3. SLMP
The following table lists error codes that are stored in the end code at abnormal completion in SLMP.
Error code
C059h
The sub command is specified incorrectly. Or, a command that is not prescribed is received.
C05Ch
The request message is incorrect.
C061h
The request data length does not correspond to the number of data points.
CCCAh
A non-existent Index is specified.
CCD0h
Number of data value differs from the prescribed value.
CCD1h
Number of data value is greater than the prescribed value.
CCD2h
Number of data value is smaller than the prescribed value.
CCD3h
A non-existent Sub Index is specified.
CCC8h
The Write only object is read.
CCC9h
(1) A value is written to the Read only object.
(2) A value is written to an object which is not the Read only object for all AL states but for the present AL state with
Write disabled.
CCC7h
(1) A value is written to the object mapped to a response message.
(2) The following writings are performed when the object mapped to a response message is not allowed to be
changed.
A value other than «0» is written to Sub Index0.
A value is written to the corresponding Sub Index 1 to 32.
CCCBh
The object that cannot be mapped to response message is written to the object mapped to a response message.
CCCCh
The total size of the object mapped to a response message exceeds 64 bytes.
CCD4h
A value outside the parameter range was written.
CCD5h
A value that is greater than the parameter range is written.
CCD6h
A value that is smaller than the parameter range is written.
CCDAh
A value is written to a parameter object outside the writing range set in the Parameter block setting.
Cause
3 — 8
|
|
Ремонт сервоусилителя Mitsubishi

Также для восстановления подобного промышленного оборудования понадобится хорошая материально-техническая база. При выполнении всех выше перечисленных условий, шансы на успешный ремонт сервоусилителя Mitsubishi возрастают в геометрической прогрессии.
Именно поэтому за ремонтом сервоусилителей, независимо от производителя лучше всего обращаться в специализированный сервисный центр, который отвечает всем техническим требованиям, такой как Кернел. Наш цент имеет отличную материально-техническую базу, а за время существования с 2002 года специалисты компании накопили бесценный опыт в том числе опыт в ремонте сервоусилителей Mitsubishi.
Особенности ремонта сервоусилителя Mitsubishi

- Аппаратная часть;
- Программная часть.
В первую очередь ремонтируется аппаратная часть промышленного сервоусилителя. После глубокой диагностики неисправного блока выявляются все неисправные компоненты, которые в последствии заменяются на оригинальные запасные части (по возможности), в случае если сервопривод уже давно снят с производства и найти оригинальные запчасти просто невозможно они заменяются на аналоги.
Данный вид ремонта называется компонентным. От других видов его отличает две немаловажные детали.
- Значительное удешевление ремонта;
- Существенное сокращение времени ремонта.
По завершении ремонта аппаратной части сервоусилителя наступает очередь программной. В зависимости от серии выбирается программный продукт и зашивается в блок.
Заключительный этап ремонта сервоусилителя Mitsubishi это проверка на специализированном стенде. Все блоки проверяются без нагрузки и с нагрузкой не менее двух часов.
Коды предупреждений и ошибок сервоусилителя Mitsubishi
При обнаружении неисправности при работе сервоусилителя будет активирована соответствующая защита и выведено предупреждающее сообщение на индикатор сервоусилителя или цифрового пульта.
Коды аварийной сигнализации выводятся при возникновении соответствующей сигнализации. При нормальной работе (отсутствие неполадок) через контакты CN1-10, CN1-11 и CN1-12 выводятся стандартные сигналы состояния (к примеру частота или направление вращения). При возникновении аварийной сигнализации, установите сигнал состояния «Серво выкл.» и прервите питание силового контура.
Коды неисправностей и предупреждений сервоусилителя Mitsubishi MR-E приведены в файле PDF который доступен по ссылке ниже. Дополнительно в файле указаны способы устранения неисправностей и их сброс.
Посмотреть все коды ошибок сервоусилителя Mitsubishi MR-E
Схемы
В некоторых случает может понадобится схема подключения сервоусилителей, ниже мы показаны схемы сервоусилителя Mitsubishi.
Базовые схемы конфигурации сервоусилителей Mitsubishi
|
Конфигурация системы MR-E-100AG-QW003 |
Конфигурация системы MR-E-200AG-QW003 |
|
|

|
Схемы типовых подключений сервоусилителей Mitsubishi
|
Сервопривод Mitsubishi Схема регулировки частоты вращения |
Сервопривод Mitsubishi Схема регулировки крутящего момента |
|
|
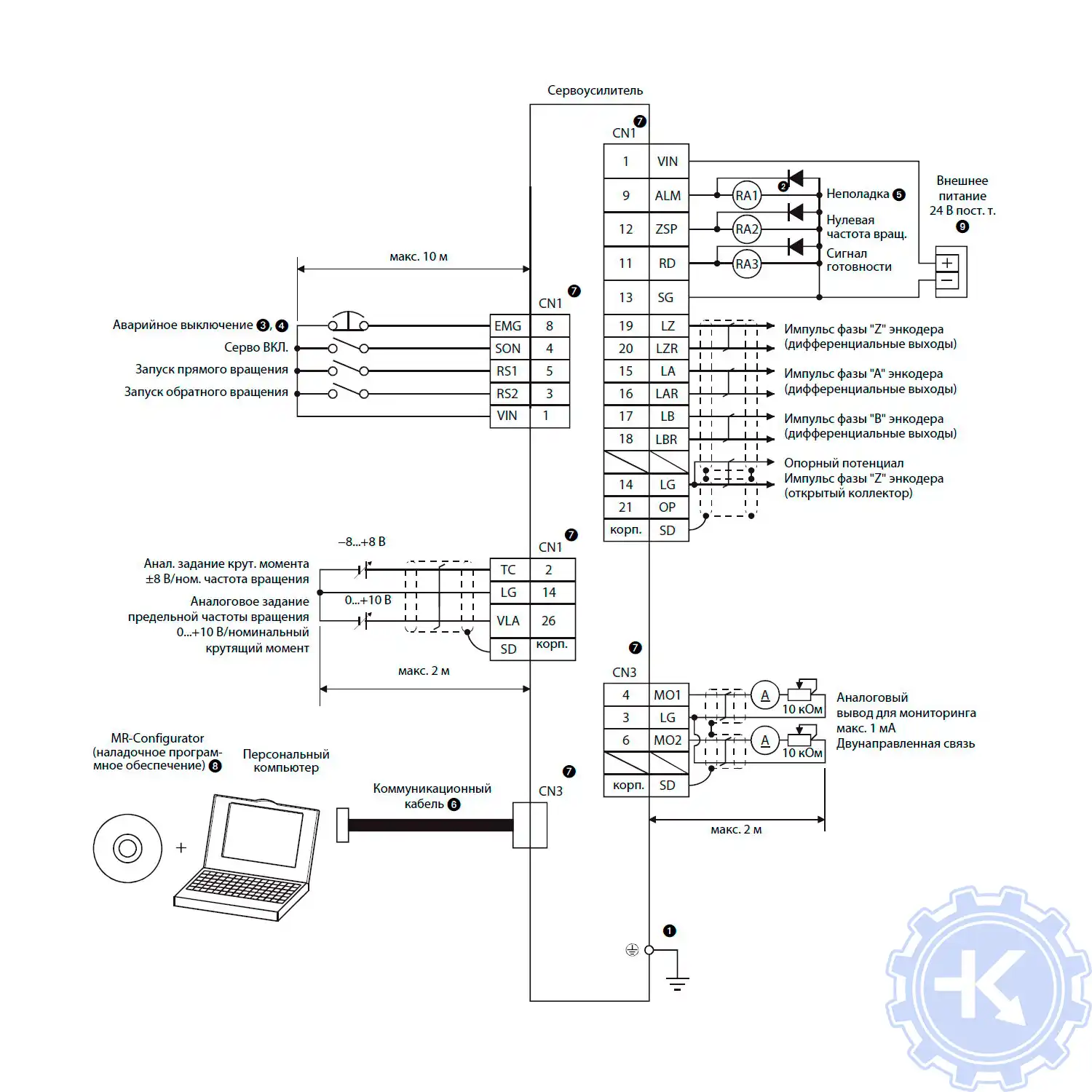
|
Блок схема сервоусилителя Mitsubishi
|
Mitsubishi MR-E-Super с аналоговым входом |

|
Преимущество ремонта сервоусилителя Mitsubishi в нашем сервисном центре
Во время эксплуатации электроприводов Mitsubishi может возникнуть проблема, далеко не всегда возникшую проблему можно исправить на месте своими силами, наш сервисный центр готов вам в этом помочь, выполнив качественный ремонт сервоусилителей Mitsubishi в сжатые сроки с полугодовой гарантией.
Мы не только восстановим неисправный блок, но и подскажем как действовать в той или иной ситуации для максимально долгой и безаварийной работы сервоусилителя.
Работы, проводимые при ремонте сервоусилителя Mitsubishi в :
- Предварительный осмотр на возможность восстановления бесплатный;
- Мы производим ремонт сервоусилителя Mitsubishi на компонентном уровне (экономия бюджета и времени)
- При ремонте сервоусилителей ни каких конструктивных изменений не вносим;
- Ремонт блоков с применением оригинальных запасных частей (по возможности).
- Вы платите исключительно за результат — работающий сервопривод;
- Гарантия на ремонт сервоусилителя Mitsubishi и на запасные части замененные в процессе ремонта 6 месяцев;
- Сроки ремонта варьируются от 5 до 15 рабочих дней;
За два десятилетия существования сервисного центра нашими специалистами были успешно проведены тысячи подобных ремонтов с каждым разом поднимая квалификацию наших инженеров. Ниже представлен далеко не полный список сервоусилителей Mitsubishi серии MR-E ремонтируемые в нашем сервисном центре.
|
MR-E Super Сервоусилитель 1(3) x 200-230В/50-60Гц (управление импульсной последовательностью) |
|
|
MR-E-10A-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-A для двигателей до 100 Вт |
|
MR-E-20A-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-A для двигателей до 200 Вт |
|
MR-E-40A-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-A для двигателей до 400 Вт |
|
MR-E-70A-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-A для двигателей до 750 Вт |
|
MR-E Super Сервоусилитель 3 x 200-230В/50-60Гц (управление импульсной последовательностью) |
|
|
MR-E-100A-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-A для двигателей до 1кВт |
|
MR-E-200A-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-A для двигателей до 2кВт |
|
MR-E Super Сервоусилитель 1(3) x 200-230В/50-60Гц (управление аналоговым сигналом) |
|
|
MR-E-10AG-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-AG для двигателей до 100 Вт |
|
MR-E-20AG-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-AG для двигателей до 200 Вт |
|
MR-E-40AG-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-AG для двигателей до 400 Вт |
|
MR-E-70AG-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-AG для двигателей до 750 Вт |
|
MR-E Super Сервоусилитель 3 x 200-230В/50-60Гц (управление аналоговым сигналом) |
|
|
MR-E-100AG-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-AG для двигателей до 1кВт |
|
MR-E-200AG-QW003 |
Ремонт сервоусилителя MR-E-AG для двигателей до 2кВт |
В таблице представлены исключительно сервоусилители Mitsubishi серии MR-E ремонт которых мы вам предлагаем, также специалисты нашей компании ремонтируют сервоусилители не зависимо от серии и под каким брендом они были выпущены.
Оставить заявку на ремонт сервоусилителя Mitsubishi
У вас остались вопросы, связанные с ремонтом или сбросом ошибок, а также программированием и настройкой сервоусилителей Mitsubishi? Оставьте заявку на ремонт сервоусилителя Mitsubishi в нашим менеджерам. Связаться с ними можно несколькими способами:
- Заказав обратный звонок (кнопка в правом нижнем углу сайта)
- Посредством чата (кнопка расположена с левой стороны сайта)
- Позвонив по номеру телефона:
- +7(8482) 79-78-54;
- +7(8482) 55-96-39;
- +7(917) 121-53-01
- Написав на электронную почту: 89171215301@mail.ru
За время существования сервисного центра нашими специалистами были отремонтированы десятки и сотни тысяч единиц промышленной электроники. Вот далеко не полный список производителей промышленной электроники и оборудования, ремонтируемой в нашей компании.
Все ошибки Mitsubishi AIRTREK, ASX, CARISMA,COLT, DELICA, DIAMANTE, DION, ECLIPSE, ENDEAVOR, GALANT, GRANDIS, GTO, i-MiEV, IO, L200, LANCER, LANCER CLASSIC, LANCER EVO, MINICA, MIRAGE, MONTERO, OUTLANDER, PAJERO, PAJERO SPORT, SPACE STAR, SPACE WAGON, TOWN BOX
FUSO, FUSO Canter, FUSO Fighter, FUSO Super Great
Ошибки Mitsubishi по протоколу OBDI. Самодиагностика.
11 – Датчик кислорода – неисправность
12 – Датчик массового расхода воздуха – неисправность
13 – Датчик температуры впускного воздуха – неисправность
14 – Датчик положения дроссельной заслонки (TPS) – неисправность
15 – Датчик положения двигателя на холостом ходу – неисправность
21 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости – неисправность
22 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала – неисправность
23 – Датчик положения распределительного вала – неисправность
24 – Датчик скорости автомобиля – неисправность
25 – Датчик барометрического давления – неисправность
31 – Датчик детонации – неисправность
32 – Датчик абсолютного давления – неисправность
36 – Неисправность сигнала регулировки времени зажигания
39 – Датчик кислорода – неисправность
41 – Неисправность форсунки / форсунок
42 – Топливный насос – неисправность
43 – Система отработавших газов (EGR) – неисправность
44 – Катушка зажигания (цилиндры № 1 и № 4) – неисправность
52 – Катушка зажигания (цилиндры № 2 и № 5) – неисправность
53 – Катушка зажигания (цилиндры № 3 и № 6) – неисправность
55 – Управление холостым ходом (IAC) – неисправность датчика положения клапана
59 – Кислородный датчик (задний) – неисправность
61 – Модуль управления трансмиссией – снижение мощности – некорректный сигнал
62 – Система VIC – неисправность датчика положения клапана
71 – Неисправность электромагнитного вакуумного клапана управления тягой (Traction Control)
72 – Неисправность соленоида вентиляционного клапана системы управления тягой (Traction Control)
Ошибки Mitsubishi по протоколу OBDII
Топливная система и воздухоподача
P0000-P0099, P0100-P0199, P0200-P0299
P0001 – Управление регулятором подачи топлива — обрыв цепи
P0002 – Управление регулятором подачи топлива — параметры цепи
P0003 – Управление регулятором подачи топлива — низкое напряжение
P0004 – Управление регулятором подачи топлива — высокое напряжение
P0005 – Клапан отсечки подачи топлива — обрыв цепи
P0006 – Клапан отсечки подачи топлива — низкий уровень сигнала
P0007 – Клапан отсечки подачи топлива — высокий уровень сигнала
P0008 – Система синхронизации фаз, банк 1 — характеристика двигателя
P0009 – Система синхронизации фаз, банк 2 — характеристика двигателя
P0010 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0011 – Положение распределительного вала, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1 — слишком ранний угол открывания клапанов / нарушение функционирования системы
P0012 – Положение распределительного вала, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1 — слишком поздний угол открывания клапанов
P0013 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0014 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, выпуск/правый/задний, банк 1 — слишком ранний угол открывания / функционирование системы
P0015 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, выпуск/правый/задний, банк 1 — слишком поздний угол открывания
P0016 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 1, датчик А — нет соответствия
P0017 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 1, датчик В — корреляция
P0018 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 2, датчик А — корреляция
P0019 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 2, датчик B — корреляция
P0020 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, впуск/левый/передний, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0021 – Положение распределительного вала, впуск/левый/передний, банк 2 — слишком ранний угол открывания клапанов / нарушение функционирования системы
P0022 – Положение распределительного вала, впуск/левый/передний, банк 2 — слишком поздний угол открывания клапанов
P0023 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, выпуск/правый/задний, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0024 – Положение распределительного вала, выпуск/правый/задний, банк 2 — слишком ранний угол открывания / функционирование системы
P0025 – Положение распределительного вала, выпуск/правый/задний, банк 2 — слишком поздний угол открывания
P0030 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0031 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем — низкое напряжение цепи
P0032 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем — высокое напряжение цепи
P0033 – Перепускной клапан турбокомпрессора — неисправность электрической цепи
P0034 – Перепускной клапан турбокомпрессора — низкий уровень сигнала
P0035 – Перепускной клапан турбокомпрессора — высокий уровень сигнала
P0036 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0037 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем — низкое напряжение цепи
P0038 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем — высокое напряжение цепи
P0039 – Перепускной клапан турбокомпрессора/перепускной клапан приводного нагнетателя, управление — диапазон/функционирование
P0040 – Перепутано подключение кислородных датчиков 1, банка 1 и банка 2
P0041 – Перепутано подключение кислородных датчиков 2, банка 1 и банка 2
P0045 – Э/м клапан управления давлением турбонаддува/ клапан управления давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — обрыв цепи
P0046 – Э/м клапан управления давлением турбонаддува / давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — диапазон/функционирование
P0047 – Э/м клапан управления давлением турбонаддува / давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — низкий уровень сигнала
P0048 – Э/м клапан управления давлением турбонаддува / давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — высокий уровень сигнала
P0049 – Турбина турбокомпрессора / нагнетателя — превышение скорости
P0050 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0051 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем — низкий уровень сигнала
P0052 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем — высокий уровень сигнала
P0053 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — сопротивление нагревателя
P0054 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — сопротивление нагревателя
P0055 – Подогреваемый кислородный, банк 1, датчик 3 — сопротивление нагревателя
P0056 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0057 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем — низкое напряжение цепи нагревателя
P0058 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем — высокий уровень сигнала
P0059 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — сопротивление нагревателя
P0060 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик, банк 2, датчик 2 — сопротивление нагревателя
P0061 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик, банк 2, датчик 3 — сопротивление нагревателя
P0065 – Форсунка с дополнительным воздушным каналом — диапазон/функционирование
P0066 – Форсунка с дополнительным воздушным каналом — неисправность электрической цепи / низкое напряжение
P0067 – Форсунка с дополнительным воздушным каналом — высоко напряжение цепи
P0068 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе/датчик расхода воздуха (MAF) — несоответствие положению дроссельной заслонки
P0069 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе / датчик атмосферного давления — корреляция
P0070 – Датчик температуры окружающего воздуха — неисправность электрической цепи
P0071 – Датчик температуры окружающего воздуха — диапазон/функционирование
P0072 – Датчик температуры окружающего воздуха — низкий уровень сигнала
P0073 – Датчик температуры окружающего воздуха — высокий уровень выходного сигнала
P0074 – Датчик температуры окружающего воздуха — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0087 – Давление в системе / в топливном коллекторе — слишком низкое
P0088 – Давление в системе / в топливном коллекторе — слишком высокое
P0089 – Регулятор давления топлива 1 — функционирование
P0090 – Регулятор давления топлива 1 — обрыв цепи
P0091 – Регулятор давления топлива 1 — короткое замыкание на массу
P0092 – Регулятор давления топлива 1 — короткое замыкание на «+»
P0093 – Значительная утечка в топливной системе
P0094 – Незначительная утечка в топливной системе
P0100 – Датчик расхода воздуха (массового — MAF) / (объемного — VAF) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0101 – Датчик расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF) — диапазон/функционирование
P0102 – Датчик расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF) — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0103 – Датчик расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF) — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0104 – Датчик расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF) — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0105 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе (МАР) / датчик атмосферного давления — неисправность электрической цепи
P0106 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе/датчик атмосферного давления — диапазон/функционирование
P0107 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе/датчик атмосферного давления — низкий уровень сигнала
P0108 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе/датчик атмосферного давления — высокий уровень сигнала
P0109 – Датчик абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе (МАР) / датчик атмосферного давления — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0110 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — неисправность электрической цепи
P0111 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — диапазон/функционирование
P0112 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — низкий уровень сигнала
P0113 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0114 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0115 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости — неисправность электрической цепи
P0116 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости — диапазон/функционирование
P0117 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости — низкий уровень сигнала
P0118 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0119 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0120 – Датчик А положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик А положения педали акселератора — неисправность электрической цепи
P0121 – Датчик А положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик А положения педали акселератора — диапазон/функционирование
P0122 – Датчик «А» положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик «А» положения педали акселератора — низкий уровень сигнала
P0123 – Датчик А положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик А положения педали акселератора — высокий уровень сигнала
P0124 – Датчик А положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик А положения педали акселератора — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0125 – Температура охлаждающей жидкости недостаточна для управления топливоподачей с обратной связью
P0126 – Температура охлаждающей жидкости недостаточна для стабильной работы
P0127 – Слишком высокая температура воздуха на впуске
P0128 – Термостат системы охлаждения — температура охлаждающей жидкости ниже температуры открывания термостата
P0129 – Слишком низкое атмосферное давление
P0130 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0131 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — низкое напряжение
P0132 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — высокое напряжение
P0133 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — малое быстродействие
P0134 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — нет отклика
P0135 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0136 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0137 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 1 — низкое напряжение
P0138 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 1 — высокое напряжение
P0139 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 1 — малое быстродействие
P0140 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 1 — нет отклика
P0141 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0148 – Неправильная подача топлива
P0149 – Неправильный угол опережения впрыска
P0150 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0151 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — низкое напряжение
P0152 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — высокое напряжение
P0153 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — малое быстродействие
P0154 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — нет отклика
P0155 – Кислородный датчик 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0156 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0157 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 2 — низкое напряжение
P0158 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 2 — высокое напряжение
P0159 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 2 — малое быстродействие
P0160 – Кислородный датчик 2, банк 2 — нет отклика
P0161 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем — неисправность электрической цепи
P0168 – Слишком высокая температура топлива
P0169 – Несоответствующий состав топлива
P0170 – Топливный баланс, банк 1 — неисправность
P0171 – Слишком бедная топливовоздушная смесь, банк 1
P0172 – Слишком богатая топливовоздушная смесь, банк 1
P0173 – Топливный баланс, банк 2 — неисправность
P0174 – Слишком бедная топливовоздушная смесь, банк 2
P0175 – Слишком богатая топливовоздушная смесь, банк 2
P0176 – Датчик состава смеси — неисправность электрической цепи
P0177 – Датчик состава смеси — диапазон/функционирование
P0178 – Датчик состава смеси — низкий уровень сигнала
P0179 – Датчик состава смеси — высокий уровень сигнала
P0180 – Датчик температуры топлива A — неисправность электрической цепи
P0181 – Датчик температуры топлива A — диапазон/функционирование
P0182 – Датчик температуры топлива A — низкий уровень сигнала
P0183 – Датчик температуры топлива A — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0184 – Датчик температуры топлива A — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0185 – Датчик температуры топлива B — неисправность электрической цепи
P0186 – Датчик температуры топлива B — диапазон/функционирование
P0187 – Датчик температуры топлива B — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0188 – Датчик температуры топлива B — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0189 – Датчик температуры топлива B — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0190 – Датчик давления в топливном коллекторе — неисправность электрической цепи
P0191 – Датчик давления в топливном коллекторе — диапазон/функционирование
P0192 – Датчик давления в топливном коллекторе — низкий уровень сигнала
P0193 – Датчик давления в топливном коллекторе — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0194 – Датчик давления в топливном коллекторе — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0195 – Датчик температуры моторного масла — неисправность электрической цепи
P0196 – Датчик температуры моторного масла — диапазон/функционирование
P0197 – Датчик температуры моторного масла — низкий уровень сигнала
P0198 – Датчик температуры моторного масла — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0199 – Датчик температуры моторного масла — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0200 – Форсунка — неисправность электрической цепи
P0201 – Форсунка 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0202 – Форсунка 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0203 – Форсунка 3 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0204 – Форсунка 4 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0205 – Форсунка 5 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0206 – Форсунка 6 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0207 – Форсунка 7 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0208 – Форсунка 8 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0213 – Форсунка холодного пуска 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0214 – Форсунка холодного пуска 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0215 – Э/м клапан отсечки подачи топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0216 – Управление углом опережения впрыска топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0217 – Перегрев двигателя
P0218 – Перегрев коробки передач
P0219 – Превышение допустимой частоты вращения коленчатого вала
P0220 – Датчик В положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик В положения педали акселератора — неисправность электрической цепи
P0221 – Датчик В положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик В положения педали акселератора — диапазон/функционирование
P0222 – Датчик В положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик В положения педали акселератора — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0223 – Датчик В положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик В положения педали акселератора — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0224 – Датчик В положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик В положения педали акселератора — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0230 – Реле топливного насоса — неисправность электрической цепи
P0231 – Реле топливного насоса — низкое напряжение цепи
P0232 – Реле топливного насоса — высокое напряжение цепи
P0233 – Реле топливного насоса — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0234 – Давление турбонаддува — превышен верхний предел
P0235 – Датчик давления наддува A турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — неисправность электрической цепи
P0236 – Датчик давления наддува A турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — диапазон/функционирование
P0237 – Датчик давления наддува A турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0238 – Датчик давления наддува A турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0239 – Датчик давления наддува B турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — неисправность электрической цепи
P0240 – Датчик давления наддува B турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — диапазон/функционирование
P0241 – Датчик давления наддува B турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0242 – Датчик давления наддува B турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0243 – Клапан А управления перепуском газов мимо турбины — неисправность цепи
P0244 – Клапан А управления перепуском газов мимо турбины — диапазон/функционирование
P0245 – Клапан А управления перепуском газов мимо турбины — низкое напряжение цепи
P0246 – Клапан А управления перепуском газов мимо турбины — высокое напряжение цепи
P0247 – Клапан управления перепуском газов мимо турбины B — неисправность цепи
P0248 – Клапан В управления перепуском газов мимо турбины — диапазон/функционирование
P0249 – Клапан управления перепуском газов мимо турбины B — низкий уровень сигнала
P0250 – Клапан управления перепуском газов мимо турбины B — высокий уровень сигнала
P0251 – Дозатор топлива А, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — неисправность электрической цепи
P0252 – Дозатор топлива А, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — диапазон/функционирование
P0253 – Дозатор топлива А, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — низкий уровень сигнала
P0254 – Дозатор топлива А, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — высокий уровень сигнала
P0255 – Дозатор топлива А, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0256 – Дозатор топлива B, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — неисправность электрической цепи
P0257 – Дозатор топлива B, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — диапазон/функционирование
P0258 – Дозатор топлива B, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — низкий уровень сигнала
P0259 – Дозатор топлива B, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — высокий уровень сигнала
P0260 – Дозатор топлива B, ротор/кулачок/форсунка — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0261 – Форсунка 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0262 – Форсунка 1 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0263 – Цилиндр 1 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0264 – Форсунка 2 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0265 – Форсунка 2 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0266 – Цилиндр 2 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0267 – Форсунка 3 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0268 – Форсунка 3 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0269 – Цилиндр 3 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0270 – Форсунка 4 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0271 – Форсунка 4 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0272 – Цилиндр 4 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0273 – Форсунка 5 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0274 – Форсунка 5 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0275 – Цилиндр 5 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0276 – Форсунка 6 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0277 – Форсунка 6 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0278 – Цилиндр 6 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0279 – Форсунка 7 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0280 – Форсунка 7 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0281 – Цилиндр 7 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0282 – Форсунка 8 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0283 – Форсунка 8 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0284 – Цилиндр 8 — неправильный баланс мощности
P0297 – Превышение допустимой скорости автомобиля
P0298 – Слишком высокая температура моторного масла
P0299 – Турбокомпрессор / приводной нагнетатель — низкое давление наддува
Система зажигания
P0300-P0399
P0300 – Случайные / множественные пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0301 – Цилиндр 1 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0302 – Цилиндр 2 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0303 – Цилиндр 3 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0304 – Цилиндр 4 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0305 – Цилиндр 5 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0306 – Цилиндр 6 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0307 – Цилиндр 7 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0308 – Цилиндр 8 — пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0313 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) — низкий уровень топлива
P0314 – Пропуск зажигания (воспламенения) в одном цилиндре — номер цилиндра не распознается
P0315 – Коленчатый вал — отсутствие изменения положения
P0316 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) при запуске — первые 1000 оборотов
P0317 – Нет данных по характеристикам неровностей дорожного покрытия
P0318 – Датчик состояния дорожного покрытия A — неисправность электрической цепи
P0319 – Датчик состояния дорожного покрытия B — неисправность электрической цепи
P0320 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала / датчик частоты вращения коленчатого вала — неисправность электрической цепи
P0321 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала / датчик частоты вращения коленчатого вала — диапазон/функционирование
P0322 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала/датчик частоты вращения коленчатого вала — нет сигнала
P0323 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала / датчик частоты вращения коленчатого вала — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0324 – Ошибка в системе управления по детонации
P0325 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0326 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0327 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0328 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0329 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0330 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0331 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0332 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0333 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0334 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0335 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — неисправность электрической цепи
P0336 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — диапазон/функционирование
P0337 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — низкий уровень сигнала
P0338 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — высокий уровень сигнала
P0339 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0340 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0341 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0342 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0343 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 1 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0344 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 1 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0345 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0346 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0347 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 2 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0348 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 2 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0349 – Датчик положения распределительного вала A, банк 2 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0350 – Катушка зажигания, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0351 – Катушка зажигания A, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0352 – Катушка зажигания В, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0353 – Катушка зажигания С, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0354 – Катушка зажигания D, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0355 – Катушка зажигания Е, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0356 – Катушка зажигания F, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0357 – Катушка зажигания G, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0358 – Катушка зажигания H, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0363 – Пропуск зажигания (воспламенения) — отсутствие подачи топлива
P0364 – Зарезервировано (ISO/SAE)
P0365 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0366 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0367 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0368 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 1 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0369 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 1 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0370 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал А высокого разрешения — неисправность
P0371 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал А высокого разрешения — слишком много импульсов
P0372 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал А высокого разрешения — слишком мало импульсов
P0373 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал А высокого разрешения — хаотичные/пропадающие импульсы
P0374 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал А высокого разрешения — нет импульсов
P0375 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал В высокого разрешения — неисправность
P0376 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал В высокого разрешения — слишком много импульсов
P0377 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал В высокого разрешения — слишком мало импульсов
P0378 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал B высокого разрешения — хаотичные/пропадающие импульсы
P0379 – Опорная точка синхронизации фаз, сигнал В высокого разрешения — нет импульсов
P0380 – Свечи накаливания, цепь А — неисправность
P0381 – Индикатор свечей накаливания — неисправность электрической цепи
P0382 – Свечи накаливания, цепь В — неисправность
P0383 – Блок управления свечами накаливания — низкий уровень сигнала
P0384 – Блок управления свечами накаливания — высокий уровень сигнала
P0385 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала B — неисправность электрической цепи
P0386 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала B — диапазон/функционирование
P0387 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала B — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0388 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала B — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0389 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала B — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0390 – Датчик «А» положения распределительного вала B, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0391 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0392 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 2 — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0393 – Датчик В положения распределительного вала, банк 2 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0394 – Датчик B положения распределительного вала, банк 2 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0395 – Датчик давления в цилиндре, цилиндр 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0396 – Датчик давления в цилиндре, цилиндр 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0397 – Датчик давления в цилиндре, цилиндр 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0398 – Датчик давления в цилиндре, цилиндр 1 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0399 – Датчик давления в цилиндре, цилиндр 1 — ненадежный/пропадающий контакт электрической цепи
Контроль выбросов
P0400-P0499
P0400 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — неисправность каналов системы
P0401 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — недостаточный уровень рециркуляции
P0402 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — чрезмерный уровень рециркуляции
P0403 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0404 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — диапазон/функционирование
P0405 – Датчик положения клапана А системы рециркуляции ОГ (EGR) — низкий уровень сигнала
P0406 – Датчик положения клапана А системы рециркуляции ОГ (EGR) — высокий уровень сигнала
P0407 – Датчик положения клапана B системы рециркуляции ОГ (EGR) — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0408 – Датчик положения клапана B системы рециркуляции ОГ (EGR) — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0409 – Датчик А системы рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0410 – Система подачи воздуха на выпуск — неисправность
P0411 – Система подачи воздуха на выпуск — некорректный расход
P0412 – Э/м клапан А подачи воздуха на выпуск — неисправность электрической цепи
P0413 – Э/м клапан А подачи воздуха на выпуск — обрыв цепи
P0414 – Э/м клапан А подачи воздуха на выпуск — короткое замыкание
P0415 – Э/м клапан B подачи воздуха на выпуск — неисправность электрической цепи
P0416 – Э/м клапан B подачи воздуха на выпуск — обрыв цепи
P0417 – Э/м клапан B подачи воздуха на выпуск — короткое замыкание в цепи
P0418 – Реле насоса А подачи воздуха на выпуск — неисправность электрической цепи
P0419 – Реле B насоса системы подачи воздуха на выпуск — неисправность электрической цепи
P0420 – Каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0421 – Прогрев каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0422 – Основной каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0423 – Подогреваемый каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0424 – Подогреваемый каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0425 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 1
P0426 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0427 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0428 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 1 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0429 – Нагреватель каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0430 – Каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 2 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0431 – Прогрев каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 2 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0432 – Основной каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 2 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0433 – Подогреваемый каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 2 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0434 – Подогреваемый каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 2 — температура ниже требуемой
P0435 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 2
P0436 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0437 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 2 — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0438 – Датчик температуры каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 2 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0439 – Нагреватель каталитического нейтрализатора, банк 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0440 – Система улавливания паров топлива — неисправность
P0441 – Система улавливания паров топлива — некорректный расход
P0442 – Система улавливания паров топлива — незначительная утечка
P0443 – Э/м клапан аккумулятора паров топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0444 – Э/м клапан аккумулятора паров топлива — обрыв цепи
P0445 – Э/м клапан аккумулятора паров топлива — короткое замыкание
P0446 – Система улавливания паров топлива, управление продувкой — неисправность электрической цепи
P0447 – Система улавливания паров топлива, управление продувкой — обрыв цепи
P0448 – Система улавливания паров топлива, управление продувкой — короткое замыкание
P0449 – Система улавливания паров топлива, клапан управления продувкой — неисправность электрической цепи
P0450 – Датчик давления системы улавливания паров топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0451 – Датчик давления системы улавливания паров топлива — диапазон/функционирование
P0452 – Датчик давления системы улавливания паров топлива — низкий уровень сигнала
P0453 – Датчик давления системы улавливания паров топлива — высокий уровень сигнала
P0454 – Датчик давления системы улавливания паров топлива — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0455 – Система улавливания паров топлива — значительная утечка
P0456 – Система улавливания паров топлива — крайне незначительная утечка
P0457 – Система улавливания паров топлива — утечка (ослабла или открыта крышка топливозаливной горловины)
P0458 – Система улавливания паров топлива, клапан аккумулятора паров топлива — низкий уровень сигнала
P0459 – Система улавливания паров топлива, клапан аккумулятора паров топлива — высокий уровень сигнала
P0460 – Датчик уровня топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0461 – Датчик уровня топлива — диапазон/функционирование
P0462 – Датчик уровня топлива — низкий уровень сигнала
P0463 – Датчик уровня топлива — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0464 – Датчик уровня топлива — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0465 – Датчик расхода через аккумулятор паров топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0466 – Датчик расхода через аккумулятор паров топлива — диапазон/функционирование
P0467 – Датчик расхода через аккумулятор паров топлива — низкий уровень сигнала
P0468 – Датчик расхода через аккумулятор паров топлива — высокий уровень сигнала
P0469 – Датчик расхода через аккумулятор паров топлива — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0470 – Датчик давления отработавших газов — неисправность электрической цепи
P0471 – Датчик давления отработавших газов — диапазон/функционирование
P0472 – Датчик давления отработавших газов — низкий уровень сигнала
P0473 – Датчик давления отработавших газов — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0474 – Датчик давления отработавших газов — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0475 – Клапан управления давлением отработавших газов — неисправность электрической цепи
P0476 – Клапан управления давлением отработавших газов — диапазон/функционирование
P0477 – Клапан управления давлением отработавших газов — низкий уровень сигнала
P0478 – Клапан управления давлением отработавших газов — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0479 – Клапан управления давлением отработавших газов — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0480 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 1 системы охлаждения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0481 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 2 системы охлаждения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0482 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения 3 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0483 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения, нормальная проверка — неисправность
P0484 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения — превышение допустимой силы тока в цепи
P0485 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения, питание / масса — неисправность электрической цепи
P0486 – Датчик положения клапана В системы рециркуляции ОГ (EGR) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0487 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR), управление положением дроссельной заслонки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0488 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR), управление положением заслонки — проблемы диапазона / функционирования
P0489 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — низкое напряжение цепи
P0490 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — высокое напряжение цепи
P0491 – Система подачи воздуха на выпуск, банк 1 — неисправность
P0492 – Система подачи воздуха на выпуск, банк 2 — неисправность
P0493 – Превышение частоты вращения электродвигателя вентилятора системы охлаждения (блокировка муфты)
P0494 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения — низкая скорость
P0495 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения — высокая скорость
P0496 – Система улавливания паров топлива — высокий расход при продувке
P0497 – Система улавливания паров топлива — низкий расход при продувке
P0498 – Система улавливания паров топлива, управление продувкой — низкий уровень сигнала
P0499 – Система улавливания паров топлива, управление продувкой — высокий уровень сигнала
Контроль скорости и холостого хода
P0500-P0599
P0500 – Датчик скорости автомобиля — неисправность электрической цепи
P0501 – Датчик скорости автомобиля — диапазон/функционирование
P0502 – Датчик скорости автомобиля — низкий уровень сигнала
P0503 – Датчик скорости автомобиля — сигналы хаотичные / пропадающие / высокого уровня
P0504 – Выключатель А/В стоп-сигналов (датчик положения педали тормоза) — корреляция
P0505 – Система управления частотой вращения холостого хода — неисправность
P0506 – Система управления частотой вращения холостого хода — частота вращения ниже допустимой
P0507 – Система управления частотой вращения холостого хода — частота вращения выше допустимой
P0508 – Управление перепуском воздуха на холостом ходу — низкий уровень сигнала
P0509 – Управление перепуском воздуха на холостом ходу — высокий уровень сигнала
P0510 – Датчик полностью закрытого положения дроссельной заслонки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0511 – Управление перепуском воздуха на холостом ходу — неисправность электрической цепи
P0512 – Цепь управления стартером — неисправность
P0513 – Некорректный ключ иммобилайзера (неправильный код)
P0514 – Датчик температуры аккумуляторной батареи — диапазон/функционирование
P0515 – Датчик температуры аккумуляторной батареи — диапазон/функционирование
P0516 – Датчик температуры аккумуляторной батареи — низкое напряжение цепи
P0517 – Датчик температуры аккумуляторной батареи — высокое напряжение цепи
P0518 – Управление перепуском воздуха на холостом ходу — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0519 – Управление перепуском воздуха на холостом ходу — функционирование
P0520 – Датчик давления моторного масла — неисправность электрической цепи
P0521 – Датчик давления моторного масла — диапазон/функционирование
P0522 – Датчик давления моторного масла — низкое напряжение
P0523 – Датчик давления моторного масла — высокое напряжение
P0524 – Давление моторного масла слишком низкое
P0525 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), управление приводом — диапазон/функционирование
P0526 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения, датчик скорости — неисправность электрической цепи
P0527 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения, датчик скорости — диапазон/функционирование
P0528 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения, датчик скорости — нет сигнала
P0529 – Электродвигатель вентилятора системы охлаждения, датчик скорости — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0530 – Датчик давления хладагента системы кондиционирования — неисправность электрической цепи
P0531 – Датчик давления хладагента системы кондиционирования — диапазон/функционирование
P0532 – Датчик давления хладагента системы кондиционирования — низкий уровень сигнала
P0533 – Датчик давления хладагента системы кондиционирования — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0534 – Недостаток хладагента в системе кондиционирования
P0535 – Датчик температуры за испарителем (кондиционер) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0536 – Датчик температуры за испарителем (кондиционер) — диапазон/функционирование
P0537 – Датчик температуры за испарителем системы кондиционирования — низкий уровень сигнала
P0538 – Датчик температуры за испарителем системы кондиционирования — высокий уровень сигнала
P0539 – Датчик температуры за испарителем системы кондиционирования — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0550 – Датчик/выключатель по давлению усилителя рулевого управления — неисправность электрической цепи
P0551 – Датчик-выключатель по давлению усилителя рулевого управления — диапазон/функционирование
P0552 – Датчик/выключатель по давлению усилителя рулевого управления — низкий уровень сигнала
P0553 – Датчик/выключатель по давлению усилителя рулевого управления — высокий уровень сигнала
P0554 – Датчик/выключатель по давлению усилителя рулевого управления — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0555 – Датчик давления в системе усилителя тормозной системы — неисправность электрической цепи
P0556 – Датчик давления в системе усилителя тормозной системы — диапазон/функционирование
P0557 – Датчик давления в системе усилителя тормозной системы — низкий уровень сигнала
P0558 – Датчик давления в системе усилителя тормозной системы — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0559 – Датчик давления в системе усилителя тормозной системы — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0564 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), многофункциональный переключатель (входной сигнал А) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0565 – Главный выключатель системы поддержания скорости (круиз-контроля), сигнал «ON» — неисправность
P0566 – Главный выключатель системы поддержания скорости (круиз-контроля), сигнал «OFF» — неисправность
P0567 – Переключатель выбора режима работы системы поддержания скорости (круиз-контроля), сигнал «RESUME» — неисправность
P0568 – Главный выключатель системы поддержания скорости (круиз-контроля), сигнал «SET» — неисправность
P0569 – Переключатель выбора режима работы системы поддержания скорости (круиз-контроля), сигнал «COAST» — неисправность
P0570 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), сигнал датчика положения педали акселератора — неисправность
P0571 – Выключатель педали тормоза A (система поддержания скорости) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0572 – Концевой выключатель А педали тормоза (система поддержания скорости) — низкий уровень сигнала
P0573 – Концевой выключатель А педали тормоза (система поддержания скорости) — высокий уровень сигнала
P0574 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль) — слишком высокая скорость автомобиля
P0575 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль) — неисправность цепи входного сигнала
P0576 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль) — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0577 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль) — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0578 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), многофункциональный переключатель (входной сигнал А) — цепь блокирована
P0579 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), многофункциональный переключатель (входной сигнал А) — диапазон/функционирование
P0580 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), многофункциональный переключатель (входной сигнал А) — низкий уровень сигнала
P0581 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), многофункциональный переключатель (входной сигнал А) — высокий уровень сигнала
P0582 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), управление разрежением — обрыв цепи
P0583 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), управление разрежением — низкое напряжение цепи
P0584 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), управление разрежением — высокое напряжение цепи
P0585 – Система поддержания скорости (круиз-контроль), многофункциональный переключатель (входной сигнал А/В) — корреляция
P0597 – Система управления нагревателем термостата — обрыв цепи
P0598 – Система управления нагревателем термостата — низкое напряжение цепи
P0599 – Система управления нагревателем термостата — высокое напряжение цепи
Электронный блок управления (ЭБУ) и его подсистемы
P0600-P0699
P0600 – Шина данных CAN — неисправность
P0601 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — ошибка контрольной суммы памяти
P0602 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — ошибка программирования
P0603 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — ошибка памяти КАМ
P0604 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — ошибка памяти RAM
P0605 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — ошибка памяти ROM
P0606 – Электронный блок управления двигателем (ECM) / блок управления силовым агрегатом (PCM) — неисправность процессора
P0607 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — функционирование
P0608 – Электронный блок управления двигателем, датчик скорости автомобиля (выходной сигнал А) — неисправность
P0609 – Электронный блок управления двигателем, датчик скорости автомобиля (выходной сигнал В) — неисправность
P0610 – Электронный блок управления двигателем — ошибка опции автомобиля
P0611 – Блок управления топливными форсунками — функционирование
P0612 – Блок управления топливными форсунками — цепь управления реле
P0613 – Электронный блок управления КПП (TCM) — ошибка процессора
P0614 – Электронный блок управления двигателем (ECM) / электронный блок управления КПП (TCM) — несоответствие
P0615 – Реле стартера — неисправность электрической цепи
P0616 – Реле стартера — низкий уровень сигнала
P0617 – Реле стартера — высокий уровень сигнала
P0618 – Блок управления подачей альтернативного топлива — ошибка памяти KAM
P0619 – Блок управления подачей альтернативного топлива — ошибка памяти RAM/ROM
P0620 – Управление генератором — неисправность электрической цепи
P0621 – Индикатор зарядки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0622 – Генератор, управление обмоткой возбуждения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0623 – Индикатор зарядки, управление — неисправность электрической цепи
P0624 – Индикатор незакрытой крышки заливной горловины, управление — неисправность электрической цепи
P0625 – Вывод обмотки возбуждения генератора — низкий уровень сигнала
P0626 – Вывод обмотки возбуждения генератора — высокий уровень сигнала
P0627 – Управление топливным насосом — обрыв цепи
P0628 – Управление топливным насосом — низкий уровень сигнала
P0629 – Управление топливным насосом — высокий уровень сигнала
P0630 – VIN не запрограммирован или не подходит — ECM/PCM
P0631 – Не запрограммирован электронный блок управления АКПП или не соответствует идентификационному номеру автомобиля
P0632 – Не запрограммирован одометр — ECM/PCM
P0633 – Не запрограммирован ключ иммобилайзера — ECM/PCM
P0634 – Электронный блок управления силовым агрегатом/двигателем/КПП (PCM/ECM/TCM) — высокая внутренняя температура
P0635 – Управление усилителем рулевого управления — неисправность электрической цепи
P0636 – Управление усилителем рулевого управления — низкий уровень сигнала
P0637 – Управление усилителем рулевого управления — высокий уровень сигнала
P0638 – Управление приводом дроссельной заслонки, банк 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0639 – Управление приводом дроссельной заслонки, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0640 – Управление подогревом воздуха на впуске — неисправность электрической цепи
P0641 – Опорное напряжение датчика A — обрыв цепи
P0642 – Опорное напряжение датчика A — низкий уровень сигнала
P0643 – Опорное напряжение датчика A — высокий уровень сигнала
P0644 – Дисплей водителя, обмен данными (последовательный) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0645 – Реле электромагнитной муфты компрессора кондиционера — неисправность электрической цепи
P0646 – Реле электромагнитной муфты компрессора кондиционера — низкий уровень сигнала
P0647 – Реле электромагнитной муфты компрессора кондиционера — высокий уровень сигнала
P0648 – Индикатор иммобилайзера, управление — неисправность электрической цепи
P0649 – Индикатор системы поддержания скорости (круиз-контроля), управление — неисправность цепи
P0650 – Индикатор неисправности (MIL), управление — неисправность электрической цепи
P0651 – Опорное напряжение датчика B — обрыв цепи
P0652 – Опорное напряжение датчика B — низкий уровень
P0653 – Опорное напряжение датчика B — высокое напряжение цепи
P0654 – Частота вращения коленчатого вала, выходной сигнал — неисправность электрической цепи
P0655 – Индикатор перегрева двигателя — неисправность электрической цепи
P0656 – Индикация уровня топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0666 – Датчик внутренней температуры электронного блока управления двигателем/КПП/силового агрегата (ECM/PCM/TCM) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0667 – Датчик внутренней температуры электронного блока управления двигателем/КПП/силового агрегата (ECM/PCM/TCM) — диапазон/функционирование
P0668 – Датчик внутренней температуры электронного блока управления двигателем/КПП/силового агрегата (ECM/PCM/TCM) — низкий уровень сигнала
P0669 – Датчик внутренней температуры электронного блока управления двигателем/КПП/силового агрегата (ECM/PCM/TCM) — высокий уровень сигнала
P0670 – Блок управления свечами накаливания — неисправность электрической цепи
P0671 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 1 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0672 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 2 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0673 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 3 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0674 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 4 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0675 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 5 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0676 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 6 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0677 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 7 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0678 – Свеча накаливания, цилиндр 8 — неисправность электрической цепи
P0683 – Связь блока управления свечами накаливания с ECM/PCM
P0684 – Связь блока управления свечами накаливания с ECM/PCM, ошибка связи — диапазон/функционирование
P0685 – Реле системы управления двигателем — обрыв цепи
P0686 – Реле системы управления двигателем — низкий уровень сигнала
P0687 – Реле системы управления двигателем — короткое замыкание на массу
P0688 – Реле системы управления двигателем — короткое замыкание на «+»
P0689 – Реле системы управления двигателем — низкий уровень сигнала в контрольной цепи
P0690 – Реле системы управления двигателем — высокий уровень сигнала в контрольной цепи
P0691 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 1 системы охлаждения — низкий уровень сигнала
P0692 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 1 системы охлаждения — высокий уровень сигнала
P0693 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 2 системы охлаждения — низкий уровень сигнала
P0694 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 2 системы охлаждения — высокий уровень сигнала
P0695 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 3 системы охлаждения — низкий уровень сигнала
P0696 – Электродвигатель вентилятора 3 системы охлаждения — высокий уровень сигнала
Трансмиссия
P0700-P0799, P0800-P0899, P0900-P0999
P0700 – Управление АКПП, запрос неисправностей (MIL) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0701 – Система управления АКПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0702 – Система управления АКПП — электрическая неисправность
P0703 – Выключатель стоп-сигналов B — неисправность электрической цепи
P0704 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) педали сцепления — неисправность электрической цепи
P0705 – Датчик положения селектора АКПП, входной сигнал PRNDL — неисправность электрической цепи
P0706 – Датчик положения селектора КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0707 – Датчик положения селектора АКПП — низкий уровень сигнала
P0708 – Датчик положения селектора АКПП — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0709 – Датчик положения селектора АКПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0710 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости АКПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0711 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0712 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости КПП — низкий уровень сигнала
P0713 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости КПП — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0714 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0715 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП (турбины гидротрансформатора) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0716 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП (турбины гидротрансформатора) — диапазон/функционирование
P0717 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП (турбины гидротрансформатора) — нет сигнала
P0718 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП (турбины гидротрансформатора) — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0719 – Выключатель стоп-сигналов B — низкий уровень сигнала
P0720 – Датчик частоты вращения выходного вала — неисправность электрической цепи
P0721 – Датчик частоты вращения выходного вала — диапазон/функционирование
P0722 – Датчик частоты вращения выходного вала — нет сигнала
P0723 – Датчик частоты вращения выходного вала — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0724 – Выключатель стоп-сигналов B — высокий уровень сигнала
P0725 – Частота вращения коленчатого вала, входной сигнал — неисправность электрической цепи
P0726 – Частота вращения коленчатого вала, входной сигнал — диапазон/функционирование
P0727 – Частота вращения коленчатого вала, входной сигнал — нет сигнала
P0728 – Частота вращения коленчатого вала, входной сигнал — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0729 – 6-я передача — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0730 – Некорректное передаточное отношение
P0731 – 1-я передача — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0732 – 2-я передача — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0733 – 3-я передача — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0734 – 4-я передача — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0735 – 5-я передача — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0736 – Передача заднего хода — некорректное передаточное отношение
P0737 – Электронный блок управления АКПП, частота вращения — выходная цепь
P0738 – Электронный блок управления АКПП, частота вращения — низкий уровень выходного сигнала
P0739 – Электронный блок управления АКПП, частота вращения — высокий уровень выходного сигнала
P0740 – Электромагнитный клапан муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора — неисправность электрической цепи
P0741 – Электромагнитный клапан муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0742 – Электромагнитный клапан муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0743 – Электромагнитный клапан муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора — электрическая неисправность
P0744 – Электромагнитный клапан муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0745 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0746 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0747 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0748 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — электрическая неисправность
P0749 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0750 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — неисправность электрической цепи
P0751 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0752 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0753 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0754 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0755 – Э/м клапан В переключения передач — неисправность электрической цепи
P0756 – Э/м клапан В переключения передач — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0757 – Э/м клапан В переключения передач — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0758 – Э/м клапан В переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0759 – Э/м клапан B переключения передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0760 – Э/м клапан С переключения передач — неисправность электрической цепи
P0761 – Э/м клапан С переключения передач — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0762 – Э/м клапан С переключения передач — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0763 – Э/м клапан С переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0764 – Э/м клапан C переключения передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0765 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — неисправность электрической цепи
P0766 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0767 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0768 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0769 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0770 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — неисправность электрической цепи
P0771 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0772 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0773 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0774 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0775 – Э/м клапан В управления давлением — неисправность
P0776 – Э/м клапан B управления давлением — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0777 – Э/м клапан В управления давлением — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0778 – Э/м клапан В управления давлением — электрическая неисправность
P0779 – Э/м клапан В управления давлением — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0780 – Выбор передачи — неисправность переключения
P0781 – Выбор передачи, 1-2 — неисправность переключения
P0782 – Выбор передачи, 2-3 — неисправность переключения
P0783 – Выбор передачи, 3-4 — неисправность переключения
P0784 – Выбор передачи, 4-5 — неисправность переключения
P0785 – Электромагнитный клапан переключения / синхронизации передач — неисправность электрической цепи
P0786 – Электромагнитный клапан переключения / синхронизации передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0787 – Электромагнитный клапан синхронизации переключения передач — низкий уровень
P0788 – Электромагнитный клапан синхронизации переключения передач — высокий уровень
P0789 – Электромагнитный клапан синхронизации переключения передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0790 – Переключатель выбора режима работы АКПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0791 – Датчик частоты вращения промежуточного вала КПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0792 – Датчик частоты вращения промежуточного вала КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0793 – Датчик частоты вращения промежуточного вала КПП — нет сигнала
P0794 – Датчик частоты вращения промежуточного вала КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0795 – Э/м клапан С управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0796 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0797 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — «залипание» в открытом состоянии
P0798 – Э/м клапан С управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — электрическая неисправность
P0799 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0800 – Управление раздаточной коробкой, запрос неисправностей (MIL) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0801 – Цепь блокировки включения передачи заднего хода — неисправность электрической цепи
P0802 – Управление АКПП, запрос неисправностей (MIL) — обрыв цепи
P0803 – Электромагнитный клапан цепи повышения передачи (1-4 передача), пропуски при переключении — неисправность электрической цепи
P0804 – Индикатор пропуска переключения в цепи повышения передачи (1-4 передача) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0805 – Датчик положения сцепления (муфты) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0806 – Датчик положения сцепления (муфты) — диапазон/функционирование
P0807 – Датчик положения сцепления (муфты) — низкий уровень сигнала
P0808 – Датчик положения сцепления (муфты) — высокий уровень сигнала
P0809 – Датчик положения сцепления (муфты) — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0810 – Ошибка в управлении сцеплением (муфтой)
P0811 – Повышенное проскальзывание сцепления (муфты)
P0812 – Передача заднего хода — неисправность входной цепи
P0813 – Передача заднего хода — неисправность выходной цепи
P0814 – Индикатор положения селектора — неисправность электрической цепи
P0815 – Переключатель выбора передач КПП, повышение передачи — неисправность электрической цепи
P0816 – Переключатель выбора передач КПП, понижение передачи — неисправность электрической цепи
P0817 – Цепь блокировки стартера — неисправность
P0818 – Датчик-выключатель разъединения потока мощности — неисправность электрической цепи
P0819 – Переключатель выбора передач КПП, повышение/понижение передачи — корреляция с диапазоном
P0820 – Датчик положения X-Y рычага переключения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0821 – Датчик положения X рычага переключения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0822 – Датчик положения Y рычага переключения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0823 – Датчик положения X рычага переключения — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0824 – Датчик положения Y рычага переключения — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0825 – Переключатель положения (рычаг переключения качающегося типа) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0826 – Переключатель выбора передач КПП, повышение/понижение передачи — неисправность электрической цепи
P0827 – Переключатель выбора передач КПП, повышение/понижение передачи — низкий уровень сигнала
P0828 – Переключатель выбора передач КПП, повышение/понижение передачи — высокий уровень сигнала
P0829 – Переключение с 5-й на 6-ю передачу
P0830 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) А педали сцепления — неисправность электрической цепи
P0831 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) А педали сцепления — низкий уровень сигнала
P0832 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) А педали сцепления — высокий уровень сигнала
P0833 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) B педали сцепления — неисправность электрической цепи
P0834 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) B педали сцепления — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0835 – Концевой выключатель (датчик положения) В педали сцепления — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0836 – Выключатель режима 4WD — неисправность электрической цепи
P0837 – Выключатель режима 4WD — диапазон/функционирование
P0838 – Выключатель режима 4WD — низкий уровень сигнала
P0839 – Выключатель режима 4WD — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0840 – Датчик А давления рабочей жидкости КПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0841 – Датчик А давления рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0842 – Датчик А давления рабочей жидкости КПП — низкий уровень сигнала
P0843 – Датчик А давления рабочей жидкости КПП — высокий уровень сигнала
P0844 – Датчик А давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0845 – Датчик B давления рабочей жидкости КПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0846 – Датчик В давления рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0847 – Датчик B давления рабочей жидкости КПП — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0848 – Датчик В давления рабочей жидкости КПП — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0849 – Датчик B давления рабочей жидкости КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0850 – Выключатель запрещения запуска («P»/»N») — неисправность цепи входного сигнала
P0851 – Выключатель запрещения запуска («P»/»N») — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0852 – Выключатель запрещения запуска («P»/»N») — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0853 – Выключатель режима движения — неисправность цепи входного сигнала
P0854 – Выключатель режима движения — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0855 – Выключатель режима движения — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0856 – Входной сигнал противобуксовочной системы — неисправность
P0857 – Входной сигнал противобуксовочной системы — диапазон/функционирование
P0858 – Входной сигнал противобуксовочной системы — низкий уровень
P0859 – Входной сигнал противобуксовочной системы — высокий уровень
P0860 – Линия связи блока управления переключением — неисправность
P0861 – Линия связи блока управления переключением — низкий уровень сигнала
P0862 – Линия связи блока управления переключением — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0863 – Электронный блок управления КПП (TCM), связь — неисправность электрической цепи
P0864 – Электронный блок управления КПП (TCM), связь — диапазон/функционирование
P0865 – Электронный блок управления КПП (TCM), связь — низкий уровень входного сигнала
P0866 – Электронный блок управления КПП (TCM), связь — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0867 – Датчик давления рабочей жидкости АКПП
P0868 – Датчик давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — низкое
P0869 – Датчик давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — высокое
P0870 – Датчик C давления рабочей жидкости КПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0871 – Датчик С давления рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0872 – Датчик C давления рабочей жидкости КПП — низкий уровень сигнала
P0873 – Датчик C давления рабочей жидкости КПП — высокий уровень сигнала
P0874 – Датчик C давления рабочей жидкости КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0875 – Датчик D давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0876 – Датчик D давления рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0877 – Датчик D давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — низкое напряжение цепи
P0878 – Датчик D давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — высокое напряжение цепи
P0879 – Датчик D давления рабочей жидкости КПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0880 – Электронный блок управления АКПП — неисправность цепи питания
P0881 – Электронный блок управления АКПП — неисправность цепи питания (диапазон / функционирование)
P0882 – Электронный блок управления АКПП — низкое напряжение цепи питания
P0883 – Электронный блок управления АКПП — высокое напряжение цепи питания
P0884 – Электронный блок управления КПП (TCM), входной сигнал питания — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0885 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM), управление — обрыв цепи
P0886 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM), управление — низкий уровень сигнала
P0887 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM), управление — высокий уровень сигнала
P0888 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM) — неисправность контрольной цепи
P0889 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM) — диапазон/функционирование контрольной цепи
P0890 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM) — низкий уровень сигнала в контрольной цепи
P0891 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM) — высокий уровень сигнала в контрольной цепи
P0892 – Реле питания электронного блока управления КПП (TCM) — ненадежный контакт контрольной цепи
P0893 – Одновременное включение нескольких передач
P0894 – Проскальзывание компонентов АКПП
P0895 – Слишком малое время переключения
P0896 – Слишком большое время переключения
P0897 – Ухудшение качества рабочей жидкости
P0898 – Управление АКПП, запрос неисправностей (MIL) — низкое напряжение цепи
P0899 – Управление АКПП, запрос неисправностей (MIL) — высокое напряжение цепи
P0900 – Привод сцепления — обрыв цепи
P0901 – Привод сцепления — диапазон/функционирование
P0902 – Привод сцепления — низкое напряжение цепи
P0903 – Привод сцепления — высокое напряжение цепи
P0904 – Цепь выбора диапазона коробки передач — неисправность
P0905 – Цепь выбора диапазона коробки передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0906 – Цепь выбора диапазона коробки передач — низкое напряжение
P0907 – Цепь выбора диапазона коробки передач — высокое напряжение
P0908 – Цепь выбора диапазона коробки передач — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0909 – Ошибка выбора диапазона коробки передач
P0910 – Привод выбора диапазона коробки передач — обрыв цепи
P0911 – Привод выбора диапазона коробки передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0912 – Привод выбора диапазона коробки передач — низкое напряжение цепи
P0913 – Привод выбора диапазона коробки передач — высокое напряжение цепи
P0914 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — неисправность
P0915 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — диапазон/функционирование
P0916 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — низкое напряжение цепи
P0917 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — высокое напряжение цепи
P0918 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0919 – Контроль включенной передачи — ошибка
P0920 – Привод включения передач переднего хода — обрыв цепи
P0921 – Привод включения передач переднего хода — диапазон/функционирование
P0922 – Привод включения передач переднего хода — низкое напряжение цепи
P0923 – Привод включения передач переднего хода — высокое напряжение цепи
P0924 – Привод включения передачи заднего хода — обрыв цепи
P0925 – Привод включения передачи заднего хода — диапазон/функционирование
P0926 – Привод включения передачи заднего хода — низкое напряжение цепи
P0927 – Привод включения передачи заднего хода — высокое напряжение цепи
P0928 – Электромагнитный клапан блокировки переключения передач — обрыв цепи
P0929 – Электромагнитный клапан блокировки переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0930 – Электромагнитный клапан блокировки переключения передач — низкое напряжение цепи
P0931 – Электромагнитный клапан блокировки переключения передач — высокое напряжение цепи
P0932 – Датчик давления в гидросистеме — неисправность электрической цепи
P0933 – Датчик давления в гидросистеме — диапазон/функционирование
P0934 – Датчик давления в гидросистеме — низкий уровень сигнала
P0935 – Датчик давления в гидросистеме — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0936 – Датчик давления в гидросистеме — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0937 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости в гидросистеме — неисправность электрической цепи
P0938 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости в гидросистеме — диапазон/функционирование
P0939 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости в гидросистеме — низкий уровень сигнала
P0940 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости в гидросистеме — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0941 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости в гидросистеме — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0942 – Блок создания давления в гидросистеме
P0943 – Блок создания давления в гидросистеме — цикл работы слишком короткий
P0944 – Блок создания давления в гидросистеме — потеря давления
P0945 – Реле насоса гидросистемы — обрыв цепи
P0946 – Реле насоса гидросистемы — диапазон/функционирование
P0947 – Реле насоса гидросистемы — низкое напряжение цепи
P0948 – Реле насоса гидросистемы — высокое напряжение цепи
P0949 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM) — не проведено адаптивное обучение
P0950 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), управление — неисправность электрической цепи
P0951 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), управление — диапазон/функционирование
P0952 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), управление — низкий уровень сигнала
P0953 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), управление — высокий уровень сигнала
P0954 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), управление — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0955 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), режим — неисправность электрической цепи
P0956 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), режим — диапазон/функционирование
P0957 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), режим — низкий уровень сигнала
P0958 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), режим — высокий уровень сигнала
P0959 – Коробка передач с автоматизированным переключением (ASM), режим — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0960 – Э/м клапан А управления давлением — обрыв цепи
P0961 – Э/м клапан А управления давлением — диапазон/функционирование
P0962 – Э/м клапан А управления давлением — низкий уровень сигнала
P0963 – Э/м клапан А управления давлением — высокий уровень сигнала
P0964 – Э/м клапан B управления давлением — обрыв цепи
P0965 – Э/м клапан B управления давлением — диапазон/функционирование
P0966 – Э/м клапан B управления давлением — низкий уровень сигнала
P0967 – Э/м клапан B управления давлением — высокий уровень сигнала
P0968 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением — обрыв цепи
P0969 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением — диапазон/функционирование
P0970 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением — низкий уровень сигнала
P0971 – Э/м клапан C управления давлением — высокий уровень сигнала
P0972 – Э/м клапан A переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0973 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — низкий уровень сигнала
P0974 – Э/м клапан А переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
P0975 – Э/м клапан В переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0976 – Э/м клапан B переключения передач — низкий уровень сигнала
P0977 – Э/м клапан B переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
P0978 – Э/м клапан C переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0979 – Э/м клапан С переключения передач — низкий уровень сигнала
P0980 – Э/м клапан C переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
P0981 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0982 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — низкий уровень сигнала
P0983 – Э/м клапан D переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
P0984 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0985 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — низкий уровень сигнала
P0986 – Э/м клапан E переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
P0987 – Датчик Е давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0988 – Датчик E давления рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0989 – Датчик Е давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — низкое напряжение цепи
P0990 – Датчик Е давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — высокое напряжение цепи
P0991 – Датчик Е давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0992 – Датчик F давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — неисправность электрической цепи
P0993 – Датчик E давления рабочей жидкости КПП — диапазон/функционирование
P0994 – Датчик F давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — низкое напряжение цепи
P0995 – Датчик F давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — высокое напряжение цепи
P0996 – Датчик F давления рабочей жидкости АКПП — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0997 – Э/м клапан F переключения передач — диапазон/функционирование
P0998 – Э/м клапан F переключения передач — низкий уровень сигнала
P0999 – Э/м клапан F переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
