Протокол SMTP используется для передачи электронной почты по интернету. Из сообщений об ошибках этого протокола можно узнать, почему не удалось доставить письма. Если входящие или исходящие письма возвращаются, в сообщениях о недоставке можно найти коды ошибок SMTP, которые помогут установить причину этого.
Сообщения об ошибках SMTP имеют указанный ниже формат. Каждая последующая цифра кода ошибки и кода статуса несет более подробную информацию.
| Код ответа | Код статуса | Текст ответа |
|---|---|---|
| xyz | x.y.z | Текстовое описание |
Ниже показан пример сообщения об ошибке SMTP. В нем указана причина ошибки и рекомендуемые действия по ее устранению.
Коды ответа
Коды ответа SMTP связаны с определенными компонентами почтового сервиса и могут указывать на различные проблемы, например:
- получатель не зарегистрирован в сервисе;
- сообщение помечено как спам, или в нем был обнаружен вирус;
- домен отправителя идентифицирован как источник спама;
- сообщение нарушает правила компании, например содержит номера кредитных карт или обсценную лексику.
Коды ответа, начинающиеся с цифр 4 и 5, свидетельствуют об ошибке, а остальные цифры указывают не ее тип. Если в начале кода стоит 4, это временная ошибка, которая не требует действий. Отправителю придется повторить попытку. Если код начинается с цифры 5, это свидетельствует о постоянной ошибке, которую нужно устранить.
Коды распространенных ошибок SMTP 400
Коды ошибки, которые начинаются на 4, означают временный сбой в работе сервера. Действие будет завершено при следующей попытке. Такие ошибки обычно связаны с сервером, получающим почту.
| Код ошибки | Описание |
|---|---|
| 421 | Сервис недоступен. Повторите попытку позже. |
| 450 | Действие не выполнено, так как недоступен почтовый ящик пользователя. |
| 451 | Письмо не отправлено из-за ошибки сервера. |
| 452 | Выполнение команды остановлено из-за нехватки места на сервере. |
| 455 | Сервер сейчас не может выполнить команду. |
Коды распространенных ошибок SMTP 500
| Код ошибки | Описание |
|---|---|
| 500 | Сервер не распознал команду из-за неправильного синтаксиса. |
| 501 | Неправильный синтаксис параметров или аргументов команды. |
| 502 | Команда не выполнена. |
| 503 | Неправильная последовательность команд на сервере. |
| 541 | Письмо отклонено по адресу получателя. |
| 550 | Команда не выполнена, так как недоступен почтовый ящик пользователя, или письмо отклонено сервером из-за подозрения на спам. |
| 551 | Почтовый ящик получателя недоступен на его сервере. |
| 552 | Письмо не отправлено из-за нехватки места в почтовом ящике получателя. |
| 553 | Выполнение команды остановлено, так как не найден почтовый ящик с указанным названием. |
| 554 | Действие не выполнено по неизвестной причине. |
После кода ошибки SMTP обычно указываются ещё три цифры. Это расширенный код статуса SMTP, который дает больше информации о причине сбоя. Вторая цифра в коде обозначает категорию ответа, а третья дает дополнительные сведения.
Код ответа 421 означает, что возникла временная ошибка в канале передачи, содержащем информационный запрос.
| Код ответа | Описание |
|---|---|
| x0z | Синтаксические ошибки |
| x1z | Ответы на запросы информации |
| x2z | Ошибки канала передачи |
| x3z | Неизвестная ошибка |
| x4z | Неизвестная ошибка |
| x5z | Статус почтовой системы |
Коды статуса
Первая цифра в коде статуса указывает на его класс, вторая – на предмет, а третья сообщает более подробные данные.
Код статуса 4.4.5 означает временную проблему с сетью или маршрутизацией, влияющую на статус протокола доставки почты.
| Код статуса | Описание |
|---|---|
| x.0.z | Неизвестно |
| x.1.z | Статус адресования |
| x.2.z | Статус почтового ящика |
| x.3.z | Статус почтовой системы |
| x.5.z | Статус протокола доставки почты |
| x.6.z | Статус содержимого сообщения или медиа |
| x.7.z | Статус безопасности или соответствия правилам |
Текст ответа
Последний раздел в сообщении об ошибке SMTP, содержащий ее описание.
Статьи по теме
- Информация об ошибках протокола SMTP
- Стандарт RFC 5321 – протокол SMTP
- Стандарт RFC 1893 – расширенные коды статуса почтовой системы
Эта информация оказалась полезной?
Как можно улучшить эту статью?
Будучи менеджером коммерческого отдела небольшой торговой компании, я выполнял задачу по отправке нескольких сотен писем постоянным и потенциальным клиентам. Базу формировали из открытых источников мы сами, предложение было реально интересным целевой аудитории. Возникла «неожиданная» проблема – часть писем стала возвращаться. Кроме того, начали приходить сообщения с указаниями кодов ошибки SMTP. Своего IT-специалиста в штате у нас не было, потому разобраться с проблемой я решил самостоятельно. О результатах этой работы, причинах возникновения таких ошибок и методах их решения расскажу в этой статье.
Как избежать ошибок при составлении и отправке писем
Причинами возникновения ошибок и, как следствие, неполучения сообщений могут служить разные факторы. Одни из них связаны с неправильным составлением исходящих писем самим пользователем, другие относятся к более глобальным программным настройкам со стороны получателя.
Самый простой способ это понять – отправить тестовое сообщение на свой ящик. Затем следует протестировать его отправку и получение, используя разные внешние почтовые сервисы: gmail, yandex, mail, rambler и другие. Если сообщение получено, следует ответить на него, проверив корректность исполнения команды «RE» вашим почтовым сервером и принятие ответа условным отправителем.
Довольно часто проблемы с попаданием писем в папку «Спам» или программной блокировкой на стороне получателя лежат в неверном оформлении ключевых полей. Особенно это касается массовых рассылок коммерческого характера. Для отправки большого количества однотипных сообщений как минимум потребуется выполнение следующих параметров настройки:
- выделенный IP-адрес с целью исключить блокировку на стороне сервера-ретранслятора или почтовой программы конечного получателя;
- криптографические подписи DKIM и SPF, помогающие подтвердить подлинность домена и минимизировать количество писем, воспринимаемых как спам.
