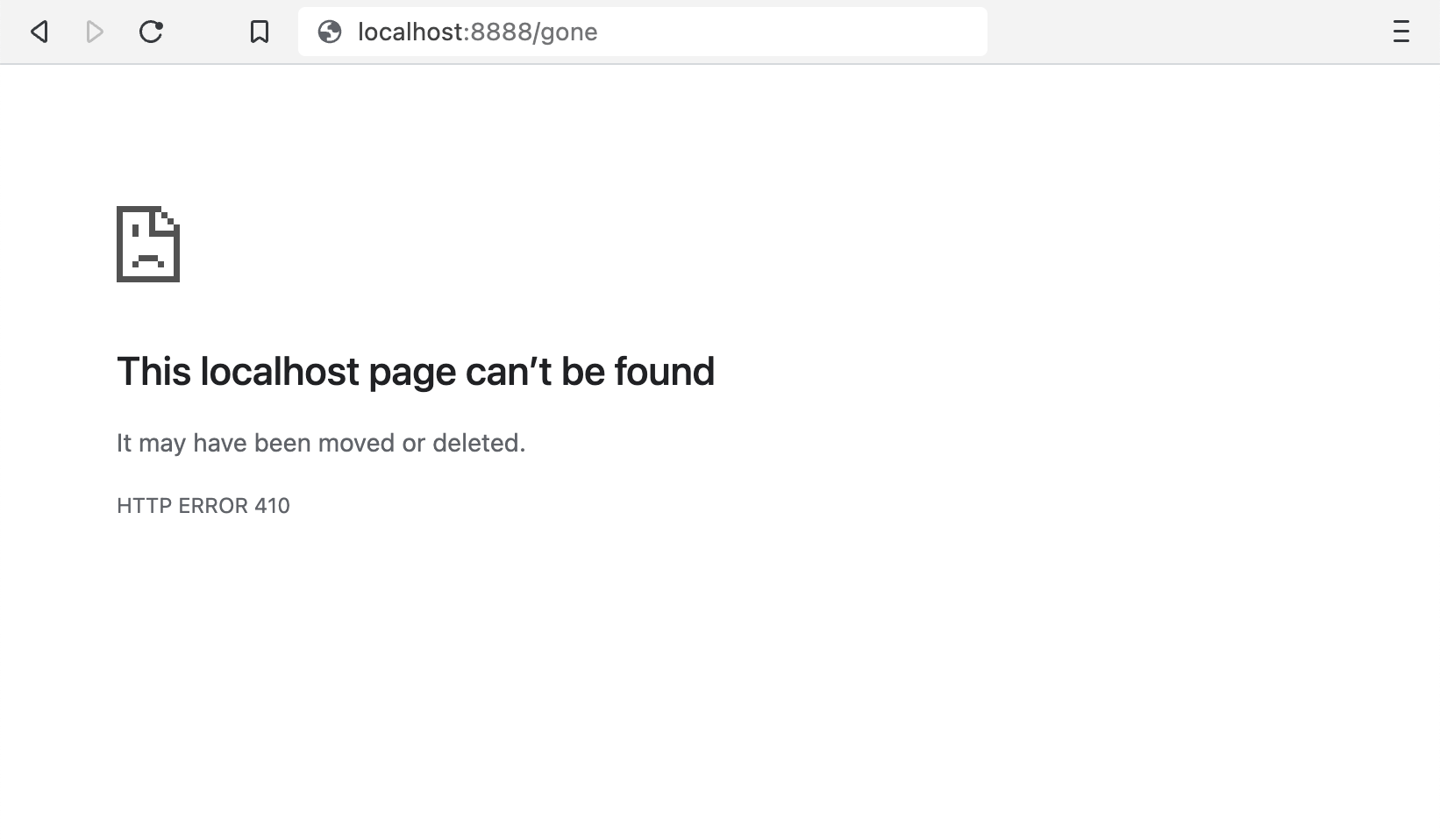
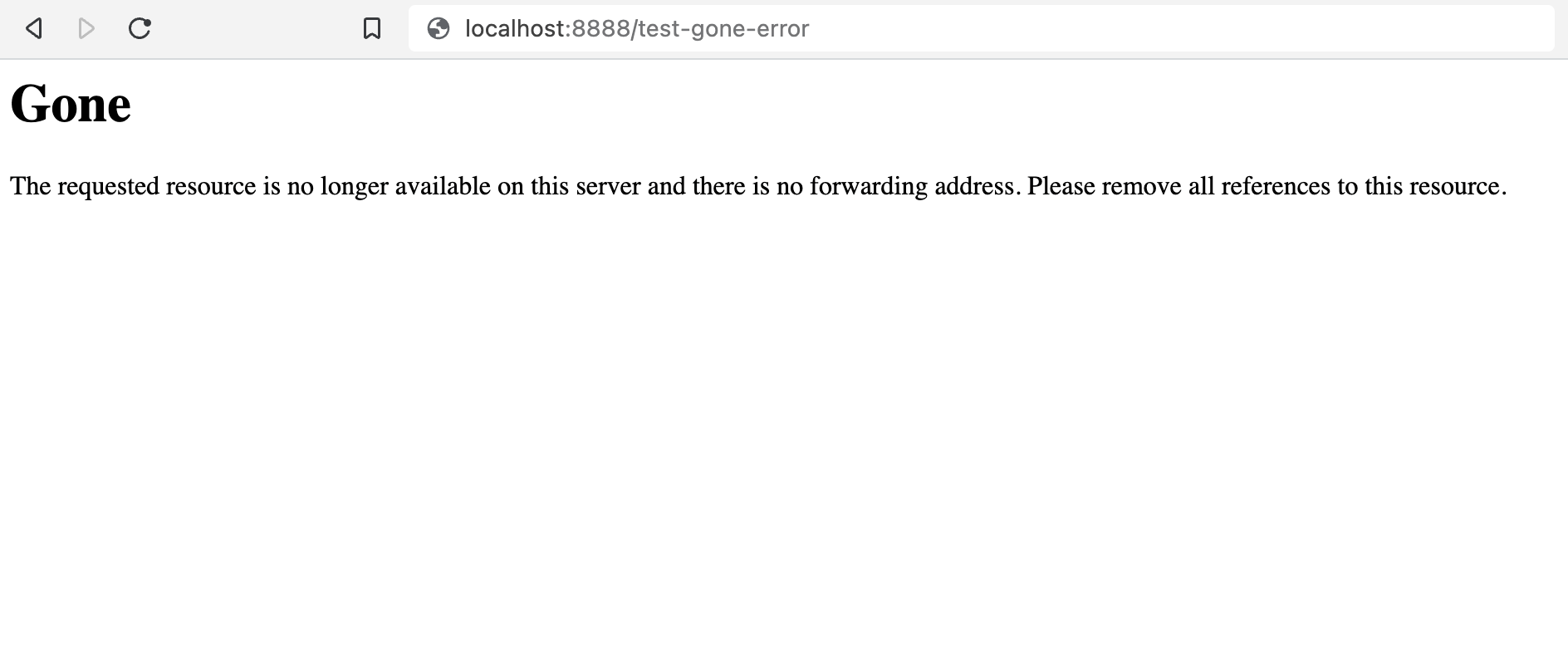
If you incorrectly type a URL, you may see a 404 error explaining that this web page doesn’t exist. However, if the page has been deleted, you’ll likely receive a “410 Gone” status code. This means you won’t be able to access the page at all.
