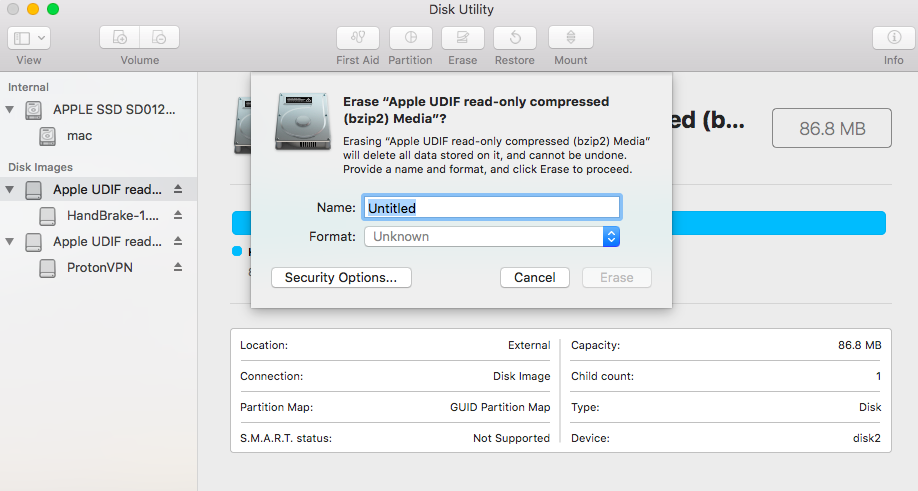
Мы имеем дело с двумя разными проблемами.
Для создания загрузочного USB вам понадобится пакет Mavericks Installer из Apple Store, 5,5-гигабайтный файл, сохраненный на MBA-, но не запущенный.
Я использовал этот процесс для создания загрузочного USB:
Загрузочный USB
Отформатируйте его с помощью Disk Utility как диск Mac OS Extended (Journaled) с именем Mavericks.
Это можно сделать на вкладке «Стереть» в приложении; убедитесь, что на USB-накопителе нет нескольких разделов (такое может случиться, поэтому перейдите на вкладку «Разделы», чтобы проверить и исправить это).
Откройте Терминал.
Стирание диска: 0%… 10%… 20%… 30%…100%…
Копирование файлов программы установки на диск… (эта часть может занять 30 минут)
Копирование завершено.
Создание загрузочного диска…
Копирование загрузочных файлов…
Копирование завершено.
Готово.
Если проблемы повторяются, приобретите другой USB-накопитель емкостью не менее 8 Гб (без разделов).
- Вторая проблема:
Восстановление жесткого диска:
Если MBP загружается в режиме восстановления с помощью cmd-r, следуйте этому процессу для восстановления установки ОС, или используйте Disk Utility для проверки/восстановления диска.
Вы можете открыть терминал и использовать команду fsck -fy для проверки и восстановления диска.
Если проблема незначительна, вы можете запустить систему в безопасном режиме, который исправит некоторые незначительные проблемы.
Looks like no one’s replied in a while. To start the conversation again, simply
ask a new question.
Trying «How to create a bootable installer for macOS» El Capitan ends up terminal saying: Error erasing disk error number (-69888, 0)
A error occurred erasing the disk. Followed the instructions exactly! 16 G Kingston USB stick.
Mac Pro
Posted on Sep 1, 2019 9:20 AM
Question marked as
Best answer
I figured it out and thought it might help others with error number (-69888, 0).
Although I renamed the new 16 GB USB stick MyVolume per instructions, it had a prior installation of it that never worked!
Because of that the disk could not be dismounted to be erased.
Solution:
I used Disk Utility to erase the stick and reformat to Mac OS Extended and named MyVolume.
then:
Following the instructions at https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT201372 again all worked perfect!
Posted on Sep 1, 2019 4:44 PM
Similar questions
-
Why does my MacBook Air come up with error when installing macOS Sierra
When installing macOS on my MacBook Air I keep coming up with “error occurred while preparing the installation”laptop given to me after previous owner erased all data.
I’m trying to install on factory settings again
319
3
-
How to fresh install MACOS? Error…
Hello,
I have a macbook 13 inch from 2009.
The harddrive was damage so i put another hard drive with windows installed and the Macbook turn on perfectly..
Now i want to put a MACOS operating system but i always get this error :
» An error ocorrer during install MAC OS X»..
already put date and time correct…
Because i have another pc with windows i use TransMAC to create a bootable USB.
Already try with EL CAPITAN, Sierra.
I use this toturial:
https://support.apple.com/pt-pt/HT208496And this:
https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT204904
I dont know what to do more…
tanks
414
4
-
My mac wound install macOS
My mac won’t install MacOS keep saying an error has occurred
152
2
1 reply
Question marked as
Best answer
Sep 1, 2019 4:44 PM in response to Walter Wedler
I figured it out and thought it might help others with error number (-69888, 0).
Although I renamed the new 16 GB USB stick MyVolume per instructions, it had a prior installation of it that never worked!
Because of that the disk could not be dismounted to be erased.
Solution:
I used Disk Utility to erase the stick and reformat to Mac OS Extended and named MyVolume.
then:
Following the instructions at https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT201372 again all worked perfect!
Why do I get an error erasing the disk has occurred?
Как справиться с ошибкой процесса стирания Ошибка на Mac (06.05.23)
Дисковая утилита обычно большую часть времени работает без проблем. Но иногда разочаровывает «процесс стирания не удался. Не удалось размонтировать диск: (-69888) ошибка на Mac может остановить любую задачу, которую утилита пытается выполнить прямо на своем пути. Эта проблема может возникать при разбиении на разделы, проверке и восстановлении диска или даже во время форматирования.
Обычно очень мало или вообще не дается дополнительных сведений о том, как решить проблему или даже о том, в чем проблема , что усложняет понимание этой проблемы пользователями.
