I installed the pyautogui module and dependencies via pip-3.2 on my raspi correctly, However when I am trying to do
import pyautogui
I am getting an import error:
ImportError: No module named pyautogui
What am I doing wrong? Did the command change?
Sorry I am a total python Noob, any help is greatly appreciated 
asked Jul 26, 2015 at 8:40
0
It might be because you’re trying it from a python 2.x shell. Instead try this command on a python3 shell and try importing the same.
answered Jul 26, 2015 at 8:57
Sentient07Sentient07
1,2701 gold badge16 silver badges24 bronze badges
0
True you would have to use python 3. First you have to make sure you checked the change system path variable while installing python 3. then open the command prompt on windows and type
pip install pyautogui
or
pip3 install pyautogui
in osx and linux.
Savad KP
1,6153 gold badges28 silver badges40 bronze badges
answered Aug 8, 2015 at 16:31
abassabass
1812 bronze badges
I also had a hard time getting pyautogui to work via Terminal on my macOS Catalina. I installed it using pip3 install pyautogui. It supposedly installed but still gave error: No module named ‘pyautogui’, when I tried to import it (after running python3). What finally worked was this command I found on the pyautogui documentation page (https://pyautogui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/install.html):
python3 -m pip install pyautogui
If it says permission denied, try:
python3 -m pip install --user pyautogui
answered Jun 23, 2020 at 10:22
1
Search in C:Python37-32Libsite-packages (Where-ever you have installed it). Check if you have pyautogui directory.
If YES then there exists a configuration issue with pycharm or IDLE.
If NO then
- Open Command Prompt
- cd
C:Python37-32Scripts pip install pillowpip install pyautogui
Check for Successfully installed response.
HAPPY CODING! 
answered Oct 12, 2018 at 8:01
1
If you run your script with sudo, you should install the module also under sudo…
answered Aug 22, 2020 at 14:47
bangkokguybangkokguy
1911 silver badge10 bronze badges
A common error you may encounter when using Python is modulenotfounderror: no module named ‘pyautogui’.
This error occurs if you do not install pyautogui before importing it into your program or install the library in the wrong environment.
You can install pyautogui in Python 3 with python3 -m pip install pyautogui.
Or conda install -c conda-forge pyautogui for conda environments.
This tutorial goes through the exact steps to troubleshoot this error for the Windows, Mac and Linux operating systems.
Table of contents
- What is ModuleNotFoundError?
- What is PyAutoGUI?
- Always Use a Virtual Environment to Install Packages
- How to Install PyAutoGUI on Windows Operating System
- How to Install PyAutoGUI on Mac Operating System using pip
- AssertionError: You must first install pyobjc-core and pyobjc
- How to Install PyAutoGUI on Linux Operating Systems
- Installing PyAutoGUI Using Anaconda
- Check PyAutoGUI Version
- Using PyAutoGUI Example
- Summary
What is ModuleNotFoundError?
The ModuleNotFoundError occurs when the module you want to use is not present in your Python environment. There are several causes of the modulenotfounderror:
The module’s name is incorrect, in which case you have to check the name of the module you tried to import. Let’s try to import the re module with a double e to see what happens:
import ree
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last) 1 import ree ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'ree'
To solve this error, ensure the module name is correct. Let’s look at the revised code:
import re print(re.__version__)
2.2.1
You may want to import a local module file, but the module is not in the same directory. Let’s look at an example package with a script and a local module to import. Let’s look at the following steps to perform from your terminal:
mkdir example_package cd example_package mkdir folder_1 cd folder_1 vi module.py
Note that we use Vim to create the module.py file in this example. You can use your preferred file editor, such as Emacs or Atom. In module.py, we will import the re module and define a simple function that prints the re version:
import re
def print_re_version():
print(re.__version__)
Close the module.py, then complete the following commands from your terminal:
cd ../ vi script.py
Inside script.py, we will try to import the module we created.
import module
if __name__ == '__main__':
mod.print_re_version()
Let’s run python script.py from the terminal to see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "script.py", line 1, in ≺module≻
import module
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'module'
To solve this error, we need to point to the correct path to module.py, which is inside folder_1. Let’s look at the revised code:
import folder_1.module as mod
if __name__ == '__main__':
mod.print_re_version()
When we run python script.py, we will get the following result:
2.2.1
You can also get the error by overriding the official module you want to import by giving your module the same name.
Lastly, you can encounter the modulenotfounderror when you import a module that is not installed in your Python environment.
