From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[34]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[35] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[36]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[37]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[38]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[38]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[39]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[40]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[41]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[42]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[43]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[44]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[45] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[46]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[47] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[48][49]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[50] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[51]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[52]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[53]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[54]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[55]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[55]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[55]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
Пользователи интернета и владельцы сайтов периодически сталкиваются с различными ошибками на веб-страницах. Одной из самых распространенных ошибок является error 500 (ошибка 500). Поговорим в нашей статье о том, что это за ошибка и как ее исправить.
Где и когда можно встретить ошибку 500
Вы можете увидеть ошибку на любом веб-ресурсе, браузере и устройстве. Она не связана с отсутствием интернет-соединения, устаревшей версией операционной системы или браузера. Кроме того, эта ошибка не указывает на то, что сайта не существует или он больше не работает.
Ошибка 500 говорит о том, что сервер не может обработать запрос к сайту, на странице которого вы находитесь. При этом браузер не может точно сообщить, что именно пошло не так.
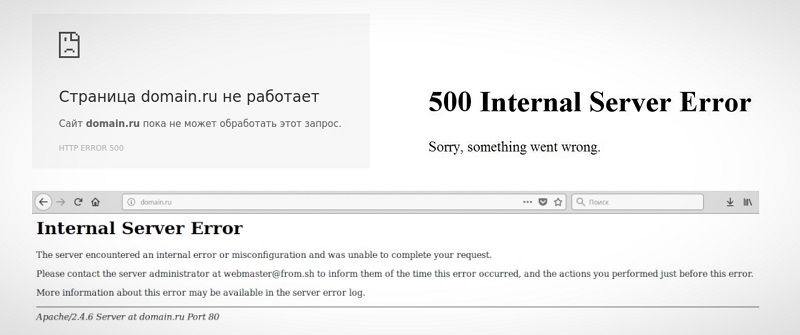
Отображаться ошибка может по-разному. Вот пример:
Если вы решили купить что-то в любимом интернет-магазине, но увидели на сайте ошибку 500, не стоит сильно огорчаться – она лишь сообщает о том, что вам нужно подождать, пока она будет исправлена.
Если ошибка появилась на вашем сайте, то нужно скорее ее исправлять. Далее я расскажу, как это можно сделать.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Причины возникновения ошибки
Итак, ошибка 500 возникает, когда серверу не удается обработать запрос к сайту. Из-за этого пользователи не могут попасть на сайт, а поисковые системы полноценно с ним работать. Очевидно, что ошибка нуждается в исправлении. В первую очередь необходимо найти проблему.
Основной причиной ошибки 500 может быть:
- Неверный синтаксис файла .htaccess. htaccess – это файл, в котором можно задавать настройки для работы с веб-сервером Apache и вносить изменения в работу сайта (управлять различными перенаправлениями, правами доступа к файлам, опциями PHP, задавать собственные страницы ошибок и т.д.).
Узнать больше о файле .htaccess можно в статье «Создание и настройка .htaccess». - Ошибки в скриптах сайта, то есть сценариях, созданных для автоматического выполнения задач или для расширения функционала сайта.
- Нехватка оперативной памяти при выполнении скрипта.
- Ошибки в коде CMS, системы управления содержимым сайта. В 80% случаев виноваты конфликтующие плагины.
Год хостинга в подарок при заказе лицензии 1С-Битрикс
Выбирайте надежную CMS с регулярными обновлениями системы и профессиональной поддержкой.
Заказать
Как получить больше данных о причине ошибки
Что означает ошибка 500, мы теперь знаем. Когда она перестала быть таким загадочным персонажем, не страшно копнуть глубже — научиться определять причину ошибки. В некоторых случаях это можно сделать самостоятельно, так что обращаться за помощью к профильному специалисту не понадобится.
Отображение ошибки бывает разным. Ее внешний облик зависит от того, чем она вызвана.
Самые частые причины ошибки 500 можно распознать по тексту ошибки или внешнему виду страницы.
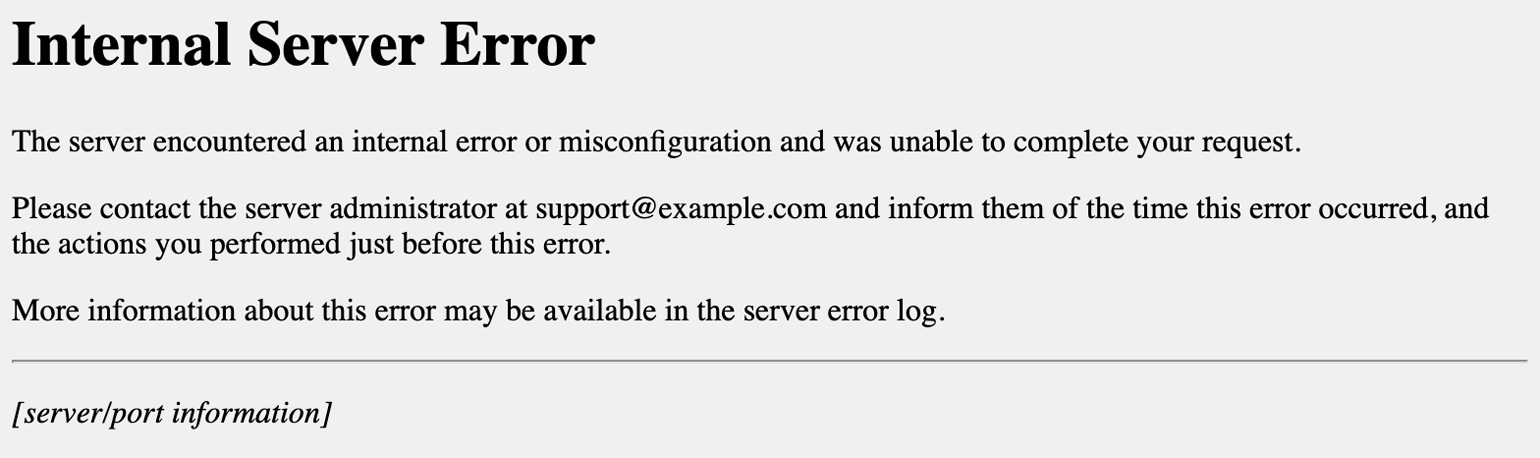
- Сообщение Internal Server Error говорит о том, что есть проблемы с файлом .htaccess (например, виновата некорректная настройка файла). Убедиться, что .htaccess является корнем проблемы, поможет следующий прием: переименуйте файл .htaccess, добавив единицу в конце названия. Это можно сделать с помощью FTP-клиента (например, FileZilla) или файлового менеджера на вашем хостинге (в Timeweb такой есть, с ним довольно удобно работать). После изменения проверьте доступность сайта. Если ошибка больше не наблюдается, вы нашли причину.
- Сообщение HTTP ERROR 500 или пустая страница говорит о проблемах со скриптами сайта. В случае с пустой страницей стоит учесть, что отсутствие содержимого сайта не всегда указывает на внутреннюю ошибку сервера 500.
Давайте узнаем, что скрывается за пустой страницей, обратившись к инструментам разработчика. Эта браузерная панель позволяет получить информацию об ошибках и другие данные (время загрузки страницы, html-элементы и т.д.).