Fortunately, there are a few easy ways to fix the “410 Gone” error. If it happens to your website, you can examine your site logs and reconfigure your server to resolve the issue. Alternatively, you can troubleshoot this error on the client side by rolling back recent updates or uninstalling new plugins.
Check Out Our Video Guide to the “410 Gone” Error
In this post, we’ll explain what error 410 is and discuss its potential causes. Then, we’ll show you how to fix it on both the client and server sides. Let’s get started!
What Is the “410 Gone” Error?
When someone clicks on a web page, their browser makes a request to the website’s server. After processing the request, the server will send the relevant site files, displaying the requested information.
Although you may not see it, the server will also send a status code in an HTTP header. These HTTP status codes indicate whether the request was a success or a failure.
Here are some different types of HTTP status codes:
- 100s: Informational requests
- 200s: Successful requests
- 300s: Redirects
- 400s: Client-side errors
- 500s: Server-side errors
The “410 Gone” error is a 400 HTTP status code that indicates that the target resource has been permanently deleted. In this case, the server can’t complete the request because the page does not exist.
Depending on your browser, the 410 error can appear in a few different ways:
- 410 Gone
- Gone
- Error 410
- HTTP Status 410
As a website owner, it’s important to monitor your status codes and fix any errors when they occur. If new visitors can’t find the information they’re looking for, they may turn to a competitor instead. To resolve the “410 Gone” error, you’ll first need to know what’s causing it.
Seeing this tricky error message? 👀 The solution is closer than you may think… ⬇️Click to Tweet
What Causes the “410 Gone” Error?
Since the “410 Gone” error is categorized as a 400 HTTP status code, you may think that it only occurs as a client-side error. However, this can happen on both the server and client sides.
A user might make a mistake when typing a URL. In many cases, this results in a “404 Not Found” error. However, it’s possible to get an error 410 if the resource once existed at that URL and the server was configured to return a “410 Gone” status code.
If you’ve recently made changes to your Content Management System (CMS), you could inadvertently trigger a “410 Gone” status code. Sometimes, new plugins, updates, or extensions can make changes to your database, leading to this error.
Alternatively, error 410 can be the result of incorrect server configuration. If you search your log files for unwanted 410 redirects, you’ll likely find the source of the issue.
The 410 HTTP status code can also be intentional. If you’re running a time-sensitive promotion on your website, that web page will only be available for a certain period:
If someone clicks on this promotional link after the sale is finished, you can redirect them to a “410 Gone” error. This will let them know that the page was taken down and won’t be coming back.
The Difference Between the “410 Gone” and the “404 Not Found” Error
Both the “410 Gone” and “404 Not Found” errors indicate that the resource cannot be retrieved. However, there are a few main differences between the two HTTP status codes.
404 Not Found is one of the most common HTTP status codes. When you see this error, it means that the requested resource doesn’t exist:
However, a “404 Not Found” error is a temporary problem. This means that you can try the URL again later to see if the problem has been resolved.
With a “410 Gone” error, the requested page has been permanently deleted. When search crawlers identify this HTTP status code, they will de-index the link. This can also inform other website owners to remove this link from their content.
If you don’t need a particular page anymore, it can be useful to implement a “410 Gone” redirect. However, if these errors happen on their own, you’ll need to fix them to keep your website performing properly.
How To Fix the “410 Gone” Error (2 Methods)
There are many ways you can fix the “410 Gone” error. By troubleshooting both the client and server sides, you can ensure that your content can be viewed by visitors and indexed by search engines. Since many of these methods involve altering site files, updates, and plugins, we recommend backing up your website first.
Method 1: Investigating a Client-Side “410 Gone” Error
Before you start making changes to your server, you can troubleshoot your website on the client side. This can be a simple way to fix the error without altering vital site files.
Step 1: Check the Requested URL
When you first experience the “410 Gone” error, it’s a good idea to check the link. As we discussed earlier, inputting an incorrect URL can cause this HTTP status code.
If you’re trying to reach a web page that has been permanently deleted, it will likely respond with a “410 Gone” error. This happens because the server disallowed access to that URL.
First, you can try retyping the address. If you still see the “410 Gone” status code, you can search for that page by typing in a few keywords in the search engine:
The website owner might have moved that page to a new URL. By searching for some keywords and entering the website’s name, you could find what you’re looking for on a new page.
Step 2: Roll Back Recent Updates
Once you notice that your web page has been replaced with a “410 Gone” error, you can consider downgrading your WordPress software to an older version. Sometimes, implementing new tools can lead to poor configuration or other unexpected problems, like the 410 error.
If you backed up your website before the update, you can easily restore this previous version. With our Kinsta hosting plans, you’ll receive automatic daily backups for all your websites, even your staging sites.
To restore your backup, open your MyKinsta dashboard. Then, go to Sites and select your website:
On the new page, click on the Backups tab. Here, you’ll see a history of your backups:
Find the backup that you want to restore. Next, locate the Restore to button and select whether you want to downgrade your live site or its staging environment:
Finally, you’ll need to confirm the backup restoration:
Once the restoration process is complete, you’ll be able to access your WordPress dashboard again. If the “410 Gone” issue persists, you’ll need to try another method.
Step 3: Uninstall Plugins and Extensions
If you have installed plugins or extensions that alter your URL structure or redirects, these can cause an error 410. You may see this HTTP status code in other cases because of general incompatibility issues. Either way, you can solve the problem by uninstalling these tools.
To see if your plugins are causing the issue, you can deactivate them all. Since 410 errors don’t usually lock you out of the WordPress dashboard, you can do this on your Plugins page.
Start by selecting all of your plugins. Then, from the Bulk actions dropdown menu, click on
Deactivate:
Finally, click on Apply. This should deactivate all the plugins on your website simultaneously.
Now you can check to see if the “410 Gone” error has been resolved. If so, you can reactivate each plugin one by one to find and delete the culprit. If it serves a vital purpose on your website, you can find a similar plugin or contact its developer about the issue.
Method 2: Investigating a Server-Side “410 Gone” Error
Since the “410 Gone” error can result from a server-side issue, you may not see any improvements on the client side of your website. After you’ve tried the first method with no results, you may need to make changes to your server configuration.
Step 1: Review Your Site Logs
You can check your server logs if you want to know whether your server is experiencing any “410 Gone” errors. This will help you monitor all your HTTP status codes and identify what’s causing errors.
If you have a Kinsta hosting plan, you can review your site logs directly from your dashboard. Once you log into MyKinsta, go to Sites > Logs:
The Log viewer will automatically show your error logs, so you’ll need to select access.log from the dropdown menu:
This will display all of the HTTP requests for your website:
Each line will look something like this:
kinstahelptesting.kinsta.cloud 98.43.13.94 [22/Sep/2021:21:26:10 +0000] GET "/wp-admin/" HTTP/1.0 302 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:92.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/92.0" 98.43.13.94 "/wp-admin/index.php" - - 472 0.562 0.560In this example, the request gained a 302 HTTP status code. The requested URL was
“/wp-admin/”You can scan your HTTP requests for 410 errors in your site logs. You can also use the search bar to narrow down your results. If you find any errors, you can identify the specific web page that is down.