What is PyAutoGUI?
The PyAutoGUI library enables Python scripts to control the mouse and keyboard and automate interactions with other applications.
The simplest way to install pyautogui is to use the package manager for Python called pip. The following installation instructions are for the major Python version 3.
Always Use a Virtual Environment to Install Packages
It is always best to install new libraries within a virtual environment. You should not install anything into your global Python interpreter when you develop locally. You may introduce incompatibilities between packages, or you may break your system if you install an incompatible version of a library that your operating system needs. Using a virtual environment helps compartmentalize your projects and their dependencies. Each project will have its environment with everything the code needs to run. Most ImportErrors and ModuleNotFoundErrors occur due to installing a library for one interpreter and trying to use the library with another interpreter. Using a virtual environment avoids this. In Python, you can use virtual environments and conda environments. We will go through how to install pyautogui with both.
How to Install PyAutoGUI on Windows Operating System
First, you need to download and install Python on your PC. Ensure you select the install launcher for all users and Add Python to PATH checkboxes. The latter ensures the interpreter is in the execution path. Pip is automatically on Windows for Python versions 2.7.9+ and 3.4+.
You can check your Python version with the following command:
python3 --version
You can install pip on Windows by downloading the installation package, opening the command line and launching the installer. You can install pip via the CMD prompt by running the following command.
python get-pip.py
You may need to run the command prompt as administrator. Check whether the installation has been successful by typing.
pip --version
virtualenv env
You can activate the environment by typing the command:
envScriptsactivate
You will see “env” in parenthesis next to the command line prompt. You can install pyautogui within the environment by running the following command from the command prompt.
python3 -m pip install pyautogui
We use python -m pip to execute pip using the Python interpreter we specify as Python. Doing this helps avoid ImportError when we try to use a package installed with one version of Python interpreter with a different version. You can use the command which python to determine which Python interpreter you are using.
How to Install PyAutoGUI on Mac Operating System using pip
Open a terminal by pressing command (⌘) + Space Bar to open the Spotlight search. Type in terminal and press enter. To get pip, first ensure you have installed Python3:
python3 --version
Python 3.8.8
Download pip by running the following curl command:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
The curl command allows you to specify a direct download link. Using the -o option sets the name of the downloaded file.
Install pip by running:
python3 get-pip.py
To install PyAutoGUI, first create the virtual environment:
python3 -m venv env
Then activate the environment using:
source env/bin/activate
You will see “env” in parenthesis next to the command line prompt. You can install PyAutoGUI within the environment by running the following command from the command prompt.
python3 -m pip install pyautogui
AssertionError: You must first install pyobjc-core and pyobjc
You may encounter the following AssertionError when trying to import and use PyAutoGUI:
AssertionError: You must first install pyobjc-core and pyobjc
In which case, you should check if you have installed the required packages and the correct versions compatible with your Python version using:
python3 -m pip list | grep pyobjc
If you try to install pyobjc and get a Requirement already satisfied message, you can use the --force argument as follows:
python3 -m pip install pyobjc --upgrade --force python3 -m pip install pyobjc-core --upgrade --force
How to Install PyAutoGUI on Linux Operating Systems
All major Linux distributions have Python installed by default. However, you will need to install pip. You can install pip from the terminal, but the installation instructions depend on the Linux distribution you are using. You will need root privileges to install pip. Open a terminal and use the commands relevant to your Linux distribution to install pip.
Installing pip for Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint
sudo apt install python-pip3
Installing pip for CentOS 8 (and newer), Fedora, and Red Hat
sudo dnf install python-pip3
Installing pip for CentOS 6 and 7, and older versions of Red Hat
sudo yum install epel-release sudo yum install python-pip3
Installing pip for Arch Linux and Manjaro
sudo pacman -S python-pip
Installing pip for OpenSUSE
sudo zypper python3-pip
PyAutoGUI installation on Linux with Pip
To install PyAutoGUI, first, create the virtual environment:
python3 -m venv env
Then activate the environment using:
source env/bin/activate
You will see “env” in parenthesis next to the command line prompt. You can install pyautogui within the environment by running the following command from the command prompt.
Once you have activated your virtual environment, you can install pyautogui using:
python3 -m pip install pyautogui
Installing PyAutoGUI Using Anaconda
Anaconda is a distribution of Python and R for scientific computing and data science. You can install Anaconda by going to the installation instructions. Once you have installed Anaconda, you can create a virtual environment and install pyautogui.