Как открыть панель разработчика
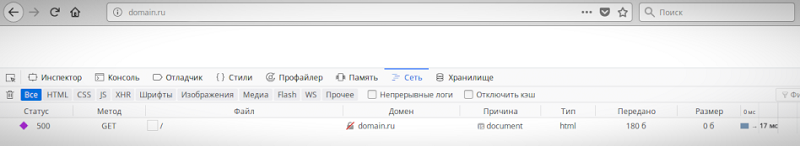
- Нажмите клавишу F12 (способ актуален для большинства браузеров на Windows). Используйте сочетание клавиш Cmd+Opt+J, если используете Google Chrome на macOS. Или примените комбинацию Cmd+Opt+C в случае Safari на macOS (но перед этим включите «Меню разработки» в разделе «Настройки» -> «Продвинутые»). Открыть инструменты разработчика также можно, если кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте веб-страницы и выбрать «Просмотреть код» в контекстном меню.
- Откройте вкладку «Сеть» (или «Network») и взгляните на число в поле «Статус». Код ответа об ошибке 500 — это соответствующая цифра.
Простыми словами: лог — это журнал, в который записывается информация об ошибках, запросах к серверу, подключениях к серверу, действиях с файлами и т.д.
Как вы видите, данных в логи записывается немало, поэтому они разделены по типам. За сведениями о нашей ошибке можно обратиться к логам ошибок (error_log). Обычно такие логи предоставляет служба поддержки хостинга, на котором размещен сайт. В Timeweb вы можете включить ведение логов и заказать необходимые данные в панели управления. Разобраться в полученных логах поможет статья «Чтение логов».
Как устранить ошибку
Теперь поговорим о том, как исправить ошибку 500. Вернемся к популярным причинам этой проблемы и рассмотрим наиболее эффективные способы решения.
Ошибки в файле .htaccess
У этого файла довольно строгий синтаксис, поэтому неверно написанные директивы (команды) могут привести к ошибке. Попробуйте поочередно удалить команды, добавленные последними, и проверьте работу сайта.
Также найти проблемную директиву можно с помощью логов ошибок (через те же инструменты разработчика в браузере). На ошибку в директиве обычно указывает фраза «Invalid command». Информацию о верном написании директивы или способе исправления ошибок в .htaccess вы можете найти в интернете. Не нужно искать, почему сервер выдает ошибку 500, просто введите в строку поиска название нужной команды или текст ошибки из логов.
Ошибки в скриптах сайта
Скрипт не запускается
Обычно это происходит, когда существует ошибка в скрипте или функция, которая не выполняется. Для успешного запуска скрипта функция должна быть верно прописана, поддерживаться сервером и выполняться от используемой версии PHP. Бывают ситуации, когда функция несовместима с определенными версиями PHP. Получить более подробную информацию о той или иной функции можно в интернете.
Не хватает оперативной памяти
Если в логах вы видите ошибку «Allowed memory size», для устранения ошибки 500 стоит оптимизировать работу скрипта. Вы можете воспользоваться специальными расширениями для анализа производительности скрипта или обратиться за помощью к специалисту, который поработает над его оптимизацией.
Если ваш сайт размещен на отдельном физическом или виртуальном сервере, можно попробовать увеличить максимальное использование оперативной памяти на процесс (memory_limit). На шаред хостинге этот параметр обычно не изменяется, но есть возможность купить хостинг помощнее.
Ошибки в CMS
Если код CMS содержит неверный синтаксис, это может вывести сайт из строя. В таком случае логи сообщат вам об ошибке 500 текстом «PHP Parse error: syntax error, unexpected». Так происходит, когда некорректно работает плагин (или тема, используемая в CMS, но реже) либо есть ошибки в коде. Ошибка может быть допущена случайно, произойти при обновлении плагина или версии CMS.
При чтении логов обратите внимание на путь, который следует за сообщением об ошибке, ведь он может указать на проблемную часть кода или плагин. Если проблема в плагине, для восстановления работы сайта переименуйте на время папку, в которой он расположен. Попробуйте обновить плагин или откатить его до прежней версии. Если ситуацию не удается исправить, от расширения стоит отказаться либо заменить его аналогом.
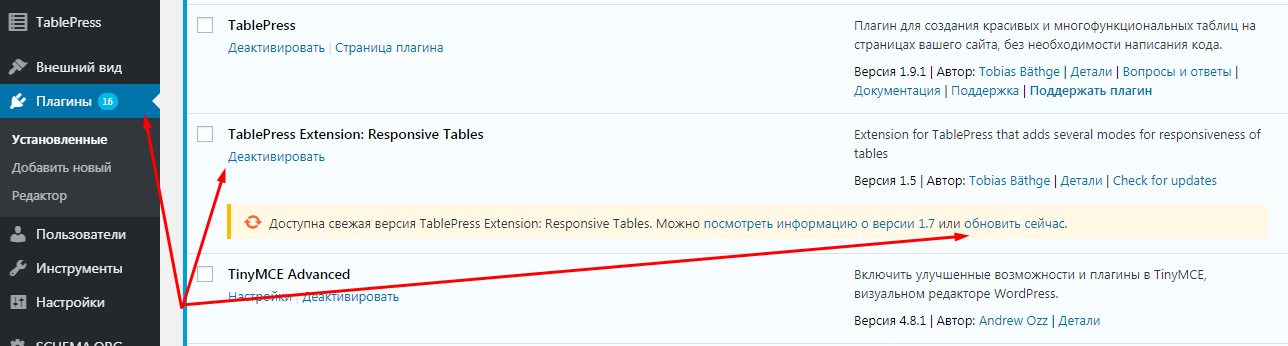
Информацию о других распространенных ошибках вы можете найти в статье «6 наиболее часто возникающих ошибок HTTP и способы их устранения».
Удачи!
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Error 500)
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[34]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[35] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[36]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[37]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[38]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[38]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[39]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[40]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[41]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[42]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[43]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[44]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[45] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[46]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[47] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[48][49]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[50] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[51]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[52]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[53]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[54]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[55]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[55]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[55]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
Что это? Ошибка 500 – это то, что препятствует открытию той или иной страницы сайта. Вместо ожидаемой, например, статьи, перед пользователем возникает фраза Internal Server Error 500. Она сообщает о проблемах ресурса с подключением к серверу.
Как исправить? Устранить ошибку можно как со стороны пользователя сайта, так и его владельца. В первом случае способы не гарантируют на 100 %, что Error 500 моментально пропадает, но попробовать стоит. Больше возможностей в этом плане у собственника ресурса.
В статье рассказывается:
- Что значит код ошибки 500
- Основные причины возникновения ошибки 500
- Текст и внешний вид ошибки
- Советы по исправлению ошибки 500 для пользователя
- Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 500 для владельца сайта
-
Пройди тест и узнай, какая сфера тебе подходит:
айти, дизайн или маркетинг.Бесплатно от Geekbrains
Значение 500 является кодом положения протокола НТТР. Из-за чего появляется ошибка 500? Происходит это потому, что случилась неисправность конфигурации сервера или пришёл сигнал о том, что компонент отказал. Когда возникает эта ошибка, программное обеспечение продолжает работать, но из-за серьёзных внутренних нарушений запросы обрабатываются некорректно.
Ошибка 500 значит, что пользовательский запрос неправильно переводится в действие. По этой причине возникают проблемы во время работы с сайтом. Нужно как можно скорее понять, из-за чего именно появилась ошибка, и устранить её.
Оповещение о том, что произошла ошибка 500, имеет текстовое описание. Наиболее частые варианты:
- Ошибка 500.
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера 500.
- Ошибка 500 Internal Server Error.
- Временная ошибка (500).
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера.
- 500 ошибка сервера.
- Внутренняя ошибка HTTP 500.
- Произошла непредвиденная ошибка.
