Здравствуйте.
Подскажите, пожалуйста: после попытки открыть сайт на локальном сервере (Open Server) в открытый доступ сайт вообще перестал открываться на компьютере. Выдается ошибка 403 Forbidden, ниже под чертой nginx/1.15.8
Очень сильно новичок, поэтому вот цепочка моих действий:
1. Делал сайт на Open Server через WordPress
2. Решил глянуть через телефон, полазил в настройках Open Server, что-то не получилось, скинул настройки.
3. Практически одновременно с этим добавил .ru к адресу сайта в настройках WordPress, было просто sitename, теперь sitename.RU
4. Теперь при попытке открыть сайт через меню Open Server — сайт выдает ошибку.
Подозреваю, что проблема в правах доступа и, видимо, это как-то связано с переименованием URL. В файле wp-config пробовал писать и старое имя, и новое.
Подскажите, как исправить. Спасибо!
-
Вопрос заданболее трёх лет назад
-
2219 просмотров
«Четырёхсотые» коды состояния описывают проблемы на стороне клиента: обычно они возникают, когда браузер отправляет серверу некорректный HTTP-запрос.
Но на практике бывает по-разному. Например, ошибка 403 может появиться из-за неправильной логики на сервере. В этой статье попробуем разобрать все возможные причины.
- Что означает ошибка 403 (Forbidden)
- Что могло пойти не так
- Ошибки на стороне пользователя
- Ошибки на стороне сайта
- Ограничения на стороне хостера или провайдера
- Как исправить ошибку 403
- Что делать владельцу сайта
- Что делать пользователю
Ошибка 403 (Forbidden) — это когда сервер понял запрос, но почему-то отказывается выполнять его и отдавать браузеру HTML-код страницы.
Помимо «Forbidden», сервер может описать ошибку и другими словами: «error access denied» (доступ запрещён), «you don’t have permission to access» (нет разрешения на вход) и так далее. Сообщения разные, но смысл один.
В идеальном мире ошибка с кодом 403 должна возникать, когда доступ к странице пытается получить кто-то, у кого его нет, — например, неавторизованный пользователь.
Но в реальности возможных причин гораздо больше: это и проблемы с устройством пользователя, и неправильно настроенные компоненты сайта, и ограничения со стороны хостера или провайдера, и много что ещё.
Нужна регистрация. Пользователь не авторизован, а для доступа к странице это обязательно. При таком сценарии исправить ошибку просто — залогиниться на сайте.
Неправильный URL-адрес. Возможно, вы случайно постучались на какую-то секретную страничку, а это ни вам, ни серверу не нужно. Банально, но стоит перепроверить ссылку ещё разок.
Проблема в устройстве. Проверить это можно, зайдя на страницу с другого девайса. Если всё откроется, значит, дело в конкретной технике. Причины у этого могут быть разные:
- Неправильные данные в кэше. Тогда можно почистить его или перезагрузить страницу сочетанием Ctrl + F5 (при таком принудительном обновлении кэш игнорируется).
- Устаревшие данные в cookies. Если проблема в этом, то достаточно почистить их, и всё заработает.
- Вы заходите на страницу со смартфона, на котором включён режим экономии трафика. Из-за него браузер может не передавать сайту какие-то нужные ему данные — это и вызывает HTTP-ошибку Forbidden. В этом случае достаточно отключить экономию трафика.
Впрочем, иногда ошибка 403 возникает правомерно. Например, если вы были заблокированы на сайте или пытаетесь получить доступ к служебной странице. В таком случае обратитесь к владельцу сайта, чтобы он снял бан или выдал нужные права.
«Forbidden» может возникнуть, если что-то не так с компонентами сайта. Вот несколько возможных проблем, которые может и должен решить администратор сайта.
Некорректный индексный файл. Это файл, который указывает на главную страницу домена или поддомена. Нужно, чтобы у него были правильное название и формат — а они, в свою очередь, определяются CMS, которой вы пользуетесь. Например, для сайтов на WordPress это может быть index.html, index.htm или index.php.
А ещё индексный файл должен находиться в корневой папке домена или поддомена — смотря к чему он относится.
Неправильно расположены файлы сайта. Как и index, другие файлы сайта тоже должны лежать в корневой директории. Где именно — зависит от CMS и хостинга, которые вы используете.
Неверно настроены права доступа. У каждого файла и папки есть права доступа, которые состоят из трёх цифр от 0 до 7: первая — права владельца, вторая — групповые права, третья — публичные права. Сама цифра означает, какие права предоставлены этой группе.
Если у пользователя нет прав на выполнение действия, то он получит HTTP-ошибку 403 Forbidden. Обычно на папки выставляют доступ 755, на файлы — 644.
Проблемы с плагином. Если вы устанавливали плагины для своей CMS, то вызвать код 403 может какой-то из них. Возможно, он не обновился до последней версии, повреждён или несовместим с конфигурациями сайта.
