Функция:
module.exports = function (date) {
td = new Date(date);
console.log(td.toLocaleString());
var dt = {
today: td,
add: function add() {
return this.today;
},
subtract: function subtract() {
return this.today;
},
};
};
Использование функции:
var time = date('2017-05-16 13:45')
.add(24,'hours')
.subtract(1, 'months')
.add(3, 'days')
.add(15, 'minutes');
assert.deepEqual(
time.value,
'2017-04-20 14:00'
);
В результате выходит это:
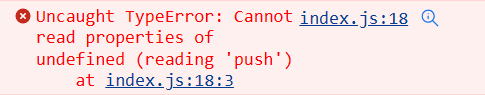
C:UsersinikulinDesktopJSнеделя3checks.js:8
.add(24,'hours')
^
TypeError: Cannot read property 'add' of undefined
Я понимаю,что программа недобита, но все же функция add даже не видна. в чем дело?
Comments
louisgv
changed the title
[SUPPORT] Cannot read property ‘add’ of undefined
[Bug] Cannot read property ‘add’ of undefined
May 29, 2017
louisgv
changed the title
[Bug] Cannot read property ‘add’ of undefined
[BUG] Cannot read property ‘add’ of undefined
May 29, 2017
domtronn
added a commit
to uswitch/ustyle-react
that referenced
this issue
Jun 9, 2017
not-an-aardvark
added a commit
to not-an-aardvark/babel
that referenced
this issue
Aug 4, 2017
hzoo
pushed a commit
to babel/babel
that referenced
this issue
Aug 4, 2017
onbjerg
added a commit
to aragon/aragon.js
that referenced
this issue
Mar 18, 2018
TheXardas
added a commit
to TheXardas/page-view-counter
that referenced
this issue
Apr 13, 2018
devongovett
added a commit
to devongovett/minify
that referenced
this issue
May 20, 2018
vicb
added a commit
to vicb/flyxc
that referenced
this issue
May 31, 2020
vicb
added a commit
to vicb/flyxc
that referenced
this issue
May 31, 2020
banjerluke
added a commit
to banjerluke/svelte-headlessui
that referenced
this issue
May 4, 2022
Some versions of babel-minify choke on function parameters that default to named constants: babel/minify#556 This moves the default assignment into the function body.
Привет народ, я начинающий в js, у меня возникла проблема(код ниже), браузер выдает ошибку (Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property ‘add’ of undefined
at create (javascript.js:42)). Не могу понять что не так.
var x = 24;
y = 10;
var mainArray = [
[1,0],
[1,0],
[1,0]
];
function create() {
var snakeBody = [
document.querySelector(`[posX = "${x}"][posY = "${y}"]`),
document.querySelector(`[posX = "${x+mainArray[0][0]}"][posY = "${y+mainArray[0][1]}"]`),
document.querySelector(`[posX = "${x+mainArray[1][0]}"][posY = "${y+mainArray[1][1]}"]`),
document.querySelector(`[posX = "${x+mainArray[2][0]}"][posY = "${y+mainArray[2][1]}"]`)
];
for(var i = 0; i < snakeBody.length; i++) {
snakeBody[i].classList.add('figure');
}
}
create();The “cannot read property of undefined” error happens when you try to access a property or method of a variable that is undefined. To fix it, add an undefined check on the variable before you access it.
Depending on your scenario, doing any one of the following might resolve the error:
- Add an
undefinedcheck on the variable before you access it. - Get the property/method from a replacement for the
undefinedvariable. - Use a fallback result instead of accessing the property.
- Check your code to find out why the variable is
undefined.
1. Add undefined check on variable
To fix the “cannot read property of undefined” error, check that the value is not undefined before accessing the property.
