Introduction
This can have a lot of causes which are broken down in following sections:
- Put servlet class in a
package - Set servlet URL in
url-pattern @WebServletworks only on Servlet 3.0 or newerjavax.servlet.*doesn’t work anymore in Servlet 5.0 or newer- Make sure compiled
*.classfile is present in built WAR - Test the servlet individually without any JSP/HTML page
- Use domain-relative URL to reference servlet from HTML
- Use straight quotes in HTML attributes
Put servlet class in a package
First of all, put the servlet class in a Java package. You should always put publicly reuseable Java classes in a package, otherwise they are invisible to classes which are in a package, such as the source code of the server itself. This way you eliminate potential environment-specific problems. Packageless servlets work only in specific Tomcat+JDK combinations and this should never be relied upon. In case you are clueless which package to pick, start with com.example.
In case of a «plain» IDE project, the class needs to be placed in its package structure inside the «Java Sources» folder, not inside «Web Content» folder, which is for web files such as JSP. Below is an example of the folder structure of a default Eclipse Dynamic Web Project as seen in Navigator view (the «Java Sources» folder is in such project by default represented by src folder):
EclipseProjectName
|-- src
| `-- com
| `-- example
| `-- YourServlet.java
|-- WebContent
| |-- WEB-INF
| | `-- web.xml
| `-- jsps
| `-- page.jsp
:
In case of a Maven project, the class needs to be placed in its package structure inside main/java and thus not main/resources, this is for non-class files and absolutely also not main/webapp, this is for web files. Below is an example of the folder structure of a default Maven webapp project as seen in Eclipse’s Navigator view:
MavenProjectName
|-- src
| `-- main
| |-- java
| | `-- com
| | `-- example
| | `-- YourServlet.java
| |-- resources
| `-- webapp
| |-- WEB-INF
| | `-- web.xml
| `-- jsps
| `-- page.jsp
:
Note that the /jsps subfolder is not strictly necessary. You can even do without it and put the JSP file directly in webcontent/webapp root, but I’m just taking over this from your question.
Set servlet URL in url-pattern
The servlet URL is specified as the «URL pattern» of the servlet mapping. It’s absolutely not per definition the classname/filename of the servlet class. The URL pattern is to be specified as value of @WebServlet annotation.
package com.example; // Use a package!
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; // or javax.*
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet; // or javax.*
@WebServlet("/servlet") // This is the URL of the servlet.
public class YourServlet extends HttpServlet { // Must be public and extend HttpServlet.
// ...
}
In case you want to support path parameters like /servlet/foo/bar, then use an URL pattern of /servlet/* instead. See also Servlet and path parameters like /xyz/{value}/test, how to map in web.xml?
Do note that it’s considered a bad practice to use a Servlet URL pattern of /* or / in an attempt to have a «front controller». So do not abuse these URL patterns in an attempt to try to catch all URLs. For an in depth explanation see also Difference between / and /* in servlet mapping url pattern.
@WebServlet works only on Servlet 3.0 or newer
In order to use @WebServlet, you need to make sure that your web.xml file, if any (it’s optional since Servlet 3.0), is declared conform Servlet 3.0+ version and thus not conform e.g. 2.5 version or lower. It should absolutely also not have any <!DOCTYPE> line. Below is a Servlet 6.0 compatible one (which matches Tomcat 10.1+, WildFly 27+ (Preview), GlassFish/Payara 7+, etc) in its entirety:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app
xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_6_0.xsd"
version="6.0"
>
<!-- Config here. -->
</web-app>
And below is a Servlet 5.0 compatible one (which matches Tomcat 10.0+, WildFly 22+ (Preview), GlassFish/Payara 6+, etc).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app
xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd"
version="5.0"
>
<!-- Config here. -->
</web-app>
And below is a Servlet 4.0 compatible one (which matches Tomcat 9+, WildFly 11+, GlassFish/Payara 5+, etc).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0"
>
<!-- Config here. -->
</web-app>
Or, in case you’re not on Servlet 3.0+ yet (e.g. Tomcat 6 or older), then remove the @WebServlet annotation (and make sure you also remove all the wrong JAR files or Maven dependencies which incorrectly made it possible for you to successfully compile the code):
package com.example;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
public class YourServlet extends HttpServlet {
// ...
