- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Добрый день!
На контроллере домена подWinServer2019
В логах появилась ошибка.
Клиент Kerberos получил ошибку KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED с сервера vldtr-bld1$. Использовалось целевое имя RPCSS/ll-hvs-so.ll.local. Это означает, что целевому серверу не удалось расшифровать билет, предоставленный клиентом. Это возможно,
когда целевое SPN-имя зарегистрировано на учетную запись, отличную от учетной записи, используемой конечной службой. Убедитесь, что целевое SPN-имя зарегистрировано только на учетную запись, используемую сервером. Эта ошибка также
может возникать, если пароль целевой службы отличается от пароля, заданного для нее в центре распространения ключей Kerberos. Убедитесь, что пароли в службе на сервере и в центре распространения ключей совпадают. Если имя сервера задано не полностью
и конечный домен (LL.LOCAL) отличается от домена клиента (LL.LOCAL), проверьте эти два домена на наличие учетных записей серверов с одинаковыми именами или используйте для идентификации сервера полное имя.Пытаюсь проверить имя SPN, но такого нет
C:Windowssystem32>setspn -Q HTTP/vldtr-bld1$.ll.local
Проверка домена DC=ll,DC=localТакое SPN не найдено.
C:Windowssystem32>setspn -Q RPCSS/ll-hvs-so.ll.local
Проверка домена DC=ll,DC=localТакое SPN не найдено.
Как мне найти где оно прописано?
Спасибо!
Answers
-
Какой IP настроен на vldtr-bld1 в реальности? Команду ipconfig на нем наберите и посмотрите. То же самое — на ll-hvs-so. А после приведите записи DNS в соответствие с существующим положением (можно — вручную).
Или существующее положение с настройкой адресов IP — в соответствие записями DNS
Слава России!
-
Edited by
Saturday, April 17, 2021 1:24 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
Андрей Михалевский
Monday, April 19, 2021 9:31 AM -
Marked as answer by
Pogreb
Monday, April 19, 2021 9:43 AM
-
Edited by
-
На DHCP включил «Всегда динамически обновлять DNS A- и PTR-записи» и записи на ДНС пришли в соответсвие.
Спасибо!
-
Marked as answer by
Pogreb
Monday, April 19, 2021 8:51 AM
-
Marked as answer by
This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: IIS Support Blog articles.
KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED is a common Kerberos failure message. This means some encrypted Kerberos authentication data sent by the client did not decrypt properly at the server.
When a Kerberos client requests a ticket for a specific service, the service is actually identified by its SPN. The KDC grants the client a service ticket that is encrypted using service’s secret key. Basically, the AD account password that that matches the SPN requested.
Under some scenarios, KDC may generate a service ticket that encrypted with password of a wrong account (or not expected one). Then, when client provide that ticket to the service for authentication, the service can’t decrypt it and authentication failed with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFED.
In short, this happens because KDC issued a ticket encrypted using password of account A, but on the service side, it tries to decrypt this using the password of account B.
Common cause for this are duplicated SPN, wrong DNS settings, two computers in different domains have the same name, client requests wrong SPN. And from IIS 7, it may due to the wrong setting of IIS (kernel/user mode authentication).
Collect data and identify the cause of Kerberos failure
Tools Used to collect data
- 1. Registry Editor(build in tool)
- 2. KList(build in for Windows 2008+)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh134826(WS.10).aspx
- 3. Ipconfig (build in tool).
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd197434(WS.10).aspx
- 4. Network Monitor
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=4865
Steps to collect data
- 1. Enable Kerberos log on both client machine.
262177 How to enable Kerberos event logging
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;262177
- 2. Open a command console with elevated privilege, and run “klist purge” to clear cached Kerberos tickets.
- 3. Run “ipconfig /flushdns” to clear DNS cache.
- 4. Run Network monitor on both client and web server.
- 5. Reproduce the problem.
- 1. Network Monitor Trace
Identify the Kerberos error
By expanding the authenticate field in the HTTP response header returned by IIS, we could locate the reason for Kerberos authentication error.