To create a conda environment you can use the following command:
conda create -n project python=3.8
You can specify a different Python 3 version if you like. Ideally, choose the latest version of Python. Next, you will activate the project container. You will see “project” in parentheses next to the command line prompt.
source activate project
Now you’re ready to install pyautogui using conda.
Once you have installed Anaconda and created your conda environment, you can install pyautogui using the following command:
conda install -c conda-forge pyautogui
Check PyAutoGUI Version
Once you have successfully installed pyautogui, you can check its version. If you used pip to install pyautogui, you can use pip show from your terminal.
python3 -m pip show pyautogui
Name: PyAutoGUI Version: 0.9.53 Summary: PyAutoGUI lets Python control the mouse and keyboard, and other GUI automation tasks. For Windows, macOS, and Linux, on Python 3 and 2. Home-page: https://github.com/asweigart/pyautogui
Second, within your python program, you can import pyautogui and then reference the __version__ attribute:
import pyautogui print(pyautogui.__version__)
0.9.53
If you used conda to install pyautogui, you could check the version using the following command:
conda list -f pyautogui
# Name Version Build Channel pyautogui 0.9.53 pypi_0 pypi
Using PyAutoGUI Example
Let’s look at an example of using the pyautogui module to get the size of the primary monitor and the XY position of the mouse:
import pyautogui screenWidth, screenHeight = pyautogui.size() # Get the size of the primary monitor. print(screenWidth, screenHeight) currentMouseX, currentMouseY = pyautogui.position() # Get the XY position of the mouse. print(currentMouseX, currentMouseY)
Let’s run the code to print the monitor size and position of the mouse to the console
1792 1120 293 293
Summary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial.
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about Python for data science and machine learning.
For further reading on missing modules in Python, go to the article:
- How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘skimage’
- How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘pymongo’
- How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘psutil’
Have fun and happy researching!

- Py Py
- Aug 26, 2022
Solution: Import the ‘pyautogui’ module
To Solve the error, add the following line to the top of your code.
import pyautoguiFor more information:
Python pyautogui
Search
Recent Posts
Tags
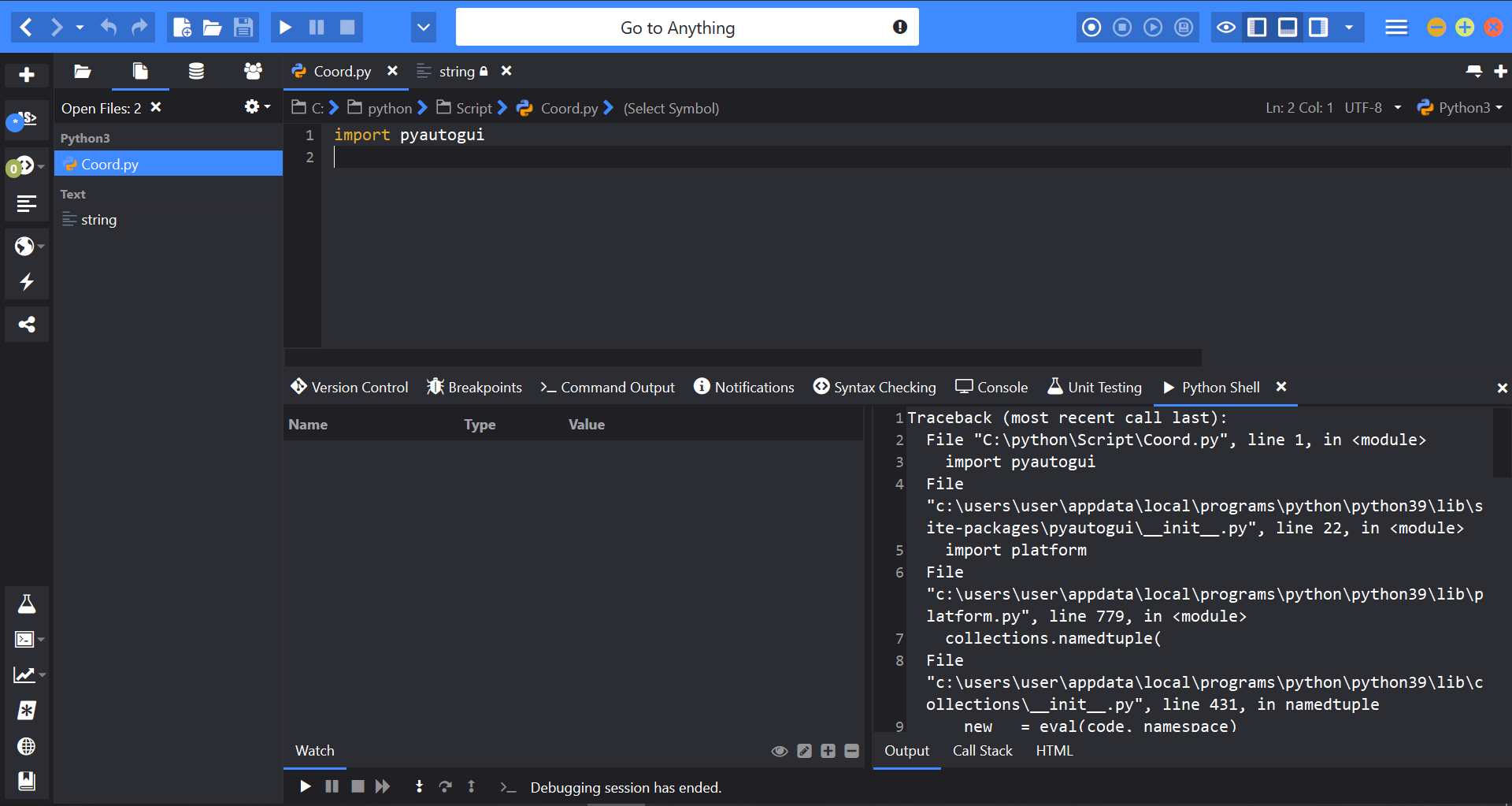
Добрый день.
Не получается импортировать модуль PyAutoGUI в программу.
Переустанавливал PyAutoGUI несколько раз, перезагружал компьютер, ничего не выходит.
(Я бессилен. Пытался найти решение в интернете, но неудачно.)
(Использую Komodo, т.к. нравится интерфейс)
Помогите, не понимаю в чем проблема и как ёё решить.