Важно! В случае несоблюдения этих элементарных правил вы рискуете не только тем, что конкретное письмо не будет доставлено адресату. При многократных попытках отправки письма в большинстве почтовых программ в блок-лист попадет вся корреспонденция, отправляемая с вашего email, и даже корпоративный домен (@domain.***).
Некорректное использование бота для отправки писем может привести к блокировке отправителя и другим нежелательным последствиям. Даже если информация, которую вы отправляете потенциальным клиентам, реально интересна им, система спам-фильтрации может воспринять данную рассылку как вредоносную. Чтобы избежать этого, лучше всего воспользоваться услугами специализированных компаний.
В моей практике был случай, когда никак не удавалось добиться получения моей электронной корреспонденции одним из сотрудников компании «Лукойл». Письма я отправлял самые простые, используя корпоративный ящик. Только после того, как мой респондент обратился в IT-службу своего предприятия, выяснилось, что данный адрес находится в блэк-листе. Попал он туда из-за каких-то ошибок, допущенных моим предшественником. Понадобилось больше недели, чтобы адрес включили в «белый список». Все это время письма, высылаемые с личного mail@yandex.ru, доходили без проблем.
Полезно: Почему не приходят письма с сайта. Пример частного случая.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Положительные и отрицательные сообщения SMTP-сервера
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) — это протокол, используемый большинством почтовых программ для отправки электронных сообщений в сети интернет. Некорректное взаимодействие между серверами, индивидуальные настройки на уровне программного обеспечения и многие другие причины приводят к появлению ошибок. В этом случае письма не доходят до получателей, возвращаются обратно или просто «пропадают». При возникновении таких ситуаций отправитель получает сообщение о наличии конкретной ошибки, отражающей SMTP-код последнего отклика сервера.
Первая цифра комбинации содержит информацию о качестве доставки:
- сообщение доставлено («SMTP OK»);
- возникла неизвестная или временная проблема («SMTP unknown»);
- критическая ошибка («SMTP error»).
Существует четыре варианта значений для первой цифры кода:
- 2xx – положительный результат, есть возможность передачи следующей команды;
- 3xx – отложенный результат, необходимо осуществление дополнительных действий;
- 4xx – сообщение не принято, но проблема носит временный характер, и запрос может быть повторен через какое-то время;
- 5xx – категорический отказ выполнения команды, отправка запроса со стороны передающего сервера в том же виде невозможна.
Вторая цифра в коде сообщает о категории ответа:
- 0 – синтаксические ошибки;
- 1 – ответы на запросы информации;
- 2 – ошибки канала передачи;
- 3 и 4 – неизвестный тип ошибки;
- 5 – статус почтовой системы.
Третья цифра дает более расширенную информацию о значении, указанном во второй цифре SMTP-ответа.
Помимо цифровой комбинации, SMTP-сообщение может содержать дополнительную текстовую информацию.
Полную информацию о кодах, их компоновке и значениях можно найти в спецификациях RFC 5321 и RFC 1893.
Следует учитывать, что SMTP-message говорит об успешном или неудачном варианте доставки именно на уровне взаимодействия почтовых серверов. Положительный ответ вовсе не означает, что ваше письмо не попало в папку «Спам».
Читайте также
Виды почтовых сервисов
На программном уровне существует несколько видов обработки электронной почтовой корреспонденции. К первой группе относятся виртуальные сервисы, доступные чаще всего в бесплатном исполнении через интернет-соединение на сайте почтового сервера. Это всем известные ресурсы:
- Gmail/Google Suite (почта от Google.com);
- Yandex.ru;
- Mail.ru;
- Rambler.ru и другие.
Более подробную информацию о значениях ответов SMTP можно получить на сайтах популярных почтовых сервисов:
- Коды ошибок SMTP почтового сервиса Gmail (Google Suite) (support.google.com)
- Создание и отправка писем на сервисе Яндекс
- Ошибки отправки писем при использовании сервера и сервиса Mail.ru
Ко второй группе относятся почтовые клиенты – программы, обладающие более расширенным функционалом, чем виртуальные сервисы. Наиболее популярными и универсальными почтовыми клиентами для Windows являются:
- Opera Mail;
- Mozilla Thunderbird;
- Koma-Mail;
- SeaMonkey;
- The Bat!;
- Microsoft Outlook.
Принципы работы почтовых клиентов несколько отличаются от процесса обработки корреспонденции виртуальными серверами. При отправке сообщения программа отсылает его не напрямую конечному получателю, а ретранслирует через сервер-релей. Этот процесс осуществляется чаще всего с использованием протокола SMTP, а получение корреспонденции обычно происходит с помощью IMAP или POP.
Коды SMTP-ответов определяются стандартом. Администратор почтового сервера может создать собственные настройки, в том числе и в части кодировки ответов сервера. Особенно это касается локальных почтовых программ, установленных непосредственно на сервере какой-нибудь компании.
О вариантах выбора и способах создания корпоративных почтовых сервисов более подробно можно прочитать здесь: Что такое почтовый сервер и зачем он нужен.
Классификация отрицательных SMTP-сообщений. Способы решения проблем
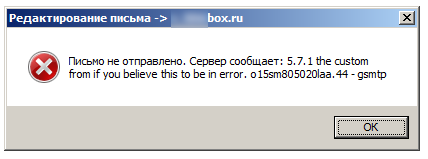
Сразу опускаю тот пакет сообщений, которые начинаются с 2хх и 3хх, так как они содержат информацию о том, что задача получения письма уже решена положительно либо получит такой статус в ближайшее время. Более подробно рассмотрим некоторые виды кодированных сообщений, начинающихся с 4хх и 5хх, т.е. отклики SMTP-сервера, которые сообщают о наличии проблем.