— Http: Response, HTTP/1.1, Status: Unauthorized, URL: / , Using GSS-API Authentication
ProtocolVersion: HTTP/1.1
StatusCode: 401, Unauthorized
Reason: Unauthorized
…
— WWWAuthenticate: Negotiate …
— Authenticate: Negotiate oWwwaqADCgEBomMEYWBfBgkqhkiG9xIBAgIDAH5QME6abcdIBBaEDAgEepBEYDzIwMTExMabcd0MDUxMDE0WqUabcd2mAwIBKakKGwhURVNULkNPTaoXMBWgAwIBAaEOMAwbCmNvbnRvc29zdmM=
WhiteSpace:
— NegotiateAuthorization:
Scheme: Negotiate
— GssAPI: 0x1
— NegotiationToken:
— ChoiceTag:
— NegTokenResp:
— ResponseToken: 0x1
— KerberosToken: 0x1
— KerberosInitToken:
…
— InnerContextToken: 0x1
— KerberosToken: 0x1
TokId: Krb5Error (0x300)
— Error: KRB_ERROR (30)
….
+ ErrorCode: KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED (41)
+ Realm: TEST.COM
+ Sname: contososvc
Date: Fri, 14 Oct 2011 05:10:14 GMT
ContentLength: 341
It would be more straightforward using Wireshark.
- 2. From the system event log of client side, follow event will be logged.
Log Name: System
Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Kerberos
Date: 10/13/2011 10:10:05 PM
Event ID: 4
Task Category: None
Level: Error
Keywords: Classic
User: N/A
Computer: IIS02.test.com
Description:
The Kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED error from the server contososvc. The target name used was HTTP/iis01.test.com. This indicates that the target server failed to decrypt the ticket provided by the client. This can occur when the target server principal name (SPN) is registered on an account other than the account the target service is using. Please ensure that the target SPN is registered on, and only registered on, the account used by the server. This error can also happen when the target service is using a different password for the target service account than what the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) has for the target service account. Please ensure that the service on the server and the KDC are both updated to use the current password. If the server name is not fully qualified, and the target domain (TEST.COM) is different from the client domain (TEST.COM), check if there are identically named server accounts in these two domains, or use the fully-qualified name to identify the server.
In this event, the SPN used is HTTP/iis01.test.com, and the account used to decrypt the ticket is contososvc. This happens because the account account used to encrypt the ticket is not contososvc.
Scenario 1: Duplicated SPN
In the case of a duplicated SPN, the same SPN was registered on at least two accounts. For example, a SPN was registered on two accounts: A and B. What happens is that KDC will generate a service ticket that may be encrypted with password of account A. Then, when the client sends that ticket to the service during authentication, the service may try to decrypt this using account B.
Detect duplicated SPN using setspn
On Windows 2008 and later, detect duplicated SPN is easier. Since Windows Server 2008, the setspn itself includes a feature to search SPNs.
Besides HTTP/ SPN, please remember to check HOST/ SPN as well. HOST/ SPN will be used as a failover/alternative if HTTP/ SPN does not exist. In case of this scenario, wrong HOST/ SPN will result in Kerberos failure as well.
Here is a sample output of setspn on Windows Server 2008 SP2. For more details about this tool, please reference this document.
SetSPN
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731241(WS.10).aspx
Find duplicated SPN using ldifde
For Windows 2003 and XP, we can use another tool named ldifde to search duplicated SPN. Here is a sample query for HTTP/contoso. Please remember, don’t forget HOST/ SPN as well.
Here is an example output of ldifde, for more details about this tool, please reference follow document.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731033(WS.10).aspx
The SPN is forest-wide object, it has to be unique inside the whole domain. For a complex environment, using follow command to search the entire forest, like this:
Ldifde -s GCName -t 3268 -f d:spn.ldf -d “dc=test, dc=com” –l ServicePrincipleName –r “(ServicePrincipalName=HTTP/contoso)”
In addition, we can use a wild card search like this:
Ldifde -s GCName -t 3268 –f d:spn.ldf -d “dc=test, dc=com” -l servicePrincipalName -r (servicePrincipalName=*contoso*)
Scenario 2: Internet Explorer (or other client) requested ticket for wrong SPN
This is a specific scenario which most related to the behavior of client. This problem occurs if the Web site uses a CNAME resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS). For example, the DNS setting looks like this:
Contoso CNAME iis01.test.com
iis01.test.com A 10.0.5.2
When you use Internet Explorer to access the Web site, Internet Explorer uses the host name of the server ((IIS01)) instead of the CNAME resource record(Contoso) to contact the server. The authentication may fail with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED.