Также после пробного запуска программы в Komodo — создается отдельный файл string.
Показано на скрине.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:pythonScriptCoord.py", line 1, in <module>
import pyautogui
File "c:usersuserappdatalocalprogramspythonpython39libsite-packagespyautogui__init__.py", line 22, in <module>
import platform
File "c:usersuserappdatalocalprogramspythonpython39libplatform.py", line 779, in <module>
collections.namedtuple(
File "c:usersuserappdatalocalprogramspythonpython39libcollections__init__.py", line 431, in namedtuple
__new__ = eval(code, namespace)
File "<string>", line 0, in <module>
TypeError: 'NoneType' object does not support item assignment
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "c:usersuserappdatalocalprogramspythonpython39libbase64.py", line 510, in _input_type_check
m = memoryview(s)
TypeError: memoryview: a bytes-like object is required, not 'str'
The above exception was the direct cause of the following exception:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgpbinpy3_dbgp.py", line 307, in <module>
sys.exit( main(sys.argv) )
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgpbinpy3_dbgp.py", line 303, in main
client.runMain(args, interactive)
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgppython3libdbgpclient.py", line 2482, in runMain
self.cmdloop()
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgppython3libdbgpclient.py", line 2552, in cmdloop
self.onecmd(data)
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgppython3libdbgpclient.py", line 2652, in onecmd
return func(argv[1:])
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgppython3libdbgpclient.py", line 3511, in do_source
source = base64_encodestring(source)
File "C:Program Files (x86)ActiveState Komodo IDE 12libsupportdbgppython3libdbgpclient.py", line 1358, in base64_encodestring
return base64.encodebytes(data).decode()
File "c:usersuserappdatalocalprogramspythonpython39libbase64.py", line 527, in encodebytes
_input_type_check(s)
File "c:usersuserappdatalocalprogramspythonpython39libbase64.py", line 513, in _input_type_check
raise TypeError(msg) from err
TypeError: expected bytes-like object, not strThe ImportError in Python can occur when a module or library is not found in the system path. In this case, the error message is specifically related to the pyautogui library. This error can occur due to various reasons, including a missing library, incorrect installation, or incorrect import statement in the code. Here are some methods to resolve this error:
Method 1: Installing the library
To fix the import error for pyautogui in Python, you can install the library using pip. Here are the steps:
-
Open your command prompt or terminal.
-
Type the following command to install
pyautogui: -
Press Enter and wait for the installation to complete.
