Very useful thread. I had pretty much the same question as @Yan Zhu, @unutbu and @FacePalm’s answeres were good, but I need to take in argv also. I came up with this, figured good because it allows me to write unit tests that don’t require sys.argv arguments.
import argparse, sys
def parse(arg_list):
p = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="my simple app")
p.add_argument('-z', '--zeta', type=str, default='[zeta from default]')
p.add_argument('-a', '--application', type=str, default='[application from default]')
return p.parse_known_args(arg_list)
code_args = [ '-a', 'a from code', '-q', 'q from code', '-o', 'o from code']
print(parse(code_args + sys.argv[1:]))
When you add a runtime param from intellij like this -a 'a from intellij' the results look like so.
/usr/local/bin/python3.7 /Users/me/IdeaProjects/co-util-py/test/varargstest.py -a "a from intellij"
(Namespace(application='a from intellij', other='o from code'), ['-q', 'q from code'])
You can see that argparse doesn’t drop the q, but it also doesn’t parse it.
Also, after lots of brain strain and testing, the only real difference between sys.argv and a list created is that sys.argv[0] is the name of the program that is being called. Drop that from the list and it doesn’t matter.
Python argparse is a parser for command line arguments and options. It allows the user of a program to pass arguments into a Python script from the command line.
This article will cover two things: a quick example of how argparse is used and why we get the “Unrecognized Arguments” error (and how to solve it).
We will use the work_through_args.py script with the following contents to demonstrate concepts.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
import argparse # Initialize the parser parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() # Arguments. # positional argument -always required parser.add_argument(‘value1’, type=float) # Another argument — set as required parser.add_argument(‘-v2’, «—value2», required = True, type=float) # Another argument — by default, it is the optional parser.add_argument(‘-v3’, ‘—value3’, type=float) # True or False argument. It stores True in this case. parser.add_argument(‘-v4’, ‘—value4’, action=‘store_true’) # Print the arguments args = parser.parse_args() print(args) # Addtion of value print(f«{args.value1}+{args.value2}=», args.value1+args.value2) |
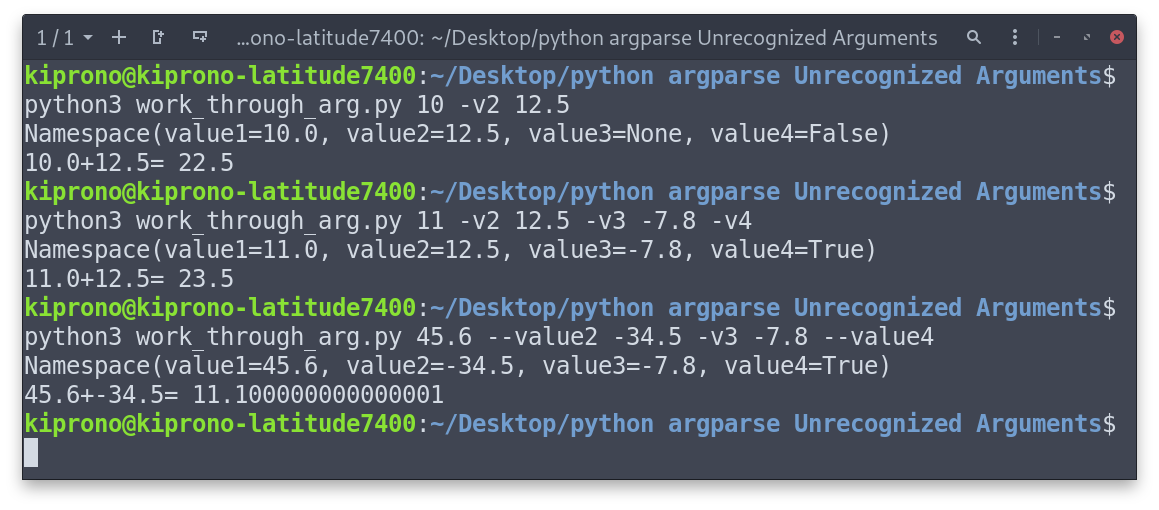
The script accepts three arguments – a positional argument, -v2/–value2, -v3/–value3, and -v4/–value4.
If we want to execute the above script from the command line, we need to run a command line this
python3 </path/to/work_through_args.py> <positional> -v2 <value> -v3 <value> -v4 <value>
See examples in the Figure below.
What Causes “Unrecognized Arguments” Error
This error is raised when we pass arguments that argparse does not expect. Here are some cases when this happens,
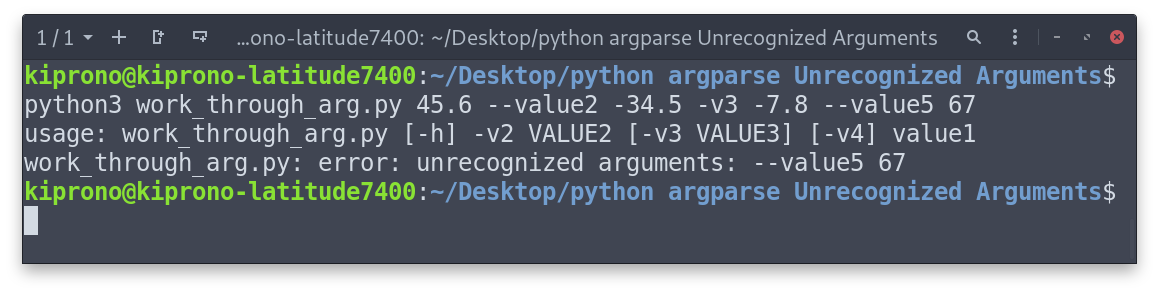
Case 1: Issuing argument that is not expected by argparse
The script above expected the arguments -v2/–value2, -v3/–value3 and -v4/–value4 NOT –value5. That is why the error was raised.