В основном, «процесс стирания не удался. Не удалось размонтировать диск: (-69888) ошибка на Mac появляется при изменении текущего загрузочного диска. Это также может произойти, если диск, который вы пытаетесь стереть, не прошел процесс с ошибкой «Не удалось отключить диск».
Если загрузочный диск модифицируется, как подсказывает первая ситуация, самое простое решение — загрузиться с другого диска и запустить Дисковую утилиту оттуда. Что касается загрузочного диска, не имеет значения, для какой версии Mac OS X или macOS он был создан, если на нем есть Дисковая утилита — что они все имеют. Это должно помочь вам решить проблему.
Что такое сбой процесса стирания Ошибка на Mac?
Вы получаете ошибку 69888 при разбиении диска на разделы? Эта ошибка чаще всего возникает, когда вы стираете данные со своего жесткого диска и пытаетесь переустановить версию macOS или OS X только для того, чтобы процесс завершился сбоем и выбросил эту ошибку. Хорошей новостью является то, что есть несколько советов по устранению неполадок, которые вы можете сделать, чтобы решить эту проблему.
Ошибка процесса стирания на Mac вызывает затруднения, поскольку пользователи не могут получить доступ к файлам и приложениям на жестком диске, пока проблема не будет устранена. Некоторые пользователи также сообщили, что эта ошибка может повлиять на скорость обработки системы и даже внезапно завершить работу, что приведет к потере данных.
Если вы столкнулись с такой же ситуацией и ищете идеальное решение для этой ошибки, вам необходимо не беспокойтесь, потому что это руководство должно помочь в этом.
Причины сбоя процесса стирания Ошибка на Mac?
Причины сбоя процесса стирания. Не удалось отключить диск: (-69888) »на Mac? Чтобы узнать о различных способах исправления ошибки процесса стирания дисковой утилиты Mac, важно сначала ее диагностировать. Ниже приведены некоторые из основных причин ошибки, которые помогут вам понять ее причины.
Возникновение ошибки терминала Mac 69888, создающей паническую ситуацию, вызвано различными причинами. Любые несоответствия, относящиеся к файловой системе Mac OS X, могут привести к повреждению данных, что сделает их полностью недоступными. Давайте рассмотрим некоторые из возможных причин того же.
- Человеческие ошибки: это может быть связано с непреднамеренными ошибками, такими как случайное удаление, форматирование файлов Mac и томов во время нормальной работы
- Очистка корзины: часто пользователи могут очистить свои файлы корзины без перекрестной проверки, что может привести к полному удалению даже важных данных Mac.
- Внезапное завершение работы системных файлов: некоторое время из-за скачка напряжения система Mac внезапно прекращает работу, из-за чего некоторые файлы не монтируются и перестают отвечать.
- Прерванная операция чтения / записи: вероятность повреждения или удаления файла Mac также имеет место, когда мы прерываем текущий процесс чтения / записи на полпути, что приводит к ситуации Mac Terminal Error 69888.
- Непреднамеренное форматирование: нажатие неправильная кнопка иногда приводит к возникновению очень критической проблемы Mac Terminal Error 69888.
- Совместное использование данных / файлов на неподдерживаемых платформах: из-за наличия неподдерживаемой платформы иногда общие файлы перестают отвечать на запросы и повреждаются.
- Атака вредоносного ПО: хотя Mac считается намного более безопасным по сравнению с Windows, для него все еще пишется мало вредоносных вирусов. Загрузка приложений и других связанных файлов приведет к проблемам с безопасностью, которые в дальнейшем повлияют на всю файловую систему.
- Модификация в настройках BIOS: Иногда, когда мы вносим некоторые изменения в сектор BIOS, это приводит к возникновению нескольких ошибочных ситуаций, связанных с проблемой Mac Terminal Error 69888, которую вы никогда бы не хотели иметь.
- Повреждение файла заголовка: файлы заголовков — это один из важнейших файлов, содержащих всю информацию о файле, к которому вы собираетесь получить доступ. Следовательно, если есть проблема, запрошенный файл не отвечает и даже генерирует сообщение Mac Terminal Error 69888 о повреждении.
- Повреждение узла файлов каталога: Каталог — это файл, созданный системой, который хранит запись типа файла и его недавних тип доступа.
- Проблема с загрузочным сектором: когда есть проблема с загрузочным сектором, система Mac не загружается, и в результате вы не можете получить доступ к сохраненным файлам данных, и возникает ошибка терминала Mac 69888.
- Проблемы с паникой ядра. Как и в случае с BSOD в Windows, пользователи Mac могут столкнуться с проблемами паники ядра.
- Неправильная установка программы: установка нежелательных приложений & amp; программы, не проверяя его img и согласование.
- Проблема с оборудованием или программным обеспечением: это также частый фактор, который в значительной степени ответственен за повреждение файлов Mac и вместо возникновения ошибочных ситуаций.
Все вышеперечисленные причины являются вероятными причинами недоступности данных Mac. Существует множество факторов, которые вызывают эту проблему с USB-устройством или внешним диском, включая модификацию загрузочного диска. Кроме того, эта ошибка может возникнуть, если другие программы используют USB-накопитель. Если вы хотите стереть данные с USB-накопителя при копировании или чтении файла, эта ошибка может возникнуть в этот момент. Короче говоря, у этой проблемы нет конкретной причины.
Как исправить ошибку процесса стирания Ошибка на Mac
Поскольку на Mac могут быть разные причины, по которым ошибка процесса стирания не удалась, вы можете поискать разные способы ее исправить. Вот несколько советов, которые вы можете реализовать, чтобы исправить ошибку процесса стирания Дисковой утилиты.
Но прежде чем вы это сделаете, вот некоторые из основных способов устранения неполадок, о которых вам следует позаботиться в первую очередь:
Выполнив описанные выше шаги, вы можете приступить к основным решениям, приведенным ниже.
Решение №1: очистите диск с помощью терминала
24212. ваш Mac, то вы можете попробовать сделать то же самое через Терминал. Это более чистый подход к стиранию с диска, который поможет вам легко удовлетворить ваши требования.