- HTTP status 500 internal server error (перевод ― HTTP статус 500 внутренняя ошибка сервера).
Скачать
файл
Визуальный вид и текстовое сопровождение ошибки могут отличаться у каждого пользователя, потому что версии страницы могут быть разными.
Вероятность столкнуться с такой неприятностью есть при работе с любым веб-ресурсом, браузером или устройством. Главное, понимать, что эта ошибка, как и другие, которые начинаются на цифру 5, является промахом разработчиков или администратора сайта и вашей вины в этом нет.
Основные причины возникновения ошибки 500
Мы уже выяснили, что данная ошибка появляется, когда сервер не смог обработать запрос, совершённый пользователем, в результате чего человек не может открыть ресурс, а поисковые системы с ним взаимодействовать. Проблему обязательно нужно устранить, но для начала следует найти причину её появления, среди которых может быть:
- Неправильный синтаксис файла .htaccess – это файл, в котором можно менять настройки при работе с веб-сервером Apache и корректировать его функционирование (управлять различными перенаправлениями, правами доступа к данным, опциями PHP, задавать собственные страницы ошибок и прочее).
- Неполадки в сценариях сайта, которые отвечают за дополнительные возможности и визуальные эффекты.
- Недостаточно оперативной памяти, чтобы выполнить скрипт.
- Ошибки в коде CMS, системы управления наполнением ресурса. В большинстве случаев (80 %) причиной являются конфликтующие плагины.
Текст и внешний вид ошибки
Вы узнали, что означает ошибка 500, теперь пришло время перейти к более подробному разбору возможных причин её появления. Иногда разобраться с этим вопросом можно и без помощи специалиста.
Вид ошибки может отличаться. Это зависит от того, из-за чего она возникла. Наиболее распространенные причины можно узнать по тому, как отображается ошибка и какой текст её сопровождает.
Internal Server Error
Данный вид ошибки – сигнал о том, что есть проблемы с файлом .htaccess (к примеру, он был неправильно настроен). Чтобы понять, действительно ли дело в .htaccess, добавьте к его названию в конце цифру один. Сделать это поможет FTP-клиент (например, FileZilla) или файловый менеджер на вашем хостинге (в Timeweb есть подобный, и он очень простой в использовании). После этой манипуляции попробуйте заново открыть сайт. Если ошибка не выскочила, значит, вы нашли, из-за чего она появилась.
Топ-30 самых востребованных и высокооплачиваемых профессий 2023
Поможет разобраться в актуальной ситуации на рынке труда
Подборка 50+ ресурсов об IT-сфере
Только лучшие телеграм-каналы, каналы Youtube, подкасты, форумы и многое другое для того, чтобы узнавать новое про IT
ТОП 50+ сервисов и приложений от Geekbrains
Безопасные и надежные программы для работы в наши дни
Уже скачали 21123
HTTP ERROR 500 или пустая страница
Подобное означает, что причина в сценариях сайта. Но надо уточнить насчёт пустой страницы, что это не только признак внутренней ошибки 500 в сервере.
Предлагаем детальнее разобраться с пустой страницей, обращаясь к инструментам разработчика. Через браузерную панель пользователь получает уведомления об ошибках и другую информацию (время запуска сайта, html-элементы и прочее).
Каким образом открывается панель разработчика? Для начала нажмите F12 (это подходит для большинства браузеров на Windows). Если вы пользуетесь Google Chrome на macOS, то вам нужно использовать сочетание кнопок Cmd+Opt+J. В случае Safari на macOS нужна комбинация Cmd+Opt+C, но перед тем, как её нажать, включите «Меню разработки» в разделе «Настройки» -> «Продвинутые».
Есть ещё один способ открыть панель разработчика: кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте сайта и в открывшемся контекстном меню выбрать «Посмотреть код». После этого откройте вкладку «Сеть» (или Network) и посмотрите, какое значение указано в строке «Статус». Если дело в ошибке 500, то будет стоять эта цифра.
Советы по исправлению ошибки 500 для пользователя
Для начала расскажем, на что лучше не тратить своё время. Данная ошибка связана с сервером, поэтому делать что-то со стороны клиента (перезагружать роутер, менять браузер, переустанавливать программу) смысла нет.
- Заново откройте сайт
Ошибка 500 может появиться не только из-за серьёзных проблем с сервером, но и по причине временной перегрузки сайта. Перезагрузить страницу можно с помощью клавиш: на ПК — F5, ноутбуке — Fn + F5, на устройствах от Apple — Cmd + R.

Читайте также
- Очистите кэш и cookies браузера
Кэш и cookies нужны для того, чтобы при повторном открытии страницы не нужно было заново прогружать все данные, то есть они сохраняют информацию с первого посещения, за счёт чего в следующий раз сайт открывается быстрее.
Если на сервере была ошибка, то даже если её уже устранили, из-за кэша может открываться старая версия страницы с этой неполадкой.
Если ничего из этого вам не помогло, то остаётся ждать, когда владелец решит эту проблему, и вернуться на сайт позже.
- Обратитесь к владельцу сайта
Когда, например, в интернет-магазине часто всплывает ошибка 500, можно связаться с его владельцем. Информация с контактными данными, как правило, находится либо внизу страницы, либо в разделе «Контакты».
Чаще всего информация закрытая, но есть форма для обратной связи. Однако не факт, что вы получите ответ. Если нужные данные вы не нашли или ответа так и нет, можно воспользоваться такими вариантами: через Whois, хостинг-провайдера или регистратора домена, с помощью сторонних сервисов.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 500 для владельца сайта
Стоит учитывать большое количество факторов: движок, на котором работает ваш сайт, на каком он хостинге расположен, какие недавние изменения были внесены. Как бы там ни было, зачастую универсальные методы убирают ошибку 500. Желательно попробовать все варианты, которые подойдут под специфику вашего ресурса.
- Устраните неполадки в синтаксисе файла .htaccess
Выше мы уже рассказывали, как понять, в нём ошибка или нет. Попробуйте изменить имя документа, к примеру, на .htaccess_, и заново открыть сайт. Если ошибка не вылезла, значит, дело всё-таки в .htaccess. Проанализируйте синтаксис документа на наличие лишних символов или опечаток. Если вы сохраняли прошлую версию настроек, то надо попробовать её вернуть, чтобы проверить, будет ли ошибка.
В некоторых случаях может помочь закомментирование строки Options в .htaccess – вставить # в её начале. Если ничего не поменялось, проделайте то же самое с другими строками, а потом по очереди убирайте # и смотрите на результат.
После изменения файла .htaccess надо проверить, сохранилось ли оно. Иногда хостер может выставить на документ права, которые мешают его менять. В этой ситуации вы можете скачать файл .htaccess к себе на устройство, открыть и отредактировать его в любом текстовом документе и залить обратно, заменив старую версию.
Только до 8.06
Скачай подборку тестов, чтобы определить свои самые конкурентные скиллы
Список документов:



Чтобы получить файл, укажите e-mail:
Подтвердите, что вы не робот,
указав номер телефона:
Уже скачали 7503
- Обновите РНР
Версии РНР, которые уже устарели, не поддерживают обновления безопасности, хуже работают и из-за них может быть некорректная работа плагинов и сценариев.
Может, для того, чтобы ваш сайт работал без перебоев, вам надо просто обновить РНР.
- Настройте права для CGL-скриптов
Одним из методов устранения ошибки 500 на сайте является выставление прав для CGL-скриптов. Если такие сценарии у вас есть, то их папки и файлы должны иметь такое право доступа: 0755 (drwxr-xr-x), которое даёт возможность менять их только владельцу, а остальные могут их лишь открывать и активировать. Когда на скриптах стоит другое право доступа, это может привести к появлению ошибки 500.
