The behaviour of these functions is affected by settings in php.ini.
| Name | Default | Changeable | Changelog |
|---|---|---|---|
| error_reporting | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_startup_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL |
Prior to PHP 8.0.0, the default value was "0".
|
| log_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| log_errors_max_len | «1024» | PHP_INI_ALL | Had no effect as of PHP 8.0.0, removed as of PHP 8.1.0. |
| ignore_repeated_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| ignore_repeated_source | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| report_memleaks | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| track_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | Deprecated as of PHP 7.2.0, removed as of PHP 8.0.0. |
| html_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| xmlrpc_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | |
| xmlrpc_error_number | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_root | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_ext | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_prepend_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_append_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log_mode | 0o644 | PHP_INI_ALL | Available as of PHP 8.2.0 |
| syslog.facility | «LOG_USER» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Available as of PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.filter | «no-ctrl» | PHP_INI_ALL | Available as of PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.ident | «php» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Available as of PHP 7.3.0. |
For further details and definitions of the
PHP_INI_* modes, see the Where a configuration setting may be set.
Here’s a short explanation of
the configuration directives.
-
error_reporting
int -
Set the error reporting level. The parameter is either an integer
representing a bit field, or named constants. The error_reporting
levels and constants are described in
Predefined Constants,
and in php.ini. To set at runtime, use the
error_reporting() function. See also the
display_errors directive.The default value is
E_ALL.Prior to PHP 8.0.0, the default value was:
E_ALL&
~E_NOTICE&
~E_STRICT&
~E_DEPRECATED
This means diagnostics of levelE_NOTICE,
E_STRICTandE_DEPRECATED
were not shown.Note:
PHP Constants outside of PHPUsing PHP Constants outside of PHP, like in httpd.conf,
will have no useful meaning so in such cases the int values
are required. And since error levels will be added over time, the maximum
value (forE_ALL) will likely change. So in place of
E_ALLconsider using a larger value to cover all bit
fields from now and well into the future, a numeric value like
2147483647(includes all errors, not just
E_ALL). -
display_errors
string -
This determines whether errors should be printed to the screen
as part of the output or if they should be hidden from the user.Value
"stderr"sends the errors tostderr
instead ofstdout.Note:
This is a feature to support your development and should never be used
on production systems (e.g. systems connected to the internet).Note:
Although display_errors may be set at runtime (with ini_set()),
it won’t have any effect if the script has fatal errors.
This is because the desired runtime action does not get executed. -
display_startup_errors
bool -
Even when display_errors is on, errors that occur during PHP’s startup
sequence are not displayed. It’s strongly recommended to keep
display_startup_errors off, except for debugging. -
log_errors
bool -
Tells whether script error messages should be logged to the
server’s error log or error_log.
This option is thus server-specific.Note:
You’re strongly advised to use error logging in place of
error displaying on production web sites. -
log_errors_max_len
int -
Set the maximum length of log_errors in bytes. In
error_log information about
the source is added. The default is 1024 and 0 allows to not apply
any maximum length at all.
This length is applied to logged errors, displayed errors and also to
$php_errormsg, but not to explicitly called functions
such as error_log().When an int is used, the
value is measured in bytes. Shorthand notation, as described
in this FAQ, may also be used.
-
ignore_repeated_errors
bool -
Do not log repeated messages. Repeated errors must occur in the same
file on the same line unless
ignore_repeated_source
is set true. -
ignore_repeated_source
bool -
Ignore source of message when ignoring repeated messages. When this setting
is On you will not log errors with repeated messages from different files or
sourcelines. -
report_memleaks
bool -
If this parameter is set to On (the default), this parameter will show a
report of memory leaks detected by the Zend memory manager. This report
will be sent to stderr on Posix platforms. On Windows, it will be sent
to the debugger using OutputDebugString() and can be viewed with tools
like » DbgView.
This parameter only has effect in a debug build and if
error_reporting includesE_WARNINGin the allowed
list. -
track_errors
bool -
If enabled, the last error message will always be present in the
variable $php_errormsg. -
html_errors
bool -
If enabled, error messages will include HTML tags. The format for HTML
errors produces clickable messages that direct the user to a page
describing the error or function in causing the error. These references
are affected by
docref_root and
docref_ext.If disabled, error message will be solely plain text.