Решение № 2: Обновите macOS
Решение № 3: вместо этого удалите выбранные тома
Иногда при форматировании всего диска пользователи получают сообщение об ошибке «Сбой при стирании» на Mac. Поэтому вместо этого вы можете рассмотреть возможность форматирования выбранных томов диска. Таким образом, вы можете проверить, связана ли проблема с выбранным томом.
Точно так же вы можете попытаться стереть весь диск для дальнейшей диагностики проблемы. Таким образом, вы можете быть уверены, что проблема связана со всем диском или с выбранными томами.
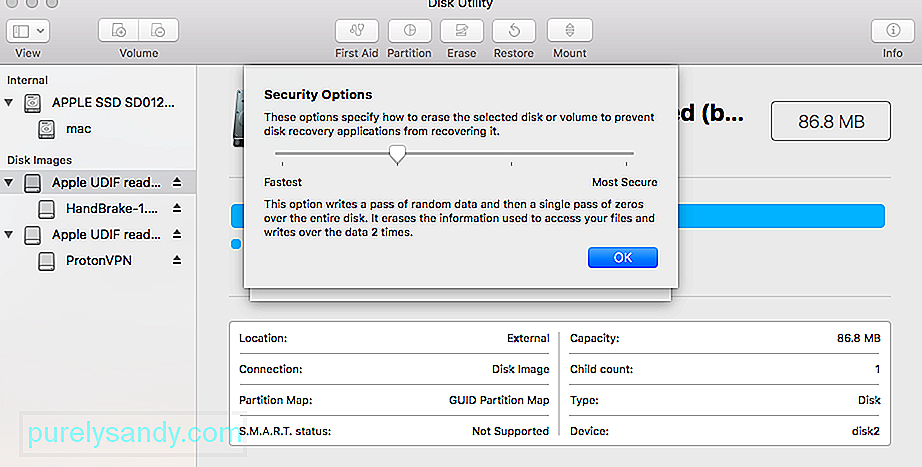
Решение №4. Отрегулируйте уровни безопасности для форматирования внешнего устройства.
Решение №5: используйте загрузочный USB-накопитель
Это рекомендуемый метод, поскольку он всегда должен исправлять ошибку. Для выполнения этой задачи вам понадобится любой загрузочный диск Mac OS X. Для этой цели я использовал загрузочный установочный диск Mavericks, но другие тоже должны работать, независимо от того, являются ли они установочными дисками или просто дисками восстановления, важно то, что они являются загрузочными и отделены от основной загрузочный диск, на котором хранится установленная ОС:
Это хороший пример того, почему очень важно иметь загрузочный USB-накопитель, настроенный с любой версией Mac OS X, на которой работает ваш Mac, потому что без отдельного загрузочного диска некоторые из этих ошибок были бы неразрешимыми. Такие загрузочные диски легко создать самостоятельно, вот инструкции по созданию загрузочных дисков для OS X 10.9, OS X 10.8 и OS X 10.7. Для старых компьютеров Mac с предыдущими версиями Mac OS X, как правило, все, что работает под OS X 10.6 или более ранней версии, будет иметь SuperDrive и, таким образом, поставляется с загрузочным DVD, который может служить той же цели.
Решение № 6: Используйте Mac Recovery Partition
Решение №7: принудительно отключить диск через терминал
Другой метод использует командную строку для принудительного отключения диска, но это не самый рекомендуемый вариант из-за возможности потери данных.
Однако при таком подходе следует проявлять осторожность, поскольку принудительное отключение диска может привести к потере данных при принудительном отключении диска. Таким образом, это уместно только в том случае, если вы планируете форматировать и стирать диск, который вы все равно принудительно извлекаете.
По завершении вы можете выйти из Терминала как обычно.
Как стереть данные с жесткого диска на Mac
Следуя приведенным выше инструкциям — перечисленные методы, вы сможете решить проблему с ошибкой процесса стирания Дисковой утилиты. Однако, если вы вообще не хотите сталкиваться с этим, убедитесь, что вы предприняли все правильные шаги, чтобы стереть данные с жесткого диска на Mac. Если вы не совершаете ошибок и в вашей системе нет проблем, вы не столкнетесь с проблемой, связанной с ошибкой процесса стирания Mac Disk Utility. 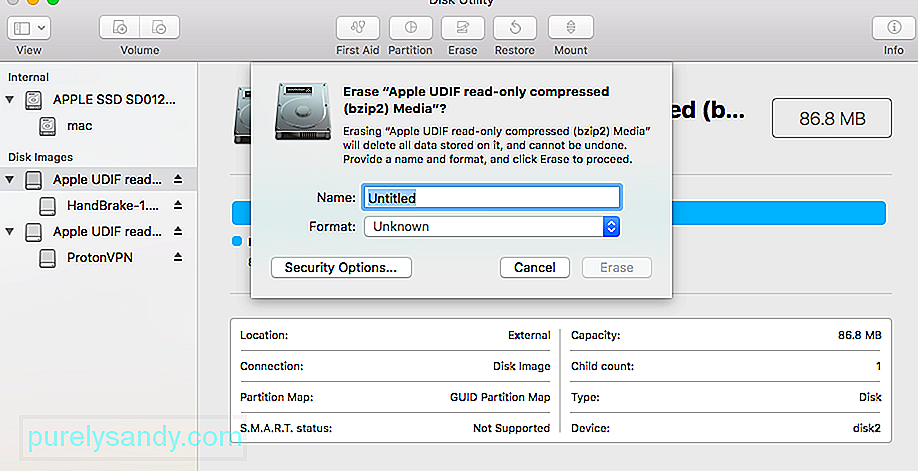
Для форматирования жесткого диска или внешнего устройства на Mac могут быть разные причины. Некоторые из них могут быть следующими:
- Возможно, вы захотите устранить проблему, отформатировав жесткий диск.
- Может быть проблема с вашим внешним устройством и его форматированием можно исправить.
- Возможно, вы захотите изменить файловую систему или стиль разделов на вашем Mac.