Вот как это проверить, если у вас WordPress:
- Перейдите в раздел wp-content и найдите папку plugins.
- Переименуйте её — это отключит работу всех плагинов.
- Если проблема уйдёт, значит, дело было в плагинах.
Далее можно включать плагины обратно и искать конкретного виновника. Чтобы это сделать, отключайте их по очереди и обновляйте страницу — где-то по пути точно обнаружите, где с каким плагином проблема.
Некорректные указания в файле .htaccess. Если вы используете Apache Web Server, попробуйте переименовать файл .htaccess. Так же как и с плагинами, это отключит его и позволит понять, виновен ли он в ошибке.
Если дело всё-таки в .htaccess, проверьте и исправьте его директивы. Вот на какие условия стоит обратить внимание:
- deny (запрещает доступ);
- allow (разрешает доступ);
- require (запрещает или разрешает доступ всем, кроме указанных пользователей);
- redirect (перенаправляет запрос на другой URL);
- RewriteRule (преобразует строку с помощью регулярных выражений).
Действия пользователя блокирует брандмауэр. Брандмауэры веб-приложений могут автоматически блокировать действия пользователей, которые считают вредоносными, и возвращать им Forbidden.
Чтобы проверить, в этом ли дело, отключите брандмауэр и повторите запрещённое действие. Если сработает — проблема найдена. Проверьте журнал брандмауэра: там должна быть указана конкретная причина блокировки запроса.
Узнав причину, добавьте её в исключения, и такие запросы будут выполняться корректно.
Тариф хостинга не поддерживает инструменты. Например, вы пишете на PHP 8, а тариф рассчитан только на PHP 7.4. В таком случае придётся либо перейти на другую версию инструмента, либо сменить тариф (а может, и целого хостера).
Бывает так: с логикой на сервере всё в порядке, HTTP-запрос составлен корректно, а ошибка 403 всё равно возникает. Но подождите кричать «Тысяча чертей!» — возможно, шайба на стороне посредника.
Хостер прекратил обслуживание сайта. Просрочка платежа, нарушение условий хостинга, блокировки Роскомнадзора и другие малоприятные истории. Самое время проверить почту — обычно доступ к сайту не отключают без предупреждения.
Не успел обновиться кэш DNS-серверов. Если ваш сайт переезжал на другой адрес, в кэше DNS-серверов могли остаться устаревшие данные. Остаётся только ждать. Обычно кэш обновляется в течение суток, но в редких случаях процесс может занять два-три дня.
Проблемы на стороне провайдера. Возможно, у него неправильно настроена конфигурация оборудования или он заблокировал вас намеренно. Выход один и для пользователя, и для владельца сайта — обратиться к провайдеру.
Да-а, такая маленькая ошибка, а проблем — как с запуском Falcon Heavy на Марс. Держите чек-лист, который поможет не запутаться и быстро всё пофиксить.
Выясните, на чьей стороне проблема. Во-первых, зайдите на сайт самостоятельно — лучше один раз увидеть, чем прочитать тысячу тикетов в техподдержке. Во-вторых, проверьте почту — нет ли там писем счастья от хостера или Роскомнадзора?
Проверьте настройки сайта. Пробегитесь по списку ошибок, о которых мы писали выше. Перебирайте один вариант за другим, пока не поймёте, где собака зарыта.
Если ничего не помогает — обратитесь за помощью к своему хостинг-провайдеру.
- Перепроверьте URL страницы: правильный ли он? Вы могли кликнуть по ошибочной ссылке или сайт переехал на другой адрес, а поисковики этого ещё не поняли.
- Проверьте, авторизованы ли вы на сайте. Залогиньтесь, если есть такая возможность.
- Зайдите на страницу с другого устройства. Если сайт заработал — проблема в устройстве. Попробуйте перезагрузить страницу, почистить кэш и cookies браузера или отключить экономию трафика.
- Включите или выключите VPN. Возможно, доступ к сайту блокируется по IP-адресу для пользователей из определённой страны или региона. Попробуйте использовать IP-адреса разных стран.
- Подключитесь к другой сети. Например, если пользуетесь 4G, перейдите на Wi-Fi. Это поможет понять, есть ли проблемы на стороне поставщика интернета.
Если ничего не помогает, значит, проблема на стороне сайта. Обратитесь в техподдержку и сообщите об ошибке — возможно, о ней ещё никто не знает.
Did you just try to access your site only to be hit by some message telling you something is “Forbidden” or that you don’t have permission to access something on your site? If so, you’ve likely run into the 403 Forbidden error.
Seeing an error on your site can be frustrating and deflating, which is why we’ve created this detailed guide to help you fix the 403 Forbidden error and get your site functioning again as quickly as possible.
Let’s get started without any further introduction because we’re sure you just want to fix your site!
Check Out Our Video Guide on Fixing a 403 Forbidden Error on Your Site
What is the 403 Forbidden Error?
