Появление сообщения об ошибке 401 Unauthorized Error («отказ в доступе») при открытии страницы сайта означает неверную авторизацию или аутентификацию пользователя на стороне сервера при обращении к определенному url-адресу. Чаще всего она возникает при ошибочном вводе имени и/или пароля посетителем ресурса при входе в свой аккаунт. Другой причиной являются неправильные настройки, допущенные при администрировании web-ресурса. Данная ошибка отображается в браузере в виде отдельной страницы с соответствующим описанием. Некоторые разработчики интернет-ресурсов, в особенности крупных порталов, вводят собственную дополнительную кодировку данного сбоя:
- 401 Unauthorized;
- Authorization Required;
- HTTP Error 401 – Ошибка авторизации.
Попробуем разобраться с наиболее распространенными причинами возникновения данной ошибки кода HTTP-соединения и обсудим способы их решения.
Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
При доступе к некоторым сайтам (или отдельным страницам этих сайтов), посетитель должен пройти определенные этапы получения прав:
- Идентификация – получение вашей учетной записи («identity») по username/login или email.
- Аутентификация («authentic») – проверка того, что вы знаете пароль от этой учетной записи.
- Авторизация – проверка вашей роли (статуса) в системе и решение о предоставлении доступа к запрошенной странице или ресурсу на определенных условиях.
Большинство пользователей сохраняют свои данные по умолчанию в истории браузеров, что позволяет быстро идентифицироваться на наиболее часто посещаемых страницах и синхронизировать настройки между устройствами. Данный способ удобен для серфинга в интернете, но может привести к проблемам с безопасностью доступа к конфиденциальной информации. При наличии большого количества авторизованных регистрационных данных к различным сайтам используйте надежный мастер-пароль, который закрывает доступ к сохраненной в браузере информации.
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления ошибки с кодом 401 для рядового пользователя является ввод неверных данных при посещении определенного ресурса. В этом и других случаях нужно попробовать сделать следующее:
- Проверьте в адресной строке правильность написания URL. Особенно это касается перехода на подстраницы сайта, требующие авторизации. Введите правильный адрес. Если переход на страницу осуществлялся после входа в аккаунт, разлогинитесь, вернитесь на главную страницу и произведите повторный вход с правильными учетными данными.
- При осуществлении входа с сохраненными данными пользователя и появлении ошибки сервера 401 проверьте их корректность в соответствующих настройках данного браузера. Возможно, авторизационные данные были вами изменены в другом браузере. Также можно очистить кэш, удалить cookies и повторить попытку входа. При удалении истории браузера или очистке кэша потребуется ручное введение логина и пароля для получения доступа. Если вы не помните пароль, пройдите процедуру восстановления, следуя инструкциям.
- Если вы считаете, что вводите правильные регистрационные данные, но не можете получить доступ к сайту, обратитесь к администратору ресурса. В этом случае лучше всего сделать скриншот проблемной страницы.
- Иногда блокировка происходит на стороне провайдера, что тоже приводит к отказу в доступе и появлению сообщения с кодировкой 401. Для проверки можно попробовать авторизоваться на том же ресурсе с альтернативного ip-адреса (например, используя VPN). При подтверждении блокировки трафика свяжитесь с провайдером и следуйте его инструкциям.
Некоторые крупные интернет-ресурсы с большим количеством подписчиков используют дополнительные настройки для обеспечения безопасности доступа. К примеру, ваш аккаунт может быть заблокирован при многократных попытках неудачной авторизации. Слишком частые попытки законнектиться могут быть восприняты как действия бота. В этом случае вы увидите соответствующее сообщение, но можете быть просто переадресованы на страницу с кодом 401. Свяжитесь с администратором сайта и решите проблему.
Иногда простая перезагрузка проблемной страницы, выход из текущей сессии или использование другого веб-браузера полностью решают проблему с 401 ошибкой авторизации.
Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
Для владельцев сайтов, столкнувшихся с появлением ошибки отказа доступа 401, решить ее порою намного сложнее, чем обычному посетителю ресурса. Есть несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут в этом:
- Обращение в службу поддержки хостинга сайта. Как и в случае возникновения проблем с провайдером, лучше всего подробно описать последовательность действий, приведших к появлению ошибки 401, приложить скриншот.
- При отсутствии проблем на стороне хостинг-провайдера можно внести следующие изменения в настройки сайта с помощью строки Disallow:/адрес проблемной страницы. Запретить индексацию страницам с ошибкой в «rоbоts.txt», после чего добавить в файл «.htассеss» строку такого типа:
Redirect 301 /oldpage.html http://site.com/newpage.html.
Где в поле /oldpage.html прописывается адрес проблемной страницы, а в http://site.com/newpage.html адрес страницы авторизации.
Таким образом вы перенаправите пользователей со всех страниц, которые выдают ошибку 401, на страницу начальной авторизации.
- Если после выполнения предыдущих рекомендаций пользователи при попытках авторизации все равно видят ошибку 401, то найдите на сервере файл «php.ini» и увеличьте время жизни сессии, изменив значения следующих параметров: «session.gc_maxlifetime» и «session.cookie_lifetime» на 1440 и 0 соответственно.
- Разработчики веб-ресурсов могут использовать более сложные методы авторизации и аутентификации доступа для создания дополнительной защиты по протоколу HTTP. Если устранить сбой простыми методами администрирования не удается, следует обратиться к специалистам, создававшим сайт, для внесения соответствующих изменений в код.