- Если вредоносная программа повредила ваш Mac, вы легко исправите это, отформатировав файл диск.
- Если вы перепродаете свой Mac, то, возможно, вы захотите отформатировать его, чтобы защитить свои данные.
Неважно, по какой причине вы форматируете жесткий диск или внешнее устройство — процесс предельно простой. Я уже представил умное решение для форматирования диска через Терминал выше, за которым вы можете следовать. Хотя для форматирования диска через графический интерфейс пользователя Mac, можно предпринять следующие шаги.
1. Запустите приложение Disk Utility
Как вы знаете, Дисковая утилита отвечает за выполнение операций форматирования и стирания на диске. Поэтому вы можете просто зайти в Finder & gt; Приложения & gt; Utility и запустите приложение Disk Utility отсюда.
2. Выберите диск или устройство для форматирования
Теперь вы можете просмотреть список всех доступных дисков и подключенных устройств на боковой панели приложения Дисковой утилиты. При желании вы можете перейти в раскрывающееся меню в верхнем левом углу, чтобы просмотреть все тома и устройства. Отсюда вы можете просто выбрать диск, том или даже внешнее устройство, которое хотите отформатировать.
3. Очистить выбранный диск
После выбора внутреннего диска или внешнего устройства по вашему выбору просто перейдите на панель инструментов Дисковой утилиты справа и нажмите кнопку «Стереть».
Откроется всплывающее окно, в котором вы сможете внести необходимые изменения для форматирования диска. Например, вы можете дать ему новое имя, изменить файловую систему или даже схему разбиения. После внесения соответствующих изменений просто нажмите кнопку «Стереть» и подождите некоторое время, пока выбранный диск не будет стерт.
Что делать, если кнопка «Стереть» в Дисковой утилите неактивна?
Вероятно, вы неактивны. прочитав эту статью, потому что кнопка «Стереть» или «Разделить» была недоступна, когда вы пытались стереть или переформатировать диск с помощью Дисковой утилиты. Выполните следующие действия, чтобы исправить это, и сообщите нам в комментариях, какой из них сработал для вас.
1. Показать все устройства и стереть родительский диск
По умолчанию Дисковая утилита показывает только тома на подключенных дисках, а не сами диски. Том — это раздел или раздел диска, на котором хранятся данные.
Откройте Дисковую утилиту и выберите «Просмотр» & gt; Показать все устройства в строке меню. Вы должны увидеть имена устройств для каждого из ваших дисков, появившиеся на боковой панели.
Или используйте сочетание клавиш Cmd + 2. Выберите родительскую папку для диска, который вы хотите переформатировать или стереть, затем нажмите кнопку «Стереть» кнопку еще раз. Обратите внимание, что когда вы стираете устройство, оно также стирает все тома, содержащиеся в нем.
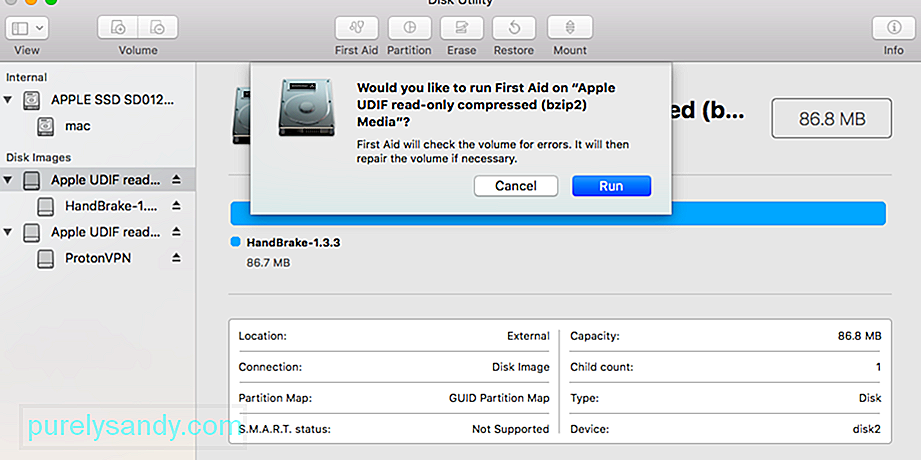
2. Выполните первую помощь, чтобы восстановить диск перед его стиранием.
Дисковая утилита имеет функцию первой помощи, которая устраняет все виды проблем, связанных с вашими дисками: низкая производительность, поврежденные файлы или неожиданное поведение. Когда вы запускаете программу First Aid, она сканирует весь диск на наличие ошибок и сообщает, если они не могут быть исправлены.
Откройте Дисковую утилиту и выберите диск, который нужно стереть, на боковой панели. Вверху окна нажмите кнопку «Первая помощь», а затем согласитесь с условиями «Выполнить первую помощь». Используйте первую помощь на любых проблемных дисках. Время, необходимое для запуска первой помощи, зависит от размера вашего диска, объема данных на нем и количества ошибок, которые необходимо исправить.
Объедините этот шаг с предыдущим, чтобы запустить первую помощь на родительское устройство для вашего диска, а также отдельные тома.
3. Загрузитесь в режим восстановления, чтобы стереть загрузочный диск
Если вы пытаетесь переформатировать или стереть загрузочный диск на вашем Mac, вам необходимо сначала загрузиться в режиме восстановления. Загрузочный диск — это основной жесткий диск вашего компьютера: на нем хранится macOS и все ваши данные. Обычно стереть загрузочный диск невозможно, потому что ваш Mac использует его для работы с macOS.
Режим восстановления — это специальный раздел на вашем Mac, который вы можете использовать для восстановления из резервной копии, переустановки macOS, получения онлайн-поддержки или очистки загрузочного диска.
Перед попыткой сделать резервную копию Mac следует создать резервную копию. сотрите или переформатируйте его.
