This function basically generates unique random API key’s and in case if it doesn’t then pop-up dialog box with error message appears
In View Page:
<div class="form-group required">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label" for="input-storename"><?php echo $entry_storename; ?></label>
<div class="col-sm-6">
<input type="text" class="apivalue" id="api_text" readonly name="API" value="<?php echo strtoupper(substr(md5(rand().microtime()), 0, 12)); ?>" class="form-control" />
<button type="button" class="changeKey1" value="Refresh">Re-Generate</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$('.changeKey1').click(function(){
debugger;
$.ajax({
url :"index.php?route=account/apiaccess/regenerate",
type :'POST',
dataType: "json",
async:false,
contentType: "application/json; charset=utf-8",
success: function(data){
var result = data.sync_id.toUpperCase();
if(result){
$('#api_text').val(result);
}
debugger;
},
error: function(xhr, ajaxOptions, thrownError) {
alert(thrownError + "rn" + xhr.statusText + "rn" + xhr.responseText);
}
});
});
});
</script>
From Controller:
public function regenerate(){
$json = array();
$api_key = substr(md5(rand(0,100).microtime()), 0, 12);
$json['sync_id'] = $api_key;
$json['message'] = 'Successfully API Generated';
$this->response->addHeader('Content-Type: application/json');
$this->response->setOutput(json_encode($json));
}
The optional callback parameter specifies a callback function to run when the load() method is completed. The callback function can have different parameters:
Type: Function( jqXHR jqXHR, String textStatus, String errorThrown )
A function to be called if the request fails.
The function receives three arguments: The jqXHR (in jQuery 1.4.x, XMLHttpRequest) object, a string describing the type of error that occurred and an optional exception object, if one occurred. Possible values for the second argument (besides null) are «timeout», «error», «abort», and «parsererror». When an HTTP error occurs, errorThrown receives the textual portion of the HTTP status, such as «Not Found» or «Internal Server Error.» As of jQuery 1.5, the error setting can accept an array of functions. Each function will be called in turn. Note: This handler is not called for cross-domain script and cross-domain JSONP requests.
Description: Perform an asynchronous HTTP (Ajax) request.
The $.ajax() function underlies all Ajax requests sent by jQuery. It is often unnecessary to directly call this function, as several higher-level alternatives like $.get() and .load() are available and are easier to use. If less common options are required, though, $.ajax() can be used more flexibly.
At its simplest, the $.ajax() function can be called with no arguments:
Note: Default settings can be set globally by using the $.ajaxSetup() function.
This example, using no options, loads the contents of the current page, but does nothing with the result. To use the result, you can implement one of the callback functions.
The jqXHR Object
The jQuery XMLHttpRequest (jqXHR) object returned by $.ajax() as of jQuery 1.5 is a superset of the browser’s native XMLHttpRequest object. For example, it contains responseText and responseXML properties, as well as a getResponseHeader() method. When the transport mechanism is something other than XMLHttpRequest (for example, a script tag for a JSONP request) the jqXHR object simulates native XHR functionality where possible.
As of jQuery 1.5.1, the jqXHR object also contains the overrideMimeType() method (it was available in jQuery 1.4.x, as well, but was temporarily removed in jQuery 1.5). The .overrideMimeType() method may be used in the beforeSend() callback function, for example, to modify the response content-type header:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
The jqXHR objects returned by $.ajax() as of jQuery 1.5 implement the Promise interface, giving them all the properties, methods, and behavior of a Promise (see Deferred object for more information). These methods take one or more function arguments that are called when the $.ajax() request terminates. This allows you to assign multiple callbacks on a single request, and even to assign callbacks after the request may have completed. (If the request is already complete, the callback is fired immediately.) Available Promise methods of the jqXHR object include:
-
jqXHR.done(function( data, textStatus, jqXHR ) {});
An alternative construct to the success callback option, refer to
deferred.done()for implementation details. -
jqXHR.fail(function( jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown ) {});
An alternative construct to the error callback option, the
.fail()method replaces the deprecated.error()method. Refer todeferred.fail()for implementation details. -
jqXHR.always(function( data|jqXHR, textStatus, jqXHR|errorThrown ) { }); (added in jQuery 1.6)
An alternative construct to the complete callback option, the
.always()method replaces the deprecated.complete()method.In response to a successful request, the function’s arguments are the same as those of
.done(): data, textStatus, and the jqXHR object. For failed requests the arguments are the same as those of.fail(): the jqXHR object, textStatus, and errorThrown. Refer todeferred.always()for implementation details. -
jqXHR.then(function( data, textStatus, jqXHR ) {}, function( jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown ) {});
Incorporates the functionality of the
.done()and.fail()methods, allowing (as of jQuery 1.8) the underlying Promise to be manipulated. Refer todeferred.then()for implementation details.
Deprecation Notice: The jqXHR.success(), jqXHR.error(), and jqXHR.complete() callbacks are removed as of jQuery 3.0. You can use jqXHR.done(), jqXHR.fail(), and jqXHR.always() instead.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
The this reference within all callbacks is the object in the context option passed to $.ajax in the settings; if context is not specified, this is a reference to the Ajax settings themselves.
For backward compatibility with XMLHttpRequest, a jqXHR object will expose the following properties and methods:
-
readyState -
responseXMLand/orresponseTextwhen the underlying request responded with xml and/or text, respectively -
status -
statusText(may be an empty string in HTTP/2) -
abort( [ statusText ] ) -
getAllResponseHeaders()as a string -
getResponseHeader( name ) -
overrideMimeType( mimeType ) -
setRequestHeader( name, value )which departs from the standard by replacing the old value with the new one rather than concatenating the new value to the old one -
statusCode( callbacksByStatusCode )
No onreadystatechange mechanism is provided, however, since done, fail, always, and statusCode cover all conceivable requirements.