Почтовый сервер сообщил об ошибке 421
Значение: Service Not Available. Сервер недоступен: канал связи будет закрыт.
|
Возможные причины |
Варианты решения |
|
Неправильно заданы параметры SMTP-соединения |
Необходимо перепроверить настройки |
|
Брандмауэр блокирует IP-адрес сервера электронной почты |
Необходимо создать новое правило в брандмауэре |
|
Блокируется трафик через порт 25 |
Попробуйте в настройках учетной записи электронной почты сменить номер порта SMTP на 465 |
|
Проблема использования VPN |
Необходимо, чтобы провайдер услуги занес ваш почтовый сервер в белый список адресов VPN |
Данная ошибка возникает наряду с грейлистингом (Greylisting – «Серый список») при интенсивном использовании бесплатного SMTP-сервера, который лимитирует количество отправляемых сообщений в единицу времени. Для решения этой проблемы можно воспользоваться высоконагруженным SMTP-сервером. Чаще всего эта услуга является платной.
Получено сообщение с кодом 451
Значение: Requested action aborted: local error in processing. Требуемое действие прерывалось: ошибка в обработке.
|
Возможные причины |
Варианты решения |
|
Превышено количество допустимых подключений или лимит обмена сообщениями за отрезок времени, письма ждут отправки в очереди |
В настройках сервера увеличить лимит или задать ограничение не на количество подключений, а на количество писем на одного пользователя. Накопившуюся очередь писем можно отправить повторно командой «force send» |
|
Неправильно настроены MX-записи домена, из-за чего происходит неправильная маршрутизация писем |
Проверьте логи, конфигурационные файлы, МХ-записи и разрешения, внесите корректировки |
Устранение проблем с доставкой электронной почты для кода ошибок 451 4.7.500–699 (ASxxx) в Exchange Online. Электронная почта из доменов onmicrosoft.com ограничена и фильтруется для предотвращения спама.
Необходимо добавить настраиваемый домен.
Ошибка почтового сервера 452
Значение: Insufficient system resources. Запрашиваемое действие не выполнено: недостаточно места в системе.
|
Возможные причины |
Варианты решения |
|
На сервере получателя закончилось место, поэтому письмо не доставляется |
Чтобы в этом убедиться, достаточно попробовать осуществить отправку письма с другого сервера |
|
В сообщении присутствует текст «Out of memory». Это значит, что недостаточно места на вашем сервере |
Необходимо проверить количество отправляемых писем в очереди, наличие свободного места на диске и объем доступной памяти |
В Microsoft Exchange Server есть специальный компонент мониторинга доступных ресурсов Back Pressure, который отслеживает свободное место на диске, на котором хранятся очереди транспортной службы Exchange. При возникновении такой ошибки можно сделать следующее:
- очистить диск от ненужных файлов;
- отключить мониторинг Back Pressure (не рекомендуется);
- перенести транспортную очередь на другой диск достаточного объема.
Сервер сообщил об ошибке SMTP 550
Значение: Mailbox unavailable. Требуемые действия не предприняты: электронный ящик недоступен
|
Возможные причины |
Варианты решения |
|
Неверно указан email-адрес получателя |
Необходимо связаться с адресатом альтернативным способом и уточнить правильность написания адреса, а также убедиться, что он является действующим |
|
Система заражена вирусом, осуществляющим массовую рассылку писем с вашего адреса |
Провести полную проверку специализированной антивирусной программой |
|
На стороне вашего интернет-провайдера установлены ограничения на отправку исходящих сообщений |
Необходимо связаться с поставщиком интернет-услуг и получить консультацию по устранению данной проблемы |
|
Сервер получателя не работает |
Отправьте тестовое письмо на другой почтовый сервер. Свяжитесь с получателем и сообщите о проблеме |
Данная ошибка может возникнуть из-за настроек программы Антиспам на стороне получателя. Проверьте корректность оформления вашего письма и другие параметры, по которым ваше сообщение может быть отнесено к нежелательным.
Почтовый сервер ответил ошибкой 571
Значение: SMTP Protocol Returned a Permanent Error 571 xxx@mail.ru prohibited. We do not relay/Spam message rejected. Ошибка на стороне получателя почты.
|
Возможные причины |
Варианты решения |
|
Ваш IP-адрес заблокирован на стороне конечного получателя спам-фильтром, антивирусом или файрволом |
Данную проблему может решить только администратор сети получателя, исключив ваши идентификационный данные из списка блокировки или добавив их в «белый список» |
|
Неверные учетные данные ретранслятора. У вас нет разрешения на отправку электронной почты через сервер, который находится между вами и получателем |
Обратитесь к администратору данного ресурса для изменения настроек |
|
У IP отправителя нет RDNS |
Проверьте настройки получения писем и разрешения для доменов-отправителей |
Как я уже писал выше, разные почтовые серверы накладывают свои ограничения на прием и отправку сообщений. Код 571 в Google Suite расшифровывается следующим образом: «Действующая политика запрещает отправку этого сообщения». Письмо может содержать защищенные или конфиденциальные данные – номера кредитных карт и т.п. Или политика администрирования запрещает отправку определенными пользователями сообщений адресатам вне установленной группы.
Сертификат почтового сервера недействителен
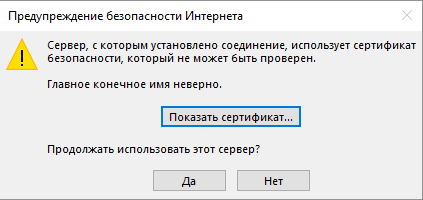
Проверка доступности почтового сервера программным методом
В данной статье описаны лишь некоторые варианты ошибок, которые могут возникнуть при отправке электронных сообщений. Полный перечень достаточно объемен и во многом зависит от настроек конкретного сервера как на стороне отправителя, так и получателя. Некоторые из ошибок могут быть легко устранены обычным пользователем, другие под силу лишь опытным администраторам.
Одним из способов предупреждения появления ошибок является онлайн-проверка доступности почтового сервера с помощью бесплатных инструментов:
- https://mxtoolbox.com
- https://www.ultratools.com
- http://mail2web.com
Эти сервисы пробуют подключиться к почтовому серверу по SMTP, подтверждают, что у него есть запись обратной зоны DNS, и замеряют время отклика. С их помощью можно диагностировать некоторые ошибки службы почтовых серверов или проверить, не занесен ли данный ресурс в черные списки из-за спама.