Хотя ошибка 401 и является проблемой на стороне клиента, ошибка пользователя на стороне сервера может привести к ложному требованию входа в систему. К примеру, сетевой администратор разрешит аутентификацию входа в систему всем пользователям, даже если это не требуется. В таком случае сообщение о несанкционированном доступе будет отображаться для всех, кто посещает сайт. Баг устраняется внесением соответствующих изменений в настройки.
Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительные данные об ошибке 401 Unauthorized в виде второго ряда цифр:
- 401, 1 – войти не удалось;
- 401, 2 – ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера;
- 401, 3 – несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс;
- 401, 501 – доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов и т.д.
Более подробную информацию об ошибке сервера 401 при использовании обычной проверки подлинности для подключения к веб-узлу, который размещен в службе MS IIS, смотрите здесь.
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке:
- 400 Bad Request;
- 403 Forbidden;
- 404 Not Found;
- 408 Request Timeout.
Как видим, появление ошибки авторизации 401 Unauthorized не является критичным для рядового посетителя сайта и чаще всего устраняется самыми простыми способами. В более сложной ситуации оказываются администраторы и владельцы интернет-ресурсов, но и они в 100% случаев разберутся с данным багом путем изменения настроек или корректировки html-кода с привлечением разработчика сайта.
Trying to access a site and being met with an error page is at best inconvenient, whether that site is yours or someone else’s. As with many HTTP response codes, part of what makes a 401 error so frustrating is the lack of information it offers for diagnosing and resolving the issue.
The 401 error can happen with any browser, so it’s a pretty common issue people face. In most cases, this problem is relatively simple and straightforward to fix.
In this post, we’ll explain what 401 error messages are and why they happen. Then, we’ll walk you through five methods you can use to fix them.
Let’s get started!
What is the 401 Error Code?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the error 401 Unauthorized as:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
An Introduction to the 401 Error Code
HTTP 400 status codes are encountered when there is a problem making a request. A 401 error, in particular, happens when your browser denies you access to the page you’re trying to visit.
As a result, instead of loading the web page, the browser will load an error message. 401 errors can happen within any browser so the message appearing may differ.
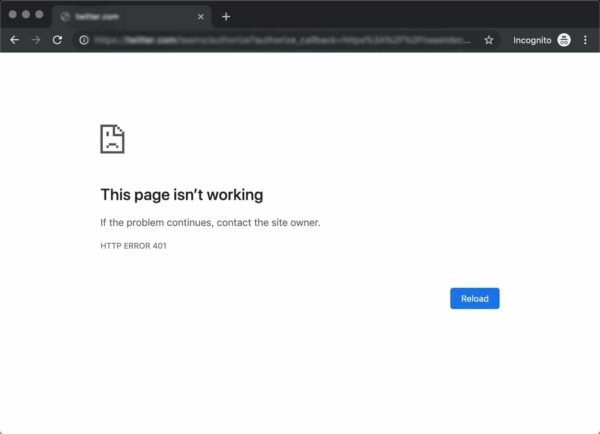
For example, in Chrome or Edge, you’ll likely see a paper icon along with a simple message telling you that the page in question isn’t working. It will include the phrase “HTTP Error 401” at the bottom, and instruct you to contact the site’s owner if the problem persists:
At other times and in other browsers, you might get a slightly less friendly warning that’s just a blank page with a “401 Authorization Required” message:
Other variations include:
- “HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized”
- “401 Unauthorized”
- “Access Denied”
These errors occur on websites that require a login in order to access them. In most cases, it means that something is either wrong with the credentials or with the browser’s ability to read them as valid.
This is similar to HTTP 403 Forbidden Error, in that access isn’t permitted to the user. However, unlike with the 403 error, the 401 error message indicates that the authentication process failed.
The code is sent via the WWW-Authenticate header, which is responsible for identifying the authentication method used for granting access to a web page or resource.
| Error Code | HTTP 401 Unauthorized Error |
| Error Type | Commonly a client-side error |
| Error Variations | 401 Authorization Required 401 Unauthorized HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized Access Denied |
| Error Causes | Outdated Browser Cache and Cookies Plugin Incompatibility Incorrect URL or Outdated Link |
The HTTP 401 error is all too common 🤦♀️ — and this guide will give you everything you need to fix it the next time you see that message showing up ✅Click to Tweet
What Causes a 401 Error?
If you encounter an error code in the 400s, you know you’re dealing with a client-side (or browser-side) issue. While the problem may be happening within your browser, however, it doesn’t necessarily always mean that’s the culprit, which we’ll explain in more detail later.
401 errors occur on restricted resources, such as password-protected pages of your WordPress site. So it’s safe to assume that the cause of the problem has something to do with the authentication credentials.
Outdated Browser Cache and Cookies
One of the most common reasons you might experience a 401 error is that your browser’s cache and cookies are out of date, preventing the authorization from successfully going through. If your browser isn’t using the valid authentication credentials (or any at all), the server will reject the request.
Plugin Incompatibility
At other times, this error is caused by a plugin incompatibility or error. For example, a firewall or security plugin can mistake your login attempt as malicious activity, and return a 401 error to protect the page.
Incorrect URL or Outdated Link
It’s also possible that the source of the problem can be attributed to a minor mistake. Common culprits in this category include an incorrectly-typed URL or an outdated link.
How to Fix the 401 Error?