The 403 Forbidden error indicates that the server understands the request but can’t provide additional access. This means that the web page you’re trying to open in your browser is a resource that you’re not allowed to access.
| Error Code | 403 |
| Error Type | Authentication error |
| Error Variations | Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server 403 – Forbidden: Access is denied Error 403 – Forbidden 403 – Forbidden Error – You are not allowed to access this address 403 Forbidden – nginx |
| Error Causes | Corrupt .htaccess file Incorrect file permissions Plugin issues |
Like many other common errors, the 403 Forbidden error is an HTTP status code that a web server uses to communicate with your web browser.
Quick background on HTTP status codes – whenever you connect to a website with your browser, the web server responds with something called an HTTP header. Usually, this all happens behind the scenes because everything is working normally (that’s a 200 status code, in case you were wondering).
However, if something goes wrong, the server will respond back with a different numbered HTTP status code. While these numbers are frustrating to encounter, they’re actually quite important because they help you diagnose exactly what’s going wrong on your site.
The 403 Forbidden error means that your web server understands the request that the client (i.e. your browser) is making, but the server will not fulfill it.
In more human-friendly terms, it basically means that your server knows exactly what you want to do, it just won’t let you do it because you don’t have the proper permissions for some reason. It’s kind of like you’re trying to get into a private event, but your name got accidentally removed from the guestlist for some reason.
Other HTTP status codes mean different things. We’ve written guides on fixing issues with:
- 404 not found errors
- 500 internal server errors
- 502 bad gateway errors
- 504 gateway timeout errors.
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error?
The two most likely causes of the 403 Forbidden Error are:
- Corrupt .htaccess file
- Incorrect file permissions
It’s also possible that you’re seeing the error because of an issue with a plugin that you’re using at your site. In this article, we’ll show you how to troubleshoot all of these potential issues.
403 Forbidden Error Variations
Like many other HTTP status codes, there are a lot of different variations for how this error code presents itself.
Here are some common variations that you might come across:
- “Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server”
- “403 – Forbidden: Access is denied”
- “Error 403 – Forbidden”
- “403 – Forbidden Error – You are not allowed to access this address”
- “403 Forbidden – nginx”
- “HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden – You do not have permission to access the document or program you requested”
- “403 Forbidden – Access to this resource on the server is denied”
- “403. That’s an error. Your client does not have permission to get URL / from this server”
- “You are not authorized to view this page”
- “It appears you don’t have permission to access this page.”
If you’re on an Nginx server, it will look like this below. Basically, if you see any mention of “forbidden” or “not allowed to access”, you’re probably dealing with a 403 Forbidden error.
How to Fix a 403 Forbidden Error?
To help you fix the 403 Forbidden Error on your site, we’ll cover nine separate troubleshooting steps in detail:
1. Refresh the Page and Double Check the Address
Sometimes the simplest solutions are the only ones capable of solving complex problems.
So try to refresh the page you are not able to access. The 403 error is often temporary, so maybe you’ll get lucky.
We also recommend checking that the URL is spelled correctly. If the address you are trying to access is a directory and not a web page, there is a chance that you will encounter a 403 error. (example: www.kinsta.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/)
2. Clear Your Browser Cache
Another very handy solution is to clear your browser’s cache.
Cache is very useful to help us see a website faster, but sometimes some mismatch can happen between the real version of a page and its cached version.
Check below some tips on how to clear cache in various browsers:
- How to Force Refresh a Single Page for All Browsers
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Google Chrome
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Mozilla Firefox
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Safari
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Internet Explorer
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Microsoft Edge
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Opera
3. Modify Your File Permissions
Each folder and file on your site’s server has its own unique file permissions that control who can:
- Read – see the data in the file/view the contents of a folder.
- Write – modify the file/add or delete files inside a folder
- Execute – run the file and/or execute it as a script/access a folder and perform functions and commands.
These permissions are indicated by a 3-digit number, with each digit indicating the level of permission for each of the 3 categories above.
Normally, these permissions just “work” for your site.
However, if something gets messed up with the file permissions at your site, it can cause the 403 Forbidden error.
To view and modify your site’s file permissions, you’ll need to connect via FTP/SFTP. Here’s how to use SFTP if you’re hosting at Kinsta.
For the screenshots in the tutorial below, we’ll be using the free FileZilla FTP program.
The basic principles will apply to any FTP program, though – you’ll just need to apply them to a different interface.
Once you’re connected to your server, you can view a file or folder’s permissions by right-clicking on it:
Of course, manually checking the permissions for each file or folder isn’t really an option.
Instead, you can automatically apply file permissions to all the files or folders inside of a folder.
According to the WordPress Codex, the ideal file permissions for WordPress are:
- Files – 644 or 640
- Directories – 755 or 750
One exception is that your wp-config.php file should be 440 or 400.
