The first code line, Option Explicit means (in simple terms) that all of your variables have to be explicitly declared by Dim statements. They can be any type, including object, integer, string, or even a variant.
This line: Dim envFrmwrkPath As Range is declaring the variable envFrmwrkPath of type Range. This means that you can only set it to a range.
This line: Set envFrmwrkPath = ActiveSheet.Range("D6").Value is attempting to set the Range type variable to a specific Value that is in cell D6. This could be a integer or a string for example (depends on what you have in that cell) but it’s not a range.
I’m assuming you want the value stored in a variable. Try something like this:
Dim MyVariableName As Integer
MyVariableName = ActiveSheet.Range("D6").Value
This assumes you have a number (like 5) in cell D6. Now your variable will have the value.
For simplicity sake of learning, you can remove or comment out the Option Explicit line and VBA will try to determine the type of variables at run time.
Try this to get through this part of your code
Dim envFrmwrkPath As String
Dim ApplicationName As String
Dim TestIterationName As String
Если вы используете Excel, вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой «Ошибка выполнения 424» с сообщением «Требуется объект».
Это ошибка в VBA (Visual Basic для приложений) и в основном проявляется, когда вы указываете на объект, который либо не существует, либо не находится за пределами текущей области.
Если вы видите ошибку, когда кто-то «обрабатывает» какой-то макрос/автоматизированную функцию в электронных таблицах Excel, вероятная проблема заключается в том, что вы называете объект «вне контекста». Это означает, что вы можете загрузить объект, но его содержимое может быть изменено или изменено. Есть также некоторые другие потенциальные проблемы, которые я объясню в этом руководстве…
причина
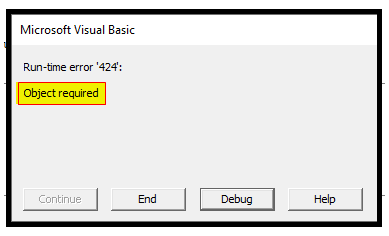
Ошибка, которую вы видите, будет иметь следующее сообщение:
Ошибка времени запуска «424»
Требуется объект
Чтобы объяснить, почему он показывает ошибку и что это значит, Microsoft выпустила свой пакет «Visual Basic» в конце 90-х.
Это обеспечивало основные возможности системы, позволяя разработчикам-любителям создавать простые приложения. VB имел большой успех.
Из-за этого Microsoft представила «VBA» (Visual Basic для приложений) в своем пакете программного обеспечения Office, а именно в Excel и Word. Это позволило типам разработчиков создавать автоматические функции в электронных таблицах Excel, указывать на «объекты» в самой электронной таблице и так далее.
Каждый раз, когда мы используем Visual Basic, мы вызываем ряд «объектов» в памяти. Эти объекты являются просто переменными, используемыми в ряде дополнительных функций, включая пользовательские функции и так далее. Проблема — и это относится к большинству языков программирования — в том, что если указать на объект, который не вызывается, приложение рухнет.
решение
Если вы хотите исправить проблему, вы должны сначала убедиться, что данные есть в системе, и тогда вы сможете правильно обращаться к ним. Этот урок объяснит, как:
1. Убедитесь, что переменные определены правильно
Основная проблема заключается в том, что вы вызываете метод для несуществующей переменной (объекта). Наиболее распространенная причина этого заключается в том, что вы просто неправильно вводите имя переменной и поэтому не объявляете ее в своем приложении VBA. Возьмем следующий пример:
Подтест ()
Application33.WorksheetFunction.Sum (диапазон (“A1: A100”))
Последняя подписка
Вышеприведенное вызовет ошибку, потому что вы пытаетесь вызвать метод WorksheetFunction для «Application33», указанного в объекте.
К сожалению, объект Application33 не существует в памяти, что не позволяет вашему приложению загрузить его. Чтобы исправить это, вам нужно просмотреть исходный код (почти всегда будут указаны неправильные ссылки) и исправить все имена объектов с ошибками.
2. Если вы используете Excel, убедитесь, что есть диапазоны/селекторы
Одна из наиболее распространенных причин ошибки заключается в том, что вы пытаетесь указать несуществующий объект или значение. Это типичная проблема при использовании одного из объектов VLookup или ActiveX. Если вы столкнулись с этой ошибкой, убедитесь, что код указывает только на существующие объекты:
Частный дополнительный тест ()
Это вызовет ошибку
Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(TeamName, Range (“TeamNameLookup”), 3, False).