Callback Function Queues
The beforeSend, error, dataFilter, success and complete options all accept callback functions that are invoked at the appropriate times.
As of jQuery 1.5, the fail and done, and, as of jQuery 1.6, always callback hooks are first-in, first-out managed queues, allowing for more than one callback for each hook. See Deferred object methods, which are implemented internally for these $.ajax() callback hooks.
The callback hooks provided by $.ajax() are as follows:
-
beforeSendcallback option is invoked; it receives thejqXHRobject and thesettingsobject as parameters. -
errorcallback option is invoked, if the request fails. It receives thejqXHR, a string indicating the error type, and an exception object if applicable. Some built-in errors will provide a string as the exception object: «abort», «timeout», «No Transport». -
dataFiltercallback option is invoked immediately upon successful receipt of response data. It receives the returned data and the value ofdataType, and must return the (possibly altered) data to pass on tosuccess. -
successcallback option is invoked, if the request succeeds. It receives the returned data, a string containing the success code, and thejqXHRobject. -
Promise callbacks —
.done(),.fail(),.always(), and.then()— are invoked, in the order they are registered. -
completecallback option fires, when the request finishes, whether in failure or success. It receives thejqXHRobject, as well as a string containing the success or error code.
Data Types
Different types of response to $.ajax() call are subjected to different kinds of pre-processing before being passed to the success handler. The type of pre-processing depends by default upon the Content-Type of the response, but can be set explicitly using the dataType option. If the dataType option is provided, the Content-Type header of the response will be disregarded.
The available data types are text, html, xml, json, jsonp, and script.
If text or html is specified, no pre-processing occurs. The data is simply passed on to the success handler, and made available through the responseText property of the jqXHR object.
If xml is specified, the response is parsed using jQuery.parseXML before being passed, as an XMLDocument, to the success handler. The XML document is made available through the responseXML property of the jqXHR object.
If json is specified, the response is parsed using jQuery.parseJSON before being passed, as an object, to the success handler. The parsed JSON object is made available through the responseJSON property of the jqXHR object.
If script is specified, $.ajax() will execute the JavaScript that is received from the server before passing it on to the success handler as a string.
If jsonp is specified, $.ajax() will automatically append a query string parameter of (by default) callback=? to the URL. The jsonp and jsonpCallback properties of the settings passed to $.ajax() can be used to specify, respectively, the name of the query string parameter and the name of the JSONP callback function. The server should return valid JavaScript that passes the JSON response into the callback function. $.ajax() will execute the returned JavaScript, calling the JSONP callback function, before passing the JSON object contained in the response to the $.ajax() success handler.
For more information on JSONP, see the original post detailing its use.
Sending Data to the Server
By default, Ajax requests are sent using the GET HTTP method. If the POST method is required, the method can be specified by setting a value for the type option. This option affects how the contents of the data option are sent to the server. POST data will always be transmitted to the server using UTF-8 charset, per the W3C XMLHTTPRequest standard.
The data option can contain either a query string of the form key1=value1&key2=value2, or an object of the form {key1: 'value1', key2: 'value2'}. If the latter form is used, the data is converted into a query string using jQuery.param() before it is sent. This processing can be circumvented by setting processData to false. The processing might be undesirable if you wish to send an XML object to the server; in this case, change the contentType option from application/x-www-form-urlencoded to a more appropriate MIME type.
Advanced Options
The global option prevents handlers registered for the ajaxSend, ajaxError, and similar events from firing when this request would trigger them. This can be useful to, for example, suppress a loading indicator that was implemented with an ajaxSend handler if the requests are frequent and brief. With cross-domain script and JSONP requests, the global option is automatically set to false. See the descriptions of these methods below for more details.
If the server performs HTTP authentication before providing a response, the user name and password pair can be sent via the username and password options.
Ajax requests are time-limited, so errors can be caught and handled to provide a better user experience. Request timeouts are usually either left at their default or set as a global default using $.ajaxSetup() rather than being overridden for specific requests with the timeout option.
By default, requests are always issued, but the browser may serve results out of its cache. To disallow use of the cached results, set cache to false. To cause the request to report failure if the asset has not been modified since the last request, set ifModified to true.
The scriptCharset allows the character set to be explicitly specified for requests that use a <script> tag (that is, a type of script or jsonp). This is useful if the script and host page have differing character sets.
The first letter in Ajax stands for «asynchronous,» meaning that the operation occurs in parallel and the order of completion is not guaranteed. The async option to $.ajax() defaults to true, indicating that code execution can continue after the request is made. Setting this option to false (and thus making the call no longer asynchronous) is strongly discouraged, as it can cause the browser to become unresponsive.
The $.ajax() function returns the XMLHttpRequest object that it creates. Normally jQuery handles the creation of this object internally, but a custom function for manufacturing one can be specified using the xhr option. The returned object can generally be discarded, but does provide a lower-level interface for observing and manipulating the request. In particular, calling .abort() on the object will halt the request before it completes.
Extending Ajax
As of jQuery 1.5, jQuery’s Ajax implementation includes prefilters, transports, and converters that allow you to extend Ajax with a great deal of flexibility.
Using Converters
$.ajax() converters support mapping data types to other data types. If, however, you want to map a custom data type to a known type (e.g json), you must add a correspondence between the response Content-Type and the actual data type using the contents option:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
This extra object is necessary because the response Content-Types and data types never have a strict one-to-one correspondence (hence the regular expression).
To convert from a supported type (e.g text, json) to a custom data type and back again, use another pass-through converter:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
The above now allows passing from text to mycustomtype and then mycustomtype to json.
Examples:
Save some data to the server and notify the user once it’s complete.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Retrieve the latest version of an HTML page.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
Send an xml document as data to the server. By setting the processData
option to false, the automatic conversion of data to strings is prevented.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Send an id as data to the server, save some data to the server, and notify the user once it’s complete. If the request fails, alert the user.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
|
Load and execute a JavaScript file.