To set these permissions, right-click on the folder that contains your site (the folder name is public at Kinsta). Then, choose File Attributes:
Enter 755 or 750 in the Numeric value box. Then, choose Recurse into subdirectories and Apply to directories only:
Once you’ve applied the correct permissions for directories, you’ll repeat the process for files. Only this time:
- Enter 644 or 640 in the Numeric value box
- Choose Recurse into subdirectories
- Choose Apply to files only
To finish the process, you just need to manually adjust the permissions for your wp-config.php file to make them 440 or 400:
If file permissions issues were causing the 403 Forbidden Error, your site should now start working again.
4. Delete and Restore the .htaccess File
Kinsta uses the NGINX web server, so this potential issue doesn’t apply if you’re hosting your site at Kinsta because Kinsta sites do not have a .htaccess file.
However, if you’re hosting elsewhere and your host uses the Apache web server, one common cause of the 403 Forbidden error is a problem in your site’s .htaccess file.
The .htaccess file is a basic configuration file used by the Apache web server. You can use it to set up redirects, restrict access to all or some of your site, etc.
Because it’s so powerful, even if a little mistake can cause a big issue, like the 403 Forbidden error.
Rather than trying to troubleshoot the .htaccess file itself, a simpler solution is to just force WordPress to generate a new, clean .htaccess file.
To do that:
- Connect to your server via FTP
- Find the
.htaccessfile in your root folder - Download a copy of the file to your computer (it’s always a good idea to have a backup just in case)
- Delete the
.htaccessfile from your server after you have a safe backup copy on your local computer
Now, you should be able to access your WordPress site if your .htaccess file was the issue.
To force WordPress to generate a new, clean .htaccess file:
- Go to Settings → Permalinks in your dashboard
- Click Save Changes at the bottom of the page (you do not need to make any changes – just click the button)
And that’s it – WordPress will now generate a new .htaccess file for you.
5. Deactivate and then Reactivate Your Plugins
If neither your site’s file permissions nor .htaccess file are the problems, the next place to look is your WordPress plugins. It could be a bug in a plugin or a compatibility issue between different plugins.
No matter what the issue is, the easiest way to find the problematic plugin is with a little trial and error. Specifically, you’ll need to deactivate all of your plugins and then reactivate them one by one until you find the culprit.
If you can still access your dashboard, you can perform this process from the normal Plugins area.
If you cannot access your dashboard, you’ll instead need to connect to your WordPress site’s server via FTP/SFTP (here’s how to connect via SFTP at Kinsta).
Once you’re connected to your server via FTP:
- Browse to the wp-content folder
- Find the plugins folder inside of the wp-content folder
- Right-click on the plugins folder and choose Rename
- Change the name of the folder. You can name it anything different, but we recommend something like plugins-disabled to make it easy to remember.
By renaming the folder, you’ve effectively disabled all the plugins at your site.
Now, try accessing your site again. If your site is working, you know that one of your plugins is causing the 403 Forbidden error.
To find the culprit, reactivate your plugins one-by-one until you find which plugin is causing the issue.
After changing the file name of the plugins folder, you should see a number of errors that say plugin file does not exist when you go to the Plugins area on your site:
To fix this issue and regain the ability to manage your plugins, use your FTP program to change the name of the folder back to plugins. So, if you renamed it to plugins-disabled, just change it back to plugins.
Once you do that, you’ll see the full list of all your plugins again. Only now, they’ll all be deactivated:
Use the Activate button to reactivate them one-by-one.
Once you find the plugin that’s causing the issue, you can either reach out to the plugin’s developer for help or choose an alternate plugin that accomplishes the same thing (we’ve collected the best WordPress plugins here).
6. Deactivate CDN Temporarily
If you’re getting 403 forbidden errors on your assets (images, JavaScript, CSS), it could be a problem with your content delivery network (CDN).
In this case, we recommend temporarily disabling your CDN and then checking your site to see if the issue is resolved. If you’re a Kinsta client, click through to your WordPress site within the MyKinsta dashboard, select CDN in the sidebar menu and then click the Disable button.
7. Check to See If Hotlink Protection Is Misconfigured
Hotlinking is when someone adds an image to their site, but the hosted link is still pointed to someone else’s site. To prevent this, some will set up what is called “hotlink protection” with their host or CDN provider.
When hotlink protection is enabled, it will typically return a 403 forbidden error. This is normal. However, if you’re seeing a 403 forbidden error on something you shouldn’t be, check to make sure hotlink protection is configured properly.
8. Disconnect From Your VPN
Another simple tip, but that can solve this problem.
Some sites block VPN users, which may be why the 403 Forbidden message is showing up for you.
To verify this, disconnect from the VPN and try connecting to the site in another way. Or try switching to a different server provided by your VPN service.
9. Reach Out to Your Hosting Provider
If none of the above solutions worked for you, then we recommend reaching out to your hosting provider. They can most likely help you pinpoint the issue and get you back up and running. If you’re a Kinsta client, open up a support ticket with our team. We are available 24/7.