HTTP/Contoso.test.com Registered on testcontososvc
HOST/IIS01.test.com Registered on testiis01(machine account)
Identify this scenario from Network Monitor trace.
- 1. IE sends request to http://contoso, and a DNS query for contoso was sent.
+ Ipv4: src=10.0.5.3, Dest = 10.0.5.1, Next Protocol = UDP, Packet ID = 9717, Total IP Length = 62
+ Udp: SrcPort = 64506, DstPort = DNS(53), Length = 42
— Dns: QueryId = 0x4BB1, QUERY (Standard query), Query for contoso.test.com of type Host Addr on class Internet
…..
- 2. DNS response for contoso
+ Ipv4: src=10.0.5.1, Dest = 10.0.5.3, Next Protocol = UDP, Packet ID = 6526, Total IP Length = 98
+ Udp: SrcPort = DNS(53), DstPort = 64506, Length = 78
— Dns: QueryId = 0x4BB1, QUERY (Standard query), Response — Success, 49, 0
QueryIdentifier: 19377 (0x4BB1)
…..
— ARecord: contoso.test.com of type CNAME on class Internet: iis01.test.com
— ARecord: iis01.test.com of type Host Addr on class Internet: 10.0.5.2
….
- 3. TGS ticket request, IE requests SPN for : HTTP/iis01.test.com instead of expected HTTP/contoso.test.com
+ Ipv4: src=10.0.5.3, Dest = 10.0.5.1, Next Protocol = TCP, Packet ID = 9728, Total IP Length = 0
+ Tcp: Flags=…AP…, SrcPort=50044, DstPort=Kerberos(88), PayloadLen=1488, Seq=4106960882 — 4106962370, Ack=354586390, Win=513 (scale factor 0x8) = 131328
— Kerberos: TGS Request Realm: TEST.COM Sname: HTTP/iis01.test.com
…
Solutions for CName
- 1. If the client is IE, KB 911149 described the solution for this problem.
Error message in Internet Explorer when you try to access a Web site that requires Kerberos authentication on a Windows XP-based computer: «HTTP Error 401 — Unauthorized: Access is denied due to invalid credentials»
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;911149
- 2. If the client is an application uses System.Net.HttpWebRequest, using CustomTargetNameDictionary.
AuthenticationManager.CustomTargetNameDictionary
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.net.authenticationmanager.customtargetnamedictionary.aspx
- 3. On DNS server side, configure the IIS server to a host record (A) instead of Alias(CNAME).
Scenario 3: SPN set to unexpected account (Wrong IIS 7+ authentication settings)
Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.0 enables kernel mode authentication by default. Kernel mode authentication runs under the machine account no matter what account is used to run the application pool. The machine account is used to decrypt the Kerberos ticket.
However, there are some scenarios you need to use a domain service account for authentication process instead of machine account. For example, a web arm scenario.
For this scenario, Instead of disabling kernel mode authentication in IIS, you can configure IIS to use the Web application pool’s identity for authentication (by setting useAppPoolCredentials=»true»).
For IIS 7+, we have 3 Windows authentication configuration. Different scenario requires register SPN on different accounts. In the scenario of improper SPN and IIS 7 configuration, it may result in authentication failure with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED if the SPN was set to unexpected account.
- · Kernel mode authentication disabled
- · Kernel mode authentication enabled, useAppPoolCredentials
- · Kernel mode authentication enabled
NOTE: Machine account includes all accounts can represent the machine on network including Network Service, Local System, Local Service and ApplicationPoolIdentity for IIS 7+. Service accounts means a domain account used as the application pool identity.
Here, I listed couple of scenarios which can result in Kerberos authentication failed with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED.