Стоимость должна быть
Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(TeamName, Sheets (“YourSheetName”). Диапазон (“TeamNameLookup”), 3, False)
Последняя подписка
Вышеупомянутое означает, что вы пытаетесь вызвать разные рабочие листы, и их соответствующий «диапазон»/«значение» работает без поиска или объявления рабочих листов. Чтобы исправить это, вам нужно убедиться, что вы вызываете «диапазон» или «значение» для соответствующих объектов.
3. Убедитесь, что у вас есть правильные определения
Наконец, одна из наиболее распространенных причин ошибок заключается в том, что вы неправильно определяете свои переменные.
От неправильного определения переменных как неверных интерпретаций объектов до вызова «Option Explicit» вы можете пытаться указать переменные/объекты, которые не определены только потому, что они определены неправильно.
Например…
Вариант очевиден
Персональный дополнительный тест ()
Здесь вам нужно объявить переменные, прежде чем пытаться указать/заполнить их
Например…
Затемните your_path как строку
Установите your_path = “x/y/z”
Последняя подписка
В приведенном выше примере, если переменная «ваш_путь» не объявлена до ее установки, вы получите ошибку 424 (поскольку объект «ваш_путь» не существует). Отсюда вы также должны убедиться, что вы можете вызывать соответствующие объекты (если вы указываете значение рабочего листа, вы должны убедиться, что рабочий лист существует и может быть загружен).
Ясно, что есть много других случаев этой ошибки. Поскольку каждый код отличается, я не могу пройтись по каждому потенциалу. Надеюсь, вы видите, что ошибка вызвана указанием на неправильную переменную в вашей системе.
Home > VBA > VBA Object Required Error (Error 424)
When VBA is not able to recognize the object for which you are referring to the property or a method it shows you the Object Required error. In simple words, if you refer to an object, but the name of that object is not correct (that object is not in the VBA’s object hierarchy) it shows error 424, like the following.

In the above code, as you can see, I have misspelled the active cell object, and when VBA’s executes that line of code can’t that object because there’s no object with that name (as I have misspelled it).
Note: If you have used the Option Explicit statement in the module then with the same, you’ll get a different error (see image below).

Used “Set” Keyword for a Non-Object Variable
When you use a variable to assign an object to it, you need to use the keyword “Set”. In the following example, you have a myWKS for the worksheet and iVal for the value from cell A1.

As you can see, in the above code you have variables out of which one is declared as a worksheet object and the second as a string. But at the time of assigning the value, we have used the “Set” keyword to the variable “iVal” which is not declared as an object but as a string.
How to Fix Object Required (Error 424) in VBA
- Go to the Debug menu in your visual basic editor.
- Use the step to run the entire code step by step.
- The moment you reach the line where you have an error VBA will show you an error.
- Correct that line of code.

The other way could be going through the code line by line by reading it to make sure you are referring to the right objects and using the correct name of the variables and objects.
You can also use the GOTO statement to surpass an error or show a message to the users once an error occurred.
What is VBA
- VBA ERROR Handling
- VBA Automation Error (Error 440)
- VBA Error 400
- VBA Invalid Procedure Call Or Argument Error (Error 5)
- VBA Object Doesn’t Support this Property or Method Error (Error 438)
- VBA Out of Memory Error (Error 7)
- VBA Overflow Error (Error 6)
- VBA Runtime Error (Error 1004)
- VBA Subscript Out of Range Runtime Error (Error 9)
- VBA Type Mismatch Error (Error 13)
The Runtime error 424: Object required occurs when Excel is not able to recognize an object that you are referring to in a VBA code. The object can be a workbook, worksheet, range, variable, class, macro, etc. Some users have also reported that this error occurred when they tried to copy the values of the cells from one workbook to another.