}
And register the servlet instead in web.xml like this:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>yourServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.example.YourServlet</servlet-class> <!-- Including the package thus -->
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>yourServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet</url-pattern> <!-- This is the URL of the servlet. -->
</servlet-mapping>
Note thus that you should not use both ways. Use either annotation based configuarion or XML based configuration. When you have both, then XML based configuration will override annotation based configuration.
javax.servlet.* doesn’t work anymore in Servlet 5.0 or newer
Since Jakarta EE 9 / Servlet 5.0 (Tomcat 10, TomEE 9, WildFly 22 Preview, GlassFish 6, Payara 6, Liberty 22, etc), the javax.* package has been renamed to jakarta.* package.
In other words, please make absolutely sure that you don’t randomly put JAR files of a different server in your WAR project such as tomcat-servlet-api-9.x.x.jar merely in order to get the javax.* package to compile. This will only cause trouble. Remove it altogether and edit the imports of your servlet class from
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
to
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
In case you’re using Maven, you can find examples of proper pom.xml declarations for Tomcat 10+, Tomcat 9-, JEE 9+ and JEE 8- in this answer: How to properly configure Jakarta EE libraries in Maven pom.xml for Tomcat? The alternative is to downgrade the server to an older version, e.g. from Tomcat 10 back to Tomcat 9 or older, but this is clearly not the recommended way to go.
In case you’re using Spring instead of Jakarta EE, Spring 6 and Spring Boot 3 are the first versions to target Servlet 5.0 and therefore also the first versions to use the jakarta.* package. Older versions still use the javax.* package. Adjust your imports accordingly and make absolutely sure that you don’t have any conflicting libraries in your dependencies which incorrectly make it possible to still successfully compile against javax.servlet.*. Using javax.servlet.* must give a compilation error in projects targeted at at least Servlet 5.0+ (so, either Jakarta EE 9+ or Spring 6+ or Spring Boot 3+).
Make sure compiled *.class file is present in built WAR
In case you’re using a build tool such as Eclipse and/or Maven, then you need to make absolutely sure that the compiled servlet class file resides in its package structure in /WEB-INF/classes folder of the produced WAR file. In case of package com.example; public class YourServlet, it must be located in /WEB-INF/classes/com/example/YourServlet.class. Otherwise you will face in case of @WebServlet also a 404 error, or in case of <servlet> a HTTP 500 error like below:
HTTP Status 500
Error instantiating servlet class com.example.YourServlet
And find in the server log a java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.example.YourServlet, followed by a java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com.example.YourServlet, in turn followed by jakarta.servlet.ServletException: Error instantiating servlet class com.example.YourServlet.
An easy way to verify if the servlet is correctly compiled and placed in classpath is to let the build tool produce a WAR file (e.g. rightclick project, Export > WAR file in Eclipse) and then inspect its contents with a ZIP tool. If the servlet class is missing in /WEB-INF/classes, or if the export causes an error, then the project is badly configured or some IDE/project configuration defaults have been mistakenly reverted (e.g. Project > Build Automatically has been disabled in Eclipse).
You also need to make sure that the project icon has no red cross indicating a build error. You can find the exact error in Problems view (Window > Show View > Other…). Usually the error message is fine Googlable. In case you have no clue, best is to restart from scratch and do not touch any IDE/project configuration defaults. In case you’re using Eclipse, you can find instructions in How do I import the javax.servlet / jakarta.servlet API in my Eclipse project?
Test the servlet individually without any JSP/HTML page
Provided that the server runs on localhost:8080, and that the WAR is successfully deployed on a context path of /contextname (which defaults to the IDE project name or the Maven build artifact file name, case sensitive!), and the servlet hasn’t failed its initialization (read server logs for any deploy/servlet success/fail messages and the actual context path and servlet mapping), then a servlet with URL pattern of /servlet is available at http://localhost:8080/contextname/servlet.
You can just enter it straight in browser’s address bar to test it invidivually. If its doGet() is properly overriden and implemented, then you will see its output in browser. Or if you don’t have any doGet() or if it incorrectly calls super.doGet(), then a «HTTP 405: HTTP method GET is not supported by this URL» error will be shown (which is still better than a 404 as a 405 is evidence that the servlet itself is actually found).
Overriding service() is a bad practice, unless you’re reinventing a MVC framework — which is very unlikely if you’re just starting out with servlets and are clueless as to the problem described in the current question 
Regardless, if the servlet already returns 404 when tested invidivually, then it’s entirely pointless to try with a HTML form instead. Logically, it’s therefore also entirely pointless to include any HTML form in questions about 404 errors from a servlet.