Scenarios result in KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED
Wrong Configuration Scenario 1
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
Web Site Binding To |
IIS server’s NetBIOS Name. Access like this way: http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN |
HTTP/ SPN registered on service account |
|
Comments |
For this scenario, the Kerberos ticket is encrypted by service account, and is decrypted by IIS server’s computer account. |
Wrong Configuration Scenario 2
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
Web Site Binding To |
A customized host header. Access like this way: http(s)://Contoso |
|
SPN |
HTTP/ SPN registered on service account |
|
Comments |
For this scenario, the Kerberos ticket is encrypted by service account, and decrypted by IIS server’s computer account. |
Wrong Configuration Scenario 3
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
True |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
Web Site Binding To |
IIS server’s NetBIOS Name. Access like this way: http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN |
HTTP/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name doesn’t registered on any account Or, registered on IIS server’s computer account |
|
Comments |
For this scenario, the Kerberos ticket is encrypted by IIS server’s computer account, and decrypted by service account. |
SPN and IIS configuration reference
Scenario 1
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
No Matter |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN requirement |
No HTTP/ SPN required. By default, the HOST/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name will be used. If you want, you can register HTTP/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name on the server name. |
|
Comments |
This is the default scenario for IIS 7+ when using IIS server’s computer name to access the web application. |
Scenario 2
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
No Matter |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on IIS server’s computer account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME IIS_SRV_NetBIOS |
|
Comments |
Some application requires this when they need special permission for application pool identity. |
Scenario 3
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
True |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
|
Scenario 4
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
True |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/IIS_SERVER_FQDN domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
You need select this scenario if you want web site binding to IIS server’s computer name and running the site with a domain account. |
Scenario 5
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
This is same for IIS 6 scenario. |
Scenario 6
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_SERVER_NetBIOS_NAME |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/ IIS_SERVER_NetBIOS_NAME domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
This is same for IIS 6 scenario. |
Scenario 7
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Machine Account |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on IIS server’s computer account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME IIS_SRV_NetBIOS |
|
Comments |
This is same for IIS 6 scenario. |
Scenario 8
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Machine Account |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_SERVER_NetBIOS_NAME |
|
SPN requirement |
No HTTP/ SPN required. By default, the HOST/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name will be used. If you want, you can register HTTP/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name on the server name. |
|
Comments |
This is similar to the default scenario of IIS 6. |
Author : Wei

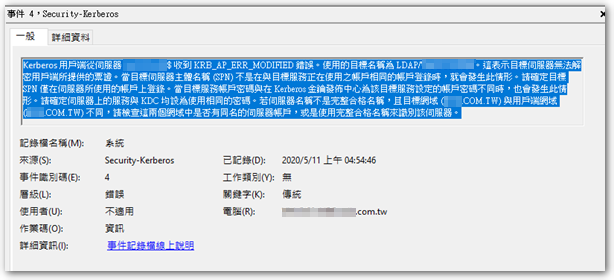
在檢查事件紀錄後,找到一項可能有相關的紀錄:
