Сервер сгенерировал новый идентификатор URI, информацию о размещении новых данных можно найти в заголовке ответа сервера Location.
-
202=»Accepted»
«Принят». Сервер приступит к обработке принятого запроса позже, но не факт, что клиент получит то, что искал. Причины невыполнения изначально принятого запроса будут указаны в пояснительном сообщении.
-
203=»Non-Authoritative Information»
«Неавторитетная информация». Таким образом сервер уведомляет клиента о том, что возвращенный документ/страница взят из другого источника или из локальной копии.
-
204=»NoContent»
«Нет контента». В ответе содержатся заголовок (который может быть полезен клиенту) и код состояния при отсутствии содержимого. Сервер указывает на отсутствие необходимости предпринимать какие-либо действия, когда пользователь щелкает, например, по пустому месту страницы или изображения.
-
205=»ResetContent»
«Сбросить содержимое». Чаще всего используется для указания на необходимость очистки используемой транзакционной формы для дополнительных входных данных. Это могут быть поля для ввода сообщений и другие формы, требующие заполнения.
-
206=»PartialContent»
«Частичный контент». Используется в ответе на запрос с указанием заголовка Range, в соответствии с которым сервер возвращает определенную часть данных и указывает их диапазон в заголовке Content-Range.
-
233 — because not everyone lives in «your country»
Соединение с сервером успешно устанавливается, но при входе в систему происходит ошибка из-за того, что на другом конце канала «отсутствует процесс». Ошибка возникает вследствие того, что на сервере не настроен прием удаленных соединений.

Перенаправление запроса (Redirection 3xx)
Коды от 300 до 399 указывают на необходимость дополнительных действий для получения релевантного ответа на запрос.
-
300=»MultipleChoices»
«Множественность выбора» в ответе сервера означает, что затребованный идентификатор ресурса ведет к нескольким страницам (к примеру, документ, переведенный на несколько языков, находится по одному адресу). Подробности ошибки можно узнать в теле ответа, но чаще всего причиной становятся заголовки или адреса.
-
301=»MovedPermanently»
«Перемещен навсегда». Указанный запрос не выполняется, поскольку затребованный URI уже не используется сервером. В заголовке ответа Location указан новый адрес документа. Чаще всего способ используется для редиректа, когда пользователь перенаправляется с одной страницы на другую.
Если запрос выполняется не методом HEAD, в теле сообщения сервер должен передать гипертекстовое пояснение. Если запросы выполняются любым методом, кроме GET и POST, необходимо уведомлять клиента об изменении ссылки. Некоторые агенты после перехода на другой адрес ошибочно меняют метод POST на GET — об этом нужно помнить.
-
302=»MovedTemporarily»
«Перемещен временно». Близок по смыслу предыдущему коду, но в данном случае старый объект оказывается недоступен на временной основе. Например, если на странице ведутся работы, мастер может создать ее дубликат с новым урлом. Новое место расположения указывается в заголовке ответа Location. Получив код 302, программа-клиент должна разрешить запрос при помощи нового идентификатора в данный момент, в дальнейшем следует использовать прежний URL.
Как и в ситуации с 301-редиректом, от сервера требуется гипертекстовое пояснение (при использовании любого метода, кроме HEAD) и уведомление клиента о смене URL (если используются методы за исключением GET и POST).

-
303=»SeeOther»
Требуемый идентификатор находится по другому URL, который указывается в заголовке ответа Location. Клиент должен сделать запрос GET-запрос, чтобы получить доступ к запрашиваемому документу/странице.
-
305=»UseProxy»
Использовать прокси-сервер, адрес которого указывается в заголовке Location. Доступ к запрашиваемому объекту можно получить только таким образом.
-
306=»(Unused)»
Больше не использовать
-
307=»TemporaryRedirect»
Временное перемещение. Похож на 302 временный редирект, но используемый метод не должен изменяться.
Ошибки со стороны клиента (ClientError 4xx)
Коды от 400 до 499 указывают на неполноту запроса, иногда от клиента требуются дополнительные данные, чтобы сервер мог возвратить информацию.
-
400=»BadRequest»
Обнаружена синтаксическая ошибка в клиентском запросе.