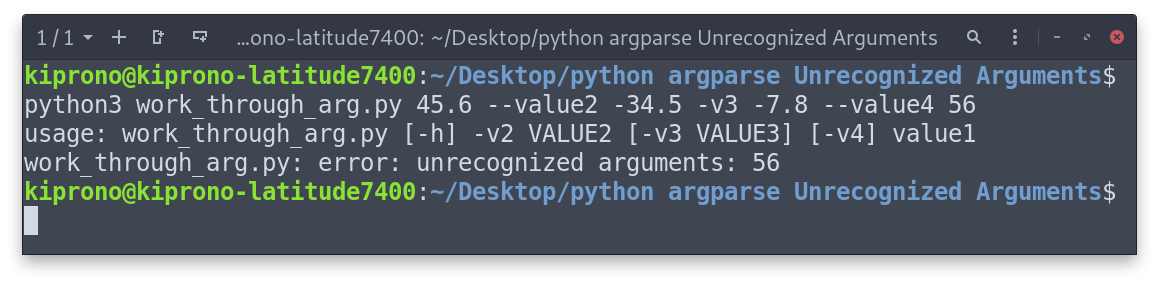
Case 2: Passing a value to an argument that does not expect the value
Some arguments do not expect the value to be passed to them. For example, -v4 in the above script does not expect any value to be supplied, and if we do, we end with an “Unrecognized Arguments” Error.
The argument -v4 already stores a value (True, if supplied; otherwise, False). That means -v4 does not accept any value, and attempts to give 56 as a value ended in error.
Solving “Unrecognized Arguments” Error
Solution 1: Verify that you are passing valid arguments
For Case 1 above – you need to pass arguments expected by argparse.
For Case 2 above – do not pass values to arguments that do not accept them.
Solution 2: Using the parser.parse_known_args() instead of parser.parse_args()
Unlike the parser.parse_args() function, parser.parse_known_args() accepts extra arguments. Here is an excerpt about it from the argparse documentation.
“Sometimes a script may only parse a few of the command-line arguments, passing the remaining arguments on to another script or program. In these cases, the parse_known_args() method can be useful. It works much like parse_args() except that it does not produce an error when extra arguments are present. Instead, it returns a two-item tuple containing the populated namespace and the list of remaining argument strings.” – Source: argparse documentation.
To use parse_known_args() in our work_through_args.py script replace the lines
|
args = parser.parse_args() print(args) |
with
|
args, unknown_args = parser.parse_known_args() print(args, unknown_args) |
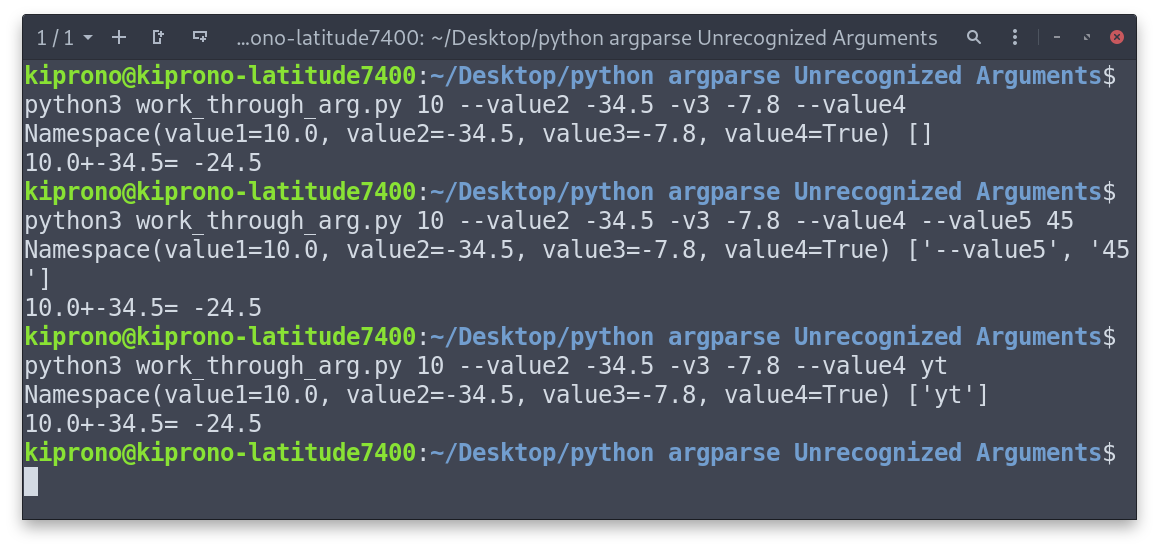
Then we can run our script with extra arguments.