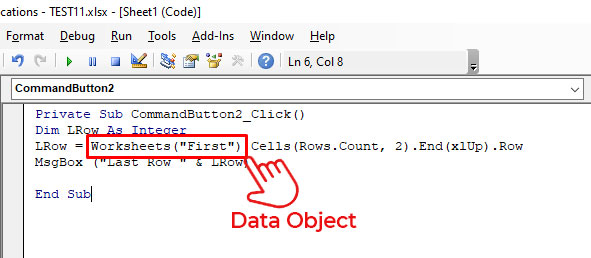
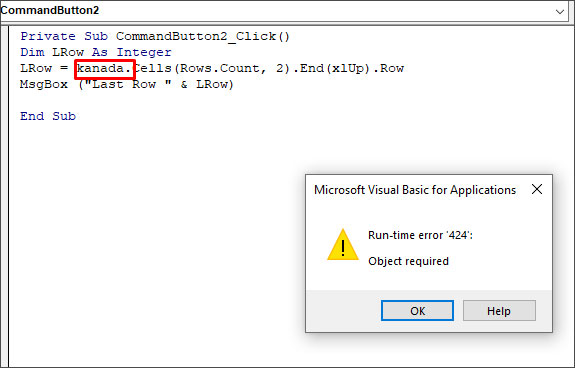
Let’s understand the error through a small scenario. Suppose, I want to check the last field row in a table in a spreadsheet named “First” using the VBA code. To do this, I have added a command button and double-clicked on it and entered the below code in the backend:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click()
Dim LRow As Integer
LRow = Worksheets(«First»).Cells(Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Row
MsgBox («Last Row » & LRow)
End Sub
In this code, Worksheets(«First») is a data object. If I mistakenly delete this data object and insert any random name (for example — kanada), then it will not be recognized by Excel. When I run this code, I will get the “Run-time error 424”.
Causes of Runtime Error 424 in Excel
The Runtime error 424: Object required can occur due to the following reasons:
- Incorrect name of the object you are trying to refer to in a code.
- You have provided an invalid qualifier to an object.
- You have not used the Set statement while assigning an object reference.
- The object is corrupted.
- Missing objects in a workbook.
- Objects you are trying to call in a code are mistakenly deleted or unavailable.
- You have used an incorrect syntax for object declaration.
- You are trying to perform an invalid action on an object in a code.
- Workbook is corrupted.
Solutions to Fix Runtime Error 424: Object Required in Excel
The VBA error ‘object required’ may occur due to different reasons. Based on the reason, you can follow the solutions mentioned below to fix the error.
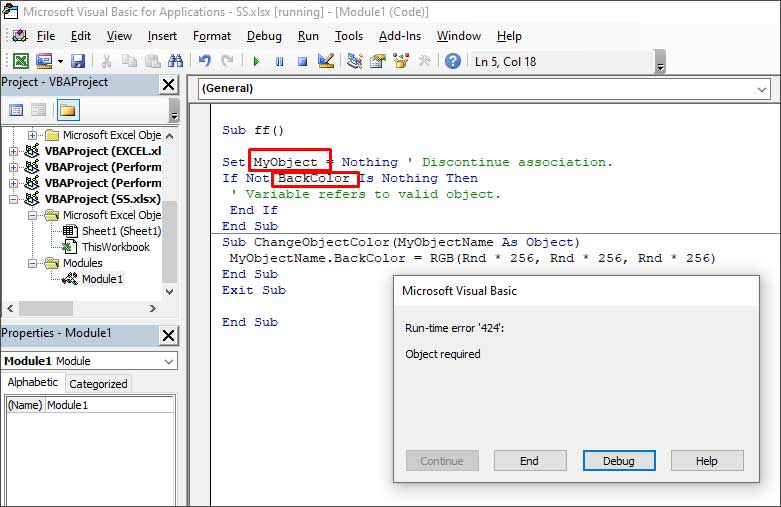
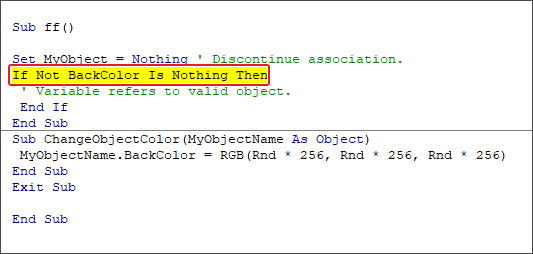
1. Check the Name of the Object
The Runtime error 424 can occur when you run the VBA code using an incorrect name of the object. For example, the object name is ‘MyObject’ but you’re using “Backcolor”.
When you click the Debug button, the line with the error will highlight.
To fix the issue, you need to provide the correct name of the object.