10. Use the Sitechecker Website Crawler Tool
The Sitechecker Website SEO Checker is able to provide you with a detailed SEO audit report by providing solutions and checkers for your website. There is a website crawler, a site monitoring tool, and a rank tracker amongst other built-in tools.
It’s important to constantly monitor your pages for 403 errors, and you can do this with Sitechecker. You can check your website not only for 403 errors but also for all other errors.
Summary
The 403 Forbidden error means that your server is working, but you no longer have permission to view all or some of your site for some reason.
The two most likely causes of this error are issues with your site’s file permissions or .htaccess file. Beyond that, some plugin issues might also cause the 403 Forbidden error. Or it could be that something is misconfigured with hotlink protection or your CDN.
By following the troubleshooting steps in this guide, you should be able to get your site back to working in no time.
Все мы, путешествуя по просторам интернета, натыкаемся на различные ошибки при загрузке сайтов. Одна из них, кстати, достаточно часто встречается – я говорю об ошибке сервера 403 Forbidden Error. Сегодня я рассмотрю причины ее возникновения и способы устранения со стороны владельца сайта и его пользователя.
Что означает ошибка 403 и почему она появляется
Ошибка сервера 403 Forbidden означает ограничение или отсутствие доступа к материалу на странице, которую вы пытаетесь загрузить. Причин ее появления может быть несколько, и вот некоторые из них:
- Формат индексного файла неверен.
- Некорректно выставленные права на папку/файл.
- Файлы были загружены в неправильную папку.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Исправление ошибки сервера 403 Forbidden
Чтобы исправить ошибку сервера 403 Forbidden, обязательно нужен доступ к панели управления вашего хостинга. Все описанные ниже шаги применимы к любой CMS, но примеры будут показаны на основе WordPress.
Проверка индексного файла
Сначала я проверю, правильно ли назван индексный файл. Все символы в его имени должны быть в нижнем регистре. Если хотя бы один символ набран заглавной буквой, возникнет ошибка 403 Forbidden. Но это больше относится к ОС Linux, которой небезразличен регистр.
Еще не стоит забывать, что индексный файл может быть нескольких форматов, в зависимости от конфигураций сайта: index.html, index.htm, или index.php. Кроме того, он должен храниться в папке public_html вашего сайта. Файл может затеряться в другой директории только в том случае, если вы переносили свой сайт.
Любое изменение в папке или файле фиксируется. Чтобы узнать, не стала ли ошибка итогом деятельности злоумышленников, просто проверьте графу «Дата изменения».
Настройка прав доступа
Ошибка 403 Forbidden появляется еще тогда, когда для папки, в которой расположен искомый файл, неправильно установлены права доступа. На все директории должны быть установлены права на владельца. Но есть другие две категории:
- группы пользователей, в числе которых есть и владелец;
- остальные, которые заходят на ваш сайт.
На директории можно устанавливать право на чтение, запись и исполнение.
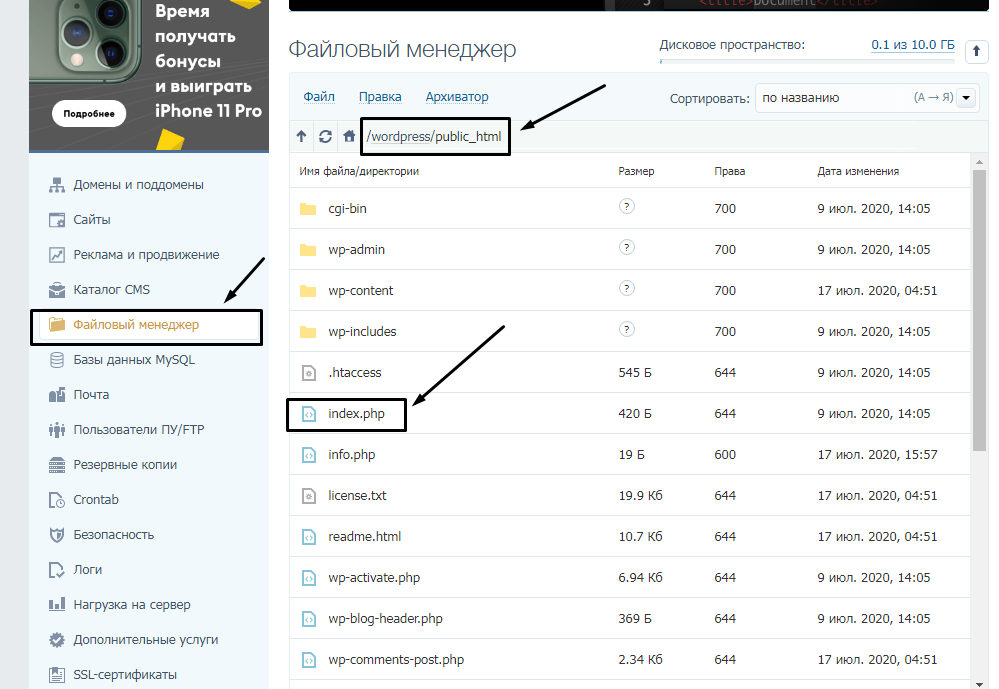
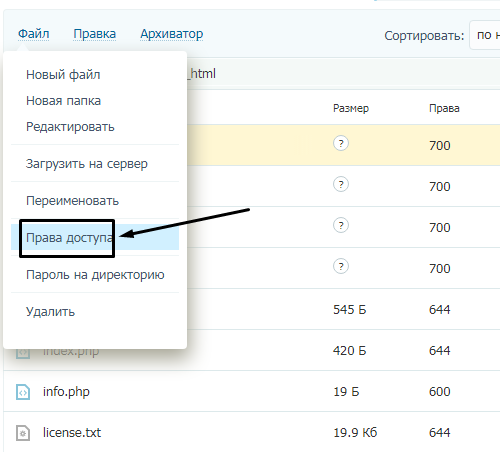
Так, по умолчанию на все папки должно быть право исполнения для владельца. Изменить их можно через панель управления TimeWeb. Для начала я зайду в раздел «Файловый менеджер», перейду к нужной папке и выделю ее. Далее жму на пункт меню «Файл», «Права доступа».