In the last two executions in the Figure above, we have supplied extra arguments (and values), but the “Unrecognized Arguments” Error was not raised.
Conclusion
“Unrecognized Arguments” Error in argparse is raised when we supply arguments not expected by argparse. To solve the error, verify that you pass valid arguments. If you must allow extra arguments, use parse_known_args() instead of parse_args().
Command i am trying to execute:
pytest --show-capture=no -v --dsn="emulator-5554" -m bat --reruns=2
LINE NUMBERS
usage: pytest [options] [file_or_dir] [file_or_dir] [...]
pytest: error: unrecognized arguments: --show-capture=no
inifile: /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/54/workspace/test/pytest.ini
rootdir: /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/54/workspace/test
usage: pytest [options] [file_or_dir] [file_or_dir] [...]
pytest: error: unrecognized arguments: --show-capture=no
inifile: /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/54/workspace/test/pytest.ini
rootdir: /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/54/workspace/test
usage: pytest [options] [file_or_dir] [file_or_dir] [...]
pytest: error: unrecognized arguments: --show-capture=no
inifile: /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/54/workspace/test/pytest.ini
rootdir: /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/54/workspace/test
Pytest version i am using:
This is pytest version 5.3.5, imported from /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-ag...-packages/pytest/__init__.py
setuptools registered plugins:
pytest-rerunfailures-8.0 at /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-ag...ages/pytest_rerunfailures.py
pytest-cov-2.3.1 at /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-ag...ackages/pytest_cov/plugin.py
whats the content of pytest.ini and whats the output of pytest --help
$ pytest --help
general:
-k EXPRESSION only run tests which match the given substring
expression. An expression is a python evaluatable
expression where all names are substring-matched
against test names and their parent classes. Example:
-k 'test_method or test_other' matches all test
functions and classes whose name contains
'test_method' or 'test_other', while -k 'not
test_method' matches those that don't contain
'test_method' in their names. Additionally keywords
are matched to classes and functions containing extra
names in their 'extra_keyword_matches' set, as well as
functions which have names assigned directly to them.
-m MARKEXPR only run tests matching given mark expression.
example: -m 'mark1 and not mark2'.
--markers show markers (builtin, plugin and per-project ones).
-x, --exitfirst exit instantly on first error or failed test.
--maxfail=num exit after first num failures or errors.
--strict marks not registered in configuration file raise
errors.
-c file load configuration from `file` instead of trying to
locate one of the implicit configuration files.
--continue-on-collection-errors
Force test execution even if collection errors occur.
--fixtures, --funcargs
show available fixtures, sorted by plugin appearance
--fixtures-per-test show fixtures per test
--import-mode={prepend,append}
prepend/append to sys.path when importing test
modules, default is to prepend.
--pdb start the interactive Python debugger on errors.
--pdbcls=modulename:classname
start a custom interactive Python debugger on errors.
For example:
--pdbcls=IPython.terminal.debugger:TerminalPdb
--capture=method per-test capturing method: one of fd|sys|no.
-s shortcut for --capture=no.
--runxfail run tests even if they are marked xfail
--lf, --last-failed rerun only the tests that failed at the last run (or
all if none failed)
--ff, --failed-first run all tests but run the last failures first. This
may re-order tests and thus lead to repeated fixture
setup/teardown
--cache-show show cache contents, don't perform collection or tests
--cache-clear remove all cache contents at start of test run.
reporting:
-v, --verbose increase verbosity.
-q, --quiet decrease verbosity.
-r chars show extra test summary info as specified by chars
(f)ailed, (E)error, (s)skipped, (x)failed, (X)passed,
(p)passed, (P)passed with output, (a)all except pP.
Warnings are displayed at all times except when
--disable-warnings is set
--disable-warnings, --disable-pytest-warnings
disable warnings summary
-l, --showlocals show locals in tracebacks (disabled by default).
--tb=style traceback print mode (auto/long/short/line/native/no).
--full-trace don't cut any tracebacks (default is to cut).
--color=color color terminal output (yes/no/auto).
--durations=N show N slowest setup/test durations (N=0 for all).
--pastebin=mode send failed|all info to bpaste.net pastebin service.
--junit-xml=path create junit-xml style report file at given path.
--junit-prefix=str prepend prefix to classnames in junit-xml output
--result-log=path DEPRECATED path for machine-readable result log.
collection:
--collect-only only collect tests, don't execute them.
--pyargs try to interpret all arguments as python packages.
--ignore=path ignore path during collection (multi-allowed).
--confcutdir=dir only load conftest.py's relative to specified dir.
--noconftest Don't load any conftest.py files.
--keep-duplicates Keep duplicate tests.
--collect-in-virtualenv
Don't ignore tests in a local virtualenv directory
--doctest-modules run doctests in all .py modules
--doctest-report={none,cdiff,ndiff,udiff,only_first_failure}
choose another output format for diffs on doctest
failure
--doctest-glob=pat doctests file matching pattern, default: test*.txt
--doctest-ignore-import-errors
ignore doctest ImportErrors
test session debugging and configuration:
--basetemp=dir base temporary directory for this test run.
