Автор оригинала: Team Python Pool.
Привет, кодеры! В этой статье мы узнаем об ошибке python list index out of range, а также о том, как её устранить. Сначала мы должны понять, что это значит? Ошибка Индекс списка вне диапазона возникает, когда мы пытаемся получить доступ к недопустимому индексу в нашем списке Python.
Иллюстрация list index out of range с примерами:
Пример 1: с функцией len()
color = ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'pink'] print(color[len(color)])
выход:
Объяснение:
В этом фрагменте кода мы создали список под названием color, содержащий четыре элемента – красный, синий, зеленый, розовый.
В python индексация элементов списка начинается с 0. Таким образом, соответствующие индексы элементов следующие:
- красный – 0
- синий – 1
- зеленый – 2
- розовый – 3
Длина списка равна 4. Таким образом, когда мы пытаемся получить доступ к color[len(color)], мы получаем доступ к элементу color[4], который не существует и выходит за пределы диапазона списка. В результате отображается ошибка list index out of range.
пример 2: с использованием цикла
def check(x):
for i in x:
print (x[i])
lst = [1,2,3,4]
check(lst)
выход:
Объяснение:
Здесь список lst содержит значение 1,2,3,4, имеющее индекс 0,1,2,3 соответственно.
Когда цикл повторяется, значение i равно элементу, а не его индексу.
Таким образом, когда значение i равно 1 (то есть первый элемент), он отображает значение x[1], которое равно 2, и так далее.
Но когда значение i становится 4, он пытается получить доступ к индексу 4, то есть x[4], который становится вне границы, таким образом отображая сообщение об ошибке.
1)Списки индексируются с нуля:
Мы должны помнить, что индексация в списке python начинается с 0, а не с 1. Итак, если мы хотим получить доступ к последнему элементу списка, оператор должен быть записан как lst[len-1] , а не last[long], где len – количество элементов, присутствующих в списке.
Итак, первый пример можно исправить следующим образом:
color = ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'pink'] print(color[len(color)-1])
выход:
Выход
объяснение:
Теперь, когда мы использовали color[lens(color)-1], он обращается к элементу color[3], который является последним элементом списка. Таким образом, вывод отображается без каких-либо href=”https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Error”>ошибка. href=”https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Error”>ошибка.
2)Используйте range() в цикле:
Когда вы перебираете список чисел, то range() должен использоваться для доступа к индексу элементов. Мы забываем использовать его вместо индекса, доступ к самому элементу осуществляется, что может привести к ошибке индекса списка вне диапазона.
Итак, чтобы устранить ошибку второго примера, мы должны выполнить следующий код:
def check(x):
for i in range(0, len(x)):
print (x[i])
lst = [1,2,3,4]
check(lst)
выход:
Выход
Объяснение:
Теперь, когда мы использовали функцию range() от 0 до длины списка, вместо прямого доступа к элементам списка мы получаем доступ к индексу списка, таким образом избегая каких-либо ошибок.
Обязательно Прочтите:
Python List Length | How to Find the Length of List in PythonHow to use Python and() | Python find() String MethodPython next() Function | Iterate Over in Python Using next
Вывод: Индекс списка Python Выходит за пределы диапазона
В повседневном программировании ошибка индекса списка вне диапазона очень распространена. Мы должны убедиться, что мы остаемся в пределах диапазона нашего списка, чтобы избежать этой проблемы. Чтобы избежать этого, мы должны проверить длину списка и код соответственно.
Однако, если у вас есть какие-либо сомнения или вопросы, дайте мне знать в разделе комментариев ниже. Я постараюсь помочь вам как можно скорее.
Счастливого Пифонирования!
In python, lists are mutable as the elements of a list can be modified. But if you try to modify a value whose index is greater than or equal to the length of the list then you will encounter an Indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Example
If ‘fruits’ is a list, fruits=[‘Apple’,’ Banana’,’ Guava’]and you try to modify fruits[5] then you will get an index error since the length of fruits list=3 which is less than index asked to modify for which is 5.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Type is", type(fruits))
fruits[5] = 'Mango'
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/example.py", line 3, in <module> fruits[5]='Mango' IndexError: list assignment index out of range
So, as you can see in the above example, we get an error when we try to modify an index that is not present in the list of fruits.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Solution
Method 1: Using insert() function
The insert(index, element) function takes two arguments, index and element, and adds a new element at the specified index.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the list of fruits on index 1.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.insert(1, "Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava'] Modified list: ['Apple', 'Mango', 'Banana', 'Guava']
It is necessary to specify the index in the insert(index, element) function, otherwise, you will an error that the insert(index, element) function needed two arguments.