-
xmlrpc_errors
bool -
If enabled, turns off normal error reporting and formats errors as
XML-RPC error message. -
xmlrpc_error_number
int -
Used as the value of the XML-RPC faultCode element.
-
docref_root
string -
The new error format contains a reference to a page describing the error or
function causing the error. In case of manual pages you can download the
manual in your language and set this ini directive to the URL of your local
copy. If your local copy of the manual can be reached by"/manual/"
you can simply usedocref_root=/manual/. Additional you have
to set docref_ext to match the fileextensions of your copy
docref_ext=.html. It is possible to use external
references. For example you can use
docref_root=http://manual/en/or
docref_root="http://landonize.it/?how=url&theme=classic&filter=Landon
&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.php.net%2F"Most of the time you want the docref_root value to end with a slash
"/".
But see the second example above which does not have nor need it.Note:
This is a feature to support your development since it makes it easy to
lookup a function description. However it should never be used on
production systems (e.g. systems connected to the internet). -
docref_ext
string -
See docref_root.
Note:
The value of docref_ext must begin with a dot
".". -
error_prepend_string
string -
String to output before an error message.
Only used when the error message is displayed on screen. The main purpose
is to be able to prepend additional HTML markup to the error message. -
error_append_string
string -
String to output after an error message.
Only used when the error message is displayed on screen. The main purpose
is to be able to append additional HTML markup to the error message. -
error_log
string -
Name of the file where script errors should be logged. The file should
be writable by the web server’s user. If the
special valuesyslogis used, the errors
are sent to the system logger instead. On Unix, this means
syslog(3) and on Windows it means the event log. See also:
syslog().
If this directive is not set, errors are sent to the SAPI error logger.
For example, it is an error log in Apache orstderr
in CLI.
See also error_log(). -
error_log_mode
int -
File mode for the file described set in
error_log. -
syslog.facility
string -
Specifies what type of program is logging the message.
Only effective if error_log is set to «syslog». -
syslog.filter
string -
Specifies the filter type to filter the logged messages. Allowed
characters are passed unmodified; all others are written in their
hexadecimal representation prefixed withx.-
all– the logged string will be split
at newline characters, and all characters are passed unaltered
-
ascii– the logged string will be split
at newline characters, and any non-printable 7-bit ASCII characters will be escaped
-
no-ctrl– the logged string will be split
at newline characters, and any non-printable characters will be escaped
-
raw– all characters are passed to the system
logger unaltered, without splitting at newlines (identical to PHP before 7.3)
This setting will affect logging via error_log set to «syslog» and calls to syslog().
Note:
The
rawfilter type is available as of PHP 7.3.8 and PHP 7.4.0.
This directive is not supported on Windows.
-
-
syslog.ident
string -
Specifies the ident string which is prepended to every message.
Only effective if error_log is set to «syslog».
cjakeman at bcs dot org ¶
14 years ago
Using
<?php ini_set('display_errors', 1); ?>
at the top of your script will not catch any parse errors. A missing ")" or ";" will still lead to a blank page.
This is because the entire script is parsed before any of it is executed. If you are unable to change php.ini and set
display_errors On
then there is a possible solution suggested under error_reporting:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("display_errors", 1);
include("file_with_errors.php");
?>
[Modified by moderator]
You should also consider setting error_reporting = -1 in your php.ini and display_errors = On if you are in development mode to see all fatal/parse errors or set error_log to your desired file to log errors instead of display_errors in production (this requires log_errors to be turned on).
ohcc at 163 dot com ¶
6 years ago
If you set the error_log directive to a relative path, it is a path relative to the document root rather than php's containing folder.
iio7 at protonmail dot com ¶
1 year ago
It's important to note that when display_errors is "on", PHP will send a HTTP 200 OK status code even when there is an error. This is not a mistake or a wrong behavior, but is because you're asking PHP to output normal HTML, i.e. the error message, to the browser.
When display_errors is set to "off", PHP will send a HTTP 500 Internal Server Error, and let the web server handle it from there. If the web server is setup to intercept FastCGI errors (in case of NGINX), it will display the 500 error page it has setup. If the web server cannot intercept FastCGI errors, or it isn't setup to do it, an empty screen will be displayed in the browser (the famous white screen of death).