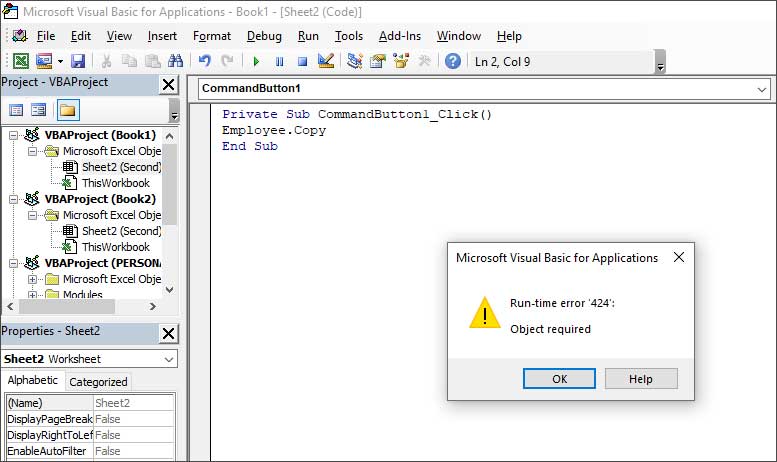
2. Check if the Object is Missing
The Runtime error 424 can occur if the object you are referring to as a method is not available or you are using the wrong object in a code. In the below example, you can see that the error occurs when an object named “Employee” is not available in the Project list.
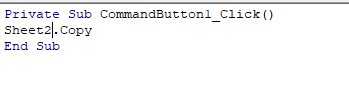
You can check and mention the object which is available. For instance, Sheet2 in the below code.
3. Check All References are Declared in the Code
You can get the Runtime error 424 if all the references are not declared. So, make sure you have declared all the references in the code. To verify this, you can use the debug mode by pressing F5 or clicking on the Debug option.
4. Check the Macro Security Settings
Sometimes, the error can occur if macros are disabled in the Macro Security settings. You can check and change the settings by following these steps:
- On the Developer tab, in the Code section, click Macro Security.
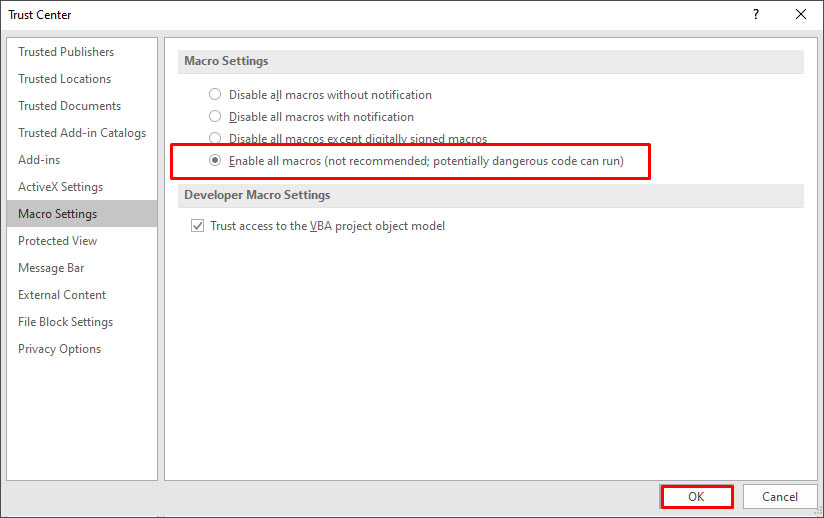
- In the Trust Center window, select Enable all macros.
- Click OK.
-
Repair your Workbook
Sometimes, the ‘Object required’ error can occur if your Excel file is damaged or corrupted. In such a case, you can try repairing the file using Microsoft’s in-built utility — Open and Repair. To use this utility, follow these steps:
- In Excel, go to File > Open > Browse.
- In the Open dialog box, click on the corrupted Excel file.
- Click the arrow next to the Open button and select Open and Repair from the dropdown.
- Select Repair to recover as much data from the file as possible.
If the Open and Repair utility fails or stops working, then you can try a professional Excel repair tool, such as Stellar Repair for Excel. It is an advanced tool that can repair severely corrupted Excel files (.xls, .xlsx, .xltm, .xltx, and .xlsm). It helps recover all the file components, including images, charts, tables, pivot tables, cell comments, chart sheets, formulas, etc., without impacting the original structure.