Now that we’ve gone through a bit of background on the 401 error, it’s time to discuss how you can resolve it.
Let’s take a look at five methods you can use:
1. Look for Errors in the URL
We’ll start off with the easiest potential fix: making sure you used the correct URL. This may sound simple, but 401 errors can sometimes appear if the URL wasn’t correctly entered in.
Another possibility is that the link you used to visit the page in question points to the wrong URL. For example, it might be outdated, or leading to a page that no longer exists (and no redirects are in place).
Therefore, it’s worth double-checking the URL you used. If you typed it in yourself, verify that you spelled everything correctly. If you clicked on a link, confirm that it’s pointing to the page you’re trying to access (or try to visit that page directly through the website).
2. Clear Your Browser’s Cache
Your browser’s cache is designed to improve your online experience, by reducing page loading times. Unfortunately, sometimes it can also cause unwanted interruptions.
As we mentioned earlier, one of the common causes of the 401 error is outdated or incorrect cache data or cookies. Therefore, if you don’t notice any issues with the page’s URL, the next step is to clear your browser’s cache.
This will clean out any invalid information that’s locally stored in your browser, which could be interrupting the authentication process. Similarly, your browser’s cookies might contain authentication data that simply needs to be refreshed.
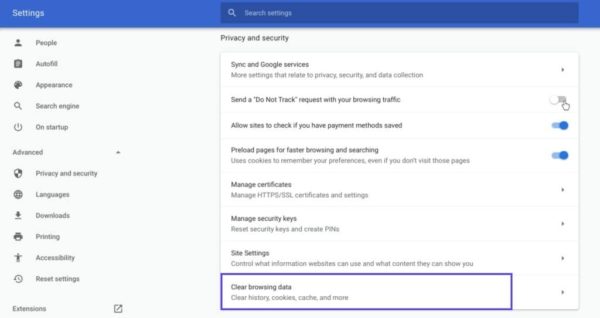
If you’re a Google Chrome user, you can do this by clicking on the menu icon in the top-right corner of the browser, and then going to Settings. Under the Privacy and security section, click on Clear browsing data:
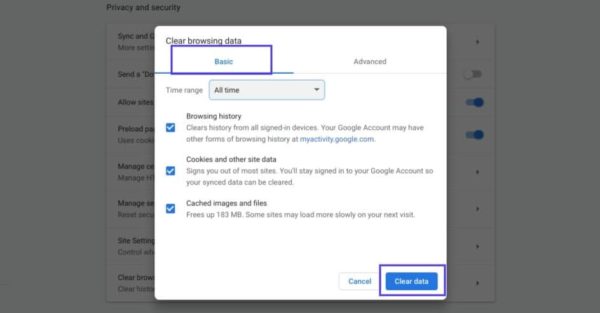
A new window will open. Under the Basic tab, make sure all three boxes are selected, and then select Clear data:
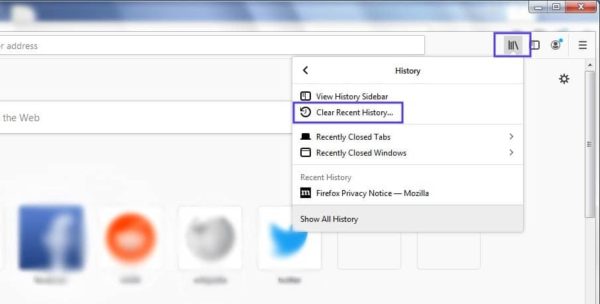
This process will look a little different in other browsers. For example, in Mozilla Firefox, you would click on the library icon in the top-right corner of the browser, followed by History > Clear Recent History:
In the panel that opens next, select Everything in the drop-down menu at the top, make sure “Cache” is selected, and then click on the Clear Now button:
If you’re using a different browser, please refer to this guide for clearing the cache
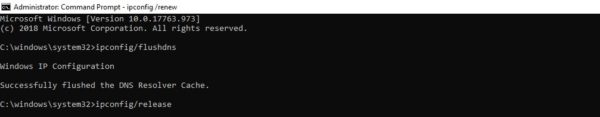
3. Flush Your DNS
Another method you can try to resolve the 401 error is flushing your Domain Name Server (DNS). While this is a rarer issue, it can be a possible cause, so it’s worth giving it a try if the first two solutions don’t work.
To do this in Windows, click on the Start button and type cmd into the search bar. Hit Enter, and the Command Prompt will open. Copy and paste the command ipconfig/flushdns, and then hit Enter again:
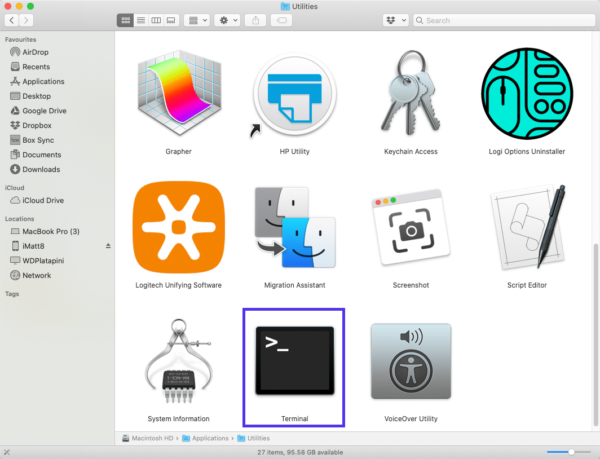
On a Mac, you can do this by going to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal:
Input the command line sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder and press Enter. Then, you can try refreshing the page you were trying to visit, to see if the 401 error has been resolved.
