Содержание
Составили подробный классификатор кодов состояния HTTP. Добавляйте в закладки, чтобы был под рукой, когда понадобится.
Что такое код ответа HTTP
Когда посетитель переходит по ссылке на сайт или вбивает её в поисковую строку вручную, отправляется запрос на сервер. Сервер обрабатывает этот запрос и выдаёт ответ — трехзначный цифровой код HTTP от 100 до 510. По коду ответа можно понять реакцию сервера на запрос.
Первая цифра в ответе обозначает класс состояния, другие две — причину, по которой мог появиться такой ответ.
Как проверить код состояния страницы
Проверить коды ответа сервера можно вручную с помощью браузера и в панелях веб‑мастеров: Яндекс.Вебмастер и Google Search Console.
В браузере
Для примера возьмём Google Chrome.
-
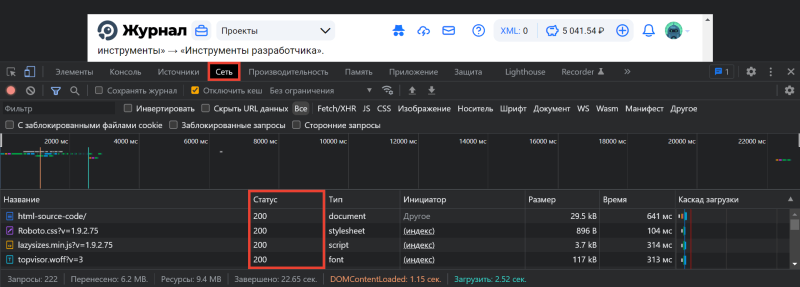
Откройте панель разработчика в браузере клавишей F12, комбинацией клавиш Ctrl + Shift + I или в меню браузера → «Дополнительные инструменты» → «Инструменты разработчика». Подробнее об этом рассказывали в статье «Как открыть исходный код страницы».
-
Переключитесь на вкладку «Сеть» в Инструментах разработчика и обновите страницу:
В Яндекс.Вебмастере
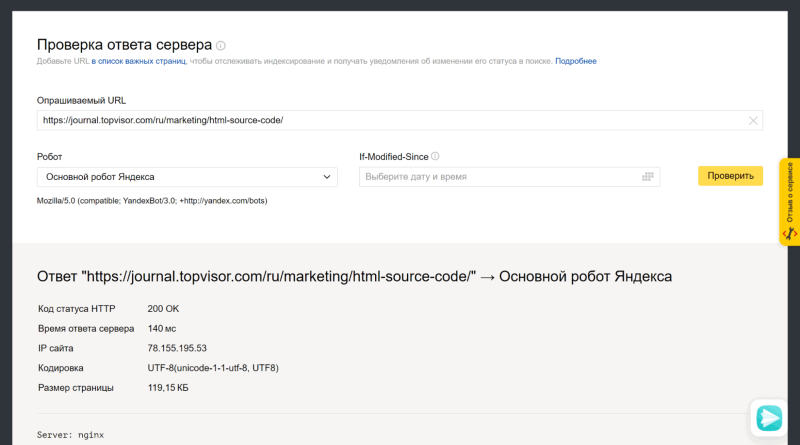
Откройте инструмент «Проверка ответа сервера» в Вебмастере. Введите URL в специальное поле и нажмите кнопку «Проверить»:
Как добавить сайт в Яндекс.Вебмастер и другие сервисы Яндекса
В Google Search Console
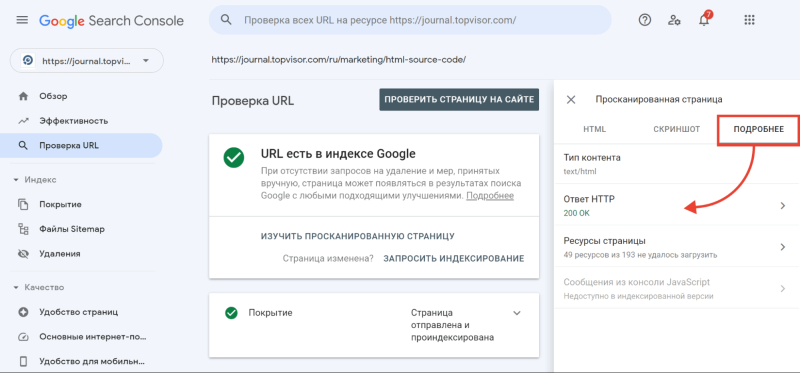
Чтобы посмотреть код ответа сервера в GSC, перейдите в инструмент проверки URL — он находится в самом верху панели:
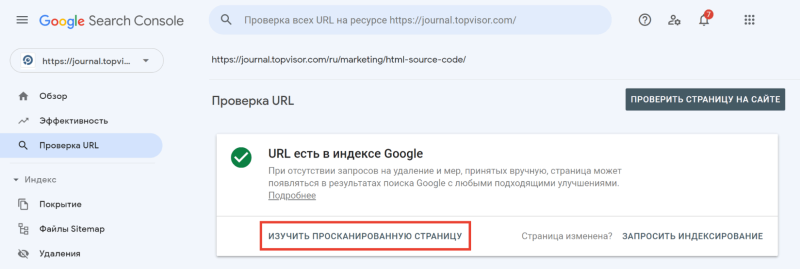
Введите ссылку на страницу, которую хотите проверить, и нажмите Enter. В результатах проверки нажмите на «Изучить просканированную страницу» в блоке «URL есть в индексе Google».