Прочитав эту статью, обратите внимание на то, как настроен ваш почтовый сервер на получение сторонних писем по SMTP-протоколу. Быть может, в данный момент ваш антиспам или локальная политика фильтрации входящих сообщений блокирует получение очень важного и нужного для вас месседжа? Проверьте сами или обратитесь к системному администратору. Если ошибку с SMTP никак не удается решить, то попробуйте обратиться в службу поддержки почтового сервера.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server.
Unless otherwise stated, all status codes described here is part of the current SMTP standard, RFC 5321. The message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided.
Basic status code[edit]
A «Basic Status Code» SMTP reply consists of a three digit number (transmitted as three numeric characters) followed by some text. The number is for use by automata (e.g., email clients) to determine what state to enter next; the text («Text Part») is for the human user.
The first digit denotes whether the response is good, bad, or incomplete:
- 2yz (Positive Completion Reply): The requested action has been successfully completed.
- 3yz (Positive Intermediate Reply): The command has been accepted, but the requested action is being held in abeyance, pending receipt of further information.
- 4yz (Transient Negative Completion Reply): The command was not accepted, and the requested action did not occur. However, the error condition is temporary, and the action may be requested again.
- 5yz (Permanent Negative Completion Reply): The command was not accepted and the requested action did not occur. The SMTP client SHOULD NOT repeat the exact request (in the same sequence).
The second digit encodes responses in specific categories:
- x0z (Syntax): These replies refer to syntax errors, syntactically correct commands that do not fit any functional category, and unimplemented or superfluous commands.
- x1z (Information): These are replies to requests for information.
- x2z (Connections): These are replies referring to the transmission channel.
- x3z : Unspecified.
- x4z : Unspecified.
- x5z (Mail system): These replies indicate the status of the receiver mail system.
Enhanced status code[edit]
The Basic Status Codes have been in SMTP from the beginning, with RFC 821 in 1982, but were extended rather extensively, and haphazardly so that by 2003 RFC 3463 rather grumpily noted that: «SMTP suffers some scars from history, most notably the unfortunate damage to the reply code extension mechanism by uncontrolled use.»
RFC 3463 defines a separate series of enhanced mail system status codes which is intended to be better structured, consisting of three numerical fields separated by «.», as follows:
class "." subject "." detail class = "2" / "4" / "5" subject = 1 to 3 digits detail = 1 to 3 digits
The classes are defined as follows:
- 2.XXX.XXX Success: Report of a positive delivery action.
- 4.XXX.XXX Persistent Transient Failure: Message as sent is valid, but persistence of some temporary conditions has caused abandonment or delay.
- 5.XXX.XXX Permanent Failure: Not likely to be resolved by resending the message in current form.
In general the class identifier MUST match the first digit of the Basic Status Code to which it applies.[1]
The subjects are defined as follows:
- X.0.XXX Other or Undefined Status
- X.1.XXX Addressing Status
- X.2.XXX Mailbox Status
- X.3.XXX Mail System Status
- X.4.XXX Network and Routing Status
- X.5.XXX Mail Delivery Protocol Status
- X.6.XXX Message Content or Media Status
- X.7.XXX Security or Policy Status
The meaning of the «detail» field depends on the class and the subject, and are listed in RFC 3463 and RFC 5248.
A server capable of replying with an Enhanced Status Code MUST preface (prepend) the Text Part of SMTP Server responses with the Enhanced Status Code followed by one or more spaces. For example, the «221 Bye» reply (after QUIT command) MUST be sent as «221 2.0.0 Bye» instead.[1]
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of these enhanced status codes.[2]
Common status codes[edit]
This section list some of the more commonly encountered SMTP Status Codes. This list is not exhaustive, and the actual text message (outside of the 3-field Enhanced Status Code) might be different.
— 2yz Positive completion[edit]
-
- 211 System status, or system help reply
-
- 214 Help message (A response to the HELP command)
-
- 220 <domain> Service ready
-
- 221 <domain> Service closing transmission channel
-
- 221 2.0.0 Goodbye [1]
-
- 235 2.7.0 Authentication succeeded [3]
-
- 240 QUIT
-
- 250 Requested mail action okay, completed
-
- 251 User not local; will forward
-
- 252 Cannot verify the user, but it will try to deliver the message anyway
— 3yz Positive intermediate[edit]
-
- 334 (Server challenge — the text part contains the Base64-encoded challenge) [3]
-
- 354 Start mail input
— 4yz Transient negative completion[edit]
«Transient Negative» means the error condition is temporary, and the action may be requested again. The sender should return to the beginning of the command sequence (if any).
The accurate meaning of «transient» needs to be agreed upon between the two different sites (receiver- and sender-SMTP agents) must agree on the interpretation. Each reply in this category might have a different time value, but the SMTP client SHOULD try again.
-
- 421 Service not available, closing transmission channel (This may be a reply to any command if the service knows it must shut down)
-
- 432 4.7.12 A password transition is needed [3]
-
- 450 Requested mail action not taken: mailbox unavailable (e.g., mailbox busy or temporarily blocked for policy reasons)
-
- 451 Requested action aborted: local error in processing
-
- 451 4.4.1 IMAP server unavailable [4]
-
- 452 Requested action not taken: insufficient system storage
-
- 454 4.7.0 Temporary authentication failure [3]
-
- 455 Server unable to accommodate parameters
— 5yz Permanent negative completion[edit]
The SMTP client SHOULD NOT repeat the exact request (in the same sequence). Even some «permanent» error conditions can be corrected, so the human user may want to direct the SMTP client to reinitiate the command sequence by direct action at some point in the future.