If you need a custom error page but cannot intercept PHP errors on the web server you're using, you can use PHPs custom error and exception handling mechanism. If you combine that with output buffering you can prevent any output to reach the client before the error/exception occurs. Just remember that parse errors are compile time errors that cannot be handled by a custom handler, use "php -l foo.php" from the terminal to check for parse errors before putting your files on production.
Roger ¶
3 years ago
When `error_log` is set to a file path, log messages will automatically be prefixed with timestamp [DD-MMM-YYYY HH:MM:SS UTC]. This appears to be hard-coded, with no formatting options.
php dot net at sp-in dot dk ¶
8 years ago
There does not appear to be a way to set a tag / ident / program for log entries in the ini file when using error_log=syslog. When I test locally, "apache2" is used.
However, calling openlog() with an ident parameter early in your script (or using an auto_prepend_file) will make PHP use that value for all subsequent log entries. closelog() will restore the original tag.
This can be done for setting facility as well, although the original value does not seem to be restored by closelog().
jaymore at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
Document says
So in place of E_ALL consider using a larger value to cover all bit fields from now and well into the future, a numeric value like 2147483647 (includes all errors, not just E_ALL).
But it is better to set "-1" as the E_ALL value.
For example, in httpd.conf or .htaccess, use
php_value error_reporting -1
to report all kind of error without be worried by the PHP version.
Когда на сервере не работает один из сайтов — причины следует искать в программном коде, прежде всего следует изучить лог ошибок РНР (актуально для большинства сайтов, РНР является самым популярным языком веб-программирования). В рамках материала рассмотрено как включить лог ошибок php.
Включение лога ошибок PHP в php.ini
Все параметры РНР — в том числе, версия — задаются в файле php.ini, в нем же включается ведение лога программных ошибок. Если для сервера используется какая-либо панель управления — логирование можно включить в ней, если настройки сделаны вручную, то и ведение лога нужно включать вручную.
Делается это следующим образом:
display_errors = Off
log_errors = On
error_log = /var/log/php-errors.log
При активации display_errors ошибки будут выводится на экран, в директиве error_log задается путь к файлу, в который будет писаться информация необходимая для отладки проекта.