Когда вы будете готовы загрузиться в режиме восстановления, перезагрузите Mac и удерживайте Cmd + R, пока он загружается. Удерживайте обе клавиши, пока не увидите логотип Apple или не услышите звук запуска. Режим восстановления отображается в виде окна служебных программ. Вы должны увидеть окно служебных программ macOS. Выберите «Дисковую утилиту» в этом окне и попробуйте снова стереть или переформатировать диск.
Как переустановить macOS после стирания данных с диска
После стирания или переформатирования загрузочного диска — если это было вашей целью — вам необходимо переустановить macOS раньше вы можете снова использовать свой Mac. Это связано с тем, что исходная установка macOS находилась на только что стертом загрузочном диске. Ниже приведены инструкции по переустановке macOS на компьютерах Mac M1.
Ваш Mac предлагает вам снова настроить его после восстановления заводских настроек. Еще раз загрузитесь в режиме восстановления, чтобы переустановить macOS, или следуйте нашему руководству по восстановлению заводских настроек на любом Mac. Когда вы переустанавливаете macOS, ваш Mac ведет себя так, как будто это совершенно новый компьютер, и на нем нет данных, ожидающих, пока вы его настроите.
YouTube видео: Как справиться с ошибкой процесса стирания Ошибка на Mac
06, 2023
I erased the SSD drive in my MacBook and was reinstalling Lion when it failed about 75% through the install. Now in Disk Utility, sometimes I see the SSD drive and sometimes I boot and it’s not there but I can never erase or partition it. I get an «error 6988 couldn’t unmount disk».
When I attempt to run fdisk to correct the MBR. fdisk doesn’t do anything.
Any ideas how to fix a disk that is this severely screwed?
-bash-3.2# diskutil list
/dev/disk0
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: *64.0 GB disk0
/dev/disk1
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: FDisk_partition_scheme *31.9 GB disk1
1: Apple_Boot Recovery HD 650.0 MB disk1s1
/dev/disk2
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: Apple_partition_scheme *1.3 GB disk2
1: Apple_partition_map 30.7 KB disk2s1
2: Apple_HFS Mac OS X Base System 1.3 GB disk2s2
/dev/disk3
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk3
/dev/disk4
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk4
/dev/disk5
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk5
/dev/disk6
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk6
/dev/disk7
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk7
/dev/disk8
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *6.3 MB disk8
/dev/disk9
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *2.1 MB disk9
/dev/disk10
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *1.0 MB disk10
/dev/disk11
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk11
/dev/disk12
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *524.3 KB disk12
/dev/disk13
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: untitled *1.0 MB disk13
-bash-3.2# diskutil info /dev/disk0
Device Identifier: disk0
Device Node: /dev/disk0
Part of Whole: disk0
Device / Media Name: Corsair Performance3 SSD Media
Volume Name: Not applicable (no file system)
Mounted: Not applicable (no file system)
File System: None
Content (IOContent): None
OS Can Be Installed: No
Media Type: Generic
Protocol: SATA
SMART Status: Verified
Total Size: 64.0 GB (64023257088 Bytes) (exactly 125045424 512-Byte-Blocks)
Volume Free Space: Not applicable (no file system)
Device Block Size: 512 Bytes
Read-Only Media: No
Read-Only Volume: Not applicable (no file system)
Ejectable: No
Whole: Yes
Internal: Yes
Solid State: Yes
OS 9 Drivers: No
Low Level Format: Not supported
-bash-3.2# fdisk -u /dev/disk0
fdisk: could not open MBR file /usr/standalone/i386/boot0: No such file or directory
-----------------------------------------------------
------ ATTENTION - UPDATING MASTER BOOT RECORD ------
-----------------------------------------------------
Do you wish to write new MBR? [n] y
-bash-3.2#
jmlumpkin
8,7756 gold badges39 silver badges75 bronze badges
asked Aug 4, 2012 at 14:48
I can’t test it but I think that if you erase the MBR (with dd instead of fdisk) and the partition table record you should be able to re-format you ssd.
Boot from cd or external hd and open terminal
this code erase the MBR:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/disk0 bs=446 count=1
this one erase the partition table also:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/disk0 bs=512 count=1
If you erase just the mbr you could use testdisk to attempt to recover data (in case you don’t have erased the disk label).
answered Apr 17, 2013 at 11:50
MnOMnO
3261 gold badge2 silver badges8 bronze badges
I got the same «error 6988 couldn’t unmount disk» message. It was due to unclosed references to the drive/partition — particularly I had a terminal window open and the PWD was on that volume. Close that window and close all Finder windows that has reference to that volume (or simply cd to a different directory outside of the mounted disk tree), redo the steps, it should work.
answered Oct 23, 2013 at 22:03
DevyDevy
1114 bronze badges
2
You have to close all the Finder’s instances pointing to the SSD/SD, same for the terminal windows etc. Don’t forget to close cloud drive apps such as Dropbox if you are sharing folders that are stored on that SSD/SD drive. In case you have your Photo library on this drive, don’t forget to kill the Photo analysis daemons (processes) — this was actually the last thing that prevented my SD to unmout before converting it to APFS. To kill those processes, you can open Activity Monitor app and type «photo» to the searchbox. You will see something like «photolibraryd» and «photoanalysisd». I had to kill these two in order to get the SD drive unlocked for unmounting.
answered Dec 31, 2017 at 10:15
I was trying to format my second, data disk in my iMac 5K (128 blade as boot) many times and it failed with the same error.
Finally, I switched to View > Show All Devices and performed the same operation again on my data volume. This time, it worked fine.
answered Feb 1, 2018 at 17:43
Josef HabrJosef Habr
4294 silver badges8 bronze badges
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Reading time: 16 Minutes
Disk Utility is a reliable tool but sometimes you may encounter an error message saying “Erase process has failed. Couldn’t unmount disk: (-69888)” on Mac. This error can occur during disk verification, repair, partitioning or formatting, and can be frustrating.
There is usually very little to no additional details given as to how to fix the problem or even what the problem is about, making it harder for users to understand this issue.