Method 2: Using append()
The append(element) function takes one argument element and adds a new element at the end of the list.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the end of the list using the append(element) function.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.append("Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava'] Modified list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava', 'Mango']
Last Updated :
04 Jan, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
If row is a list, then don’t forget that deleting an element of a list will move all following elements back one place to fill the gap, so all of the later indices into the list will be off-by-one (and each time you delete another element, the error in each index grows by one). There are a few ways to avoid this problem — to give one, try iterating through the list backwards.
To respond to how to iterate backwards, you could try using the extra parameters you can pass to range. The first two parameters give the range to iterate over (the lower bound being inclusive, and the upper bound exclusive), and the third parameter is the step:
>>> range(5)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> range(0, 5)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> range(3, 5)
[3, 4]
>>> range(3, 5, -1)
[]
>>> range(5, 3, -1)
[5, 4]
So, in your case, it seems you’d want:
range(len(row) - 1, -1, -1)
Or the easier to read (thanks to viraptor):
reversed(range(len(row))
Alternatively, you could try using list comprehensions (I’m assuming c is a list):
for row_number, row in enumerate(c):
c[row_number] = [x for i, x in enumerate(row) if i in keep]
An IndexError is nothing to worry about. It’s an error that is raised when you try to access an index that is outside of the size of a list. How do you solve this issue? Where can it be raised?
In this article, we’re going to answer those questions. We will discuss what IndexErrors are and how you can solve the “list assignment index out of range” error. We’ll walk through an example to help you see exactly what causes this error.

Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
The Problem: indexerror: list assignment index out of range
When you receive an error message, the first thing you should do is read it. An error message can tell you a lot about the nature of an error.
Our error message is: indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
IndexError tells us that there is a problem with how we are accessing an index. An index is a value inside an iterable object, such as a list or a string.
The message “list assignment index out of range” tells us that we are trying to assign an item to an index that does not exist.
In order to use indexing on a list, you need to initialize the list. If you try to assign an item into a list at an index position that does not exist, this error will be raised.
An Example Scenario
The list assignment error is commonly raised in for and while loops.
We’re going to write a program that adds all the cakes containing the word “Strawberry” into a new array. Let’s start by declaring two variables:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = []
The first variable stores our list of cakes. The second variable is an empty list that will store all of the strawberry cakes. Next, we’re going to write a loop that checks if each value in “cakes” contains the word “Strawberry”.
for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry[c] = cakes[c] print(strawberry)
If a value contains “Strawberry”, it should be added to our new array. Otherwise, nothing will happen. Once our for loop has executed, the “strawberry” array should be printed to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py", line 6, in <module> strawberry[c] = cakes[c] IndexError: list assignment index out of range
As we expected, an error has been raised. Now we get to solve it!
The Solution
Our error message tells us the line of code at which our program fails:
The problem with this code is that we are trying to assign a value inside our “strawberry” list to a position that does not exist.
When we create our strawberry array, it has no values. This means that it has no index numbers. The following values do not exist:
strawberry[0] strawberry[1] …
We are trying to assign values to these positions in our for loop. Because these positions contain no values, an error is returned.
We can solve this problem in two ways.
Solution with append()
First, we can add an item to the “strawberry” array using append():
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
The append() method adds an item to an array and creates an index position for that item. Let’s run our code: [‘Strawberry Tart’, ‘Strawberry Cheesecake’].
Our code works!
Solution with Initializing an Array
Alternatively, we can initialize our array with some values when we declare it. This will create the index positions at which we can store values inside our “strawberry” array.
To initialize an array, you can use this code:
This will create an array with 10 empty values. Our code now looks like this:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] * 10 for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
Let’s try to run our code:
['Strawberry Tart', 'Strawberry Cheesecake']
Our code successfully returns an array with all the strawberry cakes.
This method is best to use when you know exactly how many values you’re going to store in an array.
«Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!»
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Our above code is somewhat inefficient because we have initialized “strawberry” with 10 empty values. There are only a total of three cakes in our “cakes” array that could possibly contain “Strawberry”. In most cases, using the append() method is both more elegant and more efficient.
Conclusion
IndexErrors are raised when you try to use an item at an index value that does not exist. The “indexerror: list assignment index out of range” is raised when you try to assign an item to an index position that does not exist.
To solve this error, you can use append() to add an item to a list. You can also initialize a list before you start inserting values to avoid this error.
Now you’re ready to start solving the list assignment error like a professional Python developer!