А затем в открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Подробнее»:
Теперь расскажем подробнее про все классы кодов состояния HTTP.
1* класс кодов (информационные сообщения)
Это системный класс кодов, который только информирует о процессе передачи запроса. Такие ответы не являются ошибкой, хотя и могут отображаться в браузере как Error Code.
100 Continue
Этот ответ сообщает, что полученные сведения о запросе устраивают сервер и клиент может продолжать отправлять данные. Такой ответ может требоваться клиенту, если на сервер отправляется большой объём данных.
101 Switching Protocols
Сервер одобрил переключение типа протокола, которое запросил пользователь, и в настоящий момент выполняет действие.
102 Processing
Запрос принят — он находится в обработке, и на это понадобится чуть больше времени.
103 Checkpoint
Контрольная точка — используется в запросах для возобновления после прерывания запросов POST или PUT.
POST отправляет данные на сервер, PUT создает новый ресурс или заменяет существующий данными, представленными в теле запроса.
Разница между ними в том, что PUT работает без изменений: повторное его применение даёт такой же результат, что и в первый раз, а вот повторный вызов одного и того же метода POST часто меняет данные.
Пример — оформленный несколько раз интернет‑заказ. Такое часто происходит как раз по причине неоднократного использования запроса PUT.
105 Name Not Resolved
Не удается преобразовать DNS‑адрес сервера — это означает ошибку в службе DNS. Эта служба преобразует IP‑адреса в знакомые нам доменные имена.
2* класс кодов (успешно обработанные запросы)
Эти коды информируют об успешности принятия и обработки запроса. Также сервер может передать заголовки или тело сообщений.
200 ОК
Все хорошо — HTTP‑запрос успешно обработан (не ошибка).
201 Created
Создано — транзакция успешна, сформирован новый ресурс или документ.
202 Accepted
Принято — запрос принят, но ещё не обработан.
203 Non‑Authoritative Information
Информация не авторитетна — запрос успешно обработан, но передаваемая информация была взята не из первичного источника (данные могут быть устаревшими).
204 No Content
Нет содержимого — запрос успешно обработан, однако в ответе только заголовки без контента сообщения. Не нужно обновлять содержимое документа, но можно применить к нему полученные метаданные.
205 Reset Content
Сбросить содержимое. Запрос успешно обработан — но нужно сбросить введенные данные. Страницу можно не обновлять.
206 Partial Content
Частичное содержимое. Сервер успешно обработал часть GET‑запроса, а другую часть вернул.
GET — метод для чтения данных с сайта. Он говорит серверу, что клиент хочет прочитать какой‑то документ.
Представим интернет‑магазин и страницы каталога. Фильтры, которые выбирает пользователь, передаются благодаря методу GET. GET‑запрос работает с получением данных, а POST‑запрос нужен для отправки данных.
При работе с подобными ответами следует уделить внимание кэшированию.
207 Multi‑Status
Успешно выполнено несколько операций — сервер передал результаты выполнения нескольких независимых операций. Они появятся в виде XML‑документа с объектом multistatus.
226 IM Used
Успешно обработан IM‑заголовок (специальный заголовок, который отправляется клиентом и используется для передачи состояния HTTP).
3* класс кодов (перенаправление на другой адрес)
Эти коды информируют, что для достижения успешной операции нужно будет сделать другой запрос, возможно, по другому URL.
300 Multiple Choices
Множественный выбор — сервер выдает список нескольких возможных вариантов перенаправления (максимум — 5). Можно выбрать один из них.
301 Moved Permanently
Окончательно перемещено — страница перемещена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
302 Found/Moved
Временно перемещено — страница временно перенесена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
303 See Other
Ищите другую страницу — страница не найдена по данному URL, поэтому смотрите страницу по другому URL, используя метод GET.
304 Not Modified
Модификаций не было — с момента последнего визита клиента изменений не было.
305 Use Proxy
Используйте прокси — запрос к нужному ресурсу можно сделать только через прокси‑сервер, URL которого указан в поле Location заголовка.
306 Unused
Зарезервировано. Код в настоящий момент не используется.
307 Temporary Redirect
Временное перенаправление — запрашиваемый ресурс временно доступен по другому URL.
Этот код имеет ту же семантику, что код ответа 302 Found, за исключением того, что агент пользователя не должен изменять используемый метод HTTP: если в первом запросе использовался POST, то во втором запросе также должен использоваться POST.
308 Resume Incomplete
Перемещено полностью (навсегда) — запрашиваемая страница была перенесена на новый URL, указанный в поле Location заголовка. Метод запроса (GET/POST) менять не разрешается.
4* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне клиента)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны клиентов.
400 Bad Request
Неверный запрос — запрос клиента не может быть обработан, так как есть синтаксическая ошибка (возможно, опечатка).