Kerberos 用戶端從伺服器 xxx$ 收到 KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED 錯誤。使用的目標名稱為 LDAP/xxx。這表示目標伺服器無法解密用戶端所提供的票證。當目標伺服器主體名稱 (SPN) 不是在與目標服務正在使用之帳戶相同的帳戶登錄時,就會發生此情形。請確定目標 SPN 僅在伺服器所使用的帳戶上登錄。當目標服務帳戶密碼與在 Kerberos 金鑰發佈中心為該目標服務設定的帳戶密碼不同時,也會發生此情形。請確定伺服器上的服務與 KDC 均設為使用相同的密碼。若伺服器名稱不是完整合格名稱,且目標網域 (xxx.COM.TW) 與用戶端網域 (xxx.COM.TW) 不同,請檢查這兩個網域中是否有同名的伺服器帳戶,或是使用完整合格名稱來識別該伺服器。
上網搜尋文章後,找到「Jason的電腦健身房」的 這篇 文章,解決方式是去重設事件紀錄中所提到的問題 DC 的 administrator 密碼 (machine account password)。另外在「MIS 的背影」的 這篇 文章下方的問答有網友提到,發生這個問題環境,好像是因為 DC 從 2003 升到 2016 後才遇到,而我們也是相同環境。就該網友提供的 微軟文章 來看,簡單來說是因為 2012 R2 以後的 Windows 是使用 AES 加密方式,但 2003 不支援;而 2012 R2 也不支援舊的 DES 加密方式所造成。而該文章的最新更新有提到後來已經有釋出 hotfix 檔,不過我實際要安裝時,會出現我環境不符合的訊息,因此我仍是以指令重設密碼的方式來解決,步驟如下:
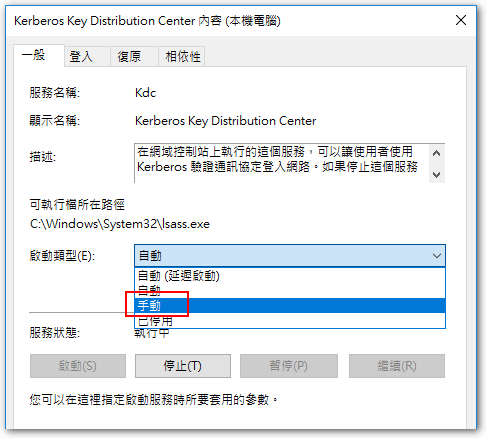
◎ 將目標 DC 伺服器上「Kerberos Key Distribution Center」服務的「啟動類型」改成 “手動”,接著重開機。
◎ 以系統管理員身分執行下列指令:
netdom resetpwd /server:DC電腦名稱 /ud:網域名稱administrator /pd:administrator的密碼
◎ 再次重開機,重開完將「Kerberos Key Distribution Center」服務的「啟動類型」改成 “自動” 即可。
另外,如果你的「網域功能等級」是 2003,而 User 作業系統是 Windows 8 以上,當 User 登入時出現密碼錯誤,而事件紀錄也跟上面描述的一樣,此應為兩者的版本差距過大的問題,可試著藉由提昇「網域功能等級」到 2008 以上來解決此問題。
【參考連結】
- Kerberos 用戶端從伺服器 XXX$ 收到 KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED 錯誤 | Jason的電腦健身房 – 點部落
- 無法使用網域帳戶登入Server (Event id 4)Kerberos 用戶端從伺服器 XXX$ 收到 KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED 錯誤 | MIS的背影
- It turns out that weird things can happen when you mix Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2012 R2 domain controllers | Microsoft Docs
- 如何使用 Netdom.exe 重設 Windows Server 網域控制站的機器帳戶密碼
- 目標帳戶名稱不正確,這應該是AD的問題目標帳戶名稱不正確,這應該是AD的問題 – iT 邦幫忙::一起幫忙解決難題,拯救 IT 人的一天
This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: IIS Support Blog articles.
KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED is a common Kerberos failure message. This means some encrypted Kerberos authentication data sent by the client did not decrypt properly at the server.
When a Kerberos client requests a ticket for a specific service, the service is actually identified by its SPN. The KDC grants the client a service ticket that is encrypted using service’s secret key. Basically, the AD account password that that matches the SPN requested.
Under some scenarios, KDC may generate a service ticket that encrypted with password of a wrong account (or not expected one). Then, when client provide that ticket to the service for authentication, the service can’t decrypt it and authentication failed with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFED.
In short, this happens because KDC issued a ticket encrypted using password of account A, but on the service side, it tries to decrypt this using the password of account B.
Common cause for this are duplicated SPN, wrong DNS settings, two computers in different domains have the same name, client requests wrong SPN. And from IIS 7, it may due to the wrong setting of IIS (kernel/user mode authentication).
Collect data and identify the cause of Kerberos failure
Tools Used to collect data
- 1. Registry Editor(build in tool)
- 2. KList(build in for Windows 2008+)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh134826(WS.10).aspx
- 3. Ipconfig (build in tool).
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd197434(WS.10).aspx
- 4. Network Monitor
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=4865
Steps to collect data
- 1. Enable Kerberos log on both client machine.
262177 How to enable Kerberos event logging
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;262177
- 2. Open a command console with elevated privilege, and run “klist purge” to clear cached Kerberos tickets.
- 3. Run “ipconfig /flushdns” to clear DNS cache.
- 4. Run Network monitor on both client and web server.
- 5. Reproduce the problem.
- 1. Network Monitor Trace
Identify the Kerberos error
By expanding the authenticate field in the HTTP response header returned by IIS, we could locate the reason for Kerberos authentication error.