--version display pytest lib version and import information.
-h, --help show help message and configuration info
-p name early-load given plugin (multi-allowed). To avoid
loading of plugins, use the `no:` prefix, e.g.
`no:doctest`.
--trace-config trace considerations of conftest.py files.
--debug store internal tracing debug information in
'pytestdebug.log'.
-o [OVERRIDE_INI [OVERRIDE_INI ...]], --override-ini=[OVERRIDE_INI [OVERRIDE_INI ...]]
override config option with option=value style, e.g.
`-o xfail_strict=True`.
--assert=MODE Control assertion debugging tools. 'plain' performs no
assertion debugging. 'rewrite' (the default) rewrites
assert statements in test modules on import to provide
assert expression information.
--setup-only only setup fixtures, do not execute tests.
--setup-show show setup of fixtures while executing tests.
--setup-plan show what fixtures and tests would be executed but
don't execute anything.
pytest-warnings:
-W PYTHONWARNINGS, --pythonwarnings=PYTHONWARNINGS
set which warnings to report, see -W option of python
itself.
logging:
--no-print-logs disable printing caught logs on failed tests.
--log-level=LOG_LEVEL
logging level used by the logging module
--log-format=LOG_FORMAT
log format as used by the logging module.
--log-date-format=LOG_DATE_FORMAT
log date format as used by the logging module.
--log-cli-level=LOG_CLI_LEVEL
cli logging level.
--log-cli-format=LOG_CLI_FORMAT
log format as used by the logging module.
--log-cli-date-format=LOG_CLI_DATE_FORMAT
log date format as used by the logging module.
--log-file=LOG_FILE path to a file when logging will be written to.
--log-file-level=LOG_FILE_LEVEL
log file logging level.
--log-file-format=LOG_FILE_FORMAT
log format as used by the logging module.
--log-file-date-format=LOG_FILE_DATE_FORMAT
log date format as used by the logging module.
re-run failing tests to eliminate flaky failures:
--reruns=RERUNS number of times to re-run failed tests. defaults to 0.
coverage reporting with distributed testing support:
--cov=[path] measure coverage for filesystem path (multi-allowed)
--cov-report=type type of report to generate: term, term-missing,
annotate, html, xml (multi-allowed). term, term-
missing may be followed by ":skip-covered".annotate,
html and xml may be be followed by ":DEST" where DEST
specifies the output location.
--cov-config=path config file for coverage, default: .coveragerc
--no-cov-on-fail do not report coverage if test run fails, default:
False
--cov-fail-under=MIN Fail if the total coverage is less than MIN.
--cov-append do not delete coverage but append to current, default:
False
custom options:
--mode=MODE my option: with_setup or without_setup
--pin=PIN my option: Yes or No
--dsn=DSN List of DSNs.
--devicetype=DEVICETYPE
Enter device varient type e.g. vega, falcon
--application={mmsdk,vega,falcon,gemini}
Enter application e.g. mmsdk, vega, falcon
[pytest] ini-options in the first pytest.ini|tox.ini|setup.cfg file found:
markers (linelist) markers for test functions
norecursedirs (args) directory patterns to avoid for recursion
testpaths (args) directories to search for tests when no files or dire
console_output_style (string) console output: classic or with additional progr
usefixtures (args) list of default fixtures to be used with this project
python_files (args) glob-style file patterns for Python test module disco
python_classes (args) prefixes or glob names for Python test class discover
python_functions (args) prefixes or glob names for Python test function and m
xfail_strict (bool) default for the strict parameter of xfail markers whe
junit_suite_name (string) Test suite name for JUnit report
doctest_optionflags (args) option flags for doctests
doctest_encoding (string) encoding used for doctest files
cache_dir (string) cache directory path.