Conclusion
The Runtime error 424 usually occurs when there is an issue with the objects in your VBA code. In this article, we have covered some effective methods to resolve the “object required” error in Excel. If the error occurs due to corruption in Excel file, then you can repair the corrupt file using Stellar Repair for Excel. It is a reliable tool that can repair severely corrupted Excel file without changing its actual formatting. You can download the free trial version of the software to evaluate its functionality.
Permalink
Cannot retrieve contributors at this time
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Object required (Error 424) |
vblr6.chm1000424 |
vblr6.chm1000424 |
office |
282292d7-d147-b71e-4d1e-149af7da8f7e |
06/08/2017 |
medium |
References to properties and methods often require an explicit object qualifier. This error has the following causes and solutions:
-
You referred to an object property or method, but didn’t provide a valid object qualifier. Specify an object qualifier if you didn’t provide one. For example, although you can omit an object qualifier when referencing a form property from within the form’s own module, you must explicitly specify the qualifier when referencing the property from a standard module.
-
You supplied an object qualifier, but it isn’t recognized as an object. Check the spelling of the object qualifier and make sure the object is visible in the part of the program in which you are referencing it. In the case of Collection objects, check any occurrences of the Add method to be sure the syntax and spelling of all the elements are correct.
-
You supplied a valid object qualifier, but some other portion of the call contained an error. An incorrect path as an argument to a host application’s File Open command could cause the error. Check arguments.
-
You didn’t use the Set statement in assigning an object reference. If you assign the return value of a CreateObject call to a Variant variable, an error doesn’t necessarily occur if the Set statement is omitted. In the following code example, an implicit instance of Microsoft Excel is created, and its default property (the string «Microsoft Excel») is returned and assigned to the Variant
RetVal. A subsequent attempt to useRetValas an object reference causes this error:Dim RetVal ' Implicitly a Variant. ' Default property is assigned to Type 8 Variant RetVal. RetVal = CreateObject("Excel.Application") RetVal.Visible = True ' Error occurs here.
Use the Set statement when assigning an object reference.
-
In rare cases, this error occurs when you have a valid object but are attempting to perform an invalid action on the object. For example, you may receive this error if you try to assign a value to a read-only property. Check the object’s documentation and make sure the action you are trying to perform is valid.
For additional information, select the item in question and press F1 (in Windows) or HELP (on the Macintosh).
[!includeSupport and feedback]
|
FeelingThis Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
#1 23.09.2016 23:24:49 Доброго времени суток. Столкнулся с такой проблемой, при выполнении выкидывает на выделенной строке с Run-Time Error «424»: Object Required:
В чем может быть проблема? Грешу на третью строку, может неправильно задал объект frmtRange(переменные BiggerColumn и LR в порядке). Изменено: FeelingThis — 23.09.2016 23:30:10 |
||
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14849 |
А что Вы хотите от 4-й строки? Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14849 |
Format — служебное слово VBA. В разных случаях это может быть функцией/свойством, и использование его в качестве названия для своей функции и есть ошибка Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
|
FeelingThis Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
Чтобы в frmtRange записался диапазон данных Cells(1, BiggerColumn), Cells(LR, BiggerColumn + 1) Изменено: FeelingThis — 23.09.2016 23:30:58 |
|
Jungl Пользователь Сообщений: 830 |
#5 23.09.2016 23:31:23 FeelingThis,
|
||
|
vikttur Пользователь Сообщений: 47199 |
FeelingThis, кнопка форматирования кода другая — <…> Sanja, возможно, строка съехала |
|
FeelingThis Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
Спасибо за замечание, название функции поменял, но проблема не изчезла |
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14849 |
Вы присвойте результат работы Вашей функции чему нибудь, как пишет Jungl, Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
|
FeelingThis Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
Jungl
, |
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14849 |
#10 23.09.2016 23:37:47
в таком случае — от 5-й Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
||
|
Ігор Гончаренко Пользователь Сообщений: 13862 |
#11 23.09.2016 23:40:26
проблемы закончатся, когда Вы перестанете программировать Программисты — это люди, решающие проблемы, о существовании которых Вы не подозревали, методами, которых Вы не понимаете! |
||
|
FeelingThis Пользователь Сообщений: 5 |
#12 23.09.2016 23:42:15
требовалось передать диапазон в функцию |
||
|
Jungl Пользователь Сообщений: 830 |
#13 23.09.2016 23:55:42 FeelingThis, смотря что вы хотите получить от функции, это вам виднее.
|
||
|
ZVI Пользователь Сообщений: 4338 |
#14 24.09.2016 02:44:56 Поясню, в чём проблема.