Step 2: Debug Your Website
If the “410 Gone” error persists, it’s time to debug your website. To do this, you can use the Query Monitor plugin. This free tool enables you to view the performance of your database queries, as well as PHP errors, enqueued scripts, HTTP API calls, and more:
First, download and install Query Monitor. Then, click on the new tab at the top of your dashboard. To monitor all of your server-side HTTP requests, select HTTP API Calls:
This will show you all of the server-side queries for your website. Here, you can see if any errors occurred while loading your website:
You’ll likely need to check your server configuration if you notice any “410 Gone” errors. However, if you need any help, you can contact your hosting provider.
Step 3: Verify Your Server Configuration
Your WordPress website has a .htaccess file that contains rules about your server configuration. If you recently made changes to this file, it could create a “410 Gone” error.
To check the configuration of the .htaccess file, you’ll need to open your site files. Often, the easiest way to do this is through a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) client. This will enable you to connect to your server.
If you’re using a Kinsta hosting plan, you can start by logging into your MyKinsta dashboard. Then, navigate to Sites and select your website.
Next, find the SFTP/SSH section. This will contain your login information for SFTP access, including the host number, username, password, and port:
Now you’ll need to open an FTP client like FileZilla. Once you download this software, you’ll need to change the settings from FTP to SFTP access. This provides a safer way to connect to your site.
To do this, go to File > Site Manager:
Here, create a new site. Then, change the Protocol to SFTP – SSH File Transfer Protocol:
Copy your host and port number from MyKinsta. Next, paste these details into their respective boxes and hit Connect:
To finish connecting to your server, enter your username and password and click on OK:
After you successfully log in, navigate to the public_html folder. Then, find the .htaccess file and open it:
Here’s what your .htaccess file might look like:
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>However, you may see some changes to this file. If you notice any rules containing a “Redirect 410”, you can go ahead and delete them. If your .htaccess file looks similar to the one listed above, you don’t have to make any changes.
Be prepared to fix this pesky issue on both the client ✨and✨ server sides with help from this guide 💪Click to Tweet
Summary
Although the “410 Gone” status code can be useful for removing expired promotions, it can also occur unexpectedly on your website. When this happens, visitors won’t be able to access your content, and search engines will consider the page permanently removed. You’ll need to fix this error to maintain your ranking in search results.
You can resolve this issue on both the client and server sides of your website. You can simply check the requested URL, downgrade your WordPress software, and uninstall your plugins to get started. To identify a “410 Gone” error on your server, you can review your site logs, debug your website, and verify your server configuration.
When you notice any errors on your website, you’ll likely want to troubleshoot them as soon as possible. Kinsta’s APM tool can immediately identify performance issues and get your content back online in no time!
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[34]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[35] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[36]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[37]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[38]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[38]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[39]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[40]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[41]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[42]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[43]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[44]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[45] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[46]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[47] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[48][49]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[50] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[51]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[52]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[53]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[54]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[55]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[55]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[55]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
HTTP response status code 410 Goneis a client error that is returned by the server to indicate that the requested resource is permanently unavailable. This is similar to 404 Not Found, although it more specifically indicates that it did exist, but is unavailable and this is expected to be permanent.
Usage
When the 410 Gone error message is received, the client knows that the address was valid at one point, but the resource no longer exists. This can be the message returned by the server after a resource, such as a document available as part of a limited-time offer, expires. If the server does not expect this to be permanent then another code, like 404 Not Found, can be used instead.
This status code is helpful for web maintenance and is specific enough that clients need to remove links to the resource.
Note
Search engines like Google will not index a URL with 410 Gone response status, and consequently, URLs that have been indexed in the past but are now returning this HTTP status code will be removed from the search results.
Example
In the example, the client requests a resource and the server responds with a 410 Gone because the promotion has ended and the content is no longer available.
Request
GET /holiday-promotion-Jan-2021.pdf HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.ai
Response
HTTP/1.1 410 Gone
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 161
<html>
<head>
<title>Promotion Expired</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>The promotional period has ended and is no longer available.</p>
</body>
</html>
Code references
.NET
HttpStatusCode.Gone
Rust
http::StatusCode::GONE
Rails
:gone
Go
http.StatusGone
Symfony
Response::HTTP_GONE
Python3.5+
http.HTTPStatus.GONE
Java
java.net.HttpURLConnection.HTTP_GONE
Apache HttpComponents Core
org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpStatus.SC_GONE
Angular
@angular/common/http/HttpStatusCode.Gone
Takeaway
The 410 Gone status code is a client error sent by the server to indicate that the requested resource has been permanently removed. Clients need to remove existing links to the resource.
See also
- 404 Not Found
- RFC 7231
Last updated: June 2, 2022
В прикладном смысле сайт — это набор файлов. Файлы каждого сайта находятся на том или ином физическом сервере. Чтобы пользователь мог перейти на нужный ресурс в интернете, нужно запросить эти файлы у сервера.
Сразу после того, как пользователь вбивает какой-то запрос в поисковик, браузер делает запрос на сервер. После этого сервер дает ответ и искомый сайт открывается в браузере. Однако иногда вместо ответа на запрос появляется ошибка.
Каждая ошибка имеет свой код. По коду можно определить возможные причины её появления. Рассмотрим, что означают ошибки 406, 410 и 505, из-за чего они появляются и как их можно исправить.
Ошибка 406 Not Acceptable
Если веб-сервер выдаёт код ошибки 406, значит запрос был заблокирован брандмауэром веб-приложений (WAF) ModSecurity. Брандмауэр ModSecurity — это программное обеспечение для веб-сервера Apache, которое фильтрует все поступающие к сайту запросы (веб-трафик). Он принимает корректные запросы и блокирует нежелательные. Например, защищает веб-ресурс от нелегитимных запросов, с помощью которых можно найти уязвимости CMS и затем взломать её.
ModSecurity по умолчанию подключают все хостинг-провайдеры для защиты сайтов клиентов. Подробнее о работе брандмауэра ModSecurity читайте на modsecurity.org.
HTTP 406 ошибка чаще всего имеет локальный характер и возникает на стороне клиента. В редких случаях, чтобы исправить проблему, необходимы действия со стороны владельца.
Основные причины
- Брандмауэр ошибочно блокирует корректные запросы.
- Временная проблема идентификации IP-адреса при подключении к Wi-Fi.
- Ваш браузер поврежден вирусами. К заражению могли привести установленные для браузера расширения или поврежденные файлы операционной системы.
- Поврежден реестр Windows. Нередко такое происходит в результате последних обновлений программного обеспечения или после удаления тех или иных его компонентов.
- Когда клиенты жалуются, что видят страницу с 406, самая вероятная причина — некорректная работа плагинов CMS. Чаще всего такое бывает на Wordpress-сайтах.