Время на прочтение
13 мин
Количество просмотров 58K

Всем привет в новой записи мы с вами разберём основные функции для Ajax запросов, которые позволяют передавать информацию с сайта в PHP скрипт без перезагрузки страницы.
Для работы Ajax запросов вам нужно подключить jQuery к вашему проекту. Ссылку на jQuery вы можете найти здесь.
Данный взяты с моего сайта Prog-Time.
Стандартная отправка данных через Ajax.
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php', /* Куда отправить запрос */
method: 'get', /* Метод запроса (post или get) */
dataType: 'html', /* Тип данных в ответе (xml, json, script, html). */
data: {text: 'Текст'}, /* Данные передаваемые в массиве */
success: function(data){ /* функция которая будет выполнена после успешного запроса. */
alert(data); /* В переменной data содержится ответ от index.php. */
}
});Отправка POST запроса через Ajax
Для отправки POST запроса используем подобный код, меняем только параметр method
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'post',
dataType: 'html',
data: {text: 'Текст'},
success: function(data){
alert(data);
}
});Отправка JSON данных через Ajax
Для отправки JSON данный через AJAX можно использовать только методом GET.
$.ajax({
url: '/json.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'json',
success: function(data){
alert(data.text); /* выведет "Текст" */
alert(data.error); /* выведет "Ошибка" */
}
});Запланировать выполнение JS скрипта
После выполнения данного запроса, скрипт указанный в параметре url сразу будет выполнен.
$.ajax({
method: 'get',
url: '/script.js',
dataType: "script"
});Сокращённые виды функций для Ajax запросов
$.post('/index.php', {text: 'Текст'}, function(data){
alert(data);
});$.get('/index.php', {text: 'Текст'}, function(data){
alert(data);
});$.getJSON('/json.php', function(data) {
alert(data.text);
alert(data.error);
});Сокращённая версия запроса на выполнение JS скрипта
$.getScript('/script.js');Обработка ошибок связанных с AJAX запросом
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'json',
success: function(data){
console.dir(data);
},
error: function (jqXHR, exception) {
if (jqXHR.status === 0) {
alert('Not connect. Verify Network.');
} else if (jqXHR.status == 404) {
alert('Requested page not found (404).');
} else if (jqXHR.status == 500) {
alert('Internal Server Error (500).');
} else if (exception === 'parsererror') {
alert('Requested JSON parse failed.');
} else if (exception === 'timeout') {
alert('Time out error.');
} else if (exception === 'abort') {
alert('Ajax request aborted.');
} else {
alert('Uncaught Error. ' + jqXHR.responseText);
}
}
});7 Основные параметры для работы с AJAX функциями
Справочные данные взяты с сайта – https://basicweb.ru/jquery/jquery_method_ajax.php
Все параметры для отправки AJAX запросов
-
async (по умолчанию: true).Тип: Boolean.По умолчанию, все запросы отправляются асинхронно и не задерживают работу других JS скриптов (это значение true), для того чтобы ждать пока выполниться Ajax запрос – поставьте значение false.Обратите внимание, что кроссдоменные запросы и элемент, параметр dataType которого имеет значение “jsonp” не поддерживают запросы в синхронном режиме. Учтите, что используя синхронные запросы вы можете временно заблокировать браузер отключив какие-либо действия пока запрос будет активен.
-
beforeSendФункция обратного вызова, которая будет вызвана перед осуществлением AJAX запроса. Функция позволяет изменить объект jqXHR (в jQuery 1.4.х объект XMLHTTPRequest) до его отправки. Объект jqXHR это надстройка расширяющая объект XMLHttpRequest, объект содержит множество свойств и методов, которые позволяет получить более полную информацию об ответе сервера, а так же объект содержит Promise методы. Если функция beforeSend возвращает false, то AJAX запрос будет отменен. Начиная с версии jQuery 1.5 функция beforeSend будет вызываться независимо от типа запроса.
-
cache (по умолчанию: true, для dataType “script” и “jsonp” false).Тип: Boolean.Если задано значение false, то это заставит запрашиваемые страницы не кэшироваться браузером. Обратите внимание, что значение false будет правильно работать только с HEAD и GET запросами.
-
complete.Тип: Function( jqXHR jqXHR, String textStatus ).Функция, которая вызывается, когда запрос заканчивается (функция выполняется после AJAX событий “success” или “error”). В функцию передаются два параметра: jqXHR (в jQuery 1.4.х объект XMLHTTPRequest) и строка соответствующая статусу запроса (“success”, “notmodified”, “nocontent”, “error”, “timeout”, “abort”, или “parsererror”). Начиная с версии jQuery 1.5 параметр complete может принимать массив из функций, которые будут вызываться по очереди.
-
contents.Тип: PlainObject.Объект состоящий из пар строка/регулярное выражение, определяющих, как jQuery будет обрабатывать (парсить) ответ в зависимости от типа содержимого. Добавлен в версии jQuery 1.5.
-
contentType (по умолчанию: “application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8”).Тип: Boolean, или String.Определяет тип содержимого, которое указывается в запросе при передаче данных на сервер. С версии с jQuery 1.6 допускается указать значение false, в этом случае jQuery не передает в заголовке поле Content-Type совсем.
-
context.Тип: PlainObject.При выполнении AJAX функций обратного вызова контекстом их выполнения является объект window. Параметр context позволяет настроить контекст исполнения функции таким образом, что $( this ) будет ссылаться на определенный DOM элемент, или объект.