4. Deactivate Your WordPress Plugins
The problem causing your 401 error might not be due to your browser. If you’re having trouble accessing your WordPress site, it’s also possible that one or more plugins are to blame.
Some plugins, especially security-focused plugins, are configured to show a 401 error when they suspect suspicious login activity that might indicate an attack. Others might just be suffering from compatibility issues. Therefore, it’s a good idea to deactivate all of your WordPress plugins and see if that resolves the issue.
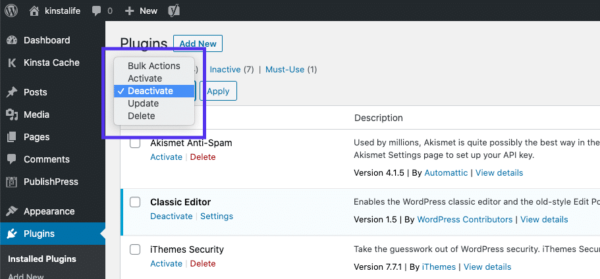
You can deactivate your plugins all at the same time in your dashboard, by going to Plugins > Installed Plugins. Check the box at the top to select all of them. Then under the Bulk Actions drop-down menu, select Deactivate and click on the Apply button:
After that, try reloading the page that returned the 401 error to see if this has resolved the issue. If it has, you can manually activate each plugin one at a time, in order to determine which one is causing the problem.
Then you can remove that plugin, replace it with a new one, or contact its developer for assistance.
5. Check the WWW-Authenticate Header Response
At this point, if the issue hasn’t been fixed, it may be caused by a server-side problem. This means our last fix will be a bit more involved.
As we saw earlier, the 401 response is sent through the WWW-Authenticate header, which appears as “WWW-Authenticate: <type> realm=<realm>”. It includes ‘challenges’, or strings of data that indicate what type of authentication is required in order for access to be granted.
In a nutshell, you’ll want to check and see if the header response was sent, and more specifically, what authentication scheme was used. At the very least, this can help narrow down the cause of the problem, and bring you one step closer to a solution.
To do this, go to the web page that’s displaying the 401 error, and access the developer console in Chrome. You can right-click on the page and select Inspect, or use Ctrl+Shift+J.
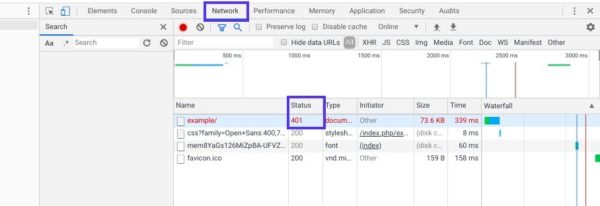
Next, click on the Network tab and reload the page. This will generate a list of resources. Select the Status header to sort the table and locate the 401 status code:
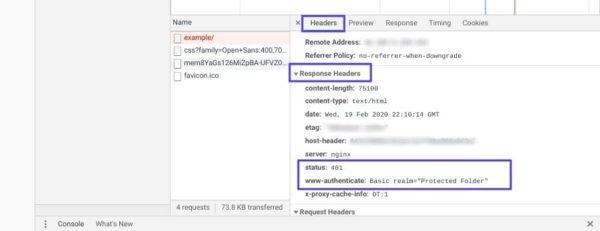
Select that entry, and then click on the Headers tab. Under Response Headers, locate the WWW-Authenticate header:
The information that is present in the response header, particularly the authentication schemes, can give you more information about what’s happening and point you towards a solution. It can help you understand what type of authentication the server is expecting.
For example, in the above example, we can see that the authentication scheme is “Basic”. This means the authentication request should only require an ID and password. For more detailed information and instructions on how to use this information, we recommend referring to the HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry.
HTTP 401 errors, begone! 🧙♂️ 5 ways to stop those pesky messages (no magic required) ✨Click to Tweet
Summary
When your browser and server have trouble communicating or authenticating requests, you’re sometimes forced to deal with errors such as the 401 error. While this problem is irritating, the message is usually temporary and fixable.
Here are five methods you can use to fix the 401 error:
- Look for errors in the URL.
- Clear your browser’s cache.
- Flush your DNS.
- Deactivate your WordPress plugins.
- Check the WWW-Authenticate header response.
I am creating a login page using Laravel API and ReactJS front end. I am using Axios in ReactJS to parse the username(email) and password. The API for login is http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/login which works correctly in postman form-data. But when I entered the email and the password in react front-end the echos is Error: Request failed with status code 401. This error throws by the catch function of axios. I am also using querystring npm also. So which throws this error?