Как исправить HTTP 406 Not Acceptable
Если вы пользователь:
- Почистите файлы cookies. Если при повторном подключении вы снова увидите ошибку, попробуйте очистить кэш браузера. Возможно, доступ уже восстановлен, но ваш браузер обращается к старой версии страницы.
- Отключите дополнительные расширения. Запустите браузер в режиме «Инкогнито». В этом режиме браузер задействует только базовые настройки. Если веб-ресурс доступен в этом режиме, значит причина ошибки в одном из дополнительных расширений, которые вы используете.
- Переустановите браузер. Если вы отключили расширения, но доступ к сайту не появился, попробуйте ввести аналогичный запрос через другой поисковик. Если страница открывается, значит есть критические нарушения в работе текущего браузера.
- Обновите драйверы компьютера. Иногда драйверы устройства отключаются и перестают автоматически работать. Это может спровоцировать нарушение в подключении. Для восстановления работы достаточно обновить драйверы.
- Отмените последние изменения, если у вас Windows. Восстановление системы позволит вернуть программы и системные файлы вашего компьютера в то состояние, когда не было сбоев в работе.
- Просканируйте системные файлы. Благодаря этому можно обнаружить поврежденные файлы и восстановить их. Это поможет оптимизировать работу компьютера и, возможно, устранить проблему.
Если указанные способы не помогли, вероятно, проблема связана с настройками сайта.
Если вы владелец сайта:
1) Если ваш сайт создан на WordPress, проверьте работу плагинов. Чтобы убедиться, что проблема именно в них, можно отключить сразу все плагины и проверить соединение.
Если вы уверены, что на работу влияет конкретный плагин — отключите его. Если не уверены, то отключайте плагины по очереди, пока не вычислите нужный. Для этого:
-
1.
Войдите в панель управления WordPress. Если вы пользуетесь услугой REG.Site, войти в панель управления CMS можно прямо из Личного кабинета.
-
2.
Перейдите на Плагины ― Установленные.
-
3.
Нажмите Деактивировать для плагина, который хотите отключить:
2) Если ваш сайт создан не на WordPress или отключение плагинов не дало результата, чтобы исправить ошибку 406, напишите заявку в техническую поддержку.
Ошибка 410 Gone
Иногда при переходе на одну из страниц сайта может встретится ошибка 410, что значит, что этой страницы больше не существует. Следовательно, проблема возникла на стороне владельца сайта.
Этим 410 похожа на ошибку 404 (страница не найдена). Их основное отличие в том, что при ошибке 404 страница либо не существовала, либо наоборот — существует, но временно не найдена (например, потому что скрыта от пользователей). Ошибка 410 же сообщает, что страница точно существовала раньше, но затем её удалили.
Также ошибки по-разному обрабатывают поисковые роботы. Если роботы встретят страницу с ошибкой 404, они перенесут индексацию сайта на 24 часа. Если сервер выдаст страницу с 410, роботы сразу отметят её как удаленную и больше не будут индексировать. Для владельца сайта это не очень хороший сценарий, поскольку не индексируемые страницы негативно влияют на позиции сайта в поисковых системах.
Как исправить
Способ исправить ошибку 410 HTTP зависит от намерений владельца.
- Если страница удалена по ошибке, можно попробовать восстановить её из резервной копии.
- Если страницу удалили намеренно, лучше всего настроить редирект. Редирект помогает сделать перенаправление одной страницы на другую. Это позволит сохранить поисковые позиции.
Ошибка 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Код ошибки 505 говорит нам о том, что проблема возникла на уровне сервера. Вот что означает ошибка 505: с её помощью сервер сообщает, что не может установить соединение по той версии HTTP-протокола, с помощью которой к нему хотят подключиться.
Основные причины
- Пользователь использует устаревший браузер, который не поддерживает новые версии протокола. То есть в этом случае браузер подключается по версии HTTP 1.1, а сервер работает по версии HTTP 2.
- Сервер не поддерживает HTTP-протокол, с помощью которого пытается подключиться клиент. Например, он работает по версии HTTP 1.1, а запрос поступает из браузера с версии HTTP 2.
- Неверные директивы, указанные в файле .htaccess.
- Неполадки в работе скриптов ресурса.
Как исправить ошибку 505
Если вы пользователь:
- Почистите файлы cookies и кэш браузера.
- Обновите версию браузера.
- Обновите операционную систему и драйверы.
- Обратитесь к интернет-провайдеру. Если все страницы показывают 505 в любых браузерах, обратитесь в службу поддержки вашего провайдера.
Если вы владелец сайта:
- Узнайте, по какой версии протокола работает ваш сайт. Обновите её до актуальной, если необходимо. Например, серверы REG.RU работают с протоколом HTTP 1.1.
- Проверьте логи веб-сервера. Определите, где кроется ошибка (в работе CGI-скриптов, директивах .htaccess или файле конфигурации веб-сервера) и исправьте её.
- Если проблема в скриптах, обратитесь к разработчику сайта.
Understand the HTTP 410 Gone Error code: What are the causes, and solutions, and why we sometimes intentionally use this error response in SEO.
Table of Contents
- What is the 410 Gone error?
- 410 error messages
- 410 Gone vs 404 Not Found
- 410 Gone vs 404 Not Found for SEO
- Solving the 410 Gone
- How to create 410 errors for no longer existing pages?
-
How to configure the 410 error with Apache
- Redirect to the 410 error page with the Apache mod_alias module:
- Redirect to 410 error pages with the Apache mod_rewrite module
- How to configure the 410 error with Nginx
- How to show the 410 error with PHP code
-
How to configure the 410 error with Apache
- All HTTP Status Codes
What is the 410 Gone error?
The HTTP 410 Gone Client Error is a response code that indicates that requested resource is no longer accessible and that this condition is likely to be permanent.
This is an error message that is usually used to explicitly indicate that a certain resource or page is no longer available.
410 error messages
Depending on the web server or browser you may find different descriptive messages for this error:
- “HTTP Status 410”
- “410 Gone”
- “This page can’t be found -It may have been moved or deleted. HTTP ERROR 410”
- “ERROR 410”
- A Blank page, e.g. Firefox Browser.
For example, in Brave browser (based on the Chromium web browser), you’ll likely see a paper icon along with a simple message telling you “This web.domain page can't be found“:
The default 410 Gone error displayed by Apache, looks like this:
410 Gone vs 404 Not Found
The “410 Gone” error can be confused with the “404 Not Found” error. Both error codes are used to communicate that the requested page or resource is not available.
The difference is subtle: The 410 Gone Error means “permanently not available” while the 404 Not Found means “temporarily not available”.
A common situation in which we encounter the 404 error is when we try to access a misspelled URL.
One use case where the HTTP 410 code is helpful is that of a malware infection. The malware may have published URLs with words in search engines that can damage our reputation. Showing a 410 is a way to indicate to crawlers that we do not have that content.
410 Gone vs 404 Not Found for SEO
When Google crawls your website to index your pages, it will treat each page or resource differently depending on the HTTP code returned by the server.
In a Webmaster Hangout, Google’s John Mueller explained the difference:
The subtle difference here is that a 410 will sometimes fall out a little faster than a 404. But usually, we’re talking on the order of a couple days or so.