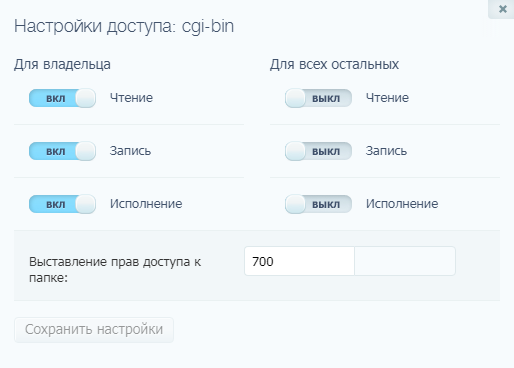
Откроется новое окно, где я могу отрегулировать права как для владельца, так и для всех остальных.
Отключение плагинов WordPress
Если даже после всех вышеперечисленных действий ошибка не исчезла, вполне допустимо, что влияние на работу сайта оказано со стороны некоторых плагинов WordPress. Быть может они повреждены или несовместимы с конфигурациями вашего сайта.
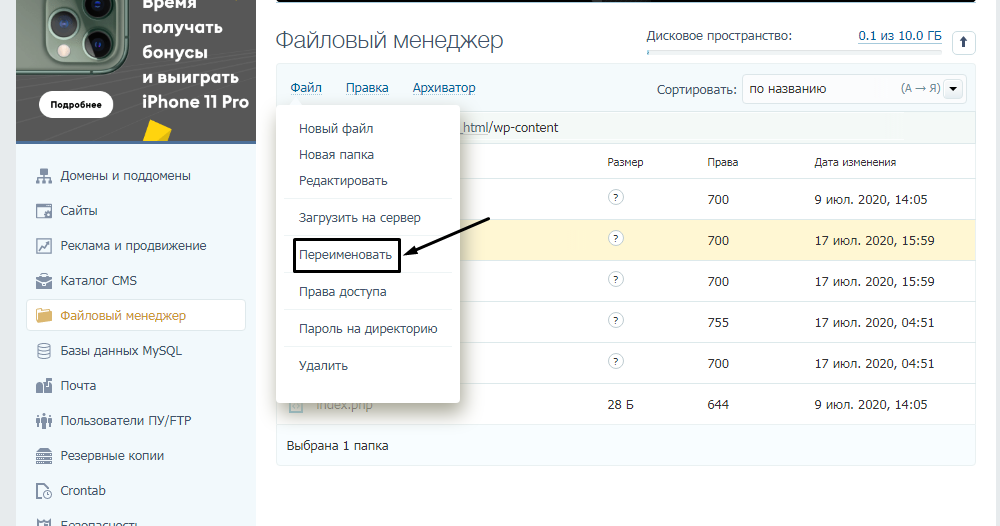
Для решения подобной проблемы необходимо просто отключить их. Но сначала надо найти папку с плагинами. Открываю папку своего сайта, перехожу в раздел «wp-content» и нахожу в нем директорию «plugins». Переименовываю папку – выделяю ее, жму на меню «Файл» и выбираю соответствующий пункт. Название можно дать вот такое: «plugins-disable». Данное действие отключит все установленные плагины.
Теперь нужно попробовать вновь загрузить страницу. Если проблема исчезла, значит, какой-то конкретный плагин отвечает за появление ошибки с кодом 403.