Basically, the “Erase process has failed. Couldn’t unmount disk: (-69888) error on Mac pops up when the current boot drive is being modified. It could also happen if the disk you are trying to erase has failed the process with a Couldn’t unmount disk error.
If the boot drive is being modified as the first situation suggests, the easiest fix is to boot from another drive and run Disk Utility from there. For the boot drive, it does matter what version of Mac OS X or macOS it was created for, as long as it has Disk Utility – which they all do. This should allow you to fix the problem.
Are you getting the error 69888 while partitioning a drive? This error mostly happens when you erase the data from your hard drive and try to reinstall your macOS or OS X version only for the process to fail along the way and throw out this error. The good news is that there’s several troubleshooting tips you can do to fix this issue.
The Erase process has failed error on Mac is troublesome because users can’t access their hard drive files and apps unless the issue has been fixed. Some users also reported that this error can affect the system’s processing speed and even terminate abruptly, resulting in data loss.
If you are facing the same situation and looking for the perfect solution for this error, then you need not worry because this guide should be able to help with that.
What Causes Erase process has failed Error on Mac?
What causes “Erase process has failed. Couldn’t unmount disk: (-69888)” error on Mac? To learn different ways to fix the Mac Disk Utility erase process has failed error, it is important to diagnose it first. The following are some of the major reasons for the error to help you understand its causes.
There are various reasons behind the emergence of Mac Terminal Error 69888 creating panic situation. Any inconsistencies pertaining to Mac OS X files system might result in corruption of data thus making it completely inaccessible. Let’s take a look at some of the probable reasons for the same.
- Human mistakes: It might be due to unintentional mistakes such as accidental deletion, formatting mac files and volumes during normal course of operation
- Emptying Trash: Many a time users might empty their trash files without cross checking them, which might result in complete wipe of even important Mac data.
- Sudden termination of system files: Some time due to power surge, Mac system gets terminated abruptly, due to which some of the files fail to mount and become unresponsive.
- Interrupted read/write operation: The chances of Mac file corruption or deletion also takes place when we interrupt the ongoing read/write process in midway resulting in Mac Terminal Error 69888 situation.
- Unintentional Formatting: Pressing wrong button will sometime lead to emergence of very critical Mac Terminal Error 69888 problem.
- Sharing of data/file on unsupported platforms: Due to presence of unsupported platform, sometimes shared files becomes unresponsive and get corrupted.
- Malware attack: Although Mac is considered a lot more safe as compared to Windows but still few nasty viruses are being written for it. Downloading apps and other related files will lead to security issues, which further influence the entire file system.
- Modification in BIOS setting: Sometime when we go for some changes into the BIOS sector it will lead to emergence of several erroneous situation related to Mac Terminal Error 69888 problem which you would never like to have.
- Corruption in header file: Header files are one of the crucial files that contain entire information about the file that you are going to access. Hence, if there is a problem the requested file fails to respond and even generates Mac Terminal Error 69888 corruption messages.
- Catalog files node corruption: Catalog is the system generated file which keeps record of file type and its recent accessing type.
- Problem with boot sector: When there is a problem with the boot sector, the Mac system fails to load and as a result you are unable to access the stored data files and there arises Mac Terminal Error 69888 issues.
- Kernel Panic issues: Like BSOD in Windows, Mac users might come across kernel panic issues.
- Improper installation of program: installing of unwanted apps & programs without checking its source and agreement.
- Hardware or software issue: It is also a common factor that is quite responsible for Mac file corruption and in a lieu emergence of erroneous situations.
All the above mentioned reasons are the probable causes for inaccessibility of Mac data. There are a lot of factors that cause this issue to a USB device or an external drive that includes the modification of the boot drive. Also, this error can occur if different other programs are using the USB drive. If you want to erase your USB when you are copying or reading a file, this error may occur at that time. In short words, there is no specific reason for this issue.
How to Fix Erase process has failed Error on Mac
Since there could be various reasons for getting the erase process has failed error on Mac, you might look for different ways to fix it. Here are some suggestions that you can implement to fix the Disk Utility erase process has failed error.
But before you do so, here are some of the basic troubleshooting you should take care of first:
- Close all applications and files before attempting the repair.
- Make sure you have enough permissions to read and write to the drive you want to modify.
- Run a scan to check for the presence of malware. Delete any malicious software detected using your antivirus and delete all related files.
- Disable your security software after running the scan because it might prevent the processes from pushing through.
- Declutter your system by cleaning up your computer with a Mac cleaning tool. This should fix any errors related to corrupted junk files or cached data on your Mac.
- Restart your computer.
Once you’ve completed the steps above, you can now proceed with the main solutions below.
Solution #1: Erase your Disk via Terminal
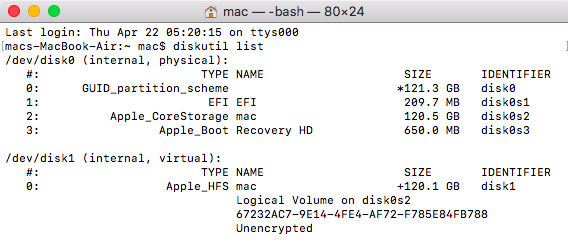
- To start with, go to Finder and navigate to Applications > Utility to launch the Terminal app as an administrator.
- Once the Terminal application is opened, just type the command “diskutil list” and press return. This will display detailed information regarding various disks and volumes in your Mac. From here, please note the identifier of the disk you wish to format (like disk2 or disk1).
- Once you have noted the identifier, use the “erase disk” command to erase the entire disk or the “ease volume” command to just erase a volume.
- The entire format of the diskutil command is diskutil erase disk. For instance, to format the disk2 in the HFS+ format, you can just enter the command “diskutil eraseDisk HFS+ DISK disk2” and press the return key.
- After that, just wait for the commands to process as your selected disk would be formatted in the supported file system.
Solution #2: Update macOS
Solution #3: Erase Selected Volumes Instead
Sometimes, users get the erase process has failed error on Mac while formatting the entire disk. Therefore, you can consider formatting selected volumes of the disk instead. In this way, you can check whether the issue is with a selected volume or not.