filterwarnings (linelist) Each line specifies a pattern for warnings.filterwar
log_print (bool) default value for --no-print-logs
log_level (string) default value for --log-level
log_format (string) default value for --log-format
log_date_format (string) default value for --log-date-format
log_cli_level (string) default value for --log-cli-level
log_cli_format (string) default value for --log-cli-format
log_cli_date_format (string) default value for --log-cli-date-format
log_file (string) default value for --log-file
log_file_level (string) default value for --log-file-level
log_file_format (string) default value for --log-file-format
log_file_date_format (string) default value for --log-file-date-format
addopts (args) extra command line options
minversion (string) minimally required pytest version
environment variables:
PYTEST_ADDOPTS extra command line options
PYTEST_PLUGINS comma-separated plugins to load during startup
PYTEST_DEBUG set to enable debug tracing of pytest's internals
Pytest version using at runtime
This is pytest version 3.3.2, imported from /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-ag...n3.7/site-packages/pytest.py
setuptools registered plugins:
pytest-rerunfailures-2.2 at /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-ag...ages/pytest_rerunfailures.py
pytest-cov-2.3.1 at /home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-ag...ackages/pytest_cov/plugin.py
# Content of Pytest.ini file [pytest] log_cli = 1 log_cli_level = INFO log_cli_format = %(asctime)s [%(levelname)s] %(message)s (%(filename)s:%(lineno)s) log_cli_date_format=%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S markers = bat: test eligible for bat run and will run in Version set stage of pipeline regression: test eligible for regression run and will run in development stage of pipeline
pytest version 3.3.2 unlike the 5.3.5 does not have the option you mention, please investigate why that environment is different
After making upgrade workaround i ran in to different issue
INTERNALERROR> Traceback (most recent call last):
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_pytest/main.py", line 191, in wrap_session
INTERNALERROR> session.exitstatus = doit(config, session) or 0
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_pytest/main.py", line 247, in _main
INTERNALERROR> config.hook.pytest_runtestloop(session=session)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/hooks.py", line 286, in __call__
INTERNALERROR> return self._hookexec(self, self.get_hookimpls(), kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 93, in _hookexec
INTERNALERROR> return self._inner_hookexec(hook, methods, kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 87, in <lambda>
INTERNALERROR> firstresult=hook.spec.opts.get("firstresult") if hook.spec else False,
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 208, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> return outcome.get_result()
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 80, in get_result
INTERNALERROR> raise ex[1].with_traceback(ex[2])
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 187, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> res = hook_impl.function(*args)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_pytest/main.py", line 272, in pytest_runtestloop
INTERNALERROR> item.config.hook.pytest_runtest_protocol(item=item, nextitem=nextitem)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/hooks.py", line 286, in __call__
INTERNALERROR> return self._hookexec(self, self.get_hookimpls(), kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 93, in _hookexec
INTERNALERROR> return self._inner_hookexec(hook, methods, kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 87, in <lambda>
INTERNALERROR> firstresult=hook.spec.opts.get("firstresult") if hook.spec else False,
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 208, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> return outcome.get_result()
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 80, in get_result
INTERNALERROR> raise ex[1].with_traceback(ex[2])
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 187, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> res = hook_impl.function(*args)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/64/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest_rerunfailures.py", line 49, in pytest_runtest_protocol
INTERNALERROR> rerun_marker = item.get_marker("flaky")
INTERNALERROR> AttributeError: 'Function' object has no attribute 'get_marker'
Please update the rerunfailures plugin as well, and please start to use the code formatting feature of github, it’s painful to read unformatted pastes
Upgrading rerunfailure didnt work i suppose or may be it need some more plugins
INTERNALERROR> Traceback (most recent call last):
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_pytest/main.py", line 191, in wrap_session
INTERNALERROR> session.exitstatus = doit(config, session) or 0
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_pytest/main.py", line 247, in _main
INTERNALERROR> config.hook.pytest_runtestloop(session=session)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/hooks.py", line 286, in __call__
INTERNALERROR> return self._hookexec(self, self.get_hookimpls(), kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 93, in _hookexec
INTERNALERROR> return self._inner_hookexec(hook, methods, kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 87, in <lambda>
INTERNALERROR> firstresult=hook.spec.opts.get("firstresult") if hook.spec else False,
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 208, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> return outcome.get_result()
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 80, in get_result
INTERNALERROR> raise ex[1].with_traceback(ex[2])
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 187, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> res = hook_impl.function(*args)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_pytest/main.py", line 272, in pytest_runtestloop
INTERNALERROR> item.config.hook.pytest_runtest_protocol(item=item, nextitem=nextitem)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/hooks.py", line 286, in __call__
INTERNALERROR> return self._hookexec(self, self.get_hookimpls(), kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 93, in _hookexec
INTERNALERROR> return self._inner_hookexec(hook, methods, kwargs)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/manager.py", line 87, in <lambda>
INTERNALERROR> firstresult=hook.spec.opts.get("firstresult") if hook.spec else False,
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 208, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> return outcome.get_result()
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 80, in get_result
INTERNALERROR> raise ex[1].with_traceback(ex[2])
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pluggy/callers.py", line 187, in _multicall
INTERNALERROR> res = hook_impl.function(*args)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest_rerunfailures.py", line 194, in pytest_runtest_protocol
INTERNALERROR> _remove_cached_results_from_failed_fixtures(item)
INTERNALERROR> File "/home/ANT.AMAZON.COM/jaiadi/kats-agent/workdir/65/workspace/.env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest_rerunfailures.py", line 135, in _remove_cached_results_from_failed_fixtures
INTERNALERROR> result, cache_key, err = getattr(fixture_def, cached_result)
INTERNALERROR> TypeError: cannot unpack non-iterable NoneType object
@RonnyPfannschmidt Formatting is not working for this log somehow. I tried that. I am getting this error consistently.
Versions used:
Successfully installed importlib-metadata-1.5.0 more-itertools-8.2.0 pluggy-0.13.1 pytest-5.4.1 wcwidth-0.1.8 zipp-3.1.0
Successfully installed pytest-rerunfailures-8.0
Please downgrade pytest as rerunfailures is currently not yet supporting pytest 5.4
Probably not the best place to report it, but I have irrelevant pytest: error: unrecognized arguments in the following case:
Directory structure:
src/
tests/
conftest.py
setup.cfg
setup.cfg contents:
[tool:pytest]
testpaths = tests
addopts = --aiohttp-fast
There is a custom argument inside tests/conftest.py:
def pytest_addoption(parser): parser.addoption( '--swagger', action='store_true', default=False, help='validate swagger schema' )
Now, it works as expected, I can run following:
pytest --swagger pytest --swagger tests/subdir/
But if I mistakingly run
pytest --swagger src/subdir/
I get pytest: error: unrecognized arguments: --swagger. If I run pytest src/subdir it outputs simply no tests ran, without errors.