For example, in this code:
const auth = undefined;
console.log(auth); // undefined
// ❌ TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'user')
console.log(auth.user.name);
We can fix the error by adding an optional chaining operator (?.) on the variable before accessing a property. If the variable is undefined or null, the operator will return undefined immediately and prevent property access.
const auth = undefined;
console.log(auth); // undefined
// ✅ No error
console.log(auth?.user?.name); // undefined
The optional chaining operator also works when using bracket notation for property access:
const auth = undefined;
console.log(auth); // undefined
// ✅ No error
console.log(auth?.['user']?.['name']); // undefined
This means that we can use it on arrays:
const arr = undefined;
console.log(arr?.[0]); // undefined
// Array containing an object
console.log(arr?.[2]?.prop); // undefined
Note
Before the optional chaining was available, the only way we could avoid this error was to manually check for the truthiness of every containing object of the property in the nested hierarchy, i.e.:
const a = undefined;
// Optional chaining
if (a?.b?.c?.d?.e) {
console.log(`e: ${e}`);
}
// No optional chaining
if (a && a.b && a.b.c && a.b.c.d && a.b.c.d.e) {
console.log(`e: ${e}`);
}
2. Use replacement for undefined variable
In the first approach, we don’t access the property or method when the variable turns out to be undefined. In this solution, we provide a fallback value that we’ll access the property or method on.
For example:
const str = undefined;
const result = (str ?? 'old str').replace('old', 'new');
console.log(result); // 'new str'
The null coalescing operator (??) returns the value to its left if it is not null or undefined. If it is, then ?? returns the value to its right.
console.log(5 ?? 10); // 5
console.log(undefined ?? 10); // 10
The logical OR (||) operator can also do this:
console.log(5 || 10); // 5
console.log(undefined || 10); // 10
3. Use fallback value instead of accessing property
Another way to solve the “cannot read property of undefined” error is to avoid the property access altogether when the variable is undefined and use a default fallback value instead.
We can do this by combining the optional chaining operator (?.) and the nullish coalescing operator (??).
For example:
const arr = undefined;
// Using "0" as a fallback value
const arrLength = arr?.length ?? 0;
console.log(arrLength); // 0
const str = undefined;
// Using "0" as a fallback value
const strLength = str?.length ?? 0;
console.log(strLength); // 0
4. Find out why the variable is undefined
The solutions above are handy when we don’t know beforehand if the variable will be undefined or not. But there are situations where the “cannot read property of undefined” error is caused by a coding error that led to the variable being undefined.
It could be that you forgot to initialize the variable:
let doubles;
const nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for (const num of nums) {
let double = num * 2;
// ❌ TypeError: cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'push')
doubles.push(double);
}
console.log(doubles);
In this example, we call the push() method on the doubles variable without first initializing it.
let doubles;
console.log(doubles); // undefined
Because an uninitialized variable has a default value of undefined in JavaScript, accessing a property/method causes the error to be thrown.
The obvious fix for the error, in this case, is to assign the variable to a defined value.
// ✅ "doubles" initialized before use
let doubles = [];
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for (const num of nums) {
let double = num * 2;
// push() called - no error thrown
doubles.push(double);
}
console.log(doubles); // [ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ]
Another common mistake that causes this error is accessing an element from an array variable before accessing an Array property/method instead of accessing the property/method on the actual array variable.
const array = [];
// ❌ TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'push')
array[0].push('html');
array[0].push('css');
array[0].push('javascript');
console.log(array);
Accessing the 0 property with bracket indexing gives us the element at the index 0 of the array. The array has no element, so arr[0] evaluates to undefined and calling push() on it causes the error.
To fix this, we need to call the method on the array variable, not one of its elements.
const array = [];
// ✅ Call push() on "array" variable, not "array[0]"
array.push('html');
array.push('css');
array.push('javascript');
console.log(array); // [ 'html', 'css', 'javascript' ]
Key takeaways
In JavaScript, the “Cannot read property of undefined” error happens when you try to access a property or method of an undefined variable. To fix it, check that the variable is defined before accessing it using the optional chaining operator (?.). You can also provide a fallback value using the null coalescing operator (??) or avoid accessing the property by using a default value with the nullish coalescing operator (??) and the optional chaining operator (?.). Lastly, try doing your debugging to see why the variable could be undefined.
11 Amazing New JavaScript Features in ES13
This guide will bring you up to speed with all the latest features added in ECMAScript 13. These powerful new features will modernize your JavaScript with shorter and more expressive code.
Sign up and receive a free copy immediately.
Ayibatari Ibaba is a software developer with years of experience building websites and apps. He has written extensively on a wide range of programming topics and has created dozens of apps and open-source libraries.