Но что делать, если у вас плагин не один, а какой из них влияет на работу сайта – неизвестно? Тогда можно вернуть все как было и провести подобные действия с папками для определенных плагинов. Таким образом, они будут отключаться по отдельности. И при этом каждый раз надо перезагружать страницу и смотреть, как работает сайт. Как только «виновник торжества» найден, следует переустановить его, удалить или найти альтернативу.
Читайте также
Как решить проблему, если вы – пользователь
Выше я рассмотрела способы устранения ошибки 403 Forbidden для владельцев сайта. Теперь же разберу методы исправления в случаях с пользователем.
- Сначала надо убедиться, что проблема заключается именно в вашем устройстве. Внимательно проверьте, правильно ли вы ввели URL сайта. Может, в нем есть лишние символы. Или, наоборот, какие-то символы отсутствуют.
- Попробуйте загрузить страницу с другого устройства. Если на нем все будет нормально, значит, проблема кроется именно в используемом вами девайсе. Если нет – надо перейти к последнему шагу.
- Еще хороший вариант – немного подождать и обновить страницу. Делается это либо кликом по иконке возле адресной строки браузера, либо нажатием на комбинацию Ctrl + F5. Можно и без Ctrl, на ваше усмотрение.
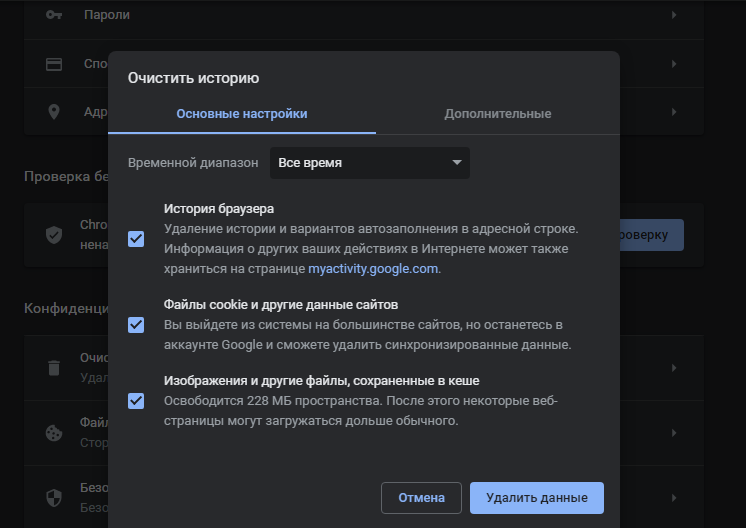
- Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не помогло, надо очистить кэш и cookies. Провести такую процедуру можно через настройки браузера. Для этого необходимо открыть историю просмотров, чтобы через нее перейти к инструменту очистки. Эту же утилиту часто можно найти в настройках, в разделе «Конфиденциальность и безопасность». В новом окне нужно отметить пункты с кэшем и cookies и нажать на кнопку для старта очистки.
- Ошибка 403 Forbidden возникает и тогда, когда пользователь пытается открыть страницу, для доступа к которой сначала надо осуществить вход в систему. Если у вас есть профиль, просто войдите в него и попробуйте вновь загрузить нужную страницу.
- Если вы заходите со смартфона, попробуйте отключить функцию экономии трафика в браузере. Она находится в настройках, в мобильном Google Chrome под нее отведен отдельный раздел.
- Последний шаг – подождать. Когда ни один способ не помогает, значит, неполадки возникли именно на сайте. Возможно, его владелец уже ищет способы решения проблемы и приступает к их исполнению, но это может занять какое-то время. Пользователям остается только дождаться, когда все работы будут завершены.
Еще одна допустимая причина появления ошибки сервера 403 – доступ к сайту запрещен для определенного региона или страны, в которой вы находитесь. Бывает и такое, что сайт доступен для использования только в одной стране. Если вы используете VPN, попробуйте отключить его и перезагрузите страницу. Вдруг получится все исправить.
Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не сработало, рекомендуется обратиться к владельцу сайта. Есть вероятность, что никто не знает о возникшей проблеме, и только ваше сообщение может изменить ситуацию.
Introduction
Apache is a popular open-source app for running web servers, owing to its reliability and stability. Despite its ease of use, it’s not uncommon to encounter a ‘403 Forbidden’ error after setting up a website using Apache.
In this tutorial, we will go over potential causes of the Apache ‘403 Forbidden’ error and different ways you can fix it.