Use domain-relative URL to reference servlet from HTML
Once you’ve verified that the servlet works fine when invoked individually, then you can advance to HTML. As to your concrete problem with the HTML form, the <form action> value needs to be a valid URL. The same applies to <a href>, <img src>, <script src>, etc. You need to understand how absolute/relative URLs work. You know, an URL is a web address as you can enter/see in the webbrowser’s address bar. If you’re specifying a relative URL as form action, i.e. without the http:// scheme, then it becomes relative to the current URL as you see in your webbrowser’s address bar. It’s thus absolutely not relative to the JSP/HTML file location in server’s WAR folder structure as many starters seem to think.
So, assuming that the JSP page with the HTML form is opened by http://localhost:8080/contextname/jsps/page.jsp (and thus not by file://...), and you need to submit to a servlet located in http://localhost:8080/contextname/servlet, here are several cases (note that you can here safely substitute <form action> with <a href>, <img src>, <script src>, etc):
-
Form action submits to an URL with a leading slash.
<form action="/servlet">The leading slash
/makes the URL relative to the domain, thus the form will submit tohttp://localhost:8080/servletBut this will likely result in a 404 as it’s in the wrong context.
-
Form action submits to an URL without a leading slash.
<form action="servlet">This makes the URL relative to the current folder of the current URL, thus the form will submit to
http://localhost:8080/contextname/jsps/servletBut this will likely result in a 404 as it’s in the wrong folder.
-
Form action submits to an URL which goes one folder up.
<form action="../servlet">This will go one folder up (exactly like as in local disk file system paths!), thus the form will submit to
http://localhost:8080/contextname/servletThis one must work!
-
The canonical approach, however, is to make the URL domain-relative so that you don’t need to fix the URLs once again when you happen to move the JSP files around into another folder.
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/servlet">This will generate
<form action="/contextname/servlet">Which will thus always submit to the right URL.
Use straight quotes in HTML attributes
You need to make absolutely sure you’re using straight quotes in HTML attributes like action="..." or action='...' and thus not curly quotes like action=”...” or action=’...’. Curly quotes are not supported in HTML and they will simply become part of the value. Watch out when copy-pasting code snippets from blogs! Some blog engines, notably WordPress, are known to by default use so-called «smart quotes» which thus also corrupts the quotes in code snippets this way. On the other hand, instead of copy-pasting code, try simply typing over the code yourself. Additional advantage of actually getting the code through your brain and fingers is that it will make you to remember and understand the code much better in long term and also make you a better developer.
See also:
- Our servlets wiki page — Contains some hello world examples
- How to call servlet class from HTML form
- doGet and doPost in Servlets
- How do I pass current item to Java method by clicking a hyperlink or button in JSP page?
Other cases of HTTP Status 404 error:
- HTTP Status 404 — Servlet [ServletName] is not available
- HTTP Status 404 — The requested resource (/ProjectName/) is not available
- HTTP Status 404 — The requested resource (/) is not available
- JSP in /WEB-INF returns «HTTP Status 404 The requested resource is not available»
- Referencing a resource placed in WEB-INF folder in JSP file returns HTTP 404 on resource
- Browser can’t access/find relative resources like CSS, images and links when calling a Servlet which forwards to a JSP
In the previous section, we had returned the proper response status of CREATED when we created the resource. In this section, we will discuss what should be the response when a user resource does not exist.
Let’s try and execute a simple response.
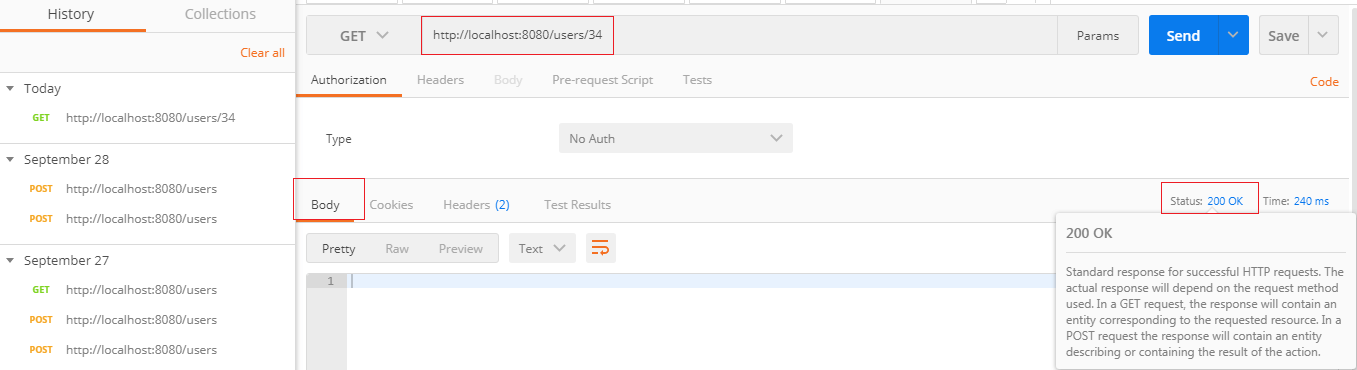
Step 1: Open Rest client Postman and select the Get method.