John Mueller, Senior Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google
Here in this Webmaster Hangout, you have the explanation from John Mueller:
Transcription:
– John Muller: “… from our point of view in the mid term, long term 404 is the same as 410, for us. So in both of these cases we drop those URLs from the index … we generally reduce crawling a little bit of those URLs, so that we don’t spend so much time crawling things that we know don’t exist. The subtle difference here is that a 410 will sometimes fall out a little bit faster than a 404. We usually are talking on the order of couple of days.”
Use the 410 Gone Status Code, if you want to speed up the process of Google removing the web page from their index.
Speeding up page removal from a search index can be especially useful after a malware intrusion, where a hacker infects a site with hundreds of spam pages and hideous URLs. Redirecting all those spam pages to a 410 Gone status page will help us speeding up the index deletion.
Solving the 410 Gone
The 410 Error tends to be an intentional error code. Webmasters use it to declare that a resource is no longer available, so we can consider that it is not a random web error or server configuration error.
Having said that, if you experience a “410 Gone” error:
- It’s a good idea to check the link you are trying to visit. If there is no mistake in the URL, then,
- Take into account that the website owner might have intentionally removed the content or moved it to a new domain or URL.
- A final workaround is to look for the “product”, “service” or “content” by using some keywords on your preferred search engine.
How to create 410 errors for no longer existing pages?
We describe below different methods to help you create 410 errors
How to configure the 410 error with Apache
You can redirect a page to the 410 Gone error using two different modules.
Redirect to the 410 error page with the Apache mod_alias module:
The easiest way to redirect to 410 error pages on Apache servers is to call the default 410 HTTP server response using the “Redirect” directive in your apache.config or .htaccess file:
Redirect gone /path/to/the/page_to_removeRedirect to 410 error pages with the Apache mod_rewrite module
If you need more sophisticated redirections you can use the RewriteRule of mod_rewrite Apache module.
Reproducing the same previous redirect with a Rewrite command in your your apache.config or .htaccess file:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^/path/to/the/page_to_remove$ - [L,NC,G]The flag “G” is the one in charge of showing the “Gone” error.
As mentioned, with this mod_rewrite module you can use regular expressions and target multiple pages at once:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^/path/to/the/(page_to_remove|page_to_eliminate|also_this_one).php$ - [L,NC,G]How to configure the 410 error with Nginx
If you are working with Nginx, edit you nginx.conf file define a location block to target your single or multiple pages. Reproducing same previous sample URL: /path/to/the/page_to_remove
location = /path/to/the/page_to_remove {
return 410;
}And you can also take advantage of the regex rules in the location section like any other nginx location configuration. Reproducing previous sample of multiple pages:
location ~ ^/path/to/the/(page_to_remove|page_to_eliminate|also_this_one) {
return 410;
}At Wetopi we use Nginx for it’s performance, and best part is that you can use your own Free development servers to test configuration changes like the ones exposed in this article.
Save you website: don’t test in production!
When testing new server configurations, it is highly recommended to work on a “localhost” or “Staging” server.
If you don’t have a development WordPress server, signup at wetopi, it’s FREE.
How to show the 410 error with PHP code
If you want to show the “410 Gone” in a PHP page, all you need is to output the 410 header.
Paste the following code at the beginning of the affected page:
<?php
header( "HTTP/1.1 410 Gone" );
exit();All HTTP Status Codes
200 OK
201 Created
202 Accepted
203 Non-Authoritative Information
204 No Content
205 Reset Content
206 Partial Content
207 Multi-Status
208 Already Reported
226 IM Used
300 Multiple Choices
301 Moved Permanently
302 Found
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
305 Use Proxy
307 Temporary Redirect
308 Permanent Redirect
400 Bad Request
401 Unauthorized
402 Payment Required
403 Forbidden
404 Not Found
405 Method Not Allowed
406 Not Acceptable
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
409 Conflict
410 Gone
411 Length Required
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
414 Request-URI Too Long
415 Unsupported Media Type
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
417 Expectation Failed
418 I’m A Teapot
421 Misdirected Request
422 Unprocessable Entity
423 Locked
424 Failed Dependency
426 Upgrade Required
428 Precondition Required
429 Too Many Requests
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
444 Connection Closed Without Response
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
499 Client Closed Request
We are techies passionate about WordPress. With wetopi, a Managed WordPress Hosting, we want to minimize the friction that every professional faces when working and hosting WordPress projects.
Not a wetopi user?
Free full performance servers for your development and test.
No credit card required.
Для удобства вывода и обработки ошибок в сети Интернет была введена классификация и структурирование. Существует целый ряд ошибок 4ххх. В этом выпуске поговорим о конкретной ошибке: ошибка 410 что это и как решить эту проблему на сайте, youtube, планшете или телефоне, который работает на андроиде.
[toc]
Определение ошибки простым языком
Не всегда достаточно просто найти, как исправить ошибку 410, к примеру, на сайте YouTube. Порой встречаются совершенно нестандартные ситуации, поэтому, если вы понимаете природы появления этой ошибки, вы легко сможете решить даже не типичную проблему.
Давайте простыми словами выясним, ошибка 410 что это? Итак, ошибка 410 – это ответ сервера на вносимые изменения разработчиком. Проще говоря, когда возникает такая ошибка, виноваты либо вы, либо прямые руки разработчика. Но часто, такую ошибку можно встретить на YouTube и старых версиях Android. Например, к старой версии Google относит Android 4.0.
Ошибка или код 410 – Gone, значит, что страница или запрашиваемый файл был удален. Частично ошибка дублируется ошибкой 404 (Not Found – Не найдено).
В результате, чтобы вы не предпринимали, вам будет выходить ошибка 410 проблемы с сетью. Но не стоит отчаиваться, есть несколько способов решить данную проблему. Единственный момент, нужно четко понимать, что данная ошибка не связана с обновлением приложения или системы сайта. В этом случае никакие танцы с бубном вас не спасут.
Наиболее распространенные места возникновения этой ошибки: на Youtube (если у вас Android), на телефоне, на планшете, просто на сайте. Ниже мы подробно рассмотрим варианты, как исправить ошибку 410.
Если ошибка 410 возникла на Ютубе
Часто данная ошибка связана именно с обновлением официального приложения. Как это исправить? Так, если вылезла ошибка 410 в ютубе на адроиде, значит нужно проверить обновление программы. Как это сделать?
- Для этого нужно зайти в Play Market
- Найти приложение YouTube
- Нажмите кнопку обновить
- Если проживаете в Крыму, не забудьте включить VPN
Используйте ВПН для обновления, если вы живете в Крыму
Если обновить приложение не получается, значит версия прошивки не поддерживает больше такие обновления. Разработчики намерено отключили возможность поддержки старых устройств, намекая на покупку нового устройства. Например, если у Вас Андроид 4.4, тогда для вас это будет проблемой.
Если причины в прошивке устройства
Какой выход? Сразу хочу предупредить, что для устройств, которые выпушены лет 6 назад, вы не получите обновлений, необходимых для работы сервисов Play Market, а значит и приложения YouTube. Однако, есть способы как решить проблему, если ошибка 410 появилась на планшете. Давайте по порядку, проверим можно ли официально обновиться.