-
401=»Unauthorized»
Передается с заголовком WWW-Authenticate. Код указывает на необходимость авторизации, поскольку без подтверждения полномочий сервер не может предоставить требуемые данные.
-
402=»PaymentRequired»
«Требуется оплата». Код не используется, является резервом на будущее.
-
403=»Forbidden»
Доступ запрещен, что не позволяет серверу предоставить клиенту ответ на запрос.
-
404=»NotFound»
Указывает, что документ не найден по указанному идентификатору.

-
405=»MethodNotAllowed»
Код «метод не поддерживается» выдается с заголовком Allow. Используемый клиентом метод деактивирован и не поддерживается для данного идентификатора.
-
406=»Not Acceptable»
Вместе с кодом сервер выдает заголовки Content-Language, Content-Encoding и Content-Type. Указывает, что указанный клиентом ресурс не содержит контента, требуемого в запросе.
-
407=»ProxyAuthenticationRequired»
Используется с заголовком Proxy-Authenticate и указывает, что прокси-сервер требует авторизоваться. Пользователь должен подтвердить полномочия, чтобы получить данные по запросу.
-
408=»RequestTime-out»
Сервер вынужден разорвать сетевое соединение, поскольку в течение отведенного на это времени пользователь не передал полный запрос.
-
409=»Conflict»
Клиентский запрос вступает в конфликт с конфигурацией сервера или другим запросом. О причинах сервер должен проинформировать в пояснении к коду, но чаще всего требуется обращаться к провайдеру.
-
410=»Gone»
Существовавшая ранее страница удалена навсегда.
-
411=»LengthRequired»
Требуется указать заголовок Content-Length, без которого запрос не будет принят сервером.
-
412=»PreconditionFailed»
В заголовках указаны невыполнимые для сервера условия.
-
413=»RequestEntityTooLarge»
Объявленный сервером лимит на размер запроса превышен, поэтому обработка не состоится.
-
414=»Request-URI TooLong»
Слишком длинный идентификатор запроса, обработки не последует.

-
415=»UnsupportedMediaType»
Тело запроса вводится в не поддерживаемом сервером формате, обработки не будет.
-
416=»RequestedRangeNotSatisfiable»
Некорректное значение в поле Range (выражается в байтах) не позволяет обработать запрос.
-
417=»ExpectationFailed»
Некорректное значение в поле Expect (Ожидание).
-
422=»UnprocessableEntity»
Запрос успешно принят, указанный вид данных может быть обработан, но имеющаяся логическая ошибка не позволяет провести обработку.
Данный код в некоторых системах отправляется клиенту, если требуются дополнительные данные для передачи: NOT ENOUGH DATA.
-
429=»You exceeded the rate limit»
Лимит запросов превышен. Может быть указано время ожидания для введения нового запроса.
-
449 — Retry with a proxy in another country.
Необходимо повторить запрос через прокси «в другой стране», потому что параметры запроса не могут быть приняты сервером.
-
450=Rating Service Unavailable
-
451=UnavailableForLegalReasons
Причины отказа в доступе кроются в юридических ограничениях.
-
452 could be site not permitted by employer
-
453 could be site not permitted by ISP
-
460 BlockedbyRepressiveRegime
Заблокировано репрессивным режимом. Проще говоря, цензура.
Ошибки сервера (ServerError 5xx)
Коды от 500 до 599 сервер отправляет, признавая свою вину в невыполнении операции.

-
500=»InternalServerError»
Часто бывает связано с ошибками в файле .htaccess, но вообще обозначает аварийный отказ компонента сервера или ошибку конфигурации.
-
501=»NotImplemented»
Непонимание метода запроса или невозможность выполнить требуемое клиентом действие.
-
502=»BadGateway»
Выступая в роли посредника, сервер получает недопустимые ответы от вышестоящего «коллеги».
-
503=»ServiceUnavailable»
Технические причины в данный момент не позволяют выполнить запрос клиента. Если сервер знает, когда доступ будет восстановлен, то уведомляет об этом в заголовке Retry-After.
-
504=»GatewayTime-out»
Превышение лимита времени вышестоящим сервером.
-
505=»HTTP Versionnotsupported»
В запросе использована версия протокола HTTP, которую сервер не поддерживает.