- Проверьте файлы CGL-скриптов
У правильных сценариев окончание строк в формате Unix (n), а не Windows (rn). Для сохранения корректного варианта нужно загружать код (в большинстве хостингов) по FTP в режиме ASCII. Если вы не помните, какие ранее были настройки, заново добавьте сценарии и посмотрите, появится или нет ошибка 500. К тому же CGL-скрипты могут быть причиной неправильных HTTP‑заголовков ответа. В данном варианте вы сможете заметить ошибку в логах.
- Проверьте плагины
Причина может скрываться в плагинах, которые вы недавно установили.
Нередко встречается такое, что отдельные элементы сайта или плагины не могут работать совместно друг с другом. Данная проблема становится причиной не только того, что сайт выдаёт ошибку 500, но и возникновения других неполадок на сервере. Если модели были установлены или обновлены не так давно, то можно попробовать их отключить через панель администратора. Есть вероятность, что после этого могут всплыть другие неполадки, но если ошибка 500 исчезла, значит, дело было в конфликте плагинов или компонентов.
- Проверьте лог ошибок
Более точный анализ проводится с помощью логов. Если объяснять простым языком, то лог – это своеобразный журнал, в котором хранится информация об ошибках, направленных запросах, подключениях, действий с документами и так далее. Так как данных в логах очень много, они делятся на категории, чтобы было проще найти то, что нужно.
Если в последнее время вы как-то меняли сайт, то это могло стать причиной появления ошибки с кодом состояния 500. Зайдите в логи и проверьте, нет ли там информации о проблемах. Если ошибки высветились, то надо их изучить и отменить последние изменения.
Как правило, хостеры предоставляют информацию о том, где найти логи и как их открыть с панели управления. Данные об этом есть в разделе помощи FAQ (frequently asked questions — часто задаваемые вопросы) на сайте хостинга.
- Оптимизируйте сценарии
Если написанные сценарии долго грузятся или вообще не могут запуститься из-за нехватки ресурсов, проанализируйте их содержимое. Может, код надо оптимизировать, чтобы он стал легче и быстрее загружался. Нередко сценариям недостаточно ресурсов при работе с виртуальным хостингом. У них есть жёсткий лимит на память, чтобы каждый пользователь имел равные возможности во время пребывания на выбранном сайте.
Разделите скрипты на части и проверьте каждый на эффективность их деятельности. Если вы обнаружили в коде много ненужных вызовов либо необходимый объём памяти постоянно растёт, нужно обязательно проработать эти моменты.
- Увеличьте объём оперативной памяти сервера
Встречаются ситуации, когда даже после оптимизации сценариев они продолжают занимать много памяти. Чтобы решить эту проблему, придётся начать пользоваться более дорогим пакетом обслуживания, который предлагает хостинг.
Либо, если есть вариант увеличить объём памяти, прибегнуть к нему. К тому же вы не будете платить за те функции, которые не нужны вашему ресурсу.
Если вы испробовали все возможные варианты, но ничего не помогло, лучше обратиться за помощью к службе технической поддержки. Укажите время, когда вылезла ошибка, и подробно расскажите, что пытались предпринять для её устранения. Специалисты подробно изучат настройки сайта и, если потребуется, обратятся к управляющим сервера на стороне хостинг-провайдера.

Читайте также
Ошибка выполнения запроса 500 является обобщенным кодом состояния НТТР, который говорит о том, что на сервере произошла какая-то неполадка, но более точно описать проблему сервер не может. Так что первым делом нужно узнать, что послужило причиной возникновения ошибки, и только после этого заниматься её устранением.
Препятствием к открытию веб-страницы являются различные ошибки, возникающие на стороне сервера или клиента (в браузере). При исправном подключении к сайту браузер получает код 200. На веб-странице его не видно, так как пользователю для доступа к контенту не нужно прикладывать дополнительных усилий. В случае ошибки на загружаемой веб-странице появляется сообщение с кодом, по которому можно понять причину отсутствия соединения с сервером. Ошибка «500 Internal Server Error» — одна из наиболее серьезных, ведь пользователь редко может устранить ее самостоятельно, чаще всего требуется вмешательство владельца сайта.
Что означает ошибка 500
Ошибка 500 (Internal Server Error) — это внутренняя ошибка сервера, причиной которой стали настройки веб-хостинга или проблемы с кодом сайта. Сообщение с текстом «500 ошибка сервера» является общим для группы неисправностей. По коду не понятно, где именно и вследствии чего произошел сбой. Известно только, что это сервер не смог обработать запрос пользователя и отправить ему нужный контент. Чтобы восстановить работоспособность сайта, придется проверить несколько возможных источников проблемы. В статье расскажем том, что означает ошибка 500, почему она появляется и как ее устранить.
Причины возникновения ошибки 500
Ошибка 500 — свидетельство того, что запрос к сайту был отправлен браузером правильно, но сервер не может его обработать и выдать корректный ответ. Пользователи не могут попасть на сайт, а поисковые роботы теряют возможность обрабатывать веб-страницы — распознавать и оценивать их контент и определять их место в поисковой выдаче. Чтобы не потерять пользователей и результаты SEO-оптимизации, нужно быстро устранить ошибку. Для этого необходимо проверить сервер и расположенные на нем файлы сайта и программы на наличие одной из следующих проблем:
- синтаксические ошибки в файле .htaccess;
- ошибки в скриптах сайта;
- нехватка оперативной памяти при выполнении процесса;
- ошибки в плагинах, шаблонах и коде CMS;
- неправильно заданные права на каталоги и файлы.
Как устранить ошибку 500 на сайте
Когда причина возникновения «error 500» точно установлена, можно выбрать соответствующий метод ее решения. Разберем способы решения каждой причины ошибки.
Ошибки в файле .htaccess
Htaccess — файл, в котором содержатся настройки веб-сервера и правила работы сайта. В нем прописывают важные параметры, влияющие взаимодействие пользователя с веб-ресурсом:
- опции PHP;
- права доступа к файлам;
- перенаправление с HTTP на HTTPS;
- условия переадресации с одной веб-страницы на другую;
- вид веб-страниц с ошибками, которые они будут иметь в браузере пользователя и т. д.
Чтобы понять, является ли htaccess причиной недоступности сайта, необходимо выполнить несколько действий:
- Проверьте файл на синтаксические ошибки.
- Обратите внимание на формат файла: правильным будет один из двух — ASCII или ANSI. Из этого следует следующий пункт.
- Убедитесь, что файл был создан в правильном редакторе: Notepad, Notepad++ и Sublime Text. Если для этой цели вы использовали Microsoft Word, файл будет иметь ошибочное расширение Unicode.
- Временно создайте условия, при которых сервер не будет обращаться к файлу. Например, переименуйте его, перезагрузив при этом сайт. Если сообщение об ошибке пропадет, значит, нужно вернуть файлу имя htaccess и исправить его.
Ошибки в скриптах
Скрипты — сценарии, созданные для автоматического решения задач и расширения функционала сайта. Для поиска ошибки в скриптах владелец сайта может:
- Проверить, верно ли прописана функция.
- Узнать у хостинг-провайдера, поддерживает ли хостинг-компьютер нужную вам функцию.
- Проверить, правильно ли выбрана версия PHP.