$ pytest --version
This is pytest version 5.3.1, imported from /usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest.py
setuptools registered plugins:
pytest-aiohttp-0.3.0 at /usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest_aiohttp/__init__.py
pytest-timeout-1.3.3 at /usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest_timeout.py
pytest-cov-2.8.1 at /usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pytest_cov/plugin.py
$ python -V
Python 3.7.4
I think I get why this error happens. Since option is defined in tests/conftest.py it exists inside tests. Whenever I run pytest outside tests I get unrecognized argument error.
Closing this issue as the problem seems to be using old or incompatible versions of pytest and plugins, rather than a bug per se.
based on the description i believe this is yet another rootdir/conftest finding issue
oh wiat, iwas misstaken, the original issue is mixing, the thrown in other issue is something else
in my case I was just missing the package
pip install pytest-asyncio==0.20.1
The “unrecognized arguments” error in Airflow indicates that the command line arguments you entered are not supported by the Airflow program. This error is typically caused by entering an incorrect command or mistyping an argument. This article will cover common causes of the “unrecognized arguments” error in Apache Airflow and provide an alternative solution, SQLake, for automating data pipeline orchestration for data engineers.
Common reasons for receiving “unrecognized arguments” in Apache Airflow:
a. The scheduler is trying to execute the DAG file as a command line argument, rather than as a Python script.
This might be because the DAG file is not being properly imported into the Airflow system, or because there is a problem with the DAG file itself.
To troubleshoot this issue, you can try the following steps:
- Confirm that the DAG file is located in the correct location within the Airflow DAGs folder, and that it has the correct file name and extension (e.g. .py).
- Check the Airflow logs for any errors or messages that might provide more context on the issue. You can find the logs in the “logs” folder within the Airflow home directory.
- Make sure that the DAG file is correctly formatted and follows the guidelines for creating a DAG in Airflow. For example, make sure that it has the correct import statements, that the DAG object is correctly defined and initialized, and that it has at least one task associated with it.
- Check the Airflow web UI to see if the DAG is listed under the “DAGs” tab. If it is not listed, it may indicate that it is not being properly imported into the system.
- Restart the Airflow scheduler and web server to see if that resolves the issue.
b. The script cannot parse the arguments being passed to it.
To fix this issue, you can try these steps:
- Confirm that the arguments are being passed correctly to the script. Make sure that you are using the correct syntax for passing arguments to the script, and that the arguments are being passed in the correct order.
- Check the syntax of the
argparse.ArgumentParser()object and theadd_argument()method. Make sure that the required arguments are marked as required using therequiredparameter, and that the correctactionandtypeare being specified for each argument. - Make sure that the
destparameter in theadd_argument()method is correctly specified. Thedestparameter specifies the name of the attribute that will be created to hold the argument’s value.
For example, if thedestparameter is set to"mac", the value of the-margument will be stored in theargs.macattribute. - Check the script for any syntax errors or other issues that might prevent it from running correctly.
- Test the script with different sets of arguments to see if the issue is consistently reproducible. This can help narrow down the cause of the issue.
c. The airflow connections command is not configured to delete connections properly.
These are the steps to take:
- Confirm that you are using the correct syntax for the
airflow connectionscommand. According to the Airflow documentation, the correct syntax for deleting a connection isairflow connections --delete --conn_id CONN_ID, whereCONN_IDis the ID of the connection you want to delete. - Make sure that you are passing the
--deleteand--conn_idoptions to theairflow connectionscommand. Without these options, the command will not recognize the arguments being passed to it. - Check the Airflow logs for any errors or messages that might provide more context. You can find the logs in the “logs” folder within the Airflow home directory.
- Make sure that the connections you are trying to delete exist in the Airflow system. You can check the list of connections by running the
airflow connections --listcommand. - If you are using the Airflow CLI inside a script, make sure that the script has the necessary permissions to execute the
airflow connectionscommand. - If you are still having trouble, you can try running the
airflow connectionscommand with the--debugoption to enable debugging output. This can help you understand what is causing the issue.
Alternative Approach – Automated Orchestration:
Airflow is a great tool, but difficult to debug. SQLake is a great alternative that allows you to automate data pipeline orchestration.
With SQLake you can
- Build reliable, maintainable, and testable data ingestion.
- Process pipelines for batch and streaming data, using familiar SQL syntax.
- Jobs are executed once and continue to run until stopped.
- There is no need for scheduling or orchestration.
- The compute cluster scales up and down automatically, simplifying the deployment and management of your data pipelines.
Here is a code example of joining multiple S3 data sources into SQLake and applying simple enrichments to the data.
/* Ingest data into SQLake */
-- 1. Create a connection to SQLake sample data source.
CREATE S3 CONNECTION upsolver_s3_samples
AWS_ROLE = 'arn:aws:iam::949275490180:role/upsolver_samples_role'
EXTERNAL_ID = 'SAMPLES'
READ_ONLY = TRUE;
-- 2. Create empty tables to use as staging for orders and sales.