Выдаст такое: Range Variant() Изменено: ZVI — 24.09.2016 02:47:17 |
||
What is Object Required Error?
VBA Object Required is a run time error which occurs
when the user does not define a valid object qualifier, or the assigned object
doesn’t exist in the specified worksheet. It is also referred as to ERROR 424. In
short, it means that the given object data type reference is invalid and needs
to be accurate.
In VBA, an explicit object qualifier is often required to
define different methods and properties. But if anything goes wrong with the
specified object reference, VBA throws an error. It becomes tough for the
beginners to debug the Object Required Errors because they cannot find the root
cause for the error.
Below are some points explaining the real-time causes for
this error:
- Object doesn’t exist — Variable and data
types are an integral part of VBA programming language. Thus, Object is also
one of the commonly used data types. If the user has declared an Object data
type and the specified object doesn’t exist in your Excel sheet, VBA will
through an Object Required error. - Invalid
Action— One of the major reasons this error occurs is when the user is
performing an invalid action for the specified object. Even if you declare a
valid object, VBA would be compelled to throw ‘Object Required’ error if you
assign an unauthorized action. Thus, forcing the user to recheck the object’s
documentation and then perform the action.
- Invalid Object Qualifier— If the user
tries to assess an object’s property or method but has not defined a valid
object qualifier. - Misspelled Qualifier— Many times, this
occurs if the user has declared an object qualifier, but the VBA compiler does
not recognize it. It happens if the specified object qualifier is misspelled or
referred to an invalid object or that object is not visible in the program.
- Error in Arguments — The specified object
qualifier has arguments and it contains some an error within its arguments. - Set Statement— This error occurs if the
user has defined the non-object variable and later tries to assign a value to
that variable using the Set statement. The vice-versa for this also throws an
error, i.e., if the user assigns a value to the object reference directly without
using the Set key.
How to handle the Object Required Error
In the coding world, even experienced developers commit
mistakes. So, it is advisable to take preventive measures to check and prefix
those errors rather than finding and latterly fixing as “Prevention is always
better than cure”. A strong coding not only includes the right output but also
triggers various segments which check and manage the code’s flow if any error
occurs. In the above part, we have
briefly discussed the causes for Object Required Error, but there are numerous
ways to handle any error. Below are some techniques through which we prevent
the Object Required error:
- Most of the time, the Object Required error
occurs because of misspelled object reference. To check all spell mistakes with
variables, we can declare the Option Explicit statement at the top of the
module. So, if there are any mistakes, it will pop up a message displaying and
highlighting the variable. - Always check twice if the referred object exists
or not. - Make sure that you have declared the correct
object quantifier. The standard way is to explicitly declare the qualifier
while referencing the property from a module. - With Collection objects, make sure that you have
used the occurrences of the Add method so as the syntax and spelling of all the
variables are valid. - Also, check the documentation for the specified
object to ensure that the action involved with that object is valid.
Example 1:
Let us obtain a brief understanding by practically using a
code where the Object Required error might occur, and it is when we have used
the set keyword to assign a value for the non-object variable. Follow the below
steps:
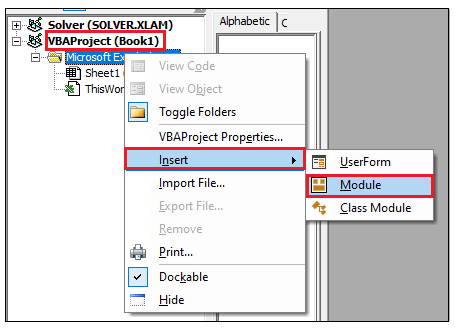
Step 1: Open the VBA developer tab either by using
the shortcut keywords Alt +F11 or click on developer window -> visual basic
editor.
Step 2: Visual Basic Editor will open. The next step
is to create a module. Right-clicking on the VBA Project-> Click on
Insert-> Click on Module.
Step 3: In the VBA Module window, Introduce the
subcategory following with your macro name.