Облако тегов
Понравилась статья? Поделитесь:
The HTTP 304 not modified status code indicates a communication problem between a user’s browser and a website’s server. If you or your users come across this status code on your site, it can block access to your content entirely.
Since it can be on the server-side or the client-side, figuring out the source of the problem can take a little work. Fortunately, there are several foolproof techniques for troubleshooting it.
In this post, we’ll discuss HTTP status codes and explain what the HTTP 304 status code is. Then we’ll walk you through six methods you (or your visitors) can use to fix it.
Let’s get started!
An Introduction to HTTP Status Codes
To understand HTTP 304, it helps to first understand status codes. Put simply, every time you make a request to your browser – such as by accessing a particular website – an HTTP status code is sent between your browser and the server in order to exchange information.
There are more than 40 different status codes that can be involved in that communication. However, there are only a handful you’ll likely come across directly. When you do encounter a status code, it usually means that something has gone wrong.
HTTP status codes fall into one of five categories, numbered between the 100s and 500s. Each series indicates a different type of problem. For example, error codes that fall into the 400s, such as the “404 Not Found” error and the ”401 error”, typically mean that there was an issue with the request and the website or page in question was unreachable.
On the other hand, codes in the 300s – such as the HTTP 304 status code we’ll focus on in this post – are redirection codes. They make it clear that the information being requested was either temporarily or permanently substituted with another resource.
When you encounter one of these status codes, it means that further action must be taken.
What is The HTTP 304 Status Code?
HTTP 304, also sometimes known as “304 Not Modified”, is a code that communicates to your browser that: “The requested resource has not been modified since the last time you accessed it.”
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the 304 Not Modified as:
The 304 (Not Modified) status code indicates that a conditional GET or HEAD request has been received and would have resulted in a 200 (OK) response if it were not for the fact that the condition evaluated to false. In other words, there is no need for the server to transfer a representation of the target resource because the request indicates that the client, which made the request conditional, already has a valid representation; the server is therefore redirecting the client to make use of that stored representation as if it were the payload of a 200 (OK) response.
Essentially, your (or your visitor’s) browser is being told by the server that the resources stored (cached) in the browser haven’t been modified since the latest time you visited that page.
In turn, your browser retrieves a saved version of the web page from the cache. The purpose of this is to improve page speed and delivery, by preventing your browser from having to repeatedly download the same information.
Check Out Our Video Guide to the 304 Not Modified Status Code and All 3xx Redirects
Understanding HTTP 304 Requests
When your browser stores a resource in the cache, it keeps what’s called the ‘Last-Modified header’ information that was sent from the server. If a browser receives a request for a web page it has a saved copy of, but it doesn’t know whether it has the latest version, it sends a ‘conditional validation’ request to the server.
The browser communicates to the server the ‘Last-Modified’ date and time for the copy of the resource it has, via the ‘If-Modified-Since’ or ‘If-None-Match’ header. The server inspects these headers and also looks at the ETag value. The latter is a unique identifier used to specify the version of a particular resource.
If the values for these files are the same, the server sends the HTTP 304 Not Modified response header and the browser uses the cached copy of the resource.
If the browser copy is outdated, meaning that the file has been modified since the last request, it sends an HTTP 200 code and a new copy is used.
Unfortunately, there are a few issues that might cause an HTTP 304 response when it’s not supposed to occur. The most common causes include:
- Server configuration or Domain Name Server (DNS) issues
- A cached resource that is infected or corrupted (i.e., malware or viruses affecting the browser)
The 304 status code can be due to a problem on either the server-side or the client-side, so it might take some troubleshooting in order to diagnose and resolve it.
The HTTP 304 status code can block access to all of your content which means understanding how to fix it is crucial 🚨 This guide has 6 methods to get things back up and running ASAP ✨Click to Tweet
How to Fix an HTTP 304 Status Code (6 Potential Methods)
The methods you can use to resolve an HTTP 304 status code vary from simple to fairly technical. Search engines are responsible for indexing and caching websites, so this issue can usually be traced back to the browser being used to access the site.
Of course, there’s only so much you can do to fix the browsers of people who are trying to access your site.