$.ajax({
url: "test.html", // адрес, на который будет отправлен запрос
context: $( ".myClass" ), // новый контекст исполнения функции
success: function(){ // если запрос успешен вызываем функцию
$( this ).html( "Всё ок" ); // добавляем текст в элемент с классом .myClass
}
});-
crossDomain (по умолчанию: false для запросов внутри того же домена, true для кроссдоменных запросов).Тип: Boolean.Если вы хотите сделать кроссдоменный запрос находясь на том же домене (например jsonp-запрос), то установите этот параметр в true. Это позволит, к примеру, сделать перенаправление запроса на другой домен с вашего сервера. Добавлен в версии jQuery 1.5.
-
data.Тип: PlainObject, или String, или Array.Данные, которые будут отправлены на сервер. Если они не является строкой, то преобразуются в строку запроса. Для GET запросов строка будет добавлена к URL. Для того, чтобы предотвратить автоматическую обработку вы можете воспользоваться параметром processData со значением false. Если данные передаются в составе объекта, то он должен состоять из пар ключ/значение. Если значение является массивом, то jQuery сериализует несколько значений с одним и тем же ключом (в зависимости от значения параметра traditional, который позволяет задействовать традиционный тип сериализации основанный на методе $.param).
-
dataFilter.Тип: Function( String data, String type ) => Anything.Функция вызывается после успешного выполнения AJAX запроса и позволяет обработать “сырые” данные, полученные из ответа сервера. Возврат данных должен происходить сразу после их обработки. Функция принимает два аргумента: data – данные полученные от сервера в виде строки и type – тип этих данных (значение параметра dataType).
-
dataType (по умолчанию: xml, json, script, или html ).Тип: String.Определяет тип данных, который вы ожидаете получить от сервера. Если тип данных не указан, то jQuery будет пытаться определить его на основе типа MIME из ответа (XML тип MIME приведет к получению XML, с версии jQuery 1.4 json будет давать объект JavaScript, script будет выполнять скрипт, а все остальное будет возвращено в виде строки).Основные типы (результат передается в качестве первого аргумента в функцию обратного вызова success):
-
“xml” – возвращает XML документ, который может быть обработан с помощью jQuery.
-
“html” – возвращает HTML как обычный текст, теги <script> будут обработаны и выполнены после вставки в объектную модель документа (DOM).
-
“script” – расценивает ответ как JavaScript и возвращает его как обычный текст. Отключает кэширование с помощью добавления параметра к строке запроса _=[TIMESTAMP], даже если парамета cache имеет значение true. Это превратит метод POST в GET для кроссдоменных запросов.
-
“json” – расценивает ответ как JSON и возвращает объект JavaScript. Кроссдоменные “json” запросы преобразуются в “jsonp”, если в параметрах запроса не указано jsonp: false. Данные JSON парсятся в строгом порядке и должны соответствовать общепринятому формату, любой некорректный JSON отвергается и выдается ошибка. С версии jQuery 1.9, пустой ответ не принимается, сервер должен вернуть в качестве ответа NULL, или {}.
-
“jsonp” – загружает данные в формате JSON, используя при этом формат загрузки JSONP. Добавляет дополнительный параметр “?callback=?” в конец URL адреса для указания имени функции обработчика. Отключает кэширование путем добавления параметра _=[TIMESTAMP] к URL адресу,даже если парамета cache имеет значение true.
-
“text” – обычная текстовая строка.
-
несколько значений – значения разделяются пробелом. Начиная с версии 1.5, jQuery может преобразовать тип данных, который получен в Content-Type заголовка, в тип данных, который вам требуется. Например, если вы хотите, чтобы текстовый ответ был расценен как XML, используйте “text XML” для этого типа данных. Вы также можете сделать JSONP запрос, получить его в виде текста и интерпретировать его в формате XML: “jsonp text XML”. Следующая строка позволит сделать тоже самое: “jsonp XML”, jQuery будет пытаться конвертировать из JSONP в XML, после неудачной попытки попытается преобразовать JSONP в текст, а затем из текста уже в XML.
-
-
error.Тип: Function( jqXHR jqXHR, String textStatus, String errorThrown ).Функция обратного вызова, которая вызывается если AJAX запрос не был выполнен. Функция получает три аргумента:
-
jqXHR – объект jqXHR (в jQuery 1.4.х, объект XMLHttpRequest).
-
textStatus – строка, описывающую тип ошибки, которая произошла. Возможные значения (кроме null) не “timeout”, “error”, “abort” и “parsererror”.
-
errorThrown – дополнительный объект исключения, если произошло. При возникновении ошибки HTTP аргумент получает текстовую часть состояния, например, “Not Found”, или “Internal Server Error”.Начиная с версии jQuery 1.5 допускается передавать в качестве значения параметра массив функций, при этом каждая функция будет вызвана в свою очедерь. Обратите внимание, что этот обработчик не вызывается для кроссдоменных скриптов и запросов JSONP.
-
-
global (по умолчанию: true).Тип: Boolean.Логический параметр, который определяет допускается ли вызвать глобальные обработчики событий AJAX для этого запроса. Значением по умолчанию является true. Если Вам необходимо предотвратить вызов глобальных обработчиков событий, таких как .ajaxStart(), или .ajaxStop(), то используйте значение false.
-
headers (по умолчанию: { }).Тип: PlainObject.Объект, который содержит пары ключ/значение дополнительных заголовков запроса, предназначенные для отправки вместе с запросом с использованием объекта XMLHttpRequest. Обращаю Ваше внимание, что заголовок X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest добавляется всегда, но значение XMLHttpRequest по умоланию допускается изменить с использованием этого параметра. Значения headers также могут быть переопределены параметром beforeSend. Добавлен в версии jQuery 1.5.