- Firstly, go to your Mac’s Finder > Applications > Utility and launch the Disk Utility application on your system.
- Once the Disk Utility application is launched, go to the top-left corner of the interface. From the dropdown menu, you can choose to view all volumes or external devices.
- Now, just select a volume from the sidebar (instead of the entire disk) and click on the “Erase” button on the toolbar to format it.
Similarly, you can try to erase the entire disk as well to further diagnose the problem. In this way, you can be sure whether the problem is with the entire disk or selected volumes.
Solution #4: Adjust the Security Levels for Formatting an External Device
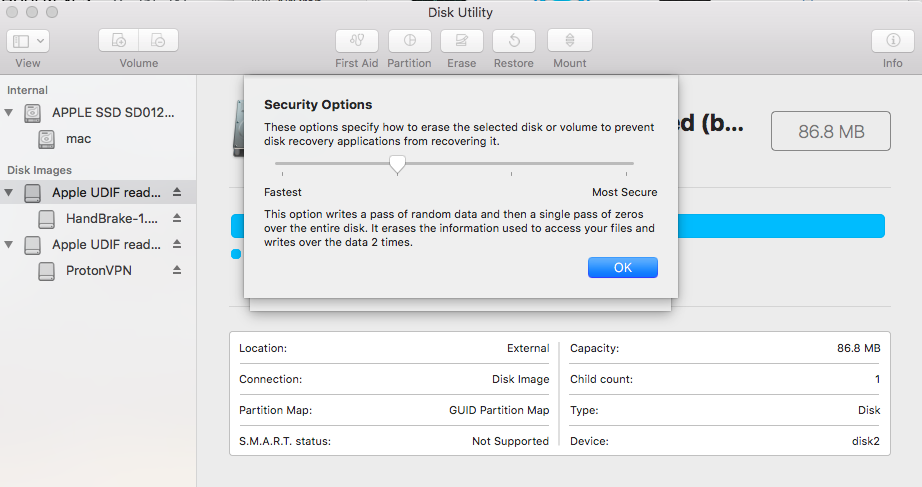
- Firstly, launch the Disk Utility application on your Mac and make sure the external device is connected to it.
- Now, select the external device from the sidebar and click on the “Erase” button. As the following pop-up would be launched, go to its Security Options.
- From here, you can just adjust the security level for formatting the external device. I would recommend keeping the security level on the lower side to avoid getting the erase process has failed error on Mac.
Solution #5: Use a USB Boot Drive
This is the recommended method because it should always fix the error. You will need any Mac OS X boot drive to complete this task, I used a Mavericks boot installer drive for this purpose but others should work too, whether they are installation drives or just recovery drives, the important thing is they are bootable and separate from the primary boot disk that stores the installed OS:
- Attach the USB boot drive to the Mac and reboot
- Hold down the OPTION key during boot, then select the attached boot drive (typically has an orange icon at the boot menu)
- At the boot menu, choose “Disk Utility” (if using an Installer disk, pull down the “Utilities” menu to access Disk Utility)
- Go to “First Aid” and verify the disk, then repair if needed
- Now perform the original task that threw the “Couldn’t Unmount” error
- I ran into this twice recently, first when attempting to modify partitions on a drive, which came right along with a separate “partition failed” error, and again was triggered when attempting to format those partitions. The above steps did the trick and everything was working again as expected.
This is a good example of why it’s very valuable to have a bootable USB thumb drive set up with whatever version of Mac OS X is running on your Macs, because without a separate boot drive some of these errors would be unresolvable. Such boot drives are easy to create on your own, here are instructions for making boot disks for OS X 10.9, OS X 10.8, and OS X 10.7. For older Macs running prior versions of Mac OS X, typically anything running OS X 10.6 or earlier will have a SuperDrive, and thus shipped with a bootable DVD that can serve this same purpose.
Solution #6: Use Mac Recovery Partition
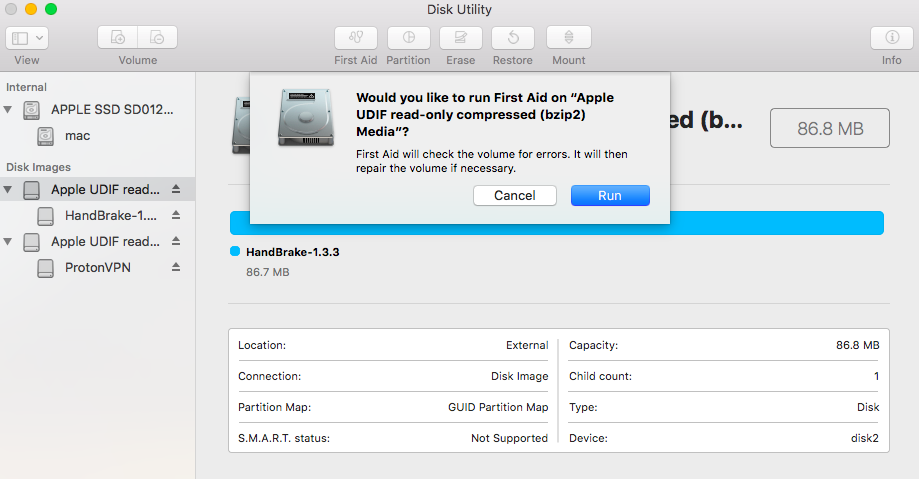
- Reboot the Mac holding down the “Option” key and choose the Recovery partition
- Select “Disk Utility” from the boot menu
- Go to “First Aid” to verify and repair the disk, or go to “Erase” to format the disk
- Again, if the disk throwing the errors is the same as the primary boot partition that Recovery is also on, the above method may not work to resolve the problem. In that case, you’ll need to boot from a separate USB drive to fix the error.
Solution #7: Forcibly Unmount a Disk via Terminal
Another method uses the command line to force unmount a disk, but this is not the top recommended option because of potential for data loss.