— Http: Response, HTTP/1.1, Status: Unauthorized, URL: / , Using GSS-API Authentication
ProtocolVersion: HTTP/1.1
StatusCode: 401, Unauthorized
Reason: Unauthorized
…
— WWWAuthenticate: Negotiate …
— Authenticate: Negotiate oWwwaqADCgEBomMEYWBfBgkqhkiG9xIBAgIDAH5QME6abcdIBBaEDAgEepBEYDzIwMTExMabcd0MDUxMDE0WqUabcd2mAwIBKakKGwhURVNULkNPTaoXMBWgAwIBAaEOMAwbCmNvbnRvc29zdmM=
WhiteSpace:
— NegotiateAuthorization:
Scheme: Negotiate
— GssAPI: 0x1
— NegotiationToken:
— ChoiceTag:
— NegTokenResp:
— ResponseToken: 0x1
— KerberosToken: 0x1
— KerberosInitToken:
…
— InnerContextToken: 0x1
— KerberosToken: 0x1
TokId: Krb5Error (0x300)
— Error: KRB_ERROR (30)
….
+ ErrorCode: KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED (41)
+ Realm: TEST.COM
+ Sname: contososvc
Date: Fri, 14 Oct 2011 05:10:14 GMT
ContentLength: 341
It would be more straightforward using Wireshark.
- 2. From the system event log of client side, follow event will be logged.
Log Name: System
Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Kerberos
Date: 10/13/2011 10:10:05 PM
Event ID: 4
Task Category: None
Level: Error
Keywords: Classic
User: N/A
Computer: IIS02.test.com
Description:
The Kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED error from the server contososvc. The target name used was HTTP/iis01.test.com. This indicates that the target server failed to decrypt the ticket provided by the client. This can occur when the target server principal name (SPN) is registered on an account other than the account the target service is using. Please ensure that the target SPN is registered on, and only registered on, the account used by the server. This error can also happen when the target service is using a different password for the target service account than what the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) has for the target service account. Please ensure that the service on the server and the KDC are both updated to use the current password. If the server name is not fully qualified, and the target domain (TEST.COM) is different from the client domain (TEST.COM), check if there are identically named server accounts in these two domains, or use the fully-qualified name to identify the server.
In this event, the SPN used is HTTP/iis01.test.com, and the account used to decrypt the ticket is contososvc. This happens because the account account used to encrypt the ticket is not contososvc.
Scenario 1: Duplicated SPN
In the case of a duplicated SPN, the same SPN was registered on at least two accounts. For example, a SPN was registered on two accounts: A and B. What happens is that KDC will generate a service ticket that may be encrypted with password of account A. Then, when the client sends that ticket to the service during authentication, the service may try to decrypt this using account B.
Detect duplicated SPN using setspn
On Windows 2008 and later, detect duplicated SPN is easier. Since Windows Server 2008, the setspn itself includes a feature to search SPNs.
Besides HTTP/ SPN, please remember to check HOST/ SPN as well. HOST/ SPN will be used as a failover/alternative if HTTP/ SPN does not exist. In case of this scenario, wrong HOST/ SPN will result in Kerberos failure as well.
Here is a sample output of setspn on Windows Server 2008 SP2. For more details about this tool, please reference this document.
SetSPN
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731241(WS.10).aspx
Find duplicated SPN using ldifde
For Windows 2003 and XP, we can use another tool named ldifde to search duplicated SPN. Here is a sample query for HTTP/contoso. Please remember, don’t forget HOST/ SPN as well.
Here is an example output of ldifde, for more details about this tool, please reference follow document.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731033(WS.10).aspx
The SPN is forest-wide object, it has to be unique inside the whole domain. For a complex environment, using follow command to search the entire forest, like this:
Ldifde -s GCName -t 3268 -f d:spn.ldf -d “dc=test, dc=com” –l ServicePrincipleName –r “(ServicePrincipalName=HTTP/contoso)”
In addition, we can use a wild card search like this:
Ldifde -s GCName -t 3268 –f d:spn.ldf -d “dc=test, dc=com” -l servicePrincipalName -r (servicePrincipalName=*contoso*)
Scenario 2: Internet Explorer (or other client) requested ticket for wrong SPN
This is a specific scenario which most related to the behavior of client. This problem occurs if the Web site uses a CNAME resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS). For example, the DNS setting looks like this:
Contoso CNAME iis01.test.com
iis01.test.com A 10.0.5.2
When you use Internet Explorer to access the Web site, Internet Explorer uses the host name of the server ((IIS01)) instead of the CNAME resource record(Contoso) to contact the server. The authentication may fail with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED.