Затем нужно создать файл php-errors.log, на него необходимо выставить права позволяющие веб-серверу записывать в файл данные. В Debian подобных системах Apache работает от имени системного пользователя www-data
touch /var/log/php-errors.log
chown www-data: /var/log/php-errors.log
Затем нужно перезапустить веб-сервер, для Debian/Ubuntu
systemctl reload apache2
Для Centos
systemctl reload httpd
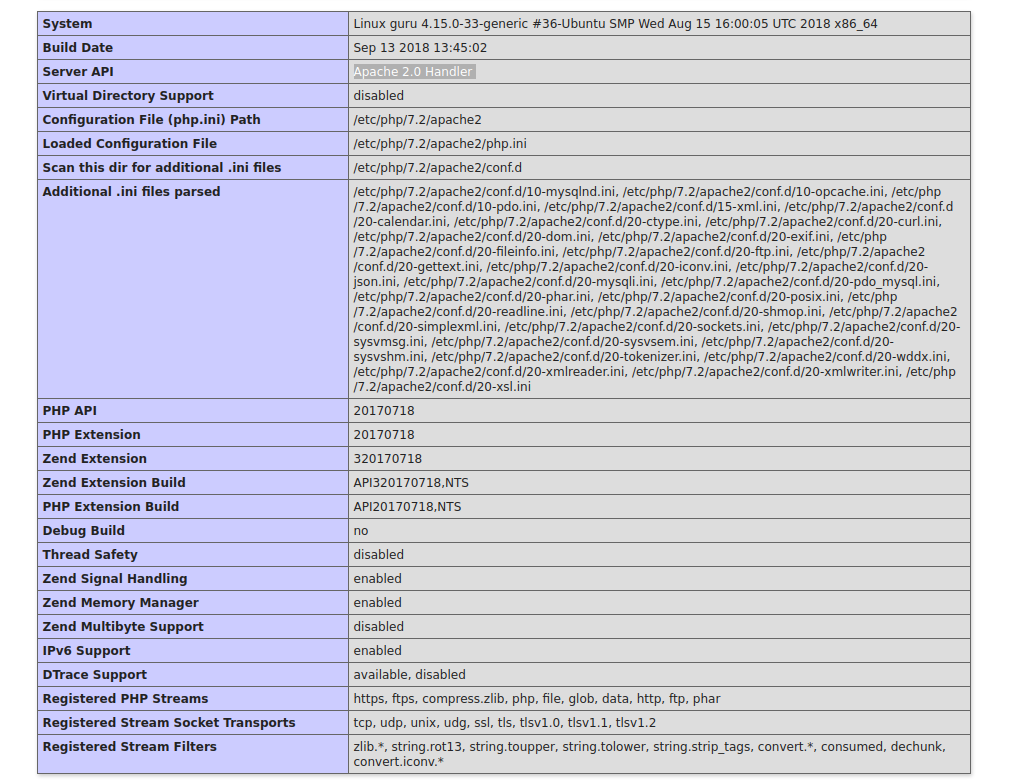
Получилось или нет можно увидеть в phpinfo. Там же можно посмотреть режим работы РНР (если это Apache Handler, то есть еще один способ включения лога, об этом ниже).
Как узнать еще режим работы PHP и текущее значение параметра error_log
Можно создать в корне сайта, работающего с сервера файл phpinfo и поместить в него одну функцию
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
И обратиться к файлу из браузера
http://sitename.com/phpinfo.php
Если применяются редиректы может потребоваться временно переименовать файл .htaccess в корне сайта.
В выводе phpinfo.php можно будет увидеть всю информацию о существующих настройках РНР
Режим работы РНР в примере Apache 2.0 Handler — РНР работает в режиме модуля веб-сервера.
Значение error_log отсутствует, значит в данной конфигурации логирование на уровне конфигурации сервера не включено.
Описанный выше порядок действий позволит включить логирование ошибок РНР при любом режиме работы РНР. При отладке работы сайта при конфигурации с mod-apache следует также проверять логи веб-сервера.
Вся информация будет в них, логи нужно искать в /var/log/apache2 и /var/log/httpd в зависимости от дистрибутива. Лог можно найти выполнив
grep -rl sitename.com /etc/apache
grep -i log файл_из_вывода_предыдущей_команды | grep log
Как включить лог ошибок php в .htacccess при использовании Apache с mod_php
При использовании Apache с mod_php есть альтернативный вариант не требующий редактирования php.ini.
В .htaccess в корне сайта добавляется:
php_flag log_errors On
php_value error_log /var/log/php-errors.log
Выключается логирование установкой основной опции в Off
php_flag log_errors Off
Плюс такого способа в том, что его можно использовать на серверах где нет root доступа. Настройки будут применяться не ко всему серверу, а только к сайту в корне которого добавлен .htaccess.
С fast_cgi директива php_flag работать не будет — возникнет ошибка 500.
Читайте про ошибку 500 и ее причины. Очень часто она появляется как следствие неверной отработки скриптов или настроек сервера не удовлетворяющим требованиям программного кода сайта.
here’s my log function:
You can edit the log rows by editing $maxLogs=5,
also the order to write your logs $logOrder='top'
<?php
lg('script start','start');
#Code......