Ошибки в плагинах и расширениях CMS
CMS — платформа, которую используют для создания сайта и управления его контентом. Ошибка может содержаться в коде самой CMS, а также в ее шаблонах и плагинах (дополнительных элементах из каталога). Другой причиной неисправности являются обновления плагинов, которые могут привести к несовместимости версий между всеми компонентами системы. Как решить проблемы:
- Открыть журнал операционной системы: если ошибка в CMS, он будет содержать ошибку 500 и сообщение «PHP Parse error: syntax error, unexpected». Журнал серверов Linux находится по адресу: /var/log/httpd/error_log.
- Найдите проблемную часть кода или плагина по пути, указанному в журнале системы.
- Отмените обновления плагина, вернув его к прежнему состоянию, или попробуйте заменить его другим, похожим по функционалу.
Не хватает оперативной памяти
При выполнении любых процессов на сервере задействуется его оперативная память. Если процесс трудоемкий, ему может понадобиться больше памяти, чем есть в его распоряжении. Когда ресурсы исчерпаны, возникает ошибка. Чтобы ее исправить, можно временно увеличить лимит памяти с помощью команды memory_limit. Расширяя лимит, помните об ограничении — нельзя указать число больше, чем есть на вашем личном сервере или хостинге.
Некорректные права на файлы и каталоги
Для файлов сайта устанавливаются правила, которые устанавливают действия, которые может с ним совершить та или иная группа пользователей. Устанавливаются права на read — чтение, write — запись и execute — выполнение. Каждое право имеет свое буквенное или числовое обозначение, например чтение — r или 4. Ошибки могут возникать, если разрешения для важных файлов установлены неправильно. Правильная конфигурация для прав — 755. Чтобы установить правильные настройки, можно воспользоваться командой: chmod 755 filename.
Заключение
Устранение ошибки 500 лежит на плечах владельца веб-ресурса. Без вашего оперативного вмешательства пользователи надолго потеряют доступ к сайту, а поисковые сети могут снизить его ранжирование.
Похожие статьи
-
У каждого устройства в интернете есть уникальный цифровой идентификатор — IP-адрес (IP-address). IP (ай пи) или Internet Protocol представляет собой некий свод правил, по которым работает наша глобальная сеть. Существует несколько видов айпи-адресов: внешние (белые) используются в публичной сети, внутренние (серые) действуют только в локальной; статические и динамические отличаются друг от друга способом назначения (первые — постоянные, вторые — изменяющиеся); а разделение на общие и выделенные характерно в основном для сферы хостинга. В статье мы объясним, что такое выделенный IP-адрес, почему он является отдельной услугой и как ее подключить.
-
С необходимостью регистрации доменного имени рано или поздно сталкивается любой веб-мастер. Есть немало способов это сделать — как бесплатно, так и на платной основе. Важно понимать, что вне зависимости от стоимости домена его нельзя «купить навсегда», а только временно арендовать и продлевать, если требуется. Все домены изначально принадлежат международной некоммерческой организации ICANN, которая управляет системой адресации в интернете. О том, как выбрать и как зарегистрировать домен самостоятельно, а также во сколько это может обойтись, читайте в нашей статье.
-
Структура и контент сайта продумываются перед началом его разработки. Каждая веб-страница находится в заранее определенном разделе и имеет свой URL-адрес. Ее содержимое тщательно продумывается и выстраивается вокруг поисковых запросов. Такая строгость нужна, чтобы веб-ресурс отвечал ожиданиям пользователей и хорошо ранжировался поисковыми системами. Изменения в архитектуре сайта происходят редко и всегда по веским причинам. Например, опубликованная информация может устареть, а функционал сайта расшириться. Некоторые веб-страницы становятся частью новых разделов, а те, которые утратили свою релевантность и перестали приносить трафик, — удаляются. На сайте могут остаться ссылки на старые страницы. Если пользователь воспользуется одной из них, сервер отправит ему ответ «Ошибка 404 — страница не найдена» или «Error 404 — Not Found». В данной статье поговорим о том, как исправить ошибку 404, каковы причины ее появления, и как найти все страницы с данным кодом ответа.
#статьи
- 29 мар 2023
-
0
Её просто найти, трудно исправить и невозможно забыть: кто эта таинственная мошенница, из-за которой компании теряли миллионы денег.
Иллюстрация: Оля Ежак для Skillbox Media
Любитель научной фантастики и технологического прогресса. Хорошо сочетает в себе заумного технаря и утончённого гуманитария. Пишет про IT и радуется этому.
Среди всех HTTP-ошибок пятисотая самая опасная — ведь никто до конца не понимает, что её вызвало. Само число 500 говорит о том, что проблема возникла на стороне сервера, но вот что именно произошло — непонятно.
У неё лаконичное описание: Internal Server Error, что означает «внутренняя ошибка сервера». Никаких подробностей и намёков на решение. Но давайте не будем унывать и постараемся разобраться, как она возникает, что означает и какими методами её можно попытаться исправить.
Ошибка 500 (Internal Server Error) — это когда сайт упал и пока его никто не смог поднять. Вообще, все ошибки, коды которых начинаются с пятёрки, указывают на вину разработчиков.
Когда возникает ошибка 500, сервер перестаёт обрабатывать запросы пользователей, продолжая при этом бодро работать и рапортовать о своих успехах. А вот пользователи в этот момент почему-то получают сообщение об ошибке. Это приводит к бесконечной попытке браузера загрузить страницу. В общем, дедовский метод с перезагрузкой тут не пройдёт.
Ошибка 500 — Internal Server Error, что в переводе означает «внутренняя ошибка сервера», а значит, решить её могут только администраторы и разработчики сайта. Но проблема в том, что она — уникальная. Сервер выдаёт её, когда остальные коды не подошли, и получается, что проблема действительно серьёзная. Решить такую проблему — всё равно что победить на городской олимпиаде по русскому языку «Русский медвежонок».
Сообщение о подобной ошибке может выглядеть так:
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
А в виде ответа на HTTP-запрос сообщение выглядит вот так:
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error Date: Tue, 14 Feb 2023 15:30:00 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.25 (Win32) OpenSSL/1.0.2j PHP/5.6.30 Content-Length: 462 Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>500 Internal Server Error</title> </head> <body> <h1>500 Internal Server Error</h1> <p>The server encountered an internal error or misconfiguration and was unable to complete your request.</p> <p>Please contact the server administrator to inform of the time the error occurred and of anything you might have done that may have caused the error.</p> <p>More information about this error may be available in the server error log.</p> </body> </html>
Здесь мы запрашиваем страницу по HTTP, а сервер возвращает примерно такое сообщение об ошибке: «Внутри сервера что-то не так, и он не может обработать запрос пользователя».
Само сообщение содержит информацию о том, что сайт не работает из-за внутренней ошибки на сервере. То есть проблема не в браузере, не на стороне пользователя, а именно на сервере: «The server encountered an internal error or misconfiguration and was unable to complete your request».
А ещё в описании есть небольшой совет пользователю, как исправить проблему (никак): «Please contact the server administrator to inform of the time the error occurred and of anything you might have done that may have caused the error». Мы не знаем ни одного человека, который бы таким советом воспользовался 🙂 Разве что вы сами — тот самый пресловутый администратор, да к тому же любитель рекурсии.
Ошибка 500 может ухудшить SEO и продвижение сайта в поисковике. Она приводит к тому, что поисковые роботы не смогут полностью проиндексировать сайт, потому что не получат доступ к некоторым страницам.
Если она возникает на регулярной основе, поисковые системы начнут понижать рейтинг вашего сайта, посчитав нестабильным и ненадёжным.