My React JS code
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Button, Card, CardBody, CardGroup, Col, Container, Input, InputGroup, InputGroupAddon, InputGroupText, Row } from 'reactstrap';
import axios from 'axios';
import { Redirect } from 'react-router-dom'
import querystring from 'querystring';
class Login extends Component
{
constructor(props)
{
super(props);
this.onClick = this.onClick.bind(this);
this.state = {
email:"",
password:""
}
}
onClick(event)
{
var self = this;
var payload={
"email":this.state.email,
"password":this.state.password,
}
//axios.post('http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/login', payload) .then((response) => {}
console.log("1. Hello before axios.post");
//axios.post('http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/login', payload)
axios.post('http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/login', querystring.stringify({payload}))
.then((response) =>
{
console.log("2. Inside axios response");
console.log(response);
if(response.data.code == 200)
{
//Set localstorage:
const userDetails = {userName: this.state.email}
localStorage.setItem('userDetails', JSON.stringify(userDetails));
console.log("Login successfull");
return <Redirect to='/Master' />
}
else if(response.data.code == 204)
{
console.log("Username password do not match");
alert(response.data.success)
}
else if(response.data.code == 401)
{
alert(response.data.success)
}
else
{
console.log("Username does not exists");
alert("Username does not exist");
}
})
.catch(function (error)
{
console.log("The error is : " + error);
});
}
render()
{
return (
<div className="app flex-row align-items-center">
<Container>
<Row className="justify-content-center">
<Col md="8">
<CardGroup>
<Card className="p-4">
<CardBody>
<h1>Login</h1>
<p className="text-muted">Sign In to your account</p>
<InputGroup className="mb-3">
<InputGroupAddon addonType="prepend">
<InputGroupText>
<i className="icon-user" />
</InputGroupText>
</InputGroupAddon>
<Input type="text" placeholder="Username" />
</InputGroup>
<InputGroup className="mb-4">
<InputGroupAddon addonType="prepend">
<InputGroupText>
<i className="icon-lock" />
</InputGroupText>
</InputGroupAddon>
<Input type="password" placeholder="Password" />
</InputGroup>
<Row>
<Col xs="6">
<Button color="primary" className="px-4" onClick={this.onClick}>
Login
</Button>
</Col>
<Col xs="6" className="text-right">
<Button color="link" className="px-0">
Forgot password?
</Button>
</Col>
</Row>
</CardBody>
</Card>
<Card
className="text-white bg-primary py-5 d-md-down-none"
style={{ width: 44 + "%" }}
>
<CardBody className="text-center">
<div>
<h2>Sign up</h2>
<p>
Are you a new user to the Restaurant system? Hooray now , you can create an account...
</p>
<Button color="primary" className="mt-3" active>
Register Now!
</Button>
</div>
</CardBody>
</Card>
</CardGroup>
</Col>
</Row>
</Container>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Login;
The following is the Laravel API login code which requires the email and password
Laravel login API code
<?php
namespace AppHttpControllersAPI;
use IlluminateHttpRequest;
use AppHttpControllersController;
use AppUser;
use IlluminateSupportFacadesAuth;
use Validator;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public $successStatus = 200;
public function login()
{
if(Auth::attempt(['email' => request('email'), 'password' => request('password')]))
{
$user = Auth::user();
$success['token'] = $user->createToken('MyApp')-> accessToken;
return response()->json(['success' => $success], $this-> successStatus);
}
else
{
return response()->json(['error'=>'Unauthorized'], 401);
}
}
}
Update
As Alex says here I changed console.log("The error is : " + error); as
console.log("The error is : " + error.response); in catch function. It echos The error is : [object Object].
The 401 Unauthorized Error is an HTTP response status code indicating that the client could not authenticate a request.
In this article, we’ll examine the 401 Error in more detail. We’ll show you how to diagnose and debug this error within your own application.
Server- or Client-Side?
All HTTP response status codes in the 4xx category are client error responses. These messages contrast with server error responses in the 5xx category, such as the 503 Service Unavailable Error.
However, the appearance of a 401 error code or any 4xx error doesn’t necessarily mean the client is the issue, where the client is the web browser or device used to access the application.
For example, if you’re trying to diagnose an issue with your application, you can ignore most client-side code. This includes HTML, cascading style sheets (CSS), client-side JavaScript, etc.
On the other hand, this doesn’t rule out the client as the actual cause of a 401 Unauthorized Error. While it’s probably not the HTML or CSS, it could be that the client may be sending a request that doesn’t contain any authentication information.
Even though the 401 Unauthorized Error is a client error response, it doesn’t mean we can rule out the server as the culprit. The server is still the network object producing the 401 Unauthorized Error and returning it as the HTTP response code to the client.
We’ll go over all this in detail in the following sections.
Start With a Thorough Application Backup
Before attempting any changes to the system, make sure to perform a full backup of your application, database, etc. If you can, create a complete copy of the application onto a secondary staging server. This will give you a clean testing ground to test all potential fixes without threatening the sanctity of your live application.
As discussed in the introduction, a 401 Unauthorized Error indicates that the client (the web browser, in most cases) has requested a restricted resource (such as a web page) from the server. Still, the client has failed to provide valid authentication credentials.
A 401 Error might occur in one of a handful of possible scenarios:
- The client sent its authentication credentials to the server, but the server rejected the credentials.
- The client failed to provide any authentication credentials within the request.
- The client is banned. Some applications use 401 Unauthorized Errors to restrict access requests from specific IP addresses.
Troubleshooting on the Client-Side
Since the 401 Unauthorized Error is a client error response code, it’s best to start by troubleshooting potential client-side issues.
Here are a handful of tips to try on the browser or device giving you problems.
Check the Requested URL
The most common cause of a 401 Unauthorized Error is an incorrect URL. As discussed before, web servers will disallow access to improper URLs. This could be anything from trying to access a file directory via a URL to gaining access to a private page meant for other users.
Double-check the exact URL returning the 401 error to ensure that it is the actual resource you intend to request.
Clear Relevant Cookies
HTTP cookies are tiny pieces of data stored on your local device. Websites and applications then use cookies to «remember» information about this particular browser and/or device.