lg('script end','End of code');
function lg($str,$mod='Your Log Category'){
$ts = microtime(true);
if(!defined('logTimer')){
define('logTimer',microtime(true));
}
$diff=abs(round(($ts-logTimer)*1000,2));
$maxLogs=5;
$logOrder='top';#new Logs at top
$filename = './log.txt';
$log=[];
if(!file_exists($filename)){
if(!file_put_contents($filename,json_encode($log,128))){
echo "Can’t open to write '$filename' Check Permissions";
return;
}
}else{
$c=file_get_contents($filename);
if(trim($c)==''){$c='[]';}
$log =@json_decode($c,true);
if(!is_Array($log)){$log=[];}
}
$new=['mod'=>$mod,'date'=> date('Y-m-d H:i:s')." Scripttime: ".$diff."ms",'log'=>$str];
if($logOrder=='top'){
array_unshift($log , $new);
$log=array_slice($log,0,$maxLogs);
}else{
$log[]=$new;
$log=array_slice($log,0-$maxLogs,$maxLogs);
}
$logs=json_encode($log,128);
if(!file_put_contents($filename,$logs) ){echo ("Can’t open to write '$filename' Check Permissions") ;return;}
return $str;
}
?>
The Output looks like:
[
{
"mod": "delete",
"date": "2022-08-04 13:48:02 0.33ms",
"log": "test 2"
},
{
"mod": "start",
"date": "2022-08-04 13:48:29 0ms",
"log": "test"
},
{
"mod": "delete",
"date": "2022-08-04 13:48:29 0.27ms",
"log": "test 2"
},
{
"mod": "start",
"date": "2022-08-04 13:48:34 0ms",
"log": "test"
},
{
"mod": "delete",
"date": "2022-08-04 13:48:34 0.92ms",
"log": "test 2"
}
]
Хостинг-провайдеры нередко отключают или блокируют вывод всех ошибок и предупреждений. Такие ограничения вводятся не просто так. Дело в том, что на рабочих серверах крайне не рекомендуется держать ошибки в открытом доступе. Информация о неисправностях может стать «наживкой» для злоумышленников.
При этом в процессе разработки сайтов и скриптов, очень важно отслеживать возникающие предупреждения. Знать о сбоях и неисправностях также важно и системным администраторам — это позволяет предотвратить проблемы на сайте или сервере.
Самый оптимальный вариант — не просто скрыть показ ошибок, но и настроить запись о них в логах. Это позволит отслеживать предупреждения и не подвергать сервер угрозе.
В статье мы расскажем, как включить и отключить через .htaccess вывод ошибок php, а также двумя другими способами — через скрипт PHP и через файл php.ini.
Обратите внимание: в некоторых случаях изменение настроек вывода возможно только через обращение в техническую поддержку хостинга.
Через .htaccess
Перейдите в каталог сайта и откройте файл .htaccess.
Вариант 1. Чтобы включить вывод, добавьте следующие строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors onЧтобы отключить ошибки PHP htaccess, введите команду:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors offТакже выключить .htaccess display errors можно командой:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
php_value docref_root 0
php_value docref_ext 0Через логи PHP
Если вам нужно проверить или выключить ошибки только в определенных файлах, это можно сделать с помощью вызова PHP-функций.
Вариант 1. Чтобы включить вывод, используйте команду error_reporting. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
А для всех типов, исключая тип Notice, так:
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)Чтобы отключить вывод, введите команду:
Чтобы отключить логирование повторяющихся ошибок, введите:
# disable repeated error logging
php_flag ignore_repeated_errors on
php_flag ignore_repeated_source onВариант 2. Чтобы проверить конкретный кусок кода, подойдет команда ниже. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, в скобках подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
ini_set('display_errors', 'On')
error_reporting(E_ALL)После этого в консоли введите:
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off')Вариант 3. Ещё один из вариантов подключения через скрипт:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors onДля отключения укажите:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors offВариант 4. Чтобы настроить вывод с логированием через конфигурацию веб-сервера, введите:
- для Apache —
ErrorLog «/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log», - для Nginx —
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log.
Подробнее о других аргументах читайте в документации на официальном сайте php.net.
Через файл php.ini
Настроить отслеживание также можно через файл php.ini. Этот вариант подойдет, когда отображение или скрытие ошибок нужно настроить для всего сайта или кода. Обратите внимание: возможность настройки через файл php.ini есть не у всех, поскольку некоторые хостинг-провайдеры частично или полностью закрывают доступ к файлу.
Вариант 1. Если у вас есть доступ, включить вывод можно командой:
После этого нужно перезагрузить сервер:
sudo apachectl -k gracefulВариант 2. Чтобы включить вывод, используйте команду error_reporting. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, после знака = подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors OnПосле ввода перезагрузите сервер:
sudo apachectl -k gracefulЧтобы скрыть отображение, во второй строке команды укажите Оff вместо On:
Теперь вы знаете, как настроить не только через PHP и php.ini, но и через htaccess отображение ошибок.
В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Как быстро показать все ошибки PHP
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.