-
- 500 Syntax error, command unrecognized (This may include errors such as command line too long)
-
- 500 5.5.6 Authentication Exchange line is too long [3]
-
- 501 Syntax error in parameters or arguments
-
- 501 5.5.2 Cannot Base64-decode Client responses [3]
-
- 501 5.7.0 Client initiated Authentication Exchange (only when the SASL mechanism specified that client does not begin the authentication exchange) [3]
-
- 502 Command not implemented
-
- 503 Bad sequence of commands
-
- 504 Command parameter is not implemented
-
- 504 5.5.4 Unrecognized authentication type [3]
-
- 521 Server does not accept mail [5]
-
- 523 Encryption Needed [6]
-
- 530 5.7.0 Authentication required [3]
-
- 534 5.7.9 Authentication mechanism is too weak [3]
-
- 535 5.7.8 Authentication credentials invalid [3]
-
- 538 5.7.11 Encryption required for requested authentication mechanism[3]
-
- 550 Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable (e.g., mailbox not found, no access, or command rejected for policy reasons)
-
- 551 User not local; please try <forward-path>
-
- 552 Requested mail action aborted: exceeded storage allocation
-
- 553 Requested action not taken: mailbox name not allowed
-
- 554 Transaction has failed (Or, in the case of a connection-opening response, «No SMTP service here»)
-
- 554 5.3.4 Message too big for system [4]
-
- 556 Domain does not accept mail [5]
Example[edit]
Below is an example SMTP connection, where a client «C» is sending to server «S»:
S: 220 smtp.example.com ESMTP Postfix C: HELO relay.example.com S: 250 smtp.example.com, I am glad to meet you C: MAIL FROM:<bob@example.com> S: 250 Ok C: RCPT TO:<alice@example.com> S: 250 Ok C: RCPT TO:<theboss@example.com> S: 250 Ok C: DATA S: 354 End data with <CR><LF>.<CR><LF> C: From: "Bob Example" <bob@example.com> C: To: Alice Example <alice@example.com> C: Cc: theboss@example.com C: Date: Tue, 15 Jan 2008 16:02:43 -0500 C: Subject: Test message C: C: Hello Alice. C: This is a test message with 5 header fields and 4 lines in the message body. C: Your friend, C: Bob C: . S: 250 Ok: queued as 12345 C: QUIT S: 221 Bye {The server closes the connection}
And below is an example of an SMTP connection in which the SMTP Server supports the Enhanced Status Code, taken from RFC 2034:
S: 220 dbc.mtview.ca.us SMTP service ready C: EHLO ymir.claremont.edu S: 250-dbc.mtview.ca.us says hello S: 250 ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES C: MAIL FROM:<ned@ymir.claremont.edu> S: 250 2.1.0 Originator <ned@ymir.claremont.edu> ok C: RCPT TO:<mrose@dbc.mtview.ca.us> S: 250 2.1.5 Recipient <mrose@dbc.mtview.ca.us> ok C: RCPT TO:<nosuchuser@dbc.mtview.ca.us> S: 550 5.1.1 Mailbox "nosuchuser" does not exist C: RCPT TO:<remoteuser@isi.edu> S: 551-5.7.1 Forwarding to remote hosts disabled S: 551 5.7.1 Select another host to act as your forwarder C: DATA S: 354 Send message, ending in CRLF.CRLF. ... C: . S: 250 2.6.0 Message accepted C: QUIT S: 221 2.0.0 Goodbye {The server closes the connection}
References[edit]
- ^ a b c RFC 2034
- ^ «Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Enhanced Status Codes Registry». IANA. Retrieved December 20, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l RFC 4954
- ^ a b RFC 4468
- ^ a b RFC 7504
- ^ RFC 5248
This document describes the set of extended status codes for use within the SMTP mail system for delivery status reports, tracking, and improved diagnostics. In combination with other information provided in the Delivery Status Notification (DSN) delivery report, these codes facilitate media and language independent rendering of message delivery status.
- These codes are documented in RFC 3463
- SMTP Server Status Codes and SMTP Error Codes
Status Code Structure[edit | edit source]
This document defines a new set of status codes to report mail system conditions. These status codes are used for media and language independent status reporting. They are not intended for system specific diagnostics.
The syntax of the new status codes is defined as:
status-code = class "." subject "." detail
class = "2"/"4"/"5" subject = 1*3digit detail = 1*3digit
White-space characters and comments are NOT allowed within a status-code. Each numeric sub-code within the status-code MUST be expressed without leading zero digits.
Status codes consist of three numerical fields separated by «.». The first sub-code indicates whether the delivery attempt was successful. The second sub-code indicates the probable source of any delivery anomalies, and the third sub-code indicates a precise error condition.
Example: 2.1.23
The code space defined is intended to be extensible only by standards track documents. Mail system specific status codes should be mapped as close as possible to the standard status codes. Servers should send only defined, registered status codes. System specific errors and diagnostics should be carried by means other than status codes.
New subject and detail codes will be added over time. Because the number space is large, it is not intended that published status codes will ever be redefined or eliminated. Clients should preserve the extensibility of the code space by reporting the general error described in the subject sub-code when the specific detail is unrecognized.
Status Codes[edit | edit source]
| Error Code | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0.1 | Cannot open connection | Typically your SMTP server or email program is unable to even start an SMTP session. Typical replies will be “SMTP Error 101, Error opening connection” or “SMTP Error 101, cannot open SMTP stream”.
All SMTP Error 101 errors usually point to a configuration problem, such as an incorrectly spelt SMTP server, or an IP address that does not exist, or an SMTP port that does not exist or which the recipient will not accept SMTP connections on, or some other process is already using the |
| 1.1.1 | Connection refused | Typically from Linux based email systems such as SquirrelMail and Mailman. The message will usually go like this : “Connection refused, 111 Can’t open SMTP stream”.
All SMTP Error 111 errors usually point to an inability of your server to communicate with the remote SMTP server (either the recipient’s SMTP server or your ISP’s SMTP server) or to a Linux/SMTP software configuration problem, typically /etc/hosts not being world readable, or a newly installed or reconfigured firewall preventing connection to the remote SMTP server, or incorrect hostnames and/or domains (e.g. does your sending hostname match your IP address in a reverse lookup?), or exim not running. Telnet and logs should help you home in on the problem. |
| Status Code 2.X.X — Success Messages | ||
| 2.1.1 | System Status message or System Help Reply | SMTP status 211 prefaces a message about the Mail Server status or a System Help reply to the user requesting help information. You might for example issue a command to the mail server to display a list of commands you can use and the server replies with an SMTP Reply 211 followed by the list you requested. |
| 2.1.4 | Help Reply message | SMTP status 214 is usually in reply to the “HELP” command.It displays information about the server, usually a URL to the FAQ page of the SMTP software running on the server. As a result this “error” is normally called a reply, as in SMTP Reply 214. |
| 2.2.0 | <Server Name> service is running | This is normally the first message you will get back from the server. It means the mail service is running (ie. your mail server is running). It will normally contain a welcome message and/or the title of the SMTP software and, sometimes, the version number of the mail server software.SMTP Reply 220 is effectively a “Hi There, I have just this second finished starting up – I am ready to go and at your command” informational message. |
| 2.2.1 | The domain service is closing the transmission channel | The server is ending the mail session – it is closing the conversation with the ISP as it has no more mail to send in this sending session.