Most modern web apps use cookies to store user authentication status. These cookies inform the web application which user is currently active and what kind of authorization to give the current client (browser). When a 401 Unauthorized Error occurs, the problem could be invalid or corrupted cookies, causing improper authentication for the server.
You only need to worry about cookies relevant to the website or application causing the problem in most cases. Cookies are stored based on the location of the domain, meaning you can remove only cookies that match the website domain (e.g., airbrake.io).
However, if you’re not experienced with manually removing certain cookies, it’s easier to clear all cookies at once.
Here are a few how-to articles to clear cookies depending on your browser:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari
Clear the Cache
Like cookies, local browser caches can cause 401 Unauthorized Error to appear. A cache is a collection of storage that retains local copies of web content on your device for later use. A browser’s cache typically stores compressed snapshots of webpages you frequently visit, including images and other binary data your browser often accesses.
With a local copy of these resources on your device, your browser doesn’t need to spend the time or bandwidth to download identical data every time you return to the same page.
For example, every time you open up Facebook, your page downloads content from the cache on your local device.
Since your browser’s cache stores local copies of web content and resources, it’s possible that a change to the live version of your application is conflicting with the cached version already on your device, causing a 401 Unauthorized Error.
Try clearing your browser’s cache to see if that fixes the issue. As with cookies, clearing the cache is browser-dependent. Here are a few links to that relevant documentation for the most popular browsers:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari
Log Out and Log In
Since the application in question likely contains some form of authentication, the last client-side step to try is to log out and then log back in.
Clearing browser cookies will usually log you out automatically the next time you load the page. So, all you need to do is log back in.
In some situations, the application may be running into a problem with your previous session, which is a string that the server sends to the client to identify that client during future requests.
Your device stores session tokens (session strings) via cookies. The client then transfers these tokens to the server during a request. The problem is if the server doesn’t recognize the session token sent by the client or the token is invalid. This will result in a 401 error.
For most web applications, logging out and logging back in will force the local session token to be recreated.
Debugging Common Platforms
Common software packages and content management systems (CMS) can also be responsible for the 401 Unauthorized Error. If you’re seeing this error, take a look at the stability and functionality of these platforms.
The most common content management systems — like WordPress, Joomla!, and Drupal — are all typically well-tested. Still, once you start making modifications to the underlying extensions or PHP code (the language in which nearly all modern content management systems are written), it’s too easy to cause an unforeseen issue resulting in a 401 error.
Here are a few tips to help you troubleshoot some of these popular software platforms.
Rollback Recent Upgrades
If you recently updated your CMS and now you’re seeing a 401 error, consider rolling back to the previous version on your CMS.
Similarly, any extensions or modules you may have recently upgraded can also cause server-side issues. If you believe this is why you’re seeing an error, revert to your previous CRM version.
However, certain CMSs don’t provide a version downgrade capability in some cases. This indicates that the base application, along with each new version released, is stable and bug-free. You’ll typically see this with more popular platforms.
Uninstall New Extensions, Modules, or Plugins
Extensions, modules, or plugins serve the same purpose across every system. They improve the capabilities and features of your CMS.
But you should be cautious with extensions because they can take full control of the system and make virtually any changes to the PHP code, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or database. As such, uninstall any new extensions that you added before the 401 error.
Check for Unexpected Database Changes
It’s worth noting that if you uninstall an extension through the CMS dashboard, this doesn’t guarantee that changes made by the extension will fully revert. This is particularly true for WordPress extensions that have been given carte blanche within the application. This often includes full access rights to the database.
There are scenarios where an extension may modify database records that don’t “belong” to the extension itself. The extension may not know how to revert alterations to database records in those scenarios, even if you uninstall it.
If you’re reasonably convinced an extension is a likely culprit for the status code 401 error, open the database and manually look through tables and records likely modified by the extension.
Troubleshooting on the Server-Side
If you aren’t running a CMS application or you’re confident the 401 Unauthorized Error isn’t related to your CSM — here are some additional tips to help you troubleshoot what might be causing the issue on the server-side.
RFC 7235 is the official standards document outlining how Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP:/1.1): Authentication should be performed on the web. This is just one of the thousands of documents published by the Internet Engineering Task Force, an open community dedicated to creating open Internet standards.
According to the RFC 7235, a 401 Unauthorized Error response code sent by a server must also include the WWW-Authenticate response header, which contains one or more challenges. Each challenge is a string indicating how proper authentication can be obtained to access the requested resource.
The syntax of a WWW-Authenticate header is: WWW-Authenticate: <type> realm=<realm>. The <type> value can be one of several valid authentication schemes. <realm> describes the area or “realm” that can be accessed.
For example, a WWW-Authenticateheader of WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=»Access to the production server» indicates to the client that authentication requests should be Basic (an id and password credential combination). This will give access to the “production server.”
With this knowledge in hand, you can attempt to diagnose the 401 Unauthorized Error you’re seeing on your application by confirming that the application is sending a valid WWW-Authenticate response header. This header can give you extra information that may lead to a solution, such as showing which particular authentication schemes are expected by the server.
You can view HTTP headers either from the server or the client web browser. View headers in Google Chrome by pressing F12 to open the developer console, select the Network tab, then load or reload the specific page/resource showing the 401 Error. This will show the list of all resources involved in the transaction, including everything from the actual document to individual images.