Step 2: Click on the History tab and choose the Get request.
Step 3: Type the URI http://localhost:8080/users/{id}. The user id should not exist.
Step 4: Click on the Send Button.
We get the Status: 200 OK and empty body which is a successful response even though the resource does not exist. But it is not the proper response when a resource does not exist.
Let’s fix that first.
Step 1: Open the UserResource.java file.
Step 2: Create a UserNotFoundException. It is a checked exception.
Step 3: Create UserNotFoundException class.
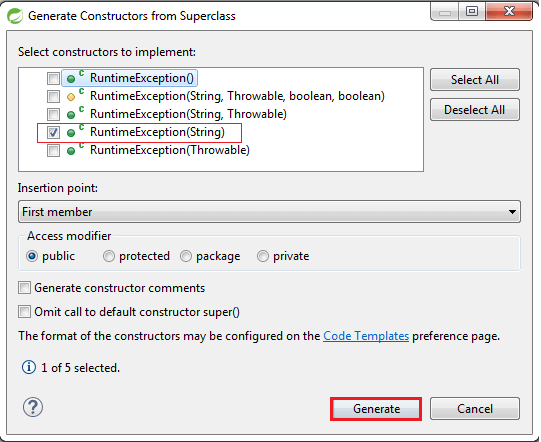
Step 4: Generate Constructors from Superclass.
Right-click on the file -> Source -> Generate Constructors from Superclass… -> check the RuntimeException(String) -> Generate.
UserNotFoundException.java
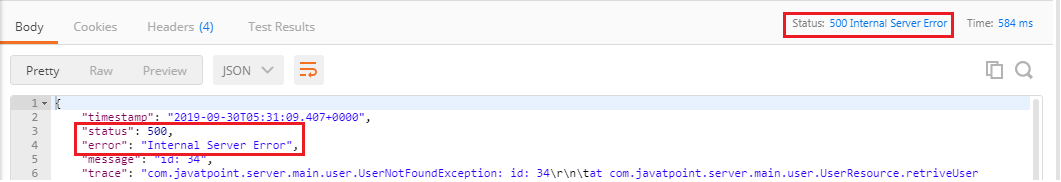
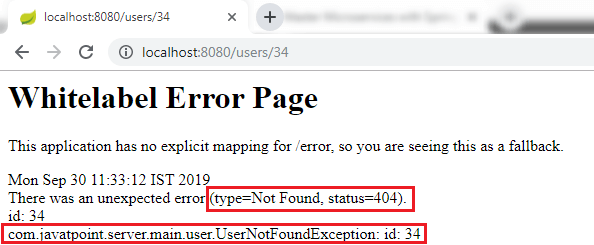
Step 5: Open the Rest Client Postman and generate a Get response as we have done before. It shows the Status: 500 Internal Server Error.
But the Status: 500 Internal Server Error is not the appropriate response for the resource not found. So, we will add an annotation @ResponseStatus to generate the Status: 404 Not Found.
UserNotFoundException.java
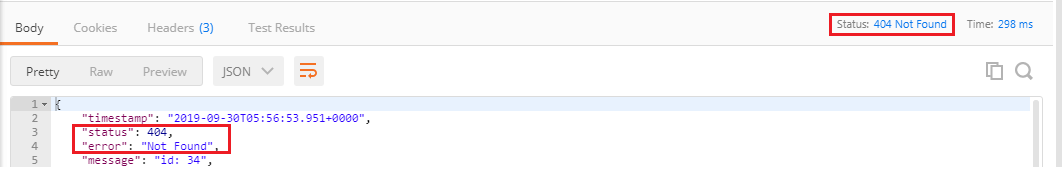
Step 6: Again move to Postman and generate a Get request.
We get the proper response Status: 404 Not Found when a user resource does not exist. The body of the request provided by default error handling that’s why we are getting this return status back.