SMTP Status 221 is often misconstrued as an error condition, when it is in fact nothing of the sort. The mail server is simply telling you that it has processed everything it was given in this particular session, and it is now going back into waiting mode. Because SMTP status 221 is often misinterpreted, with some mail servers the Network Administrators have changed the default text of SMTP Reply 221 to something more meaningful and less alarming. For example, a typical SMTP reply 221 might say “221 Goodbye” or “221 Closing connection”, or the most irritating one we’ve seen “221 Bye”, Arrrgghh–can you blame anyone for thinking there might be a problem? Of course not! So some Network Administrators are these days being quite imaginative by changing the default text of SMTP reply 221 to more user friendly messages like : “221 Thank you for your business”(I love that one!),or “221 All messages processed successfully in this session, SMTP connection is closing”. |
| 2.1.4 | Help Reply message | SMTP status 214 is usually in reply to the “HELP” command. It displays information about the server, usually a URL to the FAQ page of the SMTP software running on the server. As a result this “error” is normally called a reply, as in SMTP Reply 2.1.4. |
| 2.2.0 | <Server Name> service is running | This is normally the first message you will get back from the server. It means the mail service is running (ie. your mail server is running). It will normally contain a welcome message and/or the title of the SMTP software and, sometimes, the version number of the mail server software. SMTP Reply 220 is effectively a “Hi There, I have just this second finished starting up – I am ready to go and at your command” informational message. |
| 2.2.1 | The domain service is closing the transmission channel | The server is ending the mail session – it is closing the conversation with the ISP as it has no more mail to send in this sending session.
SMTP Status 221 is often misconstrued as an error condition, when it is in fact nothing of the sort. The mail server is simply telling you that it has processed everything it was given in this particular session, and it is now going back into waiting mode. Because SMTP status 221 is often misinterpreted, with some mail servers the Network Administrators have changed the default text of SMTP Reply 221 to something more meaningful and less alarming. For example, a typical SMTP reply 221 might say “221 Goodbye” or “221 Closing connection”, or the most irritating one we’ve seen “221 Bye”, Arrrgghh – can you blame anyone for thinking there might be a problem ? Of course not ! So some Network Administrators are these days being quite imaginative by changing the default text of SMTP reply 221 to more user friendly messages like: “221 Thank you for your business” (I love that one!), or “221 All messages processed successfully in this session, SMTP connection is closing”. |
| 2.5.0 | Requested mail action OK completed | The mail server has successfully delivered the message! This is the best SMTP reply (250) to receive — your message has been accepted and transmitted OK !  Yippee. Yippee.
250 is effectively a status code rather than an error code – there is no such thing as an SMTP error 250. |
| 2.5.1 | User not local will forward | The email account is not local to the ISP server but the ISP server will accept the email and will forward it (the server will RELAY your message, this is the
most common action for ISP Mail servers – the recipient will see your ISP in the mail header as one of the first hops on the way to the recipient’s email system). SMTP Error 251 is therefore more of an informational message for technicians tracking how a message reached its destination. |
| 2.5.2 | Cannot VRFY (verify) the user – the server will accept the message and attempt to deliver it | The user account appears to be valid but could not be verified, however the server will try do
deliver the message. There are sometimes circumstances where an email address appears to be valid but cannot be verified as definitely valid during the SMTP session between the sending server (your server) and the next server to accept your message. This can happen for example in very large corporation where the first email receiving server might only be an email exchanger server, a gateway server to the eventual server which holds the user mailboxes and which can verify if the intended recipient exists in that organization. When this happens the gateway server will reply with an SMTP Error 252 telling your sending server that it cannot verify the user part of the email address, that the domain part is OK, and that it will forward your email to a server which can do the checking and eventually deliver to the user mailbox if it exists. |
| Status Code 3.X.X — Informational | ||
| 3.5.4 | Start mail input end with <CRLF>.<CRLF>, or, as a less cryptic description – “FROM and TO information received, now please provide message body and mark its end with <CRLF>.<CRLF>” | This is normally in response to the DATA command. The server has received the From and To information and is now asking for the “Message Body”, the main part of the message which should be ended by two blank lines separated by a dot (period).
Therefore, on receiving an SMTP Reply 354 the sending server should send the body of the message to the |
| Status Code 4.X.X — Persistent Transient Failure | ||
| 4.2.0 | Timeout communication problem encountered during transmission. This is a Novell GroupWise SMTP error | In our experience only Novell GroupWise servers use this error (we use GroupWise!). You will get a GroupWise GWIA (GroupWise Internet Agent) 420 TCP Write Error or 420 TCP Read Error if there are communication problems during transmission of the actual message after the sending and receiving servers have actually connected. A small number of 420 SMTP errors is normal as occasional peaks of Internet usage may delay the transmission of an email with attachment so much that a timeout occurs. When a timeout occurs on a GWIA send, the message is queued up in the <Domain>WPGATEDEFER directory for processing at a later time (as defined in ConsoleOne or GWIA.CFG).