401 Unauthorized
Не пройдена авторизация — запрос ещё в обработке, но доступа нет, так как пользователь не авторизован.
Для доступа к запрашиваемому ресурсу клиент должен представиться, послав запрос, включив при этом в заголовок сообщения поле Authorization.
402 Payment Required
Требуется оплата — зарезервировано для использования в будущем. Код предусмотрен для платных пользовательских сервисов, а не для хостинговых компаний.
403 Forbidden
Запрещено — запрос принят, но не будет обработан, так как у клиента недостаточно прав. Может возникнуть, когда пользователь хочет открыть системные файлы (robots, htaccess) или не прошёл авторизацию.
404 Not Found
Не найдено — запрашиваемая страница не обнаружена. Сервер принял запрос, но не нашёл ресурса по указанному URL (возможно, была ошибка в URL или страница была перемещена).
405 Method Not Allowed
Метод не разрешён — запрос был сделан методом, который не поддерживается данным ресурсом. Сервер должен предложить доступные методы решения в заголовке Allow.
406 Not Acceptable
Некорректный запрос — неподдерживаемый поисковиком формат запроса (поисковый робот не поддерживает кодировку или язык).
407 Proxy Authentication Required
Нужно пройти аутентификацию прокси — ответ аналогичен коду 401, только нужно аутентифицировать прокси‑сервер.
408 Request Timeout
Тайм‑аут запроса — запрос клиента занял слишком много времени. На каждом сайте существует свое время тайм‑аута — проверьте интернет‑соединение и просто обновите страницу.
409 Conflict
Конфликт (что‑то пошло не так) — запрос не может быть выполнен из‑за конфликтного обращения к ресурсу (несовместимость двух запросов).
410 Gone
Недоступно — ресурс раньше был размещён по указанному URL, но сейчас удалён и недоступен (серверу неизвестно месторасположение).
411 Length Required
Добавьте длины — сервер отклоняет отправляемый запрос, так как длина заголовка не определена, и он не находит значение Content‑Length.
Нужно исправить заголовки на сервере, и в следующий раз робот сможет проиндексировать страницу.
412 Precondition Failed
Предварительное условие не выполнено — стоит проверить правильность HTTP‑заголовков данного запроса.
413 Request Entity Too Large
Превышен размер запроса — перелимит максимального размера запроса, принимаемого сервером. Браузеры поддерживают запросы от 2 до 8 килобайт.
414 Request‑URI Too Long
Превышена длина запроса — сервер не может обработать запрос из‑за длинного URL. Такая ошибка может возникнуть, например, когда клиент пытается передать чересчур длинные параметры через метод GET, а не POST.
415 Unsupported Media Type
Формат не поддерживается — сервер не может принять запрос, так как данные подгружаются в некорректном формате, и сервер разрывает соединение.
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
Диапазон не поддерживается — ошибка возникает в случаях, когда в самом HTTP‑заголовке прописывается некорректный байтовый диапазон.
Корректного диапазона в необходимом документе может просто не быть, или есть опечатка в синтаксисе.
417 Expectation Failed
Ожидания не оправдались — прокси некорректно идентифицировал содержимое поля «Expect: 100‑Continue».
418 I’m a teapot
Первоапрельская шутка разработчиков в 1998 году. В расшифровке звучит как «я не приготовлю вам кофе, потому что я чайник». Не используется в работе.
422 Unprocessable Entity
Объект не обработан — сервер принял запрос, но в нём есть логическая ошибка. Стоит посмотреть в сторону семантики сайта.
423 Locked
Закрыто — ресурс заблокирован для выбранного HTTP‑метода. Можно перезагрузить роутер и компьютер. А также использовать только статистический IP.
424 Failed Dependency
Неуспешная зависимость — сервер не может обработать запрос, так как один из зависимых ресурсов заблокирован.
Выполнение запроса напрямую зависит от успешности выполнения другой операции, и если она не будет успешно завершена, то вся обработка запроса будет прервана.
425 Unordered Collection
Неверный порядок в коллекции — ошибка возникает, если клиент указал номер элемента в неупорядоченном списке или запросил несколько элементов в порядке, отличном от серверного.
426 Upgrade Required
Нужно обновление — в заголовке ответа нужно корректно сформировать поля Upgrade и Connection.
Этот ответ возникает, когда серверу требуется обновление до SSL‑протокола, но клиент не имеет его поддержки.
428 Precondition Required
Нужно предварительное условие — сервер просит внести в запрос информацию о предварительных условиях обработки данных, чтобы выдавать корректную информацию по итогу.
429 Too Many Requests
Слишком много запросов — отправлено слишком много запросов за короткое время. Это может указывать, например, на попытку DDoS‑атаки, для защиты от которой запросы блокируются.
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Превышена длина заголовков — сервер может и не отвечать этим кодом, вместо этого он может просто сбросить соединение.
Исправляется это с помощью сокращения заголовков и повторной отправки запроса.
434 Requested Host Unavailable
Адрес запрашиваемой страницы недоступен.