SH (NA) 030128-B (1307) MEE Printed in Japan Specifications are subject to change without notice. This Instruction Manual uses recycled paper. MODEL MODEL CODE General-Purpose AC Servo MR-JE-_A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL HEAD OFFICE : TOKYO BLDG MARUNOUCHI TOKYO 100-8310 MODEL MR-JE-_A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL General-Purpose Interface AC Servo 1CW706 MR-JE-A SERVOAMPLIFIER INSTRUCTIONMANUAL B B A - 1 Safety Instructions Please read the instructions carefully before using the equipment. To use the equipment correctly, do not attempt to install, operate, maintain, or inspect the equipment until you have read through this Instruction Manual, Installation guide, and appended documents carefully. Do not use the equipment until you have a full knowledge of the equipment, safety information and instructions. In this Instruction Manual, the safety instruction levels are classified into "WARNING" and "CAUTION". WARNING Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in death or severe injury. CAUTION Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in medium or slight injury to personnel or may cause physical damage. Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to conditions. Please follow the instructions of both levels because they are important to personnel safety. What must not be done and what must be done are indicated by the following diagrammatic symbols. Indicates what must not be done. For example, "No Fire" is indicated by . Indicates what must be done. For example, grounding is indicated by . In this Instruction Manual, instructions at a lower level than the above, instructions for other functions, and so on are classified into "POINT". After reading this Instruction Manual, keep it accessible to the operator. A - 2 1. To prevent electric shock, note the following WARNING Before wiring and inspections, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier. Ground the servo amplifier and servo motor securely. Any person who is involved in wiring and inspection should be fully competent to do the work. Do not attempt to wire the servo amplifier and servo motor until they have been installed. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock. Do not operate switches with wet hands. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock. The cables should not be damaged, stressed, loaded, or pinched. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. When using an earth-leakage current breaker (RCD), select the type B. To avoid an electric shock, insulate the connections of the power supply terminals. 2. To prevent fire, note the following CAUTION Install the servo amplifier, servo motor, and regenerative resistor on incombustible material. Installing them directly or close to combustibles will lead to a fire. Always connect a magnetic contactor between the power supply and the power supply (L1, L2, and L3) of the servo amplifier, in order to configure a circuit that shuts down the power supply on the side of the servo amplifier’s power supply. If a magnetic contactor is not connected, continuous flow of a large current may cause a fire when the servo amplifier malfunctions. When using the regenerative resistor, switch power off with the alarm signal. Not doing so may cause a fire when a regenerative transistor malfunctions or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor. When you use a regenerative option with an MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, remove the built-in regenerative resistor and wiring from the servo amplifier. Provide adequate protection to prevent screws and other conductive matter, oil and other combustible matter from entering the servo amplifier and servo motor. Always connect a molded-case circuit breaker to the power supply of the servo amplifier. 3. To prevent injury, note the following CAUTION Only the voltage specified in the Instruction Manual should be applied to each terminal. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur. Connect cables to the correct terminals. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur. Ensure that polarity (+/-) is correct. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur. The servo amplifier heat sink, regenerative resistor, servo motor, etc. may be hot while power is on or for some time after power-off. Take safety measures, e.g. provide covers, to avoid accidentally touching the parts (cables, etc.) by hand. A - 3 4. Additional instructions The following instructions should also be fully noted. Incorrect handling may cause a malfunction, injury, electric shock, etc. (1) Transportation and installation CAUTION Transport the products correctly according to their mass. Stacking in excess of the specified number of product packages is not allowed. Do not hold the lead wire of the regenerative resistor when transporting the servo amplifier. Install the servo amplifier and the servo motor in a load-bearing place in accordance with the Instruction Manual. Do not get on or put heavy load on the equipment. The equipment must be installed in the specified direction. Leave specified clearances between the servo amplifier and the cabinet walls or other equipment. Do not install or operate the servo amplifier and servo motor which have been damaged or have any parts missing. Do not block the intake and exhaust areas of the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. Do not drop or strike the servo amplifier and servo motor. Isolate them from all impact loads. When you keep or use the equipment, please fulfill the following environment. Item Environment Operation 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C (non-freezing) Ambient temperature Storage -20 ˚C to 65 ˚C (non-freezing) Operation Ambient humidity Storage 90 %RH or less (non-condensing) Ambience Indoors (no direct sunlight), free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust, and dirt Altitude 1000 m or less above sea level Vibration resistance 5.9 m/s 2 , at 10 Hz to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y and Z axes) When the product has been stored for an extended period of time, contact your local sales office. When handling the servo amplifier, be careful about the edged parts such as corners of the servo amplifier. The servo amplifier must be installed in a metal cabinet. When fumigants that contain halogen materials such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are used for disinfecting and protecting wooden packaging from insects, they cause malfunction when entering our products. Please take necessary precautions to ensure that remaining materials from fumigant do not enter our products, or treat packaging with methods other than fumigation (heat method). Additionally, disinfect and protect wood from insects before packing products. A - 4 (2) Wiring CAUTION Before removing the CNP1 connector of MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, disconnect the lead wires of the regenerative resistor from the CNP1 connector. Wire the equipment correctly and securely. Otherwise, the servo motor may operate unexpectedly. Do not install a power capacitor, surge killer, or radio noise filter (optional FR-BIF) on the servo amplifier output side. To avoid a malfunction, connect the wires to the correct phase terminals (U, V, and W) of the servo amplifier and servo motor. Connect the servo amplifier power output (U, V, and W) to the servo motor power input (U, V, and W) directly. Do not let a magnetic contactor, etc. intervene. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. U Servo motor M V W U V W U M V W U V W Servo amplifier Servo motorServo amplifier The connection diagrams in this instruction manual are shown for sink interfaces, unless stated otherwise. The surge absorbing diode installed to the DC relay for control output should be fitted in the specified direction. Otherwise, the emergency stop and other protective circuits may not operate. DOCOM Control output signal Servo amplifier RA For sink output interface 24 V DC DOCOM Control output signal 24 V DC Servo amplifie r RA For source output interface When the cable is not tightened enough to the terminal block, the cable or terminal block may generate heat because of the poor contact. Be sure to tighten the cable with specified torque. Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. (3) Test run and adjustment CAUTION Before operation, check the parameter settings. Improper settings may cause some machines to operate unexpectedly. Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so will make the operation unstable. Do not get close to moving parts during the servo-on status. A - 5 (4) Usage CAUTION When it is assumed that a hazardous condition may occur due to a power failure or product malfunction, use a servo motor with an external brake to prevent the condition. Do not disassemble, repair, or modify the equipment. Before resetting an alarm, make sure that the run signal of the servo amplifier is off in order to prevent a sudden restart. Otherwise, it may cause an accident. Use a noise filter, etc. to minimize the influence of electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic interference may be given to the electronic equipment used near the servo amplifier. Burning or breaking a servo amplifier may cause a toxic gas. Do not burn or break it. Use the servo amplifier with the specified servo motor. The electromagnetic brake on the servo motor is designed to hold the motor shaft and should not be used for ordinary braking. For such reasons as service life and mechanical structure (e.g. where a ball screw and the servo motor are coupled via a timing belt), the electromagnetic brake may not hold the motor shaft. To ensure safety, install a stopper on the machine side. (5) Corrective actions CAUTION When it is assumed that a hazardous condition may occur due to a power failure or product malfunction, use a servo motor with an electromagnetic brake or external brake to prevent the condition. Configure an electromagnetic brake circuit so that it is activated also by an external EMG stop switch. Servo motor Electromagnetic brake B RA Contacts must be opened with the EMG stop switch. Contacts must be opened when ALM (Malfunction) or MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off. 24 V DC When any alarm has occurred, eliminate its cause, ensure safety, and deactivate the alarm before restarting operation. Provide an adequate protection to prevent unexpected restart after an instantaneous power failure. (6) Maintenance, inspection and parts replacement CAUTION With age, the electrolytic capacitor of the servo amplifier will deteriorate. To prevent a secondary accident due to a malfunction, it is recommend that the electrolytic capacitor be replaced every 10 years when it is used in general environment. For replacement, please contact your local sales office. A - 6 (7) General instruction To illustrate details, the equipment in the diagrams of this Instruction Manual may have been drawn without covers and safety guards. When the equipment is operated, the covers and safety guards must be installed as specified. Operation must be performed in accordance with this Instruction Manual. DISPOSAL OF WASTE Please dispose a servo amplifier and other options according to your local laws and regulations. EEP-ROM life The number of write times to the EEP-ROM, which stores parameter settings, etc., is limited to 100,000. If the total number of the following operations exceeds 100,000, the servo amplifier may malfunction when the EEP-ROM reaches the end of its useful life. Write to the EEP-ROM due to parameter setting changes Write to the EEP-ROM due to device changes Compliance with global standards Refer to appendix 2 for the compliance with global standard. «About the manual» You must have this Instruction Manual and the following manuals to use this servo. Ensure to prepare them to use the servo safely. Relevant manuals Manual name Manual No. MELSERVO-JE Series Instructions and Cautions for Safe Use of AC Servos (packed with the servo amplifier) IB(NA)0300194 MELSERVO HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual SH(NA)030123 EMC Installation Guidelines IB(NA)67310 «Cables used for wiring» Wires mentioned in this Instruction Manual are selected based on the ambient temperature of 40 ˚C. 1 CONTENTS 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1- 1 to 1-12 1.1 Summary........................................................................................................................................... 1- 1 1.2 Function block diagram..................................................................................................................... 1- 2 1.3 Servo amplifier standard specifications ............................................................................................ 1- 4 1.4 Combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors ........................................................................ 1- 5 1.5 Function list....................................................................................................................................... 1- 5 1.6 Model designation............................................................................................................................. 1- 7 1.7 Structure ........................................................................................................................................... 1- 8 1.7.1 Parts identification...................................................................................................................... 1- 8 1.8 Configuration including peripheral equipment ................................................................................. 1-10 2. INSTALLATION 2- 1 to 2- 6 2.1 Installation direction and clearances ................................................................................................ 2- 2 2.2 Keep out foreign materials................................................................................................................ 2- 3 2.3 Encoder cable stress ........................................................................................................................ 2- 4 2.4 Inspection items ................................................................................................................................ 2- 4 2.5 Parts having service lives ................................................................................................................. 2- 5 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3- 1 to 3-62 3.1 Input power supply circuit ................................................................................................................. 3- 2 3.2 I/O signal connection example.......................................................................................................... 3- 6 3.2.1 Position control mode................................................................................................................. 3- 6 3.2.2 Speed control mode .................................................................................................................. 3-11 3.2.3 Torque control mode ................................................................................................................. 3-13 3.3 Explanation of power supply system ............................................................................................... 3-15 3.3.1 Signal explanations ................................................................................................................... 3-15 3.3.2 Power-on sequence.................................................................................................................. 3-16 3.3.3 Wiring CNP1 and CNP2............................................................................................................ 3-17 3.4 Connectors and pin assignment ...................................................................................................... 3-19 3.5 Signal (device) explanations............................................................................................................ 3-21 3.6 Detailed explanation of signals........................................................................................................ 3-29 3.6.1 Position control mode................................................................................................................ 3-29 3.6.2 Speed control mode .................................................................................................................. 3-34 3.6.3 Torque control mode ................................................................................................................. 3-36 3.6.4 Position/speed control switching mode.....................................................................................3-39 3.6.5 Speed/torque control switching mode.......................................................................................3-41 3.6.6 Torque/position control switching mode....................................................................................3-43 3.7 Forced stop deceleration function ................................................................................................... 3-44 3.7.1 Forced stop deceleration function............................................................................................. 3-44 3.7.2 Base circuit shut-off delay time function ................................................................................... 3-46 3.7.3 Vertical axis freefall prevention function ................................................................................... 3-47 3.7.4 Residual risks of the forced stop function (EM2) ...................................................................... 3-47 3.8 Alarm occurrence timing chart......................................................................................................... 3-48 3.8.1 When you use the forced stop deceleration function................................................................ 3-48 3.8.2 When you do not use the forced stop deceleration function..................................................... 3-49 2 3.9 Interfaces ......................................................................................................................................... 3-50 3.9.1 Internal connection diagram...................................................................................................... 3-50 3.9.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces............................................................................................. 3-52 3.9.3 Source I/O interfaces ................................................................................................................ 3-56 3.10 Servo motor with an electromagnetic brake ..................................................................................3-57 3.10.1 Safety precautions .................................................................................................................. 3-57 3.10.2 Timing chart............................................................................................................................ 3-58 3.11 Grounding ...................................................................................................................................... 3-61 4. STARTUP 4- 1 to 4-36 4.1 Switching power on for the first time................................................................................................. 4- 1 4.1.1 Startup procedure ...................................................................................................................... 4- 1 4.1.2 Wiring check............................................................................................................................... 4- 2 4.1.3 Surrounding environment........................................................................................................... 4- 3 4.2 Startup in position control mode ....................................................................................................... 4- 4 4.2.1 Power on and off procedures..................................................................................................... 4- 4 4.2.2 Stop ............................................................................................................................................ 4- 4 4.2.3 Test operation............................................................................................................................ 4- 5 4.2.4 Parameter setting....................................................................................................................... 4- 6 4.2.5 Actual operation ......................................................................................................................... 4- 6 4.2.6 Trouble at start-up...................................................................................................................... 4- 7 4.3 Startup in speed control mode.......................................................................................................... 4- 9 4.3.1 Power on and off procedures..................................................................................................... 4- 9 4.3.2 Stop ............................................................................................................................................ 4- 9 4.3.3 Test operation........................................................................................................................... 4-10 4.3.4 Parameter setting...................................................................................................................... 4-11 4.3.5 Actual operation ........................................................................................................................ 4-12 4.3.6 Trouble at start-up..................................................................................................................... 4-12 4.4 Startup in torque control mode ........................................................................................................ 4-13 4.4.1 Power on and off procedures.................................................................................................... 4-13 4.4.2 Stop ........................................................................................................................................... 4-13 4.4.3 Test operation........................................................................................................................... 4-14 4.4.4 Parameter setting...................................................................................................................... 4-15 4.4.5 Actual operation ........................................................................................................................ 4-15 4.4.6 Trouble at start-up..................................................................................................................... 4-16 4.5 Display and operation sections........................................................................................................ 4-17 4.5.1 Summary ................................................................................................................................... 4-17 4.5.2 Display flowchart ....................................................................................................................... 4-18 4.5.3 Status display mode .................................................................................................................. 4-19 4.5.4 Diagnostic mode ....................................................................................................................... 4-23 4.5.5 Alarm mode ............................................................................................................................... 4-25 4.5.6 Parameter mode ....................................................................................................................... 4-26 4.5.7 External I/O signal display......................................................................................................... 4-28 4.5.8 Output signal (DO) forced output .............................................................................................. 4-31 4.5.9 Test operation mode ................................................................................................................. 4-32 5. PARAMETERS 5- 1 to 5-44 5.1 Parameter list.................................................................................................................................... 5- 1 5.1.1 Basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA_ _ ])...................................................................................... 5- 1 3 5.1.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) ............................................................................... 5- 2 5.1.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) .............................................................................. 5- 3 5.1.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) ......................................................................................... 5- 5 5.1.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ])............................................................................ 5- 6 5.1.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ])............................................................................ 5- 7 5.2 Detailed list of parameters ................................................................................................................ 5- 8 5.2.1 Basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA_ _ ])...................................................................................... 5- 8 5.2.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) .............................................................................. 5-17 5.2.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) ............................................................................. 5-28 5.2.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) ........................................................................................ 5-38 5.2.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ])........................................................................... 5-42 5.2.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ])........................................................................... 5-43 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6- 1 to 6-24 6.1 Different adjustment methods........................................................................................................... 6- 1 6.1.1 Adjustment on a single servo amplifier ...................................................................................... 6- 1 6.1.2 Adjustment using MR Configurator2 .......................................................................................... 6- 2 6.2 One-touch tuning .............................................................................................................................. 6- 3 6.2.1 One-touch tuning flowchart ........................................................................................................ 6- 3 6.2.2 Display transition and operation procedure of one-touch tuning ............................................... 6- 5 6.2.3 Caution for one-touch tuning..................................................................................................... 6-13 6.3 Auto tuning....................................................................................................................................... 6-14 6.3.1 Auto tuning mode ...................................................................................................................... 6-14 6.3.2 Auto tuning mode basis............................................................................................................. 6-15 6.3.3 Adjustment procedure by auto tuning .......................................................................................6-16 6.3.4 Response level setting in auto tuning mode ............................................................................. 6-17 6.4 Manual mode ................................................................................................................................... 6-18 6.5 2 gain adjustment mode .................................................................................................................. 6-22 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7- 1 to 7-26 7.1 Filter setting ...................................................................................................................................... 7- 1 7.1.1 Machine resonance suppression filter ....................................................................................... 7- 1 7.1.2 Adaptive filter II........................................................................................................................... 7- 4 7.1.3 Shaft resonance suppression filter............................................................................................. 7- 6 7.1.4 Low-pass filter ............................................................................................................................ 7- 7 7.1.5 Advanced vibration suppression control II .................................................................................7- 7 7.1.6 Command notch filter ................................................................................................................ 7-12 7.2 Gain switching function.................................................................................................................... 7-13 7.2.1 Applications ............................................................................................................................... 7-13 7.2.2 Function block diagram ............................................................................................................. 7-14 7.2.3 Parameter.................................................................................................................................. 7-15 7.2.4 Gain switching procedure ......................................................................................................... 7-17 7.3 Tough drive function ........................................................................................................................ 7-20 7.3.1 Vibration tough drive function.................................................................................................... 7-20 7.3.2 Instantaneous power failure tough drive function ..................................................................... 7-22 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8- 1 to 8-28 8.1 Alarm and warning list ...................................................................................................................... 8- 1 4 8.2 Remedies for alarms......................................................................................................................... 8- 6 8.3 Remedies for warnings .................................................................................................................... 8-24 9. DIMENSIONS 9- 1 to 9- 6 9.1 Servo amplifier .................................................................................................................................. 9- 1 9.2 Connector ......................................................................................................................................... 9- 4 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10- 1 to 10- 8 10.1 Overload protection characteristics .............................................................................................. 10- 1 10.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss .................................................................................. 10- 3 10.3 Dynamic brake characteristics...................................................................................................... 10- 5 10.3.1 Dynamic brake operation ....................................................................................................... 10- 5 10.3.2 Permissible load to motor inertia when the dynamic brake is used....................................... 10- 6 10.4 Cable bending life......................................................................................................................... 10- 7 10.5 Inrush current at power-on ........................................................................................................... 10- 7 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11- 1 to 11-30 11.1 Cable/connector sets .................................................................................................................... 11- 1 11.1.1 Combinations of cable/connector sets................................................................................... 11- 2 11.2 Regenerative option...................................................................................................................... 11- 4 11.2.1 Combination and regenerative power.................................................................................... 11- 4 11.2.2 Selection of regenerative option ............................................................................................ 11- 5 11.2.3 Parameter setting................................................................................................................... 11- 6 11.2.4 Selection of regenerative option ............................................................................................ 11- 7 11.2.5 Dimensions ........................................................................................................................... 11-10 11.3 Junction terminal block MR-TB50................................................................................................ 11-12 11.4 MR Configurator2 ........................................................................................................................ 11-14 11.5 Selection example of wires .......................................................................................................... 11-16 11.6 Molded-case circuit breakers, fuses, magnetic contactors (recommended)............................... 11-17 11.7 Power factor improving AC reactor.............................................................................................. 11-17 11.8 Relay (recommended) ................................................................................................................. 11-18 11.9 Noise reduction techniques ......................................................................................................... 11-19 11.10 Earth-leakage current breaker................................................................................................... 11-25 11.11 EMC filter (recommended) ........................................................................................................ 11-27 APPENDIX App. - 1 to App. -13 App. 1 Peripheral equipment manufacturer (for reference).............................................................. App.- 1 App. 2 Compliance with global standards ........................................................................................ App.- 1 App. 3 Analog monitor .....................................................................................................................App.-10 App. 4 Low-voltage directive ...........................................................................................................App.-13 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 1 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.1 Summary The Mitsubishi general-purpose AC servo MELSERVO-JE series have limited functions with keeping high performance based on MELSERVO-J4 series. The servo amplifier has position, speed, and torque control modes. In the position control mode, the maximum pulse train of 4 Mpulses/s is supported. Further, it can perform operation with the control modes switched, e.g. position/speed control, speed/torque control and torque/position control. Hence, it is applicable to a wide range of fields, not only precision positioning and smooth speed control of machine tools and general industrial machines but also line control and tension control. With one-touch tuning and real-time auto tuning, you can automatically adjust the servo gains according to the machine. The tough drive function, drive recorder function, and preventive maintenance support function strongly support machine maintenance. The servo amplifier has a USB communication interface. Therefore, you can connect the servo amplifier to the personal computer with MR Configurator2 installed to perform the parameter setting, test operation, gain adjustment, and others. The MELSERVO-JE series servo motor equipped with an incremental encoder whose resolution is 131072 pulses/rev will enable a high-accuracy positioning. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 2 1.2 Function block diagram The function block diagram of this servo is shown below. (1) MR-JE-100A or less Model position Current control Actual position control Actual speed control Virtual motor Virtual encoder Encoder (Note 2) Power supply MCMCCB Position command input Model speed Model torque CN2 Model position control Model speed control Servo motor CN3 Analog monitor (two channel) I/F USBA/D D/A USB Personal computer Analog (two channel) CN1 U U U C L3 L2 L1 Dynamic brake circuit Current detection Overcurrent protection Voltage detection Base amplifier U V W U V W Diode stack Relay P+ (Note 1) + B RA 24 V DC B1 B2 M Control circuit power CHARGE lamp Regene- rative TR Current encoder Regenerative option Electromagnetic brake DI/O control Servo-on Input command pulse. Start Malfunction, etc Note 1. The built-in regenerative resistor is not provided for MR-JE-10A and MR-JE-20A. 2. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 3 (2) MR-JE-200A or more MCMCCB Servo motor CN3 I/F USBA/D D/A USB CN1 U U U L3 L2 L1 U V W U V W B RA 24 V DC B1 B2 M CN2 N- (Note 2)CDP+ + Cooling fan (Note 1) Power supply Dynamic brake circuit Diode stack Relay CHARGE lamp Regene- rative TR Current encoder Regenerative option Encoder Current detection Overcurrent protection Voltage detection Base amplifier Control circuit power Electromagnetic brake Model position Current control Actual position control Actual speed control Virtual motor Virtual encoder Position command input Model speed Model torque Model position control Model speed control Analog monitor (two channel) Personal computer Analog (two channel) DI/O control Servo-on Input command pulse. Start Malfunction, etc Note 1. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3. 2. This is for manufacturer adjustment. Leave this open. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 4 1.3 Servo amplifier standard specifications Model: MR-JE- 10A 20A 40A 70A 100A 200A 300A Rated voltage 3-phase 170 V AC Output Rated current [A] 1.1 1.5 2.8 5.8 6.0 11.0 11.0 Voltage/Frequency 3-phase or 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz Rated current [A] 0.9 1.5 2.6 3.8 5.0 10.5 14.0 Permissible voltage fluctuation 3-phase or 1-phase 170 V AC to 264 V AC 3-phase 170 V AC to 264 V AC Permissible frequency fluctuation Within ±5% Power supply capacity [kVA] Refer to section 10.2. Power supply input Inrush current [A] Refer to section 10.5. Voltage 24 V DC ± 10% Interface power supply Current capacity [A] (Note 1) 0.3 Control method Sine-wave PWM control, current control method Dynamic brake Built-in Communication function USB: Connection to a personal computer or others (MR Configurator2-compatible) Encoder output pulses Compatible (A/B/Z-phase pulse) Analog monitor Two channels Max. input pulse frequency 4 Mpulses/s (for differential receiver) (Note 3), 200 kpulses/s (for open collector) Positioning feedback pulse Encoder resolution (resolution per servo motor revolution): 131072 pulses/rev Command pulse multiplying factor Electronic gear A:1 to 16777215, B:1 to 16777215, 1/10 < A/B < 4000 In-position range setting 0 pulse to ±65535 pulses (command pulse unit) Error excessive ±3 revolutions Position control mode Torque limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to +10 V DC/maximum torque) Speed control range Analog speed command 1: 2000, internal speed command 1: 5000 Analog speed command input 0 to ±10 V DC/rated speed (The speed at 10 V is changeable with [Pr. PC12].) Speed fluctuation ratio ±0.01% or less (load fluctuation 0% to 100%), 0% (power fluctuation ±10%), ±0.2% or less (ambient temperature 25 °C ± 10 °C) when using analog speed command Speed control mode Torque limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to +10 V DC/maximum torque) Analog torque command input 0 V DC to ±8 V DC/maximum torque (input impedance 10 k to 12 k) Torque control mode Speed limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to 10 V DC/rated speed) Protective functions Overcurrent shut-off, regenerative overvoltage shut-off, overload shut-off (electronic thermal), servo motor overheat protection, encoder error protection, regenerative error protection, undervoltage protection, instantaneous power failure protection, overspeed protection, and error excessive protection CE marking LVD: EN 61800-5-1 EMC: EN 61800-3 MD: EN ISO 13849-1, EN 61800-5-2, EN 62061 Compliance to global standards UL standard UL 508C Structure (IP rating) Natural cooling, open (IP20) Force cooling, open (IP20) Close mounting (Note 2) Possible Operation 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C (non-freezing) Ambient temperature Storage -20 ˚C to 65 ˚C (non-freezing) Operation Ambient humidity Storage 90 %RH or less (non-condensing) Ambience Indoors (no direct sunlight), free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust, and dirt Altitude 1000 m or less above sea level Environment Vibration resistance 5.9 m/s 2 , at 10 Hz to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y and Z axes) Mass [kg] 0.8 1.5 2.1 Note 1. 0.3 A is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. 2. When closely mounting the servo amplifier of 3.5 kW or less, operate them at the ambient temperatures of 0 ˚C to 45 ˚C or at 75% or smaller effective load ratio. 3. 1 Mpulse/s or lower commands are supported in the initial setting. When inputting commands over 1 Mpulse/s and 4 Mpulses/ s or lower, change the setting in [Pr. PA13]. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 5 1.4 Combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors Servo amplifier Servo motor MR-JE-10A HF-KN13 MR-JE-20A HF-KN23 MR-JE-40A HF-KN43 MR-JE-70A HF-KN73 HF-SN52 MR-JE-100A HF-SN102 MR-JE-200A HF-SN152, HF-SN202 MR-JE-300A HF-SN302 1.5 Function list The following table lists the functions of this servo. For details of the functions, refer to each section indicated in the detailed explanation field. Function Description Detailed explanation Position control mode This servo is used as a position control servo. Section 3.2.1 Section 3.6.1 Section 4.2 Speed control mode This servo is used as a speed control servo. Section 3.2.2 Section 3.6.2 Section 4.3 Torque control mode This servo is used as a torque control servo. Section 3.2.3 Section 3.6.3 Section 4.4 Position/speed control switch mode Using an input device, control can be switched between position control and speed control. Section 3.6.4 Speed/torque control switch mode Using an input device, control can be switched between speed control and torque control. Section 3.6.5 Torque/position control switch mode Using an input device, control can be switched between torque control and position control. Section 3.6.6 High-resolution encoder High-resolution encoder of 131072 pulses/rev is used for the encoder of the servo motor compatible with the MELSERVO-JE series. Gain switching function You can switch gains during rotation and during stop, and can use an input device to switch gains during operation. Section 7.2 Advanced vibration suppression control II This function suppresses vibration at the arm end or residual vibration. Section 7.1.5 Adaptive filter II Servo amplifier detects mechanical resonance and sets filter characteristics automatically to suppress mechanical vibration. Section 7.1.2 Low-pass filter Suppresses high-frequency resonance which occurs as servo system response is increased. Section 7.1.4 Machine analyzer function Analyzes the frequency characteristic of the mechanical system by simply connecting an MR Configurator2 installed personal computer and servo amplifier. MR Configurator2 is necessary for this function. Robust filter This function provides better disturbance response in case low response level that load to motor inertia ratio is high for such as roll send axes. [Pr. PE41] Slight vibration suppression control Suppresses vibration of ±1 pulse produced at a servo motor stop. [Pr. PB24] Electronic gear Input pulses can be multiplied by 1/10 to 4000. [Pr. PA06] [Pr. PA07] S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant Speed can be increased and decreased smoothly. [Pr. PC03] Auto tuning Automatically adjusts the gain to optimum value if load applied to the servo motor shaft varies. Section 6.3 Regenerative option Used when the built-in regenerative resistor of the servo amplifier does not have sufficient regenerative capability for the regenerative power generated. Section 11.2 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 6 Function Description Detailed explanation Alarm history clear Alarm history is cleared. [Pr. PC18] Output signal selection (device settings) ST1 (Forward rotation start), ST2 (Reverse rotation start), and SON (Servo-on) and other input device can be assigned to any pins. [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20] Output signal selection (device settings) The output devices including MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) can be assigned to certain pins of the CN1 connector. [Pr. PD24] to [Pr. PD28] Output signal (DO) forced output Output signal can be forced on/off independently of the servo status. Use this function for checking output signal wiring, etc. Section 4.5.8 Command pulse selection Command pulse train form can be selected from among three different types. [Pr. PA13] Torque limit Servo motor torque can be limited to any value. Section 3.6.1 (5) [Pr. PA11] [Pr. PA12] Speed limit Servo motor speed can be limited to any value. Section 3.6.3 (3) [Pr. PC05] to [Pr. PC11] Status display Servo status is shown on the 5-digit, 7-segment LED display. Section 4.5.3 External I/O signal display On/off statuses of external I/O signals are shown on the display. Section 4.5.7 Automatic VC offset Voltage is automatically offset to stop the servo motor if it does not come to a stop when VC (Analog speed command) or VLA (Analog speed limit is 0 V. Section 4.5.4 Alarm code output If an alarm has occurred, the corresponding alarm number is outputted in 3-bit code. Chapter 8 Test operation mode Jog operation, positioning operation, motor-less operation, DO forced output, and program operation MR Configurator2 is required for the positioning operation and program operation. Section 4.5.9 Analog monitor output Servo status is outputted in terms of voltage in real time. [Pr. PC14], [Pr. PC15] MR Configurator2 Using a personal computer, you can perform the parameter setting, test operation, monitoring, and others. Section 11.4 One-touch tuning Gain adjustment is performed just by one click on a certain button on MR Configurator2 or operation section. Section 6.2 Tough drive function This function makes the equipment continue operating even under the condition that an alarm occurs. The tough drive function includes two types: the vibration tough drive and the instantaneous power failure tough drive. Section 7.3 Drive recorder function This function continuously monitors the servo status and records the status transition before and after an alarm for a fixed period of time. You can check the recorded data on the drive recorder window on MR Configurator2 by clicking the "Graph" button. However, the drive recorder will not operate on the following conditions. 1. You are using the graph function of MR Configurator2. 2. You are using the machine analyzer function. 3. [Pr. PF21] is set to "-1". [Pr. PA23] Servo amplifier life diagnosis function You can check the cumulative energization time and the number of on/off times of the inrush relay. This function gives an indication of the replacement time for parts of the servo amplifier including a capacitor and a relay before they malfunction. MR Configurator2 is necessary for this function. Power monitoring function This function calculates the power running energy and the regenerative power from the data in the servo amplifier such as speed and current. Power consumption and others are displayed on MR Configurator2. Machine diagnosis function From the data in the servo amplifier, this function estimates the friction and vibrational component of the drive system in the equipment and recognizes an error in the machine parts, including a ball screw and bearing. MR Configurator2 is necessary for this function. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 7 1.6 Model designation (1) Rating plate The following shows an example of rating prate for explanation of each item. Serial numbe r Model Capacity Applicable power supply Rated output current Standard, Manual number Ambient temperature IP rating KC certification number, The year and month of manufacture Country of origin KCC-REI-MEK-TC300A745G51 DATE: 2013-05 MR-JE-10A AC SERVO SER. S33001001 POWER INPUT OUTPUT STD.: IEC/EN61800-5-1 MAN. : IB(NA)0300194 Max. Surrounding Air Temp. : 55°C IP20 : 100W : 3AC/AC200-240V 0.9A/1.5A 50/60Hz : 3PH170V 0-360Hz 1.1A TOKYO 100-8310, JAPAN MADE IN JAPAN (2) Model The following describes what each block of a model name indicates. Series Rated output General-purpose interface Symbol Rated output [kW] 10 0.1 20 0.2 40 0.4 70 0.75 100 1 200 2 300 3 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 8 1.7 Structure 1.7.1 Parts identification (1) MR-JE-100A or less No. Name/Application Detailed explanati on (1) Display The 5-digit, 7-segment LED shows the servo status and the alarm number. Section 4.5 (2) Operation section Used to perform status display, diagnostic, alarm, and parameter setting operations. Push the "MODE" and "SET" buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the one-touch tuning mode. Used to change the mode. Used to change the display or data in each mode. Used to set data. To the one-touch tuning mode Section 4.5 Section 6.2 (3) USB communication connector (CN3) Connect with the personal computer. Section 11.4 (4) I/O signal connector (CN1) Digital I/O signal, analog input signal, and analog monitor output are connected. Section 3.2 Section 3.4 (5) Encoder connector (CN2) Used to connect the servo motor encoder. Section 3.4 (6) Power connector (CNP1) Input power supply, built-in regenerative resistor, regenerative option, and servo motor are connected. Section 3.1 Section 3.3 Rating plate Section 1.6 (8) Charge lamp When the main circuit is charged, this will light up. While this lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables. (1) (2) (7) (3) (4) (5) (8) (6) (9) Bottom Side (9) Protective earth (PE) terminal Grounding terminal Section 3.1 Section 3.3 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 9 (2) MR-JE-200A or more No. Name/Application Detailed explanati on (1) Display The 5-digit, 7-segment LED shows the servo status and the alarm number. Section 4.5 (2) Operation section Used to perform status display, diagnostic, alarm, and parameter setting operations. Push the "MODE" and "SET" buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the one-touch tuning mode. Used to change the mode. Used to change the display or data in each mode. Used to set data. To the one-touch tuning mode Section 4.5 Section 6.2 (3) USB communication connector (CN3) Connect with the personal computer. Section 11.4 (4) I/O signal connector (CN1) Digital I/O signal, analog input signal, and analog monitor output are connected. Section 3.2 Section 3.4 (5) Encoder connector (CN2) Used to connect the servo motor encoder. Section 3.4 (6) Power connector (CNP1) Input power supply and regenerative option are connected. Section 3.1 Section 3.3 (7) Rating plate Section 1.6 (8) Servo motor power connector (CNP2) Connect the servo motor. Section 3.1 Section 3.3 (9) Charge lamp When the main circuit is charged, this will light up. While this lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables. (1) (2) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) Bottom Side (4) (5) (3) (10) Protective earth (PE) terminal Grounding terminal Section 3.1 Section 3.3 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 10 1.8 Configuration including peripheral equipment CAUTION Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. POINT Equipment other than the servo amplifier and servo motor are optional or recommended products. (1) MR-JE-100A or less The diagram shows MR-JE-10A. Power factor improving AC reactor (FR-HAL) Line noise filter (FR-BSF01) CN3 Servo motor Personal computer MR Configurator2 CN1 CN2 W V U L1 L2 L3 (Note 2) Magnetic contactor (MC) Molded-case circuit breaker RST Junction terminal block (Note 1) Power supply Note 1. A 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply may be used with the servo amplifier of MR-JE-70A or less. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3. 2. Depending on the power supply voltage and operation pattern, bus voltage can decrease. This can shift the mode to the dynamic brake deceleration during forced stop deceleration. When dynamic brake deceleration is not required, slow the time to turn off the magnetic contactor. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 11 (2) MR-JE-200A or more The diagram shows MR-JE-200A. Power factor improving AC reactor (FR-HAL) Line noise filter (FR-BSF01) CN3 Personal computer MR Configurator2 CN1 CN2 W V U L1 L2 L3 (Note 2) Magnetic contactor (MC) Molded-case circuit breaker RS T Junction terminal block (Note 1) Power supply Servo motor Note 1. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3. 2. Depending on the power supply voltage and operation pattern, bus voltage can decrease. This can shift the mode to the dynamic brake deceleration during forced stop deceleration. When dynamic brake deceleration is not required, slow the time to turn off the magnetic contactor. 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 12 MEMO 2. INSTALLATION 2 - 1 2. INSTALLATION WARNING To prevent electric shock, ground each equipment securely. CAUTION Stacking in excess of the specified number of product packages is not allowed. Do not hold the lead wire of the regenerative resistor when transporting the servo amplifier. Install the equipment on incombustible material. Installing them directly or close to combustibles will lead to a fire. Install the servo amplifier and the servo motor in a load-bearing place in accordance with the Instruction Manual. Do not get on or put heavy load on the equipment. Otherwise, it may cause injury. Use the equipment within the specified environment. For the environment, refer to section 1.3. Provide an adequate protection to prevent screws and other conductive matter, oil and other combustible matter from entering the servo amplifier. Do not block the intake and exhaust areas of the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. Do not drop or strike the servo amplifier. Isolate it from all impact loads. Do not install or operate the servo amplifier which has been damaged or has any parts missing. When the product has been stored for an extended period of time, contact your local sales office. When handling the servo amplifier, be careful about the edged parts such as corners of the servo amplifier. The servo amplifier must be installed in a metal cabinet. When fumigants that contain halogen materials such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are used for disinfecting and protecting wooden packaging from insects, they cause malfunction when entering our products. Please take necessary precautions to ensure that remaining materials from fumigant do not enter our products, or treat packaging with methods other than fumigation (heat method). Additionally, disinfect and protect wood from insects before packing products. 2. INSTALLATION 2 - 2 2.1 Installation direction and clearances CAUTION The equipment must be installed in the specified direction. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. Leave specified clearances between the servo amplifier and the cabinet walls or other equipment. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A have a regenerative resistor on their back face. The regenerative resistor generates heat of 100 ˚C higher than the ambient temperature. Please fully consider heat dissipation, installation position, etc. when mounting it. (1) Installation clearances of the servo amplifier (a) Installation of one servo amplifier 40 mm or more 10 mm or more 10 mm or more 40 mm or more Servo amplifier Cabinet Cabinet Wiring allowance 80 mm or more Top Bottom 2. INSTALLATION 2 - 3 (b) Installation of two or more servo amplifiers POINT Close mounting is possible for all capacity type of MR-JE servo amplifiers. Leave a large clearance between the top of the servo amplifier and the cabinet walls, and install a cooling fan to prevent the internal temperature of the cabinet from exceeding the environment. When mounting the servo amplifiers closely, leave a clearance of 1 mm between the adjacent servo amplifiers in consideration of mounting tolerances. In this case, keep the ambient temperature within 0 ˚C to 45 ˚C or use the servo amplifier with 75% or less of the effective load ratio. 100 mm or more 10 mm or more 30 mm or more 30 mm or more 40 mm or more Cabinet Top Bottom 100 mm or more 1 mm 30 mm or more 40 mm or more Cabinet 1 mm Leaving clearance Mounting closely (2) Others When using heat generating equipment such as the regenerative option, install them with full consideration of heat generation so that the servo amplifier is not affected. Install the servo amplifier on a perpendicular wall in the correct vertical direction. 2.2 Keep out foreign materials (1) When drilling in the cabinet, prevent drill chips and wire fragments from entering the servo amplifier. (2) Prevent oil, water, metallic dust, etc. from entering the servo amplifier through openings in the cabinet or a cooling fan installed on the ceiling. (3) When installing the cabinet in a place where toxic gas, dirt and dust exist, conduct an air purge (force clean air into the cabinet from outside to make the internal pressure higher than the external pressure) to prevent such materials from entering the cabinet. 2. INSTALLATION 2 - 4 2.3 Encoder cable stress (1) The way of clamping the cable must be fully examined so that bending stress and cable's own weight stress are not applied to the cable connection. (2) For use in any application where the servo motor moves, fix the cables (encoder, power supply, and brake) with having some slack from the connector connection part of the servo motor to avoid putting stress on the connector connection part. Use the optional encoder cable within the bending life range. Use the power supply and brake wiring cables within the bending life of the cables. (3) Avoid any probability that the cable sheath might be cut by sharp chips, rubbed by a machine corner or stamped by workers or vehicles. (4) For installation on a machine where the servo motor moves, the flexing radius should be made as large as possible. Refer to section 10.4 for the bending life. 2.4 Inspection items WARNING Before starting maintenance and/or inspection, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier. To avoid an electric shock, only qualified personnel should attempt inspections. For repair and parts replacement, contact your local sales office. CAUTION Do not perform insulation resistance test on the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. Do not disassemble and/or repair the equipment on customer side. It is recommended that the following points periodically be checked. (1) Check for loose terminal block screws. Retighten any loose screws. (2) Check the cables and the like for scratches or cracks. Inspect them periodically according to operating conditions especially when the servo motor is movable. (3) Check that the connector is securely connected to the servo amplifier. (4) Check that the wires are not coming out from the connector. (5) Check for dust accumulation on the servo amplifier. (6) Check for unusual noise generated from the servo amplifier. 2. INSTALLATION 2 - 5 2.5 Parts having service lives Service lives of the following parts are listed below. However, the service life vary depending or operating methods and environment. If any fault is found in the parts, they must be replaced immediately regardless of their service lives. For parts replacement, please contact your local sales office. Part name Life guideline Smoothing capacitor 10 years Relay Number of power-on and forced stop times by EM1 (Forced stop 1): 100,000 times Cooling fan 50,000 hours to 70,000 hours (7 years to 8 years) (1) Smoothing capacitor The characteristic of smoothing capacitor is deteriorated due to ripple currents, etc. The life of the capacitor greatly depends on ambient temperature and operating conditions. The capacitor will reach the end of its life in 10 years of continuous operation in normal air-conditioned environment (40 ˚C surrounding air temperature or less). (2) Relays Contact faults will occur due to contact wear arisen from switching currents. Relays will reach the end of their lives depending on their power supply capacity when the number of power-on times and number of forced stop times by EM1 (Forced stop 1) are 100,000 times in total. (3) Servo amplifier cooling fan The cooling fan bearings reach the end of their life in 50,000 hours to 70,000 hours. Normally, therefore, the cooling fan must be replaced in seven to eight years of continuous operation as a guideline. It must also be changed if unusual noise or vibration is found during inspection. The life indicates under the yearly average ambient temperature of 40 ˚C, free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt. 2. INSTALLATION 2 - 6 MEMO 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 1 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING WARNING Any person who is involved in wiring should be fully competent to do the work. Before wiring, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier. Ground the servo amplifier and servo motor securely. Do not attempt to wire the servo amplifier and servo motor until they have been installed. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock. The cables should not be damaged, stressed, loaded, or pinched. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock. To avoid an electric shock, insulate the connections of the power supply terminals. CAUTION Before removing the CNP1 connector from MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, disconnect the lead wires of the regenerative resistor from the CNP1 connector. Wire the equipment correctly and securely. Otherwise, the servo motor may operate unexpectedly, resulting in injury. Connect cables to the correct terminals. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur. Ensure that polarity (+/-) is correct. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur. The surge absorbing diode installed to the DC relay for control output should be fitted in the specified direction. Otherwise, the emergency stop and other protective circuits may not operate. DOCOM Control output signal Servo amplifier RA For sink output interface 24 V DC DOCOM Control output signal 24 V DC Servo amplifie r RA For source output interface Use a noise filter, etc. to minimize the influence of electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic interference may be given to the electronic equipment used near the servo amplifier. Do not install a power capacitor, surge killer or radio noise filter (optional FR-BIF) with the power line of the servo motor. When using the regenerative resistor, switch power off with the alarm signal. Otherwise, a transistor fault or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor, causing a fire. Do not modify the equipment. Connect the servo amplifier power output (U, V, and W) to the servo motor power input (U, V, and W) directly. Do not let a magnetic contactor, etc. intervene. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. U Servo motor M V W U V W U M V W U V W Servo amplifier Servo motorServo amplifier Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 2 3.1 Input power supply circuit CAUTION Always connect a magnetic contactor between the power supply and the power supply (L1, L2, and L3) of the servo amplifier, in order to configure a circuit that shuts down the power supply on the side of the servo amplifier’s power supply. If a magnetic contactor is not connected, continuous flow of a large current may cause a fire when the servo amplifier malfunctions. Use ALM (Malfunction) to switch power off. Not doing so may cause a fire when a regenerative transistor malfunctions or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor. Before removing the CNP1 connector from MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, disconnect the lead wires of the regenerative resistor from the CNP1 connector. Not doing so may break the lead wires of the regenerative resistor. Check the servo amplifier model, and then input proper voltage to the servo amplifier power supply. If input voltage exceeds the upper limit of the specification, the servo amplifier will break down. The servo amplifier has a built-in surge absorber (varistor) to reduce noise and to suppress lightning surge. The varistor can break down due to its aged deterioration. To prevent a fire, use a molded-case circuit breaker or fuse for input power supply. Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. POINT EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. Connect the 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply to L1 and L3. One of the connecting destinations is different from MR-E Super Series Servo Amplifier's. When using MR-JE as a replacement for MR-E Super, be careful not to connect the power to L2. Configure the wirings so that the power supply is shut off and SON (Servo-on) is turned off after deceleration to a stop due to an alarm occurring, enabled servo forced stop, etc. A molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) must be used with the input cables of the main circuit power supply. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 3 (1) For 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply of MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A (Note 5) MC ALM DOCOM CN1 (Note 3) 24 V DC (Note 8) 24 V DC (Note 8) Malfunction RA1 L1 L2 L3 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC Servo amplifier U V W (Note 1) CNP1 Servo motor U V W M Motor Encoder CN2 (Note 2) Encoder cable (Note 4, 7) RA1 Malfunction OFF MC ON MC SK EMG stop switch CN1 Forced stop 2 Servo-on (Note 3) EM2 SON DICOM (Note 6) Power supply MCCB (Note 7) C P+ Built-in regenerative resistor Note 1. MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A have a built-in regenerative resistor. (factory-wired) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 11.2. 2. For the encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. For selecting cables, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 3. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 4. For connecting servo motor power wires, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 5. Use a magnetic contactor with an operation delay time (interval between current being applied to the coil until closure of contacts) of 80 ms or less. Depending on the power supply voltage and operation pattern, bus voltage can decrease. This can shift the mode to the dynamic brake deceleration during forced stop deceleration. When dynamic brake deceleration is not required, slow the time to turn off the magnetic contactor. 6. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 7. Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. 8. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 4 (2) For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply of MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-70A POINT Connect the 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply to L1 and L3. One of the connecting destinations is different from MR-E Super Series Servo Amplifier's. When using MR-JE as a replacement for MR-E Super, be careful not to connect the power to L2. (Note 5) MC ALM DOCOM CN1 (Note 3) 24 V DC (Note 8) 24 V DC (Note 8) Malfunction RA1 L1 L2 L3 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC Servo amplifier U V W (Note 1) CNP1 Servo motor U V W M Motor Encoder CN2 (Note 2) Encoder cable (Note 4, 7) CN1 Forced stop 2 Servo-on (Note 3) EM2 SON DICOM (Note 6) Power supply MCCB (Note 7) C P+ Built-in regenerative resistor RA1 OFF MC ON MC SK EMG stop switch Malfunction Note 1. MR-JE-40A and MR-JE-70A have a built-in regenerative resistor. (factory-wired) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 11.2. 2. For the encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. For selecting cables, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 3. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 4. For connecting servo motor power wires, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 5. Use a magnetic contactor with an operation delay time (interval between current being applied to the coil until closure of contacts) of 80 ms or less. Depending on the power supply voltage and operation pattern, bus voltage can decrease. This can shift the mode to the dynamic brake deceleration during forced stop deceleration. When dynamic brake deceleration is not required, slow the time to turn off the magnetic contactor. 6. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 7. Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. 8. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 5 (3) MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A (Note 5) MC ALM DOCOM CN1 (Note 3) 24 V DC (Note 8) 24 V DC (Note 8) Malfunction RA1 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC Servo amplifier Servo motor U V W M Motor Encoder CN2 (Note 2) Encoder cable (Note 4, 7) CN1 Forced stop 2 Servo-on (Note 3) EM2 SON DICOM (Note 6) Power supply MCCB (Note 7) L1 L2 L3 P+ N- D C U V W (Note 1) CNP1 CNP2 RA1 OFF MC ON MC SK EMG stop switch Malfunction Note 1. Always connect between P+ and D terminals. (factory-wired) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 11.2. 2. For the encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. For selecting cables, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 3. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 4. For connecting servo motor power wires, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 5. Use a magnetic contactor with an operation delay time (interval between current being applied to the coil until closure of contacts) of 80 ms or less. Depending on the power supply voltage and operation pattern, bus voltage can decrease. This can shift the mode to the dynamic brake deceleration during forced stop deceleration. When dynamic brake deceleration is not required, slow the time to turn off the magnetic contactor. 6. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 7. Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. 8. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 6 3.2 I/O signal connection example 3.2.1 Position control mode (1) When you use a positioning module LD75D/QD75D (a) For sink I/O interface Servo amplifie r 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 (Note 7) CN1 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC Analog monitor 1 (Note 2) Malfunction (Note 6) Zero speed detection Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) 47 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 24 INP 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG 33 OP SD 10 m or less 2 m or less Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) (Note 7) CN1 LG DICOM 10 m or less (Note 8) 41 20 46 49 10 11 35 9 3 36 CLEARCOM 12 15 16 14 13 11 CLEAR RDYCOM READY PULSE F+ PULSE F- PG0 PG0 COM PULSE R+ PULSE R- 18 10 17 9 DOCOM CR RD PP PG NP NG LZ LZR 8 (Note 10) (Note 7) CN1 Positioning module LD75D/QD75D (Note 14) In-position Control common SD RA1 RA2 RA3 24 V DC (Note 4) 24 V DC (Note 4) 24 V DC (Note 4) Plate (Note 1) 2 m or less 10 m or less 0 V to +10 V 42 15 19 43 44 21 27 SD Plate Plate Plate SD EM2 SON RES LSP LSN DICOM TLA LG 28 (Note 7) CN1 Forced stop 2 Servo-on Reset Forward rotation stroke end Reverse rotation stroke end (Note 3, 5) (Note 5) + USB cable (option) (Note 9) MR Configurator2 CN3 Analog torque limit +10 V/maximum torque Personal computer (Note 11) Power supply Analog monitor 2 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 7 Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. 2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier will malfunction and will not output signals, disabling EM2 (Forced stop 2) and other protective circuits. 3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed. 4. Supply 24 V DC ± 10% to interfaces from outside. The total current capacity is up to 300 mA. 300 mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.9.2 (1) that gives the current value necessary for the interface. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 5. When starting operation, always turn on EM2 (Forced stop 2), LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) (normally closed contact). 6. ALM (Malfunction) turns on in normal alarm-free condition (normally closed contact). When this signal is switched off (at occurrence of an alarm), the output of the programmable controller should be stopped by the sequence program. 7. The pins with the same signal name are connected in the servo amplifier. 8. This length applies to the command pulse train input in the differential line driver type. It is 2 m or less in the open-collector type. 9. Use SW1DNC-MRC2-E. (Refer to section 11.4.) 10. This connection is not necessary for LD75D and QD75D. However, to enhance noise immunity, it is recommended to connect LG of servo amplifier and control common depending on the positioning module. 11. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 12. Plus and minus of the power of source interface are the opposite of those of sink interface. 13. CLEAR and CLEARCOM of source interface are interchanged to sink interface. 14. When a command cable malfunctions due to disconnection or noise, a position mismatch can occur. To avoid position mismatch, it is recommended that Encoder A-phase pulse and Encoder B-phase pulse be checked. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 8 (b) For source I/O interface POINT For notes, refer to (1) (a) in this section. 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC SD Servo amplifie r (Note 2) Malfunction (Note 6) Zero speed detection 47 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 24 INP 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG 33 OP SD 10 m or less 2 m or less (Note 7) CN1 LG DICOM 10 m or less (Note 8) 41 20 46 49 10 11 35 9 3 36 CLEARCOM 12 15 16 14 13 11 CLEAR RDYCOM READY PULSE F+ PULSE F- PG0 PG0 COM PULSE R+ PULSE R- 18 10 17 9 DOCOM CR RD PP PG NP NG LZ LZR 8 (Note 10) (Note 13) (Note 7) CN1 Positioning module LD75D/QD75D 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) In-position SD RA1 RA2 RA3 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) (Note 1) 2 m or less 10 m or less 42 15 19 43 44 21 27 SD EM2 SON RES LSP LSN DICOM TLA LG 28 (Note 7) CN1 + (Note 9) MR Configurator2 (Note 7) CN1 CN3 (Note 11) Power supply (Note 14) 0 V to +10 V Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) Control common Forced stop 2 Servo-on Reset Forward rotation stroke end Reverse rotation stroke end (Note 3, 5) (Note 5) Analog torque limit +10 V/maximum torque Plate Plate Plate Plate USB cable (option) Personal computer Analog monitor 1 Analog monitor 2 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 9 (2) When you use a positioning module FX 3U -_ _MT/ES (For sink I/O interface) Servo amplifier (Note 1) 2 m or less 10 m or less 42 15 19 43 44 21 27 SD EM2 SON RES LSP LSN DICOM TLA LG 28 (Note 7) CN1 + (Note 9) MR Configurator2 CN3 (Note 10) Power supply (Note 2) (Note 7) CN1 47 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG SD 8 LZ 9 LZR RA1 RA2 10 m or less (Note 7) CN1 COM3 X _ _ _ X000 RD 3 49 33 10 12 35 41 20 L N COM2 Y000 COM1 Y004 Y010 OP LG PP OPC NP DICOM DOCOM CR 46 Programmable controller FX 3U -_ _MT/ES (Note 11) S/S 24 V 0 V Programmable controller power supply 2 m or less (Note 8) 24 V DC (Note 4) 24 V DC (Note 4) 24 V DC (Note 4) (Note 15) (Note 12) (Note 13) (Note 14) X _ _ _ INP 24 SD 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC SD (Note 7) CN1 0 V to +10 V Malfunction (Note 6) Zero speed detection Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder Z-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Plate Plate Plate Plate Forced stop 2 Servo-on Reset Forward rotation stroke end Reverse rotation stroke end (Note 3, 5) (Note 5) Analog torque limit +10 V/maximum torque USB cable (option) Personal computer Analog monitor 1 Analog monitor 2 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 10 Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. 2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier will malfunction and will not output signals, disabling EM2 (Forced stop 2) and other protective circuits. 3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed. 4. Supply 24 V DC ± 10% to interfaces from outside. The total current capacity is up to 300 mA. 300 mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.9.2 (1) that gives the current value necessary for the interface. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 5. When starting operation, always turn on EM2 (Forced stop 2), LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) (normally closed contact). 6. ALM (Malfunction) turns on in normal alarm-free condition (normally closed contact). When this signal is switched off (at occurrence of an alarm), the output of the programmable controller should be stopped by the sequence program. 7. The pins with the same signal name are connected in the servo amplifier. 8. Connect them within 2 m because of open-collector type. 9. Use SW1DNC-MRC2-E. (Refer to section 11.4.) 10. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 11. Select the number of I/O points of the programmable controller depending on your system. 12. It will be COM0 for FX 3U -16MT/ES. 13. It will be COM4 for FX 3U -16MT/ES. 14. Select it within X000 to X007. 15. When a command cable malfunctions due to disconnection or noise, a position mismatch can occur. To avoid position mismatch, it is recommended that Encoder A-phase pulse and Encoder B-phase pulse be checked. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 11 3.2.2 Speed control mode (1) For sink I/O interface (Note 11) Power supply (Note 1) (Note 2) (Note 7) CN1 (Note 7) CN1 Servo amplifier (Note 7) CN1 47 DOCOM 46 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 24 SA 49 RD 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG 33 OP SD 2 m or less 8 LZ 9 LZR 20 DICOM 21DICOM 10 m or less 2 2 m or less 28 27 VC SD TLA LG + CN3 (Note 10) Analog speed command ±10 V/rated speed (Note 8) Analog torque limit +10 V/maximum torque (Note 9) MR Configurator2 RA1 RA2 RA3 RA4 24 V DC (Note 4) 24 V DC (Note 4) 42 15 19 41 43 44 EM2 SON ST1 ST2 LSP LSN Forward rotation start Reverse rotation start Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) Speed reached Ready 10 m or less 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC SD -10 V to +10 V 0 V to +10 V Forced stop 2 Servo-on Forward rotation stroke end Reverse rotation stroke end (Note 3, 5) (Note 5) Plate Plate Plate USB cable (option) Personal computer Analog monitor 1 Analog monitor 2 Malfunction (Note 6) Zero speed detection Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder Z-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. 2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier will malfunction and will not output signals, disabling EM2 (Forced stop 2) and other protective circuits. 3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed. 4. Supply 24 V DC ± 10% to interfaces from outside. The total current capacity is up to 300 mA. 300 mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.9.2 (1) that gives the current value necessary for the interface. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 5. When starting operation, always turn on EM2 (Forced stop 2), LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) (normally closed contact). 6. ALM (Malfunction) turns on in normal alarm-free condition (normally closed contact). 7. The pins with the same signal name are connected in the servo amplifier. 8. TLA will be available when TL (External torque limit selection) is enabled with [Pr. PD03], [Pr. PD11], [Pr. PD13], [Pr. PD17], and [Pr. PD19]. (Refer to section 3.6.1 (5).) 9. Use SW1DNC-MRC2-E. (Refer to section 11.4.) 10. Use an external power supply when inputting a negative voltage. 11. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 12. Plus and minus of the power of source interface are the opposite of those of sink interface. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 12 (2) For source I/O interface POINT For notes, refer to (1) in this section. (Note 1) (Note 2) (Note 7) CN1 (Note 7) CN1 (Note 7) CN1 47 DOCOM 46 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 24 SA 49 RD 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG 33 OP SD 2 m or less 8 LZ 9 LZR 20 DICOM 21DICOM 2 2 m or less 28 27 VC SD TLA LG + CN3 (Note 9) MR Configurator2 RA1 RA2 RA3 RA4 42 15 19 41 43 44 EM2 SON ST1 ST2 LSP LSN 10 m or less 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC SD 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) 10 m or less 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) -10 V to +10 V 0 V to +10 V Forward rotation start Reverse rotation start Forced stop 2 Servo-on Forward rotation stroke end Reverse rotation stroke end (Note 3, 5) (Note 5) Servo amplifie r Plate Plate Plate (Note 11) Power supply Speed reached Ready Malfunction (Note 6) Zero speed detection Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder Z-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) Analog monitor 1 Analog monitor 2 USB cable (option) Personal computer (Note 10) Analog speed command ±10 V/rated speed (Note 8) Analog torque limit +10 V/maximum torque 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 13 3.2.3 Torque control mode POINT EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. (1) For sink I/O interface Servo amplifie r (Note 6) CN1 (Note 1) 9 (Note 2) 47 DOCOM 46 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG 33 OP SD 10 m or less 2 m or less (Note 6) CN1 49 RD 8 LZ LZR (Note 6) CN1 20DICOM 21DICOM + CN3 27 2 m or less 28 2 TC SD VLA LG Analog torque command ±8 V/maximum torque (Note 8) Analog speed limit 0 to ±10 V/rated speed (Note 7) MR Configurator2 42 15 19 41 EM2 SON RS1 RS2 RA1 RA2 RA3 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC SD 24 V DC (Note 4) 10 m or less 24 V DC (Note 4) -8 V to +8 V -10 V to +10 V Forward rotation start Reverse rotation start Forced stop 2 Servo-on (Note 3) (Note 9) Power supply Plate Plate Plate Ready Malfunction (Note 6) Zero speed detection Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder Z-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) Analog monitor 1 Analog monitor 2 USB cable (option) Personal computer Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. 2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier will malfunction and will not output signals, disabling EM2 (Forced stop 2) and other protective circuits. 3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed. 4. Supply 24 V DC ± 10% to interfaces from outside. The total current capacity is up to 300 mA. 300 mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.9.2 (1) that gives the current value necessary for the interface. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 5. ALM (Malfunction) turns on in normal alarm-free condition (normally closed contact). 6. The pins with the same signal name are connected in the servo amplifier. 7. Use SW1DNC-MRC2-E. (Refer to section 11.4.) 8. Use an external power supply when inputting a negative voltage. 9. Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the servo amplifier. 10. Plus and minus of the power of source interface are the opposite of those of sink interface. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 14 (2) For source I/O interface POINT For notes, refer to (1) in this section. -8 V to +8 V -10 V to +10 V 24 V DC (Note 4, 10) Servo amplifie r (Note 6) CN1 (Note 1) 9 (Note 2) 47 DOCOM DICOM DICOM 46 DOCOM 48 ALM 23 ZSP 4 LA 5 LAR 6 LB 7 LBR 34 LG 33 OP SD 10 m or less 2 m or less (Note 6) CN1 49 RD 8 LZ LZR (Note 6) CN1 + CN3 27 2 m or less 28 2 TC SD VLA LG (Note 7) MR Configurator2 42 15 41 19 20 21 EM2 SON RS1 RS2 RA1 RA2 RA3 2 m or less 26 MO1 30 LG 29 MO2 ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC SD 10 m or less 24 V DC (Note 4, 10) Forward rotation start Reverse rotation start Forced stop 2 Servo-on (Note 3) (Note 9) Power supply Plate Plate Plate Ready Malfunction (Note 5) Zero speed detection Encoder A-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder Z-phase pulse (differential line driver) Encoder B-phase pulse (differential line driver) Control common Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) Analog monitor 1 Analog monitor 2 USB cable (option) Personal computer Analog torque command ±8 V/maximum torque (Note 8) Analog speed limit 0 to ±10 V/rated speed 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 15 3.3 Explanation of power supply system 3.3.1 Signal explanations POINT For the layout of connector and terminal block, refer to chapter 9 DIMENSIONS. Symbol Connection target (application) Description Supply the following power to L1, L2, and L3. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open. Servo amplifier Power supply MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-70A MR-JE-100A to MR-JE-300A 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz L1/L2/L3 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz L1/L3 L1/L2/L3 Power supply P+/C/D Regenerative option 1) MR-JE-100A or less MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A do not have D. When using a servo amplifier built-in regenerative resistor, connect P+ and C. (factory-wired) MR-JE-10A and MR-JE-20A do not have a built-in regenerative resistor. When using a regenerative option, disconnect wires of P+ and C for the built-in regenerative resistor. And then connect wires of the regenerative option to P+ and C. 2) MR-JE-200A or more When using a servo amplifier built-in regenerative resistor, connect P+ and D. (factory-wired) When using a regenerative option, disconnect P+ and D, and connect the regenerative option to P+ and C. Refer to section 11.2 for details. U/V/W Servo motor power output Connect them to the servo motor power supply (U, V, and W). Connect the servo amplifier power output (U, V, and W) to the servo motor power input (U, V, and W) directly. Do not let a magnetic contactor, etc. intervene. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. N- This is for manufacturer adjustment. Leave this open. MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A do not have N-. Protective earth (PE) Connect it to the grounding terminal of the servo motor and to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet for grounding. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 16 3.3.2 Power-on sequence POINT The voltage of analog monitor output, output signal, etc. may be unstable at power-on. (1) Power-on procedure 1) Always wire the power supply as shown in above section 3.1 using the magnetic contactor with the power supply (3-phase: L1, L2, and L3, 1-phase: L1 and L3). Configure an external sequence to switch off the magnetic contactor as soon as an alarm occurs. 2) The servo amplifier receives the SON (Servo-on) 2.5 s to 3.5 s after the power supply is switched on. Therefore, when SON (Servo-on) is switched on simultaneously with the power supply, the base circuit will switch on in about 2.5 s to 3.5 s, and the RD (Ready) will switch on in further about 5 ms, making the servo amplifier ready to operate. (Refer to (2) of this section.) 3) When RES (Reset) is switched on, the base circuit is shut off and the servo motor shaft coasts. (2) Timing chart 95 ms 95 ms RD (Ready) RES (Reset) SON (Servo-on) OFF ON OFF ON ON OFF Base circuit OFF ON Power supply OFF ON 10 ms5 ms 10 ms 10 ms5 ms 10 ms 5 ms 10 ms (2.5 s to 3.5 s) SON (Servo-on) accepted Alarm (OFF) No alarm (ON) ALM No alarm (Malfunction) 2.5 s to 3.5 s 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 17 3.3.3 Wiring CNP1 and CNP2 POINT For the wire sizes used for wiring, refer to section 11.5. To wire to CNP1 and CNP2, use servo amplifier power connectors packed with the amplifier or optional connectors (refer to section 11.1.1). (1) Connector (a) MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A CNP1 Servo amplifie r Table 3.1 Connector and applicable wire Applicable wire Connector Receptacle assembly Size Insulator OD Stripped length [mm] Open tool Manu- facturer CNP1 09JFAT-SAXGDK-H5.0 AWG 18 to 14 3.9 mm or shorter 9 J-FAT-OT JST (b) MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A CNP1 CNP2 Servo amplifier Table 3.2 Connector and applicable wire Applicable wire Connector Receptacle assembly Size Insulator OD Stripped length [mm] Open tool Manu- facturer CNP1 07JFAT-SAXGFK-XL CNP2 03JFAT-SAXGFK-XL AWG 16 to 10 4.7 mm or shorter 11.5 J-FAT-OT-EXL JST 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 18 (2) Cable connection procedure (a) Fabrication on cable insulator Refer to table 3.1 and 3.2 for stripped length of cable insulator. The appropriate stripped length of cables depends on their type, etc. Set the length considering their status. Insulato r Core Stripped length Twist strands lightly and straighten them as follows. Loose and bent strands Twist and straighten the strands. You can also use a ferrule to connect with the connectors. The following shows references to select ferrules according to wire sizes. Ferrule model (Phoenix Contact) Servo amplifier Wire size For one For two Crimp terminal (Phoenix Contact) AWG 16 AI1.5-10BK AI-TWIN2×1.5-10BK MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A AWG 14 AI2.5-10BU AWG 16 AI1.5-10BK AI-TWIN2×1.5-10BK AWG 14 AI2.5-10BU AI-TWIN2×2.5-10BU MR-JE-200A to MR-JE-300A AWG 12 AI4-10GY CRIMPFOX-ZA3 (b) Inserting wire Insert the open tool as follows and push down it to open the spring. While the open tool is pushed down, insert the stripped wire into the wire insertion hole. Check the insertion depth so that the wire insulator does not get caught by the spring. Release the open tool to fix the wire. Pull the wire lightly to confirm that the wire is surely connected. The following shows a connection example of the CNP2 connector for 2 kW and 3 kW. 1) Push down the open tool. 3) Release the open tool to fix the wire. 2) Insert the wire. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 19 3.4 Connectors and pin assignment POINT The pin assignment of the connectors are as viewed from the cable connector wiring section. For the CN1 connector, securely connect the external conductor of the shielded cable to the ground plate and fix it to the connector shell. Screw Screw Ground plate Cable The servo amplifier front view shown is that of the MR-JE-40A or less. Refer to chapter 9 DIMENSIONS for the appearances and connector layouts of the other servo amplifiers. CN1 The frames of the CN1 connector are connected to the protective earth terminal in the servo amplifier. CN3 (USB connector) Refer to section 11.4 This is a connector of 3M. 4 MRR 2 LG 8 6 1 P5 5 10 3 MR 7 9 CN2 MDR MD 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 25 50 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 20 The device assignment of CN1 connector pins changes depending on the control mode. For the pins which are given parameters in the related parameter column, their devices will be changed using those parameters. (Note 2) I/O signals in control modes Pin No. (Note 1) I/O P P/S S S/T T T/P Related parameter 1 2 I -/VC VC VC/VLA VLA VLA/- 3 LG LG LG LG LG LG 4 O LA LA LA LA LA LA 5 O LAR LAR LAR LAR LAR LAR 6 O LB LB LB LB LB LB 7 O LBR LBR LBR LBR LBR LBR 8 O LZ LZ LZ LZ LZ LZ 9 O LZR LZR LZR LZR LZR LZR 10 I PP PP/- -/PP 11 I PG PG/- -/PG 12 OPC OPC/- -/OPC 13 14 15 I SON SON SON SON SON SON Pr. PD03/Pr. PD04 16 17 18 19 I RES RES/ST1 ST1 ST1/RS2 RS2 RS2/RES Pr. PD11/Pr. PD12 20 DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM 21 DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM 22 23 O ZSP ZSP ZSP ZSP ZSP ZSP Pr. PD24 24 O INP INP/SA SA SA/- -/INP Pr. PD25 25 26 O MO1 MO1 MO1 MO1 MO1 MO1 Pr. PC14 27 I TLA (Note 3) TLA (Note 3) TLA (Note 3) TLA/TC TC (Note 3) TC/TLA 28 LG LG LG LG LG LG 29 O MO2 MO2 MO2 MO2 MO2 MO2 Pr. PC15 30 LG LG LG LG LG LG 31 32 33 O OP OP OP OP OP OP 34 LG LG LG LG LG LG 35 I NP NP/- -/NP 36 I NG NG/- -/NG 37 38 39 40 41 I CR CR/ST2 ST2 ST2/RS1 RS1 RS1/CR Pr. PD13/Pr. PD14 42 I EM2 EM2 EM2 EM2 EM2 EM2 43 I LSP LSP LSP LSP/- -/LSP Pr. PD17/Pr. PD18 44 I LSN LSN LSN LSN/- -/LSN Pr. PD19/Pr. PD20 45 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 21 (Note 2) I/O signals in control modes Pin No. (Note 1) I/O P P/S S S/T T T/P Related parameter 46 DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM 47 DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM 48 O ALM ALM ALM ALM ALM ALM 49 O RD RD RD RD RD RD Pr. PD28 50 Note 1. I: input signal, O: output signal 2. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode, P/S: position/speed control switching mode, S/T: speed/torque control switching mode, T/P: torque/position control switching mode 3. TLA will be available when TL (External torque limit selection) is enabled with [Pr. PD03], [Pr. PD11], [Pr. PD13], [Pr. PD17], and [Pr. PD19]. 3.5 Signal (device) explanations For the I/O interfaces (symbols in I/O division column in the table), refer to section 3.9.2. In the control mode field of the table P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode Torque control mode : devices used with initial setting status, : devices used by setting [Pr. PA04] and [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD28] The pin numbers in the connector pin No. column are those in the initial status. (1) I/O device (a) Input device Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division P S T Turn off EM2 (open between commons) to decelerate the servo motor to a stop with commands. Turn EM2 on (short between commons) in the forced stop state to reset that state. The following shows the setting of [Pr. PA04]. Deceleration method [Pr. PA04] setting EM2/EM1 EM2 or EM1 is off Alarm occurred 0 _ _ _ EM1 MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off without the forced stop deceleration. MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off without the forced stop deceleration. 2 _ _ _ EM2 MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off after the forced stop deceleration. MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off after the forced stop deceleration. Forced stop 2 EM2 CN1-42 EM2 and EM1 are mutually exclusive. EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. DI-1 Forced stop 1 EM1 (CN1-42) When using EM1, set [Pr. PA04] to "0 _ _ _" to enable EM1. Turn EM1 off (open between commons) to bring the motor to a forced stop state. The base circuit is shut off, the dynamic brake is operated and decelerate the servo motor to a stop. Turn EM1 on (short between commons) in the forced stop state to reset that state. DI-1 Servo-on SON CN1-15 Turn SON on to power on the base circuit and make the servo amplifier ready to operate. (servo-on status) Turn it off to shut off the base circuit and coast the servo motor. Set "_ _ _ 4" in [Pr. PD01] to switch this signal on (keep terminals connected) automatically in the servo amplifier. DI-1 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 22 Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Reset RES CN1-19 Turn on RES for more than 50 ms to reset the alarm. Some alarms cannot be deactivated by RES (Reset). Refer to section 8.1. Turning RES on in an alarm-free status shuts off the base circuit. The base circuit is not shut off when " _ _ 1 _ " is set in [Pr. PD30]. This device is not designed to make a stop. Do not turn it on during operation. DI-1 Forward rotation stroke end LSP CN1-43 To start operation, turn on LSP and LSN. Turn it off to bring the motor to a sudden stop and make it servo-locked. Setting [Pr. PD30] to " _ _ _ 1" will enable a slow stop. DI-1 LSN CN1-44 (Note) Input device Operation Reverse rotation stroke end LSP LSN CCW direction CW direction 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 Note. 0: Off 1: On Set [Pr. PD01] as indicated below to switch on the signals (keep terminals connected) automatically in the servo amplifier. Status [Pr. PD01] LSP LSN _ 4 _ _ Automatic on _ 8 _ _ Automatic on _ C _ _ Automatic on Automatic on When LSP or LSN turns off, [AL. 99 Stroke limit warning] occurs, and WNG (Warning) turns on. When using WNG, enable it by setting [Pr. PD24], [Pr. PD25] and [Pr. PD28]. External torque limit selection TL Turning off TL will enable [Pr. PA11 Forward torque limit] and [Pr. PA12 Reverse torque limit], and turning on it will enable TLA (Analog torque limit). For details, refer to section 3.6.1 (5). DI-1 Internal torque limit selection TL1 To select [Pr. PC35 Internal torque limit 2], enable TL1 with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. For details, refer to section 3.6.1 (5). DI-1 Forward rotation start ST1 This is used to start the servo motor. The following shows the directions. DI-1 (Note) Input device ST2 ST1 Servo motor starting direction 0 0 Stop (servo-lock) 0 1 CCW 1 0 CW 1 1 Stop (servo-lock) Note. 0: Off 1: On Reverse rotation start ST2 If both ST1 and ST2 are switched on or off during operation, the servo motor will be decelerated to a stop according to the [Pr. PC02] setting and servo-locked. When " _ _ _1" is set in [Pr. PC23], the servo motor is not servo-locked after deceleration to a stop. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 23 Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Forward rotation selection RS1 This is used to select a servo motor torque generation directions. The following shows the torque generation directions. DI-1 (Note) Input device RS2 RS1 Torque generation direction 0 0 Torque is not generated. Reverse rotation selection RS2 0 1 Forward rotation in power running mode/reverse rotation in regenerative mode 1 0 Reverse rotation in power running mode/forward rotation in regenerative mode 1 1 Torque is not generated. Note. 0: Off 1: On Speed selection 1 SP1 1. For speed control mode This is used to select the command speed for operation. DI-1 SP2 (Note) Input device DI-1 Speed selection 2 SP3 SP2 SP1 Speed command SP3 0 0 0 VC (Analog speed command) DI-1 Speed selection 3 0 0 1 Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1 0 1 0 Pr. PC06 Internal speed command 2 0 1 1 Pr. PC07 Internal speed command 3 1 0 0 Pr. PC08 Internal speed command 4 1 0 1 Pr. PC09 Internal speed command 5 1 1 0 Pr. PC10 Internal speed command 6 1 1 1 Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7 Note. 0: Off 1: On 2. For the torque control mode This is used to select the limited speed for operation. (Note) Input device SP3 SP2 SP1 Speed limit 0 0 0 VLA (Analog speed limit) 0 0 1 Pr. PC05 Internal speed limit 1 0 1 0 Pr. PC06 Internal speed limit 2 0 1 1 Pr. PC07 Internal speed limit 3 1 0 0 Pr. PC08 Internal speed limit 4 1 0 1 Pr. PC09 Internal speed limit 5 1 1 0 Pr. PC10 Internal speed limit 6 1 1 1 Pr. PC11 Internal speed limit 7 Note. 0: Off 1: On 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 24 Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Proportion control PC Turn PC on to switch the speed amplifier from the proportional integral type to the proportional type. If the servo motor at a stop is rotated even one pulse due to any external factor, it generates torque to compensate for a position shift. When the servo motor shaft is to be locked mechanically after positioning completion (stop), switching on the PC (Proportion control) upon positioning completion will suppress the unnecessary torque generated to compensate for a position shift. When the shaft is to be locked for a long time, switch on the PC (Proportion control) and TL (External torque limit selection) at the same time to make the torque less than the rated by TLA (Analog torque limit). DI-1 Clear CR CN1-41 Turn CR on to clear the position control counter droop pulse on its leading edge. The pulse width should be 10 ms or longer. The delay amount set in [Pr. PB03 Position command acceleration/deceleration time constant] is also cleared. When " _ _ _1 " is set to [Pr. PD32], the pulses are always cleared while CR is on. DI-1 Electronic gear selection 1 CM1 The combination of CM1 and CM2 enables you to select four different electronic gear numerators set in the parameters. DI-1 (Note) Input device CM2 CM1 Electronic gear numerator 0 0 Pr. PA06 CM2 0 1 Pr. PC32 DI-1 Electronic gear selection 2 1 0 Pr. PC33 1 1 Pr. PC34 Note. 0: Off 1: On Gain switching CDP Turn on CDP to use the values of [Pr. PB29] to [Pr. PB36] and [Pr. PB56] to [Pr. PB60] as the load to motor inertia ratio and gain values. DI-1 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 25 Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Control switching LOP «Position/speed control switching mode» This is used to select the control mode in the position/speed control switching mode. DI-1 (Note) LOP Control mode Refer to Function and application. 0 Position 1 Speed Note. 0: Off 1: On «Speed/torque control switch mode» This is used to select the control mode in the speed/torque control switching mode. (Note) LOP Control mode 0 Speed 1 Torque Note. 0: Off 1: On «Torque/position control switch mode» This is used to select the control mode in the torque/position control switching mode. (Note) LOP Control mode 0 Torque 1 Position Note. 0: Off 1: On Second acceleration/ deceleration selection STAB2 The device allows selection of the acceleration/deceleration time constant at servo motor rotation in the speed control mode or torque control mode. The s-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is always uniform. DI-1 (Note) STAB2 Acceleration/deceleration time constant 0 Pr. PC01 Acceleration time constant Pr. PC02 Deceleration time constant 1 Pr. PC30 Acceleration time constant 2 Pr. PC31 Deceleration time constant 2 Note. 0: Off 1: On 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 26 (b) Output device Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Malfunction ALM CN1-48 When an alarm occurs, ALM will turn off. When an alarm does not occur, ALM will turn on after 2.5 s to 3.5 s after power-on. When [Pr. PD34] is "_ _ 1 _", an alarming or warning will turn off ALM. DO-1 Ready RD CN1-49 Enabling servo-on to make the servo amplifier ready to operate will turn on RD. DO-1 In-position INP CN1-24 When the number of droop pulses is in the preset in-position range, INP will turn on. The in-position range can be changed using [Pr. PA10]. When the in-position range is increased, INP may be on during low-speed rotation. INP turns on when servo-on turns on. DO-1 Speed reached SA When the servo motor speed reaches the following range, SA will turn on. Set speed ± ((Set speed × 0.05) + 20) r/min When the preset speed is 20 r/min or less, SA always turns on. SA does not turn on even when the SON (Servo-on) is turned off or the servo motor speed by the external force reaches the preset speed while both ST1 (Forward rotation start) and ST2 (reverse rotation start) are off. DO-1 Limiting speed VLC VLC turns on when speed reaches a value limited with any of [Pr. PC05 Internal speed limit 1] to [Pr. PC11 Internal speed limit 7] or VLA (Analog speed limit). This turns off when SON (Servo-on) turns off. DO-1 Limiting torque TLC TLC turns on when a generated torque reaches a value set with any of [Pr. PA11 Forward torque limit], [Pr. PA12 Reverse torque limit], or TLA (Analog torque limit). DO-1 Zero speed detection ZSP CN1-23 ZSP turns on when the servo motor speed is zero speed (50r/min) or less. Zero speed can be changed with [Pr. PC17]. OFF ON Servo motor speed 20 r/min (Hysteresis width) [Pr. PC17] 20 r/min (Hysteresis width) OFF level -70 r/min ON level -50 r/min ON level 50 r/min OFF level 70 r/min 0 r/min [Pr. PC17] ZSP (Zero speed detection) 1) 3) 2) 4) Forward rotation direction Reverse rotation direction ZSP will turn on when the servo motor is decelerated to 50 r/min (at 1)), and will turn off when the servo motor is accelerated to 70 r/min again (at 2)). ZSP will turn on when the servo motor is decelerated again to 50 r/min (at 3)), and will turn off when the servo motor speed has reached -70 r/min (at 4)). The range from the point when the servo motor speed has reached on level, and ZSP turns on, to the point when it is accelerated again and has reached off level is called hysteresis width. Hysteresis width is 20 r/min for this servo amplifier. DO-1 Electromagnetic brake interlock MBR When using the device, set operation delay time of the electromagnetic brake in [Pr. PC16]. When a servo-off status or alarm occurs, MBR will turn off. DO-1 Warning WNG When warning has occurred, WNG turns on. When a warning is not occurring, turning on the power will turn off WNG after 2.5 s to 3.5 s. DO-1 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 27 Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Alarm code ACD0 (CN1-24) DI-1 ACD1 (CN1-23) ACD2 (CN1-49) To use these signals, set " _ _ _ 1" in [Pr. PD34]. This signal is outputted when an alarm occurs. When an alarm is not occurring, respective ordinary signals are outputted. For details of the alarm codes, refer to chapter 8. When you select alarm code output while MBR or ALM is selected for CN1-23, CN1-24, or CN1-49 pin, [AL. 37 Parameter error] will occur. Variable gain selection CDPS CDPS turns on during gain switching. DO-1 During tough drive MTTR When a tough drive is enabled in [Pr. PA20], activating the instantaneous power failure tough drive will turn on MTTR. DO-1 (2) Input signal Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Analog torque limit TLA CN1-27 To use the signal, enable TL (External torque limit selection) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. When TLA is enabled, torque is limited in the full servo motor output torque range. Apply 0 V to +10 V DC between TLA and LG. Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to TLA. The maximum torque is generated at +10 V. (Refer to section 3.6.1 (5).) If a value equal to or larger than the maximum torque is inputted to TLA, the value is clamped at the maximum torque. Resolution: 10 bits Analog input Analog torque command TC This is used to control torque in the full servo motor output torque range. Apply 0 V to ±8 V DC between TC and LG. The maximum torque is generated at ±8 V. (Refer to section 3.6.3 (1).) The speed at ±8 V can be changed with [Pr. PC13]. If a value equal to or larger than the maximum torque is inputted to TC, the value is clamped at the maximum torque. Analog input Analog speed command VC CN1-2 Apply 0 V to ±10 V DC between VC and LG. Speed set in [Pr. PC12] is provided at ±10 V. (Refer to section 3.6.2 (1).) If a value equal to or larger than the permissible speed is inputted to VC, the value is clamped at the permissible speed. Resolution: 14 bits or equivalent Analog input Analog speed limit VLA Apply 0 V to ±10 V DC between VLA and LG. Speed set in [Pr. PC12] is provided at ±10 V. (Refer to section 3.6.3 (3).) If a limited value equal to or larger than the permissible speed is inputted to VLA, the value is clamped at the permissible speed. Analog input Forward rotation pulse train Reverse rotation pulse train PP NP PG NG CN1-10 CN1-35 CN1-11 CN1-36 This is used to enter a command pulse train. The command input pulse train form, pulse train logic, and command input pulse train filter are changed in [Pr. PA13]. For open-collector type, set [Pr. PA13] to "_ 3 _ _". For differential receiver type, set [Pr. PA13] depending on the maximum input frequency. For open-collector type (sink input interface) The maximum input frequency is 200 kpulses/s. For A-phase/B-phase pulse train, 200 kpulses/s will be the frequency after multiplication by four. Input the forward rotation pulse train between PP and DOCOM. Input the reverse rotation pulse train between NP and DOCOM. For differential receiver type The maximum input frequency is 4 Mpulses/s. For A-phase/B-phase pulse train, 4 Mpulses/s will be the frequency after multiplication by four. Input the forward rotation pulse train between PG and PP. Input the reverse rotation pulse train between NG and NP. DI-2 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 28 (3) Output signal Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Encoder A- phase pulse (differential line driver) LA LAR CN1-4 CN1-5 DO-2 Encoder B- phase pulse (differential line driver) LB LBR CN1-6 CN1-7 These devices output pulses of encoder output pulse set in [Pr. PA15] in the differential line driver type. In CCW rotation of the servo motor, the encoder B-phase pulse lags the encoder A-phase pulse by a phase angle of /2. The relation between rotation direction and phase difference of the A- phase and B-phase pulses can be changed with [Pr. PC19]. Encoder Z- phase pulse (differential line driver) LZ LZR CN1-8 CN1-9 The encoder zero-point signal is outputted in the differential line driver type. One pulse is outputted per servo motor revolution. This turns on when the zero-point position is reached. (negative logic) The minimum pulse width is about 400 s. For home position return using this pulse, set the creep speed to 100 r/min. or less. DO-2 Encoder Z- phase pulse (open-collector) OP CN1-33 The encoder zero-point signal is outputted in the open-collector type. DO-2 Analog monitor 1 MO1 CN1-26 This is used to output the data set in [Pr. PC14] to between MO1 and LG in terms of voltage. Resolution: 10 bits or equivalent Analog output Analog monitor 2 MO2 CN1-29 This signal outputs the data set in [Pr. PC15] to between MO2 and LG in terms of voltage. Resolution: 10 bits or equivalent Analog output (4) Power supply Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Digital I/F power supply input DICOM CN1-20 CN1-21 Input 24 V DC (24 V DC ± 10% 300 mA) for I/O interface. The power supply capacity changes depending on the number of I/O interface points to be used. For sink interface, connect + of 24 V DC external power supply. For source interface, connect - of 24 V DC external power supply. Open-collector sink interface power supply input OPC CN1-12 When inputting a pulse train in the open-collector type with sink interface, supply this terminal with the positive (+) power of 24 V DC. Digital I/F common DOCOM CN1-46 CN1-47 Common terminal of input signal such as EM2 of the servo amplifier. This is separated from LG. For sink interface, connect - of 24 V DC external power supply. For source interface, connect + of 24 V DC external power supply. Control common LG CN1-3 CN1-28 CN1-30 CN1-34 This is a common terminal for TLA, TC, VC, VLA, OP, MO1, and MO2. Pins are connected internally. Shield SD Plate Connect the external conductor of the shielded wire. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 29 3.6 Detailed explanation of signals 3.6.1 Position control mode POINT Adjust the logic of a positioning module and command pulse as follows. Q series/L series positioning module Command pulse logic setting Signal type Q series/L series positioning module Pr. 23 setting MR-JE-_A servo amplifier [Pr. PA13] setting Positive logic Positive logic (_ _ 0 _) Open-collector type Negative logic Negative logic (_ _ 1 _) Positive logic (Note) Negative logic (_ _ 1 _) Differential line driver type Negative logic (Note) Positive logic (_ _ 0 _) Note. For Q series and L series, the logic means N-side waveform. Therefore, reverse the input pulse logic of the servo amplifier. F series positioning module Command pulse logic setting Signal type F series positioning module (fixed) MR-JE-_A servo amplifier [Pr. PA13] setting Open-collector type Differential line driver type Negative logic Negative logic (_ _ 1 _) (1) Pulse train input (a) Input pulse waveform selection You can input command pulses in any of three different forms, and can choose positive or negative logic. Set the command pulse train form in [Pr. PA13]. Refer to section 5.2.1 for details. (b) Connection and waveform 1) Open-collector type Connect as follows. 1.2 k Approx. 1.2 k Approx. SD Servo amplifie r OPC PP NP DOCOM 24 V DC (Note) Note. Pulse train input interface is comprised of a photocoupler. If a resistor is connected to the pulse train signal line, it may malfunction due to reduction in current. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 30 The following section explains about the case where the negative logic and the forward/reverse rotation pulse trains are set to "_ _ 1 0" in [Pr. PA13]. Reverse rotation commandForward rotation command (OFF) (OFF) (OFF)(ON) (ON) (ON) (OFF) (ON) (OFF) (ON) (OFF) Forward rotation pulse train (transistor) Reverse rotation pulse train (transistor) (ON) 2) Differential line driver type Connect as follows. PP NP Servo amplifie r PG NG SD Approximately 100 Approximately 100 (Note) Note. Pulse train input interface is comprised of a photocoupler. If a resistor is connected to the pulse train signal line, it may malfunction due to reduction in current. The following example shows that an input waveform has been set to the negative logic and forward/reverse rotation pulse trains by setting "_ _ 1 0" in [Pr. PA13]. The waveforms of PP, PG, NP, and NG are based on LG. Reverse rotation PP PG NP NG Reverse rotation pulse train Forward rotation pulse train Forward rotation 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 31 (2) INP (In-position) INP turns on when the number of droop pulses in the deviation counter falls within the preset in-position range ([Pr. PA10]). INP may turn on continuously during a low-speed operation with a large value set as the in-position range. In-position range INP (In-position) ON OFF ON OFF Alarm No alarm SON (Servo-on) Alarm Droop pulses (3) RD (Ready) RD (Ready) ON OFF ON OFF Alarm No alarm SON (Servo-on) Alarm 100 ms or shorter 10 ms or shorter 10 ms or shorter (4) Electronic gear switching The combination of CM1 and CM2 enables you to select four different electronic gear numerators set in the parameters. As soon as CM1/CM2 is turned on or off, the numerator of the electronic gear changes. Therefore, if a shock occurs at switching, use the position smoothing ([Pr. PB03]) to relieve the shock. (Note) Input device CM2 CM1 Electronic gear numerator 0 0 Pr. PA06 0 1 Pr. PC32 1 0 Pr. PC33 1 1 Pr. PC34 Note. 0: Off 1: On 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 32 (5) Torque limit CAUTION If the torque limit is canceled during servo-lock, the servo motor may suddenly rotate according to position deviation in respect to the command position. (a) Torque limit and torque By setting [Pr. PA11 Forward rotation torque limit] or [Pr. PA12 Reverse rotation torque limit], torque is always limited to the maximum value during operation. A relation between the limit value and servo motor torque is as follows. Torque limit value in [Pr. PA11] Maximum torque Torque 0 100 [%] Torque limit value in [Pr. PA12] 100 CCW directionCW direction A relation between the applied voltage of TLA (Analog torque limit) and the torque limit value of the servo motor is as follows. Torque limit values will vary about 5% relative to the voltage depending on products. At the voltage of less than 0.05 V, torque may vary as it may not be limited sufficiently. Therefore, use this function at the voltage of 0.05 V or more. ±5% Connection exampleTLA applied voltage vs. torque limit value TLA applied voltage [V] Maximum torque Torque 0 0 0.05 Servo amplifier 24 V DC (Note) TL DICOM TLA LG SD 0 V to +10 V Note. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. (b) Torque limit value selection The following shows how to select a torque limit using TL (External torque limit selection) from [Pr. PA11 Forward torque limit] or [Pr. PA12 Reverse torque limit] and TLA (Analog torque limit). When TL1 (Internal torque limit selection) is enabled with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD22], you can select [Pr. PC35 Internal torque limit 2]. However, if [Pr. PA11] and [Pr. PA12] value is less than the limit value selected by TL/TL1, [Pr. PA11] and [Pr. PA12] value will be enabled. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 33 (Note) Input device Enabled torque limit value TL1 TL Limit value status CCW power running/CW regeneration CW power running/CCW regeneration 0 0 Pr. PA11 Pr .PA12 TLA > Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 0 1 TLA < Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 TLA TLA Pr. PC35 > Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 1 0 Pr. PC35 < Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 Pr. PC35 Pr. PC35 TLA > Pr. PC35 Pr. PC35 Pr. PC35 1 1 TLA < Pr. PC35 TLA TLA Note. 0: Off 1: On (c) TLC (Limiting torque) TLC turns on when the servo motor torque reaches the torque limited using the forward rotation torque limit, reverse rotation torque limit or analog torque limit. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 34 3.6.2 Speed control mode (1) Speed setting (a) Speed command and speed The servo motor is run at the speeds set in the parameters or at the speed set in the applied voltage of VC (Analog speed command). A relation between VC (Analog speed command) applied voltage and the servo motor speed is as follows. Rated speed is achieved at ±10 V with initial setting. The speed at ±10 V can be changed with [Pr. PC12]. Speed [r/min] CW direction Rated speed [r/min] Rated speed [r/min] 0 CCW direction +10 -10 VC applied voltage [V] Forward rotation (CCW) Reverse rotation (CW) The following table indicates the rotation direction according to ST1 (Forward rotation start) and ST2 (Reverse rotation start) combination. (Note 1) Input device (Note 2) Rotation direction VC (Analog speed command) ST2 ST1 Polarity: + 0 V Polarity: - Internal speed command 0 0 Stop (servo-lock) Stop (servo-lock) Stop (servo-lock) Stop (servo-lock) 0 1 CCW CW CCW 1 0 CW Stop (no servo-lock) CCW CW 1 1 Stop (servo-lock) Stop (servo-lock) Stop (servo-lock) Stop (servo-lock) Note 1. 0: Off 1: On 2. If the torque limit is canceled during servo-lock, the servo motor may suddenly rotate according to position deviation in respect to the command position. Normally, connect as follows. (Note) ST1 ST2 DICOM VC LG SD Servo amplifie r 24 V DC -10 V to +10 V Note. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 35 (b) Speed command value selection To select VC (Analog speed command) and a speed command value of internal speed commands 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. (Note) Input device SP3 SP2 SP1 Speed command value 0 0 0 VC (Analog speed command) 0 0 1 Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1 0 1 0 Pr. PC06 Internal speed command 2 0 1 1 Pr. PC07 Internal speed command 3 1 0 0 Pr. PC08 Internal speed command 4 1 0 1 Pr. PC09 Internal speed command 5 1 1 0 Pr. PC10 Internal speed command 6 1 1 1 Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7 Note. 0: Off 1: On You can change the speed during rotation. To accelerate/decelerate, set acceleration/deceleration time constant in [Pr. PC01] or [Pr. PC02]. When the internal speed commands are used to command a speed, the speed does not vary with the ambient temperature. (2) SA (Speed reached) SA turns on when the servo motor speed has nearly reached the speed set to the internal speed command or analog speed command. Internal speed command 1 Internal speed command 2 Set speed selection ST1 or ST2 ON OFF Servo motor speed SA (Speed reached) ON OFF (3) Torque limit As in section 3.6.1 (5) 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 36 3.6.3 Torque control mode (1) Torque limit (a) Torque command and torque The following shows a relation between the applied voltage of TC (Analog torque command) and the torque by the servo motor. The maximum torque is generated at ±8 V. The speed at ±8 V can be changed with [Pr. PC13]. Forward rotation (CCW) Reverse rotation (CW) Maximum torque Torque CCW direction TC applied voltage [V] CW direction Maximum torque -8 +8 -0.05 +0.05 Generated torque command values will vary about 5% relative to the voltage depending on products. The torque may vary if the voltage is low (-0.05 V to 0.05 V) and the actual speed is close to the limit value. In such a case, increase the speed limit value. The following table indicates the torque generation directions determined by RS1 (Forward rotation selection) and RS2 (Reverse rotation selection) when TC (Analog torque command) is used. (Note) Input device Rotation direction TC (Analog torque command) RS2 RS1 Polarity: + 0 V Polarity: - 0 0 Torque is not generated. Torque is not generated. 0 1 CCW (Forward rotation in power running mode/reverse rotation in regenerative mode) CW (Reverse rotation in power running mode/forward rotation in regenerative mode) 1 0 CW (Reverse rotation in power running mode/forward rotation in regenerative mode) CCW (Forward rotation in power running mode/reverse rotation in regenerative mode) 1 1 Torque is not generated. Torque is not generated. Torque is not generated. Note. 0: Off 1: On Normally, connect as follows. RS2 24 V DC DICOM TC LG SD RS1 -8 V to 8 V Servo amplifier (Note) Note. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 37 (b) Analog torque command offset Using [Pr. PC38], the offset voltage of -9999 mV to 9999 mV can be added to the TC applied voltage as follows. TC applied voltage [V] Maximum torque Torque 0 8 (-8) [Pr. PC38] offset range -9999 mV to 9999 mV (2) Torque limit By setting [Pr. PA11 Forward rotation torque limit] or [Pr. PA12 Reverse rotation torque limit], torque is always limited to the maximum value during operation. A relation between limit value and servo motor torque is as in section 3.6.1 (5). Note that TLA (Analog torque limit) is unavailable. (3) Speed limit (a) Speed limit value and speed The speed is limited to the values set with [Pr. PC05 Internal speed limit 0] to [Pr. PC11 Internal speed limit 7] or the value set in the applied voltage of VLA (Analog speed limit). A relation between VLA (Analog speed limit) applied voltage and the servo motor speed is as follows. When the servo motor speed reaches the speed limit value, torque control may become unstable. Make the set value more than 100 r/min greater than the desired speed limit value. Speed [r/min] CW direction 0 CCW direction +10 -10 VLA applied voltage [V] Forward rotation (CCW) Reverse rotation (CW) Rated speed [r/min] Rated speed [r/min] The following table indicates the limit direction according to RS1 (Forward rotation selection) and RS2 (Reverse rotation selection) combination. (Note) Input device Speed limit direction VLA (Analog speed limit) RS1 RS2 Polarity: + Polarity: - Internal speed command 1 0 CCW CW CCW 0 1 CW CCW CW Note. 0: Off 1: On 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 38 Normally, connect as follows. -10 V to +10 V VLA LG SD Servo amplifie r (b) Speed limit value selection To select VLA (Analog speed limit) and a speed limit value of internal speed limit 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. (Note) Input device SP3 SP2 SP1 Speed limit 0 0 0 VLA (Analog speed limit) 0 0 1 Pr. PC05 Internal speed limit 1 0 1 0 Pr. PC06 Internal speed limit 2 0 1 1 Pr. PC07 Internal speed limit 3 1 0 0 Pr. PC08 Internal speed limit 4 1 0 1 Pr. PC09 Internal speed limit 5 1 1 0 Pr. PC10 Internal speed limit 6 1 1 1 Pr. PC11 Internal speed limit 7 Note. 0: Off 1: On When the internal speed limits 1 to 7 are used to limit a speed, the speed does not vary with the ambient temperature. (c) VLC (Limiting speed) VLC turns on when the servo motor speed reaches a speed limited with internal speed limits 1 to 7 or analog speed limit. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 39 3.6.4 Position/speed control switching mode Set " _ _ _ 1" in [Pr. PA01] to switch to the position/speed control switching mode. (1) LOP (control switching) Use LOP (Control switching) to switch between the position control mode and the speed control mode with an external contact. The following shows a relation between LOP and control modes. (Note) LOP Control mode 0 Position control mode 1 Speed control mode Note. 0: Off 1: On You can switch the control mode in the zero speed status. To ensure safety, switch modes after the servo motor has stopped. When position control mode is switched to speed control mode, droop pulses will be reset. If LOP is switched on/off at the speed higher than the zero speed, the control mode cannot be changed regardless of the speed. The following shows a switching timing chart. Zero speed level Position control mode ON OFF ON OFF LOP (Control switching) ZSP (Zero speed detection) Servo motor speed Speed control mode Position control mode (Note)(Note) Note. When ZSP is not turned on, the control mode is not switched even if LOP is turned on/off. After LOP is turned on/off, even if ZSP is turned on, the control mode is not switched. (2) Torque limit in position control mode As in section 3.6.1 (5) 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 40 (3) Speed setting in speed control mode (a) Speed command and speed The servo motor is run at the speeds set in the parameters or at the speed set in the applied voltage of VC (Analog speed command). The relation between an applied voltage of VC (Analog speed command) and servo motor speed, and the rotation direction with turning on ST1/ST2 are the same as section 3.6.2 (1) (a). Normally, connect as follows. (Note) ST1 ST2 DICOM VC LG SD Servo amplifie r 24 V DC -10 V to +10 V Note. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. (b) Speed command value selection To select VC (Analog speed command) and a speed command value of internal speed commands 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. (Note) Input device SP3 SP2 SP1 Speed command value 0 0 0 VC (Analog speed command) 0 0 1 Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1 0 1 0 Pr. PC06 Internal speed command 2 0 1 1 Pr. PC07 Internal speed command 3 1 0 0 Pr. PC08 Internal speed command 4 1 0 1 Pr. PC09 Internal speed command 5 1 1 0 Pr. PC10 Internal speed command 6 1 1 1 Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7 Note. 0: Off 1: On You can change the speed during rotation. Acceleration/deceleration is performed with the setting values of [Pr. PC01] and [Pr. PC02]. When the internal speed commands 1 to 7 are used to command a speed, the speed does not vary with the ambient temperature. (c) SA (Speed reached) As in section 3.6.2 (2) 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 41 3.6.5 Speed/torque control switching mode Set " _ _ _ 3" in [Pr. PA01] to switch to the speed/torque control switching mode. (1) LOP (control switching) Use LOP (Control switching) to switch between the speed control mode and the torque control mode with an external contact. The following shows a relation between LOP and control modes. (Note) LOP Control mode 0 Speed control mode 1 Torque control mode Note. 0: Off 1: On The control mode may be switched at any time. The following shows a switching timing chart. LOP (Control switching) Servo motor speed TC (Analog torque command) ON OFF 10V 0 (Note) Load torque Speed control mode Torque control mode Speed control mode Forward rotation in driving mode Note. When ST1 (Forward rotation start) and ST2 (Reverse rotation start) are switched off as soon as a mode is switched to the speed control, the servo motor comes to a stop according to the deceleration time constant. A shock may occur at switching control modes. (2) Speed setting in speed control mode As in section 3.6.2 (1) (3) Torque limit in speed control mode As in section 3.6.1 (5) (4) Speed limit in torque control mode (a) Speed limit value and speed The speed is limited to the limit value of the parameter or the value set in the applied voltage of VLA (Analog speed limit). A relation between the VLA (Analog speed limit) applied voltage and the limit value is as in section 3.6.3 (3) (a). 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 42 Normally, connect as follows. -10 V to +10 V VLA LG SD Servo amplifie r (b) Speed limit value selection To select VLA (Analog speed limit) and a speed limit value of internal speed limit 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. (Note) Input device SP3 SP2 SP1 Speed limit 0 0 0 VLA (Analog speed limit) 0 0 1 Pr. PC05 Internal speed limit 1 0 1 0 Pr. PC06 Internal speed limit 2 0 1 1 Pr. PC07 Internal speed limit 3 1 0 0 Pr. PC08 Internal speed limit 4 1 0 1 Pr. PC09 Internal speed limit 5 1 1 0 Pr. PC10 Internal speed limit 6 1 1 1 Pr. PC11 Internal speed limit 7 Note. 0: Off 1: On When the internal speed command 1 is used to command a speed, the speed does not vary with the ambient temperature. (c) VLC (Limiting speed) As in section 3.6.3 (3) (c) (5) Torque control in torque control mode As in section 3.6.3 (1) (6) Torque limit in torque control mode As in section 3.6.3 (2) 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 43 3.6.6 Torque/position control switching mode Set " _ _ _ 5" in [Pr. PA01] to switch to the torque/position control switching mode. (1) LOP (control switching) Use LOP (Control switching) to switch between the torque control mode and the position control mode with an external contact. The following shows a relation between LOP and control modes. (Note) LOP Control mode 0 Torque control mode 1 Position control mode Note. 0: Off 1: On You can switch the control mode in the zero speed status. To ensure safety, switch modes after the servo motor has stopped. When position control mode is switched to torque control mode, droop pulses will be reset. If LOP is switched on/off at the speed higher than the zero speed, the control mode cannot be changed regardless of the speed. The following shows a switching timing chart. Zero speed level Torque control mode Position control mode Position control mode Servo motor speed TC (Analog torque command) ZSP (Zero speed detection) LOP (Control switching) 0 V OFF (Note) (Note) ON OFF ON 10 V Note. When ZSP is not turned on, the control mode is not switched even if LOP is turned on/off. After LOP is turned on/off, even if ZSP is turned on, the control mode is not switched. (2) Speed limit in torque control mode As in section 3.6.3 (3) (3) Torque control in torque control mode As in section 3.6.3 (1) (4) Torque limit in torque control mode As in section 3.6.3 (2) (5) Torque limit in position control mode As in section 3.6.1 (5) 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 44 3.7 Forced stop deceleration function POINT When alarms not related to the forced stop function occur, control of motor deceleration can not be guaranteed. (Refer to chapter 8.) In the torque control mode, the forced stop deceleration function is not available. 3.7.1 Forced stop deceleration function When EM2 is turned off, dynamic brake will start to stop the servo motor after forced stop deceleration. During this sequence, the display shows [AL. E6 Servo forced stop warning]. During normal operation, do not use EM2 (Forced stop 2) to alternate stop and drive. The the servo amplifier life may be shortened. (1) Connection diagram Servo amplifie r Forced stop 2 DICOM EM2 24 V DC (Note) Note. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 45 (2) Timing chart POINT When LSP/LSN is turned on during a forced stop deceleration, the motor will stop depending on the setting of [Pr. PD30] as follows. [Pr. PD30] Stop system _ _ _ 0 Switching to sudden stop _ _ _ 1 Continuing forced stop deceleration When EM2 (Forced stop 2) turns off, the motor will decelerate according to [Pr. PC51 Forced stop deceleration time constant]. Once the motor speed is below [Pr. PC17 Zero speed] after completion of the deceleration command, base power is cut and the dynamic brake activates. Base circuit (Energy supply to t he servo motor) 0 r/min Servo motor speed MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) ON OFF (Enabled) ON OFF Deceleration time Command Rated speed Ordinary operation Forced stop deceleration Dynamic brake + Electromagnetic brake ON OFF (Enabled) EM2 (Forced stop 2) Zero speed ([Pr. PC17]) [Pr. PC51] 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 46 3.7.2 Base circuit shut-off delay time function The base circuit shut-off delay time function is used to prevent vertical axis from dropping at a forced stop (EM2 goes off) or alarm occurrence due to delay time of the electromagnetic brake. Use [Pr. PC16] to set the delay time between completion of EM2 (Forced stop 2) or activation of MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) due to an alarm occurrence, and shut-off of the base circuit. (1) Timing chart MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) ON OFF (Enabled) Base circuit (Energy supply to t he servo motor) 0 r/min Servo motor speed ON OFF (Enabled) EM2 (Forced stop 2) ON OFF [Pr. PC16] When EM2 (Forced stop 2) turns off or an alarm occurs during driving, the servo motor will decelerate based on the deceleration time constant. MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) will turn off, and then after the delay time set in [Pr. PC16], the servo amplifier will be base circuit shut-off status. (2) Adjustment While the servo motor is stopped, turn off EM2 (Forced stop 2), adjust the base circuit shut-off delay time in [Pr. PC16], and set the value to approximately 1.5 times of the smallest delay time in which the servo motor shaft does not freefall. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 47 3.7.3 Vertical axis freefall prevention function The vertical axis freefall prevention function avoids machine damage by pulling up the shaft slightly like the following case. When the servo motor is used for operating vertical axis, the servo motor electromagnetic brake and the base circuit shut-off delay time function avoid dropping axis at forced stop. However, the functions may not avoid dropping axis a few m due to the backlash of the servo motor electromagnetic brake. The vertical axis freefall prevention function is enabled with the following conditions. Other than "0" is set to [Pr. PC54 Vertical axis freefall prevention compensation amount]. The servo motor speed decelerates lower than the value of zero speed by turning off EM2 (Forced stop 2) or by an alarm occurrence. The base circuit shut-off delay time function is enabled. EM2 (Forced stop 2) turned off or an alarm occurred while the servo motor speed is zero speed or less. (1) Timing chart MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) ON OFF (Enabled) Base circuit (Energy supply to the servo motor) ON OFF A ctual operation of electromagnetic brake Disabled Enabled Position Travel distance ON OFF (Enabled) EM2 (Forced stop 2) Set the base circuit shut-off delay time. ([Pr. PC16]) (2) Adjustment Set the freefall prevention compensation amount in [Pr. PC54]. While the servo motor is stopped, turn off the EM2 (Forced stop 2). Adjust the base circuit shut-off delay time in [Pr. PC16] in accordance with the travel distance ([Pr. PC54). Adjust it considering the freefall prevention compensation amount by checking the servo motor speed, torque ripple, etc. 3.7.4 Residual risks of the forced stop function (EM2) (1) The forced stop function is not available for alarms that activate the dynamic brake when the alarms occur. (2) When an alarm that activates the dynamic brake during forced stop deceleration occurs, the braking distance until the servo motor stops will be longer than that of normal forced stop deceleration without the dynamic brake. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 48 3.8 Alarm occurrence timing chart CAUTION When an alarm has occurred, remove its cause, make sure that the operation signal is not being input, ensure safety, and reset the alarm before restarting operation. POINT In the torque control mode, the forced stop deceleration function is not available. To deactivate an alarm, cycle the power, push the "SET" button in the current alarm window, or cycle the RES (Reset) However, the alarm cannot be deactivated unless its cause is removed. 3.8.1 When you use the forced stop deceleration function POINT To enable the function, set "2 _ _ _ (initial value)" in [Pr. PA04]. (1) When the forced stop deceleration function is enabled Controller command is ignored. Alarm occurrence Alarm No.No alarm (Note) Model speed command 0 and equal to or less than zero speed MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) ON OFF ON (no alarm) OFF (alarm) Base circuit (Energy supply to the servo motor) ON OFF Servo amplifier display 0 r/min Servo motor speed ALM (Malfunction) Note. The model speed command is a speed command generated in the servo amplifier for forced stop deceleration of the servo motor. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 49 (2) When the forced stop deceleration function is not enabled MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) ON OFF ON (no alarm) OFF (alarm) Base circuit (Energy supply to the servo motor) ON OFF Servo amplifier display 0 r/min Servo motor speed ALM (Malfunction) No alarm Alarm No. Braking by the dynamic brake Dynamic brake + Braking by the electromagnetic brake Operation delay time of the electromagnetic brake Alarm occurrence 3.8.2 When you do not use the forced stop deceleration function POINT To disable the function, set "0 _ _ _" in [Pr. PA04]. The operation status during an alarm is the same as section 3.8.1 (2). 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 50 3.9 Interfaces 3.9.1 Internal connection diagram The following diagram is for sink I/O interface when command pulse train input is differential line driver type. 3 SON SON SON CN1 15 RES ST1 19 CR ST2 41 EM2 42 LSN 44 OPC 12 20 21 LSN LSP 43LSP DICOM DICOM RS2 RS1 PST CN1 47 23 24 48 49 DOCOM 46 DOCOM ZSP INP RD ZSP ALM RD ZSP RD SA P ST CN1 P ST 4 5 6 7 8 9 33 34 LA LAR LB LBR LZ LZR OP LG CN1 P ST MO1 MO2 LG 26 29 30 Differential line driver output (35 mA or less) Open-collector output CN1PST 2VC VLA 27 TLA TLA TC 3LG 28LG Case SD (Note 2) Approx. 6.2 k Approx. 6.2 k Analog monitor Servo amplifie r (Note 4) 24 V DC CN2 P ST 2 4 7 8 MR MRR MD MDR LG Encoder E Servo motor (Note 3) (Note 3) USB PST D+ GND D- 2 3 5 CN3 (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) ± 10 V DC ± 10 V DC (Note 4) 24 V DC RA RA M Isolated PP 10 PG 11 NP 35 NG 36 Approx. 100 Approx. 100 Approx. 1.2 k Approx. 1.2 k 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 51 Note 1. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode 2. This is for the differential line driver pulse train input. For the open-collector pulse train input, connect as follows. DOCOM 46 OPC 12 20 47 PP 10 PG 11 NP 35 NG 36 DICOM DOCOM 24 V DC 3. This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3. 4. The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they can be configured by one. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 52 3.9.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces This section provides the details of the I/O signal interfaces (refer to the I/O division in the table) given in section 3.5. Refer to this section and make connection with the external device. (1) Digital input interface DI-1 This is an input circuit whose photocoupler cathode side is input terminal. Transmit signals from sink (open-collector) type transistor output, relay switch, etc. The following is a connection diagram for sink input. Refer to section 3.9.3 for source input. Approximately 6.2 k Approximately 5 mA TR 24 V DC ± 10% 300 mA Switch For transisto r EM2 etc. Servo amplifie r DICOM V CES 1.0 V I CEO 100 A (2) Digital output interface DO-1 This is a circuit in which the collector side of the output transistor is the output terminal. When the output transistor is turned on, the current flows from the collector terminal. A lamp, relay or photocoupler can be driven. Install a diode (D) for an inductive load, or install an inrush current suppressing resistor (R) for a lamp load. (Rated current: 40 mA or less, maximum current: 50 mA or less, inrush current: 100 mA or less) A maximum of 2.6 V voltage drop occurs in the servo amplifier. The following shows a connection diagram for sink output. Refer to section 3.9.3 for source output. (Note) 24 V DC 10% 300 mA If polarity of diode is reversed, servo amplifier will malfunction. Servo amplifier ALM etc. Load DOCOM Note. If the voltage drop (maximum of 2.6 V) interferes with the relay operation, apply high voltage (maximum of 26.4 V) from external source. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 53 (3) Pulse train input interface DI-2 Give a pulse train signal in the differential line driver type or open-collector type. (a) Differential line driver type 1) Interface SD PG (NG) PP (NP) Max. input pulse frequency 4 Mpulses/s (Note 2) Servo amplifie r Am26LS31 or equivalent Approximalely 100 V OH : 2.5 V V OL : 0.5 VV (Note 1) 10 m or less Note 1. Pulse train input interface is comprised of a photocoupler. If a resistor is connected to the pulse train signal line, it may malfunction due to reduction in current. 2. When the input pulse frequency is 4 Mpulses/s, set [Pr. PA13] to "_ 0 _ _". 2) Input pulse condition 0.9 0.1 tc tLH tc tHL tF PP PG NP NG tLH = tHL < 50 ns tc > 75 ns tF > 3 µs (b) Open-collector type 1) Interface Approximately 1.2 k Servo amplifie r 24 V DC OPC PP, NP DOCOM SD Max. input pulse frequency 200 kpulses/s 2 m or less (Note) Note. Pulse train input interface is comprised of a photocoupler. If a resistor is connected to the pulse train signal line, it may malfunction due to reduction in current. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 54 2) Input pulse condition 0.9 0.1 tc tLH tc tHL tF PP NP tLH = tHL < 0.2 µs tc > 2 µs tF > 3 µs (4) Encoder output pulse DO-2 (a) Open-collector type Interface Maximum sink current: 35 mA Photocoupler Servo amplifier OP LG SD Servo amplifier OP LG SD 5 V DC to 24 V DC (b) Differential line driver type 1) Interface Maximum output current: 35 mA 150 100 Am26LS32 or equivalent Servo amplifie r LA (LB, LZ) LAR (LBR, LZR) SD LG High-speed photocoupler Servo amplifie r LAR (LBR, LZR) SD LA (LB, LZ) 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 55 2) Output pulse /2 T 400 s or more Time cycle (T) is determined by the settings of [Pr. PA15] and [Pr. PC19]. LA LAR LB LBR LZ LZR OP Servo motor CCW rotation (5) Analog input Input impedance 10 k to 12 k VC etc. LG SD Approx. 10 k Servo amplifie r (6) Analog output Output voltage: ±10 V (Note) Maximum output current: 1 mA Resolution: 10 bits or equivalent LG MO1 (MO2) Servo amplifie r Note. Output voltage range varies depending on the monitored signal. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 56 3.9.3 Source I/O interfaces In this servo amplifier, source type I/O interfaces can be used. (1) Digital input interface DI-1 This is an input circuit whose photocoupler anode side is the input terminal. Transmit signals from source (open-collector) type transistor output, relay switch, etc. Approximately 6.2 k DC 24 V ± 10 300 mA Switch For transistor EM2 etc. Servo amplifie r DICOM Approximately 5 mA V CES 1.0 V I CEO 100 A TR (2) Digital output interface DO-1 This is a circuit in which the emitter side of the output transistor is the output terminal. When the output transistor is turned on, the current flows from the output terminal to a load. A maximum of 2.6 V voltage drop occurs in the servo amplifier. (Note) 24 V DC ± 10% 300 mA Servo amplifie r ALM etc. DOCOM Load If polarity of diode is reversed, servo amplifier will malfunction. Note. If the voltage drop (maximum of 2.6 V) interferes with the relay operation, apply high voltage (maximum of 26.4 V) from external source. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 57 3.10 Servo motor with an electromagnetic brake 3.10.1 Safety precautions CAUTION Configure an electromagnetic brake circuit so that it is activated also by an external EMG stop switch. Servo motor Electromagnetic brake B U RA Contacts must be opened when ALM (Malfunction) or MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off. 24 V DC Contacts must be opened with the EMG stop switch. The electromagnetic brake is provided for holding purpose and must not be used for ordinary braking. Before operating the servo motor, be sure to confirm that the electromagnetic brake operates properly. Do not use the 24 V DC interface power supply for the electromagnetic brake. Always use the power supply designed exclusively for the electromagnetic brake. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. POINT Refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual" for specifications such as the power supply capacity and operation delay time of the electromagnetic brake. Refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual" for the selection of a surge absorber for the electromagnetic brake. Note the following when the servo motor with an electromagnetic brake is used. 1) The brake will operate when the power (24 V DC) turns off. 2) The status is base circuit shut-off during RES (Reset) on. When you use the motor in vertical axis system, use MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock). 3) Turn off SON (Servo-on) after the servo motor stopped. (1) Connection diagram B2 B1 MBR DOCOM RA1 U B Servo motor 24 V DC ALM (Malfaunction) Servo amplifie r MBR RA1 (Note 1) (Note 2) 24 V DC Note 1. Create the circuit in order to shut off by interlocking with the emergency stop switch. 2. Do not use the 24 V DC interface power supply for the electromagnetic brake. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 58 (2) Setting (a) Enable MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. (b) In [Pr. PC16 Electromagnetic brake sequence output], set the time delay (Tb) from electromagnetic brake operation to base circuit shut-off at a servo-off as in the timing chart in section 3.10.2 (1). 3.10.2 Timing chart (1) When you use the forced stop deceleration function POINT To enable the function, set "2 _ _ _ (initial value)" in [Pr. PA04]. (a) SON (Servo-on) on/off When SON (Servo-on) is turned off, the servo lock will be released after Tb [ms], and the servo motor will coast. If the electromagnetic brake is enabled during servo-lock, the brake life may be shorter. Therefore, set Tb about 1.5 times of the minimum delay time where the moving part will not drop down for a vertical axis system, etc. Approx. 95 ms Approx. 95 ms MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) (Note 1) ON OFF ON OFF 0 r/min Base circuit Servo motor speed SON (Servo-on) ON OFF Coasting Tb Operation delay time of the electromagnetic brake Release Activate Position command (Note 4) Electromagnetic brake Release delay time and external relay, etc. (Note 2) (Note 3) 0 r/min Note 1. ON: Electromagnetic brake is not activated. OFF: Electromagnetic brake has been activated. 2. Electromagnetic brake is released after the release delay time of electromagnetic brake and operation time of external circuit relay, etc. For the release delay time of electromagnetic brake, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 3. Give a position command after the electromagnetic brake is released. 4. This is in position control mode. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 59 (b) Forced stop 2 on/off POINT In the torque control mode, the forced stop deceleration function is not available. ON ON OFF (Note 2) Model speed command 0 and equal to or less than zero speed ON OFF OFF EM2 (Forced stop 2) MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) ON (no alarm) OFF (alarm) Base circuit (Energy supply to the servo motor) 0 r/min Servo motor speed A LM (Malfunction) (Note 1) Note 1. ON: Electromagnetic brake is not activated. OFF: Electromagnetic brake has been activated. 2. The model speed command is a speed command generated in the servo amplifier for forced stop deceleration of the servo motor. (c) Alarm occurrence The operation status during an alarm is the same as section 3.8. (d) Power off MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) (Note 2) ON OFF Base circuit ON OFF A larm [AL.10 Undervoltage] No alarm Alarm Approx. 10 ms Dynamic brake Dynamic brake + Electromagnetic brake Electromagnetic brake (Note 1) Operation delay time of the electromagnetic brake Servo motor speed ON OFF Power supply 0 r/min Note 1. Variable according to the operation status. 2. ON: Electromagnetic brake is not activated. OFF: Electromagnetic brake has been activated. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 60 (2) When you do not use the forced stop deceleration function POINT To disable the function, set "0 _ _ _" in [Pr. PA04]. (a) SON (Servo-on) on/off It is the same as (1) (a) in this section. (b) EM1 (Forced stop 1) on/off Dynamic brake Dynamic brake + Electromagnetic brake Electromagnetic brake MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) Operation delay time of the electromagnetic brake Approx. 210 ms Approx. 210 ms Electromagnetic brake has released. (Note) ON OFF Base circuit ON OFF Servo motor speed EM1 (Forced stop) Disabled (ON) Enabled (OFF) 0 r/min Approx. 10 ms Note. ON: Electromagnetic brake is not activated. OFF: Electromagnetic brake has been activated. (c) Alarm occurrence The operation status during an alarm is the same as section 3.8. (d) Power off It is the same as (1) (d) of this section. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 61 3.11 Grounding WARNING Ground the servo amplifier and servo motor securely. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. The servo amplifier switches the power transistor on-off to supply power to the servo motor. Depending on the wiring and ground cable routing, the servo amplifier may be affected by the switching noise (due to di/dt and dv/dt) of the transistor. To prevent such a fault, refer to the following diagram and always ground. To conform to the EMC Directive, refer to the EMC Installation Guidelines (IB(NA)67310). Ensure to connect the wire to the PE terminal of the servo amplifier. Do not connect the wire directly to the grounding of the cabinet. Line filter (Note) Power supply V U Cabinet Servo motor M U V W W Encoder CN2 Servo amplifier L1 L2 L3 CN1 Protective earth (PE) Outer box MC MCCB Programmable controller Note. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3. 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 62 MEMO 4. STARTUP 4 - 1 4. STARTUP WARNING Do not operate the switches with wet hands. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock. CAUTION Before starting operation, check the parameters. Improper settings may cause some machines to operate unexpectedly. The servo amplifier heat sink, regenerative resistor, servo motor, etc. may be hot while power is on or for some time after power-off. Take safety measures, e.g. provide covers, to avoid accidentally touching the parts (cables, etc.) by hand. During operation, never touch the rotor of the servo motor. Otherwise, it may cause injury. 4.1 Switching power on for the first time When switching power on for the first time, follow this section to make a startup. 4.1.1 Startup procedure Wiring check Parameter setting Test operation of the servo motor alone in test operation mode Test operation of the servo motor alone by commands Test operation with the servo motor and machine connected Gain adjustment Actual operation Stop Surrounding environment check Check whether the servo amplifier and servo motor are wired correctly using visual inspection, DO forced output function (section 4.5.8), etc. (Refer to section 4.1.2.) Check the surrounding environment of the servo amplifier and servo motor. (Refer to section 4.1.3.) Set the parameters as necessary, such as the used operation mode and regenerative option selection. (Refer to chapter 5, and sections 4.2.4, 4.3.4, and 4.4.4.) For the test operation, with the servo motor disconnected from the machine and operated at the speed as low as possible, check whether the servo motor rotates correctly. (Refer to sections 4.2.3, 4.3.3, and 4.4.3.) For the test operation with the servo motor disconnected from the machine and operated at the speed as low as possible, give commands to the servo amplifier and check whether the servo motor rotates correctly. After connecting the servo motor with the machine, check machine motions with sending operation commands from the controller. Make gain adjustment to optimize the machine motions. (Refer to chapter 6.) Stop giving commands and stop operation. Other conditions that stop the servo motor are mentioned in sections 4.2.2, 4.3.2, and 4.4.2. 4. STARTUP 4 - 2 4.1.2 Wiring check (1) Power supply system wiring Before switching on the power supply, check the following items. (a) Power supply system wiring The power supplied to the power input terminals (L1, L2, and L3) of the servo amplifier should satisfy the defined specifications. (Refer to section 1.3.) (b) Connection of servo amplifier and servo motor 1) The servo amplifier power output (U, V, and W) should match in phase with the servo motor power input terminals (U, V, and W). Servo amplifie r Servo moto r M U V W U V W 2) The power supplied to the servo amplifier should not be connected to the power outputs (U, V, and W). Doing so will fail the connected servo amplifier and servo motor. Servo amplifier Servo motor M U V W U V W L1 L2 L3 3) The grounding terminal of the servo motor is connected to the PE terminal of the servo amplifier. Servo amplifie r Servo moto r M 4) The CN2 connector of the servo amplifier should be connected to the encoder of the servo motor securely using the encoder cable. (c) When you use an option and peripheral equipment 1) When you use a regenerative option for 1 kW or less servo amplifiers The built-in regenerative resistor and wirings should be removed from the servo amplifier. The lead wire of built-in regenerative resistor connected to P+ terminal and C terminal should not be connected. The regenerative option should be connected to P+ terminal and C terminal. A twisted cable should be used. (Refer to section 11.2.4.) 2) When you use a regenerative option for 2 kW or more servo amplifiers The lead wire between P+ terminal and D terminal should not be connected. The regenerative option should be connected to P+ terminal and C terminal. A twisted cable should be used. (Refer to section 11.2.4.) 4. STARTUP 4 - 3 (2) I/O signal wiring (a) The I/O signals should be connected correctly. Use DO forced output to forcibly turn on/off the pins of the CN1 connector. This function can be used to perform a wiring check. Switch off SON (Servo-on) to enable the function. Refer to section 3.2 for details of I/O signal connection. (b) A voltage exceeding 24 V DC is not applied to the pins of the CN1 connector. (c) Between SD and DOCOM of the CN1 connector should not be shorted. Servo amplifie r DOCOM SD CN1 4.1.3 Surrounding environment (1) Cable routing (a) The wiring cables should not be stressed. (b) The encoder cable should not be used in excess of its bending life. (Refer to section 10.4.) (c) The connector of the servo motor should not be stressed. (2) Environment Signal cables and power cables are not shorted by wire offcuts, metallic dust or the like. 4. STARTUP 4 - 4 4.2 Startup in position control mode Make a startup in accordance with section 4.1. This section provides descriptions specific to the position control mode. 4.2.1 Power on and off procedures (1) Power-on Switch power on in the following procedure. Always follow this procedure at power-on. 1) Switch off SON (Servo-on). 2) Make sure that a command pulse train is not input. 3) Turn on the power. When main circuit power/control circuit power is switched on, the display shows "C (Cumulative feedback pulses)", and in 2 s later, shows data. (2) Power-off 1) Make sure that a command pulse train is not input. 2) Switch off SON (Servo-on). 3) Shut off the power. 4.2.2 Stop If any of the following situations occurs, the servo amplifier suspends the running of the servo motor and brings it to a stop. Refer to section 3.10 for the servo motor with an electromagnetic brake. Operation/command Stopping condition Switch off SON (Servo-on). The base circuit is shut off and the servo motor coasts. Alarm occurrence The servo motor decelerates to a stop with the command. With some alarms, however, the dynamic brake operates to bring the servo motor to a stop. (Refer to chapter 8.) EM2 (Forced stop 2) off The servo motor decelerates to a stop with the command. [AL. E6 Servo forced stop warning] occurs. EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. Refer to section 3.5 for EM1. LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) off, LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) off It will bring the motor to a sudden stop and make it servo-locked. It can be run in the opposite direction. 4. STARTUP 4 - 5 4.2.3 Test operation Before starting actual operation, perform test operation to make sure that the machine operates normally. Refer to section 4.2.1 for how to power on and off the servo amplifier. Test operation of the servo motor alone in JOG operation of test operation mode Test operation of the servo motor alone by commands Test operation with the servo motor and machine connected In this step, confirm that the servo amplifier and servo motor operate normally. With the servo motor disconnected from the machine, use the test operation mode and check whether the servo motor correctly rotates at the slowest speed. Refer to section 4.5.9 for the test operation mode. In this step, confirm that the servo motor correctly rotates at the slowest speed under the commands from the controller. Make sure that the servo motor rotates in the following procedure. 1) Switch on EM2 (Forced stop 2) and SON (Servo-on). When the servo amplifier is put in a servo-on status, RD (Ready) switches on. 2) Switch on LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end). 3) When a pulse train is input from the controller, the servo motor starts rotating. Give a low speed command at first and check the rotation direction, etc. of the servo motor. If the machine does not operate in the intended direction, check the input signal. In this step, connect the servo motor with the machine and confirm that the machine operates normally under the commands from the controller. Make sure that the servo motor rotates in the following procedure. 1) Switch on EM2 (Forced stop 2) and SON (Servo-on). When the servo amplifier is put in a servo-on status, RD (Ready) switches on. 2) Switch on LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end). 3) When a pulse train is input from the controller, the servo motor starts rotating. Give a low speed command at first and check the operation direction, etc. of the machine. If the machine does not operate in the intended direction, check the input signal. In the status display, check for any problems of the servo motor speed, command pulse frequency, load ratio, etc. 4) Then, check automatic operation with the program of the controller. 4. STARTUP 4 - 6 4.2.4 Parameter setting POINT The following encoder cables are of four-wire type. When using any of these encoder cables, set [Pr. PC22] to "1 _ _ _" to select the four-wire type. Incorrect setting will result in [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1]. MR-EKCBL30M-L MR-EKCBL30M-H MR-EKCBL40M-H MR-EKCBL50M-H In the position control mode, the servo amplifier can be used by merely changing the basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA _ _ ]) mainly. As necessary, set other parameters. 4.2.5 Actual operation Start actual operation after confirmation of normal operation by test operation and completion of the corresponding parameter settings. Perform a home position return as necessary. 4. STARTUP 4 - 7 4.2.6 Trouble at start-up CAUTION Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so will make the operation unstable. POINT Using the optional MR Configurator2, you can refer to reason for rotation failure, etc. The following faults may occur at start-up. If any of such faults occurs, take the corresponding action. (1) Troubleshooting No. Start-up sequence Fault Investigation Possible cause Reference Not improved even if CN1 and CN2 connectors are disconnected. 1. Power supply voltage fault 2. The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Improved when CN1 connector is disconnected. Power supply of CN1 cabling is shorted. 1 Power on LED is not lit. LED flickers. Improved when CN2 connector is disconnected. 1. Power supply of encoder cabling is shorted. 2. Encoder is malfunctioning. Alarm occurs. Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause. Chapter 8 2 Alarm occurs. Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause. Chapter 8 Switch on SON (Servo-on). Servo motor shaft is not servo-locked. (Servo motor shaft is free.) 1. Check the display to see if the servo amplifier is ready to operate. 2. Check the external I/O signal indication (section 4.5.7) to see if SON (Servo-on) is on. 1. SON (Servo-on) is not input. (wiring mistake) 2. 24 V DC power is not supplied to DICOM. Section 4.5.7 1. Wiring mistake (a) For open collector pulse train input, 24 V DC power is not supplied to OPC. (b) LSP and LSN are not on. 2. Pulse is not input from the controller. Section 4.5.3 Servo motor does not rotate. Mistake in setting of [Pr. PA13]. 3 Input command pulse (test operation). Servo motor run in reverse direction. Check the cumulative command pulse on the status display (section 4.5.3). 1. Mistake in wiring to controller. 2. Mistake in setting of [Pr. PA14]. Chapter 5 Rotation ripples (speed fluctuations) are large at low speed. Make gain adjustment in the following procedure. 1. Increase the auto tuning response level. 2. Repeat acceleration and deceleration several times to complete auto tuning. Gain adjustment fault Chapter 6 4 Gain adjustment Large load inertia moment causes the servo motor shaft to oscillate side to side. If the servo motor may be driven with safety, repeat acceleration and deceleration several times to complete auto tuning. Gain adjustment fault Chapter 6 5 Cyclic operation Position shift occurs Confirm the cumulative command pulses, cumulative feedback pulses and actual servo motor position. Pulse counting error, etc. due to noise. (2) of this section 4. STARTUP 4 - 8 (2) How to find the cause of position shift Encoder Q P C M L (b) Cumulative command pulses (c) Cumulative feedback pulses (d) Machine stop position M Cause B (a) Output pulse counter Cause A SON (Servo-on) input LSP/LSN (Stroke end) input Servo amplifierControlle r Servo motor Machine Electronic gear [Pr.PA05], [Pr.PA06], [Pr.PA07], [Pr.PA21] Cause C When a position shift occurs, check (a) output pulse counter Q, (b) cumulative command pulse P, (c) cumulative feedback pulse C, and (d) machine stop position M in the above diagram. Also, Causes A, B, and C indicate the causes of position mismatch. For example, Cause A indicates that noise entered the wiring between the controller and servo amplifier, causing command input pulses to be miscounted. In a normal status without position shift, there are the following relationships. 1) Q = P (Output counter = Cumulative command pulses) 2) When [Pr. PA21] is "0 _ _ _" P • CMX [Pr. PA06] CDV [Pr. PA07] = C (Cumulative command pulses × Electronic gear = Cumulative feedback pulses) 3) When [Pr. PA21] is "1 _ _ _" P • 131072 FBP [Pr. PA05] = C 4) C • = M (Cumulative feedback pulses × Travel distance per pulse = Machine position) Check for a position mismatch in the following sequence. 1) When Q P Noise entered the pulse train signal wiring between the controller and servo amplifier, causing command input pulses to be miscounted. (Cause A) Make the following check or take the following measures. Check how the shielding is done. Change the open collector type to the differential line driver type. Run wiring away from the power circuit. Install a data line filter. (Refer to section 11.9 (2) (a).) Change the [Pr. PA13 Command pulse input form] setting. 4. STARTUP 4 - 9 2) When P • CMX CDV C During operation, SON (Servo-on), LSP (Forward rotation stroke end), or LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) was switched off; or CR (Clear) or RES (Reset) was switched on. (Cause C) 3) When C • M Mechanical slip occurred between the servo motor and machine. (Cause B) 4.3 Startup in speed control mode Make a startup in accordance with section 4.1. This section provides the methods specific to the speed control mode. 4.3.1 Power on and off procedures (1) Power-on Switch power on in the following procedure. Always follow this procedure at power-on. 1) Switch off SON (Servo-on). 2) Make sure that ST1 (Forward rotation start) and ST2 (Reverse rotation start) are off. 3) Turn on the power. When main circuit power/control circuit power is switched on, the display shows "r (Servo motor speed)", and in 2 s later, shows data. (2) Power-off 1) Switch off ST1 (Forward rotation start) and ST2 (Reverse rotation start). 2) Switch off SON (Servo-on). 3) Shut off the power. 4.3.2 Stop If any of the following situations occurs, the servo amplifier suspends the running of the servo motor and brings it to a stop. Refer to section 3.10 for the servo motor with an electromagnetic brake. Operation/command Stopping condition Switch off SON (Servo-on). The base circuit is shut off and the servo motor coasts. Alarm occurrence The servo motor decelerates to a stop with the command. With some alarms, however, the dynamic brake operates to bring the servo motor to a stop. (Refer to chapter 8.) EM2 (Forced stop 2) off The servo motor decelerates to a stop with the command. [AL. E6 Servo forced stop warning] occurs. EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. Refer to section 3.5 for EM1. LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) off, LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) off It will bring the motor to a sudden stop and make it servo-locked. It can be run in the opposite direction. Simultaneous on or off of ST1 (Forward rotation start) and ST2 (Reverse rotation start) The servo motor is decelerated to a stop. 4. STARTUP 4 - 10 4.3.3 Test operation Before starting actual operation, perform test operation to make sure that the machine operates normally. Refer to section 4.3.1 for how to power on and off the servo amplifier. Test operation of the servo motor alone in JOG operation of test operation mode Test operation of the servo motor alone by commands Test operation with the servo motor and machine connected In this step, confirm that the servo amplifier and servo motor operate normally. With the servo motor disconnected from the machine, use the test operation mode and check whether the servo motor correctly rotates at the slowest speed. Refer to section 4.5.9 for the test operation mode. In this step, confirm that the servo motor correctly rotates at the slowest speed under the commands from the controller. Make sure that the servo motor rotates in the following procedure. 1) Switch on EM2 (Forced stop 2) and SON (Servo-on). When the servo amplifier is put in a servo-on status, RD (Ready) switches on. 2) Switch on LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end). 3) When VC (Analog speed command) is input from the controller and ST1 (Forward rotation start) or ST2 (Reverse rotation start) is switched on, the servo motor starts rotating. Give a low speed command at first and check the rotation direction, etc. of the servo motor. If the machine does not operate in the intended direction, check the input signal. In this step, connect the servo motor with the machine and confirm that the machine operates normally under the commands from the controller. Make sure that the servo motor rotates in the following procedure. 1) Switch on EM2 (Forced stop 2) and SON (Servo-on). When the servo amplifier is put in a servo-on status, RD (Ready) switches on. 2) Switch on LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end). 3) When VC (Analog speed command) is input from the controller and ST1 (Forward rotation start) or ST2 (Reverse rotation start) is switched on, the servo motor starts rotating. Give a low speed command at first and check the operation direction, etc. of the machine. If the machine does not operate in the intended direction, check the input signal. In the status display, check for any problems of the servo motor speed, load ratio, etc. 4) Then, check automatic operation with the program of the controller. 4. STARTUP 4 - 11 4.3.4 Parameter setting POINT The following encoder cables are of four-wire type. When using any of these encoder cables, set [Pr. PC22] to "1 _ _ _" to select the four-wire type. Incorrect setting will result in [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1]. MR-EKCBL30M-L MR-EKCBL30M-H MR-EKCBL40M-H MR-EKCBL50M-H When using this servo in the speed control mode, change [Pr. PA01] setting to select the speed control mode. In the speed control mode, the servo can be used by merely changing the basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA _ _ ]) and extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC _ _ ]) mainly. As necessary, set other parameters. 4. STARTUP 4 - 12 4.3.5 Actual operation Start actual operation after confirmation of normal operation by test operation and completion of the corresponding parameter settings. 4.3.6 Trouble at start-up CAUTION Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so will make the operation unstable. POINT Using the optional MR Configurator2, you can refer to reason for rotation failure, etc. The following faults may occur at start-up. If any of such faults occurs, take the corresponding action. No. Start-up sequence Fault Investigation Possible cause Reference Not improved even if CN1 and CN2 connectors are disconnected. 1. Power supply voltage fault 2. The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Improved when CN1 connector is disconnected. Power supply of CN1 cabling is shorted. 1 Power on LED is not lit. LED flickers. Improved when CN2 connector is disconnected. 1. Power supply of encoder cabling is shorted. 2. Encoder is malfunctioning. Alarm occurs. Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause. Chapter 8 2 Alarm occurs. Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause. Chapter 8 Switch on SON (Servo-on). Servo motor shaft is not servo-locked. (Servo motor shaft is free.) 1. Check the display to see if the servo amplifier is ready to operate. 2. Check the external I/O signal indication (section 4.5.7) to see if SON (Servo-on) is on. 1. SON (Servo-on) is not input. (wiring mistake) 2. 24 V DC power is not supplied to DICOM. Section 4.5.7 Call the status display (section 4.5.3) and check the input voltage of VC (Analog speed command). Analog speed command is 0 V. Section 4.5.3 Call the external I/O signal display (section 4.5.7) and check the on/off status of the input signal. LSP, LSN, ST1, and ST2 are off. Section 4.5.7 Check the internal speed commands 1 to 7 ([Pr. PC05] to [Pr. PC11]). Set value is 0. Section 5.2.3 Check the forward rotation torque limit ([Pr. PA11]) and the reverse rotation torque limit ([Pr. PA12]). Torque limit level is too low as compared to the load torque. Section 5.2.1 3 Switch on ST1 (Forward rotation start) or ST2 (Reverse rotation start). Servo motor does not rotate. When TLA (Analog torque limit) is usable, check the input voltage on the status display. Torque limit level is too low as compared to the load torque. Section 4.5.3 4. STARTUP 4 - 13 No. Start-up sequence Fault Investigation Possible cause Reference Rotation ripples (speed fluctuations) are large at low speed. Make gain adjustment in the following procedure. 1. Increase the auto tuning response level. 2. Repeat acceleration and deceleration several times to complete auto tuning. Gain adjustment fault Chapter 6 4 Gain adjustment Large load inertia moment causes the servo motor shaft to oscillate side to side. If the servo motor may be driven with safety, repeat acceleration and deceleration several times to complete auto tuning. Gain adjustment fault Chapter 6 4.4 Startup in torque control mode Make a startup in accordance with section 4.1. This section provides the methods specific to the torque control mode. 4.4.1 Power on and off procedures (1) Power-on Switch power on in the following procedure. Always follow this procedure at power-on. 1) Switch off SON (Servo-on). 2) Make sure that RS1 (Forward rotation selection) and RS2 (Reverse rotation selection) are off. 3) Turn on the power. Data is displayed in 2 s after "U" (Analog torque command) is displayed. (2) Power-off 1) Switch off RS1 (Forward rotation selection) or RS2 (Reverse rotation selection). 2) Switch off SON (Servo-on). 3) Shut off the power. 4.4.2 Stop If any of the following situations occurs, the servo amplifier suspends the running of the servo motor and brings it to a stop. Refer to section 3.10 for the servo motor with an electromagnetic brake. Operation/command Stopping condition Switch off SON (Servo-on). The base circuit is shut off and the servo motor coasts. Alarm occurrence The servo motor decelerates to a stop with the command. With some alarms, however, the dynamic brake operates to bring the servo motor to a stop. (Refer to chapter 8.) EM2 (Forced stop 2) off This stops the servo motor with the dynamic brake. [AL. E6 Servo forced stop warning] occurs. EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. Refer to section 3.5 for EM1. Simultaneous on or off of RS1 (Forward rotation selection) and RS2 (Reverse rotation selection) The servo motor coasts. 4. STARTUP 4 - 14 4.4.3 Test operation Before starting actual operation, perform test operation to make sure that the machine operates normally. Refer to section 4.4.1 for how to power on and off the servo amplifier. Test operation of the servo motor alone in JOG operation of test operation mode Test operation of the servo motor alone by commands Test operation with the servo motor and machine connected In this step, confirm that the servo amplifier and servo motor operate normally. With the servo motor disconnected from the machine, use the test operation mode and check whether the servo motor correctly rotates at the slowest speed. Refer to section 4.5.9 for the test operation mode. In this step, confirm that the servo motor correctly rotates at the slowest speed under the commands from the controller. Make sure that the servo motor rotates in the following procedure. 1) Switch on SON (Servo-on). When the servo amplifier is put in a servo-on status, RD (Ready) switches on. 2) When TC (Analog speed command) is input from the controller and RS1 (Forward rotation start) or RS2 (Reverse rotation start) is switched on, the servo motor starts rotating. Give a low torque command at first and check the rotation direction, etc. of the servo motor. If the machine does not operate in the intended direction, check the input signal. In this step, connect the servo motor with the machine and confirm that the machine operates normally under the commands from the controller. Make sure that the servo motor rotates in the following procedure. 1) Switch on SON (Servo-on). When the servo amplifier is put in a servo-on status, RD (Ready) switches on. 2) When TC (Analog speed command) is input from the controller and RS1 (Forward rotation start) or RS2 (Reverse rotation start) is switched on, the servo motor starts rotating. Give a low torque command at first and check the operation direction, etc. of the machine. If the machine does not operate in the intended direction, check the input signal. In the status display, check for any problems of the servo motor speed, load ratio, etc. 3) Then, check automatic operation with the program of the controller. 4. STARTUP 4 - 15 4.4.4 Parameter setting POINT The following encoder cables are of four-wire type. When using any of these encoder cables, set [Pr. PC22] to "1 _ _ _" to select the four-wire type. Incorrect setting will result in [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1]. MR-EKCBL30M-L MR-EKCBL30M-H MR-EKCBL40M-H MR-EKCBL50M-H When using this servo in the torque control mode, change [Pr. PA01] setting to select the torque control mode. In the torque control mode, the servo can be used by merely changing the basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA _ _ ]) and extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC _ _ ]) mainly. As necessary, set other parameters. 4.4.5 Actual operation Start actual operation after confirmation of normal operation by test operation and completion of the corresponding parameter settings. 4. STARTUP 4 - 16 4.4.6 Trouble at start-up CAUTION Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so will make the motion unstable. POINT Using the optional MR Configurator2, you can refer to reason for rotation failure, etc. The following faults may occur at start-up. If any of such faults occurs, take the corresponding action. No. Start-up sequence Fault Investigation Possible cause Reference Not improved even if CN1 and CN2 connectors are disconnected. 1. Power supply voltage fault 2. The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Improved when CN1 connector is disconnected. Power supply of CN1 cabling is shorted. 1 Power on LED is not lit. LED flickers. Improved when CN2 connector is disconnected. 1. Power supply of encoder cabling is shorted. 2. Encoder is malfunctioning. Alarm occurs. Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause. Chapter 8 2 Alarm occurs. Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause. Chapter 8 Switch on SON (Servo-on). Servo motor shaft is free. Call the external I/O signal display (section 4.5.7) and check the on/off status of the input signal. 1. SON (Servo-on) is not input. (wiring mistake) 2. 24 V DC power is not supplied to DICOM. Section 4.5.7 Call the status display (section 4.5.3) and check the input voltage of TC (Analog torque command). Analog torque command is 0 V. Section 4.5.3 Call the external I/O signal display (section 4.5.7) and check the on/off status of the input signal. RS1 and RS2 are off. Section 4.5.7 Check the internal speed limit 1 to 7 ([Pr. PC05] to [Pr. PC11]). Set value is 0. Section 5.2.3 Check the analog torque command maximum output ([Pr. PC13]) value. Torque command level is too low as compared to the load torque. Section 5.2.3 3 Switch on RS1 (Forward rotation start) or RS2 (Reverse rotation start). Servo motor does not rotate. Check the forward rotation torque limit ([Pr. PA11]) and the reverse rotation torque limit ([Pr. PA12]). Set value is 0. Section 5.2.1 4. STARTUP 4 - 17 4.5 Display and operation sections 4.5.1 Summary The MR-JE-A servo amplifier has the display section (5-digit, 7-segment LED) and operation section (4 pushbuttons) for servo amplifier status display, alarm display, parameter setting, etc. Push the "MODE" and "SET" buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the one-touch tuning mode. The operation section and display data are described below. Display mode change Low/High switching Decimal LED Displays the decimal points, alarm presence/absence, etc. Lit to indicate the decimal point. Decimal Lit to indicate a negative when "-" (negative) cannot be displayed. Flickers to indicate alarm occurrence. Flickers to indicate the test operation mode. 5-digit, 7-segment LED Displays data. MODE SET AUTO Display/data scrolling (UP) Display/data scrolling (DOWN) Display/data determination Data clear To the one-touch tuning mode 4. STARTUP 4 - 18 4.5.2 Display flowchart Press the "MODE" button once to shift to the next display mode. Refer to section 4.5.3 and later for the description of the corresponding display mode. To refer to and set the gain/filter parameters, extension setting parameters and I/O setting parameters, enable them with [Pr. PA19 Parameter writing inhibit]. Display mode transition Initial screen Function Reference Servo status display. appears at power-on. (Note) Section 4.5.3 One-touch tuning Select this when performing the one-touch tuning. Section 6.2 Sequence display, external signal display, output signal (DO) forced output, test operation, software version display, VC automatic offset, servo motor series ID display, servo motor type ID display, servo motor encoder ID display, drive recorder enabled/disabled display. Section 4.5.4 Current alarm display, alarm history display, parameter error number display. Section 4.5.5 Display and setting of basic setting parameters. Section 4.5.6 Display and setting of gain/filter parameters. Display and setting of extension setting parameters. Display and setting of I/O setting parameters. Display and setting of extension setting 2 parameters. Status display Diagnosis Alarms Basic setting parameters Gain/filter parameters Extension setting parameters Extension setting 2 parameters Extension setting 3 parameters I/O setting parameters Button MODE One-touch tuning Display and setting of extension setting 3 parameters. Note. When the axis name is set to the servo amplifier using MR Configurator2, the axis name is displayed and the servo status is then displayed. 4. STARTUP 4 - 19 4.5.3 Status display mode The servo status during operation is shown on the 5-digit, 7-segment LED display. Press the "UP" or "DOWN" button to change display data as desired. When the required data is selected, the corresponding symbol is displayed. Press the "SET" button to display that data. At only power-on, however, data appears after the symbol of the status display selected in [Pr. PC36] has been shown for 2 s. (1) Display transition After selecting the status display mode with the "MODE" button, pressing the "UP" or "DOWN" button changes the display as shown below. Regenerative load ratio Cumulative feedback pulses Effective load ratio Peak load ratio Instantaneous torque Within one-revolution position (1 pulse unit) Servo motor speed Within one-revolution position (1000 pulse unit) Droop pulses Cumulative command pulses Load to motor inertia ratio ABS counter (Note) Command pulse frequency Bus voltage Encoder inside temperature Settling time Oscillation detection frequency Number of tough drives Unit power consumption 1 (increment of 1 W) Unit total power consumption 1 (increment of 1 Wh) Unit power consumption 2 (increment of 1 kW) Unit total power consumption 2 (increment of 100 kWh) Unit total power consumption 2 (increment of 100 kWh) Cumulative feedback pulses Analog torque limit voltage Analog torque command voltage Analog speed command voltage Analog speed limit voltage DOWN UP Note. Travel distance from power on is displayed by counter value. 4. STARTUP 4 - 20 (2) Display examples The following table shows the display examples. Displayed data Item Status Servo amplifier display Forward rotation at 2500 r/min Servo motor speed Reverse rotation at 3000 r/min Reverse rotation is indicated by "- ". Load to motor inertia ratio 7.00 times 11252 pulses Cumulative feedback pulses -12566 pulses Lit Negative value is indicated by the lit decimal points in the upper four digits. 4. STARTUP 4 - 21 (3) Status display list The following table lists the servo statuses that may be shown. Refer to appendix 4 for the measurement point. Status display Symbol Unit Description Cumulative feedback pulses C pulse Feedback pulses from the servo motor encoder are counted and displayed. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. However, the counter shows only the lower five digits of the actual value since the servo amplifier display is five digits. Press the "SET" button to reset the display value to zero. The value of minus is indicated by the lit decimal points in the upper four digits. Servo motor speed r r/min The servo motor speed is displayed. It is displayed rounding off 0.1 r/min unit. Droop pulses E pulse The number of droop pulses in the deviation counter are displayed. The decimal points in the upper four digits are lit for reverse rotation pulses. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. However, the counter shows only the lower five digits of the actual value since the servo amplifier display is five digits. The number of pulses displayed is in the encoder pulse unit. Cumulative command pulses P pulse Position command input pulses are counted and displayed. As the value displayed is not yet multiplied by the electronic gear (CMX/CDV), it may not match the indication of the cumulative feedback pulses. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. However, the counter shows only the lower five digits of the actual value since the servo amplifier display is five digits. Press the "SET" button to reset the display value to zero. When the servo motor is rotating in the reverse direction, the decimal points in the upper four digits are lit. Command pulse frequency n kpulse/s The frequency of position command input pulses is counted and displayed. The value displayed is not multiplied by the electronic gear (CMX/CDV). 1) Torque control mode Input voltage of VLA (Analog speed limit) voltage is displayed. Analog speed command voltage Analog speed limit voltage F V 2) Speed control mode Input voltage of VC (Analog speed command) voltage is displayed 1) Position control mode and speed control mode Voltage of TLA (Analog torque limit) voltage is displayed. Analog torque command voltage Analog torque limit voltage U V 2) Torque control mode Voltage of TC (Analog torque command) voltage is displayed. Regenerative load ratio L % The ratio of regenerative power to permissible regenerative power is displayed in %. Effective load ratio J % The continuous effective load current is displayed. The effective value in the past 15 s is displayed relative to the rated current of 100 %. Peak load ratio b % The maximum occurrence torque is displayed. The highest value in the past 15 s is displayed relative to the rated current of 100 %. Instantaneous torque T % The instantaneous occurrence torque is displayed. The value of torque being occurred is displayed in real time considering a rated torque as 100%. Within one-revolution position (1 pulse unit) Cy1 pulse Position within one revolution is displayed in encoder pulses. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. However, the counter shows only the lower five digits of the actual value since the servo amplifier display is five digits. When the servo motor rotates in the CCW direction, the value is added. Within one-revolution position (1000 pulses unit) Cy2 1000 pulses The within one-revolution position is displayed in 1000 pulse increments of the encoder. When the servo motor rotates in the CCW direction, the value is added. ABS counter LS rev Travel distance from power on is displayed by counter value. Load to motor inertia ratio dC Multiplier The estimated ratio of the load inertia moment to the servo motor shaft inertia moment is displayed. 4. STARTUP 4 - 22 Status display Symbol Unit Description Bus voltage Pn V The voltage of main circuit converter (between P+ and N-) is displayed. Encoder inside temperature ETh °C Inside temperature of encoder detected by the encoder is displayed. Settling time ST ms Settling time is displayed. When it exceeds 1000 ms, "1000" will be displayed. Oscillation detection frequency oF Hz Frequency at the time of oscillation detection is displayed. Number of tough drive operations Td times The number of tough drive functions activated is displayed. Unit power consumption 1 (increment of 1 W) PC1 W Unit power consumption is displayed by increment of 1 W. Positive value indicate power running, and negative value indicate regeneration. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. However, the counter shows only the lower five digits of the actual value since the servo amplifier display is five digits. Unit power consumption 2 (increment of 1 kW) PC2 kW Unit power consumption is displayed by increment of 1 kW. Positive value indicate power running, and negative value indicate regeneration. Unit total power consumption 1 (increment of 1 Wh) TPC1 Wh Unit total power consumption is displayed by increment of 1 Wh. Positive value is cumulated during power running and negative value during regeneration. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. However, the counter shows only the lower five digits of the actual value since the servo amplifier display is five digits. Unit total power consumption 2 (increment of 100 kWh) TPC2 100 kWh Unit total power consumption is displayed by increment of 100 kWh. Positive value is cumulated during power running and negative value during regeneration. (4) Changing the status display screen The status display item of the servo amplifier display shown at power-on can be changed by changing [Pr. PC36] settings. The item displayed in the initial status changes with the control mode as follows. Control mode Status display Position Cumulative feedback pulses Position/speed Cumulative feedback pulses/servo motor speed Speed Servo motor speed Speed/torque Servo motor speed/analog torque command voltage Torque Analog torque command voltage Torque/position Analog torque command voltage/cumulative feedback pulses 4. STARTUP 4 - 23 4.5.4 Diagnostic mode Name Display Description Not ready Indicates that the servo amplifier is being initialized or an alarm has occurred. Sequence Ready Indicates that the servo was switched on after completion of initialization and the servo amplifier is ready to operate. Drive recorder enabled When an alarm occurs in the status, the drive recorder will operate and write the status of occurrence. Drive recorder enabled/disabled display Drive recorder disabled The drive recorder will not operate on the following conditions. 1. You are using the graph function of MR Configurator2. 2. You are using the machine analyzer function. 3. [Pr. PF21] is set to "-1". External I/O signal display Refer to section 4.5.7. This Indicates the on/off status of external I/O signal. The upper segments correspond to the input signals and the lower segments to the output signals. Output signal (DO) forced output This allows digital output signal to be switched on/off forcibly. For details, refer to section 4.5.8. JOG operation JOG operation can be performed when there is no command from an external controller. For details, refer to section 4.5.9 (2). Positioning operation Positioning operation can be performed when there is no command from an external controller. MR Configurator2 is required to perform positioning operation. For details, refer to section 4.5.9 (3). Motor-less operation Without connecting the servo motor, output signals or status display monitoring can be provided in response to the input device as if the servo motor is actually running. For details, refer to section 4.5.9 (4). Machine analyzer operation Merely connecting the servo amplifier allows the resonance point of the mechanical system to be measured. MR Configurator2 is required to perform machine analyzer operation. Refer to section 11.4 for details. Test operation mode For manufacturer adjustment This is for manufacturer adjustment. 4. STARTUP 4 - 24 Name Display Description Software version - Lower Indicates the version of the software. Software version - Upper Indicates the system number of the software. Automatic VC offset If offset voltages in the analog circuits inside and outside the servo amplifier cause the servo motor to rotate slowly at VC (Analog speed command) or VLA (Analog speed limit) of 0 V, this function automatically makes zero- adjustment of offset voltages. When using this function, enable the function in the following procedure. When it is enabled, [Pr. PC37] value changes to the automatically adjusted offset voltage. 1) Push "SET" once. 2) Set the number in the first digit to 1 with "UP"/"DOWN". 3) Push "SET". This function cannot be used if the input voltage of VC or VLA is - +0.4 V or less, or + 0.4 V or more. (Note) Servo motor series ID Push the "SET" button to show the series ID of the servo motor currently connected. For indication details, refer to appendix 1 of "HF-KN/HF-SN servo Motor Instruction Manual". Servo motor type ID Push the "SET" button to show the type ID of the servo motor currently connected. For indication details, refer to appendix 1 of "HF-KN/HF-SN servo Motor Instruction Manual". Servo motor encoder ID Push the "SET" button to show the encoder ID of the servo motor currently connected. For indication details, refer to appendix 1 of "HF-KN/HF-SN servo Motor Instruction Manual". For manufacturer adjustment This is for manufacturer adjustment. For manufacturer adjustment This is for manufacturer adjustment. Note. Even if Automatic VC offset is performed and 0 V is input, the servo motor may not completely stop due to an internal error. To completely stop the servo motor, switch off ST1 or ST2. 4. STARTUP 4 - 25 4.5.5 Alarm mode The current alarm, past alarm history and parameter error are displayed. The lower 2 digits on the display indicate the alarm number that has occurred or the parameter number in error. Name Display Description Indicates no occurrence of an alarm. Current alarm Indicates the occurrence of [AL. 33.1 Main circuit voltage error]. Flickers at alarm occurrence. Indicates that the last alarm is [AL. 50.1 Thermal overload error 1 during operation]. Indicates the second last alarm is [AL. 33.1 Main circuit voltage error]. Indicates the third last alarm is [AL. 10.1 Voltage drop in the power]. Indicates that there is no tenth alarm in the past. Indicates that there is no eleventh alarm in the past. Indicates that there is no twelfth alarm in the past. Alarm history Indicates that there is no sixteenth alarm in the past. This indicates no occurrence of [AL. 37 Parameter error]. Parameter error No. The data content error of [Pr. PA12 Reverse rotation torque limit]. 4. STARTUP 4 - 26 Functions at occurrence of an alarm (1) Any mode screen displays the current alarm. (2) Even during alarm occurrence, the other screen can be viewed by pressing the button in the operation area. At this time, the decimal point in the fourth digit remains flickering. (3) For any alarm, remove its cause and clear it in any of the following methods. (Refer to chapter 8 for the alarms that can be cleared.) (a) Switch power off, then on. (b) Push the "SET" button on the current alarm screen. (c) Turn on RES (Reset). (4) Use [Pr. PC18] to clear the alarm history. (5) Push "UP" or "DOWN" to move to the next history. 4.5.6 Parameter mode (1) Parameter mode transition After selecting the corresponding parameter mode with the "MODE" button, pushing the "UP" or "DOWN" button changes the display as shown below. [Pr. PB01] [Pr. PA02] [Pr. PA01] I/O setting parameters [Pr. PD01] [Pr. PD02] [Pr. PD47] [Pr. PD48] [Pr. PC01] [Pr. PC02] [Pr. PC79] Extension setting parameters [Pr. PC80] [Pr. PB02] [Pr. PB63] [Pr. PB64] To status display mode [Pr. PA31] Basic setting parameters [Pr. PA32] Extension setting 2 parameters [Pr. PE01] [Pr. PE02] [Pr. PE63] [Pr. PE64] Extension setting 3 parameters [Pr. PF01] [Pr. PF02] [Pr. PF47] [Pr. PF48] Gain/filter parameters MODE UP DOWN From an alarm mode 4. STARTUP 4 - 27 (2) Operation example (a) Parameters of 5 or less digits The following example shows the operation procedure performed after power-on to change the control mode to the speed control mode with [Pr. PA01 Operation mode]. Press "MODE" to switch to the basic setting parameter screen. The parameter number is displayed. Press "UP" or "DOWN" to change the number. The set value of the specified parameter number flickers. Press "SET" twice. Press "SET" to enter. Press "UP" twice. During flickering, the set value can be changed. Use "UP" or "DOWN". (_ _ _ 2: Speed control mode) …… …… …… To shift to the next parameter, press the "UP" or "DOWN" button. When changing the [Pr. PA01] setting, change its set value, then switch power off once and switch it on again to enable the new value. (b) Parameters of 6 or more digits The following example gives the operation procedure to change the electronic gear numerator to "123456" with [Pr. PA06 Electronic gear numerator]. The screen flickers. Press "MODE" to switch to the basic setting parameter screen. Press "UP" or "DOWN" to select [Pr. PA06]. Press "SET" once. Press "SET" once. Setting of upper 1 digit Press "UP" or "DOWN" to change the setting. Press "SET" once. Enter the setting. Press "MODE" once. Press "MODE" once. Setting of lower 4 digits …… …… …… … 4. STARTUP 4 - 28 4.5.7 External I/O signal display POINT The I/O signal settings can be changed using the I/O setting parameters [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD28]. The on/off states of the digital I/O signals connected to the servo amplifier can be confirmed. (1) Operation The display screen at power-on. Using the "MODE" button, display the diagnostic screen. Press "UP" twice. …… External I/O signal display screen (2) Display definition The 7-segment LED segments and CN1 connector pins correspond as shown below. Input signal Output signals Always lit CN1 42 CN1 41 CN1 48 CN1 19 CN1 15 CN1 23 CN1 49 CN1 24 Light on: on Light off: off CN1 33 CN1 44 CN1 43 The LED segment corresponding to the pin is lit to indicate on, and is extinguished to indicate off. The signals corresponding to the pins in the respective control modes are indicated below. 4. STARTUP 4 - 29 (a) Control modes and I/O signals (Note 2) Symbols of I/O signals in control modes Connecto r Pin No. Signal input/output (Note 1) I/O P P/S S S/T T T/P Related parameter 15 I SON SON SON SON SON SON Pr. PD03/Pr. PD04 16 17 18 19 I RES RES/ST1 ST1 ST1/RS2 RS2 RS2/RES Pr. PD11/Pr. PD12 22 23 O ZSP ZSP ZSP ZSP ZSP ZSP Pr. PD24 24 O INP INP/SA SA SA/- -/INP Pr. PD25 CN1 25 33 O OP OP OP OP OP OP 41 I CR CR/ST2 ST2 ST2/RS1 RS1 RS1/CR Pr. PD13/Pr. PD14 42 I EM2 EM2 EM2 EM2 EM2 EM2 43 I LSP LSP LSP LSP/- -/LSP Pr. PD17/Pr. PD18 44 I LSN LSN LSN LSN/- -/LSN Pr. PD19/Pr. PD20 45 48 O ALM ALM ALM ALM ALM ALM 49 O RD RD RD RD RD RD Pr. PD28 Note 1. I: input signal, O: output signal 2. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode P/S: position/speed control switching mode, S/T: speed/torque control switching mode, T/P: torque/position switching mode (b) Symbol and signal names Symbol Signal name Symbol Signal name SON Servo-on RES Reset LSP Forward rotation stroke end EM2 Forced stop 2 LSN Reverse rotation stroke end LOP Control switching CR Clear TLC Limiting torque SP1 Speed selection 1 VLC Limiting speed SP2 Speed selection 2 RD Ready PC Proportion control ZSP Zero speed detection ST1 Forward rotation start INP In-position ST2 Reverse rotation start SA Speed reached RS1 Forward rotation selection ALM Malfunction RS2 Reverse rotation selection OP Encoder Z-phase pulse (open collector) TL External torque limit selection 4. STARTUP 4 - 30 (3) Display data at initial values (a) Position control mode Light on: on Light off: off EM2 (CN1-42) Input signal Output signals OP (CN1-33) ALM (CN1-48) CR (CN1-41) RES (CN1-19) SON (CN1-15) LSN (CN1-44) LSP (CN1-43) RD (CN1-49) INP (CN1-24) ZSP (CN1-23) (b) Speed control mode Light on: on Light off: off EM2 (CN1-42) Input signal Output signals OP (CN1-33) ALM (CN1-48) ST2 (CN1-41) ST1 (CN1-19) SON (CN1-15) LSN (CN1-44) LSP (CN1-43) RD (CN1-49) SA (CN1-24) ZSP (CN1-23) (c) Torque control mode Light on: on Light off: off EM2 (CN1-42) Input signal Output signals OP (CN1-33) ALM (CN1-48) RS1 (CN1-41) RS2 (CN1-19) SON (CN1-15) RD (CN1-49) ZSP (CN1-23) 4. STARTUP 4 - 31 4.5.8 Output signal (DO) forced output POINT When the servo system is used in a vertical lift application, turning on MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) by the DO forced output after assigning it to connector CN1 will release the electromagnetic brake, causing a drop. Take drop preventive measures on the machine side. Output signals can be switched on/off forcibly independently of the servo status. This function is used for output signal wiring check, etc. This operation must be performed in the servo off state by turning off SON (Servo-on). Operation The display screen at power-on. Using the "MODE" button, display the diagnostic screen. …… …… …… …… …… Switch on/off the signal below the lit segment. Indicates on/off of output signal. Definitions of on/off are the same as those for the external I/O signals. (Light on: on, light off: off) Press "UP" three times. Press "SET" for longer than 2 s. CN1 33 CN1 48 CN1 23 CN1 24 CN1 49 Press "MODE" once. Press "UP" once. CN1-24 switches on. (Between CN1-24 and DOCOM are connected.) The lit LED moves to the upper LED of CN1-24. Press "DOWN" once. CN1-24 switches off. Press "SET" for longer than 2 s. Always lit. 4. STARTUP 4 - 32 4.5.9 Test operation mode CAUTION The test operation mode is designed for checking servo operation. Do not use it for actual operation. If the servo motor operates unexpectedly, use EM2 (Forced stop 2) to stop it. POINT MR Configurator2 is required to perform positioning operation. Test operation cannot be performed if SON (Servo-on) is not turned off. (1) Mode switching The display screen at power-on. Select JOG operation or motor-less operation in the following procedure. Using the "MODE" button, display the diagnostic screen. Press "UP" four times. Press "SET" for longer than 2 s. When this screen appears, JOG operation can be performed. Flickers in the test operation mode. …… 4. STARTUP 4 - 33 (2) JOG operation POINT When performing JOG operation, turn on EM2, LSP and LSN. LSP and LSN can be set to automatic on by setting [Pr. PD01] to " _ C _ _ ". JOG operation can be performed when there is no command from the controller. (a) Operation The servo motor rotates while holding down the "UP" or the "DOWN" button. The servo motor stops rotating by releasing the button. The operation condition can be changed using MR Configurator2. The initial operation condition and setting range for operation are listed below. Item Initial setting Setting range Speed [r/min] 200 0 to permissible instantaneous speed Acceleration/deceleration time constant [ms] 1000 0 to 50000 The following table shows how to use the buttons. Button Description "UP" Press to start CCW rotation. Release to stop. "DOWN" Press to start CW rotation. Release to stop. If the USB cable is disconnected during JOG operation using the MR Configurator2, the servo motor decelerates to a stop. (b) Status display Press the "MODE" button in the JOG operation-ready status to call the status display screen. When the JOG operation is performed using the "UP" or "DOWN" button, the servo status is displayed during the JOG operation. Every time the "MODE" button is pressed, the next status display screen appears. When one cycle of the screen display is complete, it returns to the JOG operation-ready status screen. Refer to section 4.5.3 for details of status display. Note that the status display screen cannot be changed by the "UP" or "DOWN" button during the JOG operation. (c) Termination of JOG operation To end the JOG operation, shut the power off once, or press the "MODE" button to switch to the next screen, and then hold down the "SET" button for 2 s or longer. 4. STARTUP 4 - 34 (3) Positioning operation POINT MR Configurator2 is required to perform positioning operation. Turn on EM2 (forced stop 2) when performing positioning operation. Positioning operation can be performed when there is no command from the controller. (a) Operation a) m) b) n) g) l) k)j) c) d) e) f) h) i) a) Motor speed [r/min] Enter the servo motor speed into the "Motor speed" input field. b) Acceleration/deceleration time constant [ms] Enter the acceleration/deceleration time constant into the "Accel/decel time" input field. c) Travel distance [pulse] Enter the travel distance into the "Travel distance" input field. d) LSP/LSN are automatically turned on When setting the external stroke signal to automatic on, click the check box to enable it. When it is not selected, turn on LSP and LSN externally. e) Move till Z-phase signal Travel is made until the travel distance is reached and the first Z-phase signal in the travelling direction turns on. 4. STARTUP 4 - 35 f) Travel distance unit selection Select with the option buttons whether the travel distance set in c) is in the command pulse unit or in the encoder pulse unit. When the command input pulse unit is selected, the value, which is the set travel distance multiplied by the electronic gear, will be the command value. When the encoder pulse unit is selected, the travel distance is not multiplied by the electronic gear. g) Enable repeat operation To perform repeat operation, click the check. The initial setting and setting range for the repeat operation are listed below. Item Initial setting Setting range Repeat pattern Fwd. rot. (CCW) to rev. rot. (CW) Fwd. rot. (CCW) to rev. rot. (CW) Fwd. rot. (CCW) to fwd. rot. (CCW) Rev. rot. (CW) to fwd. rot. (CCW) Rev. rot. (CW) to rev. rot. (CW) Dwell time [s] 2.0 0.1 to 50.0 Number of operations [times] 1 1 to 9999 To perform continuous operation with the repeat pattern and dwell time settings, which are set by referring to the above table, click the check box of "Make the aging function enabled". h) Forward/reverse the servo motor Click the "Forward CCW" button to rotate the servo motor in the forward rotation direction. Click the "Reverse CW" button to rotate the servo motor in the reverse rotation direction. i) Pause the servo motor Click the "Pause" button during servo motor rotation to temporarily stop the servo motor. This button is enabled during servo motor rotation. h) Stop the servo motor Click the "Stop" button during servo motor rotation to stop the servo motor. k) Forced stop Click the "Forced stop" button during servo motor rotation to make a sudden stop. This button is enabled during servo motor rotation. l) Operation status The operation status during the repeat operation, and the number of operations are displayed m) Axis No. Axis No. in operation is displayed. n) Termination of positioning operation window Click the close button to cancel the positioning operation mode and close the window. (b) Status display The status display can be monitored during positioning operation. 4. STARTUP 4 - 36 (4) Motor-less operation Without connecting the servo motor, output signals or status display can be provided in response to the input device as if the servo motor is actually running. This operation can be used to check the sequence of a controller or the like. (a) Start of motor-less operation After setting "_ _ _ 1" in [Pr. PC60], cycle the power. After that, perform external operation as in ordinary operation. (b) Termination of motor-less operation To terminate the motor-less operation, set [Pr. PC60] to "_ _ _ 0" and then turn the power off. (5) Program operation Positioning operation can be performed in two or more operation patterns combined, without using a controller. Use this operation with the forced stop reset. This operation may be used independently of whether servo-on or servo-off and whether a controller is connected or not. Exercise control on the program operation screen of MR Configurator2. For full information, refer to the MR Configurator2 Installation Guide. Operation Screen control Start Click the "Operation start" button. Stop Click the "Stop" button. Forced stop Click the "Forced Stop" button. (6) Output signal (DO) forced output Output signals can be switched on/off forcibly independently of the servo status. This function is used for output signal wiring check, etc. Exercise control on the DO forced output screen of MR Configurator2. 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 1 5. PARAMETERS CAUTION Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so will make the operation unstable. If fixed values are written in the digits of a parameter, do not change these values. Do not change parameters for manufacturer setting. Do not set a value other than the described values to each parameter. 5.1 Parameter list POINT To enable a parameter whose symbol is preceded by *, turn off the power for 1 s or more after setting and turn it on again. However, the time will be longer depending on a setting value of [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)] when "SEMI-F47 function selection (instantaneous power failure tough drive selection)" is enabled in [Pr. PA20]. The symbols in the control mode column mean as follows. P: Position control mode S: Speed control mode T: Torque control mode 5.1.1 Basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PA01 *STY Operation mode 1000h PA02 *REG Regenerative option 0000h PA03 For manufacturer setting 0000h PA04 *AOP1 Function selection A-1 2000h PA05 *FBP Number of command input pulses per revolution 10000 PA06 CMX Electronic gear numerator (command pulse multiplication numerator) 1 PA07 CDV Electronic gear denominator (command pulse multiplication denominator) 1 PA08 ATU Auto tuning mode 0001h PA09 RSP Auto tuning response 16 PA10 INP In-position range 100 [pulse] PA11 TLP Forward rotation torque limit 100.0 [%] PA12 TLN Reverse rotation torque limit 100.0 [%] PA13 *PLSS Command pulse input form 0100h PA14 *POL Rotation direction selection 0 PA15 *ENR Encoder output pulses 4000 [pulse/rev] PA16 *ENR2 Encoder output pulses 2 1 PA17 For manufacturer setting 0000h PA18 0000h PA19 *BLK Parameter writing inhibit 00AAh PA20 *TDS Tough drive setting 0000h PA21 *AOP3 Function selection A-3 0001h PA22 For manufacturer setting 0000h PA23 DRAT Drive recorder arbitrary alarm trigger setting 0000h PA24 AOP4 Function selection A-4 0000h PA25 OTHOV One-touch tuning - Overshoot permissible level 0 [%] PA26 *AOP5 Function selection A-5 0000h PA27 For manufacturer setting 0000h PA28 0000h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 2 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PA29 For manufacturer setting 0000h PA30 0000h PA31 0000h PA32 0000h 5.1.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PB01 FILT Adaptive tuning mode (adaptive filter II) 0000h PB02 VRFT Vibration suppression control tuning mode (advanced vibration suppression control II) 0000h PB03 PST Position command acceleration/deceleration time constant (position smoothing) 0 [ms] PB04 FFC Feed forward gain 0 [%] PB05 For manufacturer setting 500 PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio 7.00 [Multiplier] PB07 PG1 Model loop gain 15.0 [rad/s] PB08 PG2 Position loop gain 37.0 [rad/s] PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain 823 [rad/s] PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation 33.7 [ms] PB11 VDC Speed differential compensation 980 PB12 OVA Overshoot amount compensation 0 [%] PB13 NH1 Machine resonance suppression filter 1 4500 [Hz] PB14 NHQ1 Notch shape selection 1 0000h PB15 NH2 Machine resonance suppression filter 2 4500 [Hz] PB16 NHQ2 Notch shape selection 2 0000h PB17 NHF Shaft resonance suppression filter 0000h PB18 LPF Low-pass filter setting 3141 [rad/s] PB19 VRF11 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency 100.0 [Hz] PB20 VRF12 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency 100.0 [Hz] PB21 VRF13 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping 0.00 PB22 VRF14 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping 0.00 PB23 VFBF Low-pass filter selection 0100h PB24 *MVS Slight vibration suppression control 0000h PB25 *BOP1 Function selection B-1 0000h PB26 *CDP Gain switching function 0000h PB27 CDL Gain switching condition 10 [kpulse/s]/ [pulse]/ [r/min] PB28 CDT Gain switching time constant 1 [ms] PB29 GD2B Load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching 7.00 [Multiplier] PB30 PG2B Gain switching position loop gain 0.0 [rad/s] PB31 VG2B Gain switching speed loop gain 0 [rad/s] PB32 VICB Speed integral compensation after gain switching 0.0 [ms] PB33 VRF1B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency after gain switching 0.0 [Hz] PB34 VRF2B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency after gain switching 0.0 [Hz] PB35 VRF3B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching 0.00 PB36 VRF4B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching 0.00 PB37 For manufacturer setting 1600 PB38 0.00 PB39 0.00 PB40 0.00 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 3 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PB41 For manufacturer setting 0000h PB42 0000h PB43 0000h PB44 0.00 PB45 CNHF Command notch filter 0000h PB46 NH3 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 4500 [Hz] PB47 NHQ3 Notch shape selection 3 0000h PB48 NH4 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 4500 [Hz] PB49 NHQ4 Notch shape selection 4 0000h PB50 NH5 Machine resonance suppression filter 5 4500 [Hz] PB51 NHQ5 Notch shape selection 5 0000h PB52 VRF21 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency 100.0 [Hz] PB53 VRF22 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency 100.0 [Hz] PB54 VRF23 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping 0.00 PB55 VRF24 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping 0.00 PB56 VRF21B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency after gain switching 0.0 [Hz] PB57 VRF22B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency after gain switching 0.0 [Hz] PB58 VRF23B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching 0.00 PB59 VRF24B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching 0.00 PB60 PG1B Model loop gain after gain switching 0.0 [rad/s] PB61 For manufacturer setting 0.0 PB62 0000h PB63 0000h PB64 0000h 5.1.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PC01 STA Acceleration time constant 0 [ms] PC02 STB Deceleration time constant 0 [ms] PC03 STC S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant 0 [ms] PC04 TQC Torque command time constant 0 [ms] Internal speed command 1 PC05 SC1 Internal speed limit 1 100 [r/min] Internal speed command 2 PC06 SC2 Internal speed limit 2 500 [r/min] Internal speed command 3 PC07 SC3 Internal speed limit 3 1000 [r/min] Internal speed command 4 PC08 SC4 Internal speed limit 4 200 [r/min] Internal speed command 5 PC09 SC5 Internal speed limit 5 300 [r/min] Internal speed command 6 PC10 SC6 Internal speed limit 6 500 [r/min] Internal speed command 7 PC11 SC7 Internal speed limit 7 800 [r/min] Analog speed command - Maximum speed PC12 VCM Analog speed limit - Maximum speed 0 [r/min] PC13 TLC Analog torque command maximum output 100.0 [%] PC14 MOD1 Analog monitor 1 output 0000h PC15 MOD2 Analog monitor 2 output 0001h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 4 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PC16 MBR Electromagnetic brake sequence output 0 [ms] PC17 ZSP Zero speed 50 [r/min] PC18 *BPS Alarm history clear 0000h PC19 *ENRS Encoder output pulse selection 0000h PC20 For manufacturer setting 0 PC21 0000h PC22 *COP1 Function selection C-1 0020h PC23 *COP2 Function selection C-2 0000h PC24 *COP3 Function selection C-3 0000h PC25 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC26 *COP5 Function selection C-5 0000h PC27 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC28 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC29 0000h PC30 STA2 Acceleration time constant 2 0 [ms] PC31 STB2 Deceleration time constant 2 0 [ms] PC32 CMX2 Command input pulse multiplication numerator 2 1 PC33 CMX3 Command input pulse multiplication numerator 3 1 PC34 CMX4 Command input pulse multiplication numerator 4 1 PC35 TL2 Internal torque limit 2 100.0 [%] PC36 *DMD Status display selection 0000h Analog speed command offset PC37 VCO Analog speed limit offset 0 [mV] Analog torque command offset PC38 TPO Analog torque limit offset 0 [mV] PC39 MO1 Analog monitor 1 offset 0 [mV] PC40 MO2 Analog monitor 2 offset 0 [mV] PC41 For manufacturer setting 0 PC42 0 PC43 ERZ Error excessive alarm level 0 [rev] PC44 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC45 0000h PC46 0 PC47 0 PC48 0 PC49 0 PC50 0000h PC51 RSBR Forced stop deceleration time constant 100 [ms] PC52 For manufacturer setting 0 PC53 0 PC54 RSUP1 Vertical axis freefall prevention compensation amount 0 [0.0001rev] PC55 For manufacturer setting 0 PC56 100 PC57 0000h PC58 0 PC59 0000h PC60 *COPD Function selection C-D 0000h PC61 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC62 0000h PC63 0000h PC64 0000h PC65 0000h PC66 0000h PC67 0000h PC68 0000h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 5 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PC69 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC70 0000h PC71 0000h PC72 0000h PC73 0000h PC74 0000h PC75 0000h PC76 0000h PC77 0000h PC78 0000h PC79 0000h PC80 0000h 5.1.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PD01 *DIA1 Input signal automatic on selection 1 0000h PD02 For manufacturer setting 0000h PD03 *DI1L Input device selection 1L 0202h PD04 *DI1H Input device selection 1H 0002h PD05 For manufacturer setting 2100h PD06 0021h PD07 0704h PD08 0007h PD09 0805h PD10 0008h PD11 *DI5L Input device selection 5L 0703h PD12 *DI5H Input device selection 5H 0007h PD13 *DI6L Input device selection 6L 0806h PD14 *DI6H Input device selection 6H 0008h PD15 For manufacturer setting 0000h PD16 0000h PD17 *DI8L Input device selection 8L 0A0Ah PD18 *DI8H Input device selection 8H 0000h PD19 *DI9L Input device selection 9L 0B0Bh PD20 *DI9H Input device selection 9H 0000h PD21 For manufacturer setting 2323h PD22 0023h PD23 0004h PD24 *DO2 Output device selection 2 000Ch PD25 *DO3 Output device selection 3 0004h PD26 For manufacturer setting 0007h PD27 0003h PD28 *DO6 Output device selection 6 0002h PD29 *DIF Input filter setting 0004h PD30 *DOP1 Function selection D-1 0000h PD31 For manufacturer setting 0000h PD32 *DOP3 Function selection D-3 0000h PD33 For manufacturer setting 0000h PD34 DOP5 Function selection D-5 0000h PD35 For manufacturer setting 0000h PD36 0000h PD37 0000h PD38 0 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 6 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PD39 For manufacturer setting 0 PD40 0 PD41 0000h PD42 0000h PD43 0000h PD44 0000h PD45 0000h PD46 0000h PD47 0000h PD48 0000h 5.1.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PE01 For manufacturer setting 0000h PE02 0000h PE03 0003h PE04 1 PE05 1 PE06 400 PE07 100 PE08 10 PE09 0000h PE10 0000h PE11 0000h PE12 0000h PE13 0000h PE14 0111h PE15 20 PE16 0000h PE17 0000h PE18 0000h PE19 0000h PE20 0000h PE21 0000h PE22 0000h PE23 0000h PE24 0000h PE25 0000h PE26 0000h PE27 0000h PE28 0000h PE29 0000h PE30 0000h PE31 0000h PE32 0000h PE33 0000h PE34 1 PE35 1 PE36 0.0 PE37 0.00 PE38 0.00 PE39 20 PE40 0000h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 7 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PE41 EOP3 Function selection E-3 0000h PE42 For manufacturer setting 0 PE43 0.0 PE44 0000h PE45 0000h PE46 0000h PE47 0000h PE48 0000h PE49 0000h PE50 0000h PE51 0000h PE52 0000h PE53 0000h PE54 0000h PE55 0000h PE56 0000h PE57 0000h PE58 0000h PE59 0000h PE60 0000h PE61 0.00 PE62 0.00 PE63 0.00 PE64 0.00 5.1.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PF01 For manufacturer setting 0000h PF02 0000h PF03 0000h PF04 0 PF05 0 PF06 0000h PF07 1 PF08 1 PF09 0000h PF10 0000h PF11 0000h PF12 10000 PF13 100 PF14 100 PF15 2000 PF16 0000h PF17 10 PF18 0000h PF19 0000h PF20 0000h PF21 DRT Drive recorder switching time setting 0 [s] PF22 For manufacturer setting 200 PF23 OSCL1 Vibration tough drive - Oscillation detection level 50 [%] PF24 *OSCL2 Vibration tough drive function selection 0000h PF25 CVAT SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time) 200 [ms] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 8 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PF26 For manufacturer setting 0 PF27 0 PF28 0 PF29 0000h PF30 0 PF31 FRIC Machine diagnosis function - Friction judgement speed 0 [r/min] PF32 For manufacturer setting 50 PF33 0000h PF34 0000h PF35 0000h PF36 0000h PF37 0000h PF38 0000h PF39 0000h PF40 0000h PF41 0000h PF42 0000h PF43 0000h PF44 0000h PF45 0000h PF46 0000h PF47 0000h PF48 0000h 5.2 Detailed list of parameters POINT Set a value to each "x" in the "Setting digit" columns. 5.2.1 Basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA_ _ ]) Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA01 *STY Operation mode _ _ _ x Control mode selection Select a control mode. 0: Position control mode 1: Position control mode and speed control mode 2: Speed control mode 3: Speed control mode and torque control mode 4: Torque control mode 5: Torque control mode and position control mode 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 1h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 9 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA02 *REG Regenerative option _ _ x x Regenerative option Used to select the regenerative option. Incorrect setting may cause the regenerative option to burn. If a selected regenerative option is not for use with the servo amplifier, [AL. 37 Parameter error] occurs. 00: Regenerative option is not used. For servo amplifier of 200 W or less, regenerative resistor is not used. For servo amplifier of 0.4 kW to 3 kW, built-in regenerative resistor is used. 02: MR-RB032 03: MR-RB12 04: MR-RB32 05: MR-RB30 06: MR-RB50 (Cooling fan is required.) 00h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h PA04 _ _ _ x For manufacturer setting 0h *AOP1 _ _ x _ 0h Function selection A-1 _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ Forced stop deceleration function selection 0: Forced stop deceleration function disabled (EM1) 2: Forced stop deceleration function enabled (EM2) Refer to table 5.1 for details. 2h Table 5.1 Deceleration method Deceleration method Setting value EM2/EM1 EM2 or EM1 is off Alarm occurred 0 _ _ _ EM1 MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off without the forced stop deceleration. MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off without the forced stop deceleration. 2 _ _ _ EM2 MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off after the forced stop deceleration. MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off after the forced stop deceleration. PA05 *FBP Number of command input pulses per revolution The servo motor rotates based on set command input pulses. To enable the parameter value, select "Number of command input pulses per revolution (1 _ _ _)" of "Electronic gear selection" in [Pr. PA21]. Setting range: 1000 to 1000000 10000 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 10 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA06 CMX Electronic gear numerator (command pulse multiplication numerator) Set the numerator of the electronic gear. To enable the parameter, select "Electronic gear (0 _ _ _)" of "Electronic gear selection" in [Pr. PA21]. The following shows a standard of the setting range of the electronic gear. 1 10 CMX CDV 4000 If the set value is outside this range, noise may be generated during acceleration/deceleration or operation may not be performed at the preset speed and/or acceleration/deceleration time constants. CDV FBP Command pulse train Pt "0" (initial value) CMX Deviation counter + - Electronic gear ([Pr. PA06] [Pr. PA07]) Number of command input pulses per revolutio n ([Pr. PA05] "1000" to "1000000") Servo motor Encoder M "1" Electronic gear selection (x _ _ _ ) ([Pr. PA21]) Pt (servo motor resolution): 131072 pulses/rev Always set the electronic gear with servo-off state to prevent unexpected operation due to improper setting. Setting range: 1 to 16777215 1 PA07 CDV Electronic gear denominator (command pulse multiplication denominator) Set the denominator of the electronic gear. To enable the parameter, select "Electronic gear (0 _ _ _)" of "Electronic gear selection" in [Pr. PA21]. Setting range: 1 to 16777215 1 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 11 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA08 ATU Auto tuning mode _ _ _ x Gain adjustment mode selection Select the gain adjustment mode. 0: 2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) 1: Auto tuning mode 1 2: Auto tuning mode 2 3: Manual mode 4: 2 gain adjustment mode 2 Refer to table 5.2 for details. 1h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h Table 5.2 Gain adjustment mode selection Setting value Gain adjustment mode Automatically adjusted parameter _ _ _ 0 2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio] [Pr. PB08 Position loop gain] [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] [Pr. PB10 Speed integral compensation] _ _ _ 1 Auto tuning mode 1 [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio] [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] [Pr. PB08 Position loop gain] [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] [Pr. PB10 Speed integral compensation] _ _ _ 2 Auto tuning mode 2 [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] [Pr. PB08 Position loop gain] [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] [Pr. PB10 Speed integral compensation] _ _ _ 3 Manual mode _ _ _ 4 2 gain adjustment mode 2 [Pr. PB08 Position loop gain] [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] [Pr. PB10 Speed integral compensation] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 12 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Set a response of the auto tuning. 16 Machine characteristic Machine characteristic PA09 RSP Auto tuning response Setting value Response Guideline for machine resonance frequency [Hz] Setting value Response Guideline for machine resonance frequency [Hz] 1 Low respon se 2.7 21 Middle respon se 67.1 2 3.6 22 75.6 3 4.9 23 85.2 4 6.6 24 95.9 5 10.0 25 108.0 6 11.3 26 121.7 7 12.7 27 137.1 8 14.3 28 154.4 9 16.1 29 173.9 10 18.1 30 195.9 11 20.4 31 220.6 12 23.0 32 248.5 13 25.9 33 279.9 14 29.2 34 315.3 15 32.9 35 355.1 16 37.0 36 400.0 17 41.7 37 446.6 18 47.0 38 501.2 19 52.9 39 571.5 20 Middle respon se 59.6 40 High respon se 642.7 Setting range: 1 to 40 PA10 INP In-position range Set an in-position range per command pulse. To change it to the servo motor encoder pulse unit, set [Pr. PC24]. Setting range: 0 to 65535 100 [pulse] PA11 TLP Forward rotation torque limit You can limit the torque generated by the servo motor. Set the parameter referring section 3.6.1 (5). The larger value of [Pr. PA11 Forward rotation torque limit] or [Pr. PA12 Reverse rotation torque limit] will be the maximum output voltage (8 V). Set the parameter on the assumption that the maximum torque is 100 [%]. The parameter is for limiting the torque of the servo motor in the CCW power running or CW regeneration. Set this parameter to "0.0" to generate no torque. Setting range: 0.0 to 100.0 100.0 [%] PA12 TLN Reverse rotation torque limit You can limit the torque generated by the servo motor. Set the parameter referring section 3.6.1 (5). The larger value of [Pr. PA11 Forward rotation torque limit] or [Pr. PA12 Reverse rotation torque limit] will be the maximum output voltage (8 V). Set the parameter on the assumption that the maximum torque is 100 [%]. The parameter is for limiting the torque of the servo motor in the CW power running or CCW regeneration. Set this parameter to "0.0" to generate no torque. Setting range: 0.0 to 100.0 100.0 [%] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 13 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA13 *PLSS Command pulse input form _ _ _ x Command input pulse train form selection 0: Forward/reverse rotation pulse train 1: Signed pulse train 2: A-phase/B-phase pulse train (The servo amplifier imports input pulses after multiplying by four.) Refer to table 5.3 for settings. 0h _ _ x _ Pulse train logic selection 0: Positive logic 1: Negative logic Refer to table 5.3 for settings. 0h _ x _ _ Command input pulse train filter selection Selecting proper filter enables to enhance noise immunity. 0: Command input pulse train is 4 Mpulses/s or less. 1: Command input pulse train is 1 Mpulse/s or less. 2: Command input pulse train is 500 kpulses/s or less. 3: Command input pulse train is 200 kpulses/s or less. 1 Mpulse/s or lower commands are supported by "1". When inputting commands over 1 Mpulse/s and 4 Mpulses/s or lower, set "0". Setting a value not according to the command pulse frequency may cause the following malfunctions. Setting a value higher than actual command will lower noise immunity. Setting a value lower than actual command will cause a position mismatch. 1h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h Table 5.3 Command input pulse train form selection Setting value Pulse train form Forward rotation command Reverse rotation command _ _ 1 0h Forward rotation pulse train Reverse rotation pulse train NP PP _ _ 1 1h Negative logic Signed pulse train PP L H NP _ _ 1 2h A-phase pulse train B-phase pulse train PP NP _ _ 0 0h Forward rotation pulse train Reverse rotation pulse train NP PP _ _ 0 1h Positive logic Signed pulse train L H PP NP _ _ 0 2h A-phase pulse train B-phase pulse train PP NP Arrows in the table indicate the timing of importing pulse trains. A-phase pulse train and B-phase pulse train are imported after they have been multiplied by 4. 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 14 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Select servo motor rotation direction relative to the input pulse train. 0 Servo motor rotation direction PA14 *POL Rotation direction selection Setting value When forward rotation pulse is input When reverse rotation pulse is input 0 CCW CW 1 CW CCW The following shows the servo motor rotation directions. Forward rotation (CCW) Reverse rotation (CW) Setting range: 0, 1 PA15 *ENR Encoder output pulses Set the encoder output pulses from the servo amplifier by using the number of output pulses per revolution, dividing ratio, or electronic gear ratio. (after multiplication by 4) To set a numerator of the electronic gear, select "A-phase/B-phase pulse electronic gear setting (_ _ 3 _)" of "Encoder output pulse setting selection" in [Pr. PC19]. The maximum output frequency is 4.6 Mpulses/s. Set the parameter within this range. Setting range: 1 to 4194304 4000 [pulse/ rev] PA16 *ENR2 Encoder output pulses 2 Set a denominator of the electronic gear for the A/B-phase pulse output. To set a denominator of the electronic gear, select "A-phase/B-phase pulse electronic gear setting (_ _ 3 _)" of "Encoder output pulse setting selection" in [Pr. PC19]. Setting range: 1 to 4194304 1 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 15 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Select a reference range and writing range of the parameter. Refer to table 5.4 for settings. 00AAh Table 5.4 [Pr. PA19] setting value and reading/writing range PA19 *BLK Parameter writing inhibit PA19 Setting operation PA PB PC PD PE PF Reading Other than below Writing Reading Only 19 000Ah Writing Only 19 Reading 000Bh Writing Reading 000Ch Writing Reading 00AAh (initial value) Writing Reading 100Bh Writing Only 19 Reading 100Ch Writing Only 19 Reading 10AAh Writing Only 19 Alarms may not be avoided with the tough drive function depending on the situations of the power supply and load fluctuation. You can assign MTTR (During tough drive) to pins CN1-23, CN1-24, and CN1-49 with [Pr. PD24], [Pr. PD25], and [Pr. PD28]. PA20 *TDS Tough drive setting _ _ _ x For manufacturer setting 0h _ _ x _ Vibration tough drive selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled Selecting "1" enables to suppress vibrations by automatically changing setting values of [Pr. PB13 Machine resonance suppression filter 1] and [Pr. PB15 Machine resonance suppression filter 2] in case that the vibration exceed the value of the oscillation level set in [Pr. PF23]. To output the oscillation detection alarm as a warning, set [Pr. PF24 Vibration tough drive function selection]. Refer to section 7.3 for details. 0h _ x _ _ SEMI-F47 function selection (instantaneous power failure tough drive selection) 0: Disabled 1: Enabled Selecting "1" enables to avoid occurring [AL. 10 Undervoltage] using the electrical energy charged in the capacitor in the servo amplifier in case that an instantaneous power failure occurs during operation. In [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)], set the time until the occurrence of [AL. 10.1 Voltage drop in the power]. When the parameter is enabled, the power should be off for the setting value of [Pr. PF25] + 1.5 s or more before cycling the power to enable a parameter whose symbol is preceded by "*". 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 16 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA21 *AOP3 Function selection A-3 _ _ _ x One-touch tuning function selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled When the digit is "0", the one-touch tuning is not available. 1h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ Electronic gear selection 0: Electronic gear ([Pr. PA06] and [Pr. PA07]) 1: Number of command input pulses per revolution ([Pr. PA05]) 0h _ _ x x Alarm detail No. setting Set the digits when you execute the trigger with arbitrary alarm detail No. for the drive recorder function. When these digits are "0 0", only the arbitrary alarm No. setting will be enabled. 00h PA23 DRAT Drive recorder arbitrary alarm trigger setting x x _ _ Alarm No. setting Set the digits when you execute the trigger with arbitrary alarm No. for the drive recorder function. When "0 0" are set, arbitrary alarm trigger of the drive recorder will be disabled. 00h Setting example: To activate the drive recorder when [AL. 50 Overload 1] occurs, set "5 0 0 0". To activate the drive recorder when [AL. 50.3 Thermal overload error 4 during operation] occurs, set "5 0 0 3". PA24 AOP4 Function selection A-4 _ _ _ x Vibration suppression mode selection 0: Standard mode 1: 3 inertia mode 2: Low response mode When you select the standard mode or low response mode, "Vibration suppression control 2" is not available. When you select the 3 inertia mode, the feed forward gain is not available. Before changing the control mode during the 3 inertia mode or low response mode, stop the motor. 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h PA25 OTHOV One-touch tuning - Overshoot permissible level Set a permissible value of overshoot amount for one-touch tuning as a percentage of the in-position range. However, setting "0" will be 50%. 0 [%] PA26 *AOP5 Function selection A-5 _ _ _ x Torque limit function selection at instantaneous power failure 0: Disabled 1: Enabled Selecting "1" for this digit will limit torques to save electric energy when an instantaneous power failure occurs during operation and will make [AL. 10 Undervoltage] less likely to occur. The torque limit function at instantaneous power failure is enabled when "SEMI-F47 function selection (instantaneous power failure tough drive selection)" in [Pr. PA20] is "Enabled (_ 1 _ _)". 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 17 5.2.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB01 FILT Adaptive tuning mode (adaptive filter II) _ _ _ x Filter tuning mode selection Set the adaptive filter tuning. Select the adjustment mode of the machine resonance suppression filter 1. Refer to section 7.1.2 for details. 0: Disabled 1: Automatic setting (Do not use this in the torque control mode.) 2: Manual setting 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h _ _ _ x Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection Select the tuning mode of the vibration suppression control 1. Refer to section 7.1.5 for details. 0: Disabled 1: Automatic setting 2: Manual setting 0h PB02 VRFT Vibration suppression control tuning mode (advanced vibration suppression control II) _ _ x _ Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection Select the tuning mode of the vibration suppression control 2. To enable the digit, select "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)" of "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24]. Refer to section 7.1.5 for details. 0: Disabled 1: Automatic setting 2: Manual setting 0h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h PB03 PST Position command acceleration/d eceleration time constant (position smoothing) This is used to set the constant of a primary delay to the position command. You can select a control method from "Primary delay" or "Linear acceleration/deceleration" in [Pr. PB25 Function selection B-1]. The setting range of "Linear acceleration/deceleration" is 0 ms to 10 ms. Setting of longer than 10 ms will be recognized as 10 ms. When the linear acceleration/deceleration is selected, do not set the "Control mode selection" ([Pr. PA01]) to the setting other than "_ _ _ 0". Doing so will cause the servo motor to make a sudden stop at the time of position control mode switching. (Example) When a command is given from a synchronizing encoder, synchronous operation will start smoothly even if it start during line operation. Synchronizing encoder Start Servo motor Servo amplifier ON OFF With time constant setting Without time constant setting Servo motor speed Start t Setting range: 0 to 65535 0 [ms] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 18 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB04 FFC Feed forward gain Set the feed forward gain. When the setting is 100%, the droop pulses during operation at constant speed are nearly zero. However, sudden acceleration/deceleration will increase the overshoot. As a guideline, when the feed forward gain setting is 100%, set 1 s or more as the acceleration time constant up to the rated speed. Setting range: 0 to 100 0 [%] PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio This is used to set the load to motor inertia ratio. The setting of the parameter will be the automatic setting or manual setting depending on the [Pr. PA08] setting. Refer to the following table for details. When the parameter is automatic setting, the value will vary between 0.00 and 100.00. Setting range: 0.00 to 300.00 7.00 [Multiplier] Pr. PA08 This parameter _ _ _ 0 (2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) Automatic setting _ _ _ 1: (Auto tuning mode 1) _ _ _ 2: (Auto tuning mode 2) Manual setting _ _ _ 3: (Manual mode) _ _ _ 4: (2 gain adjustment mode 2) PB07 PG1 Model loop gain Set the response gain up to the target position. Increasing the setting value will also increase the response level to the position command but will be liable to generate vibration and/or noise. The setting of the parameter will be the automatic setting or manual setting depending on the [Pr. PA08] setting. Refer to the following table for details. Setting range: 1.0 to 2000.0 15.0 [rad/s] Pr. PA08 This parameter _ _ _ 0 (2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) Manual setting _ _ _ 1: (Auto tuning mode 1) Automatic setting _ _ _ 2: (Auto tuning mode 2) _ _ _ 3: (Manual mode) Manual setting _ _ _ 4: (2 gain adjustment mode 2) PB08 PG2 Position loop gain This is used to set the gain of the position loop. Set this parameter to increase the position response to level load disturbance. Increasing the setting value will also increase the response level to the load disturbance but will be liable to generate vibration and/or noise. The setting of the parameter will be the automatic setting or manual setting depending on the [Pr. PA08] setting. Refer to the following table for details. Setting range: 1.0 to 2000.0 37.0 [rad/s] Pr. PA08 This parameter _ _ _ 0 (2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) Automatic setting _ _ _ 1: (Auto tuning mode 1) _ _ _ 2: (Auto tuning mode 2) _ _ _ 3: (Manual mode) Manual setting _ _ _ 4: (2 gain adjustment mode 2) Automatic setting 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 19 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain This is used to set the gain of the speed loop. Set this parameter when vibration occurs on machines of low rigidity or large backlash. Increasing the setting value will also increase the response level but will be liable to generate vibration and/or noise. The setting of the parameter will be the automatic setting or manual setting depending on the [Pr. PA08] setting. Refer to the table of [Pr. PB08] for details. Setting range: 20 to 65535 823 [rad/s] PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation This is used to set the integral time constant of the speed loop. Decreasing the setting value will increase the response level but will be liable to generate vibration and/or noise. The setting of the parameter will be the automatic setting or manual setting depending on the [Pr. PA08] setting. Refer to the table of [Pr. PB08] for details. Setting range: 0.1 to 1000.0 33.7 [ms] PB11 VDC Speed differential compensation This is used to set the differential compensation. To enable the setting value, turn on PC (proportional control). Setting range: 0 to 1000 980 PB12 OVA Overshoot amount compensation Set a viscous friction torque per percent to the servo motor rated speed. When the response level is low, or when the torque is limited, the efficiency of the parameter can be lower. Setting range: 0 to 100 0 [%] PB13 NH1 Machine resonance suppression filter 1 Machine resonance suppression filter 1 Set the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter 1. When "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 1)" of "Filter tuning mode selection" is selected in [Pr. PB01], this parameter will be adjusted automatically. When you select "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)" of "Filter tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB01], the setting value will be enabled. Setting range: 10 to 4500 4500 [Hz] Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 1. When you select "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 1)" of "Filter tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB01], this parameter will be adjusted automatically. Set manually for the manual setting. PB14 NHQ1 Notch shape selection 1 _ _ _ x For manufacturer setting 0h _ _ x _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB 1: -14 dB 2: -8 dB 3: -4 dB 0h _ x _ _ Notch width selection 0: = 2 1: = 3 2: = 4 3: = 5 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h PB15 NH2 Machine resonance suppression filter 2 Set the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter 2. To enable the setting value, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 2 selection" in [Pr. PB16]. Setting range: 10 to 4500 4500 [Hz] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 20 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 2. PB16 NHQ2 Notch shape selection 2 _ _ _ x Machine resonance suppression filter 2 selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled 0h _ _ x _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB 1: -14 dB 2: -8 dB 3: -4 dB 0h _ x _ _ Notch width selection 0: = 2 1: = 3 2: = 4 3: = 5 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h PB17 NHF Shaft resonance suppression filter Set the shaft resonance suppression filter. This is used to suppress a low-frequency machine vibration. When you select "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 0)" of "Shaft resonance suppression filter selection" in [Pr. PB23], the value will be calculated automatically from the servo motor you use and load to motor inertia ratio. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ _ 1)". When "Shaft resonance suppression filter selection" is "Disabled (_ _ _ 2)" in [Pr. PB23], the setting value of this parameter will be disabled. When you select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 4 selection" in [Pr. PB49], the shaft resonance suppression filter is not available. _ _ x x Shaft resonance suppression filter setting frequency selection Refer to table 5.5 for settings. Set the value closest to the frequency you need. 00h _ x _ _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB 1: -14 dB 2: -8 dB 3: -4 dB 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h Table 5.5 Shaft resonance suppression filter setting frequency selection Setting value Frequency [Hz] Setting value Frequency [Hz] 00 Disabled 10 562 01 Disabled 11 529 02 4500 12 500 03 3000 13 473 04 2250 14 450 05 1800 15 428 06 1500 16 409 07 1285 17 391 08 1125 18 375 09 1000 19 360 0A 900 1A 346 0B 818 1B 333 0C 750 1C 321 0D 692 1D 310 0E 642 1E 300 0F 600 1F 290 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 21 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB18 LPF Low-pass filter setting Set the low-pass filter. The following shows a relation of a required parameter to this parameter. Setting range: 100 to 18000 3141 [rad/s] [Pr. PB23] [Pr. PB18] _ _ 0 _ (Initial value) Automatic setting _ _ 1 _ Setting value enabled _ _ 2 _ Setting value disabled PB19 VRF11 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency Set the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 1 to suppress low- frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 1)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". Refer to section 7.1.5 for details. Setting range: 0.1 to 300.0 100.0 [Hz] PB20 VRF12 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency Set the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 1 to suppress low- frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 1)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". Refer to section 7.1.5 for details. Setting range: 0.1 to 300.0 100.0 [Hz] PB21 VRF13 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping Set a damping of the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 1 to suppress low-frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 1)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". Refer to section 7.1.5 for details. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 PB22 VRF14 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping Set a damping of the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 1 to suppress low-frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ _ 1)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". Refer to section 7.1.5 for details. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 PB23 VFBF Low-pass filter selection _ _ _ x Shaft resonance suppression filter selection Select the shaft resonance suppression filter. 0: Automatic setting 1: Manual setting 2: Disabled When you select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 4 selection" in [Pr. PB49], the shaft resonance suppression filter is not available. 0h _ _ x _ Low-pass filter selection Select the low-pass filter. 0: Automatic setting 1: Manual setting 2: Disabled 0h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 1h x _ _ _ 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 22 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB24 *MVS Slight vibration suppression control _ _ _ x Slight vibration suppression control selection Select the slight vibration suppression control. 0: Disabled 1: Enabled To enable the slight vibration suppression control, select "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08]. Slight vibration suppression control cannot be used in the speed control mode. 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h _ _ _ x For manufacturer setting 0h PB25 *BOP1 Function selection B-1 _ _ x _ Position acceleration/deceleration filter type selection Select the position acceleration/deceleration filter type. 0: Primary delay 1: Linear acceleration/deceleration When you select "Linear acceleration/deceleration", do not switch the control mode. Doing so will cause the servo motor to make a sudden stop at the time of control mode switching. 0h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Select the gain switching condition. Set conditions to enable the gain switching values set in [Pr. PB29] to [Pr. PB36] and [Pr. PB56] to [Pr. PB60]. PB26 *CDP Gain switching function _ _ _ x Gain switching selection 0: Disabled 1: Input device (gain switching (CDP)) 2: Command frequency 3: Droop pulses 4: Servo motor speed 0h _ _ x _ Gain switching condition selection 0: Gain after switching is enabled with gain switching condition or more 1: Gain after switching is enabled with gain switching condition or less 0h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h PB27 CDL Gain switching condition This is used to set the value of gain switching (command frequency, droop pulses, and servo motor speed) selected in [Pr. PB26]. The set value unit differs depending on the switching condition item. (Refer to section 7.2.3.) Setting range: 0 to 9999 10 [kpulse/s] /[pulse] /[r/min] PB28 CDT Gain switching time constant This is used to set the time constant at which the gains will change in response to the conditions set in [Pr. PB26] and [Pr. PB27]. Setting range: 0 to 100 1 [ms] PB29 GD2B Load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching This is used to set the load to motor inertia ratio when gain switching is enabled. This parameter is enabled only when you select "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08]. Setting range: 0.00 to 300.00 7.00 [Multipli er] PB30 PG2B Gain switching position loop gain Set the position loop gain when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 1.0 rad/s, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB08]. This parameter is enabled only when you select "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08]. Setting range: 0.0 to 2000.0 0.0 [rad/s] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 23 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB31 VG2B Gain switching speed loop gain Set the speed loop gain when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 20 rad/s, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB09]. This parameter is enabled only when you select "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08]. Setting range: 0 to 65535 0 [rad/s] PB32 VICB Speed integral compensation after gain switching Set the speed integral compensation when the gain changing is enabled. When you set a value less than 0.1 ms, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB10]. This parameter is enabled only when you select "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08]. Setting range: 0.0 to 5000.0 0.0 [ms] PB33 VRF1B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency after gain switching Set the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 1 when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 0.1 Hz, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB19]. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.0 to 300.0 0.0 [Hz] PB34 VRF2B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency after gain switching Set the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 1 when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 0.1 Hz, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB20]. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.0 to 300.0 0.0 [Hz] PB35 VRF3B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching Set a damping of the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 1 when the gain switching is enabled. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 PB36 VRF4B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching Set a damping of the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 1 when the gain switching is enabled. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 24 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Set the command notch filter. _ _ x x Command notch filter setting frequency selection Refer to table 5.6 for the relation of setting values to frequency. 00h PB45 CNHF Command notch filter _ x _ _ Notch depth selection Refer to table 5.7 for details. 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h Table 5.6 Command notch filter setting frequency selection Setting value Frequency [Hz] Setting value Frequency [Hz] Setting value Frequency [Hz] 00 Disabled 20 70 40 17.6 01 2250 21 66 41 16.5 02 1125 22 62 42 15.6 03 750 23 59 43 14.8 04 562 24 56 44 14.1 05 450 25 53 45 13.4 06 375 26 51 46 12.8 07 321 27 48 47 12.2 08 281 28 46 48 11.7 09 250 29 45 49 11.3 0A 225 2A 43 4A 10.8 0B 204 2B 41 4B 10.4 0C 187 2C 40 4C 10 0D 173 2D 38 4D 9.7 0E 160 2E 37 4E 9.4 0F 150 2F 36 4F 9.1 10 140 30 35.2 50 8.8 11 132 31 33.1 51 8.3 12 125 32 31.3 52 7.8 13 118 33 29.6 53 7.4 14 112 34 28.1 54 7.0 15 107 35 26.8 55 6.7 16 102 36 25.6 56 6.4 17 97 37 24.5 57 6.1 18 93 38 23.4 58 5.9 19 90 39 22.5 59 5.6 1A 86 3A 21.6 5A 5.4 1B 83 3B 20.8 5B 5.2 1C 80 3C 20.1 5C 5.0 1D 77 3D 19.4 5D 4.9 1E 75 3E 18.8 5E 4.7 1F 72 3F 18.2 5F 4.5 Table 5.7 Notch depth selection Setting value Depth [dB] Setting value Depth [dB] 0 -40.0 8 -6.0 1 -24.1 9 -5.0 2 -18.1 A -4.1 3 -14.5 B -3.3 4 -12.0 C -2.5 5 -10.1 D -1.8 6 -8.5 E -1.2 7 -7.2 F -0.6 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 25 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB46 NH3 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 Set the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter 3. To enable the setting value, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 3 selection" in [Pr. PB47]. Setting range: 10 to 4500 4500 [Hz] Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 3. PB47 NHQ3 Notch shape selection 3 _ _ _ x Machine resonance suppression filter 3 selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled 0h _ _ x _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB 1: -14 dB 2: -8 dB 3: -4 dB 0h _ x _ _ Notch width selection 0: = 2 1: = 3 2: = 4 3: = 5 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h PB48 NH4 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 Set the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter 4. To enable the setting value, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 4 selection" in [Pr. PB49]. Setting range: 10 to 4500 4500 [Hz] Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 4. PB49 NHQ4 Notch shape selection 4 _ _ _ x Machine resonance suppression filter 4 selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled When you select "Enabled" of this digit, [Pr. PB17 Shaft resonance suppression filter] is not available. 0h _ _ x _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB 1: -14 dB 2: -8 dB 3: -4 dB 0h _ x _ _ Notch width selection 0: = 2 1: = 3 2: = 4 3: = 5 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h PB50 NH5 Machine resonance suppression filter 5 Set the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter 5. To enable the setting value, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 5 selection" in [Pr. PB51]. Setting range: 10 to 4500 4500 [Hz] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 26 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 5. When you select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Robust filter selection" in [Pr. PE41], the machine resonance suppression filter 5 is not available. PB51 NHQ5 Notch shape selection 5 _ _ _ x Machine resonance suppression filter 5 selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled 0h _ _ x _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB 1: -14 dB 2: -8 dB 3: -4 dB 0h _ x _ _ Notch width selection 0: = 2 1: = 3 2: = 4 3: = 5 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h PB52 VRF21 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency Set the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 2 to suppress low- frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ 1 _)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". To enable the digit, select "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)" of "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24]. Setting range: 0.1 to 300.0 100.0 [Hz] PB53 VRF22 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency Set the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 2 to suppress low- frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ 1 _)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". To enable the digit, select "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)" of "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24]. Setting range: 0.1 to 300.0 100.0 [Hz] PB54 VRF23 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping Set a damping of the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 2 to suppress low-frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ 1 _)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". To enable the digit, select "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)" of "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24]. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 PB55 VRF24 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping Set a damping of the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 2 to suppress low-frequency machine vibration. When "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" is "Automatic setting (_ _ 1 _)" in [Pr. PB02], this parameter will be set automatically. Set manually for "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". To enable the digit, select "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)" of "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24]. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 27 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB56 VRF21B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency after gain switching Set the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 2 when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 0.1 Hz, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB52]. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24] is "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)". "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.0 to 300.0 0.0 [Hz] PB57 VRF22B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency after gain switching Set the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 2 when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 0.1 Hz, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB53]. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24] is "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)". "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.0 to 300.0 0.0 [Hz] PB58 VRF23B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching Set a damping of the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 2 when the gain switching is enabled. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24] is "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)". "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 PB59 VRF24B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching Set a damping of the resonance frequency for vibration suppression control 2 when the gain switching is enabled. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Vibration suppression mode selection" in [Pr. PA24] is "3 inertia mode (_ _ _ 1)". "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02] is "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.00 to 0.30 0.00 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 28 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PB60 PG1B Model loop gain after gain switching Set the model loop gain when the gain switching is enabled. When you set a value less than 1.0 rad/s, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB07]. This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)". "Gain switching selection" in [Pr. PB26] is "Input device (gain switching (CDP)) (_ _ _ 1)". Switching during driving may cause a shock. Be sure to switch them after the servo motor stops. Setting range: 0.0 to 2000.0 0.0 [rad/s] 5.2.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC01 STA Acceleration time constant This is used to set the acceleration time required to reach the rated speed from 0 r/min in response to VC (Analog speed command) and [Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1] to [Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7]. If the preset speed command is lowe r than the rated speed, acceleration/ deceleration time will be shorter. Time [Pr. PC02] setting 0 r/min Rated speed Speed [Pr. PC01] setting For example for the servo motor of 3000 r/min rated speed, set 3000 (3s) to increase speed from 0 r/min to 1000 r/min in 1 second. Setting range: 0 to 50000 0 [ms] PC02 STB Deceleration time constant This is used to set the deceleration time required to reach 0 r/min from the rated speed in response to VC (Analog speed command) and [Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1] to [Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7]. Setting range: 0 to 50000 0 [ms] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 29 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC03 STC S-pattern acceleration/d eceleration time constant This is used to smooth start/stop of the servo motor. Set the time of the arc part for S-pattern acceleration/deceleration. Speed command Servo motor speed 0 r/min STA STC Time STC STB STC STC STA: Acceleration time constant ([Pr. PC01]) STB: Deceleration time constant ([Pr. PC02]) STC: S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant ([Pr. PC03]) Long setting of STA (acceleration time constant) or STB (deceleration time constant) may produce an error in the time of the arc part for the setting of the S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant. The upper limit value of the actual arc part time is limited by 2000000 STA for acceleration or by 2000000 STB for deceleration. (Example) At the setting of STA 20000, STB 5000 and STC 200, the actual arc part times are as follows. During acceleration: 100 ms 2000000 20000 = 100 [ms] 200 [ms] Therefore, it will be limited to 100 [ms]. During deceleration: 200 ms 2000000 5000 = 400 [ms] 200 [ms] Therefore, it will be 200 [ms] as you set. Setting range: 0 to 5000 0 [ms] PC04 TQC Torque command time constant This is used to set the constant of a primary delay to the torque command. TQC TQC Time Torque Torque command After filtering TQC: Torque command time constant Setting range: 0 to 50000 0 [ms] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 30 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T This is used to set speed 1 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 100 [r/min] PC05 SC1 Internal speed command 1/internal speed limit 1 This is used to set speed 1 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed This is used to set speed 2 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 500 [r/min] PC06 SC2 Internal speed command 2 Internal speed limit 2 This is used to set speed 2 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed This is used to set speed 3 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 1000 [r/min] PC07 SC3 Internal speed command 3 Internal speed limit 3 This is used to set speed 3 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed This is used to set speed 4 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 200 [r/min] PC08 SC4 Internal speed command 4 Internal speed limit 4 This is used to set speed 4 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed This is used to set speed 5 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 300 [r/min] PC09 SC5 Internal speed command 5 Internal speed limit 5 This is used to set speed 5 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed This is used to set speed 6 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 500 [r/min] PC10 SC6 Internal speed command 6 Internal speed limit 6 This is used to set speed 6 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed This is used to set speed 7 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 800 [r/min] PC11 SC7 Internal speed command 7 Internal speed limit 7 This is used to set speed 7 of internal speed limits. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 31 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T This is used to set the speed at the maximum input voltage (10 V) of VC (Analog speed command). When "0" is set, the analog speed command maximum speed would be the rated speed of the servo motor connected. If a value equal to or larger than the permissible speed is inputted to VC, the value is clamped at the permissible speed. Setting range: 0 to 50000 0 [r/min] PC12 VCM Analog speed command - Maximum speed Analog speed limit - Maximum speed This is used to set the speed at the maximum input voltage (10 V) of VLA (Analog speed limit). When "0" is set, the analog speed command maximum speed would be the rated speed of the servo motor connected. If a limited value equal to or larger than the permissible speed is inputted to VLA, the value is clamped at the permissible speed. Setting range: 0 to 50000 PC13 TLC Analog torque command maximum output This is used to set the output torque at the analog torque command voltage (TC = ±8 V) of +8 V on the assumption that the maximum torque is 100.0%. For example, set 50.0. The maximum torque × 50.0 100.0 is outputted. If a value equal to or larger than the maximum torque is inputted to TC, the value is clamped at the maximum torque. Setting range: 0.0 to 1000.0 100.0 [%] _ _ x x Analog monitor 1 output selection Select a signal to output to MO1 (Analog monitor 1). Refer to appendix 4 (3) for detection point of output selection. Refer to table 5.8 for settings. 00h PC14 MOD1 Analog monitor 1 output _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Table 5.8 Analog monitor setting value Setting value Item 00 Servo motor speed (±8 V/max. speed) 01 Torque (±8 V/max. torque) (Note 2) 02 Servo motor speed (+8 V/max. speed) 03 Torque (+8 V/max. torque) (Note 2) 04 Current command (±8 V/max. current command) 05 The command pulse frequency (±10 V/4 Mpulses/s) 06 Servo motor-side droop pulses (±10 V/100 pulses) (Note 1) 07 Servo motor-side droop pulses (±10 V/1000 pulses) (Note 1) 08 Servo motor-side droop pulses (±10 V/10000 pulses) (Note 1) 09 Servo motor-side droop pulses (±10 V/100000 pulses) (Note 1) 0D Bus voltage (+8 V/400 V) 0E Speed command 2 (±8 V/max. speed) 17 Encoder inside temperature (±10 V/±128 ˚C) Note 1. Encoder pulse unit 2. 8 V is outputted at the maximum torque. However, when [Pr. PA11] and [Pr. PA12] are set to limit torque, 8 V is outputted at the torque highly limited. 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 32 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC15 MOD2 Analog monitor 2 output _ _ x x Analog monitor 2 output selection Select a signal to output to MO2 (Analog monitor 2). Refer to appendix 4 (3) for detection point of output selection. Refer to [Pr. PC14] for settings. 01h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h PC16 MBR Electromagne tic brake sequence output This is used to set the delay time between MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) and the base drive circuit is shut-off. Setting range: 0 to 1000 0 [ms] PC17 ZSP Zero speed Used to set the output range of ZSP (Zero speed detection). ZSP (Zero speed detection) has hysteresis of 20 r/min. Setting range: 0 to 10000 50 [r/min] PC18 *BPS Alarm history clear _ _ _ x Alarm history clear selection Used to clear the alarm history. 0: Disabled 1: Enabled When you select "Enabled", the alarm history will be cleared at next power-on. After the alarm history is cleared, the setting is automatically disabled. 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h PC19 *ENRS Encoder output pulse selection _ _ _ x Encoder output pulse phase selection Select the encoder pulse direction. 0: Increasing A-phase 90° in CCW 1: Increasing A-phase 90° in CW 0h Servo motor rotation direction Setting value CCW CW 0 A -phase B-phase A -phase B-phase 1 A -phase B-phase A -phase B-phase _ _ x _ Encoder output pulse setting selection 0: Output pulse setting 1: Dividing ratio setting 2: The same output pulse setting as the command pulse 3: A-phase/B-phase pulse electronic gear setting When you select "1", the settings of [Pr. PA16 Encoder output pulses 2] will be disabled. When you select "2", the settings of [Pr. PA15 Encoder output pulses] and [Pr. PA16 Encoder output pulses 2] will be disabled. When you select the setting, do not change the settings in [Pr. PA06] and [Pr. PA07] after the power-on. 0h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 33 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T _ _ _ x For manufacturer setting 0h _ _ x _ 0h _ x _ _ 2h PC22 *COP1 Function selection C-1 x _ _ _ Encoder cable communication method selection Select the encoder cable communication method. 0: Two-wire type 1: Four-wire type If the setting is incorrect, [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1] or [AL. 20 Encoder normal communication error 1] occurs. 0h PC23 *COP2 Function selection C-2 _ _ _ x Servo-lock selection at speed control stop Select the servo-lock selection at speed control stop. In the speed control mode, the servo motor shaft can be locked to prevent the shaft from being moved by an external force. 0: Enabled (servo-lock) The operation to maintain the stop position is performed. 1: Disabled (no servo-lock) The stop position is not maintained. The control to make the speed 0 r/min is performed. 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ VC/VLA voltage averaging selection Select the VC/VLA voltage average. This is used to set the filtering time when VC (Analog speed command) or VLA (Analog speed limit) is imported. Set 0 to vary the speed to voltage fluctuation in real time. Increase the set value to vary the speed slower to voltage fluctuation. 0h Setting value Filtering time [ms] 0 0 1 0.444 2 0.888 3 1.777 4 3.555 5 7.111 x _ _ _ Speed limit selection at torque control Select the speed limit selection at torque control. 0: Enabled 1: Disabled Do not use this function except when configuring an external speed loop. 0h PC24 *COP3 Function selection C-3 _ _ _ x In-position range unit selection Select a unit of in-position range. 0: Command input pulse unit 1: Servo motor encoder pulse unit 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ Error excessive alarm level unit selection Select a setting unit of the error excessive alarm level set in [Pr. PC43]. 0: 1 rev unit 1: 0.1 rev unit 2: 0.01 rev unit 3: 0.001 rev unit 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 34 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC26 *COP5 Function selection C-5 _ _ _ x [AL. 99 Stroke limit warning] selection Select [AL. 99 Stroke limit warning]. 0: Enabled 1: Disabled 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h PC30 STA2 Acceleration time constant 2 To enable the parameter, turn on STAB2 (Speed acceleration/deceleration selection). This is used to set the acceleration time required to reach the rated speed from 0 r/min in response to VC (Analog speed command) and [Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1] to [Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7]. Setting range: 0 to 50000 0 [ms] PC31 STB2 Deceleration time constant 2 To enable the parameter, turn on STAB2 (Speed acceleration/deceleration selection). This is used to set the deceleration time required to reach 0 r/min from the rated speed in response to VC (Analog speed command) and [Pr. PC05 Internal speed command 1] to [Pr. PC11 Internal speed command 7]. Setting range: 0 to 50000 0 [ms] PC32 CMX2 Commanded pulse multiplication numerator 2 To enable the parameter, select "Electronic gear (0 _ _ _)" of "Electronic gear selection" in [Pr. PA21]. Setting range: 1 to 16777215 1 PC33 CMX3 Commanded pulse multiplication numerator 3 To enable the parameter, select "Electronic gear (0 _ _ _)" of "Electronic gear selection" in [Pr. PA21]. Setting range: 1 to 16777215 1 PC34 CMX4 Commanded pulse multiplication numerator 4 To enable the parameter, select "Electronic gear (0 _ _ _)" of "Electronic gear selection" in [Pr. PA21]. Setting range: 1 to 16777215 1 PC35 TL2 Internal torque limit 2 Set the parameter on the assumption that the maximum torque is 100 %. The parameter is for limiting the torque of the servo motor. No torquet is generated when this parameter is set to "0.0". When TL1 (Internal torque limit selection) is turned on, Internal torque limits 1 and 2 are compared and the lower value will be enabled. Setting range: 0.0 to 100.0 100.0 [%] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 35 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC36 *DMD Status display selection _ _ x x Status display selection at power-on This is used to select a status display shown at power-on. 00: Cumulative feedback pulses 01: Servo motor speed 02: Droop pulses 03: Cumulative command pulses 04: Command pulse frequency 05: Analog speed command voltage (Note 1) 06: Analog torque command voltage (Note 2) 07: Regenerative load ratio 08: Effective load ratio 09: Peak load ratio 0A: Instantaneous torque 0B: Within one-revolution position (1 pulse unit) 0C: Within one-revolution position (100 pulses unit) 0D: ABS counter (Note 3) 0E: Load to motor inertia ratio 0F: Bus voltage 10: Encoder inside temperature 11: Settling time 12: Oscillation detection frequency 13: Number of tough operations 14: Unit power consumption (increment of 1 W) 15: Unit power consumption (increment of 1 kW) 16: Unit total power consumption (increment of 1 Wh) 17: Unit total power consumption (increment of 100 kWh) 00h Note 1. It is for the speed control mode. It will be the analog speed limit voltage in the torque control mode. 2.It is for the torque control mode. It will be the analog torque limit voltage in the speed control mode and position control mode. 3.Travel distance from power on is displayed by counter value. _ x _ _ Status display at power-on in corresponding control mode 0: Depends on the control mode 0h Control mode Status display at power-on Position Cumulative feedback pulses Position/speed Cumulative feedback pulses/servo motor speed Speed Servo motor speed Speed/torque Servo motor speed/analog torque command voltage Torque Analog torque command voltage Torque/position Analog torque command voltage/cumulative feedback pulses 1: Depends on the last two digit setting of the parameter x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 36 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC37 VCO Analog speed command offset/Analog speed limit offset This is used to set the offset voltage of VC (Analog speed command). For example, if CCW rotation is provided by switching on ST1 (Forward rotation start) with applying 0 V to VC, set a negative value. When automatic VC offset is used, the automatically offset value is set to this parameter. (Refer to section 4.5.4.) The initial value is provided before shipment by the automatic VC offset function on condition that the voltage between VC and LG is 0 V. Setting range: -9999 to 9999 The value differs depend ing on the servo amplifi ers. [mV] This is used to set the offset voltage of VLA (Analog speed limit). For example, if CCW rotation is provided by switching on RS1 (Forward rotation selection) with applying 0 V to VLA, set a negative value. When automatic VC offset is used, the automatically offset value is set to this parameter. (Refer to section 4.5.4.) The initial value is provided before shipment by the automatic VC offset function on condition that the voltage between VLA and LG is 0 V. Setting range: -9999 to 9999 This is used to set the offset voltage of TC (Analog torque command). Setting range: -9999 to 9999 PC38 TPO Analog torque command offset/Analog torque limit offset This is used to set the offset voltage of TLA (Analog torque limit). Setting range: -9999 to 9999 0 [mV] PC39 MO1 Analog monitor 1 offset This is used to set the offset voltage of MO1 (Analog monitor 1). Setting range: -9999 to 9999 0 [mV] PC40 MO2 Analog monitor 2 offset This is used to set the offset voltage of MO2 (Analog monitor 2). Setting range: -9999 to 9999 0 [mV] PC43 ERZ Error excessive alarm level Set an error excessive alarm level. You can change the setting unit with "Error excessive alarm level" in [Pr. PC24]. However, setting "0" will be 3 rev. Setting over 200 rev will be clamped with 200 rev. Setting range: 0 to 1000 0 [rev] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 37 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PC51 RSBR Forced stop deceleration time constant This is used to set deceleration time constant when you use the forced stop deceleration function. Set the time per ms from the rated speed to 0 r/min. Forced stop deceleration [Pr. PC51] 0 r/min Servo motor speed Rated speed Dynamic brake deceleration [Precautions] If the servo motor torque is saturated at the maximum torque during forced stop deceleration because the set time is too short, the time to stop will be longer than the set time constant. [AL. 50 Overload alarm 1] or [AL. 51 Overload alarm 2] may occur during forced stop deceleration, depending on the set value. After an alarm that leads to a forced stop deceleration, if an alarm that does not lead to a forced stop deceleration occurs or if the power supply is cut, dynamic braking will start regardless of the deceleration time constant setting. Setting range: 0 to 20000 100 [ms] PC54 RSUP1 Vertical axis freefall prevention compensation amount Set the compensation amount of the vertical axis freefall prevention function. Set it per servo motor rotation amount. The function will pull up an shaft per rotation amount to the servo motor rotation direction at the time of inputting forward rotation pulse for a positive number, and at the time of inputting reverse rotation pulse for a negative number. For example, if a positive compensation amount is set when the [Pr. PA14 Rotation direction selection] setting is "1", compensation will be performed to the CW direction. The vertical axis freefall prevention function is performed when all of the following conditions are met. 1) Position control mode 2) The value of the parameter is other than "0". 3) The forced stop deceleration function is enabled. 4) Alarm occurs or EM2 turns off when the servo motor speed is zero speed or less. 5) MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) was enabled in [Pr. PD24], [Pr. PD25], and [Pr. PD28], and the base circuit shut-off delay time was set in [Pr. PC16]. Setting range: -25000 to 25000 0 [0.0001 rev] _ _ _ x Motor-less operation selection This is used to select the motor-less operation. 0: Disabled 1: Enabled 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h PC60 *COPD Function selection C-D x _ _ _ 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 38 5.2.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Select input devices to turn on them automatically. _ _ _ x (BIN): For manufacturer setting 0h _ _ x _ (BIN): For manufacturer setting PD01 *DIA1 Input signal automatic on selection 1 _ x _ _ (BIN): SON (Servo-on) 0: Disabled (Use for an external input signal.) 1: Enabled (automatic on) _ _ _ x (HEX) x _ _ _ (BIN): For manufacturer setting _ _ _ x (BIN): PC (Proportional control) 0h 0: Disabled (Use for an external input signal.) 1: Enabled (automatic on) _ _ x _ (BIN): TL (External torque limit selection) 0: Disabled (Use for an external input signal.) 1: Enabled (automatic on) _ x _ _ (BIN): For manufacturer setting _ _ x _ (HEX) x _ _ _ (BIN): For manufacturer setting _ _ _ x (BIN): For manufacturer setting 0h _ _ x _ (BIN): For manufacturer setting _ x _ _ (BIN): LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) 0: Disabled (Use for an external input signal.) 1: Enabled (automatic on) x _ _ _ (BIN): LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) 0: Disabled (Use for an external input signal.) _ x _ _ (HEX) 1: Enabled (automatic on) x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h Convert the setting value into hexadecimal as follows. 0 Initial value BIN HEX Signal name 0 0 0 0 0 SON (Servo-on) 0 Initial value BIN HEX Signal name 0 0 0 0 PC (Proportional control) TL (External torque limit selection) 0 BIN 0: Use for an external input signal. BIN 1: Automatic on Initial value BIN HEX Signal name 0 0 0 0 LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 39 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-15 pin. _ _ x x Position control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 for settings. 02h PD03 *DI1L Input device selection 1L x x _ _ Speed control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 for settings. 02h Table 5.9 Selectable input devices Input device (Note 1) Setting value P S T 02 SON SON SON 03 RES RES RES 04 PC PC 05 TL TL 06 CR 07 ST1 RS2 08 ST2 RS1 09 TL1 TL1 0A LSP LSP 0B LSN LSN 0D CDP CDP 20 SP1 SP1 21 SP2 SP2 22 SP3 SP3 23 LOP (Note 2) LOP (Note 2) LOP (Note 2) 24 CM1 25 CM2 26 STAB2 STAB2 Note 1. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode The diagonal lines indicate manufacturer settings. Never change the setting. 2. When assigning LOP (Control switching), assign it to the same pin in all control modes. Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-15 pin. _ _ x x Torque control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 02h PD04 *DI1H Input device selection 1H _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-19 pin. _ _ x x Position control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 03h PD11 *DI5L Input device selection 5L x x _ _ Speed control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 07h Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-19 pin. _ _ x x Torque control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 07h PD12 *DI5H Input device selection 5H _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-41 pin. _ _ x x Position control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 06h PD13 *DI6L Input device selection 6L x x _ _ Speed control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 08h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 40 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-41 pin. _ _ x x Torque control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 08h PD14 *DI6H Input device selection 6H _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-43 pin. _ _ x x Position control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 0Ah PD17 *DI8L Input device selection 8L x x _ _ Speed control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 0Ah Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-43 pin. _ _ x x Torque control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 00h PD18 *DI8H Input device selection 8H _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-44 pin. _ _ x x Position control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 0Bh PD19 *DI9L Input device selection 9L x x _ _ Speed control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 0Bh Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-44 pin. _ _ x x Torque control mode - Device selection Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. 00h PD20 *DI9H Input device selection 9H _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h _ _ x x Device selection Any output device can be assigned to the CN1-23 pin. Refer to table 5.10 for settings. 0Ch PD24 *DO2 Output device selection 2 _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Table 5.10 Selectable output devices Output device (Note) Setting value P S T 00 Always off Always off Always off 02 RD RD RD 03 ALM ALM ALM 04 INP SA Always off 05 MBR MBR MBR 07 TLC TLC VLC 08 WNG WNG WNG 0A Always off SA Always off 0B Always off Always off VLC 0C ZSP ZSP ZSP 0D MTTR MTTR MTTR 0F CDPS Always off Always off Note. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 41 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T _ _ x x Device selection Any output device can be assigned to the CN1-24 pin. Refer to table 5.10 in [Pr. PD24] for settings. 04h PD25 *DO3 Output device selection 3 _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h _ _ x x Device selection Any output device can be assigned to the CN1-49 pin. Refer to table 5.10 in [Pr. PD24] for settings. 02h PD28 *DO6 Output device selection 6 _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h Select a filter for the input signal. PD29 *DIF Input filter setting _ _ _ x Input signal filter selection If external input signal causes chattering due to noise, etc., input filter is used to suppress it. 0: None 1: 0.888 [ms] 2: 1.777 [ms] 3: 2.666 [ms] 4: 3.555 [ms] 4h _ _ x _ RES (Reset) dedicated filter selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled (50 [ms]) 0h _ x _ _ CR (Clear) dedicated filter selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled (50 [ms]) 0h x _ _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h PD30 *DOP1 Function selection D-1 _ _ _ x Stop method selection for LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) off and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) off Select a stop method for LSP (Forward rotation stroke end) off and LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) off 0: Quick stop 1: Slow stop 0h _ _ x _ Base circuit status selection for RES (Reset) on 0: Base circuit shut-off 1: No base circuit shut-off 0h _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h PD32 *DOP3 Function selection D-3 _ _ _ x CR (Clear) selection This is used to set CR (Clear). 0: Deleting droop pulses at the leading edge of turning on of CR 1: Continuous deleting of droop pulses while CR is on 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 42 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PD34 *DOP5 Function selection D-5 _ _ _ x Alarm code output This is used to select if output alarm codes. Alarm codes are outputted to pins CN1-23, CN1-24, and CN1-49. 0: Disabled 1: Enabled For details of the alarm codes, refer to chapter 8. When you select alarm code output while MBR or ALM is selected for CN1-23, CN1- 24, or CN1-49 pin, [AL. 37 Parameter error] will occur. 0h _ _ x _ Selection of output device at warning occurrence Select ALM (Malfunction) output status at warning occurrence. 0h Setting value Device status 0 OFF ON OFF ON WNG A LM Warning occurrence 1 OFF ON OFF ON WNG A LM Warning occurrence _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting 0h x _ _ _ 0h 5.2.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ]) Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PE41 EOP3 Function selection E-3 _ _ _ x Robust filter selection 0: Disabled 1: Enabled When you select "Enabled" of this digit, the machine resonance suppression filter 5 set in [Pr. PB51] is not available. 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 43 5.2.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ]) Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PF21 DRT Drive recorder switching time setting This is used to set a drive recorder switching time. When a USB communication is cut during using a graph function or a graph function is terminated, the function will be changed to the drive recorder function after the setting time of this parameter. When a value from "1" to "32767" is set, it will switch after the setting value. When "0" is set, it will switch after 600 s. When "-1" is set, the drive recorder function is disabled. Setting range: -1 to 32767 0 [s] PF23 OSCL1 Vibration tough drive - Oscillation detection level This is used to set a filter readjustment sensitivity of [Pr. PB13 Machine resonance suppression filter 1] and [Pr. PB15 Machine resonance suppression filter 2] while the vibration tough drive is enabled. Example: When you set "50" to the parameter, the filter will be readjusted at the time of 50% or more oscillation level. Setting range: 0 to 100 50 [%] PF24 *OSCL2 Vibration tough drive function selection _ _ _ x Oscillation detection alarm selection Select alarm or warning when an oscillation continues at a filter readjustment sensitivity level of [Pr. PF23]. The digit is continuously enabled regardless of the vibration tough drive in [Pr. PA20]. 0: [AL. 54 Oscillation detection] will occur at oscillation detection. 1: [AL. F3.1 Oscillation detection warning] will occur at oscillation detection. 2: Oscillation detection function disabled 0h _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting 0h _ x _ _ 0h x _ _ _ 0h PF25 CVAT SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time) Set the time of the [AL. 10.1 Voltage drop in the power] occurrence. To disable the parameter, select "Disabled (_ 0 _ _)" of "SEMI-F47 function selection (instantaneous power failure tough drive selection)" in [Pr. PA20]. When "Enabled (_ 1 _ _)" is selected of "SEMI-F47 function selection (instantaneous power failure tough drive selection)" in [Pr. PA20], the power should be off for the setting value of this parameter + 1.5 s or more before cycling the power to enable a parameter whose symbol is preceded by "*". Setting range: 30 to 2000 200 [ms] PF31 FRIC Machine diagnosis function - Friction judgement speed Set a servo motor speed to divide a friction estimation area into high and low for the friction estimation process of the machine diagnosis. However, setting "0" will be the value half of the rated speed. When your operation pattern is under rated speed, we recommend that you set half value to the maximum speed with this. Maximum speed in operation [Pr. PF31] setting Operation pattern 0 r/min Servo motor speed Forward rotation direction Reverse rotation direction Setting range: 0 to permissible speed 0 [r/min] 5. PARAMETERS 5 - 44 MEMO 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 1 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT POINT In the torque control mode, you do not need to make gain adjustment. Before making gain adjustment, check that your machine is not being operated at maximum torque of the servo motor. If operated over maximum torque, the machine may vibrate and may operate unexpectedly. In addition, make gain adjustment with a safety margin considering characteristic differences of each machine. It is recommended that generated torque during operation is under 90% of the maximum torque of the servo motor. 6.1 Different adjustment methods 6.1.1 Adjustment on a single servo amplifier The following table shows the gain adjustment modes that can be set on a single servo amplifier. For gain adjustment, first execute "Auto tuning mode 1". If you are not satisfied with the result of the adjustment, execute "Auto tuning mode 2" and "Manual mode" in this order. (1) Gain adjustment mode explanation Gain adjustment mode [Pr. PA08] setting Estimation of load to motor inertia ratio Automatically set parameters Manually set parameters Auto tuning mode 1 (initial value) _ _ _ 1 Always estimated GD2 ([Pr. PB06]) PG1 ([Pr. PB07]) PG2 ([Pr. PB08]) VG2 ([Pr. PB09]) VIC ([Pr. PB10]) RSP ([Pr. PA09]) Auto tuning mode 2 _ _ _ 2 PG1 ([Pr. PB07]) PG2 ([Pr. PB08]) VG2 ([Pr. PB09]) VIC ([Pr. PB10]) GD2 ([Pr. PB06]) RSP ([Pr. PA09]) Manual mode _ _ _ 3 Fixed to [Pr. PB06] value GD2 ([Pr. PB06]) PG1 ([Pr. PB07]) PG2 ([Pr. PB08]) VG2 ([Pr. PB09]) VIC ([Pr. PB10]) 2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) _ _ _ 0 Always estimated GD2 ([Pr. PB06]) PG2 ([Pr. PB08]) VG2 ([Pr. PB09]) VIC ([Pr. PB10]) PG1 ([Pr. PB07]) RSP ([Pr. PA09]) 2 gain adjustment mode 2 _ _ _ 4 Fixed to [Pr. PB06] value PG2 ([Pr. PB08]) VG2 ([Pr. PB09]) VIC ([Pr. PB10]) GD2 ([Pr. PB06]) PG1 ([Pr. PB07]) RSP ([Pr. PA09]) 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 2 (2) Adjustment sequence and mode usage 2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) Interpolation made for 2 or more axes? The load fluctuation is large during driving? Start End Yes No Yes No Yes No No Yes One-touch tuning Yes Yes Yes Error handling is possible? Handle the error Adjustment OK? Finished normally? 2 gain adjustment mode 2 Manual mode Auto tuning mode 1 Yes Adjustment OK? Auto tuning mode 2 No No No Adjustment OK? Adjustment OK? No 6.1.2 Adjustment using MR Configurator2 This section explains the functions and adjustment using the servo amplifier with MR Configurator2. Function Description Adjustment Machine analyzer With the machine and servo motor coupled, the characteristic of the mechanical system can be measured by giving a random vibration command from a personal computer to the servo and measuring the machine response. You can grasp the machine resonance frequency and determine the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 3 6.2 One-touch tuning You can execute the one-touch tuning with MR Configurator2 or push buttons. The following parameters are set automatically with one-touch tuning. Table 6.1 List of parameters automatically set with one-touch tuning Parameter Symbol Name Parameter Symbol Name PA08 ATU Auto tuning mode PB14 NHQ1 Notch shape selection 1 PA09 RSP Auto tuning response PB15 NH2 Machine resonance suppression filter 2 PB16 NHQ2 Notch shape selection 2 PB01 FILT Adaptive tuning mode (adaptive filter II) PB18 LPF Low-pass filter setting PB19 VRF11 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency PB02 VRFT Vibration suppression control tuning mode (advanced vibration suppression control II) PB20 VRF12 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency PB21 VRF13 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping PB03 PST Position command acceleration/deceleration time constant (position smoothing) PB22 VRF14 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB23 VFBF Low-pass filter selection PB07 PG1 Model loop gain PB47 NHQ3 Notch shape selection 3 PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB48 NH4 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB49 NHQ4 Notch shape selection 4 PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation PB51 NHQ5 Notch shape selection 5 PB12 OVA Overshoot amount compensation PE41 EOP3 Function selection E-3 PB13 NH1 Machine resonance suppression filter 1 6.2.1 One-touch tuning flowchart (1) When you use MR Configurator2 Make one-touch tuning as follows. Startup a system referring to chapter 4. Rotate the servo motor by an external controller, etc. (The one-touch tuning cannot be performed if the servo motor is not operating.) Start one-touch tuning of MR Configurator2. Select a response mode (high mode, basic mode, and low mode) in the one-touch tuning window of MR Configurator2. Start Startup of the system Operation One-touch tuning start Response mode selection One-touch tuning execution End Push the start button to start one-touch tuning. Push it during motor driving. When one-touch tuning is completed normally, the parameters described in table 6.1 will be set automatically. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 4 (2) When you use push buttons Make one-touch tuning as follows. Startup a system referring to chapter 4. Rotate the servo motor by an external controller, etc. (The one-touch tuning cannot be performed if the servo motor is not operating.) Select the initial screen ("AUTO") of the one-touch tuning with the "MODE" button during motor driving. Push the "SET" button for 2 s or more during displaying "AUTO" to switch to the response mode selection ("AUTO."). Push the "MODE" and "SET" buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the response mode selection ("AUTO.") without going through the initial screen of the one- touch tuning ("AUTO"). The initial value of response mode is "AUTO." (basic mode). As necessary, push the "UP" or "DOWN" button to select "AUTO.H" (high mode) or "AUTO.L" (low mode). Start Startup of the system Operation One-touch tuning start Response mode selection One-touch tuning execution End Push the "SET" button to start one-touch tuning. Push the "SET" button during servo motor driving. When one-touch tuning is completed normally, the parameters described in table 6.1 will be set automatically. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 5 6.2.2 Display transition and operation procedure of one-touch tuning (1) When you use MR Configurator2 (a) Response mode selection Select a response mode from three modes in the one-touch tuning window of MR Configurator2. Response mode Explanation High mode This mode is for high rigid system. Basic mode This mode is for standard system. Low mode This mode is for low rigid system. Refer to the following table for selecting a response mode. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 6 Response mode Machine characteristic Low mode Basic mode High mode Response Guideline of corresponding machine Low response High response General machine tool conveyor Arm robot Precision working machine Inserter Mounter Bonder 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 7 (b) One-touch tuning execution POINT For equipment in which overshoot during one-touch tuning is in the permissible level of the in-position range, changing the value of [Pr. PA25 One-touch tuning - Overshoot permissible level] will shorten the settling time and improve the response. After the response mode is selected in (a), pushing the start button during driving will start one-touch tuning. If the start button is pushed while the motor stops, "C 0 0 2" or "C 0 0 4" will be displayed at status in error code. (Refer to table 6.2 of (1) (d) of this section for error codes.) During processing of one-touch tuning, the status will be displayed in the progress window as follows. One-touch tuning will be finished at 100%. Completing the one-touch tuning starts writing tuning parameters to the servo amplifier. "0 0 0 0" is displayed at status in error code. In addition, settling time and overshoot amount will be displayed in "Adjustment result" after adjustment. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 8 (c) Stop of one-touch tuning During one-touch tuning, pushing the stop button stops one-touch tuning. If the one-touch tuning is stopped, "C 0 0 0" will be displayed at status in error code. (d) Error occurrence If a tuning error occurs during tuning, one-touch tuning will be forcibly terminated. With that, the following error code will be displayed in status. Check the cause of tuning error. Table 6.2 Error code list during one-touch tuning Error code Name Description Action C000 Tuning canceled The stop button or "SET" of the push button was pushed. C001 Overshoot exceeded The overshoot amount is lager than the value set in [Pr. PA10 In-position range]. Increase the in-position range. C002 Servo-off during tuning The one-touch tuning was attempted during servo-off. Perform the one-touch tuning after servo-on. C003 Control mode error The one-touch tuning was attempted while the torque control mode was selected in the control modes. Select the position control mode or speed control mode for the control mode from the controller, and then make one-touch tuning. C004 Time-out 1. One cycle time during the operation has been over 30 s. Set the one cycle time during the operation to 30 s or less. 2. The command speed is low. Set the servo motor speed to100 r/min or higher. 3. The operation interval of the continuous operation is short. Maintain the operation interval during motor driving about 200 ms. C005 Load to motor inertia ratio misestimated 1. The estimation of the load to motor inertia ratio at one-touch tuning was a failure. Drive the motor with meeting conditions as follows. Time to reach 2000 r/min is the acceleration/deceleration time constant of 5 s or less. Speed is 150 r/min or higher. The load to motor inertia ratio is 100 times or less. The acceleration/deceleration torque is 10% or more of the rated torque. 2. The load to motor inertia ratio was not estimated due to such as an oscillation. Set to the auto tuning mode that does not estimate the load to motor inertia ratio as follows, and then execute the one-touch tuning. Select "Auto tuning mode 2 (_ _ _ 2)", "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)", or "2 gain adjustment mode 2 (_ _ _ 4)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08]. Set [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio] properly with manual setting. C00F One-touch tuning disabled "One-touch tuning function selection" in [Pr. PA21] is "Disabled (_ _ _ 0)". Select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)". (e) If an alarm occurs If an alarm occurs during tuning, one-touch tuning will be forcibly terminated. Remove the cause of the alarm and execute one-touch tuning again. (f) If a warning occurs If a warning which continue the motor driving occurs during the tuning, one-touch tuning will be continued. If a warning which does not continue the motor driving occurs during the tuning, one-touch tuning will be stopped. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 9 (g) Clearing one-touch tuning You can clear the parameter values set with one-touch tuning. Refer to table 6.1 for the parameters which you can clear. Pushing "Return to value before tuning" in the one-touch tuning window of MR Configurator2 enables to rewrite the parameter to the value before pushing the start button. In addition, pushing "Return to initial value" in the one-touch tuning window enables to rewrite the parameter to the initial value. When clearing one-touch tuning is completed, the following window will be displayed. (returning to initial value) 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 10 (2) When you use push buttons POINT Push the "MODE" and "SET" buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the response mode selection ("AUTO.") without going through the initial screen of the one-touch tuning ("AUTO"). (a) Response mode selection Select a response mode of the one-touch tuning from 3 modes with "UP" or "DOWN". Refer to (1) (a) of this section for a guideline of response mode. Response mode selection display Low mode: This mode is for low rigid system. Basic mode: This mode is for standard system. High mode: This mode is for high rigid system. DOWNUP 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 11 (b) One-touch tuning execution POINT For equipment in which overshoot during one-touch tuning is in the permissible level of the in-position range, changing the value of [Pr. PA25 One-touch tuning - Overshoot permissible level] will shorten the settling time and improve the response. After the response mode is selected in (a), pushing the "SET" button will start one-touch tuning. Completing the one-touch tuning will start writing the auto-tuned parameters to the servo amplifier. The one-touch tuning progress is displayed with 0% to 100%. The decimal point moves left to right in rotation during the tuning. To switch the display to the status display during the tuning, push the "MODE" button. One-touch tuning in progress Complete (c) Stop of one-touch tuning The stop symbol and error code "C 000" (cancel during tuning) will be displayed by turns with 2 s interval. 2 s interval Error code The one-touch tuning mode can be stopped by pushing the "SET" button regardless of displayed item. Stop symbol Initial screen Pushing the "SET" button will switch to the initial screen. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 12 (d) If an error occurs Check the error cause referring table 6.2 of (1) (d) of this section. 2 s interval Error code If an error occurs during the one-touch tuning, the tuning will be forcibly terminated and the stop symbol and error code from "C 001" to "C 00F" will be displayed by turns with 2 s interval. Stop symbol Initial screen Pushing the "SET" button will switch to the initial screen. (e) If an alarm occurs If an alarm occurs during tuning, one-touch tuning will be forcibly terminated and the alarm No. will be displayed. One-touch tuning in progress Alarm display (f) If a warning occurs If a warning occurs during tuning, the alarm No. of the warning will be displayed. When the warning is one which continue the motor driving, the one-touch tuning will be continued. One-touch tuning in progress Alarm display (warning) 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 13 (g) Clearing one-touch tuning Refer to table 6.1 for the parameters which you can clear. You can initialize the parameters changed by the one-touch tuning with the clear mode. You can reset the parameters to before tuning with the back mode. 1) Push the "MODE" button to switch to the initial screen "AUTO" of the one-touch tuning. 2) Select the clear mode or back mode with the "UP" or "DOWN" button. One-touch tuning clear mode selection DOWNUP To clear the one-touch tuning, push the "SET" button for 2 s. The one-touch tuning clear mode is in progress. The clear mode symbol flickers for 3 s. Clearing one-touch tuning is completed, the initial screen will be displayed. One-touch tuning clear mode display (initializing) Initial screen Auto mode Clear mode Back mode 6.2.3 Caution for one-touch tuning (1) The tuning is not available in the torque control mode. (2) The one-touch tuning cannot be executed while an alarm or warning which withholds the motor driving is occurring. (3) You can execute the one-touch tuning during the following test operation modes marked by "". Test operation mode How to one-touch tuning Output signal (DO) forced output JOG operation Positioning operation Motor-less operation Program operation MR Configurator2 Push buttons 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 14 6.3 Auto tuning 6.3.1 Auto tuning mode The servo amplifier has a real-time auto tuning function which estimates the machine characteristic (load to motor inertia ratio) in real time and automatically sets the optimum gains according to that value. This function permits ease of gain adjustment of the servo amplifier. (1) Auto tuning mode 1 The servo amplifier is factory-set to the auto tuning mode 1. In this mode, the load to motor inertia ratio of a machine is always estimated to set the optimum gains automatically. The following parameters are automatically adjusted in the auto tuning mode 1. Parameter Symbol Name PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB07 PG1 Model loop gain PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation POINT The auto tuning mode 1 may not be performed properly if all of the following conditions are not satisfied. Time to reach 2000 r/min is the acceleration/deceleration time constant of 5 s or less. Speed is 150 r/min or higher. The load to motor inertia ratio is 100 times or less. The acceleration/deceleration torque is 10% or more of the rated torque. Under operating conditions which will impose sudden disturbance torque during acceleration/deceleration or on a machine which is extremely loose, auto tuning may not function properly, either. In such cases, use the auto tuning mode 2 or manual mode to make gain adjustment. (2) Auto tuning mode 2 Use the auto tuning mode 2 when proper gain adjustment cannot be made by auto tuning mode 1. Since the load to motor inertia ratio is not estimated in this mode, set the value of a correct load to motor inertia ratio in [Pr. PB06]. The following parameters are automatically adjusted in the auto tuning mode 2. Parameter Symbol Name PB07 PG1 Model loop gain PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 15 6.3.2 Auto tuning mode basis The block diagram of real-time auto tuning is shown below. Loop gain PG1, PG2, VG2, VIC Current control Load to motor inertia ratio estimation section Gain table [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio] Response level setting Gain adjustment mode selection [Pr. PA08] + - + - Real-time auto tuning section Set 0 or 1 to turn on. Switch Current feedback Position/speed feedback Speed feedback Load moment of inertia Encoder Command Automatic setting [Pr. PA09] M Servo motor 000 When a servo motor is accelerated/decelerated, the load to motor inertia ratio estimation section always estimates the load to motor inertia ratio from the current and speed of the servo motor. The results of estimation are written to [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio]. These results can be confirmed on the status display screen of the MR Configurator2. If you have already known the value of the load to motor inertia ratio or failed to estimate, set "Gain adjustment mode selection" to "Auto tuning mode 2 (_ _ _ 2)" in [Pr. PA08] to stop the estimation (turning off the switch in above diagram), and set the load to motor inertia ratio ([Pr. PB06]) manually. From the preset load to motor inertia ratio ([Pr. PB06]) value and response ([Pr. PA09]), the optimum loop gains are automatically set on the basis of the internal gain table. The auto tuning results are saved in the EEP-ROM of the servo amplifier every 60 minutes since power-on. At power-on, auto tuning is performed with the value of each loop gain saved in the EEP-ROM being used as an initial value. POINT If sudden disturbance torque is imposed during operation, the load to motor inertia ratio may be misestimated temporarily. In such a case, set "Gain adjustment mode selection" to "Auto tuning mode 2 (_ _ _ 2)" in [Pr. PA08] and then set the correct load to motor inertia ratio in [Pr. PB06]. When any of the auto tuning mode 1 and auto tuning mode settings is changed to the manual mode 2 setting, the current loop gains and load to motor inertia ratio estimation value are saved in the EEP-ROM. 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 16 6.3.3 Adjustment procedure by auto tuning Since auto tuning is enabled before shipment from the factory, simply running the servo motor automatically sets the optimum gains that match the machine. Merely changing the response level setting value as required completes the adjustment. The adjustment procedure is as follows. Auto tuning adjustment Acceleration/deceleration repeated Auto tuning conditions are not satisfied? (Estimation of load to motor inertia ratio is difficult.) Load to motor inertia ratio estimation value stable? Set [Pr. PA08] to "_ _ _ 2" and set [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio] manually. Adjust response level setting so that desired response is achieved on vibration-free level. To 2 gain adjustment mode 2 Requested performance satisfied? End Yes No Yes No No Yes Acceleration/deceleration repeated 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 17 6.3.4 Response level setting in auto tuning mode Set the response of the whole servo system by [Pr. PA09]. As the response level setting is increased, the track ability and settling time for a command decreases, but a too high response level will generate vibration. Hence, make setting until desired response is obtained within the vibration-free range. If the response level setting cannot be increased up to the desired response because of machine resonance beyond 100 Hz, filter tuning mode selection in [Pr. PB01] or machine resonance suppression filter in [Pr. PB13] to [Pr. PB16], and [Pr. PB46] to [Pr. PB51] may be used to suppress machine resonance. Suppressing machine resonance may allow the response level setting to increase. Refer to section 7.1.1 and 7.1.2 for settings of the adaptive tuning mode and machine resonance suppression filter. [Pr. PA09] Machine characteristic Machine characteristic Setting value Response Guideline for machine resonance frequency [Hz] Setting value Response Guideline for machine resonance frequency [Hz] 1 Low response 2.7 21 Middle response 67.1 2 3.6 22 75.6 3 4.9 23 85.2 4 6.6 24 95.9 5 10.0 25 108.0 6 11.3 26 121.7 7 12.7 27 137.1 8 14.3 28 154.4 9 16.1 29 173.9 10 18.1 30 195.9 11 20.4 31 220.6 12 23.0 32 248.5 13 25.9 33 279.9 14 29.2 34 315.3 15 32.9 35 355.1 16 37.0 36 400.0 17 41.7 37 446.6 18 47.0 38 501.2 19 52.9 39 571.5 20 Middle response 59.6 40 High response 642.7 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 18 6.4 Manual mode If you are not satisfied with the adjustment of auto tuning, you can make simple manual adjustment with three parameters. POINT If machine resonance occurs, filter tuning mode selection in [Pr. PB01] or machine resonance suppression filter in [Pr. PB13] to [Pr. PB16] and [Pr. PB46] to [Pr. PB51] may be used to suppress machine resonance. (Section 7.1.1, 7.1.2) (1) For speed control (a) Parameter The following parameters are used for gain adjustment. Parameter Symbol Name PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB07 PG1 Model loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation (b) Adjustment procedure Step Operation Description 1 Brief-adjust with auto tuning. Refer to section 6.3.3. 2 Change the setting of auto tuning to the manual mode ([Pr. PA08]: _ _ _ 3). 3 Set an estimated value to the load to motor inertia ratio. (If the estimate value with auto tuning is correct, setting change is not required.) 4 Set a slightly smaller value to the model loop gain Set a slightly larger value to the speed integral compensation. 5 Increase the speed loop gain within the vibration- and unusual noise-free range, and return slightly if vibration takes place. Increase the speed loop gain. 6 Decrease the speed integral compensation within the vibration- free range, and return slightly if vibration takes place. Decrease the time constant of the speed integral compensation. 7 Increase the model loop gain, and return slightly if overshoot takes place. Increase the model loop gain. 8 If the gains cannot be increased due to mechanical system resonance or the like and the desired response cannot be achieved, response may be increased by suppressing resonance with the adaptive tuning mode or machine resonance suppression filter and then executing steps 3 to 7. Suppression of machine resonance Refer to section 7.1.1 and 7.1.2. 9 While checking the motor status, fine-adjust each gain. Fine adjustment 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 19 (c) Parameter adjustment 1) [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] This parameter determines the response level of the speed control loop. Increasing the setting increases the response level, but the mechanical system is liable to vibrate. The actual response frequency of the speed loop is as indicated in the following expression. Speed loop response frequency [Hz] = (1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) × 2 Speed loop gain 2) [Pr. PB10 Speed integral compensation] To eliminate stationary deviation against a command, the speed control loop is under proportional integral control. For the speed integral compensation, set the time constant of this integral control. Increasing the setting lowers the response level. However, if the load to motor inertia ratio is large or the mechanical system has any vibratory element, the mechanical system is liable to vibrate unless the setting is increased to some degree. The guideline is as indicated in the following expression. Speed integral compensation setting [ms] 2000 to 3000 Speed loop gain/(1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) 3) [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] This parameter determines the response level to a speed command. Increasing the value improves track ability to a speed command, but a too high value will make overshoot liable to occur at settling. Estimated model loop gain (1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) Speed loop gain × 8 1 4 1 to (2) For position control (a) Parameter The following parameters are used for gain adjustment. Parameter Symbol Name PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB07 PG1 Model loop gain PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 20 (b) Adjustment procedure Step Operation Description 1 Brief-adjust with auto tuning. Refer to section 6.3.3. 2 Change the setting of auto tuning to the manual mode ([Pr. PA08]: _ _ _ 3). 3 Set an estimated value to the load to motor inertia ratio. (If the estimate value with auto tuning is correct, setting change is not required.) 4 Set a slightly smaller value to the model loop gain and the position loop gain. Set a slightly larger value to the speed integral compensation. 5 Increase the speed loop gain within the vibration- and unusual noise-free range, and return slightly if vibration takes place. Increase the speed loop gain. 6 Decrease the speed integral compensation within the vibration- free range, and return slightly if vibration takes place. Decrease the time constant of the speed integral compensation. 7 Increase the position loop gain, and return slightly if vibration takes place. Increase the position loop gain. 8 Increase the model loop gain, and return slightly if overshoot takes place. Increase the model loop gain. 9 If the gains cannot be increased due to mechanical system resonance or the like and the desired response cannot be achieved, response may be increased by suppressing resonance with the adaptive tuning mode or machine resonance suppression filter and then executing steps 3 to 8. Suppression of machine resonance Section 7.1.1 and 7.1.2 10 While checking the settling characteristic and motor status, fine- adjust each gain. Fine adjustment (c) Parameter adjustment 1) [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] This parameter determines the response level of the speed control loop. Increasing the setting increases the response level, but the mechanical system is liable to vibrate. The actual response frequency of the speed loop is as indicated in the following expression. Speed loop response frequency [Hz] = (1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) × 2 Speed loop gain 2) [Pr. PB10 Speed integral compensation] To eliminate stationary deviation against a command, the speed control loop is under proportional integral control. For the speed integral compensation, set the time constant of this integral control. Increasing the setting lowers the response level. However, if the load to motor inertia ratio is large or the mechanical system has any vibratory element, the mechanical system is liable to vibrate unless the setting is increased to some degree. The guideline is as indicated in the following expression. Speed integral compensation setting [ms] 2000 to 3000 Speed loop gain/(1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 21 3) [Pr. PB08 Position loop gain] This parameter determines the response level to a disturbance to the position control loop. Increasing the position loop gain increases the response level to a disturbance, but the mechanical system is liable to vibrate. Position loop gain guideline (1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) Speed loop gain × 8 1 4 1 to 4) [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] This parameter determines the response level to a position command. Increasing the value improves track ability to a position command, but a too high value will make overshoot liable to occur at settling. Estimated model loop gain (1 + Load to motor inertia ratio) Speed loop gain × 8 1 4 1 to 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 22 6.5 2 gain adjustment mode The 2 gain adjustment mode is used to match the position loop gains of the axes when performing the interpolation operation of servo motors of two or more axes for an X-Y table or the like. In this mode, manually set the model loop gain that determines command track ability. Other parameters for gain adjustment are set automatically. (1) 2 gain adjustment mode 1 For the 2 gain adjustment mode 1, manually set the model loop gain that determines command track ability. The mode constantly estimates the load to motor inertia ratio, and automatically set other parameters for gain adjustment to optimum gains using auto tuning response. The following parameters are used for 2 gain adjustment mode 1. (a) Automatically adjusted parameter The following parameters are automatically adjusted by auto tuning. Parameter Symbol Name PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation (b) Manually adjusted parameter The following parameters are adjustable manually. Parameter Symbol Name PA09 RSP Auto tuning response PB07 PG1 Model loop gain (2) 2 gain adjustment mode 2 Use 2 gain adjustment mode 2 when proper gain adjustment cannot be made with 2 gain adjustment mode 1. Since the load to motor inertia ratio is not estimated in this mode, set the value of a proper load to motor inertia ratio in [Pr. PB06]. The following parameters are used for 2 gain adjustment mode 2. (a) Automatically adjusted parameter The following parameters are automatically adjusted by auto tuning. Parameter Symbol Name PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation (b) Manually adjusted parameter The following parameters are adjustable manually. Parameter Symbol Name PA09 RSP Auto tuning response PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB07 PG1 Model loop gain 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 23 (3) Adjustment procedure of 2 gain adjustment mode POINT Set the same value in [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] for the axis used in 2 gain adjustment mode. Step Operation Description 1 Set to the auto tuning mode. Select the auto tuning mode 1. 2 During operation, increase the response level setting value in [Pr. PA09], and return the setting if vibration occurs. Adjustment in auto tuning mode 1 3 Check value of the model loop gain and the load to motor inertia ratio in advance. Check the upper setting limits. 4 Set the 2 gain adjustment mode 1 ([Pr. PA08]: _ _ _ 0). Select the 2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode). 5 When the load to motor inertia ratio is different from the design value, select the 2 gain adjustment mode 2 ([Pr. PA08]: _ _ _ 4) and then set the load to motor inertia ratio manually in [Pr. PB06]. Check the load to motor inertia ratio. 6 Set the model loop gain of all the axes to be interpolated to the same value. At that time, adjust to the setting value of the axis, which has the smallest model loop gain. Set position loop gain. 7 Considering the interpolation characteristic and motor status, fine-adjust the model loop gain and response level setting. Fine adjustment (4) Parameter adjustment [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] This parameter determines the response level of the position control loop. Increasing the value improves track ability to a position command, but a too high value will make overshoot liable to occur at settling. The droop pulse value is determined by the following expression. Number of droop pulses [pulse] = Model loop gain setting Position command frequency [pulse/s] Position command frequency = Speed [r/min] 60 × Encoder resolution (number of pulses per servo motor revolution) 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 - 24 MEMO 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 1 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS POINT The functions given in this chapter need not be used normally. Use them if you are not satisfied with the machine status after making adjustment in the methods in chapter 6. 7.1 Filter setting The following filters are available with MR-JE servo amplifiers. Command pulse train Command filter Low-pass filter setting Encoder Servo motor PWM M Load [Pr. PB18] + - Machine resonance suppression filter 1 [Pr. PB13] [Pr. PB15] [Pr. PB46] Machine resonance suppression filter 2 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 Machine resonance suppression filter 5 Shaft resonance suppression filter Robust filter [Pr. PB48] [Pr. PB50] [Pr. PB17] Speed control [Pr. PB49] [Pr. PE41] 7.1.1 Machine resonance suppression filter POINT The machine resonance suppression filter is a delay factor for the servo system. Therefore, vibration may increase if you set an incorrect resonance frequency or set notch characteristics too deep or too wide. If the frequency of machine resonance is unknown, decrease the notch frequency from higher to lower ones in order. The optimum notch frequency is set at the point where vibration is minimal. A deeper notch has a higher effect on machine resonance suppression but increases a phase delay and may increase vibration. A deeper notch has a higher effect on machine resonance suppression but increases a phase delay and may increase vibration. The machine characteristic can be grasped beforehand by the machine analyzer on MR Configurator2. This allows the required notch frequency and notch characteristics to be determined. If a mechanical system has a natural resonance point, increasing the servo system response level may cause the mechanical system to produce resonance (vibration or unusual noise) at that resonance frequency. Using the machine resonance suppression filter and adaptive tuning can suppress the resonance of the mechanical system. The setting range is 10 Hz to 4500 Hz. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 2 (1) Function The machine resonance suppression filter is a filter function (notch filter) which decreases the gain of the specific frequency to suppress the resonance of the mechanical system. You can set the gain decreasing frequency (notch frequency), gain decreasing depth and width. Response of mechanical system Notch characteristics Machine resonance point Notch frequency Frequency Frequency Notch width Notch depth You can set five machine resonance suppression filters at most. Filter Setting parameter Precaution Parameter that is reset with vibration tough drive function Parameter automatically adjusted with one- touch tuning Machine resonance suppression filter 1 PB01/PB13/PB14 The filter can be set automatically with "Filter tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB01]. PB13 PB01/PB13/PB14 Machine resonance suppression filter 2 PB15/PB16 PB15 PB15/PB16 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 PB46/PB47 PB47 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 PB48/PB49 Enabling the filter disables the shaft resonance suppression filter. The shaft resonance suppression filter is enabled for the initial setting. PB48/PB49 Machine resonance suppression filter 5 PB50/PB51 The setting of this filter is disabled while you use the robust filter. The robust filter is disabled for the initial setting. PB51 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 3 (2) Parameter (a) Machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]) Set the notch frequency, notch depth and notch width of the machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]) When you select "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)" of "Filter tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB01], the setting of the machine resonance suppression filter 1 is enabled. (b) Machine resonance suppression filter 2 ([Pr. PB15] and [Pr. PB16]) To use this filter, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 2 selection" in [Pr. PB16]. How to set the machine resonance suppression filter 2 ([Pr. PB15] and [Pr. PB16]) is the same as for the machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]). (c) Machine resonance suppression filter 3 ([Pr. PB46] and [Pr. PB47]) To use this filter, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 3 selection" in [Pr. PB47]. How to set the machine resonance suppression filter 3 ([Pr. PB46] and [Pr. PB47]) is the same as for the machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]). (d) Machine resonance suppression filter 4 ([Pr. PB48] and [Pr. PB49]) To use this filter, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 4 selection" in [Pr. PB49]. However, enabling the machine resonance suppression filter 4 disables the shaft resonance suppression filter. How to set the machine resonance suppression filter 4 ([Pr. PB48] and [Pr. PB49]) is the same as for the machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]). (e) Machine resonance suppression filter 5 ([Pr. PB50] and [Pr. PB51]) To use this filter, select "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" of "Machine resonance suppression filter 5 selection" in [Pr. PB51]. However, enabling the robust filter ([Pr. PE41: _ _ _ 1]) disables the machine resonance suppression filter 5. How to set the machine resonance suppression filter 5 ([Pr. PB50] and [Pr. PB51]) is the same as for the machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]). 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 4 7.1.2 Adaptive filter II POINT The machine resonance frequency which adaptive filter II (adaptive tuning) can respond to is about 100 Hz to 2.25 kHz. As for the resonance frequency out of the range, set manually. When adaptive tuning is executed, vibration sound increases as an excitation signal is forcibly applied for several seconds. When adaptive tuning is executed, machine resonance is detected for a maximum of 10 s and a filter is generated. After filter generation, the adaptive tuning mode automatically shifts to the manual setting. Adaptive tuning generates the optimum filter with the currently set control gains. If vibration occurs when the response setting is increased, execute adaptive tuning again. During adaptive tuning, a filter having the best notch depth at the set control gain is generated. To allow a filter margin against machine resonance, increase the notch depth in the manual setting. Adaptive vibration suppression control may provide no effect on a mechanical system which has complex resonance characteristics. (1) Function Adaptive filter II (adaptive tuning) is a function in which the servo amplifier detects machine vibration for a predetermined period of time and sets the filter characteristics automatically to suppress mechanical system vibration. Since the filter characteristics (frequency, depth) are set automatically, you need not be conscious of the resonance frequency of a mechanical system. Response of mechanical systemNotch depth Machine resonance point Notch frequency Frequency Frequency Response of mechanical systemNotch depth Machine resonance point Notch frequency Frequency Frequency When machine resonance is large and frequency is low When machine resonance is small and frequency is high (2) Parameter Select how to set the filter tuning in [Pr. PB01 Adaptive tuning mode (adaptive filter II)]. [Pr. PB01] Filter tuning mode selection 000 0 1 2 Setting value Filter tuning mode selection Disabled Automatic setting Manual setting PB13/PB14 Automatically set parameter 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 5 (3) Adaptive tuning mode procedure Tuning ends automatically after the predetermined period of time. ([Pr. PB01] will be "_ _ _ 2" or "_ _ _ 0".) Adaptive tuning Operation Is the target response reached? Decrease the response until vibration or unusual noise is resolved. End Yes No No Yes Increase the response setting. Has vibration or unusual noise occurred? Has vibration or unusual noise been resolved? Using the machine analyzer, set the filter manually. Yes No Execute or re-execute adaptive tuning. (Set [Pr. PB01] to "_ _ _ 1".) Factor The response has increased to the machine limit. The machine is too complicated to provide the optimum filter. If assumption fails after tuning is executed at a large vibration o r oscillation, decrease the response setting temporarily down to the vibration level and execute again. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 6 7.1.3 Shaft resonance suppression filter (1) Function When a load is mounted to the servo motor shaft, resonance by shaft torsion during driving may generate a mechanical vibration at high frequency. The shaft resonance suppression filter suppresses the vibration. When you select "Automatic setting", the filter will be set automatically on the basis of the motor you use and the load to motor inertia ratio. The disabled setting increases the response of the servo amplifier for high resonance frequency. (2) Parameter Set "Shaft resonance suppression filter selection" in [Pr. PB23]. [Pr. PB23] Shaft resonance suppression filter selection 0: Automatic setting 1: Manual setting 2: Disabled 010 To set [Pr. PB17 Shaft resonance suppression filter] automatically, select "Automatic setting". To set [Pr. PB17 Shaft resonance suppression filter] manually, select "Manual setting". The setting values are as follows. Shaft resonance suppression filter setting frequency selection Setting value Frequency [Hz] Setting value Frequency [Hz] _ _ 0 0 Disabled _ _ 1 0 562 _ _ 0 1 Disabled _ _ 1 1 529 _ _ 0 2 4500 _ _ 1 2 500 _ _ 0 3 3000 _ _ 1 3 473 _ _ 0 4 2250 _ _ 1 4 450 _ _ 0 5 1800 _ _ 1 5 428 _ _ 0 6 1500 _ _ 1 6 409 _ _ 0 7 1285 _ _ 1 7 391 _ _ 0 8 1125 _ _ 1 8 375 _ _ 0 9 1000 _ _ 1 9 360 _ _ 0 A 900 _ _ 1 A 346 _ _ 0 B 818 _ _ 1 B 333 _ _ 0 C 750 _ _ 1 C 321 _ _ 0 D 692 _ _ 1 D 310 _ _ 0 E 642 _ _ 1 E 300 _ _ 0 F 600 _ _ 1 F 290 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 7 7.1.4 Low-pass filter (1) Function When a ball screw or the like is used, resonance of high frequency may occur as the response level of the servo system is increased. To prevent this, the low-pass filter is enabled for a torque command as the initial value. The filter frequency of the low-pass filter is automatically adjusted to the value in the following equation. Filter frequency ([rad/s]) = 1 + GD2 VG2 × 10 To set [Pr. PB18] manually, select "Manual setting (_ _ 1 _)" of "Low-pass filter selection" in [Pr. PB23]. (2) Parameter Set "Low-pass filter selection" in [Pr. PB23]. [Pr. PB23] Low-pass filter selection 0: Automatic setting 1: Manual setting 2: Disabled 01 0 7.1.5 Advanced vibration suppression control II POINT The function is enabled when "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08] is "Auto tuning mode 2 (_ _ _ 2)", "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)", or "2 gain adjustment mode 2 (_ _ _ 4)". The machine resonance frequency supported in the vibration suppression control tuning mode is 1.0 Hz to 100.0 Hz. As for the vibration out of the range, set manually. Stop the servo motor before changing the vibration suppression control-related parameters. Otherwise, it may cause an unexpected operation. For positioning operation during execution of vibration suppression control tuning, provide a stop time to ensure a stop after vibration damping. Vibration suppression control tuning may not make normal estimation if the residual vibration at the servo motor side is small. Vibration suppression control tuning sets the optimum parameter with the currently set control gains. When the response setting is increased, set vibration suppression control tuning again. When using the vibration suppression control 2, set "_ _ _ 1" in [Pr. PA24]. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 8 (1) Function Vibration suppression control is used to further suppress load-side vibration, such as work-side vibration and base shake. The servo motor-side operation is adjusted for positioning so that the machine does not vibrate. Vibration suppression: off (normal) Servo motor side Load side t Position Vibration suppression control: on Servo motor side Load side Position t When the advanced vibration suppression control II ([Pr. PB02 Vibration suppression control tuning mode]) is executed, the vibration frequency at load side is automatically estimated to suppress machine side vibration two times at most. In the vibration suppression control tuning mode, this mode shifts to the manual setting after the positioning operation is performed the predetermined number of times. For manual setting, adjust the vibration suppression control 1 with [Pr. PB19] to [Pr. PB22] and vibration suppression control 2 with [Pr. PB52] to [Pr. PB55]. (2) Parameter Set [Pr. PB02 Vibration suppression control tuning mode (advanced vibration suppression control II)]. When you use a vibration suppression control, set "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection". When you use two vibration suppression controls, set "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" in addition. [Pr. PB02] Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode 00 _ _ _ 0 _ _ _ 1 _ _ _ 2 Setting value Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection Disabled Automatic setting Manual setting PB19/PB20/PB21/PB22 Automatically set parameter Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode _ _ 0 _ _ _ 1 _ _ _ 2 _ Setting value Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection Disabled Automatic setting Manual setting PB52/PB53/PB54/PB55 Automatically set parameter 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 9 (3) Vibration suppression control tuning procedure The following flow chart is for the vibration suppression control 1. For the vibration suppression control 2, set "_ _ 1 _" in [Pr. PB02] to execute the vibration suppression control tuning. No Vibration suppression control tuning Operation Is the target response reached? Execute or re-execute vibration suppression control tuning. (Set [Pr. PB02] to "_ _ _ 1".) Decrease the response until vibration of workpiece end/device is resolved. End Yes No No Yes Increase the response setting. Has vibration of workpiece end/device increased? Has vibration of workpiece end/device been resolved? Using a machine analyzer or considering load-side vibration waveform, set the vibration suppression control manually. Factor Estimation cannot be made as load-side vibration has not been transmitted to the servo motor side. The response of the model loop gain has increased to the load-side vibration frequency (vibration suppression control limit). Yes Tuning ends automatically after positioning operation is performed the predetermined number of times. ([Pr. PB02] will be "_ _ _ 2" or "_ _ _ 0".) Stop operation. Resume operation. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 10 (4) Vibration suppression control manual mode POINT When load-side vibration does not show up in servo motor-side vibration, the setting of the servo motor-side vibration frequency does not produce an effect. When the anti-resonance frequency and resonance frequency can be confirmed using the machine analyzer or external equipment, do not set the same value but set different values to improve the vibration suppression performance. A vibration suppression control effect is not produced if the relation between the [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] value and vibration frequency is as follows. Vibration suppression control 1: [Pr. PB19] < 2 1 (0.9 × [Pr. PB07]) [Pr. PB20] < 2 1 (0.9 × [Pr. PB07]) Vibration suppression control 2: [Pr. PB19] < [Pr. PB52] [Pr. PB52] < 5.0 + 0.1 × [Pr. PB07] [Pr. PB53] < 5.0 + 0.1 × [Pr. PB07] [Pr. PB07] < 2 (0.3 × [Pr. PB19] + 8 1 × [Pr. PB52]) 1.1 < [Pr. PB52] / [Pr. PB19] < 5.5 Measure work-side vibration and device shake with the machine analyzer or external measuring instrument, and set the following parameters to adjust vibration suppression control manually. Setting item Vibration suppression control 1 Vibration suppression control 2 Vibration suppression control - Vibration frequency [Pr. PB19] [Pr. PB52] Vibration suppression control - Resonance frequency [Pr. PB20] [Pr. PB53] Vibration suppression control - Vibration frequency damping [Pr. PB21] [Pr. PB54] Vibration suppression control - Resonance frequency damping [Pr. PB22] [Pr. PB55] Step 1. Select "Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)" of "Vibration suppression control 1 tuning mode selection" or "Manual setting (_ _ 2 _)" of "Vibration suppression control 2 tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB02]. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 11 Step 2. Set "Vibration suppression control - Vibration frequency" and "Vibration suppression control - Resonance frequency" as follows. (a) When a vibration peak can be confirmed with machine analyzer using MR Configurator2, or external equipment. 1 Hz Gain characteristics Phase -90 deg. 300 Hz Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency (anti-resonance frequency) [Pr. PB19] Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency [Pr. PB20] Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency (anti-resonance frequency) [Pr. PB52] Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency [Pr. PB53] Resonance of more than 300 Hz is not the target of control. (b) When vibration can be confirmed using monitor signal or external sensor t Motor-side vibration (droop pulses) Position command frequency t External acceleration pickup signal, etc. Vibration suppression control - Vibration frequency Vibration suppression control - Resonance frequency Set the same value. Vibration cycle [Hz] Vibration cycle [Hz] Step 3. Fine-adjust "Vibration suppression control - Vibration frequency damping" and "Vibration suppression control - Resonance frequency damping". 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 12 7.1.6 Command notch filter POINT By using the advanced vibration suppression control II and the command notch filter, the load-side vibration of three frequencies can be suppressed. The frequency range of machine vibration, which can be supported by the command notch filter, is between 4.5 Hz and 2250 Hz. Set a frequency close to the machine vibration frequency and within the range. When [Pr. PB45 Command notch filter] is changed during the positioning operation, the changed setting is not reflected. The setting is reflected approximately 150 ms after the servo motor stops (after servo-lock). (1) Function Command notch filter has a function that lowers the gain of the specified frequency contained in a position command. By lowering the gain, load-side vibration, such as work-side vibration and base shake, can be suppressed. Which frequency to lower the gain and how deep to lower the gain can be set. Position Load side t Command notch filter: disabled Load side t Position Command notch filter: enabled 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 13 (2) Parameter Set [Pr. PB45 Command notch filter] as shown below. For the command notch filter setting frequency, set the closest value to the vibration frequency [Hz] at the load side. Setting value Command notch filter setting frequency Setting value Frequency [Hz] 00 01 02 03 0 Frequency [Hz] Setting value Frequency [Hz] 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2A 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3A 3B 3C 3D 3E 3F 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 4F 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 5A 5B 5C 5D 5E 5F Disabled 2250 1125 750 562 450 375 321 281 250 225 204 187 173 160 150 140 132 125 118 112 107 102 97 93 90 86 83 80 77 75 72 70 66 62 59 56 53 51 48 46 45 43 41 40 38 37 36 35.2 33.1 31.3 29.6 28.1 26.8 25.6 24.5 23.4 22.5 21.6 20.8 20.1 19.4 18.8 18.2 17.6 16.5 15.6 14.8 14.1 13.4 12.8 12.2 11.7 11.3 10.8 10.4 10.0 9.7 9.4 9.1 8.8 8.3 7.8 7.4 7.0 6.7 6.4 6.1 5.9 5.6 5.4 5.2 5.0 4.9 4.7 4.5 Notch depth 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F Setting value Depth [dB] [Pr. PB45] -40.0 -24.1 -18.1 -14.5 -12.0 -10.1 -8.5 -7.2 -6.0 -5.0 -4.1 -3.3 -2.5 -1.8 -1.2 -0.6 7.2 Gain switching function You can switch gains with the function. You can switch gains during rotation and during stop, and can use an input device to switch gains during operation. 7.2.1 Applications The following shows when you use the function. (1) You want to increase the gains during servo-lock but decrease the gains to reduce noise during rotation. (2) You want to increase the gains during settling to shorten the stop settling time. (3) You want to change the gains using an input device to ensure stability of the servo system since the load to motor inertia ratio varies greatly during a stop (e.g. a large load is mounted on a carrier). 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 14 7.2.2 Function block diagram The control gains, load to motor inertia ratio, and vibration suppression control settings are changed according to the conditions selected by [Pr. PB26 Gain switching function] and [Pr. PB27 Gain switching condition]. Command pulse frequency + - Droop pulses Model speed Input device (CDP) Comparator Changing CDP [Pr. PB26] + - + - GD2 [Pr. PB06] GD2B [Pr. PB29] Enabled GD2 value PG1 [Pr. PB07] PG1B [Pr. PB60] Enabled PG1 value PG2 [Pr. PB08] PG2B [Pr. PB30] Enabled PG2 value VG2 [Pr. PB09] VG2B [Pr. PB31] Enabled VG2 value VIC [Pr. PB10] VICB [Pr. PB32] Enabled VIC value VRF11 [Pr. PB19] VRF11B [Pr. PB33] Enabled VRF11 value VRF12 [Pr. PB20] VRF12B [Pr. PB34] Enabled VRF12 value CDL [Pr. PB27] VRF13 [Pr. PB21] VRF13B [Pr. PB35] Enabled VRF13 value VRF14 [Pr. PB22] VRF14B [Pr. PB36] Enabled VRF14 value VRF21 [Pr. PB52] VRF21B [Pr. PB56] Enabled VRF21 value VRF22 [Pr. PB53] VRF22B [Pr. PB57] Enabled VRF22 value VRF23 [Pr. PB54] VRF23B [Pr. PB58] Enabled VRF23 value VRF24 [Pr. PB55] VRF24B [Pr. PB59] Enabled VRF24 value 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 15 7.2.3 Parameter When using the gain switching function, always select "Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)" of "Gain adjustment mode selection" in [Pr. PA08 Auto tuning mode]. The gain switching function cannot be used in the auto tuning mode. (1) Variable gain operation setting parameter Parameter Symbol Name Unit Description PB26 CDP Gain switching selection Used to select the changing condition. PB27 CDL Gain switching condition [kpulse/s] /[pulse] /[r/min] Used to set the changing condition values. PB28 CDT Gain switching time constant [ms] You can set the filter time constant for a gain change at changing. (a) [Pr. PB26 Gain switching function] Used to set the gain switching condition. Select the switching condition in the first digit and second digit. Gain switching selection 0: Disabled 1: Input device ((CDP) gain switching ) 2: Command frequency 3: Droop pulses 4: Servo motor speed 00 Gain switching condition 0: Gain after switching is enabled with gain switching condition or more 1: Gain after switching is enabled with gain switching condition or less [Pr. PB26] (b) [Pr. PB27 Gain switching condition] Set a level to switch gains after you select "Command frequency", "Droop pulses", or "Servo motor speed" in [Pr. PB26 Gain switching function]. The setting unit is as follows. Gain switching condition Unit Command frequency [kpulse/s] Droop pulses [pulse] Servo motor speed [r/min] (c) [Pr. PB28 Gain switching time constant] You can set the primary delay filter to each gain at gain switching. This parameter is used to suppress shock given to the machine if the gain difference is large at gain switching, for example. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 16 (2) Switchable gain parameter Before switching After switching Loop gain Parameter Symbol Name Parameter Symbol Name Load to motor inertia ratio PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio PB29 GD2B Gain switching Load to motor inertia ratio Model loop gain PB07 PG1 Model loop gain PB60 PG1B Gain switching Model loop gain Position loop gain PB08 PG2 Position loop gain PB30 PG2B Gain switching Position loop gain Speed loop gain PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain PB31 VG2B Gain switching Speed loop gain Speed integral compensation PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation PB32 VICB Gain switching Speed integral compensation Vibration suppression control 1 Used to set the value of the after-changing vibration suppression control vibration frequency setting. PB19 VRF11 Vibration suppression control 1 Used to set the value of the after-changing vibration suppression control vibration frequency setting. PB33 VRF11B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency after gain switching Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency PB20 VRF12 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency PB34 VRF12B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency after gain switching Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping PB21 VRF13 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping PB35 VRF13B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping PB22 VRF14 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping PB36 VRF14B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency PB52 VRF21 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency PB56 VRF21B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency after gain switching Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency PB53 VRF22 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency PB57 VRF22B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency after gain switching Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping PB54 VRF23 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping PB58 VRF23B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping PB55 VRF24 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping PB59 VRF24B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching (a) [Pr. PB06] to [Pr. PB10] These parameters are the same as in ordinary manual adjustment. Gain switching allows the values of load to motor inertia ratio, position loop gain, speed loop gain, and speed integral compensation to be switched. (b) [Pr.PB19] to [Pr.PB22]/[Pr.PB52] to [Pr.PB55] These parameters are the same as in ordinary manual adjustment. You can switch the vibration frequency, resonance frequency, vibration frequency damping, and resonance frequency damping by switching gain during motor stop. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 17 (c) [Pr. PB29 Load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching] Set the load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching. If the load to motor inertia ratio does not change, set it to the same value as [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio]. (d) [Pr. PB30 Position loop gain after gain switching], [Pr. PB31 Speed loop gain after gain switching], and [Pr. PB32 Speed integral compensation after gain switching] Set the values of after switching position loop gain, speed loop gain and speed integral compensation. (e) Vibration suppression control after gain switching ([Pr. PB33] to [Pr. PB36]/[Pr. PB56] to [Pr. PB59])/[Pr. PB60 Model loop gain after gain switching] The gain switching vibration suppression control and model loop gain are used only with input device (CDP) on/off. You can switch the vibration frequency, resonance frequency, vibration frequency damping, resonance frequency damping, and model loop gain of the vibration suppression control 1 and vibration suppression control 2. 7.2.4 Gain switching procedure This operation will be described by way of setting examples. (1) When you choose switching by input device (CDP) (a) Setting Parameter Symbol Name Setting value Unit PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio 4.00 [Multiplier] PB07 PG1 Model loop gain 100 [rad/s] PB08 PG2 Position loop gain 120 [rad/s] PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain 3000 [rad/s] PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation 20 [ms] PB19 VRF11 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency 50 [Hz] PB20 VRF12 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency 50 [Hz] PB21 VRF13 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping 0.20 PB22 VRF14 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping 0.20 PB52 VRF21 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency 20 [Hz] PB53 VRF22 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency 20 [Hz] PB54 VRF23 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping 0.10 PB55 VRF24 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping 0.10 PB29 GD2B Gain switching Load to motor inertia ratio 10.00 [Multiplier] PB60 PG1B Model loop gain after gain switching 50 [rad/s] PB30 PG2B Gain switching position loop gain 84 [rad/s] PB31 VG2B Gain switching speed loop gain 4000 [rad/s] PB32 VICB Speed integral compensation after gain switching 50 [ms] PB26 CDP Gain switching function 0001 (Switch by input device (CDP) on/off.) 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 18 Parameter Symbol Name Setting value Unit PB28 CDT Gain switching time constant 100 [ms] PB33 VRF11B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency after gain switching 60 [Hz] PB34 VRF12B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency after gain switching 60 [Hz] PB35 VRF13B Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching 0.15 PB36 VRF14B Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching 0.15 PB56 VRF21B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency after gain switching 30 [Hz] PB57 VRF22B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency after gain switching 30 [Hz] PB58 VRF23B Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping after gain switching 0.05 PB59 VRF24B Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping after gain switching 0.05 (b) Switching timing chart After-switching gain 63.4% CDT = 100 ms Before-switching gain Gain switching CDP (gain switching) OFF ON OFF Model loop gain 100 50 100 Load to motor inertia ratio 4.00 10.00 4.00 Position loop gain 120 84 120 Speed loop gain 3000 4000 3000 Speed integral compensation 20 50 20 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency 50 60 50 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency 50 60 50 Vibration suppression control 1 - Vibration frequency damping 0.20 0.15 0.20 Vibration suppression control 1 - Resonance frequency damping 0.20 0.15 0.20 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency 20 30 20 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency 20 30 20 Vibration suppression control 2 - Vibration frequency damping 0.10 0.05 0.10 Vibration suppression control 2 - Resonance frequency damping 0.10 0.05 0.10 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 19 (2) When you choose switching by droop pulses In this case, the vibration suppression control after gain switching and model loop gain after gain switching cannot be used. (a) Setting Parameter Symbol Name Setting value Unit PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio 4.00 [Multiplier] PB08 PG2 Position loop gain 120 [rad/s] PB09 VG2 Speed loop gain 3000 [rad/s] PB10 VIC Speed integral compensation 20 [ms] PB29 GD2B Load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching 10.00 [Multiplier] PB30 PG2B Gain switching position loop gain 84 [rad/s] PB31 VG2B Gain switching speed loop gain 4000 [rad/s] PB32 VICB Speed integral compensation after gain switching 50 [ms] PB26 CDP Gain switching selection 0003 (switching by droop pulses) PB27 CDL Gain switching condition 50 [pulse] PB28 CDT Gain switching time constant 100 [ms] (b) Switching timing chart After-switching gain 63.4% CDT = 100 ms Before-switching gain Gain switching Droop pulses [pulse] +CDL -CDL 0 Command pulses Droop pulses Command pulses Load to motor inertia ratio 4.00 10.00 4.00 10.00 Position loop gain 120 84 120 84 Speed loop gain 3000 4000 3000 4000 Speed integral compensation 20 50 20 50 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 20 7.3 Tough drive function POINT Set enable/disable of the tough drive function with [Pr. PA20 Tough drive setting]. (Refer to section 5.2.1.) This function makes the equipment continue operating even under the condition that an alarm occurs. 7.3.1 Vibration tough drive function This function prevents vibration by resetting a filter instantaneously when machine resonance occurs due to varied vibration frequency caused by machine aging. To reset the machine resonance suppression filters with the function, [Pr. PB13 Machine resonance suppression filter 1] and [Pr. PB15 Machine resonance suppression filter 2] should be set in advance. Set [Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB15] as follows. (1) One-touch tuning execution (section 6.2) (2) Manual setting (section 5.2.2) The vibration tough drive function operates when a detected machine resonance frequency is within ±30% for a value set in [Pr. PB13 Machine resonance suppression filter 1] or [Pr. PB15 Machine resonance suppression filter 2]. To set a detection level of the function, set sensitivity in [Pr. PF23 Vibration tough drive - Oscillation detection level]. POINT Resetting [Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB15] by the vibration tough drive function is performed constantly. However, the number of write times to the EEPROM is limited to once per hour. The vibration tough drive function does not reset [Pr. PB46 Machine resonance suppression filter 3], [Pr. PB48 Machine resonance suppression filter 4], and [Pr. PB50 Machine resonance suppression filter 5]. The vibration tough drive function does not detect a vibration of 100 Hz or less. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 21 The following shows the function block diagram of the vibration tough drive function. The function detects machine resonance frequency and compare it with [Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB15], and reset a machine resonance frequency of a parameter whose set value is closer. Filter Setting parameter Precaution Parameter that is reset with vibration tough drive function Machine resonance suppression filter 1 PB01/PB13/PB14 The filter can be set automatically with "Filter tuning mode selection" in [Pr. PB01]. PB13 Machine resonance suppression filter 2 PB15/PB16 PB15 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 PB46/PB47 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 PB48/PB49 Enabling the filter disables the shaft resonance suppression filter. The shaft resonance suppression filter is enabled for the initial setting. Machine resonance suppression filter 5 PB50/PB51 The setting of this filter is disabled while you use the robust filter. The robust filter is disabled for the initial setting. Command pulse train Command filter Encoder Servo motor PWM M Load + - Machine resonance suppression filter 1 [Pr. PB13] [Pr. PB15] [Pr. PB46] Machine resonance suppression filter 2 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 Machine resonance suppression filter 4 Machine resonance suppression filter 5 Shaft resonance suppression filter Robust filter [Pr. PB48] [Pr. PB50] [Pr. PB17] [Pr. PB49] [Pr. PE41] Updates the parameter whose setting is the closest to the machine resonance frequency. Vibration tough drive Torque ALM (Malfunction) WNG (Warning) MTTR (During tough drive) ON OFF [Pr. PF23 Vibration tough drive - Oscillation detection level] Detects the machine resonance and reconfigures the filter automatically. During tough drive (MTTR) is not turned on in the vibration tough drive function. ON OFF ON OFF 5 s 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 22 7.3.2 Instantaneous power failure tough drive function CAUTION The immunity to instantaneous power failures is increased by the instantaneous power failure tough drive function. However, it is not guarantee to comply with the SEMI-F47 standard. The instantaneous power failure tough drive function avoids [AL. 10 Undervoltage] even when an instantaneous power failure occurs during operation. When the instantaneous power failure tough drive activates, the function will increase the immunity to instantaneous power failures using the electrical energy charged in the capacitor in the servo amplifier and will change an alarm level of [AL. 10 Undervoltage] simultaneously. The [AL. 10.1 Voltage drop in the power] detection time for the power supply can be changed by [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)]. In addition, [AL.10.2 Bus voltage drop] detection level for the bus voltage is changed automatically. POINT MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) will not turn off during the instantaneous power failure tough drive. Selecting "Enabled (_ _ _ 1)" for "Torque limit function selection at instantaneous power failure" in [Pr. PA26] will limit torques to save electric energy when an instantaneous power failure occurs during operation and will make [AL. 10 Undervoltage] less likely to occur. When the load of instantaneous power failure is large, the undervoltage alarm ([AL. 10.2]) caused by the bus voltage drop may occur regardless of the set value of [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)]. 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 23 (1) Instantaneous power failure time > [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)] The alarm occurs when the instantaneous power failure time exceeds [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)]. MTTR (During tough drive) turns on after the instantaneous power failure is detected. MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off when the alarm occurs. Power supply Bus voltage Undervoltage level (158 V DC) A LM (Malfunction) [Pr. PF25] Instantaneous power failure time MTTR (During tough drive) MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) Base circuit ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF WNG (Warning) ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 24 (2) Instantaneous power failure time < [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function - Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive - detection time)] Operation status differs depending on how bus voltage decrease. (a) When the bus voltage decreases lower than 158 V DC within the instantaneous power failure time [AL. 10 Undervoltage] occurs when the bus voltage decrease lower than 158 V DC regardless of the enabled instantaneous power failure tough drive. Power supply Bus voltage Undervoltage level (158 V DC) A LM (Malfunction) [Pr. PF25] Instantaneous power failure time MTTR (During tough drive) MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) Base circuit ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF WNG (Warning) ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 25 (b) When the bus voltage does not decrease lower than 158 V DC within the instantaneous power failure time The operation continues without alarming. Power supply Bus voltage Undervoltage level (158 V DC) A LM (Malfunction) [Pr. PF25] Instantaneous power failure time MTTR (During tough drive) MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) Base circuit ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF WNG (Warning) ON OFF 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 - 26 MEMO 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 1 8. TROUBLESHOOTING POINT As soon as an alarm occurs, turn SON (Servo-on) off and interrupt the power. 8.1 Alarm and warning list When an error occurs during operation, the corresponding alarm or warning is displayed. If any alarm or warning has occurred, refer to section 8.2 or 8.3 and take the appropriate action. When an alarm occurs, ALM will turn off. To output alarm codes, set [Pr. PD34] to "_ _ _ 1". Alarm codes are outputted by on/off of bit 0 to bit 2. Warnings ([AL. 91] to [AL. F3]) do not have alarm codes. The alarm codes in the following table will be outputted when they occur. The alarm codes will not be outputted in normal condition. After its cause has been removed, the alarm can be deactivated in any of the methods marked in the alarm deactivation column. Warnings are automatically canceled after the cause of occurrence is removed. For the alarms and warnings in which "SD" is written in the stop method column, the servo motor stops with the dynamic brake after forced stop deceleration. For the alarms and warnings written "DB" in the stop method column, the servo motor stops with the dynamic brake without forced stop deceleration. Table 8.1 Alarm list Alarm code Alarm deactivation No. CN1 49 (Bit 2) CN1 23 (Bit 1) CN1 24 (Bit 0) Name Detailed display Detail name Stop method (Note 2, 3) Alarm reset (RES) Press the "SET" button on the current alarm screen. Power off to On (Note 4) 10.1 Voltage drop in the power DB 10 0 1 0 Undervoltage 10.2 Bus voltage drop SD 12.1 RAM error 1 DB Alarm 12.2 RAM error 2 DB 12 0 0 0 Memory error 1 (RAM) 12.4 RAM error 4 DB 12.5 RAM error 5 DB 13.1 Clock error 1 DB 13 0 0 0 Clock error 13.2 Clock error 2 DB 14.1 Control process error 1 DB 14.2 Control process error 2 DB 14.3 Control process error 3 DB 14.4 Control process error 4 DB 14.5 Control process error 5 DB 14 0 0 0 Control process error 14.6 Control process error 6 DB 14.7 Control process error 7 DB 14.8 Control process error 8 DB 14.9 Control process error 9 DB 14.A Control process error 10 DB 15.1 EEP-ROM error at power on DB 15 0 0 0 Memory error 2 (EEP-ROM) 15.2 EEP-ROM error during operation DB 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 2 Alarm code Alarm deactivation No. CN1 49 (Bit 2) CN1 23 (Bit 1) CN1 24 (Bit 0) Name Detailed display Detail name Stop method (Note 2, 3) Alarm reset (RES) Press the "SET" button on the current alarm screen. Power off to On (Note 4) 16.1 Encoder initial communication - Receive data error 1 DB 16.2 Encoder initial communication - Receive data error 2 DB 16.3 Encoder initial communication - Receive data error 3 DB Alarm 16.5 Encoder initial communication - Transmission data error 1 DB 16.6 Encoder initial communication - Transmission data error 2 DB 16.7 Encoder initial communication - Transmission data error 3 DB 16 1 1 0 Encoder initial communication error 1 16.A Encoder initial communication - Process error 1 DB 16.B Encoder initial communication - Process error 2 DB 16.C Encoder initial communication - Process error 3 DB 16.D Encoder initial communication - Process error 4 DB 16.E Encoder initial communication - Process error 5 DB 16.F Encoder initial communication - Process error 6 DB 17.1 Board error 1 DB 17 0 0 0 Board error 17.3 Board error 2 DB 17.4 Board error 3 DB 19.1 FLASH-ROM error 1 DB 19 0 0 0 Memory error 3 (FLASH-ROM) 19.2 FLASH-ROM error 2 DB 1A 1 1 0 Servo motor combination error 1A.1 Servo motor combination error DB 1E 1 1 0 Encoder initial communication error 2 1E.1 Encoder malfunction DB 1F 1 1 0 Encoder initial communication error 3 1F.1 Incompatible encoder DB 20.1 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 1 DB 20.2 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 2 DB 20.3 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 3 DB 20.5 Encoder normal communication - Transmission data error 1 DB 20 1 1 0 Encoder normal communication error 1 20.6 Encoder normal communication - Transmission data error 2 DB 20.7 Encoder normal communication - Transmission data error 3 DB 20.9 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 4 DB 20.A Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 5 DB 21.1 Encoder data error 1 DB 21.2 Encoder data update error DB 21.3 Encoder data waveform error DB 21 1 1 0 Encoder normal communication error 2 21.5 Encoder hardware error 1 DB 21.6 Encoder hardware error 2 DB 21.9 Encoder data error 2 DB 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 3 Alarm code Alarm deactivation No. CN1 49 (Bit 2) CN1 23 (Bit 1) CN1 24 (Bit 0) Name Detailed display Detail name Stop method (Note 2, 3) Alarm reset (RES) Press the "SET" button on the current alarm screen. Power off to On (Note 4) 24.1 Ground fault detected by hardware detection circuit DB Alarm 24 1 0 0 Main circuit error 24.2 Ground fault detected by software detection function DB 30.1 Regeneration heat error DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 30 0 0 1 Regenerative error (Note 1) 30.2 Regeneration signal error DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 30.3 Regeneration feedback signal error DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 31 1 0 1 Overspeed 31.1 Abnormal motor speed SD 32.1 Overcurrent detected at hardware detection circuit (during operation) DB 32.2 Overcurrent detected at software detection function (during operation) DB 32 1 0 0 Overcurrent 32.3 Overcurrent detected at hardware detection circuit (during a stop) DB 32.4 Overcurrent detected at software detection function (during a stop) DB 33 0 0 1 Overvoltage 33.1 Main circuit voltage error DB 35 1 0 1 Command frequency error 35.1 Command frequency error SD 37.1 Parameter setting range error DB 37 0 0 0 Parameter error 37.2 Parameter combination error DB 45 0 1 1 Main circuit device overheat (Note 1) 45.1 Main circuit device overheat error SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 46.1 Abnormal temperature of servo motor 1 SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 46 0 1 1 Servo motor overheat (Note 1) 46.5 Abnormal temperature of servo motor 3 DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 46.6 Abnormal temperature of servo motor 4 DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 47 0 1 1 Cooling fan error 47.2 Cooling fan speed reduction error SD 50.1 Thermal overload error 1 during operation SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 50.2 Thermal overload error 2 during operation SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 50.3 Thermal overload error 4 during operation SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 50 0 1 1 Overload 1 (Note 1) 50.4 Thermal overload error 1 during a stop SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 50.5 Thermal overload error 2 during a stop SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 50.6 Thermal overload error 4 during a stop SD (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 51.1 Thermal overload error 3 during operation DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 51 0 1 1 Overload 2 (Note 1) 51.2 Thermal overload error 3 during a stop DB (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 1) 52.1 Excess droop pulse 1 SD 52.3 Excess droop pulse 2 SD 52 1 0 1 Error excessive 52.4 Error excessive during 0 torque limit SD 52.5 Excess droop pulse 3 DB 54 0 1 1 Oscillation detection 54.1 Oscillation detection error DB 56.2 Over speed during forced stop DB 56 1 1 0 Forced stop error 56.3 Estimated distance over during forced stop DB 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 4 Alarm code Alarm deactivation No. CN1 49 (Bit 2) CN1 23 (Bit 1) CN1 24 (Bit 0) Name Detailed display Detail name Stop method (Note 2, 3) Alarm reset (RES) Press the "SET" button on the current alarm screen. Power off to On (Note 4) 8A 0 0 0 USB communication time- out error 8A.1 USB communication time-out error SD Alarm 8E.1 USB communication receive error SD 8E.2 USB communication checksum error SD 8E 0 0 0 USB communication error 8E.3 USB communication character error SD 8E.4 USB communication command error SD 8E.5 USB communication data number error SD 88888 Watchdog 8888._Watchdog SD Note 1. Leave for about 30 minutes of cooling time after removing the cause of occurrence. 2. Stop method indicates as follows: DB: Stop with dynamic brake SD: Forced stop deceleration 3. This is applicable when [Pr. PA04] is set to the initial value. The stop system of SD can be changed to DB using [Pr. PA04]. 4. To cancel the alarm, turn off the power and check that the 5-digit, 7-segment LED display is off, and then turn on the power. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 5 Table 8.2 Warning list No. Name Detailed display Detail name Stop method (Note 2, 3) 91 Servo amplifier overheat warning (Note 1) 91.1 Main circuit device overheat warning 99.1 Forward rotation stroke end off (Note 4) Warning 99 Stroke limit warning 99.2 Reverse rotation stroke end off (Note 4) E0 Excessive regeneration warning (Note 1) E0.1 Excessive regeneration warning E1.1 Thermal overload warning 1 during operation E1.2 Thermal overload warning 2 during operation E1.3 Thermal overload warning 3 during operation E1 Overload warning 1 (Note 1) E1.4 Thermal overload warning 4 during operation E1.5 Thermal overload error 1 during a stop E1.6 Thermal overload error 2 during a stop E1.7 Thermal overload error 3 during a stop E1.8 Thermal overload error 4 during a stop E6 Servo forced stop warning E6.1 Forced stop warning SD E8 Cooling fan speed reduction warning E8.1 Decreased cooling fan speed warning E9.1 Servo-on signal on during main circuit off DB E9 Main circuit off warning E9.2 Bus voltage drop during low speed operation DB EC Overload warning 2 (Note 1) EC.1 Overload warning 2 ED Output watt excess warning ED.1 Output watt excess warning F0.1 Instantaneous power failure tough drive warning F0 Tough drive warning F0.3 Vibration tough drive warning F2.1 Drive recorder - Area writing time-out warning F2 Drive recorder - Miswriting warning F2.2 Drive recorder - Data miswriting warning F3 Oscillation detection warning F3.1 Oscillation detection warning Note 1. Leave for about 30 minutes of cooling time after removing the cause of occurrence. 2. Stop method indicates as follows: DB: Stop with dynamic brake SD: Forced stop deceleration 3. This is applicable when [Pr. PA04] is set to the initial value. The stop system of SD can be changed to DB using [Pr. PA04]. 4. Quick stop or slow stop can be selected using [Pr. PD30]. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 6 8.2 Remedies for alarms CAUTION When any alarm has occurred, eliminate its cause, ensure safety, and deactivate the alarm before restarting operation. Otherwise, it may cause injury. As soon as an alarm occurs, make the Servo-off status and interrupt the power. POINT When any of the following alarms has occurred, do not cycle the power repeatedly to restart. Doing so will cause a malfunction of the servo amplifier and servo motor. Remove its cause and allow about 30 minutes for cooling before resuming the operation. [AL. 30 Regenerative error] [AL. 45 Main circuit device overheat] [AL. 46 Servo motor overheat] [AL. 50 Overload 1] [AL. 51 Overload 2] Remove the cause of the alarm in accordance with this section. Use MR Configurator2 to refer to the cause of alarm occurrence. Alarm No.: 10 or less Name: Undervoltage Alarm content The power supply voltage dropped. The bus voltage dropped. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 10.1 Voltage drop in the power (1) Check the power connector. It has a failure. Connect it correctly. The connection of the power connector has a failure. It has no failure. Check (2). (2) Power supply voltage is low. The voltage is lower than 160 V AC. Review the voltage of the power supply. Check if the voltage of the power supply is 160 V AC or lower. The voltage is higher than 160 V AC. Check (3). (3) An instantaneous power failure has occurred for longer time than the specified time. The time will be 60 ms when [Pr. PA20] is "_ 0 _ _". The time will be the value set in [Pr. PF25] when [Pr. PA20] is "_ 1 _ _". Check if the power has a problem. It has a problem. Review the power. 10.2 (1) It has a failure. Connect it correctly. Bus voltage drop The connection of the power connector has a failure. Check the power connector. It has no failure. Check (2). (2) Power supply voltage is low. The voltage is lower than 160 V AC. Increase the power supply voltage. Check if the voltage of the power supply is 160 V AC or lower. The voltage is higher than 160 V AC. Check (3). (3) The alarm has occurred during acceleration. Check that the bus voltage during acceleration is 200 V DC or more. The voltage is less than 200 V DC. Increase the acceleration time constant. Or increase the power supply capacity. The voltage is 200 V DC or more. Check (4). (4) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Check the bus voltage value. The voltage of the power supply is 160 V AC or more, and the bus voltage is less than 200 V DC. Replace the servo amplifier. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 7 Alarm No.: 12 Name: Memory error 1 (RAM) Alarm content A part (RAM) in the servo amplifier is failure. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 12.1 RAM error 1 (1) A part in the servo amplifier is failure. It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Disconnect the cables except the power supply, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the power supply for noise. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 12.2 RAM error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 12.1]. 12.4 RAM error 4 12.5 RAM error 5 Alarm No.: 13 Name: Clock error Alarm content A part in the servo amplifier is failure. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 13.1 Clock error 1 (1) A part in the servo amplifier is failure. It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Disconnect the cables except the power supply, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the power supply for noise. Check if the connector is shorted. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 13.2 Clock error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 13.1]. Alarm No.: 14 Name: Control process error Alarm content The process did not complete within the specified time. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 14.1 (1) It is incorrect. Set it correctly. Control process error 1 The parameter setting is incorrect. Check if the parameter setting is incorrect. It is correct. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Check the power supply for noise. Check if the connector is shorted. It has no failure. Check (3). (3) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. 14.2 (1) It is incorrect. Set it correctly. Control process error 2 The parameter setting is incorrect. Check if the parameter setting is incorrect. It is correct. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Check the power supply for noise. Check if the connector is shorted. It has no failure. Check (3). (3) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. 14.3 Control process error 3 Check it with the check method for [AL. 14.1]. 14.4 Control process error 4 14.5 Control process error 5 14.6 Control process error 6 14.7 Control process error 7 14.8 Control process error 8 14.9 Control process error 9 14.A Control process error 10 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 8 Alarm No.: 15 Name: Memory error 2 (EEP-ROM) Alarm content A part (EEP-ROM) in the servo amplifier is failure. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 15.1 EEP-ROM error at power on (1) It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. EEP-ROM is malfunctioning at power on. Disconnect the cables except the power supply, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Check the power supply for noise. Check if the connector is shorted. It has no failure. Check (3). (3) The number of write times exceeded 100,000. Check if parameters has been used very frequently. It has a failure. Replace the servo amplifier. Change the process to use parameters less frequently after replacement. 15.2 EEP-ROM error during operation (1) It occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. EEP-ROM is malfunctioning during normal operation. Check if the error occurs when you change parameters during normal operation. It does not occur. Check (2). (2) It takes an hour or more. Replace the servo amplifier. A write error occurred while tuning results was processed. Check if the alarm occurs after an hour from power on. It takes less than an hour. Check (3). (3) Something near the device caused it. Check the power supply for noise. Check if the connector is shorted. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Alarm No.: 16 Name: Encoder initial communication error 1 Alarm content An error occurred in the communication between an encoder and servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 16.1 (1) An encoder cable is malfunctioning. It has a failure. Replace or repair the cable. Check if the encoder cable is disconnected or shorted. It has no failure. Check (2). Encoder initial communication - Receive data error 1 (2) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (3). (3) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (4). (4) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, vibration, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 16.2 Encoder initial communication - Receive data error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 16.1]. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 9 Alarm No.: 16 Name: Encoder initial communication error 1 Alarm content An error occurred in the communication between an encoder and servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 16.3 (1) It is not connected. Connect it correctly. An encoder cable was disconnected. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is connected. Check (2). Encoder initial communication - Receive data error 3 (2) The setting is incorrect. Set it correctly. The parameter setting of two-wire type/four-wire type is incorrect. Check the [Pr. PC22] setting. The setting is correct. Check (3). (3) An encoder cable is malfunctioning. It has a failure. Replace or repair the cable. Check if the encoder cable is disconnected or shorted. It has no failure. Check (4). (4) The power voltage has been unstable. Check the power voltage. It is an instantaneous power failure. Review the power and related parts. It has no failure. Check (5). (5) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (6). (6) An encoder is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (7). (7) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, vibration, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 16.5 Encoder initial communication - Transmission data error 1 Check it with the check method for [AL. 16.1]. 16.6 Encoder initial communication - Transmission data error 2 16.7 Encoder initial communication - Transmission data error 3 16.A (1) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Encoder initial communication - Process error 1 Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (3). (3) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, vibration, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 16.B Encoder initial communication - Process error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 16.A]. 16.C Encoder initial communication - Process error 3 16.D Encoder initial communication - Process error 4 16.E Encoder initial communication - Process error 5 16.F Encoder initial communication - Process error 6 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 10 Alarm No.: 17 Name: Board error Alarm content A part in the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 17.1 Board error 1 (1) A current detection circuit is malfunctioning. It occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. Check if the alarm occurs during the servo- on status. It does not occur. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 17.3 Board error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 17.1]. 17.4 Board error 3 (1) It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. The servo amplifier recognition signal was not read properly. Disconnect the cables except the power supply, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Alarm No.: 19 Name: Memory error 3 (FLASH-ROM) Alarm content A part (Flash-ROM) in the servo amplifier is failure. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 19.1 FLASH-ROM error 1 (1) The Flash-ROM is malfunctioning. It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Disconnect the cables except the power supply, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 19.2 FLASH-ROM error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 19.1]. Alarm No.: 1A Name: Servo motor combination error Alarm content The combination of servo amplifier and servo motor is incorrect. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 1A.1 (1) The combination is incorrect. Use them in the correct combination. Servo motor combination error The servo amplifier and the servo motor was connected incorrectly. Check the model name of the servo motor and corresponding servo amplifier. The combination is correct. Check (2). (2) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. Alarm No.: 1E Name: Encoder initial communication error 2 Alarm content An encoder is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 1E.1 (1) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. Encoder malfunction An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, vibration, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 11 Alarm No.: 1F Name: Encoder initial communication error 3 Alarm content The connected encoder is not compatible with the servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 1F.1 Incompatible encoder (1) Check the model of the servo motor. It is not compatible with the amplifier. Replace it with the servo motor which is compatible. A servo motor, which is not compatible with the servo amplifier, was connected. It is compatible with the amplifier. Check (2). (2) The software version of the servo amplifier does not support the servo motor. Check if the software version supports the servo motor. It is not supported. Replace the servo amplifier to one which software version supports the servo motor. It is supported. Check (3). (3) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Alarm No.: 20 Name: Encoder normal communication error 1 Alarm content An error occurred in the communication between an encoder and servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 20.1 (1) An encoder cable is malfunctioning. It has a failure. Repair or replace the cable. Check if the encoder cable is disconnected or shorted. It has no failure. Check (2). Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 1 (2) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (3). (3) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (4). (4) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, vibration, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 20.2 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 20.1]. 20.3 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 3 20.5 Encoder normal communication - Transmission data error 1 20.6 Encoder normal communication - Transmission data error 2 20.7 Encoder normal communication - Transmission data error 3 20.9 Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 4 20.A Encoder normal communication - Receive data error 5 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 12 Alarm No.: 21 Name: Encoder normal communication error 2 Alarm content The encoder detected an error signal. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 21.1 Encoder data error 1 (1) It is not repeatable. Use the encoder with low loop gain. The encoder detected a high speed/acceleration rate due to an oscillation or other factors. Decrease the loop gain, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (3). (3) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, vibration, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 21.2 (1) It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. Encoder data update error An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 21.3 Encoder data waveform error Check it with the check method for [AL. 21.2]. 21.5 Encoder hardware error 1 Check it with the check method for [AL. 21.2]. 21.6 Encoder hardware error 2 21.9 Encoder data error 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 21.1]. Alarm No.: 24 Name: Main circuit error Alarm content A ground fault occurred on the servo motor power lines. A ground fault occurred at the servo motor. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 24.1 (1) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. Ground fault detected by hardware detection circuit Disconnect the servo motor power cables (U, V, and W) and check if the alarm occurs. It does not occur. Check (2). (2) It is shorted. Replace the servo motor power cable. A ground fault or short occurred at the servo motor power cable. Check if only the servo motor power cable is shorted. It is not shorted. Check (3). (3) A ground fault occurred at the servo motor. It is shorted. Replace the servo motor. Disconnect the servo motor power cables on motor side, and check insulation of the motor (between U, V, W, and ). It is not shorted. Check (4). (4) They are in contact. Correct the wiring. The servo amplifier power input cable and servo motor power input cable were shorted. Shut off the power, and check if the servo amplifier power input cable and servo motor power input cable are in contact. They are not in contact. Check (5). (5) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 24.2 Ground fault detected by software detection function Check it with the check method for [AL. 24.1]. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 13 Alarm No.: 30 Name: Regenerative error Alarm content Permissible regenerative power of the built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option is exceeded. A regenerative transistor in the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 30.1 Regeneration heat error (1) The setting value is incorrect. Set it correctly. The setting of the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is incorrect. Check the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) and [Pr. PA02] setting. It is set correctly. Check (2). (2) It is not connected correctly. Connect it correctly. The regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is not connected. Check if the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is connected correctly. It is connected correctly. Check (3). (3) Power supply voltage high. Check the input power supply voltage. It is over 240 V AC. Reduce the power supply voltage. It is 240 V AC or less. Check (4). (4) The regenerative load ratio has been over 100%. Check the regenerative load ratio when alarm occurs. It is 100% or more. Reduce the frequency of positioning. Reduce the load. Use a regenerative option if it is not being used. Review the regenerative option capacity. 30.2 Regeneration signal error (1) A detection circuit of the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Check if the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is overheating. It is overheating abnormally. Replace the servo amplifier. 30.3 (1) The alarm occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. Regeneration feedback signal error A detection circuit of the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Remove the regenerative option or built-in regenerative resistor and then check if the alarm occur at power on. The alarm does not occur. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ground fault, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Alarm No.: 31 Name: Overspeed Alarm content The servo motor seed has exceeded the permissible instantaneous speed. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 31.1 (1) The command pulse frequency is high. Check the command pulse frequency. The command pulse frequency is high. Check operation pattern. Abnormal motor speed The command pulse frequency is low. Check (2). (2) The servo motor was at the maximum torque at the time of acceleration. It is the maximum torque. Increase the acceleration/deceleration time constant. Or reduce the load. Check if the torque at the time of acceleration is the maximum torque. It is lower than the maximum torque. Check (3). (3) The servo system is unstable and oscillating. Check if the servo motor is oscillating. It is oscillating. Adjust the servo gain. Or reduce the load. It is not oscillating. Check (4). (4) The velocity waveform has overshot. It is overshooting. Increase the acceleration/deceleration time constant. Check if it is overshooting because the acceleration time constant is too short. It is not overshooting. Check (5). (5) An encoder is malfunctioning. Check if the alarm is occurring during less than permissible instantaneous speed. It is occurring during less than permissible instantaneous speed. Replace the servo motor. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 14 Alarm No.: 32 Name: Overcurrent Alarm content A current higher than the permissible current was applied to the servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 32.1 (1) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. Disconnect the servo motor power cables (U, V, and W) and check if the alarm occurs. It does not occur. Check (2). Overcurrent detected at hardware detection circuit (during operation) (2) It is shorted. Replace the servo motor power cable. A ground fault or short occurred at the servo motor power cable. Check if only the servo motor power cable is shorted. It is not shorted. Check (3). (3) The servo motor is malfunctioning. A ground fault is occurring. Replace the servo motor. Disconnect the servo motor power cables on motor side, and check insulation of the motor (between U, V, W, and ). A ground fault is not occurring. Check (4). (4) The dynamic brake is malfunctioning. It occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. Check if the error occurs when you turn on the servo-on command. It does not occur. Check (5). (5) It is not correct. Wire it correctly. The connection destination of the encoder cable is incorrect. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is correct. Check (6). (6) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 32.2 (1) The servo gain is high. Check if an oscillation is occurring. An oscillation is occurring. Reduce the speed loop gain ([Pr. PB09]). An oscillation is not occurring. Check (2). Overcurrent detected at software detection function (during operation) (2) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It occurs. Replace the servo amplifier. Disconnect the servo motor power cables (U, V, and W) and check if the alarm occurs. It does not occur. Check (3). (3) It is shorted. Replace the servo motor power cable. A ground fault or short occurred at the servo motor power cable. Check if only the servo motor power cable is shorted. It is not shorted. Check (4). (4) The servo motor is malfunctioning. A ground fault is occurring. Replace the servo motor. Disconnect the servo motor power cables on motor side, and check insulation of the motor (between U, V, W, and ). A ground fault is not occurring. Check (5). (5) It is not correct. Connect it correctly. The connection destination of the encoder cable is incorrect. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is correct. Check (6). (6) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. 32.3 Overcurrent detected at hardware detection circuit (during a stop) Check it with the check method for [AL. 32.1]. 32.4 Overcurrent detected at software detection function (during a stop) Check it with the check method for [AL. 32.2]. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 15 Alarm No.: 33 Name: Overvoltage Alarm content The value of the bus voltage exceeded 400 V DC. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 33.1 Main circuit voltage error (1) The setting value is incorrect. Set it correctly. The setting of the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is incorrect. Check the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) and [Pr. PA02] setting. It is set correctly. Check (2). (2) It is not connected correctly. Connect it correctly. The regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is not connected. Check if the regenerative resistor (regenerative option) is connected correctly. It is connected correctly. Check (3). (3) Wire breakage of built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option Measure the resistance of the built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option. The resistance is abnormal. When using a built-in regenerative resistor, replace the servo amplifier. When using a regenerative option, replace the regenerative option. The resistance is normal. Check (4). (4) The regeneration capacity is insufficient. Set a longer deceleration time constant, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. When using a built-in regenerative resistor, use a regenerative option. When using a regenerative option, use a larger capacity one. It is repeatable. Check (5). (5) Power supply voltage high. Check the input voltage. It is over 264 V AC. Reduce the input voltage. It is 264 V AC or less. Check (6). (6) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Alarm No.: 35 Name: Command frequency error Alarm content Input pulse frequency of command pulse is too high. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 35.1 Command frequency error (1) The command pulse frequency is high. Check the command pulse frequency. The command pulse frequency is high. Check operation pattern. The command pulse frequency is low. Check (2). (2) Something near the device caused it. Check the noise, ambient temperature, etc. It has a failure. Take countermeasures against its cause. Alarm No.: 37 Name: Parameter error Alarm content Parameter setting is incorrect. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 37.1 (1) It is out of setting range. Set it within the range. Parameter setting range error A parameter was set out of setting range. Check the parameter error No. and setting value. It is within the setting range. Check (2). (2) The parameter setting has changed due to a servo amplifier malfunction. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. 37.2 Parameter combination error (1) A parameter setting contradicts another. Check the parameter error No. and setting value. A setting value is incorrect. Correct the setting value. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 16 Alarm No.: 45 Name: Main circuit device overheat Alarm content Inside of the servo amplifier overheated. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 45.1 (1) Ambient temperature has exceeded 55 ˚C. Check the ambient temperature. It is over 55 ˚C. Lower the ambient temperature. Main circuit device overheat error It is less than 55 ˚C. Check (2). (2) The close mounting is out of specifications. Check the specifications of close mounting. It is out of specifications. Use within the range of specifications. It is within specifications. Check (3). (3) It occurred. Check operation pattern. Turning on and off were repeated under the overload status. Check if the overload status occurred many times. It did not occur. Check (4). (4) It is not repeatable. Clean it periodically. A cooling fan, heat sink, or openings is clogged with foreign matter. Clean the cooling fan, heat sink, or openings, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (5). (5) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Alarm No.: 46 Name: Servo motor overheat Alarm content The servo motor overheated. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 46.1 (1) It is over 40 ˚C. Lower the ambient temperature. Abnormal temperature of servo motor 1 Ambient temperature of the servo motor has exceeded 40 ˚C. Check the ambient temperature of the servo motor. It is less than 40 ˚C. Check (2). (2) Servo motor is overloaded. Check the effective load ratio. The effective load ratio is high. Reduce the load or review the operation pattern. The effective load ratio is small. Check (3). (3) The thermal sensor in the encoder is malfunctioning. Check the servo motor temperature when the alarm occurs. The servo motor temperature is low. Replace the servo motor. 46.5 Abnormal temperature of servo motor 3 Check it with the check method for [AL. 46.1]. 46.6 Abnormal temperature of servo motor 4 (1) A current was applied to the servo amplifier in excess of its continuous output current. Check the effective load ratio. The effective load ratio is high. Reduce the load or review the operation pattern. Or use a larger capacity motor. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 17 Alarm No.: 47 Name: Cooling fan error Alarm content The speed of the servo amplifier cooling fan decreased. Or the cooling fan speed decreased to the alarm occurrence level or less. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 47.2 (1) Foreign matter was caught in the cooling fan. Something has been caught. Remove the foreign matter. Cooling fan speed reduction error Check if a foreign matter is caught in the cooling fan. Nothing has been caught. Check (2). (2) Cooling fan life expired. Check the cooling fan speed. The fan speed is less than the alarm occurrence level. Replace the servo amplifier. Alarm No.: 50 Name: Overload 1 Alarm content Load exceeded overload protection characteristic of servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 50.1 Thermal overload error 1 during operation (1) The servo motor power cable was disconnected. Check the servo motor power cable. It is disconnected. Repair or replace the servo motor power cable. It is not disconnected. Check (2). (2) It is incorrect. Connect it correctly. The connection of the servo motor is incorrect. Check the wiring of U, V, and W. It is correct. Check (3). (3) It is not released. Release the electromagnetic brake. The electromagnetic brake has not released. (The electromagnetic brake has been activated.) Check if the electromagnetic brake is released during operation. It is released. Check (4). (4) Check the effective load ratio. The effective load ratio is high. Reduce the load. Or use a larger capacity motor. A current was applied to the servo amplifier in excess of its continuous output current. The effective load ratio is small. Check (5). (5) It is not correct. Connect it correctly. The connection destination of the encoder cable is incorrect. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is correct. Check (6). (6) Check if it is resonating. It is resonating. Adjust gains. The servo system is unstable and resonating. It is not resonating. Check (7). (7) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (8). (8) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. 50.2 Thermal overload error 2 during operation Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.1]. 50.3 Thermal overload error 4 during operation 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 18 Alarm No.: 50 Name: Overload 1 Alarm content Load exceeded overload protection characteristic of servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 50.4 (1) Check if it collided. It collided. Check operation pattern. A moving part collided against the machine. It did not collide. Check (2). Thermal overload error 1 during a stop (2) The servo motor power cable was disconnected. Check the servo motor power cable. It is disconnected. Repair or replace the servo motor power cable. It is not disconnected. Check (3). (3) The hunting is occurring. Adjust gains. Hunting occurs during servo-lock. Check if the hunting is occurring. The hunting is not occurring. Check (4). (4) It is not released. Release the electromagnetic brake. The electromagnetic brake has not released. (The electromagnetic brake has been activated.) Check if the electromagnetic brake is released. It is released. Check (5). (5) Check the effective load ratio. The effective load ratio is high. Reduce the load. Or use a larger capacity motor. A current was applied to the servo amplifier in excess of its continuous output current. The effective load ratio is small. Check (6). (6) It is not correct. Connect it correctly. The connection destination of the encoder cable is incorrect. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is correct. Check (7). (7) Check if it is resonating. It is resonating. Adjust gains. The servo system is unstable and resonating. It is not resonating. Check (8). (8) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (9). (9) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. 50.5 Thermal overload error 2 during a stop Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.4]. 50.6 Thermal overload error 4 during a stop 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 19 Alarm No.: 51 Name: Overload 2 Alarm content Maximum output current flowed continuously due to machine collision or the like. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 51.1 Thermal overload error 3 during operation (1) The servo motor power cable was disconnected. Check the servo motor power cable. It is disconnected. Repair or replace the servo motor power cable. It is not disconnected. Check (2). (2) It is incorrect. Connect it correctly. The connection of the servo motor is incorrect. Check the wiring of U, V, and W. It is correct. Check (3). (3) It is incorrect. Connect it correctly. The connection of the encoder cable is incorrect. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is correct. Check (4). (4) The torque is insufficient.Check the peak load ratio. The torque is saturated. Reduce the load or review the operation pattern. Or use a larger capacity motor. The torque is not saturated. Check (5). (5) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (6). (6) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. 51.2 (1) Check if it collided. It collided. Check operation pattern. A moving part collided against the machine. It did not collide. Refer to (2). Thermal overload error 3 during a stop (2) The servo motor power cable was disconnected. Check it with the check method for [AL. 51.1]. (3) The connection of the servo motor is incorrect. (4) The connection of the encoder cable is incorrect. (5) The torque is saturated. (6) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. (7) An encoder is malfunctioning. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 20 Alarm No.: 52 Name: Error excessive Alarm content Droop pulses have exceeded the alarm occurrence level. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 52.1 Excess droop pulse 1 (1) The servo motor power cable was disconnected. Check the servo motor power cable. It is disconnected. Repair or replace the servo motor power cable. It is not disconnected. Check (2). (2) It is incorrect. Connect it correctly. The connection of the servo motor is incorrect. Check the wiring of U, V, and W. It is correct. Check (3). (3) It is incorrect. Connect it correctly. The connection of the encoder cable is incorrect. Check if the encoder cable is connected correctly. It is correct. Check (4). (4) The torque limit has been enabled. The limiting torque is in progress. Increase the torque limit value. Check if the limiting torque is in progress. The limiting torque is not in progress. Check (5). (5) Check if it collided. It collided. Check operation pattern. A moving part collided against the machine. It did not collide. Check (6). (6) The torque is insufficient.Check the peak load ratio. The torque is saturated. Reduce the load or review the operation pattern. Or use a larger capacity motor. The torque is not saturated. Check (7). (7) Power supply voltage dropped. Check the bus voltage value. The bus voltage is low. Check the power supply voltage and power supply capacity. The bus voltage is high. Check (8). (8) Acceleration/deceleration time constant is too short. Set a longer deceleration time constant, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Increase the acceleration/deceleration time constant. It is repeatable. Check (9). (9) The position loop gain is small. It is not repeatable. Increase the position loop gain ([Pr. PB08]). Increase the position loop gain, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (10). (10) It is rotated by external force. Review the machine. Servo motor shaft was rotated by external force. Measure the actual position under the servo- lock status. It is not rotated by external force. Check (11). (11) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. 52.3 Excess droop pulse 2 Check it with the check method for [AL. 52.1]. 52.4 Error excessive during 0 torque limit (1) The torque limit has been 0. Check the torque limit value. The torque limit has been 0. Do not input a command while the torque limit value is 0. 52.5 Excess droop pulse 3 Check it with the check method for [AL. 52.1]. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 21 Alarm No.: 54 Name: Oscillation detection Alarm content An oscillation of the servo motor was detected. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 54.1 Oscillation detection error (1) The servo system is unstable and oscillating. Check if the servo motor is oscillating. Check the torque ripple with MR Configurator2. The torque ripple is vibrating. Adjust the servo gain with the auto tuning. Set the machine resonance suppression filter. The torque ripple is not vibrating. Check (2). (2) The resonance frequency has changed due to deterioration. The resonance frequency of the equipment is different from the filter setting value. Change the setting value of the machine resonance suppression filter. Measure the resonance frequency of the equipment and compare it with the setting value o f the machine resonance suppression filter. The resonance frequency of the equipment is the same as the filter setting value. Check (3). (3) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. Alarm No.: 56 Name: Forced stop error Alarm content The servo motor does not decelerate normally during forced stop deceleration. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 56.2 (1) It is not repeatable. Adjust the deceleration time constant. Over speed during forced stop The forced stop deceleration time constant is short. Increase the parameter setting value of [Pr. PC51], and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) The torque limit has been enabled. The limiting torque is in progress. Review the torque limit value. Check if the limiting torque is in progress. The limiting torque is not in progress. Check (3). (3) The servo system is unstable and oscillating. Check if the servo motor is oscillating. Check the torque ripple with MR Configurator2. The torque ripple is vibrating. Adjust the servo gain. Set the machine resonance suppression filter. The torque ripple is not vibrating. Check (4). (4) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. 56.3 (1) It is not repeatable. Adjust the deceleration time constant. Estimated distance over during forced stop The forced stop deceleration time constant is short. Increase the parameter setting value of [Pr. PC51], and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) The torque limit has been enabled. The limiting torque is in progress. Review the torque limit value. Check if the limiting torque is in progress. The limiting torque is not in progress. Check (3). (3) An encoder is malfunctioning. Replace the servo motor, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo motor. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 22 Alarm No.: 8A Name: USB communication time-out error Alarm content Communication between the servo amplifier and a personal computer, etc. stopped for the specified time or longer. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 8A.1 (1) It was not transmitted. Transmit a command. Communication commands have not been transmitted. Check if a command was transmitted from the personal computer, etc. It was transmitted. Check (2). USB communication time-out error (2) It is not repeatable. Replace the USB cable. A USB cable was disconnected. Replace the USB cable, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (3). (3) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Alarm No.: 8E Name: USB communication error Alarm content A communication error occurred between servo amplifier and a personal computer, etc. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 8E.1 (1) It is not repeatable. Replace the USB cable. USB communication receive error A USB cable is malfunctioning. Check the USB cable, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Check (2). (2) It is incorrect. Review the settings. The setting of the personal computer, etc. is incorrect. Check the setting of the personal computer, etc. It is correct. Check (3). (3) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. 8E.2 USB communication checksum error (1) The setting of the personal computer, etc. is incorrect. Check the setting of the personal computer, etc. It is incorrect. Review the settings. 8E.3 (1) The transmitted character is out of specifications. Check the character code at the time of transmission. The transmitted character is out of specifications. Correct the transmission data. USB communication character error The transmitted character is within specifications. Check (2). (2) The communication protocol is failure. It is not conforming. Modify the transmission data according to the communication protocol. Check if transmission data conforms the communication protocol. It is conforming. Check (3). (3) The setting of the personal computer, etc. is incorrect. Check the setting of the personal computer, etc. It is incorrect. Review the settings. 8E.4 (1) The transmitted command is out of specifications. Check the command at the time of transmission. The transmitted command is out of specifications. Correct the transmission data. USB communication command error The transmitted command is within specifications. Check (2). (2) The communication protocol is failure. It is not conforming. Modify the transmission data according to the communication protocol. Check if transmission data conforms the communication protocol. It is conforming. Check (3). (3) The setting of the personal computer, etc. is incorrect. Check the setting of the personal computer, etc. It is incorrect. Review the settings. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 23 Alarm No.: 8E Name: USB communication error Alarm content A communication error occurred between servo amplifier and a personal computer, etc. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 8E.5 (1) The transmitted data number is out of specifications. Check the data number at the time of transmission. The transmitted data number is out of specifications. Correct the transmission data. USB communication data number error The transmitted data number is within specifications. Check (2). (2) The communication protocol is failure. It is not conforming. Modify the transmission data according to the communication protocol. Check if transmission data conforms the communication protocol. It is conforming. Check (3). (3) The setting of the personal computer, etc. is incorrect. Check the setting of the personal computer, etc. It is incorrect. Review the settings. Alarm No.: 88888 Name: Watchdog Alarm content A part such as CPU is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 8888._ Watchdog (1) A part in the servo amplifier is failure. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 24 8.3 Remedies for warnings POINT When any of the following alarms has occurred, do not cycle the power of the servo amplifier repeatedly to restart. Doing so will cause a malfunction of the servo amplifier and servo motor. If the power of the servo amplifier is switched off/on during the alarms, allow more than 30 minutes for cooling before resuming operation. [AL. 91 Servo amplifier overheat warning] [AL. E0 Excessive regeneration warning] [AL.E1 Overload warning 1] [AL.EC Overload warning 2] If [AL. E6] or [AL. E9] occurs, the amplifier will be the servo-off status. If any other warning occurs, operation can be continued but an alarm may take place or proper operation may not be performed. Remove the cause of warning according to this section. Use MR Configurator2 to refer to the cause of warning occurrence. Alarm No.: 91 Name: Servo amplifier overheat warning Alarm content The temperature inside of the servo amplifier reached a warning level. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 91.1 (1) Check the ambient temperature. It is over 55 ˚C. Lower the ambient temperature. Ambient temperature of the servo amplifier has exceeded 55 ˚C. It is less than 55 ˚C. Check (2). Main circuit device overheat warning (2) The close mounting is out of specifications. Check the specifications of close mounting. It is out of specifications. Use within the range of specifications. Alarm No.: 99 Name: Stroke limit warning Alarm content The stroke limit signal is off. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 99.1 (1) It is not connected. Connect it correctly. Forward rotation stroke end off The forward rotation stroke limit switch has not connected. Check if the limit switch is connected correctly. It is connected. Check (2). (2) The forward rotation stroke limit was exceeded during driving. Check if the forward rotation stroke limit switch turned off. It turned off. Check operation pattern. 99.2 (1) It is not connected. Connect it correctly. Reverse rotation stroke end off The reverse rotation stroke limit switch has not connected. Check if the limit switch is connected correctly. It is connected. Check (2). (2) The reverse rotation stroke limit was exceeded during driving. Check if the reverse rotation stroke limit switch turned off. It turned off. Check operation pattern. Alarm No.: E0 Name: Excessive regeneration warning Alarm content There is a possibility that regenerative power may exceed permissible regenerative power of built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E0.1 Excessive regeneration warning (1) The regenerative power exceeded 85% of the permissible regenerative power of the built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option. Check the effective load ratio. It is 85% or more. Reduce the frequency of positioning. Increase the deceleration time constant. Reduce the load. Use a regenerative option if it is not being used. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 25 Alarm No.: E1 Name: Overload warning 1 Alarm content [AL.50 Overload 1] or [AL.51 Overload 2] may occur. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E1.1 Thermal overload warning 1 during operation (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 50.1 Thermal overload error 1 during operation]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.1]. E1.2 Thermal overload warning 2 during operation (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 50.2 Thermal overload error 2 during operation]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.2]. E1.3 Thermal overload warning 3 during operation (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 51.1 Thermal overload error 3 during operation]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 51.1]. E1.4 Thermal overload warning 4 during operation (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 50.3 Thermal overload error 4 during operation]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.3]. E1.5 Thermal overload error 1 during a stop (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 50.4 Thermal overload error 1 during a stop]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.4]. E1.6 Thermal overload error 2 during a stop (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 50.5 Thermal overload error 2 during a stop]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.5]. E1.7 Thermal overload error 3 during a stop (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 51.2 Thermal overload error 3 during operation]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 51.2]. E1.8 Thermal overload error 4 during a stop (1) The load was over 85% to the alarm level of [AL. 50.6 Thermal overload error 4 during a stop]. Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.6]. Alarm No.: E6 Name: Servo forced stop warning Alarm content EM2/EM1 (Forced stop) turned off. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E6.1 Forced stop warning (1) EM2/EM1 (Forced stop) turned off. Check the status of EM2/EM1. It is off. Ensure safety and turn on EM2/EM1 (Forced stop). It is on. Check (2). (2) It is not inputted. Input the 24 V DC power supply. An external 24 V DC power supply have not inputted. Check if the external 24 V DC power supply is inputted. It is inputted. Check (3). (3) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Replace the servo amplifier, and then check the repeatability. It is not repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. Alarm No.: E8 Name: Cooling fan speed reduction warning Alarm content The cooling fan speed decreased to the warning occurrence level or less. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E8.1 (1) Something has been caught. Remove the foreign matter. Decreased cooling fan speed warning Foreign matter was caught in the cooling fan. Check if a foreign matter is caught in the cooling fan. Nothing has been caught. Check (2). (2) Cooling fan life expired. Check the total of power on time of the servo amplifier. It exceed the cooling fan life. Replace the servo amplifier. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 26 Alarm No.: E9 Name: Main circuit off warning Alarm content The servo-on command was inputted with power supply off. The bus voltage dropped during the servo motor driving under 50 r/min. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E9.1 Servo-on signal on during main circuit off (1) The bus voltage is less than 215 V DC. Check the bus voltage. It is less than 215 V DC. Review the wiring. Check the power supply capacity. (2) The servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Check the bus voltage value. The voltage of the power supply is 160 V AC or more, and the bus voltage is less than 200 V DC. Replace the servo amplifier. E9.2 Bus voltage drop during low speed operation (1) The bus voltage dropped during the servo motor driving under 50 r/min. Check the bus voltage. It is less than 200 V DC. Review the power supply capacity. Increase the acceleration time constant. Alarm No.: EC Name: Overload warning 2 Alarm content Operations over rated output were repeated while the servo motor shaft was not rotated. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action EC.1 Overload warning 2 (1) The load is too large or the capacity is not enough. Check the effective load ratio. The effective load ratio is high. Reduce the load. Replace the servo motor with the one of larger capacity. Alarm No.: ED Name: Output watt excess warning Alarm content The status, in which the output wattage (speed × torque) of the servo motor exceeded the rated output, continued steadily. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action ED.1 Output watt excess warning (1) The status, in which the output wattage (speed × torque) of the servo motor exceeded 150% of the rated output, continued steadily. Check the servo motor speed and torque. The output wattage is 150% of rating. Reduce the servo motor speed. Reduce the load. Alarm No.: F0 Name: Tough drive warning Alarm content Tough drive function was activated. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action F0.1 Instantaneous power failure tough drive warning (1) The power supply voltage dropped. Check it with the check method for [AL. 10.1]. F0.3 Vibration tough drive warning (1) The setting value of the machine resonance suppression filter was changed due to a machine resonance. Check if it was changed frequently. It was changed frequently. Set the machine resonance suppression filter. Check the machine status if screws are loose or the like. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 27 Alarm No.: F2 Name: Drive recorder - Miswriting warning Alarm content A waveform measured by the drive recorder function was not recorded. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action F2.1 Drive recorder - Area writing time-out warning (1) The Flash-ROM is malfunctioning. Disconnect the cables except the power supply, and then check the repeatability. It is repeatable. Replace the servo amplifier. F2.2 Drive recorder - Data miswriting warning (1) Data were not written to the drive recorder area. Check if the records have all written. They have all written. Delete the records in the drive recorder window of MR Configurator2. If records cannot be written after deletion, replace the servo amplifier. Alarm No.: F3 Name: Oscillation detection warning Alarm content [AL. 54 Oscillation detection] may occur. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action F3.1 Oscillation detection warning Check it with the check method for [AL. 54.1]. 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 28 MEMO 9. DIMENSIONS 9 - 1 9. DIMENSIONS 9.1 Servo amplifier (1) MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-40A [Unit: mm] Approx. 80 135 50 168 6 6 15666 2.9 6 mounting hole The built-in regenerative resistor (lead wire) is mounted only in MR-JE-40A. 6 PE CNP1 CN1 CN2 CN3 Mass: 0.8 [kg] L2 L3 P+ C U V W L1 PE Terminal CNP1 Screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] A pprox. 6 Approx. 50 156 ± 0.5 Approx. 6 Approx. 6 Approx. 168 2-M5 screw Mounting hole process drawing 9. DIMENSIONS 9 - 2 (2) MR-JE-70A/MR-JE-100A [Unit: mm] 70 Approx. 80 185 3.3 168 4222 22 15666 6 mounting hole 6 PE CNP1 CN1 CN2 CN3 Mass: 1.5 [kg] L2 L3 P+ C U V W L1 PE Terminal CNP1 Screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] Approx. 6 Approx. 6 Approx. 168 156 ± 0.5 Approx. 70 42 ± 0.3 Approx. 22 Approx. 6 3-M5 screw Mounting hole process drawing 9. DIMENSIONS 9 - 3 (3) MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A [Unit: mm] 6 6 6 78 168 6 156 45 90 85 Approx. 80 195 161 6 CNP1 6 mounting hole CNP2 PE Cooling fan air intake Exhaust CN1 CN2 CN3 Mass: 2.1 [kg] L2 L3 N- C D P+ U V W L1 CNP2 Terminal CNP1 Screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] PE Mounting screw Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] Approx. 90 78 ± 0.3 A pprox. 6 Approx. 6 Approx. 168 156 ± 0.5 Approx. 6 Approx. 6 Mounting hole process drawing 3-M5 screw 9. DIMENSIONS 9 - 4 9.2 Connector (1) Miniature delta ribbon (MDR) system (3M) (a) One-touch lock type [Unit: mm] E B A 23.8 39.0 12.7 C Logo etc, are indicated here. D Variable dimensions Connector Shell kit A B C D E 10150-3000PE 10350-52F0-008 41.1 52.4 18.0 14.0 17.0 (b) Jack screw M2.6 type This is not available as option. [Unit: mm] E B A 23.8 39.0 12.7 C Logo etc, are indicated here. 5.2 F D Variable dimensions Connector Shell kit A B C D E F 10150-3000PE 10350-52A0-008 41.1 52.4 18.0 14.0 17.0 46.5 9. DIMENSIONS 9 - 5 (2) SCR connector system (3M) Receptacle: 36210-0100PL Shell kit: 36310-3200-008 [Unit: mm] 34.8 39.5 22.4 11.0 9. DIMENSIONS 9 - 6 MEMO 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 1 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10.1 Overload protection characteristics An electronic thermal is built in the servo amplifier to protect the servo motor, servo amplifier and servo motor power wires from overloads. [AL. 50 Overload 1] occurs if overload operation performed is above the electronic thermal protection curve shown in fig. 10.1. [AL. 51 Overload 2] occurs if the maximum current is applied continuously for several seconds due to machine collision, etc. Use the equipment on the left-side area of the continuous or broken line in the graph. For the system where the unbalanced torque occurs, such as a vertical axis system, it is recommended that the unbalanced torque of the machine be kept at 70% or less of the motor's rated torque. This servo amplifier has servo motor overload protective function. (The servo motor overload current (full load current) is set on the basis of 120% rated current of the servo amplifier.) 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 2 Operation time [s] 1000 100 10 1 0.1 100 200 300 0 Servo-lock Operating 50 150 250 (Note) Load ratio [%] 320 1000 100 10 1 0.1 100 200 3000 50 150 250 320 Operation time [s] Servo-lock Operating (Note) Load ratio [%] HF-KN13, HF-KN23, HF-KN43 HF-KN73, HF-SN52, HF-SN102 HF-SN152, HF-SN202, HF-SN302 Note. If operation that generates torque more than 100% of the rating is performed with an abnormally high frequency in a servo motor stop status (servo-lock status) or in a 30 r/min or less low-speed operation status, the servo amplifier may malfunction regardless of the electronic thermal protection. Fig. 10.1 Electronic thermal protection characteristics 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 3 10.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss (1) Amount of heat generated by the servo amplifier Table 10.1 indicates servo amplifiers' power supply capacities and losses generated under rated load. For thermal design of an enclosed type cabinet, use the values in the table in consideration for the worst operating conditions. The actual amount of generated heat will be intermediate between values at rated torque and servo-off according to the duty used during operation. When the servo motor is run at less than the rated speed, the power supply capacity will be smaller than the value in the table, but the servo amplifier's generated heat will not change. Table 10.1 Power supply capacity and generated loss per servo motor at rated output (Note 2) Servo amplifier- generated heat [W] Servo amplifier Servo motor (Note 1) Power supply capacity [kVA] At rated output With servo-off Area required for heat dissipation [m 2 ] MR-JE-10A HF-KN13 0.3 25 15 0.5 MR-JE-20A HF-KN23 0.5 25 15 0.5 MR-JE-40A HF-KN43 0.9 35 15 0.7 HF-KN73 1.3 50 15 1.0 MR-JE-70A HF-SN52 1.0 40 15 0.8 MR-JE-100A HF-SN102 1.7 50 15 1.0 HF-SN152 2.5 MR-JE-200A HF-SN202 3.5 90 20 1.8 MR-JE-300A HF-SN302 4.8 120 20 2.4 Note 1. Note that the power supply capacity will vary according to the power supply impedance. This value is applicable when the power factor improving AC reactor is not used. 2. Heat generated during regeneration is not included in the servo amplifier-generated heat. To calculate heat generated by the regenerative option, refer to section 11.2. 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 4 (2) Heat dissipation area for an enclosed type cabinet The enclosed type cabinet (hereafter called the cabinet) which will contain the servo amplifier should be designed to ensure that its temperature rise is within +10 ˚C at the ambient temperature of 40 ˚C. (With an approximately 5 ˚C safety margin, the system should operate within a maximum 55 ˚C limit.) The necessary cabinet heat dissipation area can be calculated by equation 10.1. A = K • T P ·········································································································································· (10.1) A P T K : Heat dissipation area [m 2 ] : Loss generated in the cabinet [W] : Difference between internal and ambient temperatures [˚C] : Heat dissipation coefficient [5 to 6] When calculating the heat dissipation area with equation 10.1, assume that P is the sum of all losses generated in the cabinet. Refer to table 10.1 for heat generated by the servo amplifier. "A" indicates the effective area for heat dissipation, but if the cabinet is directly installed on an insulated wall, that extra amount must be added to the cabinet's surface area. The required heat dissipation area will vary with the conditions in the cabinet. If convection in the cabinet is poor and heat builds up, effective heat dissipation will not be possible. Therefore, arrangement of the equipment in the cabinet and the use of a cooling fan should be considered. Table 10.1 lists the cabinet dissipation area for each servo amplifier (guideline) when the servo amplifier is operated at the ambient temperature of 40 ˚C under rated load. Fig. 10.2 Temperature distribution in an enclosed type cabinet When air flows along the outer wall of the cabinet, effective heat exchange will be possible, because the temperature slope inside and outside the cabinet will be steeper. 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 5 10.3 Dynamic brake characteristics POINT Do not use dynamic brake to stop in a normal operation as it is the function to stop in emergency. For a machine operating at the recommended load to motor inertia ratio or less, the estimated number of usage times of the dynamic brake is 1000 times while the machine decelerates from the rated speed to a stop once in 10 minutes. Be sure to enable EM1 (Forced stop 1) after servo motor stops when using EM1 (Forced stop 1) frequently in other than emergency. 10.3.1 Dynamic brake operation (1) Calculation of coasting distance Fig. 10.3 shows the pattern in which the servo motor comes to a stop when the dynamic brake is operated. Use equation 10.2 to calculate an approximate coasting distance to a stop. The dynamic brake time constant varies with the servo motor and machine operation speeds. (Refer to (2) of this section.) A working part generally has a friction force. Therefore, actual coasting distance will be shorter than a maximum coasting distance calculated with the following equation. V 0 OFF ON Machine speed t e Time EM1 (Forced stop 1) Dynamic brake time constant Fig. 10.3 Dynamic brake operation diagram L max = 60 V 0 • J M t e +1 + J L ··············································································································· (10.2) L max : Maximum coasting distance ·········································································································[mm] V 0 : Machine's fast feed speed ······································································································· [mm/min] J M : Moment of inertia of the servo motor ··············································································· [× 10 -4 kg•m 2 ] J L : Load moment of inertia converted into equivalent value on servo motor shaft·················[× 10 -4 kg•m 2 ] : Dynamic brake time constant ················································································································ [s] t e : Delay time of control section ················································································································ [s] There is internal relay delay time of about 10 ms. 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 6 (2) Dynamic brake time constant The following shows necessary dynamic brake time constant for equation 10.2. 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4500 4000 73 43 23 13 Dynamic brake time constant [ms] Speed [r/min] 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 102 52 202 302 152 Dynamic brake time constant [ms] Speed [r/min] HF-KN series HF-SN series 10.3.2 Permissible load to motor inertia when the dynamic brake is used Use the dynamic brake under the load to motor inertia ratio indicated in the following table. If the ratio is higher than this value, the dynamic brake may burn. If there is a possibility that the ratio may exceed the value, contact your local sales office. The values of the permissible load to motor inertia ratio in the table are the values at the maximum rotation speed of the servo motor. Servo motor Permissible load to motor inertia ratio [multiplier] HF-KN13 HF-KN23 HF-KN43 HF-KN73 HF-SN52 30 HF-SN102 HF-SN152 HF-SN202 HF-SN302 16 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 7 10.4 Cable bending life The bending life of the cables is shown below. This graph calculated values. Since they are not guaranteed values, provide a little allowance for these values. a: b: Standard encoder cable Standard motor power cable Standard electromagnetic brake cable Long bending life encoder cable Long bending life motor power cable Long bending life electromagnetic brake cable Number of bending times 1 × 10 8 5 × 10 7 1 × 10 7 5 × 10 6 1 × 10 6 5 × 10 5 1 × 10 5 5 × 10 4 1 × 10 4 5 × 10 3 1 × 10 3 4 7 10 20 40 70 100 200 Bend radius [mm] a b 10.5 Inrush current at power-on The following table indicates the inrush currents (reference data) that will flow when 240 V AC is applied at the power supply capacity of 2500 kVA and the wiring length of 1 m. Even when you use a 1-phase 200 V AC power supply with MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-70A, the inrush currents will be the same. Servo amplifier Inrush currents (A 0-P ) MR-JE-10A, MR-JE-20A, MR-JE-40A 32 A (attenuated to approx. 3 A in 20 ms) MR-JE-70A, MR-JE-100A 36 A (attenuated to approx. 7 A in 20 ms) MR-JE-200A, MR-JE-300A 102 A (attenuated to approx. 12 A in 20 ms) Since large inrush currents flow in the power supplies, always use molded-case circuit breakers and magnetic contactors. (Refer to section 11.6.) When circuit protectors are used, it is recommended that the inertia delay type, which is not tripped by an inrush current, be used. 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10 - 8 MEMO 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 1 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT WARNING Before connecting options and peripheral equipment, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier. CAUTION Use the specified peripheral equipment and options to prevent a malfunction or a fire. POINT We recommend using HIV wires to wire the servo amplifiers, options, and peripheral equipment. Therefore, the recommended wire sizes may differ from those used for the previous servo amplifiers. 11.1 Cable/connector sets POINT The IP rating indicated for cables and connectors is their protection against ingress of dust and raindrops when they are connected to a servo amplifier or servo motor. If the IP rating of the cable, connector, servo amplifier and servo motor vary, the overall IP rating depends on the lowest IP rating of all components. Please purchase the cable and connector options indicated in this section. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 2 11.1.1 Combinations of cable/connector sets Refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual" for options for servo motor power supply, electromagnetic brake, and encoder. (Note) Personal computer 5) 1) (Packed with the servo amplifier) To 24 V DC power supply for electromagnetic brake Servo motor Encoder connector Servo amplifier Operation panel Controller 2) 3) 4) CN3 CN1 CN2 Power connector Brake connector CNP1 Note. Connectors for 1 kW or less. Refer to section 3.3.3 (1) (b) for 2 kW or more. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 3 No. Product name Model Description Application 1) Servo amplifier CNP1 power connector MR-JECNP1-01 CNP1 Connector: 09JFAT-SAXGDK-H5.0 (JST) Supplied with servo amplifiers of 1 kW or less Applicable wire size: AWG 18 to 14 Insulator OD: to 3.9 mm Open tool J-FAT-OT (JST) MR-JECNP1-02 Supplied with servo amplifiers of 2 kW and 3 kW CNP1 Connector: 07JFAT-SAXGFK-XL (JST) Applicable wire size: AWG 16 to 10 Insulator OD: to 4.7 mm Open tool J-FAT-OT-EXL (JST) MR-JECNP2-02 Servo amplifier power connector CNP2 Connector: 03JFAT-SAXGFK-XL (JST) Applicable wire size: AWG 16 to 10 Insulator OD: to 4.7 mm 2) Junction terminal block cable Junction terminal block connector Connector: D7950-B500FL (3M) CN1 connector Connector: 10150-6000EL Shell kit: 10350-3210-000 (3M or equivalent) For junction terminal block connection MR-J2M- CN1TBL_M Cable length: 0.5 m, 1 m (Refer to section 11.3.) 3) CN1 connector set MR-J3CN1 Connector: 10150-3000PE Shell kit: 10350-52F0-008 (3M or equivalent) 4) Junction terminal block MR-TB50 Refer to section 11.3. 5) USB cable MR-J3USBCBL3M Cable length: 3 m CN5 connector mini-B connector (5 pins) Personal computer connector A connector For connection with PC-AT compatible personal computer 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 4 11.2 Regenerative option CAUTION Do not use servo amplifiers with regenerative options other than the combinations specified below. Otherwise, it may cause a fire. 11.2.1 Combination and regenerative power The power values in the table are resistor-generated powers and not rated powers. Regenerative power [W] Servo amplifier Built-in regenerative resistor MR-RB032 [40 ] MR-RB12 [40 ] MR-RB30 [13 ] MR-RB32 [40 ] (Note) MR-RB50 [13 ] MR-JE-10A 30 MR-JE-20A 30 100 MR-JE-40A 10 30 100 MR-JE-70A 20 30 100 300 MR-JE-100A 20 30 100 300 MR-JE-200A 100 300 500 MR-JE-300A 100 300 500 Note. Always install a cooling fan. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 5 11.2.2 Selection of regenerative option Use the following method when regeneration occurs continuously in vertical motion applications or when it is desired to make an in-depth selection of the regenerative option. (1) Regenerative energy calculation M Friction torque Unbalance torque TF TU Servo motor speedGenerated torque Time Up V tf (1 cycle) Down (+) (-) (Power running) (Regenerative) tpsd2 t2 t3 t4t1 tpsa2tpsd1 tpsa1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Formulas for calculating torque and energy in operation Regenerative power Torque applied to servo motor [N•m] Energy E [J] 1) T 1 = 9.55 • 10 4 (J L / + J M ) • V • t psa1 1 + T U + T F E 1 = 2 0.1047 • V • T 1 • t psa1 2) T 2 = T U + T F E 2 = 0.1047 • V • T 2 • t 1 3) T 3 = 9.55 • 10 4 -(J L • + J M ) • V • t psa2 1 + T U + T F E 3 = 2 0.1047 • V • T 3 • t psa2 4), 8) T 4 , T 8 = T U E 4 , E 8 0 (No regeneration) 5) T 5 = 9.55 • 10 4 (J L / + J M ) • V • t psd2 1 - T U + T F E 5 = 2 0.1047 • V • T 5 • t psd2 6) T 6 = -T U + T F E 6 = 0.1047 • V • T 6 • t 3 7) T 7 = 9.55 • 10 4 -(J L • + J M ) • V • t psd2 1 - T U + T F E 7 = 2 0.1047 • V • T 7 • t psd2 From the calculation results in 1) to 8), find the absolute value (Es) of the sum total of negative energies. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 6 (2) Losses of servo motor and servo amplifier in regenerative mode The following table lists the efficiencies and other data of the servo motor and servo amplifier in the regenerative mode. Servo amplifier Inverse efficiency [%] Capacitor charging [J] Servo amplifier Inverse efficiency [%] Capacitor charging [J] MR-JE-10A 55 11 MR-JE-100A 85 25 MR-JE-20A 75 11 MR-JE-200A 85 42 MR-JE-40A 85 14 MR-JE-300A 85 42 MR-JE-70A 85 25 Inverse efficiency (): Efficiency including some efficiencies of the servo motor and servo amplifier when rated (regenerative) torque is generated at rated speed. Since the efficiency varies with the speed and generated torque, allow for about 10%. Capacitor charging (Ec): Energy charged into the electrolytic capacitor in the servo amplifier Subtract the capacitor charging from the result of multiplying the sum total of regenerative energies by the inverse efficiency to calculate the energy consumed by the regenerative option. ER [J] = • Es - Ec Calculate the power consumption of the regenerative option on the basis of one-cycle operation period tf [s] to select the necessary regenerative option. PR [W] = ER/tf 11.2.3 Parameter setting Set [Pr. PA02] according to the option to be used. Regenerative option selection 00: Regenerative option is not used. For servo amplifier of 200 W, regenerative resistor is not used. For servo amplifier of 0.4 kW to 3 kW, built-in regenerative resistor is used. 02: MR-RB032 03: MR-RB12 04: MR-RB32 05: MR-RB30 06: MR-RB50 (Cooling fan is required) 00 [Pr. PA02] 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 7 11.2.4 Selection of regenerative option POINT When you use a regenerative option with an MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, remove the built-in regenerative resistor and wiring from the servo amplifier. When MR-RB50 is used, a cooling fan is required to cool it. The cooling fan should be prepared by the customer. For the wire sizes used for wiring, refer to section 11.5. A built-in regenerative resistor should not be mounted/removed frequently. When you remount a built-in regenerative resistor, check the lead wires of the built-in regenerative resistor for scratches or cracks. The regenerative option generates heat of 100 ˚C higher than the ambient temperature. Fully consider heat dissipation, installation position, wires used, etc. before installing the option. For wiring, use flame-resistant wires or make the wires flame-resistant and keep them away from the regenerative option. Always use twisted cables of max. 5 m length for connection with the servo amplifier. (1) MR-JE-100A or less When you use a regenerative option for MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, remove wirings of P+ and C, remove the built-in regenerative resistor, and then connect the regenerative option between P+ and C. G3 and G4 are terminals for thermal sensor. Between G3 and G4 is opened when the regenerative option overheats abnormally. Always remove the wiring (across P+ to C) of th e servo amplifier built-in regenerative resistor. P+ C G4 G3 C P Regenerative option 5 m or less Servo amplifier (Note 2) (Note 1) Note 1. The built-in regenerative resistor is not provided for MR-JE-10A and MR-JE-20A. 2. Make up a sequence which will switch off the magnetic contactor when abnormal heating occurs. G3-G4 contact specifications Maximum voltage: 120 V AC/DC Maximum current: 0.5 A/4.8 V DC Maximum capacity: 2.4 VA 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 8 To remove the built-in regenerative resistor mounted on the back of MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, follow the procedures 1) to 3) with referring the illustration. 1) Disconnect the wirings of the built-in regenerative resistor from the power connector (CNP1). (Refer to (3) (b) of 3.3.2.) 2) Remove the wirings of the built-in regenerative resistor from the closest position to the power connector (CNP1) in order. Please pay full attention not to break the wirings. 3) Remove the screw fixing the built-in regenerative resistor and dismount the built-in regenerative resistor. (Note) 3) 1) 2) Note. Screw size: M3 Tightening torque: 0.72 [N•m] 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 9 (2) MR-JE-200A or more Always remove the wiring from across P+ to D and fit the regenerative option across P+ to C. G3 and G4 are terminals for thermal sensor. Between G3 and G4 is opened when the regenerative option overheats abnormally. D P+ C G4 G3 C P Regenerative option 5 m or less Servo amplifier Always remove the lead from across P+ to D. (Note 3) Cooling fan (Note 1, 2) Note 1. When using the MR-RB50, forcibly cool it with a cooling fan (1.0 m 3 /min or more, 92 mm × 92 mm). 2. When the ambient temperature is more than 55 °C and the regenerative load ratio is more than 60% in MR-RB30 and MR-RB32, forcefully cool the air with a cooling fan (1.0 m 3 /min or more, 92 mm × 92 mm). A cooling fan is not required if the ambient temperature is 35 °C or less. (A cooling fan is required for the shaded area in the following graph.) 100 60 0 0 Ambient temperature [°C] 35 55 A cooling fan is not required. A cooling fan is required. Load ratio [%] 3. Make up a sequence which will switch off the magnetic contactor when abnormal heating occurs. G3-G4 contact specifications Maximum voltage: 120 V AC/DC Maximum current: 0.5 A/4.8 V DC Maximum capacity: 2.4 VA 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 10 11.2.5 Dimensions (1) MR-RB12 [Unit: mm] 5 144 Approx. 20 169 168 1566 12 6 36 40 6 mounting hole T E1 15 Approx. 6 149 2 TE1 terminal block G3 G4 P C Applicable wire size: 0.2 mm 2 to 2.5 mm 2 (AWG 24 to 12) Tightening torque: 0.5 to 0.6 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] Mass: 1.1 [kg] (2) MR-RB30/MR-RB32 [Unit: mm] 8.5125 150 Approx. 30 142 79 82.530 8.5 10 90 101.5 82.5 318 17 335 Air intake 7 100 Cooling fan mounting screw (2-M4 screw) Terminal block P C G3 G4 Terminal screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M6 Tightening torque: 5.4 [N•m] Mass: 2.9 [kg] 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 11 (3) MR-RB50 [Unit: mm] 2.3 133 82.5 49 82.5 Cooling fan mounting screw (2-M3 screw) On opposite side 200 17 217 8120 108 12 12.5 162.5 350 162.5 12.5 7 Approx. 30 7 × 14 slotted hole Air intake Terminal block P C G3 G4 Terminal screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M6 Tightening torque: 5.4 [N•m] Mass: 5.6 [kg] (4) MR-RB032 [Unit: mm] T E1 30 15 99 1.6 119 14412 156 168 6 6 5 Approx. 6 Approx. 12 Approx. 20 6 mounting hole TE1 terminal block G3 G4 P C Applicable wire size: 0.2 mm 2 to 2.5 mm 2 (AWG 24 to 12) Tightening torque: 0.5 to 0.6 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] Mass: 0.5 [kg] 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 12 11.3 Junction terminal block MR-TB50 (1) Usage Always use the junction terminal block (MR-TB50) with the option cable (MR-J2M-CN1TBL_M) as a set. Servo amplifier CN1 Junction terminal block MR-TB50 Junction terminal block cable (MR-J2M-CN1TBL_M) Cable clamp Install the junction terminal block cable on the junction terminal block side with the supplied cable clamp fitting (AERSBAN-ESET). For the use of the cable clamp fitting, refer to section 11.9, (2) (c). (2) Terminal block label Use the following for the terminal label. For the input/output pin assignment in the control mode, refer to (4) (b) of this section. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 (3) Dimensions [Unit: mm] 235 50 25 Approx. 25 9 2 1 50 49 MITSUBISHI MR-TB50 4.5 244 2.5 46.5 1 3 5 7 9 1113 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 3133 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 34 36 3840 42 4446 48 50 2- Terminal screw: M3.5 Applicable wire: 2 mm 2 Crimp terminal width: 7.2 mm or shorter 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 13 (4) Junction terminal block cable MR-J2M-CN1TBL_M (a) Model explanations Model: 05 1 Symbol Cable length [m] 0.5 1 (b) Connection diagram 10150-6000EL (Servo amplifier side) D7650-B500FL (Junction terminal side) Position LG LA LAR LB LBR LZ LZR PP PG OPC SON RES DICOM DICOM ZSP INP MO1 TLA LG MO2 LG OP LG NP NG CR EM2 LSP LSN DOCOM DOCOM ALM RD SD Speed VC LG LA LAR LB LBR LZ LZR SON ST1 DICOM DICOM ZSP SA MO1 TLA LG MO2 LG OP LG ST2 EM2 LSP LSN DOCOM DOCOM ALM RD SD Torque VLA LG LA LAR LB LBR LZ LZR SON RS2 DICOM DICOM ZSP MO1 TC LG MO2 LG OP LG RS1 EM2 DOCOM DOCOM ALM RD SD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Plate 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Signal symbol Pin No. Pin No. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 14 11.4 MR Configurator2 POINT For the MR-JE servo amplifier, use MR Configurator2 with software version 1.19V or later. MR Configurator2 (SW1DNC-MRC2-E) uses the communication function of the servo amplifier to perform parameter setting changes, graph display, test operation, etc. on a personal computer. (1) Specifications Item Description Project Create/read/save/delete project, system setting, and print Parameter Parameter setting, axis name setting Monitor Display all, I/O monitor, and graph Diagnosis Alarm display, alarm onset data, drive recorder, no motor rotation, system configuration, life diagnosis, machine diagnosis Test operation Jog operation, positioning operation, motor-less operation, DO forced output, and program operation, test mode information Adjustment One-touch tuning, tuning, and machine analyzer Others Servo assistant, parameter setting range update, machine unit conversion setting, and help display (2) System requirements (a) Components To use this software, the following components are required in addition to the servo amplifier and servo motor. Equipment (Note 1) Description OS Microsoft ® Windows ® 7 Enterprise [Service Pack none/1] Microsoft ® Windows ® 7 Ultimate [Service Pack none/1] Microsoft ® Windows ® 7 Professional [Service Pack none/1] Microsoft ® Windows ® 7 Home Premium [Service Pack none/1] Microsoft ® Windows ® 7 Starter [Service Pack none/1] Microsoft ® Windows Vista ® Enterprise [Service Pack none /1/2] Microsoft ® Windows Vista ® Ultimate [Service Pack none/1/2] Microsoft ® Windows Vista ® Business [Service Pack none/1/2] Microsoft ® Windows Vista ® Home Premium [Service Pack none/1/2] Microsoft ® Windows Vista ® Home Basic [Service Pack none/1/2] Microsoft ® Windows ® XP Professional [Service Pack 2/3] Microsoft ® Windows ® XP Home Edition [Service Pack 2/3] Microsoft ® Windows ® 2000 Professional [Service Pack 4] CPU Desktop personal computer: Intel ® Celeron ® processor 2.8GHz or more is recommended. Laptop personal computer: Intel ® Pentium ® M processor 1.7GHz or more is recommended. Memory 512 MB or more (for 32-bit OS) and 1 GB or more (for 64-bit OS) Hard Disk 1GB or more of free space (Note 2, 3, 4, 5) Personal computer Communication interface USB port Browser Windows ® Internet Explorer ® 4.0 or more (Note 1) Display One whose resolution is 1024 × 768 or more and that can provide a high color (16 bit) display. Connectable with the above personal computer. Keyboard Connectable with the above personal computer. Mouse Connectable with the above personal computer. Printer Connectable with the above personal computer. USB cable MR-J3USBCBL3M 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 15 Note 1. Microsoft, Windows, Internet Explorer and Windows Vista are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries. Celeron and Pentium are the registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. 2. On some personal computers, MR Configurator2 may not run properly. 3. When Microsoft ® Windows ® 7, Microsoft ® Windows Vista ® , or Microsoft ® Windows ® XP is used, the following functions cannot be used. Windows Program Compatibility mode Fast User Switching Remote Desktop Large Fonts Mode (Display property) DPI settings other than 96 DPI (Display property) For 64-bit operating system, this software is compatible with Windows ® 7. 4. When Windows ® 7 is used, the following functions cannot be used. Windows XP Mode Windows touch 5. When using this software with Windows Vista ® and Windows ® 7, log in as a user having USER authority or higher. (b) Connection with servo amplifier To USB connector USB cable MR-J3USBCBL3M (Option) Personal compute r Servo amplifier CN3 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 16 11.5 Selection example of wires POINT To comply with the UL/CSA standard, use the wires shown in appendix 2 for wiring. To comply with other standards, use a wire that is complied with each standard. Selection conditions of wire size is as follows. Construction condition: One wire is constructed in the air. Wiring length: 30 m or shorter The following diagram shows the wires used for wiring. Use the wires given in this section or equivalent. 3) Regenerative option lead Regenerative option C P+ L1 L2 L3 1) Power lead Power supply Servo amplifier U V W 2) Servo motor power supply lead M Table 11.1 shows examples for using the 600 V Grade heat-resistant polyvinyl chloride insulated wire (HIV wire). Table 11.1 Wire size selection example (HIV wire) Wire [mm 2 ] Servo amplifier 1) L1/L2/L3/ 3) P+•C 2) U/V/W/ (Note 1) MR-JE-10A MR-JE-20A MR-JE-40A MR-JE-70A 2 (AWG 14) 2 (AWG 14) AWG 18 to 14 (Note 2) MR-JE-100A MR-JE-200A MR-JE-300A 3.5 (AWG 12) AWG 16 to 10 Note 1. The wire size shows applicable size of the servo amplifier connector. For wires connecting to the servo motor, refer to "HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual". 2. Be sure to use the size of 2 mm 2 when corresponding to UL/CSA standard. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 17 11.6 Molded-case circuit breakers, fuses, magnetic contactors (recommended) Always use one molded-case circuit breaker and one magnetic contactor with one servo amplifier. When using a fuse instead of the molded-case circuit breaker, use the one having the specifications given in this section. Molded-case circuit breaker (Note 1) Fuse Servo amplifier Frame, rated current Voltage AC [V] Class Current [A] Voltage AC [V] Magnetic contactor (Note 2) MR-JE-10A MR-JE-20A 30 A frame 5 A 10 MR-JE-40A 30 A frame 10 A 15 MR-JE-70A MR-JE-100A 30 A frame 15 A 20 S-N10 S-T10 MR-JE-200A 30 A frame 20 A 40 S-N20 (Note 3) S-T21 MR-JE-300A 30 A frame 30 A 240 T 70 300 S-N20 S-T21 Note 1. When having the servo amplifier comply with the UL/CSA standard, refer to appendix 2. 2.Use a magnetic contactor with an operation delay time (interval between current being applied to the coil until closure of contacts) of 80 ms or less. 3.S-N18 can be used when auxiliary contact is not required. 11.7 Power factor improving AC reactor The following shows the advantages of using power factor improving AC reactor. It improves the power factor by increasing the form factor of the servo amplifier's input current. It decreases the power supply capacity. The input power factor is improved to about 80%. When using power factor improving reactors for two servo amplifiers or more, be sure to connect a power factor improving reactor to each servo amplifier. If using only one power factor improving reactor, enough improvement effect of phase factor cannot be obtained unless all servo amplifiers are operated. (1) Connection example Y Z S T Y Z S T MCMCCB MCMCCB FR-HAL Servo amplifie r 3-phase 200 V class XR L1 L2 L3 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC FR-HAL Servo amplifier 1-phase 200 V class XR L1 L2 (Note) 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC L3 Note. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 18 (2) Dimensions 4-d mounting hole (Varnish is removed from front right mounting hole (face and back side).) (Note 1) Terminal layout RX ZSYT Max. W (Note 2) W1 D1 D2 H D or less Fig. 11.1 Dimensions [mm] Servo amplifier Power factor improving AC reactor Dimens ions W W1 H D (Note 3) D1 D2 d Terminal size Mass [kg] MR-JE-10A, MR-JE-20A FR-HAL-0.4K 104 84 99 72 51 40 M5 M4 0.6 MR-JE-40A FR-HAL-0.75K 104 84 99 74 56 44 M5 M4 0.8 MR-JE-70A FR-HAL-1.5K 104 84 99 77 61 50 M5 M4 1.1 MR-JE-100A FR-HAL-2.2K Fig. 11.1 115 (Note 3) 40 115 77 71 57 M6 M4 1.5 MR-JE-200A FR-HAL-3.7K 115 (Note 3) 40 115 83 81 67 M6 M4 2.2 MR-JE-300A FR-HAL-5.5K 115 (Note 3) 40 115 83 81 67 M6 M4 2.3 Note 1. Use this for grounding. 2. W ± 2 is applicable for FR-HAL-0.4K to FR-HAL-1.5K. 3. Maximum dimensions. The dimension varies depending on the input/output lines. 11.8 Relay (recommended) The following relays should be used with the interfaces. Interface Selection example Digital input (interface DI-1) Relay used for digital input command signals To prevent defective contacts, use a relay for small signal (twin contacts). (Ex.) Omron: type G2A, type MY Digital output (interface DO-1) Relay used for digital output signals Small relay with 12 V DC or 24 V DC of rated current 40 mA or less (Ex.) Omron: type MY 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 19 11.9 Noise reduction techniques Noises are classified into external noises which enter the servo amplifier to cause it to malfunction and those radiated by the servo amplifier to cause peripheral equipment to malfunction. Since the servo amplifier is an electronic device which handles small signals, the following general noise reduction techniques are required. Also, the servo amplifier can be a source of noise as its outputs are chopped by high carrier frequencies. If peripheral equipment malfunction due to noises produced by the servo amplifier, noise suppression measures must be taken. The measures will vary slightly with the routes of noise transmission. (1) Noise reduction techniques (a) General reduction techniques Avoid bundling power lines (input/output) and signal cables together or running them in parallel to each other. Separate the power lines from the signal cables. Use a shielded twisted pair cable for connection with the encoder and for control signal transmission, and connect the external conductor of the cable to the SD terminal. Ground the servo amplifier, servo motor, etc. together at one point. (Refer to section 3.11.) (b) Reduction techniques for external noises that cause the servo amplifier to malfunction If there are noise sources (such as a magnetic contactor, an electromagnetic brake, and many relays which make a large amount of noise) near the servo amplifier and the servo amplifier may malfunction, the following countermeasures are required. Provide surge absorbers on the noise sources to suppress noises. Attach data line filters to the signal cables. Ground the shields of the encoder connecting cable and the control signal cables with cable clamp fittings. Although a surge absorber is built into the servo amplifier, to protect the servo amplifier and other equipment against large exogenous noise and lightning surge, attaching a varistor to the power input section of the equipment is recommended. (c) Techniques for noises radiated by the servo amplifier that cause peripheral equipment to malfunction Noises produced by the servo amplifier are classified into those radiated from the cables connected to the servo amplifier and its main circuits (input and output circuits), those induced electromagnetically or statically by the signal cables of the peripheral equipment located near the main circuit cables, and those transmitted through the power supply cables. Noises produced by servo amplifier Noises transmitted in the air Noise radiated directly from servo amplifier Noise radiated from the power supply cable Noise radiated from servo motor cable Magnetic induction noise Static induction noise Noises transmitted through electric channels Noise transmitted through power supply cable Noise sneaking from grounding cable due to leakage current Routes 4) and 5) Route 1) Route 2) Route 3) Route 7) Route 8) Route 6) 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 20 Instrument Receiver Servo amplifier Servo motor M 2) 2) 8) 1) 7) 7) 7) 5) 3) 4) 6) 3) Sensor power supply Sensor Noise transmission route Suppression techniques 1) 2) 3) When measuring instruments, receivers, sensors, etc. which handle weak signals and may malfunction due to noise and/or their signal cables are contained in a cabinet together with the servo amplifier or run near the servo amplifier, such devices may malfunction due to noises transmitted through the air. The following techniques are required. 1. Provide maximum clearance between easily affected devices and the servo amplifier. 2. Provide maximum clearance between easily affected signal cables and the I/O cables of the servo amplifier. 3. Avoid wiring the power lines (input/output lines of the servo amplifier) and signal lines side by side or bundling them together. 4. Insert a line noise filter to the I/O cables or a radio noise filter on the input line. 5. Use shielded wires for the signal and power lines, or put the lines in separate metal conduits. 4) 5) 6) When the power lines and the signal lines are laid side by side or bundled together, magnetic induction noise and static induction noise will be transmitted through the signal cables and malfunction may occur. The following techniques are required. 1. Provide maximum clearance between easily affected devices and the servo amplifier. 2. Provide maximum clearance between easily affected signal cables and the I/O cables of the servo amplifier. 3. Avoid wiring the power lines (input/output lines of the servo amplifier) and signal lines side by side or bundling them together. 4. Use shielded wires for the signal and power lines, or put the lines in separate metal conduits. 7) When the power supply of peripheral equipment is connected to the power supply of the servo amplifier system, noises produced by the servo amplifier may be transmitted back through the power supply cable and the devices may malfunction. The following techniques are required. 1. Install the radio noise filter (FR-BIF) on the power lines (Input lines) of the servo amplifier. 2. Install the line noise filter (FR-BSF01) on the power lines of the servo amplifier. 8) When the cables of peripheral equipment are connected to the servo amplifier to make a closed loop circuit, leakage current may flow to malfunction the peripheral equipment. If so, malfunction may be prevented by disconnecting the grounding cable of the peripheral device. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 21 (2) Noise reduction techniques (a) Data line filter (recommended) Noise can be prevented by installing a data line filter onto the encoder cable, etc. For example, ZCAT3035-1330 by TDK, ESD-SR-250 by NEC TOKIN, and GRFC-13 by Kitagawa Industries are available as data line filters. As a reference example, the impedance specifications of the ZCAT3035-1330 (TDK) are indicated below. This impedances are reference values and not guaranteed values. Impedance [] 10 MHz to 100 MHz 100 MHz to 500 MHz 80 150 [Unit: mm] Outline drawing (ZCAT3035-1330) Loop for fixing the cable band Lot number Product name TDK 39 ± 1 34 ± 1 13 ± 1 30 ± 1 (b) Surge killer (recommended) Use of a surge killer is recommended for AC relay, magnetic contactor or the like near the servo amplifier. Use the following surge killer or equivalent. MC SK Surge killer Relay Surge killer MC ON OFF This distance should be short (within 20 cm). (Ex.) CR-50500 Okaya Electric Industries) Dimensions [Unit: mm] Rated voltage AC [V] C [µF ± 20%] R [ ± 30%] Test voltage 250 0.5 50 (1/2 W) Between terminals: 625 V AC, 50/60 Hz 60 s Between terminal and case: 2000 V AC, 50/60 Hz 60 s 6 ± 1 300 min. 300 min. Soldered Band (clear) AWG 18 Twisted wire 15 ± 1 48 ± 1.5 CR-50500 6 ± 1 16 ± 1 (18.5 + 5) max. 3.6 (18.5 + 2) ± 1 Note that a diode should be installed to a DC relay or the like. Maximum voltage: not less than four times the drive voltage of the relay or the like Maximum current: not less than two times the drive current of the relay or the like -+ Diode RA 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 22 (c) Cable clamp fitting AERSBAN-_SET Generally, the grounding of the shielded wire may only be connected to the connector's SD terminal. However, the effect can be increased by directly connecting the cable to an grounding plate as shown below. Install the grounding plate near the servo amplifier for the encoder cable. Peel part of the cable sheath to expose the external conductor, and press that part against the grounding plate with the cable clamp. If the cable is thin, clamp several cables in a bunch. The cable clamp comes as a set with the grounding plate. [Unit: mm] Cable clamp (A, B) Cable Earth plate External conductor Clamp section diagram 40 Strip the cable sheath o f the clamped area. cutter cable Dimensions [Unit: mm] Earth plate (Note) M4 screw 11 3 6 C A 6 22 17.5 35 35 7 24 0 -0.2 B ± 0.3 2- 5 hole installation hole [Unit: mm] Clamp section diagram L or less 10 30 24 + 0.3 0 Note. Screw hole for grounding. Connect it to the grounding plate of the cabinet. Model A B C Accessory fittings Clamp fitting L AERSBAN-DSET 100 86 30 Clamp A: 2pcs. A 70 AERSBAN-ESET 70 56 Clamp B: 1pc. B 45 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 23 (d) Line noise filter (FR-BSF01) This filter is effective in suppressing noises radiated from the power supply side and output side of the servo amplifier and also in suppressing high-frequency leakage current (0-phase current). It especially affects the noises between 0.5 MHz and 5 MHz band. Connection diagram Dimensions [Unit: mm] FR-BSF01 (for wire size 3.5 mm 2 (AWG 12) or less) 33 4.5 Approx. 110 95 ± 0.5 Approx. 22.5 Approx. 65 Approx. 65 2- 5 11.25 ± 0.5 Use the line noise filters for lines of the power supply (L1, L2, and L3) and of the servo motor power (U, V, and W). Pass each of the wires through the line noise filter an equal number of times in the same direction. For the power supply, the effect of the filter rises as the number of passes increases, but generally four passes would be appropriate. For the servo motor power lines, passes must be four times or less. Do not pass the grounding wire through the filter. or the effect of the filter will drop. Wind the wires by passing through the filter to satisfy the required number of passes as shown in Example 1. If the wires are too thick to wind, use two or more filters to have the required number of passes as shown in Example 2. Place the line noise filters as close to the servo amplifier as possible for their best performance. MCMCCB Example 1 Power supply Power supply Servo amplifier Line noise filter L1 L2 L3 (Number of passes: 4) MCMCCB Line noise filter Example 2 Servo amplifier L1 L2 L3 Two filters are used (Total number of passes: 4) 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 24 (e) Radio noise filter (FR-BIF) This filter is effective in suppressing noises radiated from the power supply side of the servo amplifier especially in 10 MHz and lower radio frequency bands. The FR-BIF is designed for the input only. 200 V class: FR-BIF Connection diagram Dimensions [Unit: mm] Make the connection cables as short as possible. Grounding is always required. When using the FR-BIF with a single-phase power supply, always insulate the lead wires that are not used for wiring. Radio noise filter Servo amplifier Power supply MC MCCB L3 L2 L1 Terminal block hole Leakage current: 4 m A 29 58 42 4 Red BlueWhite Green 44 29 7 5 Approx. 300 (f) Varistor for input power supply (recommended) Varistors are effective to prevent exogenous noise and lightning surge from entering the servo amplifier. When using a varistor, connect it between each phase of the input power supply of the equipment. For varistors, the TND20V-431K and TND20V-471K, manufactured by NIPPON CHEMI- CON, are recommended. For detailed specification and usage of the varistors, refer to the manufacturer catalog. Maximum rating Maximum limit voltage Permissible circuit voltage Surge current immunity Energy immunity Rated pulse power Static capacity (reference value) Varistor voltage rating (range) V1 mA Power supply voltage Varistor AC [Vrms] DC [V] 8/20 µs [A] 2 ms [J] [W] [A] [V] [pF] [V] TND20V-431K 275 350 10000/1 times 195 710 1300 430 (387 to 473) 200 V class TND20V-471K 300 385 7000/2 times 215 1.0 100 775 1200 470 (423 to 517) [Unit: mm] Model D Max. H Max. T Max. E ±1.0 (Note) L min. d ±0.05 W ±1.0 TND20V-431K 6.4 3.3 TND20V-471K 21.5 24.5 6.6 3.5 20 0.8 10.0 Note. For special purpose items for lead length (L), contact the manufacturer. WE H D L T d 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 25 11.10 Earth-leakage current breaker (1) Selection method High-frequency chopper currents controlled by pulse width modulation flow in the AC servo circuits. Leakage currents containing harmonic contents are larger than those of the motor which is run with a commercial power supply. Select an earth-leakage current breaker according to the following formula, and ground the servo amplifier, servo motor, etc. securely. To minimize leakage currents, make the input and output cables as short as possible, and make the grounding cable longer than 30 cm. Rated sensitivity current 10 • {Ig1 + Ign + Iga + K • (Ig2 + Igm)} [mA]············································· (11.1) Earth-leakage current breaker Type Mitsubishi products K Models provided with harmonic and surge reduction techniques NV-SP NV-SW NV-CP NV-CW NV-HW 1 Ign Noise filter Cable Ig1 Iga Ig2 Igm M Servo amplifier NV Cable General models BV-C1 NFB NV-L 3 Ig1: Leakage current on the electric channel from the earth-leakage current breaker to the input terminals of the servo amplifier (Found from Fig. 11.2.) Ig2: Leakage current on the electric channel from the output terminals of the servo amplifier to the servo motor (found from Fig. 11.2.) Ign: Leakage current when a filter is connected to the input side (4.4 mA per one FR-BIF) Iga: Leakage current of the servo amplifier (Found from table 11.3.) Igm: Leakage current of the servo motor (Found from table 11.2.) Leakage current [mA] Cable size [mm 2 ] 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 2 5.5 14 3.5 8 38100 22 30 60150 80 Fig. 11.2 Example of leakage current per km (lg1, lg2) for CV cable run in metal conduit 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 26 Table 11.2 Servo motor leakage current example (lgm) Servo motor power [kW] Leakage current [mA] 0.1 to 1 0.1 2 0.2 3 0.3 Table 11.3 Servo amplifier leakage current example (Iga) Servo amplifier capacity [kW] Leakage current [mA] 0.1 to 0.6 0.1 0.75 to 3 0.15 Table 11.4 Earth-leakage current breaker selection example Servo amplifier capacity [kW] Rated sensitivity current of earth- leakage current breaker [mA] MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-300A 15 (2) Selection example Indicated below is an example of selecting an earth-leakage current breaker under the following conditions. Servo motor HF-KN43 2 mm 2 × 5 m 2 mm 2 × 5 m M NV Ig1 Iga Ig2 Igm Servo amplifier MR-JE-40A Use an earth-leakage current breaker designed for suppressing harmonics/surges. Find the terms of equation (11.1) from the diagram. Ig1 = 20 • 5 1000 = 0.1 [mA] Ig2 = 20 • 5 1000 = 0.1 [mA] Ign = 0 (not used) Iga = 0.1 [mA] Igm = 0.1 [mA] Insert these values in equation (11.1). Ig 10 • {0.1 + 0 + 0.1 + 1 • (0.1 + 0.1)} 4 [mA] According to the result of calculation, use an earth-leakage current breaker having the rated sensitivity current (Ig) of 4.0 mA or more. An earth-leakage current breaker having Ig of 15 mA is used with the NV-SP/SW/CP/CW/HW series. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 27 11.11 EMC filter (recommended) It is recommended that one of the following filters be used to comply with EN EMC directive. Some EMC filters have large in leakage current. (1) Combination with the servo amplifier Recommended filter (Soshin Electric) Servo amplifier Model Rated current [A] Rated voltage [V AC] Leakage current [mA] Mass [kg] MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A (Note) HF3010A-UN 10 3.5 MR-JE-200A, MR-JE-300A (Note) HF3030A-UN 30 250 5 5.5 Note. A surge protector is separately required to use any of these EMC filters. (2) Connection example MCCB Servo amplifier 1 2 3 (Note 2) Surge protector (RSPD-250-U4) (OKAYA Electric Industries Co., Ltd.) (Note 1) Power supply 123 MC EMC filter L1 L2 L3 4 5 6 E Note 1. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open. 2. The example is when a surge protector is connected. 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 28 (3) Dimensions (a) EMC filter HF3010A-UN [Unit: mm] 32 ± 2 85 ± 2 110 ± 4 258 ± 4 273 ± 2 288 ± 4 300 ± 5 M4 IN 3-M4 65 ± 4 Approx. 41 4-5.5 × 73-M4 HF3030A-UN [Unit: mm] 125 ± 2 44 ± 1 260 ± 5 140 ± 2 70 ± 2 140 ± 1 155 ± 2 3-M5 6-R3.25 length:8 3-M5 M4 85 ± 1 210 ± 2 85 ± 1 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 29 (b) Surge protector RSPD-250-U4 41 ± 1 28.5 ± 1 28 ± 1 4.2 ± 0.5 5.5 ± 1 11 ± 1 +30 0 200 4.5 ± 0.5 132 Lead Case Resin [Unit: mm] 123 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 - 30 MEMO APPENDIX App. - 1 App. 1 Peripheral equipment manufacturer (for reference) Names given in the table are as of July 2013. Manufacturer Contact information JST J.S.T. Mfg. Co., Ltd. 3M 3M Soshin Electric Soshin Electric Co., Ltd. App. 2 Compliance with global standards App. 2.1 About safety This section explains safety of users and machine operators. Please read the section carefully before mounting the equipment. App. 2.1.1 Professional engineer Only professional engineers should mount MR-JE servo amplifiers. Here, professional engineers are persons who have taken proper engineering training qualified persons who are engaged in electrical equipment. Please note if you can take a proper engineering training at your local Mitsubishi Electric office. Contact your local sales office for schedules and locations. App. 2.1.2 Applications of the devices MR-JE servo amplifiers comply with the following safety standards. IEC/EN 61800-5-1, IEC/EN 61800-3 App. 2.1.3 Correct use Always use the MR-JE servo amplifiers within specifications (voltage, temperature, etc. Refer to section 1.3 for details.). Mitsubishi Electric Co. accepts no claims for liability if the equipment is used in any other way or if modifications are made to the device, even in the context of mounting and installation. WARNING It takes 15 minutes for capacitor discharging. Do not touch the unit and terminals immediately after power off. APPENDIX App. - 2 (1) Peripheral device and power wiring (a) Local wiring Use only copper wires rated at 75 ˚C for wiring. The following table shows wires [AWG] rated at 75 ˚C. Wire [AWG] Servo amplifier (Note 2) L1/L2/L3/ P+/C (Note 1, 2) U/V/W/ MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A/MR-JE-70A/MR-JE-100A/ MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A 14 14 14 Note 1. Select wire sizes depending on the rated output of the servo motors. The values in the table are sizes based on rated output of the servo amplifiers. 2. The following shows the PE terminal specifications of the servo amplifier. Screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Recommended crimp terminals: R2-4 (JST) Crimping tool: YPT-60-21 (JST) (b) Selection example of MCCB and fuse When a servo amplifier is protected by T class fuses or circuit breaker having an interrupting rating not less than 300 A effective value and 240 V maximum, use T class fuses or molded-case circuit breaker (UL489 Listed MCCB) as the following table. The T class fuses and molded-case circuit breakers in the table are selected examples based on rated I/O of the servo amplifiers. When you select a smaller capacity servo motor to connect it to the servo amplifier, you can also use smaller capacity T class fuses or molded-case circuit breaker than ones in the table. For selecting ones other than Class T fuses and molded-case circuit breakers below, refer to section 11.6. Servo amplifier Molded-case circuit breaker (240 V AC) Fuse (300 V) MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A/MR-JE-70A NF50-SWU-5A (50 A frame 5 A) 10 A MR-JE-70A (Note)/MR-JE-100A NF50-SWU-10A (50 A frame 10 A) 15 A MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A NF50-SWU-15A (50 A frame 15 A) 30 A Note. For 1-phase 200 V AC power input (c) Power supply This servo amplifier can be supplied from star-connected supply with grounded neutral point of overvoltage category III set forth in IEC/EN 60664-1. However, when you use the neutral point for single phase supply, a reinforced insulating transformer is required in the power input section. For the interface power supply, use an external 24 V DC power supply with reinforced insulation on I/O terminals. (d) Grounding To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. Do not connect two grounding cables to the same protective earth (PE) terminal. Always connect cables to the terminals one-to-one. If using an earth-leakage current breaker, always ground the protective earth (PE) terminal of the servo amplifier to prevent an electric shock. Only an RCD (earth-leakage current breaker) of type B can be used for the power supply side of the product. PE terminals PE terminals APPENDIX App. - 3 (2) EU compliance The MR-JE servo amplifiers are designed to comply with the following directions to meet requirements for mounting, using, and periodic technical inspections: EMC directive (2004/108/EC) and Low-voltage directive (2006/95/EC). (a) EMC requirement MR-JE servo amplifiers comply with category C3 in accordance with IEC/EN 61800-3. Use a EMC filter and surge protector on the primary side. As for I/O signal wires (max. length 10 m) and encoder cables (max. length 50 m), connect them to a shielded grounding. However, when the encoder cable length is longer than 30 m for MR-JE-70A and MR-JE-100A, set a radio noise filter (FR-BIF) to the input power supply side of the servo amplifier. The following shows recommended products. EMC filter: Soshin Electric HF3000A-UN series Surge protector: Okaya Electric Industries RSPD-250-U4 series Radio noise filter: Mitsubishi Electric FR-BIF - MR-JE Series are not intended to be used on a low-voltage public network which supplies domestic premises; - radio frequency interference is expected if used on such a network. The installer shall provide a guide for Installation and use, including recommended mitigation devices. (b) For Declaration of Conformity (DoC) Hereby, MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC EUROPE B.V., declares that the servo amplifiers are in compliance with the necessary requirements and standards (2004/108/EC and 2006/95/EC). For the copy of Declaration of Conformity, contact your local sales office. (3) USA/Canada compliance This servo amplifier is designed in compliance with UL 508C and CSA C22.2 No.14. (a) Installation The minimum cabinet size is 150% of MR-JE servo amplifier's volume. Also, design the cabinet so that the ambient temperature in the cabinet is 55 °C or less. The servo amplifier must be installed in the metal cabinet. For environment, the units should be used in open type (UL 50) and overvoltage category III or lower. The servo amplifier needs to be installed at or below of pollution degree 2. For connection, use copper wires. (b) Short-circuit current rating (SCCR) Suitable For Use On A Circuit Capable Of Delivering Not More Than 100 kA rms Symmetrical Amperes, 500 Volts Maximum. (c) Overload protection characteristics The MR-JE servo amplifiers have servo motor overload protective function. (It is set on the basis (full load current) of 120% rated current of the servo amplifier.) (d) Over-temperature protection for motor Motor Over temperature sensing is not provided by the drive. (e) Capacitor discharge It takes 15 minutes for capacitor discharging. Do not touch the unit and terminals immediately after power off. APPENDIX App. - 4 (f) Branch circuit protection For installation in United States, branch circuit protection must be provided, in accordance with the National Electrical Code and any applicable local codes. For installation in Canada, branch circuit protection must be provided, in accordance with the Canada Electrical Code and any applicable provincial codes. (4) South Korea compliance This product complies with the Radio Wave Law (KC mark). Please note the following to use the product. (A ) . (The product is for business use (Class A) and meets the electromagnetic compatibility requirements. The seller and the user must note the above point, and use the product in a place except for home.) App. 2.1.4 General cautions for safety protection and protective measures Observe the following items to ensure proper use of the MELSERVO MR-JE servo amplifiers. (1) Only qualified personnel and professional engineers should perform system installation. (2) When mounting, installing, and using the MELSERVO MR-JE servo amplifier, always observe standards and directives applicable in the country. App. 2.1.5 Disposal Disposal of unusable or irreparable devices should always occur in accordance with the applicable country- specific waste disposal regulations. (Example: European Waste 16 02 14) App. 2.2 Mounting/dismounting Installation direction and clearances CAUTION The devices must be installed in the specified direction. Not doing so may cause a malfunction. Mount the servo amplifier on a cabinet which meets IP54 in the correct vertical direction to maintain pollution degree 2. 10 mm or more 80 mm or longer for wiring 10 mm or more Top Bottom 40 mm or more 40 mm or more Cabinet Servo amplifier Servo amplifier Cabinet APPENDIX App. - 5 App. 2.3 Electrical Installation and configuration diagram WARNING Turn off the molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) to avoid electrical shocks or damages to the product before starting the installation or wiring. CAUTION Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo amplifier may cause a malfunction. The following shows representative configuration examples to conform to the IEC/EN/UL/CSA standards. (1) 3-phase input MCCB or fuse Controller Encoder cable (3-phase 230 V AC) Powe r suppl y (3-phase 4 00 V AC) Transformer (star-connected) PE MC Servo amplifier Cabinet side Machine side Encoder Servo motor L1 U/V/W/PE CN2 CN1 L2 L3 (2) 1-phase input MCCB or fuse Controller Encoder cable (3-phase 230 V AC) Power supply (3-phase 400 V AC) Transformer (star-connected) PE MC Servo amplifier Cabinet side Machine side Encoder Servo motor L1 U/V/W/PE CN2 CN1 L2 L3 The control circuit connectors described by rectangles are safely separated from the main circuits described by circles. The connected motors will be limited as follows. HF-KN/HF-SN series servo motors (Mfg.: Mitsubishi Electric) APPENDIX App. - 6 App. 2.4 Signal App. 2.4.1 Signal The following shows CN1 connector signals as a typical example. Refer to section 3.4 for other connectors. 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 TLA MO1 MO2 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 LG LA LG LAR LB LG LBR LZ OP LZR LG EM2 DICOM DICOM DOCOM DOCOM ALM CN1 PP OPC PG SON CR LSP RES ZSP RDINP LSN NP NG This is in position control mode. App. 2.4.2 Input/output device The following shows typical I/O devices. Refer to section 3.5 for other devices. Input device Symbol Device Connector Pin No. SON Servo-on 15 RES Reset 19 CR Clear 41 EM2 Forced stop 2 CN1 42 LSP Forward rotation stroke end 43 LSN Reverse rotation stroke end 44 APPENDIX App. - 7 Output device Symbol Device Connector Pin No. ZSP Zero speed detection 23 INP In-position 24 ALM Malfunction CN1 48 RD Ready 49 Power supply Symbol Device Connector Pin No. DICOM Digital I/F power supply input 20, 21 DOCOM Digital I/F common CN1 46, 47 SD Shield Plate App. 2.5 Maintenance and service WARNING To avoid an electric shock, only qualified personnel should attempt inspections. For repair and parts replacement, contact your local sales office. CAUTION Do not perform insulation resistance test on the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. Do not disassemble and/or repair the equipment on customer side. App. 2.5.1 Inspection items It is recommended that the following points periodically be checked. (1) Check for loose protective earth (PE) terminal screws of the servo amplifier. Retighten any loose screws. (Tightening torque: 1.2 N•m) (2) Check servo motor bearings, brake section, etc. for unusual noise. (3) Check the cables and the like for scratches or cracks. Perform periodic inspection according to operating conditions. (4) Check that the connectors are securely connected to the servo motor. (5) Check that the wires are not coming out from the connector. (6) Check for dust accumulation on the servo amplifier. (7) Check for unusual noise generated from the servo amplifier. (8) Check the servo motor shaft and coupling for connection. APPENDIX App. - 8 App. 2.5.2 Parts having service lives Service lives of the following parts are listed below. However, the service life vary depending or operating methods and environment. If any fault is found in the parts, they must be replaced immediately regardless of their service lives. For parts replacement, please contact your local sales office. Part name Life guideline Smoothing capacitor (Note) 10 years Relay Number of power-on times and forced stop times: 100,000 in total Cooling fan 50,000 hours to 70,000 hours (7 years to 8 years) Note. The characteristic of smoothing capacitor is deteriorated due to ripple currents, etc. The life of the capacitor greatly depends on ambient temperature and operating conditions. The capacitor will reach the end of its life in 10 years of continuous operation in normal air-conditioned environment (40 ˚C surrounding air temperature or less). App. 2.6 Transportation and storage CAUTION Transport the products correctly according to their mass. Stacking in excess of the limited number of product packages is not allowed. Install the servo amplifier and servo motor in a load-bearing place in accordance with "MR-JE-_A Servo Amplifier Instruction Manual". Do not get on or put heavy load on the equipment. Do not hold the lead wire of the regenerative resistor when transporting the servo amplifier. When you keep or use it, please fulfill the following environment. Item Environment Operation [°C] 0 to 55 Class 3K3 (IEC/EN 60721-3-3) Transportation (Note) [°C] -20 to 65 Class 2K4 (IEC/EN 60721-3-2) Ambient temperature Storage (Note) [°C] -20 to 65 Class 1K4 (IEC/EN 60721-3-1) Ambient humidity Operation, transportation, storage 5% to 90 %RH Test values 10 Hz to 57 Hz with constant deviation of 0.075 mm 57 Hz to 150 Hz with constant acceleration of 9.8 m/s 2 (1 g) to IEC/EN 61800-5-1 (Test Fc of IEC 60068-2-6) Operation 5.9 m/s 2 (0.6 g) Transportation (Note) Class 2M3 (IEC/EN 60721-3-2) Vibration load Storage Class 1M2 (IEC/EN 60721-3-2) Pollution degree 2 IP20 (IEC/EN 60529) IP rating Open type (UL 50) Operation, storage 1000 m or less above sea level Altitude Transportation 10000 m or less above sea level Note. In regular transport packaging APPENDIX App. - 9 App. 2.7 Technical data App. 2.7.1 MR-JE servo amplifier Item MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A/ MR-JE-70A MR-JE-100A/MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A Line voltage 3-phase or 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz Power supply Interface (SELV) 24 V DC, (required current capacity: 300 mA) Control method Sine-wave PWM control, current control method Pollution degree 2 (IEC/EN 60664-1) Overvoltage category III (IEC/EN 60664-1) Protection class I (IEC/EN 61800-5-1) Short-circuit current rating (SCCR) 100 kA App. 2.7.2 Servo amplifier dimensions Variable dimension table [mm] Servo amplifier W H D Mass [kg] MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A 50 168 135 0.8 MR-JE-70A/MR-JE-100A 70 168 185 1.5 MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A 90 168 195 2.1 WD H Front Side App. 2.7.3 Mounting hole Variable dimensions [mm] Servo amplifier a a1 b c d Screw size e MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A 6 6 156 ± 0.5 6 M5 MR-JE-70A/MR-JE-100A 22 22 156 ± 0.5 6 42 ± 0.3 M5 MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A 6 45 156 ± 0.5 6 78 ± 0.3 M5 da c b c a1 e APPENDIX App. - 10 App. 3 Analog monitor POINT A voltage of analog monitor output may be irregular at power-on. The servo status can be outputted to two channels in terms of voltage. (1) Setting Change the following digits of [Pr. PC14] and [Pr. PC15]. Analog monitor 1 output selection (the signal provided to the output across MO1 and LG) 00 [Pr. PC14] Analog monitor 2 output selection (the signal provided to the output across MO2 and LG) 00 [Pr. PC15] [Pr. PC39] and [Pr. PC40] can be used to set the offset voltages to the analog output voltages. Setting value is -9999 mV to 9999 mV. Parameter Description Setting range [mV] PC39 This is used to set the offset voltage of MO1 (Analog monitor 1). PC40 This is used to set the offset voltage of MO2 (Analog monitor 2). -9999 to 9999 APPENDIX App. - 11 (2) Setting The servo amplifier is factory-set to output the servo motor speed to MO1 (Analog monitor 1) and the torque to MO2 (Analog monitor 2). The setting can be changed as listed below by setting the [Pr. PC14] and [Pr. PC15] value. Refer to (3) for the detection point. Setting value Output item Description Setting value Output item Description 00 Servo motor speed Maximum speed CW direction CCW direction Maximum speed 0 8 [V] -8 [V] 01 Torque Maximum torque Power running in CW direction Power running in CCW direction Maximum torque 0 8 [V] -8 [V] 02 Servo motor speed Maximum speed CW direction CCW direction Maximum speed 0 8 [V] 03 Torque Maximum torque Power running in CW direction Power running in CCW direction Maximum torque 0 8 [V] 04 Current command Maximum current command (Maximum torque command) CW direction CCW direction Maximum current command (Maximum torqu e command) 0 8 [V] -8 [V] 05 The command pulse frequency (±10 V/±4 Mpulses/s) 4 [Mpulse/s] CW direction CCW direction 4 [Mpulse/s] 0 10 [V] -10 [V] 06 Servo motor-side droop pulses (Note 1, 2, 3) (±10 V/100 pulses) 100 [pulse] CW direction CCW direction 100 [pulse] 0 10 [V] -10 [V] 07 Servo motor-side droop pulses (Note 1, 2, 3) (±10 V/1000 pulses) 1000 [pulse] CW direction CCW direction 1000 [pulse] 0 10 [V] -10 [V] 08 Servo motor-side droop pulses (Note 1, 2, 3) (±10 V/10000 pulses) 10000 [pulse] CW direction CCW direction 10000 [pulse] 0 10 [V] -10 [V] 09 Servo motor-side droop pulses (Note 1, 2, 3) (±10 V/100000 pulses) 100000 [pulse] CW direction CCW direction 100000 [pulse] 0 10 [V] -10 [V] 0D Bus voltage 400 [V] 0 8 [V] 0E Speed command 2 (Note 2) Maximum speed CW direction CCW direction Maximum speed 0 8 [V] -8 [V] 17 Encoder inside temperature (±10 V/±128 ˚C) 128 [°C] -128 [°C] 0 10 [V] -10 [V] APPENDIX App. - 12 Note 1. Encoder pulse unit 2. This cannot be used in the torque control mode. 3. This cannot be used in the speed control mode. (3) Analog monitor block diagram Droop pulses Speed command Position control Speed control PWM Current control Current command Bus voltage Speed command Current encoder + Servo motor Encoder Current feedback Position feedback M Command pulse Differen- tiation Encoder inside temperature Servo motor speed Torque + + - - + - Speed command 2 APPENDIX App. - 13 App. 4 Low-voltage directive MR-JE series servo amplifiers are certificated in compliance with Low-voltage directive. The following shows a certificate by the Certification Body. Supplementation: Refer to section 1.6 (2) for the models shown in "(see Appendix 1)". REVISIONS *The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover. Print Data *Manual Number Revision May. 2013 SH(NA)030128-A First edition Jul. 2013 SH(NA)030128-B 4. Additional instructions (3) Transportation and installation Section 1.3 Section 1.6 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Section 3.2.1 Section 3.4 Section 3.5 Section 3.6.1 Section 3.9.1 Section 3.9.2 Section 3.9.3 Section 5.2.1 Section 11.3 Section 11.6 App. 2 Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. CAUTION is partially changed. CAUTION is partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially deleted. Partially added and partially changed in Pr. PA13. Partially changed. Partially changed. Partially changed. This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual. 2013 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION Country/Region Sales office Tel/Fax USA Germany Italy China Taiwan Korea Singapore Mitsubishi Electric Automation Inc. 500 Corporate Woods Parkway, Vernon Hills, IL 60061, USA Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V. German Branch Gothaer Strasse 8, D-40880 Ratingen, Germany Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V. Italian Branch Viale Colleoni 7 1-20041 Agrate Brianza (Milano), Italy Mitsubishi Electric Automation (China) Ltd. 4F Zhi Fu Plazz, No. 80 Xin Chang Road Shanghai 200003, China Setsuyo Enterprise Co., Ltd. 6F, No.105 Wu-Kung 3rd Rd, Wu-Ku Hsiang, Taipei Hsine, Taiwan Mitsubishi Electric Automation Korea Co., Ltd. 3F, 1480-6, Gayang-dong, Gangseo-gu, Seoul 157-200, Korea Mitsubishi Electric Asia Pte, Ltd. 307 Alexandra Road #05-01/02, Mitsubishi Electric Building Singapore 159943 Tel Fax Tel Fax Tel Fax Tel Fax Tel Fax Tel Fax Tel Fax : +1-847-478-2100 : +1-847-478-0327 : +49-2102-486-0 : +49-2102-486-1120 : +39-39-60531 : +39-39-6053312 : +86-21-6120-0808 : +86-21-6121-2444 : +886-2-2299-2499 : +886-2-2299-2509 : +82-2-3660-9552 : +82-2-3664-8372 : +65-6470-2460 : +65-6476-7439 Warranty 1. Warranty period and coverage We will repair any failure or defect hereinafter referred to as "failure" in our FA equipment hereinafter referred to as the "Product" arisen during warranty period at no charge due to causes for which we are responsible through the distributor from which you purchased the Product or our service provider. However, we will charge the actual cost of dispatching our engineer for an on-site repair work on request by customer in Japan or overseas countries. We are not responsible for any on-site readjustment and/or trial run that may be required after a defective unit are repaired or replaced. [Term] The term of warranty for Product is twelve (12) months after your purchase or delivery of the Product to a place designated by you or eighteen (18) months from the date of manufacture whichever comes first (“Warranty Period”). Warranty period for repaired Product cannot exceed beyond the original warranty period before any repair work. [Limitations] (1) You are requested to conduct an initial failure diagnosis by yourself, as a general rule. It can also be carried out by us or our service company upon your request and the actual cost will be charged. However, it will not be charged if we are responsible for the cause of the failure. (2) This limited warranty applies only when the condition, method, environment, etc. of use are in compliance with the terms and conditions and instructions that are set forth in the instruction manual and user manual for the Product and the caution label affixed to the Product. (3) Even during the term of warranty, the repair cost will be charged on you in the following cases; (i) a failure caused by your improper storing or handling, carelessness or negligence, etc., and a failure caused by your hardware or software problem (ii) a failure caused by any alteration, etc. to the Product made on your side without our approval (iii) a failure which may be regarded as avoidable, if your equipment in which the Product is incorporated is equipped with a safety device required by applicable laws and has any function or structure considered to be indispensable according to a common sense in the industry (iv) a failure which may be regarded as avoidable if consumable parts designated in the instruction manual, etc. are duly maintained and replaced (v) any replacement of consumable parts (battery, fan, smoothing capacitor, etc.) (vi) a failure caused by external factors such as inevitable accidents, including without limitation fire and abnormal fluctuation of voltage, and acts of God, including without limitation earthquake, lightning and natural disasters (vii) a failure generated by an unforeseeable cause with a scientific technology that was not available at the time of the shipment of the Product from our company (viii) any other failures which we are not responsible for or which you acknowledge we are not responsible for 2. Term of warranty after the stop of production (1) We may accept the repair at charge for another seven (7) years after the production of the product is discontinued. The announcement of the stop of production for each model can be seen in our Sales and Service, etc. (2) Please note that the Product (including its spare parts) cannot be ordered after its stop of production. 3. Service in overseas countries Our regional FA Center in overseas countries will accept the repair work of the Product. However, the terms and conditions of the repair work may differ depending on each FA Center. Please ask your local FA center for details. 4. Exclusion of responsibility for compensation against loss of opportunity, secondary loss, etc. Whether under or after the term of warranty, we assume no responsibility for any damages arisen from causes for which we are not responsible, any losses of opportunity and/or profit incurred by you due to a failure of the Product, any damages, secondary damages or compensation for accidents arisen under a specific circumstance that are foreseen or unforeseen by our company, any damages to products other than the Product, and also compensation for any replacement work, readjustment, start-up test run of local machines and the Product and any other operations conducted by you. 5. Change of Product specifications Specifications listed in our catalogs, manuals or technical documents may be changed without notice. 6. Application and use of the Product (1) For the use of our General-Purpose AC Servo, its applications should be those that may not result in a serious damage even if any failure or malfunction occurs in General-Purpose AC Servo, and a backup or fail-safe function should operate on an external system to General-Purpose AC Servo when any failure or malfunction occurs. (2) Our General-Purpose AC Servo is designed and manufactured as a general purpose product for use at general industries. Therefore, applications substantially influential on the public interest for such as atomic power plants and other power plants of electric power companies, and also which require a special quality assurance system, including applications for railway companies and government or public offices are not recommended, and we assume no responsibility for any failure caused by these applications when used In addition, applications which may be substantially influential to human lives or properties for such as airlines, medical treatments, railway service, incineration and fuel systems, man-operated material handling equipment, entertainment machines, safety machines, etc. are not recommended, and we assume no responsibility for any failure caused by these applications when used. We will review the acceptability of the abovementioned applications, if you agree not to require a specific quality for a specific application. Please contact us for consultation. SH(NA)030128-B SH (NA) 030128-B (1307) MEE Printed in Japan Specifications are subject to change without notice. This Instruction Manual uses recycled paper. MODEL MODEL CODE General-Purpose AC Servo MR-JE-_A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL HEAD OFFICE : TOKYO BLDG MARUNOUCHI TOKYO 100-8310 MODEL MR-JE-_A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL General-Purpose Interface AC Servo 1CW706 MR-JE-A SERVOAMPLIFIER INSTRUCTIONMANUAL B B
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Troubleshooting
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
General-Purpose AC Servo
General-Purpose Interface AC Servo
MODEL
MR-JE-_A
SERVO AMPLIFIER
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
B
Related Manuals for Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A
Summary of Contents for Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A
-
Page 1
General-Purpose AC Servo General-Purpose Interface AC Servo MODEL MR-JE-_A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL… -
Page 2: Safety Instructions
Safety Instructions Please read the instructions carefully before using the equipment. To use the equipment correctly, do not attempt to install, operate, maintain, or inspect the equipment until you have read through this Instruction Manual, Installation guide, and appended documents carefully. Do not use the equipment until you have a full knowledge of the equipment, safety information and instructions.
-
Page 3
1. To prevent electric shock, note the following WARNING Before wiring and inspections, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier. -
Page 4
4. Additional instructions The following instructions should also be fully noted. Incorrect handling may cause a malfunction, injury, electric shock, etc. (1) Transportation and installation CAUTION Transport the products correctly according to their mass. Stacking in excess of the specified number of product packages is not allowed. Do not hold the lead wire of the regenerative resistor when transporting the servo amplifier. -
Page 5
(2) Wiring CAUTION Before removing the CNP1 connector of MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, disconnect the lead wires of the regenerative resistor from the CNP1 connector. Wire the equipment correctly and securely. Otherwise, the servo motor may operate unexpectedly. Do not install a power capacitor, surge killer, or radio noise filter (optional FR-BIF) on the servo amplifier output side. -
Page 6
(4) Usage CAUTION When it is assumed that a hazardous condition may occur due to a power failure or product malfunction, use a servo motor with an external brake to prevent the condition. Do not disassemble, repair, or modify the equipment. Before resetting an alarm, make sure that the run signal of the servo amplifier is off in order to prevent a sudden restart. -
Page 7
(7) General instruction To illustrate details, the equipment in the diagrams of this Instruction Manual may have been drawn without covers and safety guards. When the equipment is operated, the covers and safety guards must be installed as specified. Operation must be performed in accordance with this Instruction Manual. DISPOSAL OF WASTE Please dispose a servo amplifier and other options according to your local laws and regulations. -
Page 8: Table Of Contents
CONTENTS 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1- 1 to 1-12 1.1 Summary……………………….1- 1 1.2 Function block diagram……………………1- 2 1.3 Servo amplifier standard specifications ……………….. 1- 4 1.4 Combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors ……………. 1- 5 1.5 Function list……………………….1- 5 1.6 Model designation……………………..
-
Page 9
3.9 Interfaces ……………………….3-50 3.9.1 Internal connection diagram…………………. 3-50 3.9.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces………………… 3-52 3.9.3 Source I/O interfaces …………………… 3-56 3.10 Servo motor with an electromagnetic brake ……………… 3-57 3.10.1 Safety precautions ……………………3-57 3.10.2 Timing chart ……………………..3-58 3.11 Grounding ………………………. -
Page 10
5.1.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) …………….5- 2 5.1.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) …………….5- 3 5.1.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) ………………5- 5 5.1.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ])…………….5- 6 5.1.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. -
Page 11
8.2 Remedies for alarms……………………. 8- 6 8.3 Remedies for warnings ……………………8-24 9. DIMENSIONS 9- 1 to 9- 6 9.1 Servo amplifier ……………………..9- 1 9.2 Connector ……………………….9- 4 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10- 1 to 10- 8 10.1 Overload protection characteristics ………………..10- 1 10.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss ……………… -
Page 12: Functions And Configuration
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.1 Summary The Mitsubishi general-purpose AC servo MELSERVO-JE series have limited functions with keeping high performance based on MELSERVO-J4 series. The servo amplifier has position, speed, and torque control modes. In the position control mode, the maximum pulse train of 4 Mpulses/s is supported.
-
Page 13: Function Block Diagram
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.2 Function block diagram The function block diagram of this servo is shown below. (1) MR-JE-100A or less Regenerative option Servo motor Diode Dynamic stack Relay brake circuit (Note 1) MCCB (Note 2) Current Power Regene- encoder supply rative…
-
Page 14
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION (2) MR-JE-200A or more Regenerative option Servo motor N- (Note 2) Diode Dynamic stack brake circuit Relay MCCB (Note 1) Current Power encoder Regene- supply rative CHARGE lamp Cooling fan Electromagnetic 24 V DC brake Control circuit Base Voltage… -
Page 15: Servo Amplifier Standard Specifications
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.3 Servo amplifier standard specifications Model: MR-JE- 100A 200A 300A Rated voltage 3-phase 170 V AC Output Rated current 11.0 11.0 3-phase or 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Voltage/Frequency Hz/60 Hz Hz/60 Hz…
-
Page 16: Combinations Of Servo Amplifiers And Servo Motors
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.4 Combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors Servo amplifier Servo motor MR-JE-10A HF-KN13 MR-JE-20A HF-KN23 MR-JE-40A HF-KN43 MR-JE-70A HF-KN73 HF-SN52 MR-JE-100A HF-SN102 MR-JE-200A HF-SN152, HF-SN202 MR-JE-300A HF-SN302 1.5 Function list The following table lists the functions of this servo. For details of the functions, refer to each section indicated in the detailed explanation field.
-
Page 17
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION Detailed Function Description explanation Alarm history clear Alarm history is cleared. [Pr. PC18] Output signal selection ST1 (Forward rotation start), ST2 (Reverse rotation start), and SON (Servo-on) and [Pr. PD03] to (device settings) other input device can be assigned to any pins. [Pr. -
Page 18: Model Designation
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.6 Model designation (1) Rating plate The following shows an example of rating prate for explanation of each item. Serial number AC SERVO SER. S33001001 Model MR-JE-10A Capacity POWER : 100W Applicable power supply INPUT : 3AC/AC200-240V 0.9A/1.5A 50/60Hz Rated output current OUTPUT : 3PH170V 0-360Hz 1.1A…
-
Page 19: Structure
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.7 Structure 1.7.1 Parts identification (1) MR-JE-100A or less Detailed Name/Application explanati Display Section The 5-digit, 7-segment LED shows the servo status and the alarm number. Operation section Used to perform status display, diagnostic, alarm, and parameter setting operations. Push the «MODE» and «SET»…
-
Page 20
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION (2) MR-JE-200A or more Detailed Name/Application explanati Display Section The 5-digit, 7-segment LED shows the servo status and the alarm number. Operation section Used to perform status display, diagnostic, alarm, and parameter setting operations. Push the «MODE» and «SET»… -
Page 21: Configuration Including Peripheral Equipment
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1.8 Configuration including peripheral equipment Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the servo CAUTION amplifier may cause a malfunction. POINT Equipment other than the servo amplifier and servo motor are optional or recommended products.
-
Page 22
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION (2) MR-JE-200A or more The diagram shows MR-JE-200A. R S T (Note 1) Power supply Molded-case circuit breaker Personal computer MR Configurator2 (Note 2) Magnetic contactor (MC) Power factor improving AC reactor (FR-HAL) Line noise filter (FR-BSF01) Junction terminal block Servo motor… -
Page 23
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION MEMO 1 — 12… -
Page 24: Installation
2. INSTALLATION 2. INSTALLATION WARNING To prevent electric shock, ground each equipment securely. Stacking in excess of the specified number of product packages is not allowed. Do not hold the lead wire of the regenerative resistor when transporting the servo amplifier.
-
Page 25: Installation Direction And Clearances
2. INSTALLATION 2.1 Installation direction and clearances The equipment must be installed in the specified direction. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. CAUTION Leave specified clearances between the servo amplifier and the cabinet walls or other equipment. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction. MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A have a regenerative resistor on their back face.
-
Page 26: Keep Out Foreign Materials
2. INSTALLATION (b) Installation of two or more servo amplifiers POINT Close mounting is possible for all capacity type of MR-JE servo amplifiers. Leave a large clearance between the top of the servo amplifier and the cabinet walls, and install a cooling fan to prevent the internal temperature of the cabinet from exceeding the environment.
-
Page 27: Encoder Cable Stress
2. INSTALLATION 2.3 Encoder cable stress (1) The way of clamping the cable must be fully examined so that bending stress and cable’s own weight stress are not applied to the cable connection. (2) For use in any application where the servo motor moves, fix the cables (encoder, power supply, and brake) with having some slack from the connector connection part of the servo motor to avoid putting stress on the connector connection part.
-
Page 28: Parts Having Service Lives
2. INSTALLATION 2.5 Parts having service lives Service lives of the following parts are listed below. However, the service life vary depending or operating methods and environment. If any fault is found in the parts, they must be replaced immediately regardless of their service lives.
-
Page 29
2. INSTALLATION MEMO 2 — 6… -
Page 30: Signals And Wiring
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Any person who is involved in wiring should be fully competent to do the work. Before wiring, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier.
-
Page 31: Input Power Supply Circuit
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.1 Input power supply circuit Always connect a magnetic contactor between the power supply and the power supply (L1, L2, and L3) of the servo amplifier, in order to configure a circuit that shuts down the power supply on the side of the servo amplifier’s power supply. If a magnetic contactor is not connected, continuous flow of a large current may cause a fire when the servo amplifier malfunctions.
-
Page 32
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (1) For 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply of MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A EMG stop switch Malfunction Servo amplifier Servo motor (Note 5) MCCB CNP1 3-phase (Note 4, 7) Built-in 200 V AC to Motor regenerative 240 V AC… -
Page 33
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply of MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-70A POINT Connect the 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply to L1 and L3. One of the connecting destinations is different from MR-E Super Series Servo Amplifier’s. -
Page 34
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (3) MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A EMG stop switch Malfunction Servo amplifier Servo motor (Note 5) MCCB CNP1 3-phase CNP2 (Note 4, 7) 200 V AC to Motor 240 V AC (Note 1) (Note 7) (Note 2) Encoder Encoder cable (Note 6) Power supply… -
Page 35: I/O Signal Connection Example
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.2 I/O signal connection example 3.2.1 Position control mode (1) When you use a positioning module LD75D/QD75D (a) For sink I/O interface Servo amplifier 24 V DC (Note 4) (Note 7) Positioning module 24 V DC (Note 4) LD75D/QD75D (Note 7) DOCOM…
-
Page 36
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. 2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier will malfunction and will not output signals, disabling EM2 (Forced stop 2) and other protective circuits. -
Page 37
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (b) For source I/O interface POINT For notes, refer to (1) (a) in this section. Servo amplifier 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) (Note 7) Positioning module 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) LD75D/QD75D (Note 7) DOCOM (Note 2) (Note 14) -
Page 38
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) When you use a positioning module FX -_ _MT/ES (For sink I/O interface) 2 m or less (NoteProgrammable controller -_ _MT/ES (Note 11) (Note 15) 24 V Servo amplifier (Note 7) (Note 7) 24 V DC 24 V DC (Note 4) Programmable…
-
Page 39
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. 2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier will malfunction and will not output signals, disabling EM2 (Forced stop 2) and other protective circuits. -
Page 40: Speed Control Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.2.2 Speed control mode (1) For sink I/O interface Servo amplifier (Note 7) 24 V DC (Note 4) DOCOM DOCOM (Note 2) 10 m or less Malfunction (Note 6) (Note 7) (Note 11) Power supply Zero speed detection (Note 3, 5) Forced stop 2 Servo-on…
-
Page 41
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) For source I/O interface POINT For notes, refer to (1) in this section. Servo amplifier (Note 7) 24 V DC (Note 4, 12) DOCOM DOCOM (Note 2) 10 m or less Malfunction (Note 6) (Note 7) (Note 11) Power supply Zero speed detection… -
Page 42: Torque Control Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.2.3 Torque control mode POINT EM2 has the same function as EM1 in the torque control mode. (1) For sink I/O interface Servo amplifier (Note 6) 24 V DC (Note 4) DOCOM DOCOM (Note 2) 10 m or less Malfunction (Note 6) (Note 6) (Note 9)
-
Page 43
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) For source I/O interface POINT For notes, refer to (1) in this section. Servo amplifier (Note 6) 24 V DC (Note 4, 10) DOCOM DOCOM (Note 2) 10 m or less Malfunction (Note 5) (Note 6) (Note 9) Power supply Zero speed detection… -
Page 44: Explanation Of Power Supply System
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.3 Explanation of power supply system 3.3.1 Signal explanations POINT For the layout of connector and terminal block, refer to chapter 9 DIMENSIONS. Connection target Symbol Description (application) Supply the following power to L1, L2, and L3. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3.
-
Page 45: Power-On Sequence
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.3.2 Power-on sequence POINT The voltage of analog monitor output, output signal, etc. may be unstable at power-on. (1) Power-on procedure 1) Always wire the power supply as shown in above section 3.1 using the magnetic contactor with the power supply (3-phase: L1, L2, and L3, 1-phase: L1 and L3).
-
Page 46: Wiring Cnp1 And Cnp2
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.3.3 Wiring CNP1 and CNP2 POINT For the wire sizes used for wiring, refer to section 11.5. To wire to CNP1 and CNP2, use servo amplifier power connectors packed with the amplifier or optional connectors (refer to section 11.1.1). (1) Connector (a) MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-100A Servo amplifier…
-
Page 47
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) Cable connection procedure (a) Fabrication on cable insulator Refer to table 3.1 and 3.2 for stripped length of cable insulator. The appropriate stripped length of cables depends on their type, etc. Set the length considering their status. Insulator Core Stripped length… -
Page 48: Connectors And Pin Assignment
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.4 Connectors and pin assignment POINT The pin assignment of the connectors are as viewed from the cable connector wiring section. For the CN1 connector, securely connect the external conductor of the shielded cable to the ground plate and fix it to the connector shell. Screw Cable Screw…
-
Page 49
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING The device assignment of CN1 connector pins changes depending on the control mode. For the pins which are given parameters in the related parameter column, their devices will be changed using those parameters. (Note 2) I/O signals in control modes (Note 1) Pin No. -
Page 50: Signal (Device) Explanations
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (Note 2) I/O signals in control modes (Note 1) Pin No. Related parameter DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM DOCOM Pr. PD28 Note 1. I: input signal, O: output signal 2. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode, P/S: position/speed control switching mode, S/T: speed/torque control switching mode, T/P: torque/position control switching mode 3.
-
Page 51
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Reset CN1-19 Turn on RES for more than 50 ms to reset the alarm. DI-1 Some alarms cannot be deactivated by RES (Reset). Refer to section 8.1. Turning RES on in an alarm-free status shuts off the base circuit. -
Page 52
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Forward rotation This is used to select a servo motor torque generation directions. DI-1 selection The following shows the torque generation directions. (Note) Input device Torque generation direction Torque is not generated. -
Page 53
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Proportion Turn PC on to switch the speed amplifier from the proportional integral type DI-1 control to the proportional type. If the servo motor at a stop is rotated even one pulse due to any external factor, it generates torque to compensate for a position shift. -
Page 54
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Control switching «Position/speed control switching mode» DI-1 Refer to Function This is used to select the control mode in the position/speed control switching mode. application. (Note) Control mode… -
Page 55
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (b) Output device Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Malfunction CN1-48 When an alarm occurs, ALM will turn off. DO-1 When an alarm does not occur, ALM will turn on after 2.5 s to 3.5 s after power-on. -
Page 56
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Alarm code ACD0 (CN1-24) To use these signals, set » _ _ _ 1″ in [Pr. PD34]. DI-1 This signal is outputted when an alarm occurs. ACD1 (CN1-23) When an alarm is not occurring, respective ordinary signals are outputted. -
Page 57
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (3) Output signal Control Connector Device Symbol Function and application mode pin No. division Encoder A- CN1-4 These devices output pulses of encoder output pulse set in [Pr. PA15] in DO-2 phase pulse the differential line driver type. CN1-5 (differential line In CCW rotation of the servo motor, the encoder B-phase pulse lags the… -
Page 58: Detailed Explanation Of Signals
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.6 Detailed explanation of signals 3.6.1 Position control mode POINT Adjust the logic of a positioning module and command pulse as follows. Q series/L series positioning module Command pulse logic setting Signal type MR-JE-_A servo amplifier Q series/L series positioning module Pr.
-
Page 59
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING The following section explains about the case where the negative logic and the forward/reverse rotation pulse trains are set to «_ _ 1 0» in [Pr. PA13]. (ON) (ON) (ON) (OFF) (OFF) (OFF) Forward rotation pulse train (transistor) Reverse rotation pulse train (OFF) -
Page 60
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) INP (In-position) INP turns on when the number of droop pulses in the deviation counter falls within the preset in-position range ([Pr. PA10]). INP may turn on continuously during a low-speed operation with a large value set as the in-position range. -
Page 61
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (5) Torque limit If the torque limit is canceled during servo-lock, the servo motor may suddenly CAUTION rotate according to position deviation in respect to the command position. (a) Torque limit and torque By setting [Pr. PA11 Forward rotation torque limit] or [Pr. PA12 Reverse rotation torque limit], torque is always limited to the maximum value during operation. -
Page 62
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (Note) Input device Enabled torque limit value Limit value status CCW power running/CW CW power running/CCW regeneration regeneration Pr. PA11 Pr .PA12 Pr. PA11 > Pr. PA11 Pr. PA12 Pr. PA12 Pr. PA11 < Pr. PA12 Pr. -
Page 63: Speed Control Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.6.2 Speed control mode (1) Speed setting (a) Speed command and speed The servo motor is run at the speeds set in the parameters or at the speed set in the applied voltage of VC (Analog speed command). A relation between VC (Analog speed command) applied voltage and the servo motor speed is as follows.
-
Page 64
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (b) Speed command value selection To select VC (Analog speed command) and a speed command value of internal speed commands 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. -
Page 65: Torque Control Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.6.3 Torque control mode (1) Torque limit (a) Torque command and torque The following shows a relation between the applied voltage of TC (Analog torque command) and the torque by the servo motor. The maximum torque is generated at ±8 V. The speed at ±8 V can be changed with [Pr. PC13]. CCW direction Forward rotation Maximum torque…
-
Page 66
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (b) Analog torque command offset Using [Pr. PC38], the offset voltage of -9999 mV to 9999 mV can be added to the TC applied voltage as follows. Maximum torque Torque [Pr. PC38] offset range -9999 mV to 9999 mV 8 (-8) TC applied voltage [V] (2) Torque limit… -
Page 67
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Normally, connect as follows. Servo amplifier -10 V to +10 V (b) Speed limit value selection To select VLA (Analog speed limit) and a speed limit value of internal speed limit 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. -
Page 68: Position/Speed Control Switching Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.6.4 Position/speed control switching mode Set » _ _ _ 1″ in [Pr. PA01] to switch to the position/speed control switching mode. (1) LOP (control switching) Use LOP (Control switching) to switch between the position control mode and the speed control mode with an external contact.
-
Page 69
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (3) Speed setting in speed control mode (a) Speed command and speed The servo motor is run at the speeds set in the parameters or at the speed set in the applied voltage of VC (Analog speed command). The relation between an applied voltage of VC (Analog speed command) and servo motor speed, and the rotation direction with turning on ST1/ST2 are the same as section 3.6.2 (1) (a). -
Page 70: Speed/Torque Control Switching Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.6.5 Speed/torque control switching mode Set » _ _ _ 3″ in [Pr. PA01] to switch to the speed/torque control switching mode. (1) LOP (control switching) Use LOP (Control switching) to switch between the speed control mode and the torque control mode with an external contact.
-
Page 71
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Normally, connect as follows. Servo amplifier -10 V to +10 V (b) Speed limit value selection To select VLA (Analog speed limit) and a speed limit value of internal speed limit 1 to 7, enable SP1 (Speed selection 1), SP2 (Speed selection 2), and SP3 (Speed selection 3) with [Pr. -
Page 72: Torque/Position Control Switching Mode
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.6.6 Torque/position control switching mode Set » _ _ _ 5″ in [Pr. PA01] to switch to the torque/position control switching mode. (1) LOP (control switching) Use LOP (Control switching) to switch between the torque control mode and the position control mode with an external contact.
-
Page 73: Forced Stop Deceleration Function
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.7 Forced stop deceleration function POINT When alarms not related to the forced stop function occur, control of motor deceleration can not be guaranteed. (Refer to chapter 8.) In the torque control mode, the forced stop deceleration function is not available. 3.7.1 Forced stop deceleration function When EM2 is turned off, dynamic brake will start to stop the servo motor after forced stop deceleration.
-
Page 74
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) Timing chart POINT When LSP/LSN is turned on during a forced stop deceleration, the motor will stop depending on the setting of [Pr. PD30] as follows. [Pr. PD30] Stop system _ _ _ 0 Switching to sudden stop _ _ _ 1 Continuing forced stop deceleration When EM2 (Forced stop 2) turns off, the motor will decelerate according to [Pr. -
Page 75: Base Circuit Shut-Off Delay Time Function
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.7.2 Base circuit shut-off delay time function The base circuit shut-off delay time function is used to prevent vertical axis from dropping at a forced stop (EM2 goes off) or alarm occurrence due to delay time of the electromagnetic brake. Use [Pr. PC16] to set the delay time between completion of EM2 (Forced stop 2) or activation of MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) due to an alarm occurrence, and shut-off of the base circuit.
-
Page 76: Vertical Axis Freefall Prevention Function
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.7.3 Vertical axis freefall prevention function The vertical axis freefall prevention function avoids machine damage by pulling up the shaft slightly like the following case. When the servo motor is used for operating vertical axis, the servo motor electromagnetic brake and the base circuit shut-off delay time function avoid dropping axis at forced stop.
-
Page 77: Alarm Occurrence Timing Chart
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.8 Alarm occurrence timing chart When an alarm has occurred, remove its cause, make sure that the operation CAUTION signal is not being input, ensure safety, and reset the alarm before restarting operation. POINT In the torque control mode, the forced stop deceleration function is not available. To deactivate an alarm, cycle the power, push the «SET»…
-
Page 78: When You Do Not Use The Forced Stop Deceleration Function
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) When the forced stop deceleration function is not enabled Alarm occurrence Braking by the dynamic brake Dynamic brake + Braking by the electromagnetic brake Servo motor speed 0 r/min Base circuit (Energy supply to the servo motor) Servo amplifier No alarm Alarm No.
-
Page 79: Interfaces
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.9 Interfaces 3.9.1 Internal connection diagram The following diagram is for sink I/O interface when command pulse train input is differential line driver type. Servo amplifier (Note 1) (Note 4) 24 V DC (Note 1) DOCOM Approx.
-
Page 80
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING Note 1. P: position control mode, S: speed control mode, T: torque control mode 2. This is for the differential line driver pulse train input. For the open-collector pulse train input, connect as follows. DOCOM 24 V DC DICOM DOCOM 3. -
Page 81: Detailed Explanation Of Interfaces
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.9.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces This section provides the details of the I/O signal interfaces (refer to the I/O division in the table) given in section 3.5. Refer to this section and make connection with the external device. (1) Digital input interface DI-1 This is an input circuit whose photocoupler cathode side is input terminal.