However, understanding what may be causing the issue for visitors can be helpful, either when trying to find a solution on your end or assisting them directly.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at six methods you can use to try and fix an HTTP 304 status code!
1. Clear the Browser’s Cache Data
First up, cleaning your browser data to clear the cache might help with accessing the desired URL. This includes deleting all of the browsing data, cookies, and cache information.
The instructions for executing this process will vary depending on the browser you’re using. If you’re unsure how to do it on your device, feel free to refer to our guide on clearing the cache for all major browsers.
2. Run a Malware Scan
Corrupted browsers that have been infected with a virus or malware may be another culprit. Therefore, it’s a good idea to run a malware scan on your system. Doing so can help identify and remove any issues that might be interrupting or interfering with the header request, including problematic extensions.
If you’re using the Windows version of Chrome, you can run the Malware Scanner and Cleanup Tool that comes built-in.
To do this, first make sure you’re running the latest version of Chrome by opening up a new tab and clicking on the menu icon, followed by About Chrome:
If your browser isn’t updated to the current version, you can resolve that in the same place. Then, open a new Chrome tab and enter “chrome://settings/cleanup” into the URL bar.
Hit Enter, and then next to Find and remove harmful software click on the Find button:
The scanner will begin running, then report back with the results.
Unfortunately, some other browsers such as Firefox and Edge, as well as the macOS and Linux OSs, do not come with their own versions of this built-in tool. Instead, you’ll have to run a malware scan using the antivirus software on your computer.
3. Disable Your Browser’s Extensions
Your browser’s extensions may also become infected and interfere with requests and server communication. That’s why you may also want to disable them. You can do this by opening Chrome’s menu and going to Settings > Extensions:
On the Extensions page, you can disable each one by clicking on the corresponding toggle switch.
You can also delete unused or outdated extensions via the Remove button:
Again, this process will vary slightly depending on your browser. The goal is to remove or disable each extension manually and then check to see if that resolves the HTTP 304 issue.
Then, you can try turning them back on one by one.
4. Flush the DNS and Reset the TCP/IP
If the problem hasn’t been resolved at this point, there could be an issue with the DNS settings. For example, using an outdated IP address might cause an HTTP 304 status code.
Therefore, another approach to try is flushing the DNS and resetting the TCP/IP.
With Chrome, you can flush the browser DNS by entering “chrome://net-internals/#dns” into a new tab.
Hit Enter, and then click on the Clear host cache button:
You can also flush the DNS and reset the TCP/IP in your OS. If you need detailed guidance, you can refer to our tutorial on How to Flush DNS Cache (Windows, Mac, Chrome).
5. Try Using the Google Public DNS
Another potential cause is an incorrect DNS address. Therefore, it’s worth using the Google Public DNS to see if that resolves the problem.
On Windows, you can do this by pressing the Win + R keys. In the Run window that appears, type “ncpa.cpl” into the command box, and then hit Ok.
In the Network Connections window that opens next, locate the network connection you’re using and right-click on it. Next, select Properties:
From there, double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4:
Select the option to “Use the following DNS server addresses”, then enter the value “8.8.8.8” under Preferred and “8.8.4.4” under Alternate:
When you’re done, click on Ok. Then restart your system, and try accessing the website again.
To change your DNS server settings using macOS, you would go to Apple > System Preferences > Network:
In the window that opens, select your connection, then click on Advanced followed by the DNS tab:
Click the + icon next to the IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, to replace the existing addresses with the Google Public IPs.
For further instructions or for guidance on using Google Public DNS on a Linux or another OS, check out Google’s own DNS guide.
6. Check Your Server Configuration Files for Incorrect Redirect Instructions
An HTTP 304 Not Modified status code can occur due to both server- and client-related problems. If none of the methods we’ve covered so far have corrected the issue, your server configuration files may be at fault. For example, it’s possible that there are incorrect redirect instructions present.
The process for checking your server configuration files depends on whether you’re using Nginx or Apache.
At Kinsta, we use the Nginx web server. So if you’re a Kinsta user, you won’t have access to the .htaccess file that Apache users do.
However, you can still perform similar functions. For example, after logging in to MyKinsta, you can check the Analytics > Response section of the dashboard for a breakdown of response codes and redirects:
You can also check the error logs. If you have a specific question or request about editing the configuration files, your best bet is to reach out to our support team.