444 No Response
Нет ответа — код отображается в лог‑файлах, чтобы подтвердить, что сервер никак не отреагировал на запрос пользователя и прервал соединение. Возвращается только сервером nginx.
Nginx — программное обеспечение с открытым исходным кодом. Его используют для создания веб‑серверов, а также в качестве почтового или обратного прокси‑сервера. Nginx решает проблему падения производительности из‑за роста трафика.
449 Retry With
Повторите попытку — ошибка говорит о необходимости скорректировать запрос и повторить его снова. Причиной становятся неверно указанные параметры (возможно, недостаточно данных).
450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
Заблокировано родительским контролем — говорит о том, что с компьютера попытались зайти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать этой ошибки можно изменением параметров системы родительского контроля.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Недоступно по юридическим причинам — доступ к ресурсу закрыт, например, по требованию органов государственной власти или по требованию правообладателя в случае нарушения авторских прав.
456 Unrecoverable Error
Неустранимая ошибка — при обработке запроса возникла ошибка, которая вызывает некорректируемые сбои в таблицах баз данных.
499 Client Closed Request
Запрос закрыт клиентом — нестандартный код, используемый nginx в ситуациях, когда клиент закрыл соединение, пока nginx обрабатывал запрос.
5* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне сервера)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны серверов.
При использовании всех методов, кроме HEAD, сервер должен вернуть в теле сообщения гипертекстовое пояснение для пользователя. И его можно использовать в работе.
500 Internal Server Error
Внутренняя ошибка сервера — сервер столкнулся с неким условием, из‑за которого не может выполнить запрос.
Проверяйте, корректно ли указаны директивы в системных файлах (особенно htaccess) и нет ли ошибки прав доступа к файлам. Обратите внимание на ошибки внутри скриптов и их медленную работу.
501 Not Implemented
Не выполнено — код отдается, когда сам сервер не может идентифицировать метод запроса.
Сами вы эту ошибку не исправите. Устранить её может только сервер.
502 Bad Gateway
Ошибка шлюза — появляется, когда сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, получил ответное сообщение от вышестоящего сервера о несоответствии протоколов.
Актуально исключительно для прокси и шлюзовых конфигураций.
503 Service Unavailable
Временно не доступен — сервер временно не имеет возможности обрабатывать запросы по техническим причинам (обслуживание, перегрузка и прочее).
В поле Retry‑After заголовка сервер укажет время, через которое можно повторить запрос.
504 Gateway Timeout
Тайм‑аут шлюза — сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, не получил ответа от вышестоящего сервера в нужное время.
Исправить эту ошибку самостоятельно не получится. Здесь дело в прокси, часто — в веб‑сервере.
Первым делом просто обновите веб‑страницу. Если это не помогло, нужно почистить DNS‑кэш. Для этого нажмите горячие клавиши Windows+R и введите команду cmd (Control+пробел). В открывшемся окне укажите команду ipconfig / flushdns и подтвердите её нажатием Enter.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Сервер не поддерживает версию протокола — отсутствует поддержка текущей версии HTTP‑протокола. Нужно обеспечить клиента и сервер одинаковой версией.
506 Variant Also Negotiates
Неуспешные переговоры — с такой ошибкой сталкиваются, если сервер изначально настроен неправильно. По причине ошибочной конфигурации выбранный вариант указывает сам на себя, из‑за чего процесс и прерывается.
507 Insufficient Storage
Не хватает места для хранения — серверу недостаточно места в хранилище. Нужно либо расчистить место, либо увеличить доступное пространство.
508 Loop Detected
Обнаружен цикл — ошибка означает провал запроса и выполняемой операции в целом.
509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Превышена пропускная способность — используется при чрезмерном потреблении трафика. Владельцу площадки следует обратиться к своему хостинг‑провайдеру.
510 Not Extended
Не продлён — ошибка говорит, что на сервере отсутствует нужное для клиента расширение. Чтобы исправить проблему, надо убрать часть неподдерживаемого расширения из запроса или добавить поддержку на сервер.
511 Network Authentication Required
Требуется аутентификация — ошибка генерируется сервером‑посредником, к примеру, сервером интернет‑провайдера, если нужно ввести пароль для получения доступа к сети через платную точку доступа.
Quick Answer / TL;DR
For the lazy people out there:
Install-Package MagicalUnicornMvcErrorToolkit -Version 1.0
Then remove this line from global.asax
GlobalFilters.Filters.Add(new HandleErrorAttribute());
And this is only for IIS7+ and IIS Express.
If you’re using Cassini .. well .. um .. er.. awkward …
Long, explained answer
I know this has been answered. But the answer is REALLY SIMPLE (cheers to David Fowler and Damian Edwards for really answering this).
There is no need to do anything custom.
For ASP.NET MVC3, all the bits and pieces are there.
Step 1 -> Update your web.config in TWO spots.
<system.web>
<customErrors mode="On" defaultRedirect="/ServerError">
<error statusCode="404" redirect="/NotFound" />
</customErrors>
and
<system.webServer>
<httpErrors errorMode="Custom">
<remove statusCode="404" subStatusCode="-1" />
<error statusCode="404" path="/NotFound" responseMode="ExecuteURL" />
<remove statusCode="500" subStatusCode="-1" />
<error statusCode="500" path="/ServerError" responseMode="ExecuteURL" />
</httpErrors>
...