If you experience 420 errors only with specific recipient then it is quite likely that the recipient’s antispam firewall does not like your server, your server’s external IP address, or that your server’s HELO command uses an outbound identification that does not match your server’s external IP address (check that your sending domain’s DNS is set up correctly). In an ideal world a well behaved recipient server should really be issuing your GroupWise server with a 554 error rather than timing out and causing the GroupWise GWIA to fault with a 420 error. If you experience too many 420 errors with all email communications, then you have a physical communication problem somewhere. This could be your server’s network card, the network point that your server is plugged into, your switch(es), your router(s), your firewall, or your Internet line – problems caused by routers with different MTU sizes is a classic issue. Unless the logs of all those various problem points can give you an instant answer, the only way you will get to the bottom of the problem is to use a packet tracing and inspection program like Ethereal or Wireshark, its successor, if you’re running GroupWise on a Windows or Linux server; on NetWare your only choice is PacketScan which you can get here http://support.novell.com/docs/Readmes/InfoDocument/2967287.html. In the final analysis, if the tracing of packets, and the changing of hardware does not help then do not discount a slightly faulty hard disk being the cause of all your problems (even if your RAID controller or your hard disk testing software does not detect any problem!). |
| 4.2.1 | The SMTP service/server you use has a limit on the number of concurrent SMTP streams your server can use | The Mail transfer service is unavailable because of a transient event. SMTP reply
421 can be caused by many things but generally indicates that the mail server which returns this status code is currently unavailable but may be available later. For example, the server administrator may have stopped the mail service to troubleshoot a problem, or the mail server is right in the middle of rebooting, or the mail server is currently processing too many incoming messages or incoming requests, etc… Note : “Mail Server” in this case can be any of the mail servers on the message’s route – the sending server (your server), the ISP SMTP server, or the recipient’s mail server. Clearly, if you repeatedly receive an SMTP status 421 then the problem is no longer of a transient nature and you need to investigate or inform the relevant network administrator, ISP tech support, or the recipient. SMTP Response 421 can also be received as a result of your message server sending an email where the total |
| 4.2.2 | The recipient’s mailbox is over its storage limit
( OR ) The size of the message exceeds the recipient’s size limits for incoming email |
Either the recipient’s mailbox is over its storage limit or the message delivery directory (folder) on the recipient’s mail server is currently over a size limit imposed by the Network Administrator (e.g. possibly as a result of the mail server having been down for some time, having been repaired, and currently in the process of collecting thousands of queued up messages).
However, SMTP response 422 can also be received if the email being sent is larger than the incoming emails size limit in operation at the recipient’s mail server (particularly when that recipient’s mail server is Exchange Server). |
| 4.3.1 | The recipient’s mail server is experiencing a Disk Full condition | The recipient’s mail server is experiencing a Disk Full error condition, or an Out of Memory (too many file handles) error condition (Microsoft Exchange). |
| 4.3.2 | The recipient’s Exchange Server incoming mail queue has been stopped | This is an SMTP status response specific to Microsoft Exchange Server. It indicates that the recipient’s mail queue on their Exchange Server has been stopped (frozen), probably while the Network Administrator troubleshoots some problem. |
| 4.4.1 | The recipient’s server is not responding | This is an error emanating from your server indicating that the recipient’s server is not responding. Your server will automatically try again a number of times – how many depends on how your server has been configured. |
| 4.4.2 | The connection was dropped during transmission | Your server started delivering the message but the connection was broken during transmission. This may be an unusual transient error – however, if it keeps happening you should investigate possible problems with your server’s network card, your Internet routers, processes hogging the resources of your server, and anything else which could result in a network connection being broken. |
| 4.4.6 | The maximum hop count was exceeded for the message | The maximum hop count was exceeded for your message. The most likely cause of this error status code is that your message is looping internally on your server, internally between two of your organisation’s servers, or, sometimes, looping between your server and the recipient’s server. |
| 4.4.7 | Your outgoing message timed out. | Your outgoing message timed out because of problems with the receiving server who objected to your message. Typically there is a problem with the message header (such as too many recipients, in most cases, or a protocol timeout between the two servers). |
| 4.4.9 | Routing error | This is a Microsoft Exchange Server specific error code. As per Microsoft’s documentation this error code is returned when either of the following conditions occurs: an SMTP connector is configured to use DNS without a smart host and also uses a non-SMTP address space (e.g. X.400), or A message was sent to a recipient who was identified as a member of a routing group that was deleted. |
| 4.5.0 | Requested action was not taken – The mailbox was unavailable at the remote end. A secondary SMTP error code may follow “450” to refine the reason for the failure to transmit the message, e.g. “SMTP Error 450”. | The server could not access the mailbox to deliver the message. This could be caused by a process on the remote server tidying up the mailbox, or the remote mailbox could be corrupt, or the remote mailbox may be stored on another server which is currently offline, or the network connection went down while sending, or the remote mail server does not want to accept mail from your server for some reason (IP address, blacklisting, etc..).
In general SMTP Error 450 is a transient error at the remote end (the destination), or at one of the routers or servers en route to the remote end, and should induce your mail server to retry after it’s preset retry interval. Example of an SMTP Error 450 reply message: “450 Please try again later”, or a classic Novell GroupWise 450 status message: “The message that you sent has been delayed. The reason given for the delay: 450 Host down (relay.clara.net)”. SMTP Error 450 is often followed by a second SMTP error code to refine the reason for the email not reaching its destination. For example: “SMTP Error 450 5.2.3 Msg Size greater than allowed by Remote Host”. When that is the case and If the error message is not as clearly worded as in this example, then simply search this document for the secondary error code. In this case searching this document for SMTP Error 523 or SMTP Error 5.2.3 would yield an explanation identical to the wording above. |
| 4.5.1 | Requested action aborted – Local error in processing.( OR ) Requested action delayed – Local problem( OR ) <IP_Address> has recently sent spam |
The action has been aborted by the ISP’s server. “Local” (Local Problem, Local Error) refers to the next server that your message will go through after leaving your server, typically your ISP’s server, or the SMTP relaying service you are using, or, if your mail server is sending directly to the destinations, the destination mail server. This error is usually due to overloading at your ISP or your SMTP relaying service from [temporarily] too many messages or some other similar transient failure. Typically some [hopefully] temporary event prevents the successful sending of the message. The next attempt to send by your server may prove successful.