If your server is running on Apache, then you’ll want to look for the .htaccess file in the root directory of your site. You can do this by logging into the File Manager for your hosting account, and navigating to the public_html folder.
Once you open that file, look for a mod_cache module section. It should look something like this:
LoadModule cache_module modules/mod_cache.so
<IfModule mod_cache.c>
LoadModule cache_disk_module modules/mod_cache_disk.so
<IfModule mod_cache_disk.c>
CacheRoot "c:/cacheroot"
CacheEnable disk "/"
CacheDirLevels 5
CacheDirLength 3
</IfModule>
# When acting as a proxy, don't cache the list of security updates
CacheDisable "http://security.update.server/update-list/"
</IfModule>We don’t recommend deleting anything, as that can cause severe damage. Instead, you can try temporarily commenting out the cache section by adding a “#” symbol at the beginning of each line.
After you save your changes, check to see if this resolved the HTTP 304 status code.
Don’t let an HTTP 304 status code stand in the way of your site ❌ Find all the troubleshooting tricks you need in this in-depth guideClick to Tweet
Summary
300s redirection codes are used to improve page speed and performance. Unfortunately, when a server or browser isn’t properly configured, communication between the two can get interrupted and result in an HTTP 304 not modified status code. There are six methods you can use to fix it, specifically:
- Clearing your browser’s cache data.
- Running a malware scan.
- Disabling your browser extensions.
- Flushing the DNS and resetting the TCI/IP.
- Trying the Google Public DNS.
- Checking your server configuration files for incorrect redirect instructions.
The other night I was searching «Best Pasta Dish Recipes» on Google.
I clicked the first link and was stopped by the dreaded error code.
I’m willing to bet something similar has happened to you, at one point or another.
When that happens, it’s not just my brain experiencing technical difficulties.
These error codes are HTTP status codes. If you receive an error code, something went wrong when your browser requested the information from a web server. An HTTP status code is sent every time you go to a new web page. However, you’ll only see them if something isn’t right.
For marketers, it’s important to discover and fix these issues so your website visitors don’t have a negative experience.
Below, let’s review what an HTTP 304 not modified status code is, and what’s causing it.
An HTTP 304 not modified status code means that the website you’re requesting hasn’t been updated since the last time you accessed it. Typically, your browser will save (or cache) web pages so it doesn’t have to repeatedly download the same information. This is an attempt to speed up page delivery. However, if this happens to your site, visitors could be prevented from accessing your web pages.
When you click on a web page or URL, your browser requests access to it from a web server. If it has not been modified since the last time you accessed it, the web server will send back a 304 not modified status code, which lets your browser know to use a cached version of the web page.
Usually, you’ll only see this error code if you’re on a search engine because search engines index and cache websites.
If your browser receives this code, it’ll try to show you a saved version of the page. But sometimes it might prevent you from accessing the URL because it’s outdated.
As a marketer, you could lose out on traffic and leads if visitors are prevented from seeing your site.
So, what causes a 304 not modified code?
Causes of an HTTP 304 Not Modified Status Code
If a user sees a 304 not modified status code on your site, there isn’t much you can do. This is because the problem is most likely on their side of the screen.
Users could receive a 304 not modified status code for a variety of reasons:
1. You have a virus.
If you have a virus or malware on your computer, it most likely has corrupted your browser. This could impact your browser’s ability to communicate with web servers and cache web pages.
2. You’ve recently installed or uninstalled software.
Sometimes when you install or uninstall software on your computer, the registry could become corrupt. Again, this impacts your browser.
3. An application has corrupted files.
If there are corrupted files related to your internet browser, it will impact its ability to save web pages and update information.
How to Fix a 304 Not Modified Status Code
Although marketers can’t do much if a user sees a 304 not modified status code, users can try a few things to get the web page to show up on their browser.
1. Clear browsing data.
Clearing your browsing data will make sure your cache is cleared so it can try to access the URL you’re requesting.