Проверьте обновления Вашей системы Android
- Пройдите в Настройки телефона или планшета.
- Найдите последний пункт «Об устройстве»
- Найдите пункт обновление и проверьте доступны ли они для вас.
- Если обновления есть – нужно скачать и установить, используя инструкции.
- По завершению обновления, перейдите в Play Market
- Найдите в ней программу YouTube и выполните обновление. После этого Ошибка 410 YouTube вас беспокоить не будет.
Убедитесь, что ошибка 410 не из-за устаревшей прошивки
Если устройство старое, то вероятно, обновлений не будет. Вариантов решения вопроса не много: либо установить прошивку новую не официальную, либо установить другую программу для просмотра YouTube. Благо таких программ полно:
- Vutube Player
- Newpipe
- OGYouTube
- YouTube Vanced
Кроме возможности смотреть видео с ютуба, программа блокирует любую рекламу. Однако, войти в свой аккаунт не выйдет, так программа не привязана к сервисам Google Play Market. Также есть моды официального приложения для старых прошивок, начиная с версии Андроид 2.2. Найти такую программу можно на сайте 4pda. Чтобы скачать, потребуется регистрация. Поэтому, если возникает ошибка 410 на адроид, что делать вы уже знаете.
ВАЖНО: перед установкой программ в настройках придется установить разрешение на сторонние приложения. Это нормально и ничего криминального в этом нет, тем более для вашего не столь нового устройства.
Если ошибка 410 появилась на сайте
Иногда ошибка 410 встречается на сайте, в том числе на популярных порталах. Сразу хочется сказать, что, если вы не администратор ресурса, то вам не стоит паниковать. Исправить вы ничего не сможете, если конечно сбой не носит системный характер.
- Проверьте настройки времени на своей ПК или ноутбуке. Обычно, ошибка 410 на сайте может возникать, если установлены не корректная дата в системе. Порой происходит сбой и время «слетает». Попробуйте решить вопрос включением автоматического времени.
- Также, проблема ошибки 410 может возникнуть от блокировки сайта антивирусом. Особенно это встречается в бесплатных версиях антивирусов Avast. Редко, но можно встретить такую беду и в антивирусе Dr.Web. Решается просто: кликните по значку антивируса правой кнопкой мыши и нажмите «Отключить». После этого пройдите на сайт. Если ничего не изменилось, ищите проблему дальше.
- Если вы администратор сайта и только что внесли изменения в файлах или настройках, нужно немного подождать. Конфигурация обновляется обычно в течении часа. Если через час ничего не изменилось, даже после очистки кэша браузера, свяжитесь с хостинг провайдером для выяснения причины проблемы. Иногда она возникает после обновления версии PHP на 7.1.
Обратите внимание: Действия на компьютере нужно делать, если вы уверены на 100%, что проблема именно на вашей стороне. Проверьте сайт на другом устройстве. Если ошибка 410 на планшете или телефоне не возникает, тогда поработайте над своим компьютером. Иногда вопрос может решиться только переустановкой системы Windows.
Если возникла проблема с сетью
Иногда бывают ситуации, когда ни один из вышеперечисленного не решает проблему. Например, у вас возникла ошибка 410 на телефоне, хотя прошивка свежая, да и программы обновлены. Что делать в этом случае? Как правило, причина проблема всего одна – ваш роутер. Что нужно сделать?
- Просто отключите ваш роутер на 15 минут. Желательно полностью отключить из розетки, а не выключить кнопкой на устройстве. Иногда такие сбои происходят ввиду постоянной работы вашего роутера.
- Время и DNS настроены не верно. Если вы разбираетесь в настройках роутера, тогда пройдите по адресу 192.168.0.1 (обычно это стандартный адрес настроек роутера) и найдите настройки самого устройства. Проверьте дату. Также в настройках интернета проверьте совпадает ли DNS с выданным вашим провайдером. Если ничего вам не давали – DNS должен быть пустым.
- Обновите прошивку роутера. Крайний случай, когда возникает проблема с сетью ошибка 410 – это перепрошить или обновить роутер. Например, компания Huawei выпустила роутер с явно сырой прошивкой W550, после чего, буквально через месяц выкатили свежее обновление.
Заключение
Ошибка 410 возникает чаще всего по вине администратора сайта или владельца приложения. При возникновении сбоя, не спешите искать проблему на своем устройстве. В первую очередь нужно убелиться, что проблема не является общей на всех устройствах. Удачи.
- Ошибка 400 (Bad Request) причины появления и способы устранения
- Ошибка 410 (Gone): причины появления и способы устранения
Ошибка 400 (Bad Request)
Ошибка 400 значит, что запрос к серверу содержит синтаксическую ошибку. Но иногда проблема вызвана факторами, которые не имеют прямого отношения к запросу.
Причины появления ошибки 400
- Доступ к странице заблокирован антивирусом, файрволом или оборудованием интернет-провайдера сети, через которую вы обращаетесь к сайту. Проблема может появиться после обновления системы безопасности, когда меняются ее настройки.
- Владелец сайта неверно настроил правила перенаправления в используемых на сайте скриптах или в конфигурации веб-сервера.
- Посетителем сайта действительно допущена синтаксическая ошибка (которая делает введённый в браузере адрес неверным URL с точки зрения сервера).
Способы устранения ошибки 400 Bad Request
Для пользователей:
- очистите кеш и куки браузера;
- проверьте настройки антивируса и брандмауэра;
- проверьте не заблокирован ли сайт интернет-провайдером.
Для владельца сайта:
- проверьте правила перенаправления запросов в .htaccess;
- проверьте корректность выдачи заголовков перенаправления, выдаваемых используемыми на сайте скриптами.
Ошибка 410 (Gone)
Появление ошибки связано с удалением исходной страницы, поэтому она похожа на страницу 404, когда страница не найдена. Разница в том, что второй случай допускает обращение к странице, которая никогда не существовала, а 410 относится только к удаленным.
Но роботы поисковых систем по-разному реагируют на ошибки 404 и 410. Встретив ошибку 404, система отложит индексацию на сутки. При 410 ошибке робот фиксирует это, после чего не заходит на такую страницу и исключает ее из поиска.
Способы устранения ошибки 410 Gone
Если отсутствие страницы обусловлено внутренними работами – верстка текста, исправление ошибок, то лучше отмечать ее кодом 404. Если страница удалена случайно, то вы можете восстановить ее при наличии резервной копии.
Умные люди придумали коды, по которым можно определить, что произошло с HTTP-запросом. Успешен ли он, произошло ли перенаправление. Или же все закончилось ошибкой. Как раз об ошибках и будем говорить в этой статье. Вкратце расскажу, какие они бывают и с чем связаны.
А еще тут будет парочка забавных (и не очень) пикч и анимаций на тему описанных ошибок. Хоть какое-то развлечение.
Ошибки со стороны клиента (4xx)
Для начала перечислим коды ошибок на стороне клиента. Вина за их появление ложится на плечи обоих участников соединения.