HTTP/Contoso.test.com Registered on testcontososvc
HOST/IIS01.test.com Registered on testiis01(machine account)
Identify this scenario from Network Monitor trace.
- 1. IE sends request to http://contoso, and a DNS query for contoso was sent.
+ Ipv4: src=10.0.5.3, Dest = 10.0.5.1, Next Protocol = UDP, Packet ID = 9717, Total IP Length = 62
+ Udp: SrcPort = 64506, DstPort = DNS(53), Length = 42
— Dns: QueryId = 0x4BB1, QUERY (Standard query), Query for contoso.test.com of type Host Addr on class Internet
…..
- 2. DNS response for contoso
+ Ipv4: src=10.0.5.1, Dest = 10.0.5.3, Next Protocol = UDP, Packet ID = 6526, Total IP Length = 98
+ Udp: SrcPort = DNS(53), DstPort = 64506, Length = 78
— Dns: QueryId = 0x4BB1, QUERY (Standard query), Response — Success, 49, 0
QueryIdentifier: 19377 (0x4BB1)
…..
— ARecord: contoso.test.com of type CNAME on class Internet: iis01.test.com
— ARecord: iis01.test.com of type Host Addr on class Internet: 10.0.5.2
….
- 3. TGS ticket request, IE requests SPN for : HTTP/iis01.test.com instead of expected HTTP/contoso.test.com
+ Ipv4: src=10.0.5.3, Dest = 10.0.5.1, Next Protocol = TCP, Packet ID = 9728, Total IP Length = 0
+ Tcp: Flags=…AP…, SrcPort=50044, DstPort=Kerberos(88), PayloadLen=1488, Seq=4106960882 — 4106962370, Ack=354586390, Win=513 (scale factor 0x8) = 131328
— Kerberos: TGS Request Realm: TEST.COM Sname: HTTP/iis01.test.com
…
Solutions for CName
- 1. If the client is IE, KB 911149 described the solution for this problem.
Error message in Internet Explorer when you try to access a Web site that requires Kerberos authentication on a Windows XP-based computer: «HTTP Error 401 — Unauthorized: Access is denied due to invalid credentials»
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;911149
- 2. If the client is an application uses System.Net.HttpWebRequest, using CustomTargetNameDictionary.
AuthenticationManager.CustomTargetNameDictionary
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.net.authenticationmanager.customtargetnamedictionary.aspx
- 3. On DNS server side, configure the IIS server to a host record (A) instead of Alias(CNAME).
Scenario 3: SPN set to unexpected account (Wrong IIS 7+ authentication settings)
Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.0 enables kernel mode authentication by default. Kernel mode authentication runs under the machine account no matter what account is used to run the application pool. The machine account is used to decrypt the Kerberos ticket.
However, there are some scenarios you need to use a domain service account for authentication process instead of machine account. For example, a web arm scenario.
For this scenario, Instead of disabling kernel mode authentication in IIS, you can configure IIS to use the Web application pool’s identity for authentication (by setting useAppPoolCredentials=»true»).
For IIS 7+, we have 3 Windows authentication configuration. Different scenario requires register SPN on different accounts. In the scenario of improper SPN and IIS 7 configuration, it may result in authentication failure with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED if the SPN was set to unexpected account.
- · Kernel mode authentication disabled
- · Kernel mode authentication enabled, useAppPoolCredentials
- · Kernel mode authentication enabled
NOTE: Machine account includes all accounts can represent the machine on network including Network Service, Local System, Local Service and ApplicationPoolIdentity for IIS 7+. Service accounts means a domain account used as the application pool identity.
Here, I listed couple of scenarios which can result in Kerberos authentication failed with KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED.