To clear your browsing data, go to your History and then click «Clear browsing data.» In Chrome, it looks like this:
Once you click that, make sure you check off all three options. Then, you’ll want to change the time frame to «All Time.» It should look like this:
2. Run cleaners to get rid of viruses and malware.
A 304 not modified code could be happening because your browser is corrupted with a virus or malware. Run a check to make sure that isn’t the issue and clean up your computer.
3. Disable extensions.
There could be something wrong with your extensions. For example, they could be corrupt, which impacts your browser’s ability to receive information. Disable your extensions to see if this is the issue.
If these things don’t work, fixing a 304 not modified can be a more technical process. You might consider asking a web developer or someone in IT to take a look.
If you receive an HTTP 304 not modified error code, it’s because the URL you requested has outdated information. To fix it, you’ll want to double-check that the error isn’t on your side — the client’s — but instead on the server-side.
Are you getting a 304 not modified status code when you try to access a website in your web browser? This can be frustrating, but the good news is that it is usually easy to fix. In this post, we’ll show you how to fix the 304 not modified in your web browser.
It is possible that you have seen the 304 not modified status code in the past. But what does it mean exactly? Is it a problem with the client or a bug with the server? We will find out together.
It can be confusing to understand the HTTP 304 status code. Although it’s not as simple as other HTTP codes. However, you can fix it with some knowledge and the right tools.
We’ll discuss the meaning of the HTTP 304 not modified status code and how we can fix it. We’ll also discuss some of the most common causes of 304s.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the HTTP 304 Status code?
- 2 HTTP Status Codes
- 3 Understanding HTTP 304 Requests
- 4 What does 304 Not Modified mean?
- 5 What causes a 304 not modified status code?
- 6 6 Potential Methods to Fix an HTTP 304 errors
- 6.1 Clear the Browser’s Cookies
- 6.2 Run a Malware Scan
- 6.3 Disable extensions in your browser
- 6.4 Clear the DNS and reset the TCP/IP
- 6.5 Use the Google Public DNS
- 6.6 Check server configuration
- 7 Final Lines
What is the HTTP 304 Status code?
A status code HTTP 304 indicates that the website you are trying to access is not up-to-date since the last time it was accessed.
Your browser will typically save web pages (or cached them) so that it doesn’t have the same information downloaded again and again. This is a way to speed up page delivery and also a way to save bandwidth for both the server and the client (especially those who use data on mobile).
HTTP 304 Not Modified client response code means that the requested resources do not need to be retransmitted. This is an implicit redirection of the cached resource. This occurs when the request method is secure, such as a GET and a HEAD.
Before we get into the 304 status code that has not been modified, let’s first understand what HTTP status codes are.
HTTP Status Codes
It is important to understand the status codes in order to understand HTTP 304. Simply put, each time your browser requests information (e.g. to access a website), an HTTP status code is sent to the server.
There are over 40 status codes that can be used in this communication. There are only a few that you will likely encounter directly. If you do find a status code it is usually a sign that something is wrong.
HTTP status codes can be classified into one of five groups, which are numbered from 100 to 500. Each series represents a different kind of problem. If an error code falls within the 400s (e.g., 404 Not Found or 401 error), it usually means that the request was not being processed correctly and that the page or website in question is unavailable.
Codes in the 300s, such as the HTTP 304 status code (which we will focus on in this article), are redirection codes. These codes indicate that the requested information was either temporarily or permanently replaced with another resource.
Understanding HTTP 304 Requests
Your browser keeps the information known as the ‘Last Modified header’ information sent by the server when it stores a resource in its cache. A browser will send a “conditional validation” request to the server if it receives a request for web pages it already has but doesn’t know if it has the most recent version.
Through the header ‘If-Modified-Since or ‘If Non-Match’, the browser informs the server of the ‘Last Modified’ date and the time it created the resource. These headers are checked by the server, who also checks for the Etag value. This is a unique identifier that specifies the version of a resource.
If these files have the same values, the server will send the HTTP 304 Not modified response header to the browser.
If the browser copy is out of date, which means that it has been modified since the last request was made, the browser sends an HTTP 200 code. A new copy is then created.
There are several reasons why an HTTP 304 response might occur when it is not intended. These are the most common reasons:
Server configuration issues or Domain Name Server (DNS), issues cached resource that has been infected (i.e. malware or viruses affecting your browser).