-
ifModified (по умолчанию: false).Тип: Boolean.По умолчанию значение false, игнорирует поля заголовка HTTP запроса, а при значении true AJAX запрос переводится в статус успешно (success), только в том случае, если ответ от сервера изменился с момента последнего запроса. Проверка производится путем проверки поля заголовка Last-Modified. Начиная с версии jQuery 1.4, помимо заголовка Last-Modified производится проверка и “etag” (entity tag) – это закрытый идентификатор, присвоенный веб-сервером на определенную версию ресурса, найденного на URL. Если содержание ресурса для этого адреса меняется на новое, назначается и новый etag.
-
isLocal (по умолчанию: зависит от текущего местоположения).Тип: Boolean.Используйте значение true для определения текущего окружения как “локального” (например, file:///url), даже если jQuery не распознает его таким по умоланию. Следующие протоколы в настоящее время признаются как локальные: file, *-extension и widget. Если Вам необходимо изменить параметр isLocal, то рекомендуется сделать это один раз при помощи функции $.ajaxSetup(). Добавлен в версии jQuery 1.5.1.
-
jsonpТип: Boolean, или String.Переопределяет имя функции обратного вызова в JSONP запросе. Это значение будет использоваться вместо “callback“ (“http://domain.ru/test.php?callback=?”) в составе части строки запроса в URL адресе. Например, значение {jsonp: “onLoad“} передастся на сервер в виде следующей строки запроса “http://domain/test.php?onLoad=?”.Начиная с версии jQuery 1.5 при установке значения параметра jsonp в значение false предотвращает добавление строки “?callback” к URL адресу, или попытки использовать “=?” для преобразования ответа. В этом случае Вы дополнительно должны указать значение параметра jsonpCallback. По соображениям безопасности, если Вы не доверяете цели ваших AJAX запросов, то рекомендуется установить значение параметра jsonp в значение false.
{
jsonp: false,
jsonpCallback: "callbackName"
}-
jsonpCallback.Тип: String, или Function.Задает имя функции обратного вызова для JSONP запроса. Это значение будет использоваться вместо случайного имени, которое автоматически генерируется и присваивается библиотекой jQuery. Рекомендуется, чтобы jQuery самостоятелно генерировало уникальное имя, это позволит легче управлять запросами и обрабатывать возможные ошибки. В некоторых случаях установка собственного имени функции позволит улучшить браузерное кеширование GET запросов.Начиная с версии jQuery 1.5, вы можете в качестве значения параметра jsonpCallback указать функцию. В этом случае, в значение параметра jsonpCallback должно быть установлено возвращаемое значение этой функцией.
-
method (по умолчанию: “GET”).Тип: String.Метод HTTP, используемый для запроса (например, “POST”, “GET”, “PUT”). Добавлен в версии jQuery 1.9.0.
-
mimeType.Тип: String.MIME тип, который переопределяет MIME тип, указанынй в объекте XHR по умолчанию. Добавлен в версии jQuery 1.5.1.
-
password.Тип: String.Пароль, который будет использован с XMLHttpRequest в ответе на запрос проверки подлинности доступа HTTP.
-
processData (по умолчанию: true).Тип: Boolean.По умолчанию данные, передаваемые в параметр data в качестве объекта будут обработаны и преобразованы в строку запроса, подходящую для типа данных по умолчанию “application/x-www-form-urlencoded”. Если Вам необходимо отправить DOMDocument, или другие не обработанные данные, то установите значение этого параметра в false.
-
scriptCharset.Тип: String.Устанавливает атрибут charset (кодировка символов) на HTML тег <script>, используемый в запросе. Используется, когда кодировка на странице отличается от кодировки удаленного скрипта. Обратите внимание, что параметр scriptCharset применяется только в кроссдоменных запросах с параметром type со значением “GET” (по умолчанию) и параметром dataType со значением “jsonp”, или “script”.
-
statusCode (по умолчанию: { }).Тип: PlainObject.Объект числовых кодов HTTP и функции, которые будут вызываться, когда код ответа сервера имеет соотвествующее значение (определенный код HTTP). Например, следующая функция будет вызвана, если от сервера получен код ответа 404, или “Not found” (стандартный код ответа HTTP о том, что клиент был в состоянии общаться с сервером, но сервер не может найти данные согласно запросу.)
$.ajax({
statusCode: {
404: function(){ // выполнить функцию если код ответа HTTP 404
alert( "страница не найдена" );
},
403: function(){ // выполнить функцию если код ответа HTTP 403
alert( "доступ запрещен" );
}
}
});-
success.Тип: Function( Anything data, String textStatus, jqXHR jqXHR ).Функция обратного вызова, которая вызывается если AJAX запрос выполнится успешно. Функции передаются три аргумента:
-
data – данные возвращенные с сервера. Данные форматируюся в соответствии с параметрами dataType, или dataFilter, если они указаны
-
textStatus – строка описывающая статус запроса.
-
jqXHR – объект jqXHR (до версии jQuery 1.4.x объект XMLHttpRequest).Начиная с версии jQuery 1.5 допускается передавать в качестве значения параметра массив функций, при этом каждая функция будет вызвана в свою очедерь.
-
-
timeout.Тип: Number.Устанавливает в миллисекундах таймаут для запроса. Значение 0 означает, что таймаут не установлен. Обращаю Ваше внимание, что этот параметр переопределяет значение таймаута, установленного с помощью функции $.ajaxSetup(). Таймаут ожидания начинается в момент вызова метода $.ajax().
-
traditional.Тип: Boolean.Если вы планируете использовать традиционные параметры сериализации (подходит для использования в строке URL запроса или запроса AJAX), то установите значение этого параметра в true.
-
type (по умолчанию: “GET”).Тип: String.Псевдоним (алиас) для параметра method. Вы должны использовать type, если вы используете версии jQuery до 1.9.0.
-
url (по умолчанию: текущая страница).Тип: String.Строка, содержащая URL адрес, на который отправляется запрос.