Решил посмотреть как можно сделать сортировщик массивов на python. Нашёл программу, разобрался в ней, но вот интегрировать с другим кодом не получается, тогда начал частично переносить код в этот. После переноса создания массива вылезает ошибка «list assignment index out of range». Что делать?
Сам код:
def quicksort(array):
if len(array) < 2:#Базовый случай: массивы с 0 и 1 элементом уже отсортированы
return array
else:
pivot=array[0]#Рекурсивный Случай
#print("Опорный элемент pivot --> ",pivot)
less = [i for i in array[1:] if i <= pivot]#Подмассив всех элементов, меньших опорного
#print("Меньших опорного --> less",less)
greater = [i for i in array[1:] if i > pivot]#Подмассив всех элементов, больших опорного
#print("Больших опорного --> greter",greater)
return quicksort(less) + [pivot] + quicksort(greater)
i = 0
n = int(input('Введите кол-во чисел для сортировки: '))
A = [n]
for i in range(0,n) :
i = int(i)
A[i]=input('Введите число: ')
i+=1
print(quicksort(A))The IndexError is a common error that occurs in Python when you try to access an index that is out of range for a list. This error can occur when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in the list. In this tutorial, we will discuss how to fix the IndexError list assignment index out of range in Python.
Understanding the Error
Before we dive into the solution, let’s first understand what causes the IndexError list assignment index out of range error. This error occurs when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in the list. For example, consider the following code:
my_list = [1, 2, 3] my_list[3] = 4
Output:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IndexError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[1], line 2
1 my_list = [1, 2, 3]
----> 2 my_list[3] = 4
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
In the above code, we are trying to assign the value 4 to the index 3 of the my_list list. However, the my_list list only has three elements, so the index 3 does not exist. This results in the IndexError list assignment index out of range error.
Fixing the Error
To fix the IndexError list assignment index out of range error, you need to make sure that the index you are trying to access or assign a value to exists in the list. You can use an if statement to check if the index exists in the list.
Note that Python sequences also allow negative indexing so be mindful of this when checking if an index exists in a list or not. Let’s look at an example.
# create a list
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
# index to assign the value
index = 3
# check if the index exits, if yes, then assign the value
if -len(my_list) <= index < len(my_list):
# perform the assignment operation
my_list[3] = 4
else:
print("Assingnment index is out of range")
Output:
Assingnment index is out of range
Note that if you’re sure that the given index is not negative, you can just check if the index lies in the range 0 to the length of the list using index < len(my_list).
If your end goal is to add an element to a list, you can instead use the list append() or insert() functions.
The append() method adds an element to the end of the list, so you don’t have to worry about the index. For example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3] my_list.append(4) print(my_list)
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
Here, we added the element 4 to the end of the list and we didn’t need to provide an index.
If you need to add an element to a specific index in the list, you can use the insert() method. The insert() method takes two arguments: the index where you want to insert the element and the element itself.
my_list = [1, 2, 3] # insert the element 4 at index 3 my_list.insert(3, 4) print(my_list)
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
In this code, we are using the insert() method to insert the value 4 at the index 3 of the my_list list. Since we are inserting the element at a specific index, the IndexError list assignment index out of range error will be avoided.
Conclusion
The IndexError list assignment index out of range error occurs when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in the list. To fix this error, you need to make sure that the index you are trying to access or assign a value to exists in the list. You can do this by checking the length of the list. If you want to add values to a list, you can use the append() method to add elements to the end of the list, or the insert() method to insert elements at a specific index.
You might also be interested in –
- Understand and Fix IndexError in Python
- Python List Append, Extend and Insert
-
Piyush is a data professional passionate about using data to understand things better and make informed decisions. He has experience working as a Data Scientist in the consulting domain and holds an engineering degree from IIT Roorkee. His hobbies include watching cricket, reading, and working on side projects.
View all posts
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
List elements can be modified and assigned new value by accessing the index of that element. But if you try to assign a value to a list index that is out of the list’s range, there will be an error. You will encounter an IndexError list assignment index out of range. Suppose the list has 4 elements and you are trying to assign a value into the 6th position, this error will be raised.