It is possible for the 304 status code to be caused by a problem on the client-side or server-side. This may require some troubleshooting to identify and fix the problem.
You can be blocked from accessing all your content by using the HTTP 304 status code. This guide explains how to fix it.
What does 304 Not Modified mean?
HTTP 304 is a status message that informs your browser that the requested resource has not changed since the last time it was accessed. This indicates that the client who made the request conditional has a valid representation.
The server informs your browser or visitor that the resources in your browser have not been updated since your last visit to that page.
To speed up page delivery and speed, the browser will save the page to the cache.
According to Mozilla, the HTTP 304 Not Modified client redirection response code indicates that there is no need to retransmit the requested resources. It is an implicit redirection to a cached resource.
Usually, the 304 not modified code occurs when there is a cached system, and the requests from the user to the server will go through the cache system.
If the cache system does not allow checking with the origin server, it will always return a cached version if the request time is still within the cached period.
At this point, although the origin server may have a new version or updated content, the end-user will have to receive the cached version.
Only when the term of this cached version expires will it automatically get a new version from the server and update the cached version.
However, most of the caching plugins or caching systems have a function to match the original server, if the original server has a new version, update the cached version so that the cached version also has new content, then the end-user will always get new content.
In this case, if you still receive the HTTP code 304 not modified, it means that the cached system has a problem or an error has occurred, which needs to be fixed.
What causes a 304 not modified status code?
A 304 Not Modified error is often due to an issue on the client’s side. In most cases, the user is the one who must solve the problem.
These are the three most common reasons for a 304 not being modified:
- A virus or malware has infected the user’s computer and has corrupted his browser.
- The registry has been corrupted by the user who has installed or uninstalled the software on their computer. The browser will also be affected if the registry is corrupted.
- Corrupted files have been created by the user in their internet browser. Corrupted files stop the internet browser from saving web pages or updating information.
There are many ways to fix an HTTP 304 status code. Some of them are very simple, others can be quite technical. This issue is usually traced back to the browser used to access the site. Search engines are responsible for indexing and caching websites.
You can only do so much to fix the browsers of those trying to access your site. Understanding the problem can help visitors either find a solution or assist them directly. Let’s now take a look at six ways to fix the HTTP 304 status code.
Clear the Browser’s Cookies
Clearing your browser cache and clearing all data may help you access the desired URL. This involves deleting all browsing data, cookies, and cache information.
It will depend on which browser you are using to execute this task. You can refer to our guide to clearing the cache on all major browsers if you are unsure.
Run a Malware Scan
Another culprit could be corrupted browsers infected by a virus, malware, or both. It’s a good idea for your computer to run a malware scanner. This will help to identify and fix any problems that may be interfering with the header request.
You can use the Malware Scanner & Cleanup Tool, which comes with Chrome for Windows.
First, open a new tab, then click on the menu icon. Next, click on About Chrome.
You can also update your browser to the latest version if it isn’t. Then, open a new Chrome tab and enter “chrome://settings/cleanup” into the URL bar.
Click on Enter to activate the Find and Remove Software button.
The scanner will start running and then report back with its results.
Other browsers like Edge and Firefox, along with the macOS and Linux operating systems, don’t have their own versions. You will need to run a malware scanner using your antivirus software.
Disable extensions in your browser
Extensions in your browser can also be infected, causing problems with server communication and requests. You may want to disable them. This can be done by opening Chrome’s menu and then going to Settings > Extensions.
You can disable each extension by clicking on its toggle switch.
You can also remove obsolete or unutilized extensions by using the Remove button
This process may vary depending on the browser. It is important to manually remove or disable any extension and then verify that the HTTP 304 problem has been resolved.
You can then turn them one at a time.
Clear the DNS and reset the TCP/IP
If the problem persists, it could be a DNS issue. An example: An outdated IP address could cause an HTTP status code of 304.
Another option is to flush the DNS and reset the TCP/IP.
With Chrome, you can flush the browser DNS by entering “chrome://net-internals/#dns” into a new tab.
Click on Clear host cache and hit Enter.
It will then reset TCP/IP and flush DNS in your OS.
Use the Google Public DNS
An incorrect DNS address could also be a possible cause. It’s worth trying the Google Public DNS to resolve the problem.