-
username.Тип: String.Имя пользователя, которое будет использовано с XMLHttpRequest в ответе на запрос проверки подлинности доступа HTTP.
-
xhr (по умолчанию: ActiveXObject, когда доступен (Internet Explorer), в других случаях XMLHttpRequest.Тип: Function().Обратный вызов для создания объекта XMLHttpRequest. С помощью этого параметра Вы можете переопределить объект XMLHttpRequest, чтобы обеспечить свою собственную реализацию.
-
xhrFields.Тип: PlainObject.Объект, содержащий пары имя_поля: значение_поля, которые будут установлены на объект XHR. Например, вы можете определить, должны ли создаваться кроссдоменные запросы с использованием таких идентификационных данных как cookie, авторизационные заголовки или TLS сертификаты
$.ajax({
url: "cross_domain_url", // адрес, на который будет отправлен запрос
xhrFields: {
withCredentials: true // поддерживается в jQuery 1.5.1 +
}
});Форма с отправкой файлов методом AJAX
Создаём форму с 2 текстовыми полями name и phone, и одним полем для передачи файла (fileImage)
HTML
<form id="feedBack" method="post" onsubmit="return false">
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="Имя">
<input type="tel" name="phone" placeholder="Телефон">
<input type="file" name="fileImage" accept=".jpg, .jpeg, .png" multiple="multiple">
<input type="submit" value="Отправить">
</form>
JQUERY
/* запускаем скрипт после полной загрузки документа /
$("document").ready(function() {
/ вешаем событие на ранее созданную форму /
$("#feedBack").on("submit", function() {
/ создаём объект с данными из полей /
let formData = new FormData(feedBack)
/ добавляем дополнительные данные для отправки */
formData.append("url_query", "prog-time");
/* записываем в переменную данные картинок из формы */
let allfiles = $(this).find('input[name="fileImage"]');
/* пробегаем покартинкам и записываем их в массив для отправки */
for(var i = 0; i < allfiles[0].files.length; i++){
formData.append("file_"+i, allfiles[0].files[i]);
}
/* отправляем AJAX запрос */
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: '/query.php',
contentType: false,
processData: false,
data: formData,
success: function(data){
console.log(data)
},
});
})
})11 PHP
/* ... прописываем необходимые проверки и обработки данных */
/* сохраняем картинки на сервере */
foreach(image["name"], $image["tmp_name"]);
}На этом всё!
Прокачивайте свои навыки на нашем канале.
AJAX позволяет отправить и получить данные без перезагрузки страницы. Например, делать проверку форм, подгружать контент и т.д. А функции JQuery значительно упрощают работу.
Полное описание функции AJAX на jquery.com.
1
GET запрос
Запрос идет на index.php с параметром «text» и значением «Текст» через метод GET.
По сути это то же самое что перейти в браузере по адресу – http://site.com/index.php?text=Текст
В результате запроса index.php вернет строку «Данные приняты – Текст», которая будет выведена в сообщении alert.
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php', /* Куда пойдет запрос */
method: 'get', /* Метод передачи (post или get) */
dataType: 'html', /* Тип данных в ответе (xml, json, script, html). */
data: {text: 'Текст'}, /* Параметры передаваемые в запросе. */
success: function(data){ /* функция которая будет выполнена после успешного запроса. */
alert(data); /* В переменной data содержится ответ от index.php. */
}
});JS
Код можно сократить используя функцию $.get
$.get('/index.php', {text: 'Текст'}, function(data){
alert(data);
});JS
Код файла index.php
echo 'Данные приняты - ' . $_GET['text'];PHP
GET запросы могут кэшироваться браузером или сервером, чтобы этого избежать нужно добавить в функцию параметр – cache: false.
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'get',
cache: false
});JS
2
POST запросы
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'post',
dataType: 'html',
data: {text: 'Текст'},
success: function(data){
alert(data);
}
});JS
Или сокращенная версия – функция $.post
$.post('/index.php', {text: 'Текст'}, function(data){
alert(data);
});JS
Код файла index.php
echo 'Данные приняты - ' . $_POST['text'];PHP
POST запросы ни когда не кэшироваться.
3
Отправка формы через AJAX
При отправке формы применяется функция serialize(), подробнее на jquery.com.
Она обходит форму и собирает названия и заполненные пользователем значения полей и возвращает в виде массива – {login: 'ЗНАЧЕНИЯ_ПОЛЯ', password: 'ЗНАЧЕНИЯ_ПОЛЯ'}.
Особенности serialize():
- Кнопки формы по которым был клик игнорируются, в результате функции их не будет.
- serialize можно применить только к тегу form и полям формы, т.е.
$('div.form_container').serialize();– вернет пустой результат.
Пример отправки и обработки формы:
<div class="form_container">
<div id="message"></div>
<form id="form">
<input type="text" name="login">
<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" name="send" value="Отправить">
</form>
</div>
<script>
$("#form").on("submit", function(){
$.ajax({
url: '/handler.php',
method: 'post',
dataType: 'html',
data: $(this).serialize(),
success: function(data){
$('#message').html(data);
}
});
});
</script>HTML
Код файла handler.php
if (empty($_POST['login'])) {
echo 'Укажите логин';
} elseif (empty($_POST['password'])) {
echo 'Укажите пароль';
} else {
echo 'Авторизация...';
}PHP
4
Работа с JSON
Идеальный вариант когда нужно работать с массивами данных.
$.ajax({
url: '/json.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'json',
success: function(data){
alert(data.text); /* выведет "Текст" */
alert(data.error); /* выведет "Ошибка" */
}
});JS
Короткая версия
$.getJSON('/json.php', function(data) {
alert(data.text);
alert(data.error);
});JS
$.getJSON передает запрос только через GET.