Example:
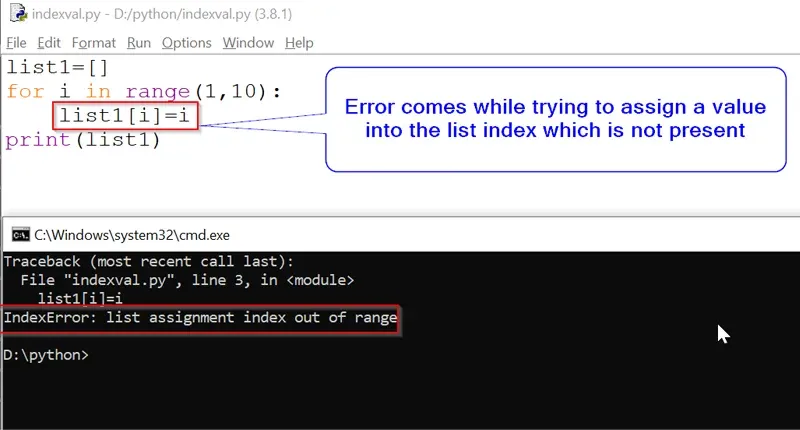
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1[i]=i
print(list1)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeIn the above example we have initialized a “list1“ which is an empty list and we are trying to assign a value at list1[1] which is not present, this is the reason python compiler is throwing “IndexError: list assignment index out of range”.
We can solve this error by using the following methods.
Using append()
We can use append() function to assign a value to “list1“, append() will generate a new element automatically which will add at the end of the list.
Correct Code:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1.append(i)
print(list1)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]In the above example we can see that “list1” is empty and instead of assigning a value to list, we append the list with new value using append() function.
Using insert()
By using insert() function we can insert a new element directly at i’th position to the list.
Example:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1.insert(i,i)
print(list1)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]In the above example we can see that “list1” is an empty list and instead of assigning a value to list, we have inserted a new value to the list using insert() function.
Example with While loop
num = []
i = 1
while(i <= 10):
num[i] = I
i=i+1
print(num)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeCorrect example:
num = []
i = 1
while(i <= 10):
num.append(i)
i=i+1
print(num)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]Conclusion:
Always check the indices before assigning values into them. To assign values at the end of the list, use the append() method. To add an element at a specific position, use the insert() method.
An IndexError exception is generally raised when the index issued is out of range.
In particular, “IndexError: list assignment index out of range” is raised when we attempt to assign a value to an index that is out of range (does not exist).
Reproducing the Error
|
lst = [1, 4, 5, 6] lst[2]=9 print(lst) lst[7]=11 |
Output:
[1, 4, 9, 6] IndexError: list assignment index out of range
lst[2] = 9 assigned index 2 (the third value), the value 9 without an error because lst has 4 values (indices 0, 1, 2, and 3).
lst[7]=11 leads to an “IndexError: list assignment index out of range” error because lst does not have index 7. The list ends with index 3.
Solutions to the Error
Solution 1: Using the <list>.append(<value>)
Use this method if you need to add an item to the end of the list. This prevents us from assigning a value to an index that does not exist.
|
# Initialize the list lst = [1, 4, 5, 6] # Append the value 11 to the end of the list lst.append(11) print(lst) |
Output:
[1, 4, 5, 6, 11]
Solution 2: Using if-condition
In this case, we want to check if the index is within the range of the list. If the index is within the range, we assign the value we want; otherwise, we do something else.
|
lst = [1, 4, 5, 6] length_of_lst = len(lst) index1 = 7 if index1 < length_of_lst: # if the index issued is less than the length of the list lst[index1] = 11 print(lst) else: # else if the index issued is greater than the length of the list # you can do anything else here. print(f‘index {index1} is out of range’) |
Output:
index 7 is out of range
In the above case, we have avoided the “IndexError: list assignment index out of range” error by using the if-condition.
Solution 3: Using a try-except statement
In this method, we attempt to assign a value to a given index, and if that results in IndexError, we do something else.
|
lst = [1, 4, 5, 6] try: lst[9]=11 except IndexError as e: print(e) lst.append(11) print(lst) |
Output:
list assignment index out of range [1, 4, 5, 6, 11]
lst[9]=11 resulted in IndexError, then we resorted to appending the value 11 to lst.
Solution 4: Using the list.insert() function
The <list>.insert(<idx>, <value>) inserts <value> to the list at index <idx>. If the index provided is out of range, the value is inserted as the last element in the list.
|
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # Inserting out-of-range value lst.insert(15,«out of range value») print(lst) # Inserting within range value. lst.insert(3, «within range») print(lst) |
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'out of range value'] [1, 2, 3, 'within range', 4, 5, 'out of range value']
Conclusion
The exception IndexError: List Assignment Index Out of Range Python occurs when we try to assign a value to a list at an index that is out of range. In this article, we propose the best solution is to insert the element at the end of the list using the list.append() method.
Other solutions discussed included if-condition to check if the index supplied is within range, try-except to catch IndexError exception, and list.insert() method to insert value at an index (if out of range, the element is appended as the last item in the list).