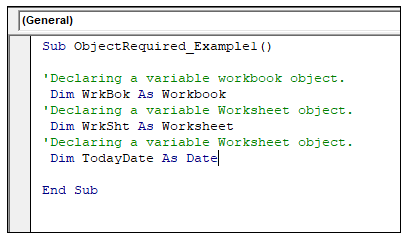
Step 4: Declare three variables one with WorkBook object
data type, another with worksheet object data type, and the last ‘TodayDate’
with the date data type.
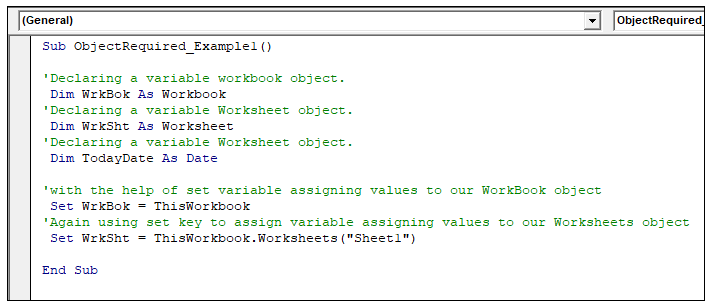
Step 5: Next, we will assign values to our object
data types i.e., WorkSheet (WrkSht) and WorkBook (WrkBok), with the help of a set
keyword.
Step 6: Although ‘TodayDate’ is not an object data
type still, we have used the set key to assign the value of the cell A1 value
in this workbook (WrkBok) and the worksheet “Sheet1” (WrkSht).
Step 7: At last, Display the value of the data variable
with the help of a MsgBox.
Code:
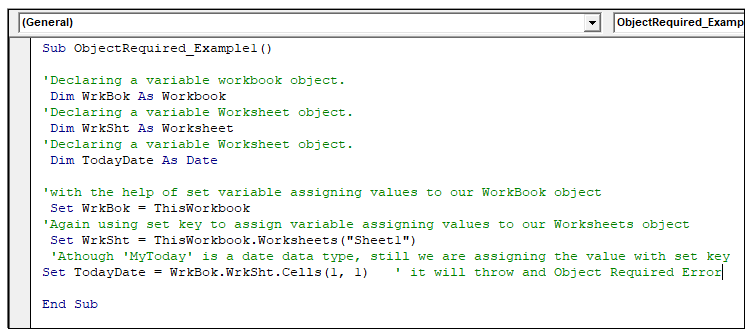
Sub ObjectRequired_Example1()
‘Declaring a variable workbook object.
Dim WrkBok As Workbook
‘Declaring a variable Worksheet object.
Dim WrkSht As Worksheet
‘Declaring a variable Worksheet object.
Dim TodayDate As Date
‘with the help of set variable assigning values to our WorkBook object
Set WrkBok = ThisWorkbook
‘Again, using set key to assign variable assigning values to our Worksheets object
Set WrkSht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
‘Although ‘MyToday’ is a date data type, still we are assigning the value with set key
Set TodayDate = WrkBok. WrkSht.Cells(1, 1) ‘ it will throw and Object Required Error
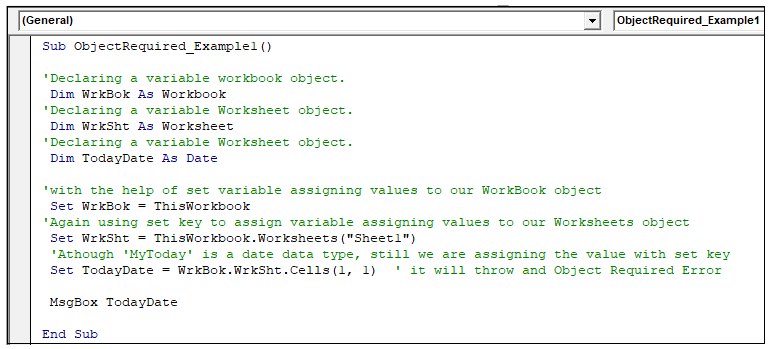
‘displaying the value for the variable TodayDate
MsgBox TodayDate
End Sub
Output
Step
8: Execute the above code either by pressing the F5 shortcut key or by
clicking on the Run button.