400 Bad Request
Такой ответ от браузера можно получить в том случае, если сервер не смог правильно отреагировать на запрос со стороны пользователя. Часто код 400 возникает при попытке клиента получить доступ к серверу без соблюдения правил оформления синтаксиса протокола передачи гипертекста (HTTP). Повторный запрос не стоит отправлять до тех пор, пока не будет исправлена ошибка (или несколько из них).
401 Unauthorized
Код 401 возникает при попытке клиента получить доступ к серверу, используя неправильные данные для авторизации. По сути, используется, когда пользователь вводит неправильный логин и пароль на ресурсе, где требуется эта информация для входа. Читайте: Как исправить ошибку 401
402 Payment Required
Эта ошибка сообщает клиенту о том, что для успешного выполнения запроса ему необходимо оплатить доступ к серверу. Изначально код 402 должен был стать неким стандартом для цифровой валюты и оплаты контента в сети. Но не срослось. До сих пор нет единого решения по поводу того, как должны выглядеть платежи в сети. Также нет и единого решения по поводу того, как стоит использовать 402.
Все еще считается, что код существует с расчетом на будущее. Сейчас почти не используется и поддерживается не всеми браузерами.
403 Forbidden
Почти то же, что и 401. Сервер снова не разрешает к нему подключиться, хотя с запросом все в порядке. Просто нет доступа. Причем повторная авторизация с другими логином и паролем никак не помогут. Все вопросы к владельцам сервера (но не всегда). Инструкция по устранению ошибки.
Творчество на тему знаменитой киносаги
404 Not Found
Легендарная ошибка, ставшая популярным мемом. 404 оповещает клиента о том, что его запрос ведет в никуда. Код возникает, когда пользователь пытается попасть на страницу, которой не существует. Например, когда случайно ошибается при вводе ссылки и вводит ее с опечаткой. Или же пытается получить доступ к странице, которой на сайте уже нет.
В отличие от других кодов, страницу с 404 частенько кастомизируют, создавая для нее уникальный дизайн. Мало того, что это выглядит симпатичнее, так еще и полезнее для посетителей. Можно прямо на странице с ошибкой разъяснить, что произошло и как дальше действовать.
И таких вариаций тысячи. Каждый пытается добавить в оформление что-то свое.
405 Method Not Allowed
405 сообщает клиенту о том, что метод, используемый при запросе, не разрешен. В качестве примера можно привести попытку со стороны клиента ввести данные в форму с помощью GET, когда она работает только с POST. Ну и в таком же духе.
406 Not Acceptable
Ошибка 406 сообщает о том, что страница передает контент, который не может быть распознан клиентом. Возможно, проблема в методе сжатия или в формате страницы. Иногда сюда же приплетают неправильные настройки кодировки.
Этот код редко используют на практике, так как его появления можно избежать, предоставив пользователю информацию на сайте в том виде, который его браузер способен принять. Посетитель сайта по итогу получит не то, что ожидал, но хотя бы не ошибку.
407 Proxy Authentication Required
Этот код тоже похож на 401. Только на этот раз логин и пароль нужны не для основного сервера, а для прокси, который находится между клиентом и сервером. Обычно в теле ошибки содержится информация о том, как можно правильно пройти авторизацию и получить доступ к ресурсу.
408 Request Timeout
408 говорит нам о том, что сервер пожелал разорвать соединение с клиентом, потому что оно никак не используется. Происходит это в том случае, если сервер буквально устал ждать, пока наладится соединение с ним. Поэтому такую ошибку часто можно лицезреть после очень долгой и безуспешной загрузки какого-нибудь сайта.
Многие серверы не отправляют никаких сообщений, а просто прерывают соединение по той же причине. На запрос уходит больше времени, чем на то полагается.
В Мистере Роботе частенько называли серии в честь ошибок HTTP (весь четвертый сезон в нумерации 4хх). В честь 408, например, назвали восьмую серию четвертого сезона
409 Conflict
Сообщение о конфликте возникает, когда запрос со стороны клиента не соответствует тому, чего ожидает сервер. В качестве примера приводят проблемы при проверки версий, когда пользователь пытается с помощью метода PUT загрузить на сервер новый файл, но там уже имеется более новая версия того же файла. Конфликта версий можно легко избежать, загрузив корректную версию.
410 Gone
Своего рода аналог 404. Разница лишь в том, что 410 намекает на перманентность отсутствия страницы. Так что этот код стоит использовать, когда на 100% уверен, что страница ушла в небытие (ну или с текущего адреса) навсегда. В любом другом случае есть универсальный 404.
411 Length Required
411 оповещает пользователя о том, что сервер не желает принимать запрос со стороны клиента, потому что в нем не определен заголовок Content-Length. Да, это первый код в подборке, который смогут понять только люди, сведущие в настройке серверов. По-простому уложить сущность HTML-заголовков в этот материал не получится.
412 Precondition Failed
Еще один код, сообщающий о том, что сервер отклонил запрос пользователя и не разрешает доступ к выбранному ресурсу. Проблемы возникают при неправильной настройке работы методов, отличающихся от GET и HEAD.
413 Payload Too Large/Request Entity Too Large
Код 413 говорит нам, что запрос, который посылает клиент на сервер, слишком большой. Поэтому сервер отказывается его обрабатывать и разрывает соединение. Обычно это происходит при попытке загрузить на ресурс какой-то файл, превышающий ограничение, выставленное в настройках сервера. Соответственно, решается проблема изменением настроек сервера.
414 URI Too Long
Чем-то этот код похож на предыдущий. Здесь тоже идет речь о превышение лимита. Только теперь это касается не запроса со стороны клиента, а длины URI. То есть ссылки. Выходит, что адрес, используемый клиентом, больше, чем тот, что может обработать сервер. Как-то так.
Такая ошибка иногда выскакивает при попытке взломать ресурс. Сайт так реагирует на слишком частые попытки воспользоваться потенциальными дырами в безопасности.
415 Unsupported Media Type
Ошибка 415 возникает, когда клиент пытается загрузить на сервер данные в неподходящем формате. В таком случае сервер просто отказывается принимать посылаемые файлы и разрывает соединение. Как и в случае с 413.
416 Range Not Satisfiable
Подобный ответ можно ожидать, если клиент запрашивает у сервера определенные данные, но эти данные на сервере не соответствуют запросу. То есть, грубо говоря, вы просите у сервера какой-то набор данных с заранее заданным размером, а в итоге оказывается, что размер этих данных меньше, чем объем, указанный в запросе. Серверу ничего не остается, кроме как послать вас, ведь он не обучен поведению в таких ситуациях.
417 Expectation Failed
Такая ошибка высвечивается, когда ожидания сервера не совпадают с данными в запросе клиента. Сведения об ожиданиях прописываются в заголовке Expect заранее. Так что можно ознакомиться с ними, чтобы выяснить, как решить названную проблему.
418 I’m a teapot
Код 418 можно увидеть, если сервер откажется варить кофе, потому что он чайник. Это первоапрельская шутка. Естественно, 418 не используется нигде всерьез и просто существует как дань памяти программистам-юмористам, придумавшим это в 1998 году.
У Google получился такой симпатичный чайник
421 Misdirected Request
Появляется когда запрос клиента переправляется на сервер, который не может дать на него адекватный ответ. Например, если запрос был отправлен на ресурс, который вообще не настроен обрабатывать запросы извне.