CREATE TABLE default_glue_catalog.database_a137bd.orders_raw_data()
PARTITIONED BY $event_date;
CREATE TABLE default_glue_catalog.database_a137bd.sales_info_raw_data()
PARTITIONED BY $event_date;
-- 3. Create streaming jobs to ingest raw orders and sales data into the staging tables..
CREATE SYNC JOB load_orders_raw_data_from_s3
CONTENT_TYPE = JSON
AS COPY FROM S3 upsolver_s3_samples
BUCKET = 'upsolver-samples'
PREFIX = 'orders/'
INTO default_glue_catalog.database_a137bd.orders_raw_data;
CREATE SYNC JOB load_sales_info_raw_data_from_s3
CONTENT_TYPE = JSON
AS COPY FROM S3 upsolver_s3_samples
BUCKET = 'upsolver-samples'
PREFIX = 'sales_info/'
INTO default_glue_catalog.database_a137bd.sales_info_raw_data;
Upsolver enables any data engineer to build continuous SQL data pipelines for cloud data lake. Our team of expert solution architects is always available to chat about your next data project. Get in touch
При создании консольных программ в Python очень часто необходимо разобрать параметры (аргументы) передаваемые через командную строку, это можно сделать используя переменную argv из модуля sys, а так же с помощью модуля argparse из стандартной библиотеки Pyhton.
Второй способ более предпочтительный и удобный, далее ему мы уделим больше внимания.
Статья ниже не является полным описание всех возможностей модуля argparse, это просто общий обзор.
Ниже я иногда пишу аргументы командной строки, иногда параметры командной строки… Имеется ввиду одно и тоже
Получение параметров без использования argparse
Например, мы хотим написать программу после запуска выводящую в консоль «Привет <переданное_имя>». Имя мы будем передавать через параметр в командной строке, далее его нужно получить в нашей программе. Как это сделать?
Мы можем сделать это используя стандартный модуль sys и его переменную argv, она содержит список переданных параметров (нулевой элемент списка содержит имя нашего скрипта).
Другими словами, чтобы вывести имя, которое мы передаем аргументом, необходимо обратиться к sys.argv[1]:
import sys
print(f'Привет {sys.argv[1]}')Сохраним код в файле hello.py и запустим его с параметром «Александр» (аргументом):
python hello.py Александр
Получаем ожидаемое:
Привет Александр
Но если попытаться запустить скрипт без параметра, то получаем ошибку поскольку в списке нет элемента с индексом 1. Исправим это сделав проверку на наличии передаваемого параметра и если он не передается, будет выводиться «Привет мир!»
import sys
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print('Привет мир!')
else:
print(f'Привет {sys.argv[1]}')
Теперь немного усложним задачу, что если мы хотим передавать имя с помощью именованного параметра —name, доработаем наш код:
import sys
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print('Привет мир!')
else:
p_name = sys.argv[1]
p_value = sys.argv[2]
if p_name == '--name':
print(f'Привет {p_value}')
else:
print(f'Неизвесный параметр {p_name}')
Запустив скрипт таким образом:
python hello.py --name Александр
Получаем нужный результат, если в место «—name» передать другое значение, то получаем предупреждение.
Но, если мы передадим один параметр вместо двух, то скрипт не запуститься, нам необходимо добавить еще один if для проверки существование минимум двух параметров.
А если нам нужно добавить еще несколько параметров, а если не все из них обязательные… короче код начнется превращаться в ужас, вот здесь нам на помощь и придет модуль argparse стандартной питоновской библиотеки.
Использование модуля argparse
Этот модуль облегчит нам разбор и дальнейшее использование передаваемых скрипту аргументов из командной строки.
Начнем переписывать наш пример:
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('name', nargs='?', default='мир!')
args = parser.parse_args()
print(f'Привет {args.name}')
Сохраним код в новый файл hello2.py и выполним передав ему в качестве параметра «Александр»:
python hello2.py Александр
Мы получим то, что требовалось:
Привет Александр
Разберем подробнее строку:
parser.add_argument('name', nargs='?', default='мир!')
В ней мы с помощью метода add_argument и передаваемых ему параметров, задали необязательный (для этого указали nargs=’?’) позиционный аргумент. Если аргумент не передается, то он принимает значение указанное в default.
Важно помнить, что при позиционных аргументах важен их порядок в момент, когда мы вызываем скрипт. Первый аргумент, переданный скрипту, становится первым позиционным аргументом, второй аргумент — вторым позиционным аргументом и т.д.
Продолжим доработку кода. Теперь мы хотим, чтобы Имя передавалось именованным параметром —name
Для этого всего лишь надо изменить одну строку создания аргумента
parser.add_argument('--name', default='мир!')
Теперь можно запустить скрипт с именованным параметром —name:
python hello2.py --name Александр
Мы получим «Привет Александр», а при отсутствии параметра, будет выводится значение по умолчанию «Привет мир».
У названия параметра может быть краткая форма, она записывается с одним «—«, например:
parser.add_argument('-n', '--name', default='мир!')