The error “Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined” occurs when we are trying to access a property from a null or undefined object. A more direct approach is assigning the variable with more appropriate values to avoid “undefined” values.
The four common ways to fix the “cannot read property of undefined JavaScript” error are as follows:
- Wrap the code in a try…catch() to avoid the error from breaking the application. Additionally, console.log statements in the catch() section will provide more help with debugging.
- If the error is caused by a variable associated with an async operation, JavaScript concepts such as async/await, Promise, etc, must be used to ensure that the object property is accessed after the time delay.
- When the error is associated with a DOM element, the “defer” attribute in HTML <script> tag ensures the execution of JavaScript code after the browser window is completely loaded.
- The Optional chaining(?.) JavaScript feature only accesses defined properties from the object or returns undefined, thus avoiding errors.
1) Debug error with try…catch() statement
Wrapping the JavaScript code with a try statement prevents JavaScript errors from breaking the application. The try…catch() statement is executed as follows:
- Execute JavaScript code of the try {} section until any error is encountered.
- If a JavaScript error occurs, the execution of the remaining code of try {} section is skipped, and catch {} section is executed.
- Only try {} section is executed when no error is encountered.
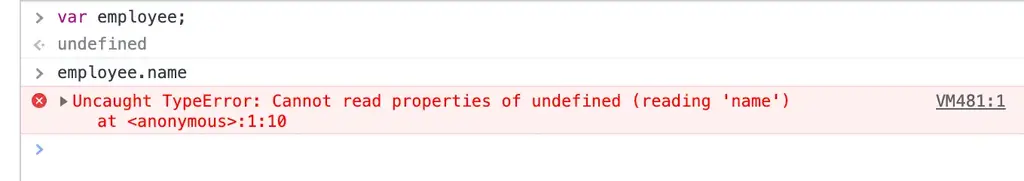
try {
var employee;
console.log(employee.name)
} catch (error) {
// employee value
console.log(employee)
// error details
console.error(error);
}2) Accessing properties from variables associated with Async operation
Sometimes, JavaScript code is very tricky with a combination of synchronous and asynchronous operations. The variable’s value can be “undefined” if it is dependent on an async function.
The undefined error caused by asynchronous execution must be fixed through JavaScript concepts such as Promise, Async/Await, etc.
var employee; //undefined
// 2 seconds time delay
setTimeout(() => {
employee = { name: "Emp1" };
}, 2000);
console.log(employee.name) //Error
/* Solution */
// Timeout function wrapped by JS Promise
function getEmployeeDetails() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({ name: "Emp1" });
}, 2000);
});
}
// Handle time delay with Async/Await
var employee = await getEmployeeDetails();
console.log(employee.name) //Emp13) Accessing DOM element before window load
When HTML DOM elements are accessed in JavaScript, it is important to ensure that JavaScript code is executed after the browser window is loaded. Any attempts to access DOM elements before loading HTML code will lead to undefined or null errors.
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
<script>
var container = document.getElementById("main");
container.innerText = "Sample Text"; //Error
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="id"></div>
</body>
</html>The “defer” attribute of the <script> tag ensures that the JavaScript code is executed after the browser window is completely loaded.
<! – Solution – >
<script defer>
var container = document.getElementById("main");
container.innerText = "Sample Text";
</script>4) Optional chaining (?.)
In some scenarios, function or REST API calls are expected to return a “null” value. Accessing properties from “undefined” or “null” objects will throw a JavaScript error.
The optional chaining (?.) feature in JavaScript allows accessing object properties that may or may not exist without causing any error. This feature is especially useful when dealing with nested objects.
var employee;
console.log(employee.name) //Error
console.log(employee?.name) //undefined
console.log(employee?.address?.city) //undefined5) Handling Array objects
Accessing JavaScript array-based properties from an “undefined” variable is another cause for the error. Therefore, every Array-based object must be assigned with “[ ]”(empty array) as the default value.
var employeeList;
//Error
if(employeeList.length == 0){
console.log("no Emplyees");
}
/* Solution */
employeeList = [];
if(employeeList.length == 0){
console.log("no Emplyees");
}