Чтобы исправить проблему, можно попробовать переподключиться к ресурсу заново или попробовать другое соединение.
422 Unprocessable Entity
Код 422 говорит, что сервер вроде бы принял запрос, понял его, все хорошо, но из-за семантических ошибок корректно обработать не смог. Значит, где-то в запросе затаилась логическая ошибка, мешающая корректному взаимодействию клиента и сервера. Надо ее найти и исправить.
423 Locked
Обычно на этот код напарываются, когда запрашиваемый ресурс оказывается под защитой. Используемые клиентом методы блокируются на уровне сервера. Это делается, чтобы обезопасить данные, хранящиеся на защищенной странице. Без логина и пароля выудить информацию с такого сервера не получится.
424 Failed Dependency
424 сообщает о том, что для выполнения запроса со стороны клиента успешно должна завершиться еще одна или несколько параллельных операций. Если какая-то из них «провалится», то «помрет» все соединение сразу, и обработать запрос до конца не получится. Аналогичное происходит, если некорректно был обработан один из предыдущих запросов.
425 Too Early
Появляется в ответ на запрос, который может быть моментально запущен заново. Сервер не рискует и не берется за его обработку, чтобы не подставиться под так называемую «атаку повторного воспроизведения».
426 Upgrade Required
Тут нам прямо сообщают, что сервер не желает с нами общаться, пока мы не перейдем на более современный протокол. Наткнуться на такую ошибку очень тяжело, но в случае появления, скорее всего, будет достаточно установить браузер посвежее.
428 Precondition Required
428 выскакивает, если пользователь отправляет запрос на сервер, но получает некорректные или неактуальные данные. Так ресурс оповещает о необходимости внести в запрос информацию о предварительных условиях обработки данных. Только так он сможет гарантировать получение клиентом нужной информации.
429 Too Many Requests
Здесь все просто. Ошибка появляется, когда клиент отправляет на сервер слишком много запросов в короткий промежуток времени. Очень похоже на поведение взломщиков. По этой причине запрос моментально блокируется.
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Из названия понятно, что ошибка с кодом 431 появляется из-за того, что в запросе клиента используются слишком длинные заголовки (неважно, один или несколько из них). Исправляется это с помощью сокращения заголовков и повторной отправки запроса. В теле ошибки обычно отображается краткая информация о том, как пользователь может решить эту проблему самостоятельно.
444 No Response
Этот код вам вряд ли удастся увидеть. Он отображается в лог-файлах, чтобы подтвердить, что сервер никак не отреагировал на запрос пользователя и прервал соединение.
449 Retry With
Код используется в расширениях компании Microsoft. Он сигнализирует о том, что запрос от клиента не может быть принят сервером. Причиной становятся неверно указанные параметры. Сама 449 ошибка говорит о необходимости скорректировать запрос и повторить его снова, подготовив к работе с сервером.
450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
450 код увидят дети, попавшие под действие системы «Родительский контроль» компании Microsoft. По сути, ошибка говорит о том, что с компьютера попытались зайти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать этой ошибки можно изменением параметров родительского контроля.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Этот код сообщает клиенту, что он не может попасть на запрашиваемый ресурс из юридических соображений. Скорее всего, доступ был заблокирован из-за каких-нибудь государственных санкций, нового законодательства или цензуры со стороны властей. В общем, все вопросы к государству и провайдеру связи.
Читайте также
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Список ошибок на стороне сервера (5xx)
Теперь поговорим об ошибках, которые возникают где-то на сервере. Все они связаны с запросами, которые не удается обработать на том конце. Пользователь зачастую в их появлении не виноват.
500 Internal Server Error
Этот код возникает, когда сервер сталкивается с непредвиденными обстоятельствами. Такими, которые и сам не может пояснить. Как, собственно, и завершить запрос со стороны пользователя. По факту, эта ошибка говорит нам что-то вроде «Я не могу подобрать более подходящий код ошибки, поэтому лови 500 и делай с этим, что хочешь». Мы писали о нем чуть подробнее тут.
Дело не в тебе, дело во мне (С)
501 Not Implemented
501 говорит нам, что функциональность, необходимая для обработки запроса со стороны клиента, попросту не реализована на сервере. Он не сможет корректно обработать используемый метод.
Иногда в теле ошибки еще пишут что-то в духе «Приходите попозже, возможно, в будущем нужная функция появится».
502 Bad Getaway
Можно встретить в том случае, если запрашиваемый сервер выступает в роли шлюза или прокси. Возникает из-за несогласования протоколов между вышестоящим серверов и его шлюзом. Рассказываем о том, как ее исправить, в этой статье.
503 Service Unavailable
Появляется, когда сервер не может обработать запрос клиента по одной из двух технических причин:
- Слишком много пользователей в текущий момент пытаются отправить запросы, и у сервера не остается ресурсов, чтобы ответить кому-либо еще.
- На сервере ведутся технические работы, временно блокирующие его работу.
Обычно ошибка 503 носит временный характер, и для ее решения достаточно немного подождать.
504 Gateway Timeout
Ошибка похожа на 408. Здесь же прокси-сервер пытается выйти на контакт с вышестоящим сервером, но не успевает это сделать до истечения тайм-аута. Отсюда и ошибка.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Этот код похож на 426. Он тоже связан с неподходящей версией протокола HTTP. В этом случае нужно обеспечить и клиента, и сервер единой версией. Она, как правило, указывается в запросе со стороны пользователя.
506 Variant Also Negotiates
Обычно с такой ошибкой сталкиваются только в том случае, если сервер изначально настроен неправильно. То есть это не сиюминутная проблема, а что-то серьезное на уровне базовой конфигурации. Тут придется потрудиться разработчикам. Выявить проблему и разрешить ее.
507 Insufficient Storage
Код 507 встречается в тех ситуациях, когда серверу не хватает пространства в хранилище для обработки запроса со стороны клиента. Проблема решается освобождением места или расширением доступного пространства. Тогда сервер сможет без проблем обработать запрос пользователя.
508 Loop Detected
Таким кодом сервер отзовется в случае, если заметит бесконечный цикл в запросе клиента. Можно расценивать его как провал запроса и выполняемой операции в целом.
509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Возникает, если сервер начинает потреблять больше трафика, чем ему позволено.
510 Not Extended
Появляется, если клиент посылает запрос на использование какого-либо расширения, отсутствующего на сервере. Чтобы исправить проблему, надо убрать декларирование неподдерживаемого расширения из запроса или добавить поддержку на сервер.
511 Network Authentication Required
511 код говорит о том, что перед тем как выйти в сеть, надо авторизоваться (ввести логин и пароль). Можно воспринимать это неким PPPoE подключением, когда от клиента требуются данные для авторизации.
Заключение
Закончили. Это все ошибки, которыми отзывается HTTP, если на стороне сервера или клиента что-то пошло не так. Наткнуться на большую их часть довольно тяжело. Особенно, если вы раньше только серфили в интернете, а не занимались разработкой сайтов. А тем, кто входит в эту стезю, полезно знать основные ошибки, так как, скорее всего, придется не раз их исправлять.