Prerequisites
- A user account with root or sudo privileges
- Access to the command line terminal
- An installed version of Apache web server
Apache 403 Forbidden: Effects and Possible Causes
The Apache ‘403 Forbidden’ error appears when you try to load a web page with restricted access. Depending on your browser and the website in question, there are different versions of the 403 error message:
- Forbidden
- Error 403
- HTTP Error 403.14 – Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden
- HTTP 403
- Forbidden: You don’t have permission to access the site using this server
- Error 403 – Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
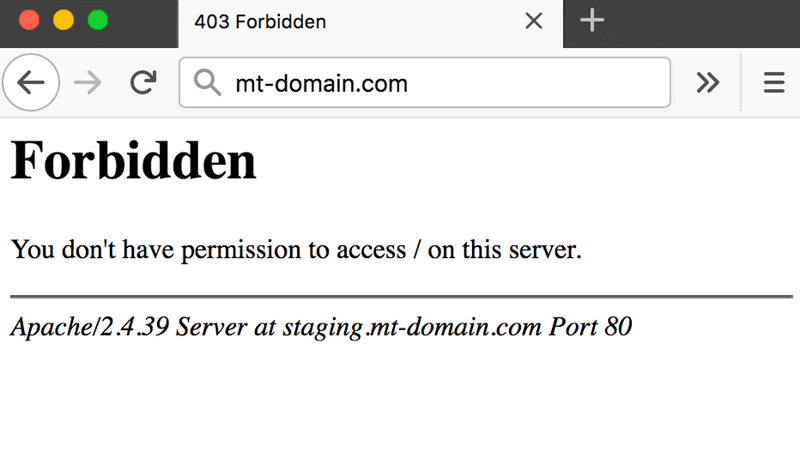
There are several potential reasons why the Apache 403 error occurs:
- The first option is a permission error in the webroot directory, where users don’t have access to website files.
- The second possible reason for a 403 error is missing or incorrect settings in the Apache configuration files.
- Finally, failing to set up a default directory index also triggers a 403 error message in Apache.
How to Fix ‘403 Forbidden’ in Apache
If you have come across an Apache ‘403 Forbidden’ message, there are several ways to fix it:
Method 1: Setting File Permissions and Ownership
If you suspect the cause of the 403 error to be incorrect file permissions, use:
sudo chmod -R 775 /path/to/webroot/directoryThe chmod command sets the execute permission for the webroot directory and read permission for the index.html file.
To change directory ownership, use:
sudo chown -R user:group /path/to/webroot/directoryWhere:
useris the user account with root privileges on your web server.groupiswww-dataorapache.
Restart the Apache web server for the changes to take effect.
If you are working with Ubuntu, use the following command to restart Apache:
sudo systemctl restart apache2If you are working with Centos, use:
sudo systemctl restart httpdMethod 2: Setting Apache Directives
It is possible that the proper require directive is not configured and restricts access to resources. To fix it:
1. Access Apache’s main configuration file. For Ubuntu, use:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.confFor Centos, use:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/httpd.conf2. Once you open the configuration file, scroll down to the following section:
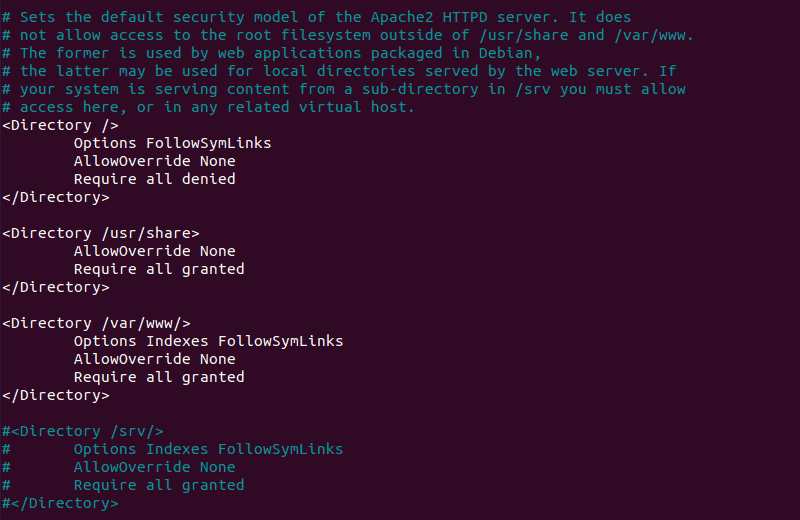
3. If the final line in the <Directory /var/www/> section contains Require all denied, change it to Require all granted.
4. Press Ctrl+X and then Y to save changes to the Apache configuration file.
5. Restart the Apache web server for the changes to take effect. For Ubuntu, use:
sudo systemctl restart apache2For Centos, use:
sudo systemctl restart httpdMethod 3: Adding a Default Directory Index
When a user visits a URL that requests a directory, the web server looks for a file in the given directory. If the file or any similar files are not found, and directory index listings are disabled, the web server displays the ‘403 Forbidden’ error message.
To fix the issue, add a default directory index.
1. Access Apache’s main configuration file by using:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf2. Scroll down to find out the default index file name:
DirectoryIndex index.html index.cgi index.pl index.php index.xhtml3. Make sure there is a file in the webroot folder with this name and upload it if it’s missing.
Conclusion
After following this tutorial, you should be able to determine the cause of an Apache ‘403 Forbidden’ error and fix any issues you may find.
If you want to find out more about 403 forbidden error, read our article 403 forbidden error — what is it and how to fix it.