Windows users can do this by pressing Win + R. The Run window will open. Type ” NCPA.cpl” in the command box. Click OK.
Next, locate the network connection that you are using in the Network Connections window and right-click it. Next, click Properties.
Double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 from there
Select “Use these DNS server addresses” and then enter “1.1.1.1” Under Alternate, type “8.8.8.8” (Here we use 1 DNS of Cloudflare and 1 Google Public DNS.).
Once you are done, click OK to restart your computer and then try again accessing the site.
You can change the DNS server settings with macOS by going to Apple > System Preferences > network:
Select your connection in the window that opens. Next, click on Advanced and then the DNS tab.
To replace existing addresses with Google Public IPs, click the + icon beside the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
You can refer to Google’s DNS guide which provides additional instructions and guidance for using Google Public DNS on Linux or other OSes.
Check server configuration
If you own the website, you can inspect your server configuration files to see if any errors may have caused a 304 error.
The above 5 ways are for end-users, and this way (number 6) is only for website administrators and information technology professionals who understand what they do. This way requires access to the server and having skills in testing and handling tasks on the hosting server or domain name, or DNS system.
An HTTP 304 Not Modified status can be caused by both client- and server-related issues. Your server configuration files could be responsible if none of the above methods have worked. It is possible, for example, that incorrect redirect instructions are present.
Depending on whether you are using Apache or Nginx, the process of checking your server configuration files will differ.
You can also view the error logs. You can also reach our support team if you have any questions or requests regarding editing configuration files.
Apache is the operating system of your server. You will need to search for the .htaccess files in your root directory. Logging into your hosting account’s File Manager and going to the public_html directory will allow you to do this.
After you have opened the file, search for mod_cache module sections. You should see something like this.
LoadModule cache_module modules/mod_cache.so LoadModule cache_disk_module modules/mod_cache_disk.so CacheRoot "c:/cacheroot" CacheEnable disk "/" CacheDirLevels 5 CacheDirLength 3 # When acting as a proxy, don't cache the list of security updates CacheDisable "https://security.update.server/update-list/"
As this can cause serious damage, we don’t recommend that you delete anything. You can temporarily comment out the cache section by inserting a # symbol at each line’s beginning.
Save your changes, restart the server and check if the HTTP 304 status code has been resolved.
Final Lines
To improve page performance and speed, 300s redirection codes can be used. If a browser or server is not properly configured, communication can be disrupted and cause an HTTP 304 status code.
You have six options to fix it.
- Clearing browser cache data.
- Run a malware scan
- Disabling your browser extensions.
- Flushing DNS and resetting TCI/IP
- Try the Google Public DNS.
- For incorrect redirect instructions, make sure you check your server configuration files.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between 304 status code and 305 status code?
The difference between the two status codes 304 and 305 is in the server response. While 304 allows access to resources, 305 prevents and forces users to use the correct proxy declared with the server to continue to access the resource.
Another difference is that 304 is still in use, and 305 is no longer in use.
Is 304 status code an error?
In most cases the HTTP status code 304 is not an error, it means Not Modified. This means that the website you requested hasn’t had any changes since the last time you visited. Your browser will then retrieve the cached version of the website in your local storage. As a result, the page loading speed will be much faster.
The most common files that return 304 code are CSS, Javascript files, and static content. This code will check against the cached version on the user’s machine and the version on the server to see if it should return the cached content on the user’s machine or get the latest data on the server and download it. the user’s computer to bring up the browser.
How does a 304 work?
304 Not Modified is the HTTP status code returned to the client from the server-side. It tells a client application, such as a browser, or an application on that client, that the file requested by the client has NOT been changed since it was last accessed. Usually, this comparison is based on the Last-Modified header sent from the server and the copy on the client to see if there was any change in the file’s last-modified time. 304 status code is returned when there is NO change in the requested file’s Last-Modified header.
Which HTTP status code is usually returned when the resource is cached?
Code 304 usually means that the client is sending an «If-Modified-Since» conditional request to the Web server. If the file has not been updated since the date it was sent by the browser, the Web server will return a 304 response code. This lets the client application know whether to use the cached file on the client or to download the latest version. at the server.
- References: