Just in case somebody is deperately trying to fix their problem just to realize there is nothing wrong with their reverse proxy setup:
In my case, the error persisted even after I’ve removed all location directives but a single one that only provides static content.
The error message was caused because Nginx wasn’t able to log it’s log to the syslog server:
access_log syslog:server=10.0.1.48:514,facility=local4,tag=nginx,severity=debug,nohostname main;
Summary:
If you are using a syslog log server, make sure it is available. To test whether the error originates from the logging setup, comment out all logging configs so that Nginx falls back to the native logging scheme.
I hope this saves some people time debugging a fully valid reverse proxy config, just to fid the error somewhere else 
If you’ve encountered the «Connect() Failed (111: Connection Refused) Error While Connecting to Upstream» issue while working with Nginx, you’re not alone. This error often occurs when Nginx is unable to establish a connection with the upstream server. In this guide, we’ll explain the root causes of this error and walk you through the process of resolving it step-by-step.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Error
- Step 1: Check the Upstream Server
- Step 2: Verify Nginx Configuration
- Step 3: Check Firewall and Security Group Rules
- Step 4: Monitor Logs
- Step 5: Test Connectivity
- FAQs
Understanding the Error
The connect() failed (111: Connection refused) error while connecting to upstream error occurs when Nginx is unable to establish a connection with the specified upstream server. This can be caused by several factors, including:
- The upstream server is down or not responding
- Incorrect configuration settings in Nginx
- Firewall or security group rules blocking the connection
- Network issues between Nginx and the upstream server
Step 1: Check the Upstream Server
Before diving into the Nginx configuration, first, make sure the upstream server is running and responding to requests. You can use the following command to check if the upstream server is listening on the expected port:
sudo netstat -tuln | grep LISTEN
If the upstream server is not running or not responding, restart it and ensure it’s running correctly.
Step 2: Verify Nginx Configuration
Next, examine your Nginx configuration files to ensure you’ve specified the correct upstream server settings. Look for the upstream and proxy_pass directives in your Nginx configuration file (usually located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/sites-available/default):
http {
upstream backend {
server backend_server_ip:backend_server_port;
}
server {
...
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
...
}
}
Ensure that the backend_server_ip and backend_server_port values are correct, and the upstream server is listening on the specified port.
After making any necessary changes, reload the Nginx configuration using:
sudo nginx -t && sudo nginx -s reload
Step 3: Check Firewall and Security Group Rules
Firewalls or security group rules might be blocking Nginx from connecting to the upstream server. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the required ports are open:
- On Linux systems, use
iptablesorfirewalldto check and update firewall rules. - On cloud platforms like AWS or GCP, verify the security group rules associated with your instances.
Ensure that the rules allow incoming connections on the port used by the upstream server.
Step 4: Monitor Logs
Keep an eye on both the Nginx and upstream server logs to identify any issues. The Nginx error log is usually located at /var/log/nginx/error.log. Tail the log in real-time using:
sudo tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
For the upstream server, check the relevant logs, depending on the application or service you’re using.
Step 5: Test Connectivity
After completing the previous steps, test the connectivity between Nginx and the upstream server using tools like curl, telnet, or nc. For example:
curl http://backend_server_ip:backend_server_port
If the connection is successful, you should no longer encounter the «Connect() Failed (111: Connection Refused) Error While Connecting to Upstream» error.
FAQs
Q1: Can SELinux cause the «Connect() Failed (111: Connection Refused) Error While Connecting to Upstream»?
Yes, SELinux can be a source of this error. If you suspect that SELinux is the cause, you can temporarily disable it using the command sudo setenforce 0 and retest the connection. If the error disappears, you’ll need to properly configure SELinux to allow the connection.
Q2: How can I check if my Nginx configuration has errors?
You can use the nginx -t command to test your Nginx configuration for any syntax errors:
sudo nginx -t
Q3: How do I restart Nginx after making changes to the configuration files?
To restart Nginx, use the following command:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Q4: Can I use multiple upstream servers in my configuration?
Yes, Nginx supports load balancing and failover using multiple upstream servers. You can specify multiple server directives within the upstream block:
http {
upstream backend {
server backend_server1_ip:backend_server1_port;
server backend_server2_ip:backend_server2_port;
}
...
}
Q5: How can I enable SSL between Nginx and the upstream server?
To enable SSL between Nginx and the upstream server, you’ll need to configure Nginx with the necessary SSL certificates and update the proxy_pass directive to use https. Check out this SSL configuration guide for detailed instructions.
- Nginx Load Balancing and Failover
- Configuring HTTPS Servers with Nginx
- SELinux Users and Administrators Guide
Answer
These all point to no http server response, which means your http server is not answering requests.
The exact part that points this out in the logs is the following.
connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream
server: , request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://127.0.0.1:
Make sure you have taken steps to start that, and ensure its currently running at the time the error is generated.
It can also possibly point to configuration error on the the http server js file itself.
To get a better idea, view error logs in /var/log/nginx/error.log. If you see connection errors to your proxy backend, like above, then that is probably the case.
To see if its having a problem connecting to a proxy that was defined. Make sure the node process manager is running and configured correctly on that proxied port. e.g. If your running a node app, look for pm2, or whatever node module you use to start your http server with.
pm2 show
The OA assumed your backed was simply misconfigured, and wasnt clear that an entire http server was needed behind it. Some users are trying to launch apps that contain task managers that are trying to launch things that done exist, and dont realize entire back-end was not needed or running, like myself at the time being.
Generally, in python, the connection error is not something that you will face every day, but it can sometimes happen due to various reasons. One such reason is the connection Refuse. This causes the generation of ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused message. If you are facing this error message in your coding, this might help you.
What is socket error?
A socket programming in python is used to form a bidirectional communications channel. It is generally a process of making the two unrelated network nodes communicate with each other by making a connection. This connection can be made if you know the IP address of the server.
What is ConnectionError?
Whether you are someone new to the python language or not, you must be aware of the term connection error. As suggested by the name, it is a class of exception errors related to the errors generated due to issues in the connection. It is a type of socket error that is observed in many other libraries and platforms.
In python, the ConnectionError is generally referred to as an error generated by the failure in any of the internal connections that are the connection between the application and the DBMS server mediating a peer. This type of error can be caused by various failures, such as local errors caused by the errors reported directly to the user interface programs, then local and remote errors caused while trying to connect from the local communication server to the remote communication server and the server installation. These ConnectionErrors also report directly to the applications.
Types Of ConnectionError
There are mainly three subclasses of ConnectionError such as ConnectionAbortedError, ConnectionResetError, and ConnectionRefusedError. These errors generally arise when the error is raised due to the attempt the interruption in connection with the actions of peers.
The ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused is a subclass of the ConnectionError which is caused when the peer refuses the attempts for the connection between the application and the server. This type of error corresponds to errno ECONNREFUSED messages.
The ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused is generated when the initial SYN packet to the host to be connected was responded with an RST packet instead of a SYN+ACK packet. This resulted in the declination of the program on the remote computer that needed to be connected.
This type of error can cause by many libraries and computing platforms, but the solutions to this problem are similar.
The generation of the error can be understood efficiently by using an example:
As the connection has to be made from both end so it is done in two parts:
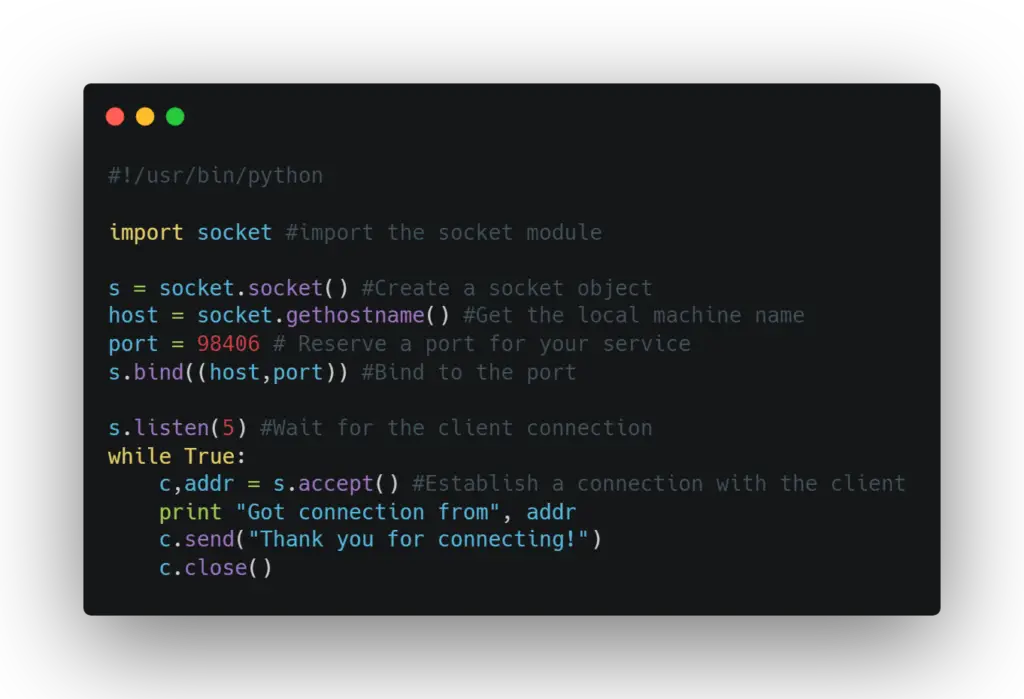
The Server script:
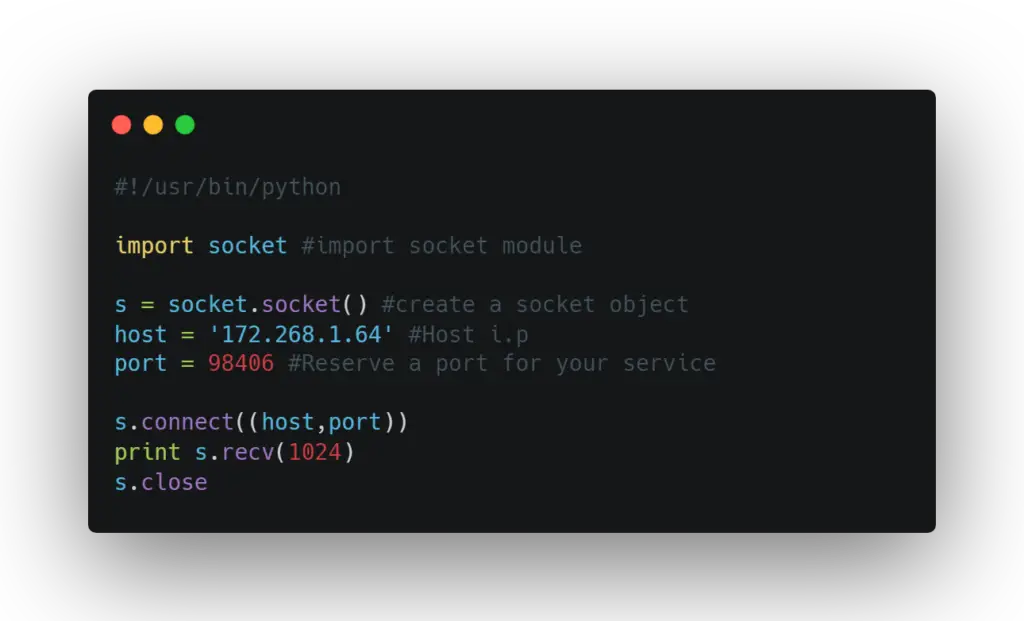
The client script:
These codes might seem good, but this will result in the socket.error: [Errno 111] Connection refused message.
How to solve the ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused?
As this is a connection-based error, so the errors have to be checked on both ends that is, on the client and the server end. The ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused can be resolved using one of the following reasons.
Checking the connection
- Ensure the IP address is of the client, and both servers are on the same LAN. If the servers are not on the same router or firewall, then you may face traffic blocking.
- Make sure that the port is listening to the server and if not then try “netstat -ntulp”.
- Make sure that you are accepting the connections to the server.
- Make sure you have access to the port server of the client.
Selectively restrict the listening socket
In the example for the generation of the ConnectionRefusedError by the server you can see that there is a line as follows:
host = socket.gethostname() #Get the local machine name
port = 98406 # Reserve a port for your service
s.bind((host,port)) #Bind to the portInstead of the above code, you can try:
port = 98406 # Reserve a port for your service
s.bind(('', port)) #Bind to the portThis way, the listening socket will not be too restricted and will ensure the connection precisely on both ends.
Proper guidance to get an IP address
To avoid ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused while coding you need to make sure to get the right IP address for that you have to put the hostname and port number for the receiver end correctly.
Due to DNS resolution, the hostname might not get translated into the local address and returned properly. So instead of the usual code:
host = socket.gethostname() #Get the local machine name
port = 98406 # Reserve a port for your service
s.bind((host,port)) #Bind to the portYou can try the code below.
host = socket.gethostbyname("localhost")
s.connect((host, port))FAQ
How do you fix a socket error?
As the ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused is a type of socket error, resolving this may help in resolving the former error.
- This error can be fixed by specifying the port number for which you can use the following code:
m SimpleHTTPServer (Port Number)- You can also free up the port by terminating the previous programs.
What is the socket address in computer networks?
The socket address is a crucial part of establishing the connection. It is generally a combination of two identifiers, that is both IP address and port number. It is defined in a header where it is specified by a data structure.
Conclusion
The ConnectionRefusedError errno 111 connection refused is a socket error that results when there is a failure in the establishment of connection when the connection is refused. Which can later be resolved by managing the data necessary for establishing the connection.
References
- Dizzy coding
- GeeksforGeeks socket programming
To learn more about some common errors follow python clear’s errors section.
When I attempt to install packages through sudo apt-get install, no matter what I try to install, it returns a 111: Connection Refused error.
The web browser appears to work, but not sudo apt-get install. I attempted to install Ruby, PHP, and open-shift RHC tools, and I also attempted to use Synaptic to update/install packages, and I was unable to.
I get errors similar to the following, every time:
W: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main /liby/libyaml > /libyaml-0-2_0.1.4-3ubuntu3.1_i386.deb
Could not connect to 155.238.4.87:8080 (155.238.4.87). - connect (111: Connection refused)
I am using Ubuntu 14.04.1 LTS.
I connect to my adsl router via wireless, and am running an image that i got from my university running on vmware, using Windows 10. The university used a proxy but I edited it out in the M2 setting file and edited firefox to auto detect proxy to get my internet working
Please can someone help me figure out how to fix this?