<system.webServer>
...
</system.web>
Now take careful note of the ROUTES I’ve decided to use. You can use anything, but my routes are
/NotFound<- for a 404 not found, error page./ServerError<- for any other error, include errors that happen in my code. this is a 500 Internal Server Error
See how the first section in <system.web> only has one custom entry? The statusCode="404" entry? I’ve only listed one status code because all other errors, including the 500 Server Error (ie. those pesky error that happens when your code has a bug and crashes the user’s request) .. all the other errors are handled by the setting defaultRedirect="/ServerError" .. which says, if you are not a 404 page not found, then please goto the route /ServerError.
Ok. that’s out of the way.. now to my routes listed in global.asax
Step 2 — Creating the routes in Global.asax
Here’s my full route section..
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.IgnoreRoute("{*favicon}", new {favicon = @"(.*/)?favicon.ico(/.*)?"});
routes.MapRoute(
"Error - 404",
"NotFound",
new { controller = "Error", action = "NotFound" }
);
routes.MapRoute(
"Error - 500",
"ServerError",
new { controller = "Error", action = "ServerError"}
);
routes.MapRoute(
"Default", // Route name
"{controller}/{action}/{id}", // URL with parameters
new {controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional}
);
}
That lists two ignore routes -> axd's and favicons (ooo! bonus ignore route, for you!)
Then (and the order is IMPERATIVE HERE), I have my two explicit error handling routes .. followed by any other routes. In this case, the default one. Of course, I have more, but that’s special to my web site. Just make sure the error routes are at the top of the list. Order is imperative.
Finally, while we are inside our global.asax file, we do NOT globally register the HandleError attribute. No, no, no sir. Nadda. Nope. Nien. Negative. Noooooooooo…
Remove this line from global.asax
GlobalFilters.Filters.Add(new HandleErrorAttribute());
Step 3 — Create the controller with the action methods
Now .. we add a controller with two action methods …
public class ErrorController : Controller
{
public ActionResult NotFound()
{
Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
return View();
}
public ActionResult ServerError()
{
Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
// Todo: Pass the exception into the view model, which you can make.
// That's an exercise, dear reader, for -you-.
// In case u want to pass it to the view, if you're admin, etc.
// if (User.IsAdmin) // <-- I just made that up :) U get the idea...
// {
// var exception = Server.GetLastError();
// // etc..
// }
return View();
}
// Shhh .. secret test method .. ooOOooOooOOOooohhhhhhhh
public ActionResult ThrowError()
{
throw new NotImplementedException("Pew ^ Pew");
}
}
Ok, lets check this out. First of all, there is NO [HandleError] attribute here. Why? Because the built in ASP.NET framework is already handling errors AND we have specified all the shit we need to do to handle an error 
Next, I have the two action methods. Nothing tough there. If u wish to show any exception info, then u can use Server.GetLastError() to get that info.
Bonus WTF: Yes, I made a third action method, to test error handling.
Step 4 — Create the Views
And finally, create two views. Put em in the normal view spot, for this controller.
Bonus comments
- You don’t need an
Application_Error(object sender, EventArgs e) - The above steps all work 100% perfectly with Elmah. Elmah fraking wroxs!
And that, my friends, should be it.
Now, congrats for reading this much and have a Unicorn as a prize!
Отправка статусных кодов
Последнее обновление: 21.03.2022
Нередко возникает необходимость отправить в ответ на запрос какой-либо статусный код.
Например, если пользователь пытается получить доступ к ресурсу, который недоступен, или для которого у пользователя нету прав. Либо если просто нужно
уведомить браузер пользователя с помощью статусного кода об успешном выполнении операции, как иногда применяется в ajax-запросах. Для этого в ASP.NET Core MVC
определена богатая палитра классов, которые можно использовать для отправки статусного кода.
StatusCodeResult
StatusCodeResult позволяет отправить любой статусный код клиенту:
public IActionResult Index()
{
return StatusCode(401);
}
Для создания этого результата используется метод StatusCode(), в который передается отправляемый код статуса.
Подобным образом мы можем послать браузеру любой другой статусный код. Но для отдельных кодов статуса предназначены свои отдельные классы.
HttpNotFoundResult и HttpNotFoundObjectResult
NotFoundResult и NotFoundObjectResult посылает код 404, уведомляя браузер о том, что ресурс
не найден. Второй класс в дополнении к статусному коду позволяет отправить доплнительную информацию, которая потом отобразится в браузере.
Объекты обоих классов создаются методом NotFound. Для первого класса — это метод без параметров, для второго класса — метод,
который в качестве параметра принимает отправляемую информацию. Например, используем NotFoundObjectResult:
public IActionResult Index()
{
return NotFound("Resource not found");
}
UnauthorizedResult и UnauthorizedObjectResult
UnauthorizedResult посылает код 401, уведомляя пользователя, что он не автризован для доступа к ресурсу:
public IActionResult Index(int age)
{
if (age < 18) return Unauthorized();
return Content("Access is available");
}
Для создания ответа используется метод Unauthorized().