Sort the results by the Status by clicking the Status table header, then find the “401” status code. Select that entry in the list, and you should be able to view the Headers tab for that request. Look under Response Headers for the associated WWW-Authenticate header.
Check Your Web Server Configuration
Most modern web servers provide one or more configuration files that allow you to easily adjust the server behavior based on a wide range of circumstances. For example, the server may reject requests to certain directories or URLs, resulting in a 401 Unauthorized Error.
Configuration options for each type of web server can vary dramatically. Here’s a list of a few popular servers:
- Apache
- Nginx
- IIS
- Node.js
- Apache Tomcat
Look Through the Logs
Nearly every web application will keep some form of server-side logs. Application logs are the history of what the application did. The log will show requested pages, connected servers, database results, etc. Server logs are related to the actual hardware running the application and will often provide details about the health and status of all connected services or even just the server itself. Google “logs [PLATFORM_NAME]” if you’re using a CMS, or “logs [PROGRAMMING_LANGUAGE]” and “logs [OPERATING_SYSTEM]” if you’re running a custom application, to get more information on finding the logs in question.
Debug Your Application Code or Scripts
Finally, if all else fails, it may be that a problem in some custom code within your application is causing the issue. Try to diagnose where the issue may be coming from by manually debugging your application and parsing through application and server logs.
Ideally, make a copy of the entire application to a local development machine and perform a step-by-step debug process, allowing you to recreate the exact scenario where the 401 Unauthorized Error occurred.
No matter the cause — and even if you managed to fix it this time — the appearance of an issue like the 401 Unauthorized Error within your own application is a good indication you may want to implement an error management tool. Error monitoring will help you automatically detect errors and report them to you when they occur. Here’s another blog you can read to learn more about error monitoring vs. logging.
Airbrake’s error monitoring software provides real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all your development projects. Airbrake’s state-of-the-art web dashboard ensures you receive round-the-clock status updates on your application’s health and error rates. Plus, Airbrake makes it easy to customize exception parameters, so you only gather the errors that matter most.
Check out Airbrake’s error monitoring software today and see why so many of the world’s best engineering teams use Airbrake!
Note: We published this post in November 2017 and recently updated it in May 2022.
Written By: Frances Banks
Страница с ошибкой при обращении к WordPress-сайту всегда вызывает неудобства, вне зависимости от того, ваш это сайт или чужой. Как и в случае со многими другими кодами ответов HTTP, ошибка 401 не содержит детальных данных для диагностики и решения проблемы.
Ошибка 401 может появиться в любом браузере. В большинстве случаев ее легко решить.
В этой статье мы расскажем, что означает 401 ошибка, почему она происходит, и какие методы ее устранения существуют.
Итак, приступим!
Содержание
- Код ошибки 401 – что это?
- Что вызывает ошибку 401
- Как исправить ошибку 401 (5 методов)
Код ошибки 401 – что это?
Коды состояния HTTP 400 возникают в случае проблем с выполнением запросов. В частности, ошибка 401 появляется, когда браузер отказывает вам в доступе к странице, которую вы хотите посетить.
В результате вместо загрузки страниц браузер выведет сообщение об ошибке. Ошибки 401 могут возникать в любом браузере, потому отображаемое сообщение может варьироваться.
К примеру, в Chrome и Edge вы, скорее всего, увидите иконку бумаги с простым сообщением о том, что запрашиваемая страница не отвечает. Вы увидите фразу «HTTP Error 401». Вам будет предложено связаться с владельцем сайта, если ошибка не пропадет:
В иных случаях и в других браузерах вы можете получить менее дружелюбное предупреждение. К примеру, может выводиться пустая страница с сообщением «401 Authorization Required»:
Другие вариации текста:
- HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized
- 401 Unauthorized
- Access Denied
Эти ошибки часто появляются на сайтах, где требуется вводить данные для входа. В большинстве случаев это означает, что что-то не так с учетными данными. Возможно, браузер перестал считать их действительными.
Эта ошибка похожа на HTTP 403 Forbidden Error, когда доступ к сайту для пользователя запрещен. Однако, в отличие от ошибки 403, сообщение об ошибке 401 указывает, что процесс аутентификации завершился неудачно.
Код ошибки передается через заголовок WWW-Authenticate, который отвечает за определение метода аутентификации, используемого для предоставления доступа к веб-странице или ресурсу.
Что вызывает ошибку 401
Если вы столкнулись с кодом ошибки в кодах 400, вы должны знать, что проблема произошла на стороне клиента (либо на стороне браузера). Случается, что виновником проблемы является браузер, но так бывает не всегда. Об этом мы еще расскажем позже.
Ошибки 401 возникают на ресурсах с ограниченным доступом – к примеру, на страницах, защищенных паролем. Потому можно предположить, что причина проблемы связана с данными аутентификации.
Устаревшие Cookie и кэш браузера
Одной из наиболее распространенных причин возникновения ошибки 401 является то, что кэш и файлы cookie вашего браузера устарели, что не позволяет выполнить авторизацию. Если ваш браузер использует недействительные данные для авторизации (либо вообще их не использует их), сервер отклонит запрос.
Несовместимые плагины
Также бывают ситуации, когда ошибка вызвана несовместимостью плагинов или какими-либо сбоями в них. К примеру, плагин безопасности может ошибочно принять вашу попытку входа за вредоносную активность, а потому будет возвращена ошибка 401 для защиты страницы.
Неверный URL или устаревшая ссылка
Бывает, что источником проблемы является незначительная оплошность. К примеру, был неверно введен URL, ссылка была устаревшей и т.д.
Как исправить ошибку 401 (5 методов)
Теперь, когда мы разобрались с причинами ошибки 401, пришло время обсудить, как ее устранить.
Давайте рассмотрим 5 методов, которые вы можете использовать.
- Проверьте ваш URL.
Начнем с самого простого потенциального решения: убедитесь, что вы использовали верный URL. Это может выглядеть банально, но 401 ошибки нередко появляются, если URL-адрес был введен неправильно.
Еще один вариант: ссылка, которую вы использовали для перехода на запрашиваемую страницу, указывает на неправильный URL. К примеру, ссылка устарела, ведет на страницу, которой больше нет (и редиректов не задано).
Стоит тщательно перепроверить URL-адрес, который вы использовали. Если вы набирали адрес самостоятельно, убедитесь, что все написано безошибочно. Если вы переходили по ссылке, убедитесь в том, что она ведет на страницу, к которой вы хотите получить доступ (либо попробуйте перейти на эту страницу непосредственно через сайт).
- Почистите кэш браузера.
Кэш браузера предназначен для улучшения процесса взаимодействия с сайтами в сети за счет сокращения времени загрузки страниц. К сожалению, иногда это может вести к нежелательным последствиям.
Как мы уже говорили выше, одной из распространенных причин появления ошибки 401 являются устаревшие или неправильные данные кэша или cookies. Потому, если URL введен верно, следующий шаг – чистка кэша браузера.
В итоге вы удалите любую недействительную информацию, которая хранится локально в вашем браузере и может приводить к прерываниям процесса аутентификации. Аналогично, файлы cookie вашего браузера могут содержать аутентификационные данные, которые нужно обновить.
Если вы пользуетесь Chrome, вам нужно щелкнуть по иконке с меню в правом верхнем углу браузера и выбрать пункт Settings. В разделе «Privacy and security» нажмите «Clear browsing data:»
Далее вводим URL требуемого сайта и очищаем для него данные.
В других браузерах процесс очистки кэша и cookie может отличаться. К примеру, в Firefox нужно щелкать по иконке с библиотекой и выбирать History > Clear Recent History:
Информацию по остальным браузерам вы можете найти в поисковиках.
- Очистка DNS.
Еще один метод, который вы можете попробовать для устранения ошибки 401 – это очистка DNS. Эта причина встречается относительно редко, но стоит попробовать и такой подход, особенно если первые два ничего не дали.
Чтобы очистить DNS, перейдите в Windows к меню «Пуск» и там уже введите в строку поиска cmd. Нажмите Enter. Откроется командная строка. Далее вставьте команду ipconfig/flushdns, после чего снова нажмите Enter.
Если вы пользуетесь Mac, вы можете открыть командную строку следующим образом: Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
Введите команду sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder и нажмите Enter. Затем вы можете обновить страницу, чтобы посмотреть, пропала ли ошибка 401 или нет.
- Деактивируйте ваши плагины
Проблема может возникать и по вине плагинов.
Некоторые плагины, особенно связанные с безопасностью, могут выдавать ошибку 401 при подозрении на вредоносную активность. Также у них могут быть проблемы с совместимостью. Потому лучше всего деактивировать все плагины и посмотреть, будет ли страница работать.
Вы можете деактивировать все плагины разом, перейдя в раздел Plugins > Installed Plugins в консоли WordPress. Выберите все плагины и в меню Bulk Actions задайте Deactivate, после чего щелкните по кнопке Apply:
После этого попробуйте перезагрузить страницу с ошибкой. Если ошибка пропала, вы можете вручную по одному активировать плагины заново, чтобы выявить виновника всех бед.
Далее вы уже можете либо удалить плагин, либо написать его разработчикам, чтобы они предоставили рабочее решение.
- Проверьте заголовок WWW-Authenticate
Если проблема все еще остается, то в таком случае она может быть связана с ошибками на сервере. А значит, исправить ее будет чуть сложнее.
Как мы уже писали ранее, ответ 401 передается через заголовок WWW-Authenticate, который отображается как “WWW-Authenticate: <type> realm=<realm>”. Он включает в себя строки данных, указывающие на то, какой тип аутентификации требуется для предоставления доступа.
Вам нужно посмотреть, был ли отправлен ответ в WWW-Authenticate, а точнее какая схема аутентификации была использована. По крайней мере, это позволит вам приблизиться на один шаг к решению.
Перейдите на страницу с ошибкой 401 и откройте консоль разработчика в Chrome. Вы можете щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши на странице и выбрать Inspect (Ctrl+Shift+J).
Далее перейдите на вкладку Network и перезагрузите страницу. Это позволит сгенерировать список ресурсов. Выберите заголовок Status, чтобы отсортировать таблицу, и найдите код 401:
Выберите данную запись, после чего перейдите на вкладку Headers. В Response Headers найдите заголовок WWW-Authenticate:
Информация, представленная в заголовке ответа, в частности, в схеме аутентификации, даст вам больше сведений о том, что произошло, и укажет на решение. Это позволит вам понять, какой тип аутентификации требуется серверу.
К примеру, в приведенном выше примере мы видим, что схема аутентификации задана как «Basic». Это означает, что запрос аутентификации требует только ID и password. Для получения более подробной информации и инструкций мы рекомендуем обратиться к HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry.
Источник: kinsta.com