Код файла json.php
header('Content-Type: application/json');
$result = array(
'text' => 'Текст',
'error' => 'Ошибка'
);
echo json_encode($result);PHP
Возможные проблемы
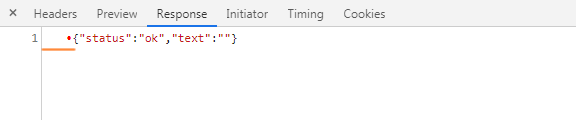
При работе с JSON может всплыть одна ошибка – после запроса сервер отдал результат, все хорошо, но метод success не срабатывает. Причина кроется в серверной части (PHP) т.к. перед данными могут появится управляющие символы, например:
Из-за них ответ считается не валидным и считается как ошибочный запрос.
В таких случаях помогает очистка буфера вывода ob_end_clean (если он используется на сайте).
...
// Очистка буфера
ob_end_clean();
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($result, JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE);
exit();PHP
5
Выполнение JS загруженного через AJAX
В JQuery реализована функция подгруздки кода JS через AJAX, после успешного запроса он будет сразу выполнен.
$.ajax({
method: 'get',
url: '/script.js',
dataType: "script"
});JS
Или
$.getScript('/script.js');JS
6
Дождаться выполнения AJAX запроса
По умолчанию в JQuery AJAX запросы выполняются асинхронно. Т.е. запрос не задерживает выполнение программы пока ждет результатов, а работает параллельно.
Простой пример:
var text = '';
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'html',
success: function(data){
text = data;
}
});
alert(text); /* Переменная будет пустая. */JS
Переменная text будет пустая, а не как ожидается текст который вернул index.php
Чтобы включить синхронный режим нужно добавить параметр async: false.
Соответственно синхронный запрос будет вешать прогрузку страницы если код выполняется в <head> страницы.
var text = '';
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'html',
async: false,
success: function(data){
text = data;
}
});
alert(text); /* В переменной будет результат из index.php. */JS
7
Отправка HTTP заголовков
Через AJAX можно отправить заголовки HEAD, они указываются в параметре headers.
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'html',
headers: {'Token_value': 123},
success: function(data){
console.dir(data);
}
});JS
В PHP они будут доступны в массиве $_SERVER, ключ массива переводится в верхний регистр с приставкой HTTP_, например:
<?php
echo $_SERVER['HTTP_TOKEN_VALUE']; // 123PHP
8
Обработка ошибок
Через параметр error задается callback-функция, которая будет вызвана в случаи если запрашиваемый ресурс отдал 404, 500 или другой код.
$.ajax({
url: '/index.php',
method: 'get',
dataType: 'json',
success: function(data){
console.dir(data);
},
error: function (jqXHR, exception) {
if (jqXHR.status === 0) {
alert('Not connect. Verify Network.');
} else if (jqXHR.status == 404) {
alert('Requested page not found (404).');
} else if (jqXHR.status == 500) {
alert('Internal Server Error (500).');
} else if (exception === 'parsererror') {
alert('Requested JSON parse failed.');
} else if (exception === 'timeout') {
alert('Time out error.');
} else if (exception === 'abort') {
alert('Ajax request aborted.');
} else {
alert('Uncaught Error. ' + jqXHR.responseText);
}
}
});JS
Через $.ajaxSetup можно задать обработчик ошибок для всех AJAX-запросов на сайте.
$.ajaxSetup({
error: function (jqXHR, exception) {
...
}
});JS
In this article I will explain how to handle errors and exceptions in jQuery AJAX calls and show (display) Custom Exception messages using jQuery Dialog.
There are two types of Exceptions which is caught by jQuery
1. When exception object is in the form of JSON object.
2. When exception object is in the form of plain text or HTML.
I will explain both the types with detailed explanation and also how to display the exception error details in both the cases.
WebMethod for testing both types
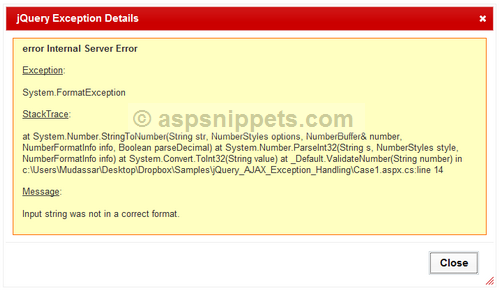
In order to test both the cases I have created the following WebMethod which simply tries to convert the received string value to integer.
[System.Web.Services.WebMethod]
public static void ValidateNumber(string number)
{
int no = Convert.ToInt32(number);
}
1. When exception object is in the form of JSON object
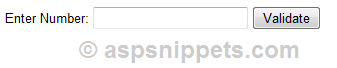
In the following HTML Markup, I have created a simple form with a TextBox and a Button which prompts user to enter a Numeric value.
The value entered is passed to the WebMethod using a jQuery AJAX call where it is converts string value to integer.
If it is a valid number then an alert message is displayed inside the jQuery AJAX Success event handler and if an exception occurs in the WebMethod, the thrown exception is caught inside the jQuery AJAX Error event handler and which makes a call to the OnError JavaScript function which processes and displays the exception details.