UnauthorizedObjectResult также посылает код 401, только позволяет добавить в ответ некоторый объект с информацией об ошибке:
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index(int age)
{
if (age < 18) return Unauthorized(new Error("Access is denied"));
return Content("Access is available");
}
}
record class Error(string Message);
BadResult и BadObjectResult
BadResult и BadObjectResult посылают код 400, что говорит о том, что запрос некорректный.
Второй класс в дополнении к статусному коду позволяет отправить доплнительную информацию, которая потом отобразится в браузере.
Эти классы можно применять, например, если в запросе нет каких-то параметров или данные представляют совсем не те типы, которые мы ожидаем получить, и т.д.
Объекты обоих классов создаются методом BadRequest. Для первого класса — это метод без параметров, для второго класса — метод,
который в качестве параметра принимает отправляемую информацию:
public IActionResult Index(string? name)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name)) return BadRequest("Name undefined");
return Content($"Name: {name}");
}
OkResult и OkObjectResult
OkResult и OkObjectResult посылают код 200, уведомляя об успешном выполнении запроса.
Второй класс в дополнении к статусному коду позволяет отправить дополнительную информацию, которая потом отправляется клиенту в формате json.
Объекты обоих классов создаются методом Ok(). Для первого класса — это метод без параметров, для второго класса — метод,
который в качестве параметра принимает отправляемую информацию:
public IActionResult Index()
{
return Ok("Don't worry. Be happy");
}
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer network communications, the HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404, 404 error, page not found or file not found error message is a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) standard response code, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information.[1]
The website hosting server will typically generate a «404 Not Found» web page when a user attempts to follow a broken or dead link; hence the 404 error is one of the most recognizable errors encountered on the World Wide Web.
English Wikipedia’s 404 Page
Overview
When communicating via HTTP, a server is required to respond to a request, such as a web browser request for a web page, with a numeric response code and an optional, mandatory, or disallowed (based upon the status code) message. In code 404, the first digit indicates a client error, such as a mistyped Uniform Resource Locator (URL). The following two digits indicate the specific error encountered. HTTP’s use of three-digit codes is similar to the use of such codes in earlier protocols such as FTP and NNTP. At the HTTP level, a 404 response code is followed by a human-readable «reason phrase». The HTTP specification suggests the phrase «Not Found»[1] and many web servers by default issue an HTML page that includes both the 404 code and the «Not Found» phrase.
A 404 error is often returned when pages have been moved or deleted. In the first case, it is better to employ URL mapping or URL redirection by returning a 301 Moved Permanently response, which can be configured in most server configuration files, or through URL rewriting; in the second case, a 410 Gone should be returned. Because these two options require special server configuration, most websites do not make use of them.
404 errors should not be confused with DNS errors, which appear when the given URL refers to a server name that does not exist. A 404 error indicates that the server itself was found, but that the server was not able to retrieve the requested page.
History
The origin of the 404 error code dates back to the early days of the World Wide Web. In 1992, Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the Web, and his team at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, created the first web server software, called CERN httpd.[2] This software used a simple file system to store and retrieve web pages, and it assigned a three-digit number to each type of request and response. The number 404 was chosen to indicate that the requested file was not found on the server.[3]
The term «404 Not Found» was coined by Berners-Lee himself, who explained in a 1998 interview that he wanted to make the error message «slightly apologetic».[4][3] He also said that he considered using «400 Bad Request» instead, but decided that it was too vague and technical.[4][3]
The first documented case of a 404 error appearing on a web page was in 1993, when a user tried to access a page about the Mosaic web browser on the NCSA website. The page had been moved to a different location, but the link had not been updated.[2] The user reported the error to the NCSA team, who fixed the link and added a humorous message to their 404 page: «We’re sorry, but the document you requested is not here. Maybe you should try someplace else.»[3]
Since then, 404 errors have become one of the most common and recognizable errors on the Web. Many websites have customized their 404 pages with creative designs, messages, or features to entertain or assist their visitors. For example, Google’s 404 page features a broken robot and a link to its homepage,[5] while GitHub’s 404 page shows a random image of a parallax star field and a link to its status page.[6] Some websites have also used their 404 pages to showcase their brand personality, humor, or social causes. For instance, Lego’s 404 page shows an image of a Lego character searching for a missing brick,[7] while Amazon’s 404 page displays the image of a dog with a message about conservation.[8]
Soft 404 errors
Some websites report a «not found» error by returning a standard web page with a «200 OK» response code, falsely reporting that the page loaded properly; this is known as a soft 404. The term «soft 404» was introduced in 2004 by Ziv Bar-Yossef et al.[9]
Soft 404s are problematic for automated methods of discovering whether a link is broken. Some search engines, like Yahoo and Google, use automated processes to detect soft 404s.[10] Soft 404s can occur as a result of configuration errors when using certain HTTP server software, for example with the Apache software, when an Error Document 404 (specified in a .htaccess file) is specified as an absolute path (e.g. http://example.com/error.html) rather than a relative path (/error.html).[11] This can also be done on purpose to force some browsers (like Internet Explorer) to display a customized 404 error message rather than replacing what is served with a browser-specific «friendly» error message (in Internet Explorer, this behavior is triggered when a 404 is served and the received HTML is shorter than a certain length, and can be manually disabled by the user).