Но важнее всего вот что: когда пользователи сталкиваются с такой проблемой, они закрывают ваш сайт и уходят на страницы конкурентов. Растёт показатель отказов. А поисковые системы учитывают поведенческие факторы при ранжировании сайтов.
Итог очевиден — если вы заметили, что на вашем сайте часто возникает ошибка 500, стоит немедленно её исправить. Это поможет сохранить репутацию сайта и позиции в поисковых системах.
Ошибка 500 может возникнуть когда угодно, но чаще всего это происходит, когда на сайте проводятся технические работы — например, разработчики меняют конфигурацию сервера или он вовсе вышел из строя.
Причины возникновения чаще всего включают в себя следующее:
- Проблемы на сервере. Например, неправильный синтаксис, неправильная настройка сервера или проблемы с базой данных.
- Проблемы с файлами сайта. Это могут быть те же проблемы с синтаксисом, неправильное размещение файлов или неправильное использование функций.
- Проблемы с соединением. Например, неполадки в сети, медленное или нестабильное соединение, проблемы с DNS.
Если на сайте возникла ошибка 500, вы, как пользователь, это заметите не мгновенно — для этого вам придётся отправить на сайт какой-то запрос, например обновить страницу или заполнить какую-то форму (ведь чаще всего мы просматриваем уже закэшированные страницы). Тогда-то браузер попытается вступить в диалог с сервером и выдаст Internal Server Error.
Чтобы узнать больше о возникшей проблеме, для начала проверьте журналы ошибок на сервере. Для этого можно использовать SSH, FTP или панель управления хостингом.
В журналах, или логах, находятся записи о том, какие запросы были отправлены на сервер и как он на них ответил. Ещё там можно найти информацию о том, какие скрипты или приложения вызвали ошибку, а также о других деталях, которые способны помочь в определении проблемы.
Вот пример лога с ошибкой 500:
[Sun Jan 05 15:33:31.122031 2020] [core:error] [pid 3987] [client 192.168.1.5:58427] End of script output before headers: index.php
В этом примере лог сообщает, что при обработке запроса на получение страницы index.php произошла ошибка. Сервер не смог правильно обработать скрипт и вывести заголовки страницы, что привело к Internal Server Error. Для определения точной причины придётся провести дополнительный анализ.
Ещё одна распространённая причина — повреждения в файле .htaccess, где хранятся настройки сервера: управление доступом для пользователей, кэширование и редиректы. Повредить его можно, просто неправильно написав команду:
RewriteEngine on.
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php/$1 [L]
Проблема в первой строке — точка там лишняя. И эта мелочь вполне может вызвать ошибку 500. При этом обнаружить такую деталь будет очень непросто, потому что она практически незаметна.
Кроме логов можно использовать другие инструменты — например, инспектор браузера или специализированные программы для анализа логов. Ряд CMS вроде WordPress или Drupal могут также указать на причины проблемы благодаря встроенным инструментам. Дело в том, что у каждой CMS есть собственная система мониторинга таких проблем. Вот пример сообщения в WordPress:
Internal Server Error
The server encountered an internal error or misconfiguration and was unable to complete your request.
Please contact the server administrator, and inform them of the time the error occurred, and anything you might have done that may have caused the error.
More information about this error may be available in the server error log.
Как правило, CMS предоставляют очень ограниченную информацию о причинах, поэтому лучше всё-таки изучать логи.
Если вы пользователь, то исправить проблему, скорее всего, никак не получится. Но можно попробовать сделать следующее:
- Перезагрузить страницу. Иногда ошибка возникает из-за временной нагрузки на сервер, а перезагрузка страницы может решить проблему.
- Проверить соединение. Убедитесь, что ваше интернет-соединение работает стабильно.
Чтобы исправить ошибку на стороне сервера, нужно приложить больше усилий. Вероятно, придётся использовать средства отладки и тестирования кода. Ниже представлены несколько шагов, которые помогут вам найти и исправить ситуацию:
- Проверьте логи сервера. Это позволит определить, что вызывает ошибку и где это происходит.
- Проверьте базу данных. Убедитесь, что база данных работает корректно.
- Проверьте код на наличие ошибок. Проблема может возникнуть из-за опечаток, ошибок синтаксиса, неправильных путей к файлам и неправильных конфигураций.
- Измените настройки сервера. Попробуйте поменять разные конфигурации и посмотреть, к чему это приведёт.
- Проверьте файл .htaccess. Убедитесь, что в нём нет ошибок, таких как неправильная настройка редиректов, блокировка IP-адресов или неправильное форматирование.
- Проверьте сторонние плагины и расширения. Иногда проблема может возникнуть из-за их неправильной работы. Проверьте, что все они работают корректно.
- Проверьте файлы сервера. В них тоже могут быть ошибки или неправильные настройки.
- Попробуйте переустановить CMS или рабочее окружение. К этому имеет смысл прибегать, если все другие способы не сработали. Но это уж совсем радикальный совет — лучше обратитесь к кому-то более опытному, наверняка он поможет.
- Если же не помогло даже это, пора писать три письма и бросать программирование (конечно, чтобы открыть свою кофейню).
Борьба может затянуться надолго — ведь главная причина часто бывает непредсказуема, неочевидна и весьма коварна.
Важные факты об ошибке 500 (Internal Server Error), которые стоит запомнить:
- Ошибка 500 (Internal Server Error) — это сообщение о проблеме, которое может появиться при попытке получить доступ к веб-странице.
- Она может возникнуть по разным причинам — например, из-за проблем на стороне сервера, неправильных настроек сайта или ошибок в коде.
- Для того чтобы исправить проблему, нужно определить её причину. Обратитесь к логам сервера или к специалистам по веб-разработке.
- Она негативно влияет на SEO-продвижение сайта. Поэтому исправляйте её сразу же.
- Обновляйте ПО и проверяйте код на ошибки — это лучший способ держать сайт в хорошем техническом состоянии.

Научитесь: Профессия Веб-разработчик
Узнать больше
В статье мы расскажем, как исправить ошибку (код состояния) 500 со стороны пользователя и администратора сайта, а также подробно разберём, что такое ошибка запроса 500.
Что такое внутренняя ошибка сервера 500
Код ошибки 5хх говорит о том, что браузер отправил запрос корректно, но сервер не смог его обработать. Что значит ошибка 500? Это проблема сервера, причину которой он не может распознать.
Сообщение об ошибке сопровождается описанием. Самые популярные варианты:
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера 500,
- Ошибка 500 Internal Server Error,
- Временная ошибка (500),
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера,
- 500 ошибка сервера,
- Внутренняя ошибка HTTP 500,
- Произошла непредвиденная ошибка,
- Ошибка 500,
- HTTP status 500 internal server error (перевод ― HTTP статус 500 внутренняя ошибка сервера).
Дизайн и описание ошибки 500 может быть любым, так как каждый владелец сайта может создать свою версию страницы. Например, так выглядит страница с ошибкой на REG.RU:
Как ошибка 500 влияет на SEO-продвижение
Для продвижения сайта в поисковых системах используются поисковые роботы. Они сканируют страницы сайта, проверяя их доступность. Если страница работает корректно, роботы анализируют её содержимое. После этого формируются поисковые запросы, по которым можно найти ресурс в поиске.
Когда поисковый робот сканирует страницу с ошибкой 500, он не изменяет её статус в течение суток. В течение этого времени администратор может исправить ошибку. Если робот перейдёт на страницу и снова столкнётся с ошибкой, он исключит эту страницу из поисковой выдачи.