<html xmlns=»http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml»>
<head runat=»server»>
<title></title>
<style type=»text/css»>
body { font-family: Arial; font-size: 10pt; }
#dialog { height: 600px; overflow: auto; font-size: 10pt !important; font-weight: normal !important; background-color: #FFFFC1; margin: 10px; border: 1px solid #ff6a00; }
#dialog div { margin-bottom: 15px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id=»form1″ runat=»server»>
<u>1: When exception object is in the form of JSON object</u>
<br/>
<br/>
Enter Number:
<input id=»txtNumber1″ type=»text»/>
<input id=»btnValidate1″ type=»button» value=»Validate»/>
<div id=»dialog» style=»display: none»></div>
<script type=»text/javascript» src=»http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.2/jquery.min.js»></script>
<script src=»http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery.ui/1.8.9/jquery-ui.js» type=»text/javascript»></script>
<link href=»http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery.ui/1.8.9/themes/blitzer/jquery-ui.css»
rel=»stylesheet» type=»text/css»/>
<script type=»text/javascript»>
$(function () {
$(«#btnValidate1»).click(function () {
var number = $(«#txtNumber1»).val();
$.ajax({
type: «POST»,
url: » Default.aspx/ValidateNumber»,
data: ‘{number: «‘ + number + ‘»}’,
contentType: «application/json; charset=utf-8»,
dataType: «json»,
success: function (r) {
alert(«Valid number.»);
},
error: OnError
});
});
});
function OnError(xhr, errorType, exception) {
var responseText;
$(«#dialog»).html(«»);
try {
responseText = jQuery.parseJSON(xhr.responseText);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><b>» + errorType + » « + exception + «</b></div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>Exception</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.ExceptionType + «</div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>StackTrace</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.StackTrace + «</div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>Message</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.Message + «</div>»);
} catch (e) {
responseText = xhr.responseText;
$(«#dialog»).html(responseText);
}
$(«#dialog»).dialog({
title: «jQuery Exception Details»,
width: 700,
buttons: {
Close: function () {
$(this).dialog(‘close’);
}
}
});
}
</script>
</form>
</body>
</html>
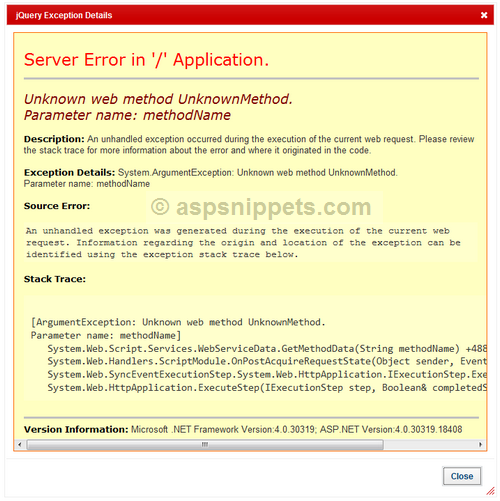
2. When exception object is in the form of HTML or plain text
The second case is similar to the first one. In order to receive a Non-JSON response I have just set incorrect WebMethod name in the jQuery AJAX so that it generates an error.
<html xmlns=»http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml»>
<head runat=»server»>
<title></title>
<style type=»text/css»>
body { font-family: Arial; font-size: 10pt; }
#dialog { height: 600px; overflow: auto; font-size: 10pt! important; font-weight: normal !important; background-color: #FFFFC1; margin: 10px; border: 1px solid #ff6a00; }
#dialog div { margin-bottom: 15px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id=»form1″ runat=»server»>
<u>2: When exception object is in the form of HTML or plain text</u>
<br/>
<br/>
Enter Number:
<inputi d=»txtNumber2″ type=»text»/>
<input id=»btnValidate2″ type=»button» value=»Validate»/>
<div id=»dialog» style=»display: none»></div>
<script type=»text/javascript» src=»http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.2/jquery.min.js»></script>
<script src=»http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery.ui/1.8.9/jquery-ui.js» type=»text/javascript»></script>
<link href=»http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery.ui/1.8.9/themes/blitzer/jquery-ui.css»
rel=»stylesheet» type=»text/css»/>
<script type=»text/javascript»>
$(function () {
$(«#btnValidate2»).click(function () {
var number = $(«#txtNumber2»).val();
$.ajax({
type: «POST»,
url: «Default.aspx/UnknownMethod»,
data: ‘{number: «‘ + number + ‘»}’,
contentType: «application/json; charset=utf-8»,
dataType: «json»,
success: function (r) {
alert(«Valid number.»);
},
error: OnError
});
});
});
function OnError(xhr, errorType, exception) {
var responseText;
$(«#dialog»).html(«»);
try {
responseText = jQuery.parseJSON(xhr.responseText);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><b>» + errorType + » « + exception + «</b></div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>Exception</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.ExceptionType + «</div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>StackTrace</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.StackTrace + «</div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>Message</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.Message + «</div>»);
} catch (e) {
responseText = xhr.responseText;
$(«#dialog»).html(responseText);
}
$(«#dialog»).dialog({
title: «jQuery Exception Details»,
width: 700,
buttons: {
Close: function () {
$(this).dialog(‘close’);
}
}
});
}
</script>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Parsing the received Exception response using jQuery
Here I am explaining the details of the OnError JavaScript function which is called by the Error event handler in both the above case.
This function accepts the following three parameters
xhr – It is the error response object.
errorType – It describes the type of error.
exception – It contains the title of the exception occurred.
Inside this function, I have placed a TRY CATCH block and within the TRY block, the Exception received is parsed to a JSON object and then the details of the exception are displayed using jQuery Dialog Modal Popup.
If an error occurs during the process of parsing the JSON string, it means it is a Non-JSON response i.e. HTML or plain text and then it is handled inside the CATCH block where I am displaying the exception directly without any processing.
function OnError(xhr, errorType, exception) {
var responseText;
$(«#dialog»).html(«»);
try {
responseText = jQuery.parseJSON(xhr.responseText);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><b>» + errorType + » « + exception + «</b></div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>Exception</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.ExceptionType + «</div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>StackTrace</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.StackTrace + «</div>»);
$(«#dialog»).append(«<div><u>Message</u>:<br /><br />» + responseText.Message + «</div>»);
} catch (e) {
responseText = xhr.responseText;
$(«#dialog»).html(responseText);
}
$(«#dialog»).dialog({
title: «jQuery Exception Details»,
width: 700,
buttons: {
Close: function () {
$(this).dialog(‘close’);
}
}
});
}
Demo
Downloads