There are also «soft 3XX» errors where content is returned with a status 200 but comes from a redirected page, such as when missing pages are redirected to the domain root/home page.
Proxy servers
Some proxy servers generate a 404 error when a 500-range error code would be more correct. If the proxy server is unable to satisfy a request for a page because of a problem with the remote host (such as hostname resolution failures or refused TCP connections), this should be described as a 5xx Internal Server Error, but might deliver a 404 instead. This can confuse programs that expect and act on specific responses, as they can no longer easily distinguish between an absent web server and a missing web page on a web server that is present.
Intentional 404s
In July 2004, the UK telecom provider BT Group deployed the Cleanfeed content blocking system, which returns a 404 error to any request for content identified as potentially illegal by the Internet Watch Foundation.[12] Other ISPs return a HTTP 403 «forbidden» error in the same circumstances.[13] The practice of employing fake 404 errors as a means to conceal censorship has also been reported in Thailand[14] and Tunisia.[15] In Tunisia, where censorship was severe before the 2011 revolution, people became aware of the nature of the fake 404 errors and created an imaginary character named «Ammar 404» who represents «the invisible censor».[16]
Microsoft Internet Server 404 substatus error codes
The webserver software developed by Microsoft, Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS), returns a set of substatus codes with its 404 responses. The substatus codes take the form of decimal numbers appended to the 404 status code. The substatus codes are not officially recognized by IANA and are not returned by non-Microsoft servers.
Substatus codes
Microsoft’s IIS 7.0, IIS 7.5, and IIS 8.0 servers define the following HTTP substatus codes to indicate a more specific cause of a 404 error:
- 404.0 – Not found.
- 404.1 – Site Not Found.
- 404.2 – ISAPI or CGI restriction.
- 404.3 – MIME type restriction.
- 404.4 – No handler configured.
- 404.5 – Denied by request filtering configuration.
- 404.6 – Verb denied.
- 404.7 – File extension denied.
- 404.8 – Hidden namespace.
- 404.9 – File attribute hidden.
- 404.10 – Request header too long.
- 404.11 – Request contains double escape sequence.
- 404.12 – Request contains high-bit characters.
- 404.13 – Content length too large.
- 404.14 – Request URL too long.
- 404.15 – Query string too long.
- 404.16 – DAV request sent to the static file handler.
- 404.17 – Dynamic content mapped to the static file handler via a wildcard MIME mapping.
- 404.18 – Query string sequence denied.
- 404.19 – Denied by filtering rule.
- 404.20 – Too Many URL Segments.
Custom error pages
The Wikimedia 404 message
Web servers can typically be configured to display a customised 404 error page, including a more natural description, the parent site’s branding, and sometimes a site map, a search form or 404-page widget. The protocol level phrase, which is hidden from the user, is rarely customized. Internet Explorer, however, will not display custom pages unless they are larger than 512 bytes, opting instead to display a «friendly» error page.[17] Google Chrome included similar functionality, where the 404 is replaced with alternative suggestions generated by Google algorithms, if the page is under 512 bytes in size.[18] Another problem is that if the page does not provide a favicon, and a separate custom 404-page exists, extra traffic and longer loading times will be generated on every page view.[19][20]
Many organizations use 404 error pages as an opportunity to inject humor into what may otherwise be a serious website. For example, Metro UK shows a polar bear on a skateboard, and the web development agency Left Logic has a simple drawing program.[21] During the 2015 UK general election campaign the main political parties all used their 404 pages to either take aim at political opponents or show relevant policies to potential supporters.[22] In Europe, the NotFound project, created by multiple European organizations including Missing Children Europe and Child Focus, encourages site operators to add a snippet of code to serve customized 404 error pages[23] which provide data about missing children.[24]
While many websites send additional information in a 404 error message—such as a link to the homepage of a website or a search box—some also endeavor to find the correct web page the user wanted. Extensions are available for some content management systems (CMSs) to do this.[25]
Tracking 404 errors
A number of tools exist that crawl through a website to find pages that return 404 status codes. These tools can be helpful in finding links that exist within a particular website. The limitation of these tools is that they only find links within one particular website, and ignore 404s resulting from links on other websites. As a result, these tools miss out on 83% of the 404s on websites.[26] One way around this is to find 404 errors by analyzing external links.[27]
One of the most effective ways to discover 404 errors is by using Google Search Console, Google Analytics or crawling software.
Another common method is tracking traffic to 404 pages using log file analysis.[28] This can be useful to understand more about what 404s users reached on the site. Another method of tracking traffic to 404 pages is using JavaScript-based traffic tracking tools.[29]
Causes
There are many possible causes for a page not to exist. Some of the common ones are:[30][31][32]
- The page was deleted by the owner or administrator of the website.
- The page was moved to a different location or renamed without updating the links that point to it.
- The page was never created in the first place or is still under construction.
- The page is temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or technical issues.