Caution must be used with this approach however because forcibly unmounting a disk can cause data loss of the drive being forcibly unmounted. Thus this is only appropriate if you plan on formatting and erasing the disk that you are force ejecting anyway.
- From the command line of Mac OS, enter the following string: diskutil unmountDisk force /Volumes/DRIVENAME
- Replace “DRIVENAME” with the name of the volume you want to unmount, then hit RETURN key to force the drive to unmount.
- If that doesn’t work, you can take this a step further:
- You might also need to target the disk by device identifier to forcibly unmount it, in which case you can first find the disk with:diskutil list
- Then when you find the matching disk to the identifier (/dev/disk1, /dev/disk2, /dev/disk3, etc), you can target the disk to unmount as so. For the example syntax here we’ll use /dev/disk3 to forcibly unmount from command line, and using sudo which will gain superuser privileges for the task: sudo diskutil unmountDisk force /dev/disk3
- Hit return and enter the admin password to forcibly unmount the disk from the Mac.
When finished you can quit out of Terminal as usual.
How to Erase Hard Drive on Mac
By following the above-listed techniques, you would be able to overcome the Disk Utility erase process has failed issue. Though, if you don’t want to encounter it in the first place, then make sure you take all the right steps to erase a hard drive on Mac. If you don’t make any mistakes and there are no issues with your system, then you will not encounter the Mac Disk Utility erase process has failed issue.
There can be different reasons for formatting a hard drive or an external device on Mac. Some of them can be as follows:
- You might wish to troubleshoot an issue by formatting the hard disk.
- There can be an issue with your external device and formatting it can fix it.
- You might want to change the file system or the partition style of your Mac’s drive.
- If malware has corrupted your Mac, then you easily fix it by formatting the disk.
- If you are reselling your Mac, then you might wish to format it to protect your data.
It doesn’t matter what your reason for formatting a hard drive or external device is – the process is extremely easy. I have already provided a smart solution to format a disk via Terminal above that you can follow. Although to format the disk via Mac’s graphic user interface, the following steps can be taken.
1. Launch the Disk Utility application
As you know, Disk Utility is responsible for running formatting and erasing operations on the disk. Therefore, you can just go to Finder > Applications > Utility and launch the Disk Utility application from here.
2. Select a Disk or Device to format
Now, you can view a list of all the available disks and the connected devices on the sidebar of the Disk Utility application. If you want, you can go to the dropdown menu from the top-left corner to view all volumes and devices. From here, you can just select a disk, volume, or even an external device that you wish to format.
3. Erase the selected disk
After selecting the internal drive or the external device of your choice, just go to the Disk Utility toolbar on the right and click on the “Erase” button.
This will launch a pop-up window so that you can make the needed changes to format the drive. For instance, you can give it a new name, change its file system, or even its partitioning scheme. After making the appropriate changes, just click on the “Erase” button and wait for a while as the selected drive would be erased.
What if the Erase Button in Disk Utility is Grayed Out?
You’re probably reading this article because the Erase or Partition button was grayed out when you tried to erase or reformat a drive using Disk Utility. Use the steps below to fix it and let us know in the comments which one worked for you.
1. Show All Devices and Erase the Parent Drive
By default, Disk Utility only shows the Volumes on your connected drives, rather than the drives themselves. A Volume is the partition or section of a drive you store data in.
Open Disk Utility and select View > Show All Devices from the menu bar. You should see the device names for each of your drives appear in the sidebar.
Alternatively, use the shortcut Cmd + 2. Select the parent folder for the drive you want to reformat or erase, then click the Erase button again. Take note that when you erase a device, it erases all the Volumes contained within it as well.
2. Run First Aid to Repair Your Drive Before Erasing It
Disk Utility has a First Aid feature that fixes all kinds of issues related to your drives: slow performance, corrupt files, or unexpected behavior. When you run First Aid, it scans the entire disk for errors and lets you know if there are any it can’t repair.
Open Disk Utility and select the drive you want to erase from the sidebar. At the top of the window, click the First Aid button, then agree to Run First Aid. Run First Aid on any problematic drives. The length of time First Aid takes to run depends on the size of your drive, how much data is on it, and how many errors need fixing.
Combine this step with the previous one to run First Aid on the parent device for your drive, as well as the individual Volumes.
3. Boot Into Recovery Mode to Erase Your Startup Disk
If you’re trying to reformat or erase the startup disk on your Mac, you need to boot into Recovery Mode first. The startup disk is the main hard drive on your computer: the one that stores macOS and all your data. It’s not usually possible to erase the startup disk because your Mac is using it to run macOS.
Recovery Mode is a special partition on your Mac you can use to restore from a backup, reinstall macOS, get online support, or erase your startup disk.
You should back up your Mac before trying to erase or reformat it.
When you’re ready to boot into Recovery Mode, restart your Mac and hold Cmd + R while it boots up. Keep holding both keys until you see an Apple logo or hear a startup sound. Recovery Mode appears as a Utilities window.You should see a macOS Utilities window appear. Select Disk Utility from this window and try erasing or reformatting your drive again.
How to Reinstall macOS After Erasing Your Drive
After erasing or reformatting the startup disk—if that was your goal—you need to reinstall macOS before you can use your Mac again. This is because the original macOS installation was on the startup disk you just erased. Here are the instructions on how to reinstall macOS on M1 Macs.
Your Mac prompts you to set it up again after you factory reset it. Boot into Recovery Mode once more to reinstall macOS or follow our guide to factory reset any Mac. When you reinstall macOS, your Mac behaves as though it’s a brand new machine, with no data on it waiting for you to set it up.
Give us some love and rate our post!

Vicrey Makapagal
Vic is a tech enthusiast who loves to be up-to-date with the latest and greatest technology in the world. He creates content that educates and helps users with their tech-related questions. Vic manages our website to ensure that our readers have a seamless experience while browsing. He excels in troubleshooting errors and resolving Windows issues for gaming and work purposes.