Проверить, осталась ли страница на прежних позициях, можно с помощью Google Search Console. Если робот исключил страницу из поисковой выдачи, её можно добавить снова.
Код ошибки 500: причины
Если сервер вернул ошибку 500, это могло случиться из-за настроек на web-хостинге или проблем с кодом сайта. Самые распространённые причины:
- ошибки в файле .htaccess,
- неподходящая версия PHP,
- некорректные права на файлы и каталоги,
- большое количество запущенных процессов,
- большие скрипты,
- несовместимые или устаревшие плагины.
Решить проблему с сервером можно только на стороне владельца веб-ресурса. Однако пользователь тоже может выполнить несколько действий, чтобы продолжить работу на сайте.
Что делать, если вы пользователь
Если на определённом ресурсе часто возникает ошибка 500, вы можете связаться с владельцем сайта по инструкции.
Перезагрузите страницу
Удаленный сервер возвращает ошибку не только из-за серьёзных проблем на сервере. Иногда 500 ошибка сервера может быть вызвана небольшими перегрузками сайта.
Чтобы устранить ошибку, перезагрузите страницу с помощью сочетания клавиш:
- на ПК — F5,
- на ноутбуке — Fn + F5,
- на устройствах от Apple — Cmd + R.
Обратите внимание! Если вы приобретаете товары в интернет-магазине и при оформлении заказа появляется 500 Internal Server Error (перевод — внутренняя ошибка сервера), при перезагрузке страницы может создаться несколько заказов. Поэтому сначала проверьте, оформился ли ваш предыдущий заказ. Если нет, попробуйте оформить заказ заново.
Очистите кэш и cookies браузера
Кэш и cookies сохраняют данные посещаемых сайтов и данные аутентификаций, чтобы в будущем загружать веб-ресурсы быстрее. Если на ресурсе уже был статус ошибки 500, при повторном входе на сайт может загружаться старая версия страницы с ошибкой из кэша, хотя на самом деле страница уже работает. Очистить кэш и куки браузера вам поможет инструкция.
Если ни одно из этих действий не решило проблему, значит, некорректно работает сам сервер сайта. Вернитесь на страницу позже, как только владелец решит проблему.
Что делать, если вы владелец сайта
В большинстве случаев устранить проблему может только владелец сайта. Как правило, ошибка связана с проблемами в коде. Реже проблемы могут быть на физическом сервере хостинг-провайдера.
Ниже рассмотрим самые популярные причины и способы решения.
Ошибки в файле .htaccess
Неверные правила в файле .htaccess — частая причина возникновения ошибки. Чтобы это проверить, найдите .htaccess в файлах сайта и переименуйте его (например, в test). Так директивы, прописанные в файле, не повлияют на работу сервера. Если сайт заработал, переименуйте файл обратно в .htaccess и найдите ошибку в директивах. Если вы самостоятельно вносили изменения в .htaccess, закомментируйте новые строки и проверьте доступность сайта.Также может помочь замена текущего файла .htaccess на стандартный в зависимости от CMS.
Найти директиву с ошибкой можно с помощью онлайн-тестировщика. Введите содержимое .htaccess и ссылку на сайт, начиная с https://. Затем нажмите Test:
Произошла непредвиденная ошибка
На экране появится отчёт. Если в .htaccess есть ошибки, они будут выделены красным цветом:
500 ошибка nginx
Активирована устаревшая версия PHP
Устаревшие версии PHP не получают обновления безопасности, работают медленнее и могут вызывать проблемы с плагинами и скриптами. Возможно, для работы вашего веб-ресурса нужна более новая версия PHP. Попробуйте сменить версию PHP на другую по инструкции.
Установлены некорректные права на файлы и каталоги сайта
В большинстве случаев корректными правами для каталогов являются «755», для файлов — «644». Проверьте, правильно ли они установлены, и при необходимости измените права на файлы и папки.
Запущено максимальное количество процессов
На тарифах виртуального хостинга REG.RU установлены ограничения на количество одновременно запущенных процессов. Например, на тарифах линейки «Эконом» установлено ограничение в 18 одновременно запущенных процессов, на тарифах «+Мощность» ― 48 процессов. Если лимит превышен, новый процесс не запускается и возникает системная ошибка 500.
Такое большое число одновременных процессов может складываться из CRON-заданий, частых подключений с помощью почтовых клиентов по протоколу IMAP, подключения по FTP или других процессов.
Чтобы проверить количество процессов, подключитесь по SSH. Выполните команду:
ps aux | grep [u]1234567 |wc -lВместо u1234567 укажите ваш логин хостинга: Как узнать логин хостинга.
Чтобы посмотреть, какие процессы запущены, введите команду:
Вместо u1234567 укажите логин услуги хостинга.
Командная строка отобразит запущенные процессы:
Код ошибки 500
Где:
- u1234567 — логин услуги хостинга,
- 40522 — PID процесса,
- S — приоритет процесса,
- /usr/libexec/sftp-server — название процесса.
Процесс можно завершить командой kill, например:
Вместо 40522 укажите PID процесса.
Чтобы решить проблему, вы также можете:
- увеличить интервал запуска заданий CRON,
- ограничить количество IMAP-соединений в настройках почтового клиента. Подробнее в статье Ограничение IMAP-соединений,
- проанализировать запущенные процессы самостоятельно или обратившись за помощью к разработчикам сайта.
Если вам не удалось самостоятельно устранить ошибку 500, обратитесь в техподдержку.
Скрипты работают слишком медленно
На каждом виртуальном хостинге есть ограничения на время выполнения скрипта. Если за установленное время скрипт не успевает выполниться, возникает ошибка сервера 500. Для решения проблемы обратитесь к разработчику сайта и оптимизируйте скрипты. Если оптимизировать нельзя, перейдите на более мощный вид сервера.
У пользователей VPS есть возможность увеличить максимальное использование оперативной памяти на процесс, но лучше делать скрипты меньшего размера.
Ошибка 500 на сайте, созданном на WordPress
WordPress предлагает много плагинов для создания хорошего сайта. Они значительно расширяют возможности CMS. Однако они же могут нарушать работу сайта и вызывать ошибку 500. Вызвать ошибку могут как недавно установленные плагины, так и старые.
Для начала проверьте, нужно ли обновить плагины. Часто устаревшие плагины перестают работать и вызывают проблемы работы сайта. Если все плагины обновлены, но 500 Internal Server Error остаётся, отключите все плагины, чтобы убедиться, что именно они мешают работе сайта. Как только станет понятно, что виноват один из плагинов, отключайте их по очереди, пока не найдёте тот, который нарушает работу сервера.
Как отключить плагин в WordPress
- 1.
-
2.
Перейдите во вкладку «Плагины» ― «Установленные».
-
3.
Нажмите Деактивировать у плагина, который, как вам кажется, повлиял на работу сайта:
Если все ваши действия не решили проблему или вы не уверены в своих технических знаниях, обратитесь к службе технической поддержки. Сообщите время обнаружения проблемы и опишите все действия, которые вы предприняли перед обращением. Специалисты сделают детальную проверку настроек вашего сайта и при необходимости обратятся к администраторам сервера на стороне хостинг-провайдера.
Содержание:
- Что означает код ошибки 500 и почему она возникает?
- Где можно встретить ошибку 500?
- Все причины возникновения ошибки
-
Что делать при появлении ошибки?
- Подождать
- Сообщить администратору
-
Что делать администратору при появлении ошибки?