Scenarios result in KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED
Wrong Configuration Scenario 1
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
Web Site Binding To |
IIS server’s NetBIOS Name. Access like this way: http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN |
HTTP/ SPN registered on service account |
|
Comments |
For this scenario, the Kerberos ticket is encrypted by service account, and is decrypted by IIS server’s computer account. |
Wrong Configuration Scenario 2
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
Web Site Binding To |
A customized host header. Access like this way: http(s)://Contoso |
|
SPN |
HTTP/ SPN registered on service account |
|
Comments |
For this scenario, the Kerberos ticket is encrypted by service account, and decrypted by IIS server’s computer account. |
Wrong Configuration Scenario 3
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
True |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
Web Site Binding To |
IIS server’s NetBIOS Name. Access like this way: http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN |
HTTP/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name doesn’t registered on any account Or, registered on IIS server’s computer account |
|
Comments |
For this scenario, the Kerberos ticket is encrypted by IIS server’s computer account, and decrypted by service account. |
SPN and IIS configuration reference
Scenario 1
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
No Matter |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN requirement |
No HTTP/ SPN required. By default, the HOST/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name will be used. If you want, you can register HTTP/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name on the server name. |
|
Comments |
This is the default scenario for IIS 7+ when using IIS server’s computer name to access the web application. |
Scenario 2
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
False(default) |
|
Application Pool Identity |
No Matter |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on IIS server’s computer account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME IIS_SRV_NetBIOS |
|
Comments |
Some application requires this when they need special permission for application pool identity. |
Scenario 3
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
True |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
|
Scenario 4
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Enabled(default) |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
True |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name http(s)://IIS_Server_FQDN |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/IIS_SERVER_FQDN domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
You need select this scenario if you want web site binding to IIS server’s computer name and running the site with a domain account. |
Scenario 5
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
This is same for IIS 6 scenario. |
Scenario 6
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Service Account like (domaincontosoService) |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_SERVER_NetBIOS_NAME |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on service account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/ IIS_SERVER_NetBIOS_NAME domaincontosoService |
|
Comments |
This is same for IIS 6 scenario. |
Scenario 7
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Machine Account |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://Customer_Host_Name |
|
SPN requirement |
Need register SPN on IIS server’s computer account, like: SetSPN -a HTTP/Customer_Host_NAME IIS_SRV_NetBIOS |
|
Comments |
This is same for IIS 6 scenario. |
Scenario 8
|
Kernel Mode Authentication |
Disabled |
|
useAppPoolCredentials |
No Matter |
|
Application Pool Identity |
Machine Account |
|
URL used to access web site |
http(s)://IIS_SERVER_NetBIOS_NAME |
|
SPN requirement |
No HTTP/ SPN required. By default, the HOST/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name will be used. If you want, you can register HTTP/ IIS_Server_NetBIOS_Name on the server name. |
|
Comments |
This is similar to the default scenario of IIS 6. |
Author : Wei
Hi,
We are getting this error from some servers in our environment when trying to connect to a SQL Server, but not from all (so, we do have some that are able to connect fine to it)
The Kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED error from the server <SQLServiceAccount>. The target name used was MSSQLSvc/<SQLServerName-FQDN>:1433. This indicates that the target server failed to decrypt the ticket provided by the client.
This can occur when the target server principal name (SPN) is registered on an account other than the account the target service is using. Ensure that the target SPN is only registered on the account used by the server. This error can also happen if the target
service account password is different than what is configured on the Kerberos Key Distribution Center for that target service. Ensure that the service on the server and the KDC are both configured to use the same password. If the server name is not fully qualified,
and the target domain (<Domain>) is different from the client domain (<Domain>), check if there are identically named server accounts in these two domains, or use the fully-qualified name to identify the server.
Details:
| Server | <SQLServiceAccount> |
| Targetname | MSSQLSvc/<SQLServerName-FQDN>:1433 |
We are trying to test using an UDL File, and when Kerberos Logging is enabled, we are seeing this (Source: Security-Kerberos, Event 3):
A Kerberos error message was received:
on logon session
Client Time:
Server Time: 15:0:15.0000 1/8/2019 Z
Error Code: 0x29 KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED
Extended Error:
Client Realm:
Client Name:
Server Realm: <Domain>
Server Name: <SQLServiceAccount>
Target Name:
Error Text:
File: 3
Line: 587
Error Data is in record data.
SPNs look ok when checking with the Kerberos Configuration Troubleshooting tool (and the fact that other servers in the same environment are working (there are multiple working, and multiple failing)… All are in the same domain (single domain environment)..
and all of them are able to talk to other SQL Servers that coexist with the problematic one.
Any ideas/suggestions, on what I can look at next to troubleshoot this?