-
Page 82
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (3) Pulse train input interface DI-2 Give a pulse train signal in the differential line driver type or open-collector type. (a) Differential line driver type 1) Interface Servo amplifier Max. input pulse frequency 4 Mpulses/s (Note 2) 10 m or less PP (NP) Approximalely… -
Page 83
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 2) Input pulse condition tLH = tHL < 0.2 µs tc > 2 µs tF > 3 µs (4) Encoder output pulse DO-2 (a) Open-collector type Interface Maximum sink current: 35 mA 5 V DC to 24 V DC Servo amplifier Servo amplifier Photocoupler… -
Page 84
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 2) Output pulse Servo motor CCW rotation Time cycle (T) is determined by the settings of [Pr. PA15] and [Pr. PC19]. 400 s or more (5) Analog input Input impedance 10 k to 12 k Servo amplifier VC etc. -
Page 85: Source I/O Interfaces
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.9.3 Source I/O interfaces In this servo amplifier, source type I/O interfaces can be used. (1) Digital input interface DI-1 This is an input circuit whose photocoupler anode side is the input terminal. Transmit signals from source (open-collector) type transistor output, relay switch, etc.
-
Page 86: Servo Motor With An Electromagnetic Brake
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.10 Servo motor with an electromagnetic brake 3.10.1 Safety precautions Configure an electromagnetic brake circuit so that it is activated also by an external EMG stop switch. Contacts must be opened when ALM (Malfunction) Contacts must be opened with the or MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) turns off.
-
Page 87: Timing Chart
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) Setting (a) Enable MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) with [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD20]. (b) In [Pr. PC16 Electromagnetic brake sequence output], set the time delay (Tb) from electromagnetic brake operation to base circuit shut-off at a servo-off as in the timing chart in section 3.10.2 (1). 3.10.2 Timing chart (1) When you use the forced stop deceleration function POINT…
-
Page 88
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (b) Forced stop 2 on/off POINT In the torque control mode, the forced stop deceleration function is not available. (Note 2) Model speed command 0 and equal to or less than zero speed Servo motor speed 0 r/min Base circuit (Energy supply to… -
Page 89
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING (2) When you do not use the forced stop deceleration function POINT To disable the function, set «0 _ _ _» in [Pr. PA04]. (a) SON (Servo-on) on/off It is the same as (1) (a) in this section. (b) EM1 (Forced stop 1) on/off Dynamic brake Dynamic brake… -
Page 90: Grounding
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3.11 Grounding Ground the servo amplifier and servo motor securely. WARNING To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet. The servo amplifier switches the power transistor on-off to supply power to the servo motor.
-
Page 91
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING MEMO 3 — 62… -
Page 92: Startup
4. STARTUP 4. STARTUP Do not operate the switches with wet hands. Otherwise, it may cause an electric WARNING shock. Before starting operation, check the parameters. Improper settings may cause some machines to operate unexpectedly. The servo amplifier heat sink, regenerative resistor, servo motor, etc. may be hot CAUTION while power is on or for some time after power-off.
-
Page 93: Wiring Check
4. STARTUP 4.1.2 Wiring check (1) Power supply system wiring Before switching on the power supply, check the following items. (a) Power supply system wiring The power supplied to the power input terminals (L1, L2, and L3) of the servo amplifier should satisfy the defined specifications.
-
Page 94: Surrounding Environment
4. STARTUP (2) I/O signal wiring (a) The I/O signals should be connected correctly. Use DO forced output to forcibly turn on/off the pins of the CN1 connector. This function can be used to perform a wiring check. Switch off SON (Servo-on) to enable the function. Refer to section 3.2 for details of I/O signal connection.
-
Page 95: Startup In Position Control Mode
4. STARTUP 4.2 Startup in position control mode Make a startup in accordance with section 4.1. This section provides descriptions specific to the position control mode. 4.2.1 Power on and off procedures (1) Power-on Switch power on in the following procedure. Always follow this procedure at power-on. 1) Switch off SON (Servo-on).
-
Page 96: Test Operation
4. STARTUP 4.2.3 Test operation Before starting actual operation, perform test operation to make sure that the machine operates normally. Refer to section 4.2.1 for how to power on and off the servo amplifier. Test operation of the servo motor In this step, confirm that the servo amplifier and servo motor operate alone in JOG operation of test normally.
-
Page 97: Parameter Setting
4. STARTUP 4.2.4 Parameter setting POINT The following encoder cables are of four-wire type. When using any of these encoder cables, set [Pr. PC22] to «1 _ _ _» to select the four-wire type. Incorrect setting will result in [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1]. MR-EKCBL30M-L MR-EKCBL30M-H MR-EKCBL40M-H…
-
Page 98: Trouble At Start-Up
4. STARTUP 4.2.6 Trouble at start-up Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so CAUTION will make the operation unstable. POINT Using the optional MR Configurator2, you can refer to reason for rotation failure, etc.
-
Page 99
4. STARTUP (2) How to find the cause of position shift Controller Servo amplifier Machine (a) Output pulse Servo motor counter Electronic gear [Pr.PA05], [Pr.PA06], (d) Machine stop position M [Pr.PA07], [Pr.PA21] (b) Cumulative command pulses Cause B Cause A SON (Servo-on) input LSP/LSN (Stroke end) input Encoder… -
Page 100: Startup In Speed Control Mode
4. STARTUP 2) When P • During operation, SON (Servo-on), LSP (Forward rotation stroke end), or LSN (Reverse rotation stroke end) was switched off; or CR (Clear) or RES (Reset) was switched on. (Cause C) 3) When C • Mechanical slip occurred between the servo motor and machine. (Cause B) 4.3 Startup in speed control mode Make a startup in accordance with section 4.1.
-
Page 101: Test Operation
4. STARTUP 4.3.3 Test operation Before starting actual operation, perform test operation to make sure that the machine operates normally. Refer to section 4.3.1 for how to power on and off the servo amplifier. Test operation of the servo motor In this step, confirm that the servo amplifier and servo motor operate alone in JOG operation of test normally.
-
Page 102: Parameter Setting
4. STARTUP 4.3.4 Parameter setting POINT The following encoder cables are of four-wire type. When using any of these encoder cables, set [Pr. PC22] to «1 _ _ _» to select the four-wire type. Incorrect setting will result in [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1]. MR-EKCBL30M-L MR-EKCBL30M-H MR-EKCBL40M-H…
-
Page 103: Actual Operation
4. STARTUP 4.3.5 Actual operation Start actual operation after confirmation of normal operation by test operation and completion of the corresponding parameter settings. 4.3.6 Trouble at start-up Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so CAUTION will make the operation unstable.
-
Page 104: Startup In Torque Control Mode
4. STARTUP Start-up sequence Fault Investigation Possible cause Reference Gain adjustment Rotation ripples (speed Make gain adjustment in the Gain adjustment fault Chapter fluctuations) are large following procedure. at low speed. 1. Increase the auto tuning response level. 2. Repeat acceleration and deceleration several times to complete auto tuning.
-
Page 105: Test Operation
4. STARTUP 4.4.3 Test operation Before starting actual operation, perform test operation to make sure that the machine operates normally. Refer to section 4.4.1 for how to power on and off the servo amplifier. Test operation of the servo motor In this step, confirm that the servo amplifier and servo motor operate alone in JOG operation of test normally.
-
Page 106: Parameter Setting
4. STARTUP 4.4.4 Parameter setting POINT The following encoder cables are of four-wire type. When using any of these encoder cables, set [Pr. PC22] to «1 _ _ _» to select the four-wire type. Incorrect setting will result in [AL. 16 Encoder initial communication error 1]. MR-EKCBL30M-L MR-EKCBL30M-H MR-EKCBL40M-H…
-
Page 107: Trouble At Start-Up
4. STARTUP 4.4.6 Trouble at start-up Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so CAUTION will make the motion unstable. POINT Using the optional MR Configurator2, you can refer to reason for rotation failure, etc.
-
Page 108: Display And Operation Sections
4. STARTUP 4.5 Display and operation sections 4.5.1 Summary The MR-JE-A servo amplifier has the display section (5-digit, 7-segment LED) and operation section (4 pushbuttons) for servo amplifier status display, alarm display, parameter setting, etc. Push the «MODE» and «SET» buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the one-touch tuning mode. The operation section and display data are described below.
-
Page 109: Display Flowchart
4. STARTUP 4.5.2 Display flowchart Press the «MODE» button once to shift to the next display mode. Refer to section 4.5.3 and later for the description of the corresponding display mode. To refer to and set the gain/filter parameters, extension setting parameters and I/O setting parameters, enable them with [Pr.
-
Page 110: Status Display Mode
4. STARTUP 4.5.3 Status display mode The servo status during operation is shown on the 5-digit, 7-segment LED display. Press the «UP» or «DOWN» button to change display data as desired. When the required data is selected, the corresponding symbol is displayed. Press the «SET» button to display that data. At only power-on, however, data appears after the symbol of the status display selected in [Pr.
-
Page 111
4. STARTUP (2) Display examples The following table shows the display examples. Displayed data Item Status Servo amplifier display Forward rotation at 2500 r/min Servo motor speed Reverse rotation at 3000 r/min Reverse rotation is indicated by «- «. Load to motor inertia ratio 7.00 times 11252 pulses Cumulative feedback pulses… -
Page 112
4. STARTUP (3) Status display list The following table lists the servo statuses that may be shown. Refer to appendix 4 for the measurement point. Status display Symbol Unit Description Feedback pulses from the servo motor encoder are counted and displayed. The values in excess of ±99999 can be counted. -
Page 113
4. STARTUP Status display Symbol Unit Description Bus voltage The voltage of main circuit converter (between P+ and N-) is displayed. Encoder inside temperature °C Inside temperature of encoder detected by the encoder is displayed. Settling time Settling time is displayed. When it exceeds 1000 ms, «1000» will be displayed. Oscillation detection Frequency at the time of oscillation detection is displayed. -
Page 114: Diagnostic Mode
4. STARTUP 4.5.4 Diagnostic mode Name Display Description Not ready Indicates that the servo amplifier is being initialized or an alarm has occurred. Sequence Ready Indicates that the servo was switched on after completion of initialization and the servo amplifier is ready to operate. Drive recorder enabled When an alarm occurs in the status, the drive recorder will operate and write the status of…
-
Page 115
4. STARTUP Name Display Description Indicates the version of the software. Software version — Lower Indicates the system number of the software. Software version — Upper If offset voltages in the analog circuits inside and outside the servo amplifier cause the servo motor to rotate slowly at VC (Analog speed command) or VLA (Analog speed limit) of 0… -
Page 116: Alarm Mode
4. STARTUP 4.5.5 Alarm mode The current alarm, past alarm history and parameter error are displayed. The lower 2 digits on the display indicate the alarm number that has occurred or the parameter number in error. Name Display Description Indicates no occurrence of an alarm. Current alarm Indicates the occurrence of [AL.
-
Page 117: Parameter Mode
4. STARTUP Functions at occurrence of an alarm (1) Any mode screen displays the current alarm. (2) Even during alarm occurrence, the other screen can be viewed by pressing the button in the operation area. At this time, the decimal point in the fourth digit remains flickering. (3) For any alarm, remove its cause and clear it in any of the following methods.
-
Page 118
4. STARTUP (2) Operation example (a) Parameters of 5 or less digits The following example shows the operation procedure performed after power-on to change the control mode to the speed control mode with [Pr. PA01 Operation mode]. Press «MODE» to switch to the basic setting parameter screen. -
Page 119: External I/O Signal Display
4. STARTUP 4.5.7 External I/O signal display POINT The I/O signal settings can be changed using the I/O setting parameters [Pr. PD03] to [Pr. PD28]. The on/off states of the digital I/O signals connected to the servo amplifier can be confirmed. (1) Operation The display screen at power-on.
-
Page 120
4. STARTUP (a) Control modes and I/O signals Signal (Note 2) Symbols of I/O signals in control modes Connector Pin No. input/output Related parameter (Note 1) I/O Pr. PD03/Pr. PD04 RES/ST1 ST1/RS2 RS2/RES Pr. PD11/Pr. PD12 Pr. PD24 INP/SA SA/- -/INP Pr. -
Page 121
4. STARTUP (3) Display data at initial values (a) Position control mode CR (CN1-41) RES (CN1-19) SON (CN1-15) LSN (CN1-44) EM2 (CN1-42) LSP (CN1-43) Input signal Light on: on Output signals Light off: off OP (CN1-33) RD (CN1-49) ALM (CN1-48) INP (CN1-24) ZSP (CN1-23) (b) Speed control mode… -
Page 122: Output Signal (Do) Forced Output
4. STARTUP 4.5.8 Output signal (DO) forced output POINT When the servo system is used in a vertical lift application, turning on MBR (Electromagnetic brake interlock) by the DO forced output after assigning it to connector CN1 will release the electromagnetic brake, causing a drop. Take drop preventive measures on the machine side.
-
Page 123: Test Operation Mode
4. STARTUP 4.5.9 Test operation mode The test operation mode is designed for checking servo operation. Do not use it CAUTION for actual operation. If the servo motor operates unexpectedly, use EM2 (Forced stop 2) to stop it. POINT MR Configurator2 is required to perform positioning operation. Test operation cannot be performed if SON (Servo-on) is not turned off.
-
Page 124
4. STARTUP (2) JOG operation POINT When performing JOG operation, turn on EM2, LSP and LSN. LSP and LSN can be set to automatic on by setting [Pr. PD01] to » _ C _ _ «. JOG operation can be performed when there is no command from the controller. (a) Operation The servo motor rotates while holding down the «UP»… -
Page 125
4. STARTUP (3) Positioning operation POINT MR Configurator2 is required to perform positioning operation. Turn on EM2 (forced stop 2) when performing positioning operation. Positioning operation can be performed when there is no command from the controller. (a) Operation a) Motor speed [r/min] Enter the servo motor speed into the «Motor speed»… -
Page 126
4. STARTUP f) Travel distance unit selection Select with the option buttons whether the travel distance set in c) is in the command pulse unit or in the encoder pulse unit. When the command input pulse unit is selected, the value, which is the set travel distance multiplied by the electronic gear, will be the command value. -
Page 127
4. STARTUP (4) Motor-less operation Without connecting the servo motor, output signals or status display can be provided in response to the input device as if the servo motor is actually running. This operation can be used to check the sequence of a controller or the like. -
Page 128: Parameters
5. PARAMETERS 5. PARAMETERS Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so will make the operation unstable. CAUTION If fixed values are written in the digits of a parameter, do not change these values. Do not change parameters for manufacturer setting.
-
Page 129
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PA29 For manufacturer setting 0000h PA30 0000h PA31 0000h PA32 0000h 5.1.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) Initial Control mode Symbol Name Unit value PB01 FILT Adaptive tuning mode (adaptive filter II) 0000h VRFT Vibration suppression control tuning mode (advanced vibration… -
Page 130
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PB41 For manufacturer setting 0000h PB42 0000h PB43 0000h PB44 0.00 PB45 CNHF Command notch filter 0000h PB46 Machine resonance suppression filter 3 4500 [Hz] PB47 NHQ3 Notch shape selection 3 0000h PB48 Machine resonance suppression filter 4… -
Page 131
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PC16 Electromagnetic brake sequence output [ms] PC17 Zero speed [r/min] PC18 *BPS Alarm history clear 0000h PC19 *ENRS Encoder output pulse selection 0000h PC20 For manufacturer setting PC21 0000h PC22 *COP1 Function selection C-1 0020h PC23… -
Page 132
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PC69 For manufacturer setting 0000h PC70 0000h PC71 0000h PC72 0000h PC73 0000h PC74 0000h PC75 0000h PC76 0000h PC77 0000h PC78 0000h PC79 0000h PC80 0000h 5.1.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) Initial Control mode Symbol… -
Page 133: Extension Setting 2 Parameters ([Pr. Pe_ _ ])
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PD39 For manufacturer setting PD40 PD41 0000h PD42 0000h PD43 0000h PD44 0000h PD45 0000h PD46 0000h PD47 0000h PD48 0000h 5.1.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ]) Initial Control mode Symbol Name…
-
Page 134
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PE41 EOP3 Function selection E-3 0000h PE42 For manufacturer setting PE43 PE44 0000h PE45 0000h PE46 0000h PE47 0000h PE48 0000h PE49 0000h PE50 0000h PE51 0000h PE52 0000h PE53 0000h PE54 0000h PE55… -
Page 135: Basic Setting Parameters ([Pr. Pa
5. PARAMETERS Control mode Initial Symbol Name Unit value PF26 For manufacturer setting PF27 PF28 PF29 0000h PF30 PF31 FRIC Machine diagnosis function — Friction judgement speed [r/min] PF32 For manufacturer setting PF33 0000h PF34 0000h PF35 0000h PF36 0000h PF37 0000h PF38…
-
Page 136
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA02 _ _ x x Regenerative option *REG Used to select the regenerative option. Regenerative Incorrect setting may cause the regenerative option to burn. option If a selected regenerative option is not for use with the servo amplifier, [AL. 37 Parameter error] occurs. -
Page 137
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA06 Set the numerator of the electronic gear. To enable the parameter, select «Electronic gear (0 _ _ _)» of «Electronic gear selection» in [Pr. PA21]. Electronic gear The following shows a standard of the setting range of the electronic gear. -
Page 138
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA08 _ _ _ x Gain adjustment mode selection Select the gain adjustment mode. Auto tuning 0: 2 gain adjustment mode 1 (interpolation mode) mode 1: Auto tuning mode 1 2: Auto tuning mode 2 3: Manual mode 4: 2 gain adjustment mode 2… -
Page 139
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA09 Set a response of the auto tuning. Machine characteristic Machine characteristic Auto tuning Guideline for Guideline for response Setting Setting machine machine value value Response Response resonance resonance frequency [Hz] frequency [Hz]… -
Page 140
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA13 _ _ _ x Command input pulse train form selection *PLSS 0: Forward/reverse rotation pulse train Command 1: Signed pulse train pulse input 2: A-phase/B-phase pulse train (The servo amplifier imports input pulses after form multiplying by four.) Refer to table 5.3 for settings. -
Page 141
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA14 Select servo motor rotation direction relative to the input pulse train. *POL Servo motor rotation direction Rotation Setting When forward rotation When reverse rotation direction value pulse is input pulse is input selection The following shows the servo motor rotation directions. -
Page 142
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA19 Select a reference range and writing range of the parameter. 00AAh *BLK Refer to table 5.4 for settings. Parameter writing inhibit Table 5.4 [Pr. PA19] setting value and reading/writing range Setting PA19 operation… -
Page 143
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PA21 _ _ _ x One-touch tuning function selection *AOP3 0: Disabled Function 1: Enabled selection A-3 When the digit is «0», the one-touch tuning is not available. _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting _ x _ _ x _ _ _ Electronic gear selection… -
Page 144: Gain/Filter Setting Parameters ([Pr. Pb
5. PARAMETERS 5.2.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB01 _ _ _ x Filter tuning mode selection FILT Set the adaptive filter tuning. Adaptive Select the adjustment mode of the machine resonance suppression filter 1. Refer to tuning mode section 7.1.2 for details.
-
Page 145
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB04 Set the feed forward gain. When the setting is 100%, the droop pulses during operation at constant speed are nearly zero. However, sudden acceleration/deceleration will increase the overshoot. Feed forward As a guideline, when the feed forward gain setting is 100%, set 1 s or more as the gain… -
Page 146
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB09 This is used to set the gain of the speed loop. [rad/s] Set this parameter when vibration occurs on machines of low rigidity or large backlash. Increasing the setting value will also increase the response level but will Speed loop be liable to generate vibration and/or noise. -
Page 147
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB16 Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 2. NHQ2 _ _ _ x Machine resonance suppression filter 2 selection Notch shape 0: Disabled selection 2 1: Enabled _ _ x _ Notch depth selection 0: -40 dB… -
Page 148
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB18 Set the low-pass filter. 3141 [rad/s] The following shows a relation of a required parameter to this parameter. Low-pass filter setting Setting range: 100 to 18000 [Pr. PB23] [Pr. -
Page 149
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB24 _ _ _ x Slight vibration suppression control selection *MVS Select the slight vibration suppression control. Slight 0: Disabled vibration 1: Enabled suppression To enable the slight vibration suppression control, select «Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)» of control «Gain adjustment mode selection»… -
Page 150
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB31 Set the speed loop gain when the gain switching is enabled. [rad/s] VG2B When you set a value less than 20 rad/s, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB09]. Gain This parameter is enabled only when you select «Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)»… -
Page 151
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB45 Set the command notch filter. CNHF _ _ x x Command notch filter setting frequency selection Command Refer to table 5.6 for the relation of setting values to frequency. notch filter _ x _ _ Notch depth selection Refer to table 5.7 for details. -
Page 152
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB46 Set the notch frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter 3. 4500 [Hz] To enable the setting value, select «Enabled (_ _ _ 1)» of «Machine resonance suppression filter 3 selection»… -
Page 153
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB51 Set the shape of the machine resonance suppression filter 5. NHQ5 When you select «Enabled (_ _ _ 1)» of «Robust filter selection» in [Pr. PE41], the machine resonance suppression filter 5 is not available. -
Page 154
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB56 Set the vibration frequency for vibration suppression control 2 when the gain switching is enabled. [Hz] VRF21B When you set a value less than 0.1 Hz, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB52]. Vibration suppression This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled. -
Page 155: Extension Setting Parameters ([Pr. Pc
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PB60 Set the model loop gain when the gain switching is enabled. [rad/s] PG1B When you set a value less than 1.0 rad/s, the value will be the same as [Pr. PB07]. Model loop This parameter will be enabled only when the following conditions are fulfilled.
-
Page 156
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC03 This is used to smooth start/stop of the servo motor. [ms] Set the time of the arc part for S-pattern acceleration/deceleration. S-pattern acceleration/d Speed eceleration command time constant 0 r/min Time STA: Acceleration time constant ([Pr. -
Page 157
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC05 This is used to set speed 1 of internal speed commands. [r/min] Internal Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed speed This is used to set speed 1 of internal speed limits. command 1/internal Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed… -
Page 158
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC12 This is used to set the speed at the maximum input voltage (10 V) of VC (Analog speed command). [r/min] When «0» is set, the analog speed command maximum speed would be the rated Analog speed speed of the servo motor connected. -
Page 159
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC15 _ _ x x Analog monitor 2 output selection MOD2 Select a signal to output to MO2 (Analog monitor 2). Refer to appendix 4 (3) for detection point of output selection. Analog monitor 2 Refer to [Pr. -
Page 160
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC22 _ _ _ x For manufacturer setting *COP1 _ _ x _ Function _ x _ _ selection C-1 x _ _ _ Encoder cable communication method selection Select the encoder cable communication method. -
Page 161
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC26 _ _ _ x [AL. 99 Stroke limit warning] selection *COP5 Select [AL. 99 Stroke limit warning]. Function 0: Enabled selection C-5 1: Disabled _ _ x _ For manufacturer setting _ x _ _ x _ _ _ PC30… -
Page 162
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC36 _ _ x x Status display selection at power-on *DMD This is used to select a status display shown at power-on. Status display 00: Cumulative feedback pulses selection 01: Servo motor speed 02: Droop pulses… -
Page 163
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC37 This is used to set the offset voltage of VC (Analog speed command). value For example, if CCW rotation is provided by switching on ST1 (Forward rotation differs start) with applying 0 V to VC, set a negative value. -
Page 164
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PC51 This is used to set deceleration time constant when you use the forced stop deceleration function. [ms] RSBR Set the time per ms from the rated speed to 0 r/min. Forced stop deceleration time constant… -
Page 165
5. PARAMETERS 5.2.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PD01 Select input devices to turn on them automatically. *DIA1 _ _ _ x _ _ _ x (BIN): For manufacturer setting Input signal (HEX) _ _ x _ (BIN): For manufacturer setting… -
Page 166
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PD03 Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-15 pin. *DI1L _ _ x x Position control mode — Device selection Input device Refer to table 5.9 for settings. selection 1L x x _ _ Speed control mode — Device selection… -
Page 167
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PD14 Any input device can be assigned to the CN1-41 pin. *DI6H _ _ x x Torque control mode — Device selection Input device Refer to table 5.9 in [Pr. PD03] for settings. selection 6H _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting x _ _ _… -
Page 168
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PD25 _ _ x x Device selection *DO3 Any output device can be assigned to the CN1-24 pin. Output device Refer to table 5.10 in [Pr. PD24] for settings. selection 3 _ x _ _ For manufacturer setting… -
Page 169: Extension Setting 2 Parameters ([Pr. Pe
5. PARAMETERS Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PD34 _ _ _ x Alarm code output *DOP5 This is used to select if output alarm codes. Function Alarm codes are outputted to pins CN1-23, CN1-24, and CN1-49. selection D-5 0: Disabled 1: Enabled…
-
Page 170: Extension Setting 3 Parameters ([Pr. Pf
5. PARAMETERS 5.2.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ]) Initial Control mode No./ Setting Function value symbol/name digit [unit] PF21 This is used to set a drive recorder switching time. When a USB communication is cut during using a graph function or a graph function is terminated, the function will be changed to the drive recorder function after the Drive setting time of this parameter.
-
Page 171
5. PARAMETERS MEMO 5 — 44… -
Page 172: Normal Gain Adjustment
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT POINT In the torque control mode, you do not need to make gain adjustment. Before making gain adjustment, check that your machine is not being operated at maximum torque of the servo motor. If operated over maximum torque, the machine may vibrate and may operate unexpectedly.
-
Page 173: Adjustment Using Mr Configurator2
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (2) Adjustment sequence and mode usage Start Interpolation 2 gain adjustment mode 1 made for 2 or more (interpolation mode) axes? The load fluctuation is large during driving? One-touch tuning Handle the error Error handling Finished normally? Auto tuning mode 1 is possible? Adjustment OK?
-
Page 174: One-Touch Tuning
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.2 One-touch tuning You can execute the one-touch tuning with MR Configurator2 or push buttons. The following parameters are set automatically with one-touch tuning. Table 6.1 List of parameters automatically set with one-touch tuning Parameter Symbol Name Parameter Symbol…
-
Page 175
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (2) When you use push buttons Make one-touch tuning as follows. Start Startup a system referring to chapter 4. Startup of the system Rotate the servo motor by an external controller, etc. (The one-touch tuning cannot be performed if the Operation servo motor is not operating.) Select the initial screen («AUTO») of the one-touch tuning with the «MODE»… -
Page 176: Display Transition And Operation Procedure Of One-Touch Tuning
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.2.2 Display transition and operation procedure of one-touch tuning (1) When you use MR Configurator2 (a) Response mode selection Select a response mode from three modes in the one-touch tuning window of MR Configurator2. Response mode Explanation High mode This mode is for high rigid system.
-
Page 177
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT Response mode Machine characteristic Response Low mode Basic mode High mode Guideline of corresponding machine Low response Arm robot General machine tool conveyor Precision working machine Inserter Mounter Bonder High response 6 — 6… -
Page 178
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (b) One-touch tuning execution POINT For equipment in which overshoot during one-touch tuning is in the permissible level of the in-position range, changing the value of [Pr. PA25 One-touch tuning — Overshoot permissible level] will shorten the settling time and improve the response. -
Page 179
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (c) Stop of one-touch tuning During one-touch tuning, pushing the stop button stops one-touch tuning. If the one-touch tuning is stopped, «C 0 0 0» will be displayed at status in error code. (d) Error occurrence If a tuning error occurs during tuning, one-touch tuning will be forcibly terminated. -
Page 180
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (g) Clearing one-touch tuning You can clear the parameter values set with one-touch tuning. Refer to table 6.1 for the parameters which you can clear. Pushing «Return to value before tuning» in the one-touch tuning window of MR Configurator2 enables to rewrite the parameter to the value before pushing the start button. -
Page 181
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (2) When you use push buttons POINT Push the «MODE» and «SET» buttons at the same time for 3 s or more to switch to the response mode selection («AUTO.») without going through the initial screen of the one-touch tuning («AUTO»). (a) Response mode selection Select a response mode of the one-touch tuning from 3 modes with «UP»… -
Page 182
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (b) One-touch tuning execution POINT For equipment in which overshoot during one-touch tuning is in the permissible level of the in-position range, changing the value of [Pr. PA25 One-touch tuning — Overshoot permissible level] will shorten the settling time and improve the response. -
Page 183
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (d) If an error occurs Stop symbol If an error occurs during the one-touch tuning, the tuning will be forcibly terminated and the stop symbol and error code from «C 001» to «C 00F» will be displayed by turns with 2 s interval. -
Page 184: Caution For One-Touch Tuning
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (g) Clearing one-touch tuning Refer to table 6.1 for the parameters which you can clear. You can initialize the parameters changed by the one-touch tuning with the clear mode. You can reset the parameters to before tuning with the back mode. 1) Push the «MODE»…
-
Page 185: Auto Tuning
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.3 Auto tuning 6.3.1 Auto tuning mode The servo amplifier has a real-time auto tuning function which estimates the machine characteristic (load to motor inertia ratio) in real time and automatically sets the optimum gains according to that value. This function permits ease of gain adjustment of the servo amplifier.
-
Page 186: Auto Tuning Mode Basis
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.3.2 Auto tuning mode basis The block diagram of real-time auto tuning is shown below. Load moment Automatic setting of inertia Encoder Loop gain Command Current PG1, PG2, control VG2, VIC Servo motor Current feedback Real-time Position/speed Set 0 or 1 to turn on.
-
Page 187: Adjustment Procedure By Auto Tuning
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.3.3 Adjustment procedure by auto tuning Since auto tuning is enabled before shipment from the factory, simply running the servo motor automatically sets the optimum gains that match the machine. Merely changing the response level setting value as required completes the adjustment.
-
Page 188: Response Level Setting In Auto Tuning Mode
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.3.4 Response level setting in auto tuning mode Set the response of the whole servo system by [Pr. PA09]. As the response level setting is increased, the track ability and settling time for a command decreases, but a too high response level will generate vibration. Hence, make setting until desired response is obtained within the vibration-free range.
-
Page 189: Manual Mode
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.4 Manual mode If you are not satisfied with the adjustment of auto tuning, you can make simple manual adjustment with three parameters. POINT If machine resonance occurs, filter tuning mode selection in [Pr. PB01] or machine resonance suppression filter in [Pr.
-
Page 190
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (c) Parameter adjustment 1) [Pr. PB09 Speed loop gain] This parameter determines the response level of the speed control loop. Increasing the setting increases the response level, but the mechanical system is liable to vibrate. The actual response frequency of the speed loop is as indicated in the following expression. -
Page 191
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (b) Adjustment procedure Step Operation Description Brief-adjust with auto tuning. Refer to section 6.3.3. Change the setting of auto tuning to the manual mode ([Pr. PA08]: _ _ _ 3). Set an estimated value to the load to motor inertia ratio. (If the estimate value with auto tuning is correct, setting change is not required.) Set a slightly smaller value to the model loop gain and the… -
Page 192
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 3) [Pr. PB08 Position loop gain] This parameter determines the response level to a disturbance to the position control loop. Increasing the position loop gain increases the response level to a disturbance, but the mechanical system is liable to vibrate. Speed loop gain Position loop gain guideline ×… -
Page 193: Gain Adjustment Mode
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6.5 2 gain adjustment mode The 2 gain adjustment mode is used to match the position loop gains of the axes when performing the interpolation operation of servo motors of two or more axes for an X-Y table or the like. In this mode, manually set the model loop gain that determines command track ability.
-
Page 194
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT (3) Adjustment procedure of 2 gain adjustment mode POINT Set the same value in [Pr. PB07 Model loop gain] for the axis used in 2 gain adjustment mode. Step Operation Description Set to the auto tuning mode. Select the auto tuning mode 1. -
Page 195
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT MEMO 6 — 24… -
Page 196: Special Adjustment Functions
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS POINT The functions given in this chapter need not be used normally. Use them if you are not satisfied with the machine status after making adjustment in the methods in chapter 6. 7.1 Filter setting The following filters are available with MR-JE servo amplifiers.
-
Page 197
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (1) Function The machine resonance suppression filter is a filter function (notch filter) which decreases the gain of the specific frequency to suppress the resonance of the mechanical system. You can set the gain decreasing frequency (notch frequency), gain decreasing depth and width. Machine resonance point Frequency Notch width… -
Page 198
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (2) Parameter (a) Machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]) Set the notch frequency, notch depth and notch width of the machine resonance suppression filter 1 ([Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB14]) When you select «Manual setting (_ _ _ 2)» of «Filter tuning mode selection» in [Pr. PB01], the setting of the machine resonance suppression filter 1 is enabled. -
Page 199: Adaptive Filter Ii
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.1.2 Adaptive filter II POINT The machine resonance frequency which adaptive filter II (adaptive tuning) can respond to is about 100 Hz to 2.25 kHz. As for the resonance frequency out of the range, set manually. When adaptive tuning is executed, vibration sound increases as an excitation signal is forcibly applied for several seconds.
-
Page 200
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (3) Adaptive tuning mode procedure Adaptive tuning Operation Is the target response reached? Increase the response setting. Has vibration or unusual noise occurred? Execute or re-execute adaptive tuning. (Set [Pr. PB01] to «_ _ _ 1».) Tuning ends automatically after the If assumption fails after tuning is executed at a large vibration or predetermined period of time. -
Page 201: Shaft Resonance Suppression Filter
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.1.3 Shaft resonance suppression filter (1) Function When a load is mounted to the servo motor shaft, resonance by shaft torsion during driving may generate a mechanical vibration at high frequency. The shaft resonance suppression filter suppresses the vibration.
-
Page 202: Low-Pass Filter
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.1.4 Low-pass filter (1) Function When a ball screw or the like is used, resonance of high frequency may occur as the response level of the servo system is increased. To prevent this, the low-pass filter is enabled for a torque command as the initial value.
-
Page 203
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (1) Function Vibration suppression control is used to further suppress load-side vibration, such as work-side vibration and base shake. The servo motor-side operation is adjusted for positioning so that the machine does not vibrate. Servo motor side Servo motor side Load side Load side… -
Page 204
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (3) Vibration suppression control tuning procedure The following flow chart is for the vibration suppression control 1. For the vibration suppression control 2, set «_ _ 1 _» in [Pr. PB02] to execute the vibration suppression control tuning. Vibration suppression control tuning Operation Is the target response… -
Page 205
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (4) Vibration suppression control manual mode POINT When load-side vibration does not show up in servo motor-side vibration, the setting of the servo motor-side vibration frequency does not produce an effect. When the anti-resonance frequency and resonance frequency can be confirmed using the machine analyzer or external equipment, do not set the same value but set different values to improve the vibration suppression performance. -
Page 206
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS Step 2. Set «Vibration suppression control — Vibration frequency» and «Vibration suppression control — Resonance frequency» as follows. (a) When a vibration peak can be confirmed with machine analyzer using MR Configurator2, or external equipment. Vibration suppression control 2 — Vibration frequency (anti-resonance frequency) [Pr. -
Page 207: Command Notch Filter
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.1.6 Command notch filter POINT By using the advanced vibration suppression control II and the command notch filter, the load-side vibration of three frequencies can be suppressed. The frequency range of machine vibration, which can be supported by the command notch filter, is between 4.5 Hz and 2250 Hz.
-
Page 208: Gain Switching Function
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (2) Parameter Set [Pr. PB45 Command notch filter] as shown below. For the command notch filter setting frequency, set the closest value to the vibration frequency [Hz] at the load side. [Pr. PB45] Notch depth Command notch filter setting frequency Depth Setting Setting…
-
Page 209: Function Block Diagram
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.2.2 Function block diagram The control gains, load to motor inertia ratio, and vibration suppression control settings are changed according to the conditions selected by [Pr. PB26 Gain switching function] and [Pr. PB27 Gain switching condition]. [Pr.
-
Page 210: Parameter
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.2.3 Parameter When using the gain switching function, always select «Manual mode (_ _ _ 3)» of «Gain adjustment mode selection» in [Pr. PA08 Auto tuning mode]. The gain switching function cannot be used in the auto tuning mode.
-
Page 211
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (2) Switchable gain parameter Before switching After switching Loop gain Parameter Symbol Name Parameter Symbol Name Load to motor inertia ratio PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio PB29 GD2B Gain switching Load to motor inertia ratio Model loop gain PB07 Model loop gain… -
Page 212: Gain Switching Procedure
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (c) [Pr. PB29 Load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching] Set the load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching. If the load to motor inertia ratio does not change, set it to the same value as [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio]. (d) [Pr.
-
Page 213
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS Parameter Symbol Name Setting value Unit PB28 Gain switching time constant [ms] PB33 VRF11B Vibration suppression control 1 — [Hz] Vibration frequency after gain switching PB34 VRF12B Vibration suppression control 1 — [Hz] Resonance frequency after gain switching PB35 VRF13B Vibration suppression control 1 -… -
Page 214
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (2) When you choose switching by droop pulses In this case, the vibration suppression control after gain switching and model loop gain after gain switching cannot be used. (a) Setting Parameter Symbol Name Setting value Unit PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio 4.00… -
Page 215: Tough Drive Function
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.3 Tough drive function POINT Set enable/disable of the tough drive function with [Pr. PA20 Tough drive setting]. (Refer to section 5.2.1.) This function makes the equipment continue operating even under the condition that an alarm occurs. 7.3.1 Vibration tough drive function This function prevents vibration by resetting a filter instantaneously when machine resonance occurs due to varied vibration frequency caused by machine aging.
-
Page 216
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS The following shows the function block diagram of the vibration tough drive function. The function detects machine resonance frequency and compare it with [Pr. PB13] and [Pr. PB15], and reset a machine resonance frequency of a parameter whose set value is closer. Parameter that is Filter Setting parameter… -
Page 217: Instantaneous Power Failure Tough Drive Function
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7.3.2 Instantaneous power failure tough drive function The immunity to instantaneous power failures is increased by the instantaneous CAUTION power failure tough drive function. However, it is not guarantee to comply with the SEMI-F47 standard. The instantaneous power failure tough drive function avoids [AL. 10 Undervoltage] even when an instantaneous power failure occurs during operation.
-
Page 218
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (1) Instantaneous power failure time > [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function — Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive — detection time)] The alarm occurs when the instantaneous power failure time exceeds [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function — Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive — detection time)]. -
Page 219
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (2) Instantaneous power failure time < [Pr. PF25 SEMI-F47 function — Instantaneous power failure detection time (instantaneous power failure tough drive — detection time)] Operation status differs depending on how bus voltage decrease. (a) When the bus voltage decreases lower than 158 V DC within the instantaneous power failure time [AL. -
Page 220
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS (b) When the bus voltage does not decrease lower than 158 V DC within the instantaneous power failure time The operation continues without alarming. Instantaneous power failure time Power supply [Pr. PF25] Bus voltage Undervoltage level (158 V DC) (Malfunction) (Warning) -
Page 221
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS MEMO 7 — 26… -
Page 222: Troubleshooting
8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8. TROUBLESHOOTING POINT As soon as an alarm occurs, turn SON (Servo-on) off and interrupt the power. 8.1 Alarm and warning list When an error occurs during operation, the corresponding alarm or warning is displayed. If any alarm or warning has occurred, refer to section 8.2 or 8.3 and take the appropriate action.
-
Page 223
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm code Alarm deactivation Press Stop Power «SET» Detailed method Alarm Name Detail name off to button display (Note 2, reset on the (RES) current (Bit 2) (Bit 1) (Bit 0) (Note 4) alarm screen. Encoder initial communication — Receive 16.1 data error 1 Encoder initial communication — Receive… -
Page 224
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm code Alarm deactivation Press Stop Power «SET» Detailed method Alarm Name Detail name off to button display (Note 2, reset on the (RES) current (Bit 2) (Bit 1) (Bit 0) (Note 4) alarm screen. Ground fault detected by hardware 24.1 detection circuit Main circuit error… -
Page 225
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm code Alarm deactivation Press Stop Power «SET» Detailed method Alarm Name Detail name off to button display (Note 2, reset on the (RES) current (Bit 2) (Bit 1) (Bit 0) (Note 4) alarm screen. USB communication time- 8A.1 USB communication time-out error out error… -
Page 226
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Table 8.2 Warning list Stop Detailed method Name Detail name display (Note 2, Servo amplifier overheat 91.1 Main circuit device overheat warning warning (Note 1) 99.1 Forward rotation stroke end off (Note 4) Stroke limit warning 99.2 Reverse rotation stroke end off (Note 4) Excessive regeneration E0.1… -
Page 227: Remedies For Alarms
8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8.2 Remedies for alarms When any alarm has occurred, eliminate its cause, ensure safety, and deactivate CAUTION the alarm before restarting operation. Otherwise, it may cause injury. As soon as an alarm occurs, make the Servo-off status and interrupt the power. POINT When any of the following alarms has occurred, do not cycle the power repeatedly to restart.
-
Page 228
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 12 Name: Memory error 1 (RAM) Alarm content A part (RAM) in the servo amplifier is failure. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 12.1 RAM error 1 (1) A part in the servo Disconnect the cables It is repeatable. -
Page 229
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 15 Name: Memory error 2 (EEP-ROM) Alarm content A part (EEP-ROM) in the servo amplifier is failure. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 15.1 EEP-ROM error EEP-ROM is Disconnect the cables It is repeatable. Replace the servo at power on malfunctioning at power… -
Page 230
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 16 Name: Encoder initial communication error 1 Alarm content An error occurred in the communication between an encoder and servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 16.3 Encoder initial An encoder cable was Check if the encoder It is not connected. -
Page 231
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 17 Name: Board error Alarm content A part in the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 17.1 Board error 1 (1) A current detection Check if the alarm It occurs. Replace the servo circuit is malfunctioning. -
Page 232
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 1F Name: Encoder initial communication error 3 Alarm content The connected encoder is not compatible with the servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 1F.1 Incompatible A servo motor, which is Check the model of the It is not compatible with Replace it with the servo encoder… -
Page 233
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 21 Name: Encoder normal communication error 2 Alarm content The encoder detected an error signal. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 21.1 Encoder data The encoder detected a Decrease the loop gain, It is not repeatable. Use the encoder with low error 1 high speed/acceleration… -
Page 234
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 30 Name: Regenerative error Permissible regenerative power of the built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option is exceeded. Alarm content A regenerative transistor in the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 30.1 Regeneration… -
Page 235
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 32 Name: Overcurrent Alarm content A current higher than the permissible current was applied to the servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 32.1 Overcurrent (1) The servo amplifier is Disconnect the servo It occurs. -
Page 236
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 33 Name: Overvoltage Alarm content The value of the bus voltage exceeded 400 V DC. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 33.1 Main circuit The setting of the Check the regenerative The setting value is Set it correctly. -
Page 237
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 45 Name: Main circuit device overheat Alarm content Inside of the servo amplifier overheated. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 45.1 Main circuit (1) Ambient temperature has Check the ambient It is over 55 ˚C. Lower the ambient device exceeded 55 ˚C. -
Page 238
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 47 Name: Cooling fan error The speed of the servo amplifier cooling fan decreased. Alarm content Or the cooling fan speed decreased to the alarm occurrence level or less. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 47.2 Cooling fan… -
Page 239
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 50 Name: Overload 1 Alarm content Load exceeded overload protection characteristic of servo amplifier. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 50.4 Thermal A moving part collided Check if it collided. It collided. Check operation pattern. overload error 1 against the machine. -
Page 240
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 51 Name: Overload 2 Alarm content Maximum output current flowed continuously due to machine collision or the like. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 51.1 Thermal (1) The servo motor power Check the servo motor It is disconnected. -
Page 241
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 52 Name: Error excessive Alarm content Droop pulses have exceeded the alarm occurrence level. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 52.1 Excess droop (1) The servo motor power Check the servo motor It is disconnected. Repair or replace the pulse 1 cable was disconnected. -
Page 242
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 54 Name: Oscillation detection Alarm content An oscillation of the servo motor was detected. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 54.1 Oscillation (1) The servo system is Check if the servo motor The torque ripple is Adjust the servo gain detection error unstable and oscillating. -
Page 243
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 8A Name: USB communication time-out error Communication between the servo amplifier and a personal computer, etc. stopped for the specified time Alarm content or longer. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 8A.1 Communication Check if a command It was not transmitted. -
Page 244
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: 8E Name: USB communication error Alarm content A communication error occurred between servo amplifier and a personal computer, etc. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 8E.5 (1) The transmitted data Check the data number The transmitted data Correct the transmission communication… -
Page 245: Remedies For Warnings
8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8.3 Remedies for warnings POINT When any of the following alarms has occurred, do not cycle the power of the servo amplifier repeatedly to restart. Doing so will cause a malfunction of the servo amplifier and servo motor. If the power of the servo amplifier is switched off/on during the alarms, allow more than 30 minutes for cooling before resuming operation.
-
Page 246
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: E1 Name: Overload warning 1 Alarm content [AL.50 Overload 1] or [AL.51 Overload 2] may occur. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E1.1 Thermal (1) The load was over 85% Check it with the check method for [AL. 50.1]. overload to the alarm level of [AL. -
Page 247
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: E9 Name: Main circuit off warning The servo-on command was inputted with power supply off. Alarm content The bus voltage dropped during the servo motor driving under 50 r/min. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action E9.1 Servo-on signal… -
Page 248
8. TROUBLESHOOTING Alarm No.: F2 Name: Drive recorder — Miswriting warning Alarm content A waveform measured by the drive recorder function was not recorded. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action F2.1 Drive recorder — (1) The Flash-ROM is Disconnect the cables It is repeatable. -
Page 249
8. TROUBLESHOOTING MEMO 8 — 28… -
Page 250: Dimensions
9. DIMENSIONS 9. DIMENSIONS 9.1 Servo amplifier (1) MR-JE-10A to MR-JE-40A [Unit: mm] 6 mounting hole Approx. 80 CNP1 The built-in regenerative resistor (lead wire) is mounted only in MR-JE-40A. Mass: 0.8 [kg] Mounting screw Terminal Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] CNP1 Approx.
-
Page 251
9. DIMENSIONS (2) MR-JE-70A/MR-JE-100A [Unit: mm] 6 mounting hole Approx. 80 CNP1 Mass: 1.5 [kg] Mounting screw Terminal Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] CNP1 Approx. 70 3-M5 screw Screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] 42 ± 0.3 Approx. -
Page 252
9. DIMENSIONS (3) MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A [Unit: mm] 6 mounting hole Approx. 80 Exhaust CNP1 CNP2 Cooling fan air intake Mass: 2.1 [kg] Mounting screw Terminal Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] CNP1 Approx. 90 CNP2 3-M5 screw Screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Approx. -
Page 253: Connector
9. DIMENSIONS 9.2 Connector (1) Miniature delta ribbon (MDR) system (3M) (a) One-touch lock type [Unit: mm] Logo etc, are indicated here. 12.7 Variable dimensions Connector Shell kit 10150-3000PE 10350-52F0-008 41.1 52.4 18.0 14.0 17.0 (b) Jack screw M2.6 type This is not available as option.
-
Page 254
9. DIMENSIONS (2) SCR connector system (3M) Receptacle: 36210-0100PL Shell kit: 36310-3200-008 [Unit: mm] 39.5 34.8 9 — 5… -
Page 255
9. DIMENSIONS MEMO 9 — 6… -
Page 256: Characteristics
10. CHARACTERISTICS 10. CHARACTERISTICS 10.1 Overload protection characteristics An electronic thermal is built in the servo amplifier to protect the servo motor, servo amplifier and servo motor power wires from overloads. [AL. 50 Overload 1] occurs if overload operation performed is above the electronic thermal protection curve shown in fig.
-
Page 257
10. CHARACTERISTICS 1000 1000 Operating Operating Servo-lock Servo-lock (Note) Load ratio [%] (Note) Load ratio [%] HF-KN13, HF-KN23, HF-KN43 HF-SN152, HF-SN202, HF-SN302 HF-KN73, HF-SN52, HF-SN102 Note. If operation that generates torque more than 100% of the rating is performed with an abnormally high frequency in a servo motor stop status (servo-lock status) or in a 30 r/min or less low-speed operation status, the servo amplifier may malfunction regardless of the electronic thermal protection. -
Page 258: Power Supply Capacity And Generated Loss
10. CHARACTERISTICS 10.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss (1) Amount of heat generated by the servo amplifier Table 10.1 indicates servo amplifiers’ power supply capacities and losses generated under rated load. For thermal design of an enclosed type cabinet, use the values in the table in consideration for the worst operating conditions.
-
Page 259
10. CHARACTERISTICS (2) Heat dissipation area for an enclosed type cabinet The enclosed type cabinet (hereafter called the cabinet) which will contain the servo amplifier should be designed to ensure that its temperature rise is within +10 ˚C at the ambient temperature of 40 ˚C. (With an approximately 5 ˚C safety margin, the system should operate within a maximum 55 ˚C limit.) The necessary cabinet heat dissipation area can be calculated by equation 10.1. -
Page 260: Dynamic Brake Characteristics
10. CHARACTERISTICS 10.3 Dynamic brake characteristics POINT Do not use dynamic brake to stop in a normal operation as it is the function to stop in emergency. For a machine operating at the recommended load to motor inertia ratio or less, the estimated number of usage times of the dynamic brake is 1000 times while the machine decelerates from the rated speed to a stop once in 10 minutes.
-
Page 261: Permissible Load To Motor Inertia When The Dynamic Brake Is Used
10. CHARACTERISTICS (2) Dynamic brake time constant The following shows necessary dynamic brake time constant for equation 10.2. 0 500 1500 2500 3500 4500 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 1000 2000 3000 4000 Speed [r/min] Speed [r/min] HF-KN series HF-SN series 10.3.2 Permissible load to motor inertia when the dynamic brake is used Use the dynamic brake under the load to motor inertia ratio indicated in the following table.
-
Page 262: Cable Bending Life
10. CHARACTERISTICS 10.4 Cable bending life The bending life of the cables is shown below. This graph calculated values. Since they are not guaranteed values, provide a little allowance for these values. 1 × 10 5 × 10 1 × 10 Long bending life encoder cable 5 ×…
-
Page 263
10. CHARACTERISTICS MEMO 10 — 8… -
Page 264: Options And Peripheral Equipment
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT Before connecting options and peripheral equipment, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Otherwise, an electric WARNING shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier.
-
Page 265: Combinations Of Cable/Connector Sets
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.1.1 Combinations of cable/connector sets Operation panel Servo amplifier Personal computer Controller 1) (Packed with the servo amplifier) (Note) CNP1 Refer to «HF-KN/HF-SN Servo Motor Instruction Manual» for options for servo motor power supply, electromagnetic brake, and encoder. To 24 V DC power supply for electromagnetic brake Servo motor…
-
Page 266
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT Product name Model Description Application Servo amplifier MR-JECNP1-01 Supplied with servo CNP1 power amplifiers connector of 1 kW or less CNP1 Connector: 09JFAT-SAXGDK-H5.0 (JST) Applicable wire size: AWG 18 to 14 Insulator OD: to 3.9 mm Open tool J-FAT-OT (JST) -
Page 267: Regenerative Option
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.2 Regenerative option Do not use servo amplifiers with regenerative options other than the combinations CAUTION specified below. Otherwise, it may cause a fire. 11.2.1 Combination and regenerative power The power values in the table are resistor-generated powers and not rated powers. Regenerative power [W] Servo (Note)
-
Page 268: Selection Of Regenerative Option
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.2.2 Selection of regenerative option Use the following method when regeneration occurs continuously in vertical motion applications or when it is desired to make an in-depth selection of the regenerative option. (1) Regenerative energy calculation tf (1 cycle) Time Down…
-
Page 269
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (2) Losses of servo motor and servo amplifier in regenerative mode The following table lists the efficiencies and other data of the servo motor and servo amplifier in the regenerative mode. Inverse Capacitor Inverse Capacitor Servo amplifier Servo amplifier efficiency [%]… -
Page 270: Selection Of Regenerative Option
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.2.4 Selection of regenerative option POINT When you use a regenerative option with an MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, remove the built-in regenerative resistor and wiring from the servo amplifier. When MR-RB50 is used, a cooling fan is required to cool it. The cooling fan should be prepared by the customer.
-
Page 271
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT To remove the built-in regenerative resistor mounted on the back of MR-JE-40A to MR-JE-100A, follow the procedures 1) to 3) with referring the illustration. 1) Disconnect the wirings of the built-in regenerative resistor from the power connector (CNP1). (Refer to (3) (b) of 3.3.2.) 2) Remove the wirings of the built-in regenerative resistor from the closest position to the power connector (CNP1) in order. -
Page 272
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (2) MR-JE-200A or more Always remove the wiring from across P+ to D and fit the regenerative option across P+ to C. G3 and G4 are terminals for thermal sensor. Between G3 and G4 is opened when the regenerative option overheats abnormally. -
Page 273: Dimensions
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.2.5 Dimensions (1) MR-RB12 [Unit: mm] TE1 terminal block 6 mounting hole Applicable wire size: 0.2 mm to 2.5 mm (AWG 24 to Tightening torque: 0.5 to 0.6 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M5 Tightening torque: 3.24 [N•m] Mass: 1.1 [kg] Approx.
-
Page 274
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (3) MR-RB50 [Unit: mm] Terminal block Cooling fan mounting screw (2-M3 screw) On opposite side 7 × 14 82.5 slotted hole Terminal screw size: M4 Tightening torque: 1.2 [N•m] Mounting screw Screw size: M6 intake Tightening torque: 5.4 [N•m] Mass: 5.6 [kg] Approx. -
Page 275: Junction Terminal Block Mr-Tb50
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.3 Junction terminal block MR-TB50 (1) Usage Always use the junction terminal block (MR-TB50) with the option cable (MR-J2M-CN1TBL_M) as a set. Servo amplifier Junction terminal block MR-TB50 Cable clamp Junction terminal block cable (MR-J2M-CN1TBL_M) Install the junction terminal block cable on the junction terminal block side with the supplied cable clamp fitting (AERSBAN-ESET).
-
Page 276
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (4) Junction terminal block cable MR-J2M-CN1TBL_M (a) Model explanations Model: Symbol Cable length [m] (b) Connection diagram 10150-6000EL D7650-B500FL (Servo amplifier side) (Junction terminal side) Signal symbol Pin No. Pin No. Position Speed Torque DICOM DICOM DICOM DICOM… -
Page 277: Mr Configurator2
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.4 MR Configurator2 POINT For the MR-JE servo amplifier, use MR Configurator2 with software version 1.19V or later. MR Configurator2 (SW1DNC-MRC2-E) uses the communication function of the servo amplifier to perform parameter setting changes, graph display, test operation, etc. on a personal computer. (1) Specifications Item Description…
-
Page 278
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT Note 1. Microsoft, Windows, Internet Explorer and Windows Vista are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries. Celeron and Pentium are the registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. 2. On some personal computers, MR Configurator2 may not run properly. ®… -
Page 279: Selection Example Of Wires
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.5 Selection example of wires POINT To comply with the UL/CSA standard, use the wires shown in appendix 2 for wiring. To comply with other standards, use a wire that is complied with each standard. Selection conditions of wire size is as follows.
-
Page 280: Molded-Case Circuit Breakers, Fuses, Magnetic Contactors (Recommended)
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.6 Molded-case circuit breakers, fuses, magnetic contactors (recommended) Always use one molded-case circuit breaker and one magnetic contactor with one servo amplifier. When using a fuse instead of the molded-case circuit breaker, use the one having the specifications given in this section.
-
Page 281: Relay (Recommended)
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (2) Dimensions Terminal layout S Y T 4-d mounting hole (Varnish is removed from front right mounting hole (face and back side).) (Note 1) D or less Max. W (Note 2) Fig. 11.1 Power factor Dimensions [mm] Mass Dimens…
-
Page 282: Noise Reduction Techniques
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.9 Noise reduction techniques Noises are classified into external noises which enter the servo amplifier to cause it to malfunction and those radiated by the servo amplifier to cause peripheral equipment to malfunction. Since the servo amplifier is an electronic device which handles small signals, the following general noise reduction techniques are required.
-
Page 283
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT Sensor power supply Servo amplifier Instrument Receiver Sensor Servo motor Noise transmission Suppression techniques route When measuring instruments, receivers, sensors, etc. which handle weak signals and may malfunction due to noise and/or their signal cables are contained in a cabinet together with the servo amplifier or run near the servo amplifier, such devices may malfunction due to noises transmitted through the air. -
Page 284
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (2) Noise reduction techniques (a) Data line filter (recommended) Noise can be prevented by installing a data line filter onto the encoder cable, etc. For example, ZCAT3035-1330 by TDK, ESD-SR-250 by NEC TOKIN, and GRFC-13 by Kitagawa Industries are available as data line filters. -
Page 285
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (c) Cable clamp fitting AERSBAN-_SET Generally, the grounding of the shielded wire may only be connected to the connector’s SD terminal. However, the effect can be increased by directly connecting the cable to an grounding plate as shown below. -
Page 286
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (d) Line noise filter (FR-BSF01) This filter is effective in suppressing noises radiated from the power supply side and output side of the servo amplifier and also in suppressing high-frequency leakage current (0-phase current). It especially affects the noises between 0.5 MHz and 5 MHz band. -
Page 287
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (e) Radio noise filter (FR-BIF) This filter is effective in suppressing noises radiated from the power supply side of the servo amplifier especially in 10 MHz and lower radio frequency bands. The FR-BIF is designed for the input only. -
Page 288: Earth-Leakage Current Breaker
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.10 Earth-leakage current breaker (1) Selection method High-frequency chopper currents controlled by pulse width modulation flow in the AC servo circuits. Leakage currents containing harmonic contents are larger than those of the motor which is run with a commercial power supply.
-
Page 289
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT Table 11.2 Servo motor leakage current example (lgm) Servo motor power [kW] Leakage current [mA] 0.1 to 1 Table 11.3 Servo amplifier leakage current example (Iga) Servo amplifier capacity [kW] Leakage current [mA] 0.1 to 0.6 0.75 to 3 0.15 Table 11.4 Earth-leakage current breaker selection example… -
Page 290: Emc Filter (Recommended)
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11.11 EMC filter (recommended) It is recommended that one of the following filters be used to comply with EN EMC directive. Some EMC filters have large in leakage current. (1) Combination with the servo amplifier Recommended filter (Soshin Electric) Servo amplifier Mass [kg]…
-
Page 291
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (3) Dimensions (a) EMC filter HF3010A-UN [Unit: mm] 3-M4 4-5.5 × 7 3-M4 Approx. 41 258 ± 4 65 ± 4 273 ± 2 288 ± 4 300 ± 5 HF3030A-UN [Unit: mm] 6-R3.25 length:8 3-M5 3-M5 70 ±… -
Page 292
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT (b) Surge protector RSPD-250-U4 [Unit: mm] 4.2 ± 0.5 Resin Lead Case 41 ± 1 11 — 29… -
Page 293
11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT MEMO 11 — 30… -
Page 294: Appendix
Always use the MR-JE servo amplifiers within specifications (voltage, temperature, etc. Refer to section 1.3 for details.). Mitsubishi Electric Co. accepts no claims for liability if the equipment is used in any other way or if modifications are made to the device, even in the context of mounting and installation.
-
Page 295
APPENDIX (1) Peripheral device and power wiring (a) Local wiring Use only copper wires rated at 75 ˚C for wiring. The following table shows wires [AWG] rated at 75 ˚C. Wire [AWG] Servo amplifier (Note 2) (Note 1, 2) P+/C U/V/W/ L1/L2/L3/ MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A/MR-JE-70A/MR-JE-100A/… -
Page 296
(b) For Declaration of Conformity (DoC) Hereby, MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC EUROPE B.V., declares that the servo amplifiers are in compliance with the necessary requirements and standards (2004/108/EC and 2006/95/EC). For the copy of Declaration of Conformity, contact your local sales office. -
Page 297
APPENDIX (f) Branch circuit protection For installation in United States, branch circuit protection must be provided, in accordance with the National Electrical Code and any applicable local codes. For installation in Canada, branch circuit protection must be provided, in accordance with the Canada Electrical Code and any applicable provincial codes. -
Page 298
Machine side Servo motor Encoder The control circuit connectors described by rectangles are safely separated from the main circuits described by circles. The connected motors will be limited as follows. HF-KN/HF-SN series servo motors (Mfg.: Mitsubishi Electric) App. — 5… -
Page 299
APPENDIX App. 2.4 Signal App. 2.4.1 Signal The following shows CN1 connector signals as a typical example. Refer to section 3.4 for other connectors. DICOM DICOM DOCOM DOCOM This is in position control mode. App. 2.4.2 Input/output device The following shows typical I/O devices. Refer to section 3.5 for other devices. Input device Symbol Device… -
Page 300
APPENDIX Output device Symbol Device Connector Pin No. Zero speed detection In-position Malfunction Ready Power supply Symbol Device Connector Pin No. DICOM Digital I/F power supply input 20, 21 DOCOM Digital I/F common 46, 47 Shield Plate App. 2.5 Maintenance and service To avoid an electric shock, only qualified personnel should attempt inspections. -
Page 301
APPENDIX App. 2.5.2 Parts having service lives Service lives of the following parts are listed below. However, the service life vary depending or operating methods and environment. If any fault is found in the parts, they must be replaced immediately regardless of their service lives. -
Page 302
APPENDIX App. 2.7 Technical data App. 2.7.1 MR-JE servo amplifier MR-JE-10A/MR-JE-20A/MR-JE-40A/ Item MR-JE-100A/MR-JE-200A/MR-JE-300A MR-JE-70A 3-phase or 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Power Line voltage 3-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz Hz/60 Hz supply Interface (SELV) 24 V DC, (required current capacity: 300 mA) -
Page 303: App. 3 Analog Monitor
APPENDIX App. 3 Analog monitor POINT A voltage of analog monitor output may be irregular at power-on. The servo status can be outputted to two channels in terms of voltage. (1) Setting Change the following digits of [Pr. PC14] and [Pr. PC15]. [Pr.
-
Page 304
APPENDIX (2) Setting The servo amplifier is factory-set to output the servo motor speed to MO1 (Analog monitor 1) and the torque to MO2 (Analog monitor 2). The setting can be changed as listed below by setting the [Pr. PC14] and [Pr. -
Page 305
APPENDIX Note 1. Encoder pulse unit 2. This cannot be used in the torque control mode. 3. This cannot be used in the speed control mode. (3) Analog monitor block diagram Speed Speed Current Droop pulses Bus voltage command command 2 command Current encoder… -
Page 306: App. 4 Low-Voltage Directive
APPENDIX App. 4 Low-voltage directive MR-JE series servo amplifiers are certificated in compliance with Low-voltage directive. The following shows a certificate by the Certification Body. Supplementation: Refer to section 1.6 (2) for the models shown in «(see Appendix 1)». App. — 13…
-
Page 307
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual. -
Page 308
Mitsubishi Electric Automation Inc. : +1-847-478-2100 500 Corporate Woods Parkway, Vernon Hills, IL 60061, USA : +1-847-478-0327 Germany Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V. German Branch : +49-2102-486-0 Gothaer Strasse 8, D-40880 Ratingen, Germany : +49-2102-486-1120 Italy Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V. Italian Branch… -
Page 309
Warranty 1. Warranty period and coverage We will repair any failure or defect hereinafter referred to as «failure» in our FA equipment hereinafter referred to as the «Product» arisen during warranty period at no charge due to causes for which we are responsible through the distributor from which you purchased the Product or our service provider. -
Page 310
MR-JE-A SERVOAMPLIFIER MODEL INSTRUCTIONMANUAL MODEL 1CW706 CODE HEAD OFFICE : TOKYO BLDG MARUNOUCHI TOKYO 100-8310 This Instruction Manual uses recycled paper. SH (NA) 030128-B (1307) MEE Printed in Japan Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Specifications:826/826149-melservoje_mrje70a.pdf file (09 Jan 2023) |
Accompanying Data:
Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A Amplifier PDF Instruction Manual (Updated: Monday 9th of January 2023 02:26:01 AM)
Rating: 4.6 (rated by 29 users)
Compatible devices: Melservo MR-J5-A, MR-J3-B-RJ006, MR-J3-B, MR-J2S-*B Series, MR-J4W2-22B, MELSERVO MRJ2S-B, MELSERVO-J3W Series, MELSERVO J5 Series.
Recommended Documentation:
Text of Instruction Manual
(Ocr-Read Version Summary of Contents, UPD: 09 January 2023)
-
111, Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A 4. STARTUP 4 — 20 (2) Display examples The following table shows the display examples. Displayed data Item Status Servo amplifier display Forward rotation at 2500 r/min Servo motor speed Reverse rotation at 3000 r/min Reverse rotation is indicated by «- «. Load to motor inertia ratio 7.00 times 11252 pulses …
-
133, 5. PARAMETERS 5 — 6 Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit P S T PD39 For manufacturer setting 0 PD40 0 PD41 0000h PD42 0000h PD43 0000h PD44 0000h PD45 0000h PD46 0000h PD47 0000h PD48 0000h 5.1.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ]) Control mode No. Symbol Name Initial value Unit …
-
140, 5. PARAMETERS 5 — 13 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T PA13 *PLSS Command pulse input form _ _ _ x Command input pulse train form selection 0: Forward/reverse rotation pulse train 1: Signed pulse train 2: A-phase/B-phase pulse train (The servo amplifier imports input pulses after multiplying by four.) Refer to…
-
212, 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 — 17 (c) [Pr. PB29 Load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching] Set the load to motor inertia ratio after gain switching. If the load to motor inertia ratio does not change, set it to the same value as [Pr. PB06 Load to motor inertia ratio]. (d) [Pr. PB30 Position loop gain after gain switching], [Pr. PB31 Speed loop gain after gain switchi…
-
52, 3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 — 23 Control mode Device Symbol Connector pin No. Function and application I/O division PST Forward rotation selection RS1 This is used to select a servo motor torque generation directions. The following shows the torque generation directions. DI-1 (Note) Input device RS2 RS1 Torque generation direction 0 0 …
-
214, Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A 7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 — 19 (2) When you choose switching by droop pulses In this case, the vibration suppression control after gain switching and model loop gain after gain switching cannot be used. (a) Setting Parameter Symbol Name Setting value Unit PB06 GD2 Load to motor inertia ratio 4.00 [Multiplier] PB08 PG2 Position loo…
-
291, Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 — 28 (3) Dimensions (a) EMC filter HF3010A-UN [Unit: mm] 32 ± 2 85 ± 2 110 ± 4 258 ± 4 273 ± 2 288 ± 4 300 ± 5 M4 IN 3-M4 65 ± 4 Approx. 41 4-5.5 × 73-M4 HF3030A-UN [Unit: mm] 125 ± 2 44 ± 1 260 ± 5 140 ± 2 70 ± 2 140 ± 1 155 ± 2 3-M5 6-R3.25 length:8 3-M5 M4 85 ± 1 210 ± 2 85 ± 1
… -
9, 2 3.9 Interfaces ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 3-50 3.9.1 Internal connection diagram………………………………………………………………………………………… 3-50 3.9.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces……………………………………….…
-
282, 11. OPTIONS AND PERIPHERAL EQUIPMENT 11 — 19 11.9 Noise reduction techniques Noises are classified into external noises which enter the servo amplifier to cause it to malfunction and those radiated by the servo amplifier to cause peripheral equipment to malfunction. Since the servo amplifier is an electronic device which handles small signals, the following general noise reduct…
-
157, 5. PARAMETERS 5 — 30 Control mode No./ symbol/name Setting digit Function Initial value [unit] P S T This is used to set speed 1 of internal speed commands. Setting range: 0 to permissible instantaneous speed 100 [r/min] PC05 SC1 Internal speed command 1/internal speed limit 1 This is used to set speed 1 of internal speed limits. Setting…
-
234, Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A 8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8 — 13 Alarm No.: 30 Name: Regenerative error Alarm content Permissible regenerative power of the built-in regenerative resistor or regenerative option is exceeded. A regenerative transistor in the servo amplifier is malfunctioning. Display Detail name Cause Check method Check result Action 30.1 Regeneration heat error (1) The setting value…
Mitsubishi Electric MELSERVO-JE MR-JE-70A Recommended Instructions:
M2R-FVM, ProLite L460W, V-RD151-4, COMPAQ DC5750, CZ202
-
AUDIO TELEX
AT120RC
*r)OO TEt+f r . ,,-‘.-,- rA-U)OCOMMUN tcAftoz4<_=c8<.cosso «Mixer omplifier wiih built-inRodio Receiver, Auto ReverseCossette Deck, Speoker ZoneSeleclor, 4 Tone Generotor ondMonilor Speoker.POWER OUTPUT.I20 WATTS RMS.MAXIMUM LOAD80 Ohms @ 100 VoltsPOWER BANDWIDTH50Hz- lskHz < 0.5% IHDFREQUENCY RESPONSE60Hz l5kHz +- 3dBTOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION0.5% @ …
AT120RC 2
-
Monacor
PA-24AFE
BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNGINSTRUCTION MANUALMODE D’EMPLOIISTRUZIONI PER L’USOCONSEJOS DE SEGURIDADINSTRUKCJA OBSLUGIVEILIGHEIDSVOORSCHRIFTENSIKKERHEDSOPLYSNINGERSÄKERHETSFÖRESKRIFTERTURVALLISUUDESTAELA-LINIENSTROMÜBERWACHUNGPA LINE CURRENT MONITORING UNITPA-24AFEBest.-Nr. 24.3110® …
PA-24AFE 9
-
AMERITRON
ALS-500M
AMERITRON ALS-500MINSTRUCTION MANUAL116 Willow RoadStarkville, MS 39759 USA662-323-8211Version 2APrinted in U.S.A.500 WATT SOLID STATE MOBILE AMPLIFIERPLEASE READ THIS MANUAL BEFORE OPERATING THIS EQUIPMENT !The Ameritron ALS-500M is a 500 watt PEP output solid state linear amplifier using rugged, conservatively rated bipolar RF devices in the power output section. The ALS-500M operates …
ALS-500M 20
-
Sony
XM-7557 Primary
1XM-7557US ModelCanadian ModelAEP ModelUK ModelE ModelSPECIFICATIONSSERVICE MANUALSTEREO POWER AMPLIFERSony Corporatione Vehicle CompanyPublished by Sony Engineering Corporation9-926-590-122004D02-1© 2004.04Ver 1.1 2004. 04 …
XM-7557 Primary 56
-
Arcam
ALPHA ONE
H / P P S E MANALPHA ONE/7R/8R/8P AMPLIFIER SERVICE MANUAL1Arcam Alpha One/ 7R/ 8R/ 8P Amplifier Service ManualIssue 1 Serial Number 001 — (Paul Newton/ Haider Bahrani Sept ‘98)Circuit DescriptionThe Alpha One / 7R/8R and 8P share a commonpcb. The circuits are very similar and the maindifferences are the remote volume facility and extrapower output on the 7R and 8 …
ALPHA ONE 16
-
Univox
DLS-380
Setup INSTRUCTIONS forUNIVOX DLS-380WARNING!LIVE TERMINALS ENCLOSED.Always remove the power cord cablebefore opening the amplifier!LOOPAREAFig.1Fig.2ADoor BellFig.2BFig.2CFig.2D12V ACMax. 1.6AIN1IN2IN3/Mic & Scart12V DCMAX 30mA0 dBOUT142376Fig.3AFig.3B12V ACMax. 1.6A(With loop beep signal)2004-01-20E-mail: [email protected]: www.edin.se(With loopbeep signal)(With loo …
DLS-380 2






 Programmable controller -_ _MT/ES (Note 11) (Note 15) 24 V Servo amplifier (Note 7) (Note 7) 24 V DC 24 V DC (Note 4) Programmable…
Programmable controller -_ _MT/ES (Note 11) (Note 15) 24 V Servo amplifier (Note 7) (Note 7) 24 V DC 24 V DC (Note 4) Programmable… 