Once you have installed pyautogui, you can import it into your Python script using the following code:
Here are some examples of how to use pyautogui:
-
To move the mouse cursor to a specific position on the screen:
-
To click the mouse:
-
To type a string:
pyautogui.typewrite('Hello, World!') -
To take a screenshot:
screenshot = pyautogui.screenshot() screenshot.save('screenshot.png') -
To find an image on the screen:
location = pyautogui.locateOnScreen('image.png')
These are just a few examples of what you can do with pyautogui. For more information, you can refer to the official documentation at https://pyautogui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html.
Method 2: Checking the correct version of Python
If you are encountering an import error for PyAutoGUI, one possible reason is that you are using the wrong version of Python. To fix this error, you need to check that you are using the correct version of Python that is compatible with PyAutoGUI.
Here are the steps to check the correct version of Python:
-
First, make sure that you have installed PyAutoGUI. You can install it using pip by running the following command in your terminal:
-
Next, open your Python interpreter by running the following command in your terminal:
-
Once you are in the Python interpreter, type the following code to check the version of Python that you are using:
import sys print(sys.version)This will print the version of Python that you are using.
-
Check the PyAutoGUI documentation to see which versions of Python are compatible with PyAutoGUI. For example, as of this writing, PyAutoGUI is compatible with Python 2.7 and 3.4-3.9.
-
If you are using an incompatible version of Python, you will need to switch to a compatible version. You can do this by installing the correct version of Python and setting up a virtual environment.
For example, if you need to switch to Python 3.8, you can install it by running the following command:
sudo apt-get install python3.8Once you have installed the correct version of Python, you can set up a virtual environment by running the following commands:
python3.8 -m venv myenv source myenv/bin/activateThis will create a virtual environment and activate it.
-
Finally, you can test if PyAutoGUI is working by running the following code in your Python interpreter:
import pyautogui pyautogui.moveTo(100, 100, duration=0.25)This will move your mouse cursor to the position (100, 100) on your screen.
If you follow these steps, you should be able to fix the import error for PyAutoGUI by checking the correct version of Python.
Method 3: Verifying the installation location
If you are facing an import error for pyautogui in Python, one way to fix it is to verify the installation location. Here are the steps to do it:
- Open a Python shell or terminal window.
- Type the following code to import pyautogui:
- If you get an error message like «ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pyautogui'», it means that pyautogui is not installed or not installed in the right location.
- To verify the installation location, type the following code:
import sys
print(sys.path)This will print a list of directories where Python looks for modules. Look for the directory that contains pyautogui.
5. If pyautogui is not in any of the directories listed, you need to install it. You can do this by typing the following command in your terminal:
- If pyautogui is in one of the directories listed, make sure that the directory is included in your system’s PATH environment variable. You can do this by typing the following code in your terminal:
export PATH=$PATH:/path/to/pyautoguiReplace «/path/to/pyautogui» with the actual path to the directory that contains pyautogui.
7. Once you have verified the installation location and included the directory in your system’s PATH environment variable, try importing pyautogui again:
If you don’t get any error messages, you have successfully fixed the import error for pyautogui.
That’s it! By following these steps, you should be able to fix the import error for pyautogui in Python by verifying the installation location.
Method 4: Updating the system path
If you are encountering an import error for PyAutoGUI in Python, it is likely because the module is not installed or the Python interpreter cannot find the module. One way to fix this issue is to update the system path to include the directory where PyAutoGUI is installed.
Here are the steps to update the system path in Python:
Step 1: Find the Directory where PyAutoGUI is Installed
To find the directory where PyAutoGUI is installed, you can use the following code:
import pyautogui
print(pyautogui.__file__)This will print the path to the PyAutoGUI module. Copy the directory path for the next step.
Step 2: Update the System Path
To update the system path, you can use the sys.path.append() method. This method adds a directory to the list of directories where Python looks for modules.
import sys
sys.path.append('path/to/pyautogui')Replace 'path/to/pyautogui' with the directory path you copied in step 1.
Step 3: Test the Installation
To test if PyAutoGUI is installed correctly, you can import the module and call one of its functions:
import pyautogui
pyautogui.moveTo(100, 100, duration=0.25)This code should move the mouse cursor to the coordinates (100, 100) on the screen.
If you still encounter an import error, make sure that PyAutoGUI is installed correctly and that the directory path you added to the system path is correct.
That’s it! By following these steps, you should be able to fix the import error for PyAutoGUI in Python by updating the system path.