- The page is blocked by the user’s network or firewall settings.
- The page is restricted by the website’s privacy or security policies.
- The page contains illegal or harmful content that was removed by the authorities or the website itself.
Solutions
If a user encounters a page that doesn’t exist, there are some steps they can take to try to find the information they are looking for or to report the problem.[30][31][32]
- Check the URL of the page. Sometimes, a simple typo or spelling mistake can cause a page not to load. Make sure the correct address is entered and try again.
- Refresh the page. Sometimes, a temporary glitch or network issue can prevent a page from loading. Try reloading the page by pressing F5 or clicking on the refresh button on the browser.
- Go back to the previous page. Sometimes, a link might be broken or outdated. Try going back to the page where the link was found and see if there is an updated or alternative link to the same information.
- Use a search engine. Sometimes, a page might be indexed by a search engine even if it doesn’t exist anymore. Try searching for keywords related to the topic of the page and see if other sources of information can be found.
- Contact the website owner or administrator. Sometimes, a page might be removed or moved without notice. Try contacting the person or organization responsible for the website and ask them about the status of the page. Their contact information can usually be found on their homepage or in their footer section.
- Report the error. Sometimes, a page might not exist due to an error on the website’s part. Try reporting the error to the website owner or administrator so they can fix it as soon as possible. Their feedback form or email address can usually be found on their homepage or in their footer section.
See also
- Blue screen of death
- Funky caching
- Link rot
- List of HTTP status codes
References
- ^ a b Fielding, R.; Reschke, J. (June 2014). Fielding, R; Reschke, J (eds.). «RFC 7231, HTTP/1.1 Semantics and Content, Section 6.5.4 404 Not Found». ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC7231. S2CID 14399078. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b «404 page design: best practices and awesome examples». www.justinmind.com. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b c d «What is a 404 error and what should I do if I get one? » Internet » Windows » Tech Ease». Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b What is the world wide web? — Twila Camp, retrieved 19 May 2023
- ^ «Google 404 Error Page». Google. CS1 maint: url-status (link)
- ^ «Github 404 Error Page». Github. CS1 maint: url-status (link)
- ^ «LEGO 404 Error Page». Lego. CS1 maint: url-status (link)
- ^ «Amazon’s 404 error page». Amazon. CS1 maint: url-status (link)
- ^ Ziv Bar-Yossef; Andrei Z. Broder; Ravi Kumar; Andrew Tompkins (2004). Sic Transit Gloria Telae: Towards an Understanding of the Web’s Decay. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW). pp. 328–337. doi:10.1145/988672.988716. ISBN 978-1581138443. S2CID 587547.
- ^ «Why is your crawler asking for strange URLs that have never existed on my site?». Yahoo Ysearch Help page. Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2013.
- ^ «Farewell to soft 404s». Google Official Blog. Retrieved 20 September 2008.
- ^ «LINX Public Affairs » Cleanfeed: the facts». Publicaffairs.linx.net. 10 September 2004. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ «DEMON – Error 403». Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ Sambandaraksa, Don (18 February 2009). «The old fake ‘404 Not Found’ routine — Dead link». Bangkok Post. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ^ Noman, Helmi (12 September 2008). «Tunisian journalist sues government agency for blocking Facebook, claims damage for the use of 404 error message instead of 403». Open Net Initiative. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ «Anti-censorship movement in Tunisia: creativity, courage and hope!». Global Voices Advocacy. 27 May 2010. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Friendly HTTP Error Pages». msdn.com. 18 August 2010. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ «Issue 1695: Chrome needs option to turn off «Friendly 404″ displays». bugs.chromium.org. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ Heng, Christopher (7 September 2008). «What is Favicon.ico and How to Create a Favicon Icon for Your Website». The Site Wizard. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ^ «The Dastardly «favicon.ico not found» Error». Internet Folks. 3 August 1999.
- ^ «From skateboarding bears to missing children: The power of the 404 Not Found error page». Metro. 6 June 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ «The political Page 404 war». BBC Newsbeat. 27 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- ^ «Notfound.org». notfound. notfound. Archived from the original on 2 September 2014.
- ^ «Missing children messages go on 404 error pages». BBC News. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ^ Swenson, Sahala (19 August 2008). «Make your 404 pages more useful». Official Google Webmaster Central Blog. Google, Inc. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ «Sources Leading To 404s». SpringTrax. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ Cushing, Anne (2 April 2013). «A Data-Centric Approach To Identifying 404 Pages Worth Saving». Search Engine Land. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Tracking and Preventing 404 Errors». 404errorpages.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Understand 404 Errors». SpringTrax.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ a b Edgar, Matthew (11 April 2023). «How To Fix 404 Errors On Your Website». Matthew Edgar. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b Frickey, Dean (18 November 2008). «A More Useful 404». A List Apart. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b «What ‘Error 404’ means and how to fix it». IONOS Digital Guide. 31 January 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
External links
- A More Useful 404
- 404 Not Found of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content specification, at the Internet Engineering Task Force
- ErrorDocument Directive – instructions on custom error pages for the Apache 2.0 web server
- 404: Not Found – an award-winning song about the error code