А что если в качестве параметра —name мы заходим передать Имя + Фамилия?
python hello2.py --name Александр Третьяков
Выполнив это сейчас мы получим ошибку error: unrecognized arguments: Третьяков поскольку модуль argparse решил что фамилия это отдельный аргумент.
Чтобы поправить ситуацию, используем дополнительный параметр метода add_argument — nargs со значением «+», который обозначает, что мы ожидаем одно или более значений аргумента.
Теперь повторно вызвав скрипт, получим все переданные параметры в виде списка:
Привет ['Александр', 'Третьяков']
Выбор агрументов из определенных вариантов
Иногда может потребоваться, чтобы пользователь программы указал аргумент из заранее заданных вариантов (например нужно указать расширение конвертируемого файла или качество сохраняемого видео).
Если брать наш пример выше, можем добавить, чтобы скрипт принимал только определенные имена: Александр, Екатерина, Татьяна, Евгений. Для этого добавим в метод add_argument параметр choices, в котором укажем список возможных значений параметра (в нашем случае список имен).
parser.add_argument ('-n', '--name', choices=['Александр', 'Екатерина', 'Татьяна', 'Евгений'])
Теперь при вызове скрипта мы должны обязательно указать параметр —name со значением из этого списка иначе возникнет ошибка:
python hello2.py --name Екатерина
Получим:
Привет Екатерина
А если попробуем передать имя не из одобренного списка:
hello2.py --name Ольга
Получим ошибку:
usage: hello2.py [-h] [-n {Александр,Екатерина,Татьяна,Евгений}]
hello2.py: error: argument -n/--name: invalid choice: 'Ольга' (choose from 'Александр', 'Екатерина', 'Татьяна', 'Евгений')
Справка (помощь) по аргументам
Выше мы ограничили список возможных значений аргумента —name четырьмя именами, но как узнать об этом пользователю, который в первый раз использует скрипт, ему придаться вчитываться в текст ошибки, чтобы понять чего от него хочет программа. Как пользователю узнать о всех возможных аргументах, порядке их применения и их назначении?
Для этого мы можем оформить справку для программы, которая будет вызываться аргументом —help или -h. В справочной информации мы сможем указать название и версию программы, копирайт, описание того, что она делает, и список ожидаемых параметров.
Итак изменим 2 строчки нашего кода, добавив в него справочную информацию:
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
prog='Greeting Script',
description='Программа, которая говорит "Привет"',
epilog='(c) Информация об авторе программы'
)
parser.add_argument ('-n', '--name', choices=['Александр', 'Екатерина', 'Татьяна', 'Евгений'], help='Список из имен, которые я могу приветствовать')
Теперь вызвав:
python hello2.py --help
Мы получим справку о нашей программе:
usage: Greeting Script [-h] [-n {Александр,Екатерина,Татьяна,Евгений}]
Программа, которая говорит "Привет"
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-n {Александр,Екатерина,Татьяна,Евгений}, --name {Александр,Екатерина,Татьяна,Евгений}
Список из имен, которые я могу приветствовать
(c) Информация об авторе программы
Аргументы как флаги
А что если мы хотим сделать так, чтобы при указании флага -bye программа говорила нам «До свидания»?
Для этого добавим строку:
parser.add_argument ('-bye', action='store_const', const=True, help='Установите, если нужно ли прощаться с пользователем')
В метод add_argument мы добавили 2 новых параметра. Первый — action, он предназначен для выполнения некоторых действий над значениями переданного аргумента. В нашем случае мы передали значение параметра action — store_const, оно обозначает, что если данный аргумент (‘-bye’) указан, то он всегда будет принимать значение, указанное в другом параметре метода add_argument — const. А если аргумент передан не будет, то его значение будет равно None.
Так же в конце скрипта добавим вывод «До свидания», в случае установленного флага -bye:
if args.bye:
print ('До свидания')Теперь если добавить флаг -bye при вызове скрипта:
python hello2.py --name Александр -bye
Получим:
Привет Александр
До свиданияБез добавления -bye мы получим просто:
Привет Александр
Флаги со значениями True и False используются часто, поэтому для этих целей предусмотрено 2 специальных значения для параметра action: store_true и store_false.
Можно переписать наш код так:
parser.add_argument ('-bye', action='store_true', help='Установите, если нужно ли прощаться с пользователем')
Мы использовали store_true, т.е. если параметр ‘-bye’ передан, он примет значение True.
Кстати, выше мы увидели что для добавление второго, третьего и т.д. аргумента, нам нужно просто еще раз вызвать метод add_argument и передать ему значения параметра.
Окончательный код нашего файла hello2.py:
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
prog='Greeting Script',
description='Программа, которая говорит "Привет"',
epilog='(c) Информация об авторе программы'
)
parser.add_argument ('-n', '--name', choices=['Александр', 'Екатерина', 'Татьяна', 'Евгений'], help='Список из имен, которые я могу приветствовать')
parser.add_argument ('-bye', action='store_true', help='Установите, если нужно ли прощаться с пользователем')
args = parser.parse_args()
print(f'Привет {args.name}')
if args.bye:
print ('До свидания')
На этом все, думаю общее представление о модуле argsparse вы получили, подробнее о нем можно почитать в официальной документации https://docs.python.org/3/library/argparse.html.