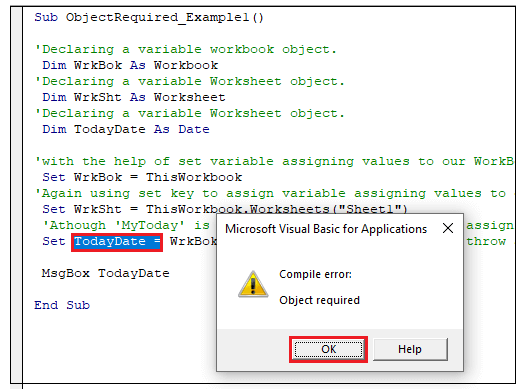
Step
9: You will notice that the message dialog box has pop up displaying the
“Object Required” compile error and highlighting the ‘TodayDate’ variable.
Explanation:
The above error occurred because we have used the set
keyword to assign a value to the variable which was not of “Object” data type.
So, the moment the VBA compiler read the Set keyword, it searched for its
object reference. The date data type is not of Object, so it threw the error
immediately.
Example
2:
Let’s work with a second example where the Object Required error
might occur, and it is when we have typed the wrong spelling for a worksheet
object. Follow the below steps:
Step 1: On the VB Editor, create a module and
introduce your sub-block following with your macro name.
Step 2: With the help of the Sum worksheet function,
we will calculate the total for the range of cells in between A1 to A10.
Step 3: And will store the return sum value to cell
address A11.
Code:
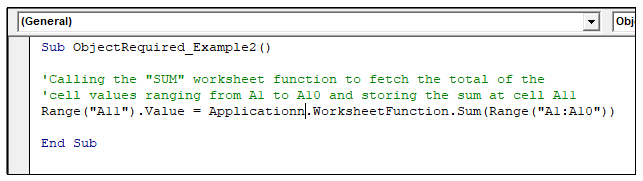
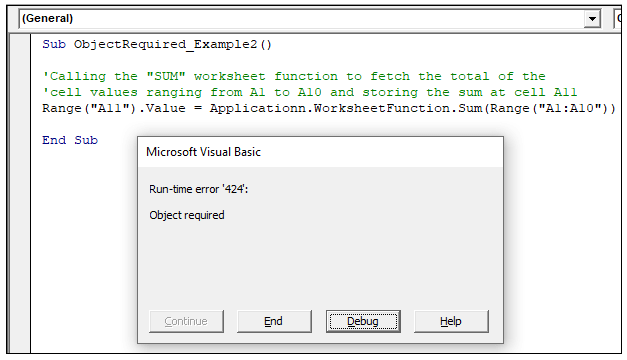
Sub ObjectRequired_Example2()
‘Calling the “SUM” worksheet function to fetch the total of the
‘cell values ranging from A1 to A10 and storing the sum at cell A11
Range("A11").Value = Applicationn.WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("A1:A10"))
End Sub
Output
Step
8: Execute the above code either by pressing the F5 shortcut key or by
clicking on the Run button.
Step 9: You will notice that the message dialog box
has pop up displaying the “Object Required” compile error.
Explanation
If you look meticulously, you will notice that in the above
code, we have misspelled the Application object as “Applicationn”. Thus, the
compiler could not recognize this word and will through the error.
Debug
Step 10: Either search for the mistake manually, or
else the easiest method to declare the ‘Option Explicit’ keyword at the top as
silly and typing mistakes are very common in coding.
Code:
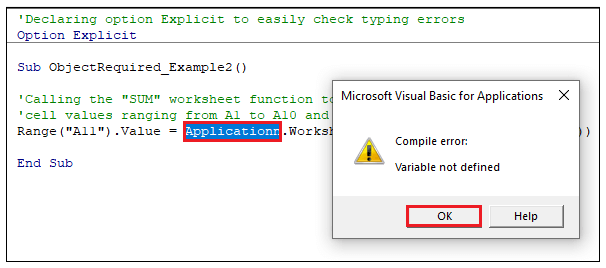
'Declaring option Explicit to check typing error quickly.
Option Explicit
Sub ObjectRequired_Example2()
'Calling the "SUM" worksheet function to fetch the total of the
'cell values ranging from A1 to A10 and storing the sum at cell A11
Range("A11").Value = Applicationn.WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("A1:A10"))
End Sub
Step 11: Run the code. VBA will throw an error
highlighting the misspelled object.
Step 12: Correct the spelling ad re-run the code
again. The sum will be calculated and displayed on your Excel sheet.