- Проверить файл htaccess
- Проверить лог ошибок
- Проверить содержимое CGI-скриптов
- Проверить плагины и компоненты
- Увеличить объем оперативной памяти сервера
Что означает код ошибки 500 и почему она возникает?
Коды состояния HTTP сообщают браузеру интернет-пользователя (клиенту), успешно ли выполнен запрос (получение доступа к сайту). К примеру, если браузер получает код состояния 200, то все прошло успешно. Это сообщение не видно пользователю — вместо него появляется запрошенный контент.
С кодами состояния 400 и 500 дело обстоит иначе. Первый означает, что ошибка связана с клиентом, а второй — с сервером.
Internal Server Error 500 — общий код состояния для ошибок со стороны сервера. По этой причине невозможно сразу определить, где именно возникла проблема: известно лишь то, что сервер сообщил о ней. Когда это происходит, сайт отображает посетителям страницу с сообщением об ошибке.
Где можно встретить ошибку 500?
Поскольку эта ошибка является частью спецификации HTTP для сайтов, она может появляться в любом браузере и на любом компьютере, в том числе на мобильных устройствах.
Ошибка 500 может отображаться различными способами, но в большинстве случаев сообщение включает код состояния 500, фразу «внутренняя ошибка сервера» или и то, и другое. Вот несколько распространенных примеров:
- 500 Internal Server Error;
- HTTP 500 — Internal Server Error;
- Temporary Error (500);
- Internal Server Error;
- HTTP 500 Internal Error;
- 500 Error;
- HTTP Error 500;
- 500. That’s an error.
Обычно эта ошибка отображается в окне браузера, как стандартная веб-страница.
Все причины возникновения ошибки
Internal Server Error 500 возникает, когда запрос обрабатывается сервером. Этот код состояния включает все незапланированные события, которые могут произойти на стороне сервера и помешать загрузке сайта. Одна из возможных причин — ошибка в конфигурации сервера.
Вот несколько типичных источников проблем.
- Доступ запрещен — разрешения основных файлов и папок заданы неправильно.
- Тайм-аут сеанса PHP — скрипт пытается получить доступ к внешнему ресурсу и сталкивается с задержкой.
- Некорректный код в htaccess — структура htaccess, файла для локальной настройки сервера Apache, может быть неправильной.
- Ошибка в синтаксисе и коде скриптов CGI и Perl — в этих скриптах могут встречаться неточности, в частности несогласованность путей.
- Лимит памяти PHP — процесс превышает пределы памяти и поэтому не может быть выполнен правильно.
Если сайт работает на WordPress или другой системе управления контентом, причиной ошибки может стать неисправное или несовместимое расширение. Плагины и темы — особенно от сторонних провайдеров — могут повлиять на весь сайт.
Если ошибка сохраняется в течение длительного времени, это может негативно повлиять на SEO сайта. К счастью, большинство из этих проблем можно исправить.
Что делать при появлении ошибки?
Если вы попытались открыть веб-страницу, но увидели Internal Server Error 500, можно сделать следующее.
Подождать
Поскольку ошибка исходит со стороны сервера, владельцы сайта, скорее всего, уже работают над ее устранением. Попробуйте подождать несколько минут или около часа, а затем перезагрузите страницу.
Также можно заглянуть на сайт downforeveryoneorjustme.com и вставить в поисковую строку URL-адрес страницы, на которой произошла внутренняя ошибка сервера.
Сервис сообщит, возникла ли проблема только у вас или же у всех пользователей.
Сообщить администратору
Еще один вариант — связаться с владельцами сайта. Если вы предполагаете, что они еще не знают об ошибке, лучше всего сообщить им — это поможет и вам, и другим пользователям.
У большинства сайтов и сервисов есть аккаунты в социальных сетях, а на некоторых даже указаны email-адреса и номера телефона.
Что делать администратору при появлении ошибки?
Если ошибка 500 появилась на вашем сайте, попробуйте следующие способы.
Проверить файл htaccess
Загляните в файл htaccess: даже небольшая синтаксическая ошибка может вызывать внутреннюю ошибку сервера. Не менее часто случается так, что этот файл неправильно отформатирован. Его нужно создавать в формате ASCII или ANSI, а не в Unicode. Следовательно, писать его следует в текстовом редакторе, например в Notepad, Notepad++ и Sublime Text, а не в Microsoft Word.
Чтобы проверить, является ли файл htaccess причиной ошибки, можно временно переименовать его и перезагрузить сайт. После этого сервер не будет обращаться к htaccess при загрузке страницы. Если сообщение об ошибке больше не появляется, значит стоит исправить этот файл или создать новый.
Проверить лог ошибок
Загляните в лог-файл, например для серверов Linux его можно найти по адресу /var/log/httpd/error_log. Попробуйте перезагрузить сайт, чтобы воспроизвести код ошибки 500, и посмотреть, как создается лог-файл. Это поможет быстро найти источник проблемы.
Проверить содержимое CGI-скриптов
Ошибки могут возникать, если разрешения для важных файлов установлены неправильно. Есть три типа прав:
- read (r) — чтение;
- write (w) — запись;
- execute (x) — выполнение.
Эти разрешения можно предоставлять трем типам пользователей:
- владельцу файла;
- группе пользователей;
- все остальным.
Права указываются либо с помощью сокращений r, w и x, либо с помощью числовых значений: 4 — для чтения, 2 — для записи и 1 — для выполнения. Они добавляются для каждого типа пользователей и идут один за другим: rwxr-xr-x (rwx — для владельца, r-x — для группы и r-x — для всех остальных) или 755.
По умолчанию должна быть установлена конфигурация 755. Если разрешения предоставляются иначе, может возникнуть ошибка. Эту настройку можно изменить с помощью команды: chmod 755 filename.
Если проблема не решится, можно также провести тестирование, предоставив все права для каждой группы: chmod 777 filename. Однако к этой настройке следует прибегать только для определения проблемы — если любой пользователь сможет переписывать файл, безопасность сайта окажется под угрозой.
Проверить плагины и компоненты
Новое ПО, надстройки и сторонние скрипты могут конфликтовать с текущей конфигурацией сервера. Чтобы выявить причину ошибки 500, попробуйте поочередно отключить или удалить программные дополнения.
И напротив, если вы недавно обновили ПО, текущие плагины и темы могут оказаться несовместимы с обновлением. Деактивация дополнений по порядку — лучший способ найти основную причину проблемы.
Увеличить объем оперативной памяти сервера
Лимит памяти определяет, какой ее объем может задействовать процесс. Если какой-либо процесс требует больше памяти, чем доступно, может возникать ошибка 500.
Чтобы это исправить, можно временно увеличить лимит памяти. Для этого добавьте в php.ini команду, подобную этой: memory_limit = 512M. Этот пример устанавливает лимит на 512 МБ.
Учитывайте, что хостинг-провайдер допускает лишь определенный лимит сеанса PHP в рамках используемого вами пакета. Если будет введено большее значение, сервер проигнорирует его. Также помните, что это лишь временное решение: как только сайт заработает, потребуется выяснить причину высокого потребления памяти. Высока вероятность, что в коде содержится ошибка.
Если ни один из этих способов не помог, стоит связаться с хостинг-провайдером. Но прежде чем сделать это, проверьте состояние серверов: при возникновении проблем многие провайдеры сообщают эту информацию на странице состояния или в социальных сетях.
В статье использовались материалы следующих источников:
Blog.hubspot.com
Ionos.com
Businessinsider.com
Lifewire.com
Подписывайтесь на наш Telegram-канал, чтобы быть в курсе последних новостей и событий!