The combination of Spring Boot and Spring Web MVC framework provides error handling. Spring Boot auto-configures some default exception handling. It is important to have a consistent exception message which is obtained for all the services inside our enterprise.
If we have a big organization and each of the services returns the exception messages in a different way, so it is not good. It would be good if we define a standard exception structure which is followed by across all the RESTful Services.
Обработка ошибок
Последнее обновление: 17.09.2018

Файл web.xml позволяет указать, какие страницы html или jsp будут отправляться пользователю при отправке статусных кодов ошибок.
Для этого в web.xml применяется элемент <error-page>.
Внутри этого элемента с помощью элемента <error-code> указывается
статусный код ошибки, который надо обработать. А элемент <location> указывает на путь к
странице html или jsp, которая будет отправляться пользователю.
Например, добавим в проект в папку WebContent новый файл 404.html со следующим кодом:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Not Found</title> </head> <body> <h2>Resource not found!</h2> </body> </html>
В файле web.xml определим следующее содержимое:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/404.html</location>
</error-page>
</web-app>
В данном случае элемент error-code указывает, что мы будем обрабатывать ошибки со статусным кодом 404 (то есть такие ошибки,
которые подразумевают отсутствие ресурса на сервере). А элемент location указывает, что в случае обращения к несуществующему ресурсу
пользователю будет отправляться страница 404.html.
Обработка исключений
Кроме настройки обработки стандартных ошибок протокола http,типа 404 или 403, файл web.xml позволяет настроить обработку исключений,
которые могут возникнуть при обработке запроса. Для этого в web.xml применяется элемент <exception-type.
Например, добавим в проект в папку WebContent новый файл error.jsp и определим
в нем следующий код:
<% String message = pageContext.getException().getMessage(); String exception = pageContext.getException().getClass().toString(); %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Exception</title> </head> <body> <h2>Exception occurred while processing the request</h2> <p>Type: <%= exception%></p> <p>Message: <%= message %></p> </body> </html>
Данная страница jsp будет отображать информацию об исключении. Через глобальный объект pageContext в страницу передается контекст.
Если при обработке запроса возникло какое-нибудь исключение, то метод pageContext.getException() возвратит это исключение в
виде объекта Exception. И далее мы можем исследовать этот объект и вызывать его методы, например, получить тип исключения и сообщение об исключении.
Симитируем с сервлете какое-нибудь исключение:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/hello")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
int x = 0;
int y = 8 / x;
}
}
В данном случае мы получаем ошибку деления на нуль, которая представлена типом java.lang.ArithmeticException.
Теперь определим следующий файл web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.Throwable</exception-type>
<location>/error.jsp</location>
</error-page>
</web-app>
Элемент exception-type указывает, что обрабатываться будут исключения типа java.lang.Throwable. Поскольку это базовый класс для всех типов исключений,
то фактически мы будем обрабатывать все исключения. Хотя можно конкретизировать тип исключения, например, указать тот же java.lang.ArithmeticException.
Элемент location определяет страницу, которая отправляется пользователю при возникновении исключении. В данном случае это
error.jsp.
В итоге при обращении к сервлету будет сгенерировано исключение, и мы увидим информацию о нем:
This error indicates that the server could not find the desired resource. This resource can be any file such as JSP, HTML, or image resource. Usually, the resource is present, but it is referenced incorrectly. In most cases, you can fix this by correcting the URL. Here are three strategies you can use to look for errors:
- Java servlets do not handle URL
- Servlet forwarding the resource does not exist
- URL is case-sensitive
1. Java servlets do not handle URL
Your @Webservlet() may handle for URL/name; however, the URL requested may be URL/this_name (different reference). You can fix this by correcting the reference URL or URL mapping.
In code, it may look something like this:
@WebServlet("/name")
public class Name extends HttpServlet {
...
}
However, your website requested /this_name instead of /name. One way you can correct this is by changing /name to /this_name in your URL mapping.
2. Servlet forwarding the resource does not exist
Make sure that the forwarded resource exists. If the resource you are trying to reference is not named correctly, you may also run into this problem. For instance, you are referencing signupForm.jsp, but the name of the resource is signup_Form.jsp. In code it may look something like this:
String signupForm= "frontend/signupForm.jsp";
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(signupForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
You can fix this by correcting the servlet’s path which, in this case, would be to change signupForm.jsp to signup_Form.jsp.
3. URL is case-sensitive
If you typed the URL yourself, you might have mistyped it. Tomcat URLs are case-sensitive. For instance, signup is different than signUp. Make sure your URL is case-sensitive.