If this error keeps occurring to the point that it has effectively lost its transient nature and has become… frequent (!!), then the problem is at your end and you should check your own mail server (if you email out of a corporate network), communications on your side (router, server network card), or inform your ISP if your mail server relays through your ISP or if you are a home user emailing out through Outlook, Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or similar email program. Examples of typical SMTP Error 451 return messages: “SMTP error 451 Unable to complete command, DNS not available or timed out” or “451 Domain of sender address does not resolve” or “451 Error getting LDAP results in map”, or “451 4.7.1 Greylisting in action, please come back in 00:02:00 [minutes]” or “The message that you sent has been delayed. The reason given for the delay : 451 Temporary local problem — please try later.”. With the original SMTP standards having been invented before spam became the scourge of the Internet, there are no SMTP error codes dedicated to anti-spam errors. As a result, SMTP Error 451 is now increasingly also used to indicate that a message has been rejected by the remote server because of anti-spam measures. A typical error might be, for example: “SMTP error from remote mail server after end of data, host <host_address>: 451 <ip_address> has recently sent spam. If you are not a spammer, please try later.”. If all anti-spam related SMTP 451 errors are as descriptive as the one above, then the error itself will tell you what you need to do. As a general rule, however, you will most times need to take some measures to have either your server, or your ISP’s server, taken off some Internet blacklist used by the recipient. |
| 4.5.2 | Requested action not taken – Insufficient storage. | The ISP server’s disk system has run out of storage space, so the action had to be cancelled. Unless you are with an ISP which is so slack that they have not implemented Disk Full Alerts, this error usually indicates that your ISP’s mail server is overloaded from too many messages. This can happen even to the best ISPs when, for example, there have been problems and none of the ISP’s customers could send mail; as soon as the problems are fixed there is almost always a situation where thousands of users and organizations are trying to send mail all at the same time, and those numbers can occasionally result in the ISP’s mail servers’ hard disks temporarily filling up, with SMTP Error 452 being the result. The next attempt to send by your server may prove successful. |
| 4.6.5 | Code Page unavailable on the recipient server | This is an Exchange Server-specific error code. This error is returned by the recipient’s server if the incoming email specifies a Code Page that is not installed on the recipient’s server, normally because not all language files were installed on the server during either the installation of Windows or of Exchange Server. |
| 4.7.1 | This is a local error with the sending server and is often followed with “Please try again later” | This is always a local error with your own mail server. SMTP Error 471 (or 4.7.1) is usually tagged onto a primary SMTP error code, for example “SMTP Error 450 4.7.1”, or “SMTP Error 451 4.7.1”, or “SMTP Error 550 4.7.1”; example: “451 4.7.1 Greylisting in action, please come back in 00:02:00 [minutes]”. In all the cases that we have seen SMTP Error 471 is usually caused by anti-spam or virus scanning software on your server (the sending server) getting into problems through a bug in the software, or because of a bad automatic update from the antivirus/anti-spam manufacturer, because of lack of memory on your server, or because of hard disk problems. |
| Status Code 5.X.X — Errors | ||
| 5.0.0 | Syntax error command not recognized. | SMTP Error 500 : The last command sent by your server was not recognized as a valid SMTP or ESMTP command, or is not formatted in the way the server expected. This includes situations where the command is too long.
Note that commands that are recognized, but not implemented, are handled by different status messages (see 502 and 504). Note: A «500 unrecognized command» server response is often a case of antivirus software and/or firewall interfering with incoming and/or outgoing SMTP communications. Read your antivirus / firewall software documentation thoroughly to solve the problem. Examples of SMTP Error 500 error messages: SMTP Permanent Error: 500 Access Denied By Port Access” or “SMTP Error 500 Line too long. |
| 5.0.1 | Syntax error in parameters or arguments (e.g. invalid email address) Can sometimes also be indicative of communication problems. |
The command was correct and recognised, but the parameters (the arguments, e.g. email address) were not valid.
For example, the following email address will definitely give an SMTP Error 501 with most mail servers, happy[email protected], as “” is not allowed in email addresses, which makes this email address invalid. In the vast majority of cases SMTP Error 501 is caused by invalid email addresses, an invalid domain name recipient, or a Unix / Linux SEND MAIL command which does not follow the established standards. For example, a typical return error message might be: «<remote-server-ip-address> does not like recipient. Remote host said: 501 Invalid Address«. In cases where the error is not caused by an invalid email address, or by the failure to assign a valid email address to the mandatory «From» property, an SMTP Error 501, particularly if repeated, can be indicative of communications problems, such as a noisy line, intermittent drops in network connections, etc… |
| 5.0.2 | Command not implemented | The command or function issued by your mail server is valid but has not been activated (typically, it is not supported on this particular server). |
| 5.0.3 | Bad sequence of commands.( OR ) This mail server requires authentication. |
In the original standards SMTP Status 503 indicates that the commands have been sent in the wrong order, for example your mail server has sent the “Hello” command before sending the “Mail” command.
This can often be caused by a drop in network connection just as your server was sending a command, resulting in SMTP Reply Code 503 is nowadays more often an indicator that the SMTP server you are trying to use requires authentication and you tried to send a message without authentication (username + password). This SMTP Error 503 is permanent in that the SMTP server will not log any errors in its log and it will not retry – you will have to resend the email using authentication. Example of such an error : “SMTP Error (state 13): 503 This mail server requires authentication when attempting to send to a non-local e-mail address. Please check your mail client settings or contact your administrator to verify that the domain or address is defined for this server”. |
| 5.0.4 | Command parameter not implemented. | The command and parameter are both valid, but the parameter is not implemented on the ISP server, or an additional parameter or action is missing.
For example, an often encountered SMTP Error 504 is : “504 Need to authenticate first” |
| 5.1.0 | Bad Email Address | Bad email address. This status code is generated by the sender’s local mail server.
If the email was addressed internally, then it means that the addressee, as written in the email’s TO, CC, or BCC fields, does not exist in your organization’s email system. If the email was addressed externally, then the recipient’s email address was misspelt. |
| 5.1.1 | Bad Email Address | Bad email address. This error is similar to error 510 and as with error 510, this status code is generated by the sender’s local mail server.
If the email was addressed internally, then it means that the addressee, as written in the email’s TO, CC, or BCC fields, does not exist in your organization’s email system. If the email was addressed externally, then the recipient’s email address was misspelt. |
| 5.1.2 | The host server for the recipient’s domain name cannot be found (DNS error) | This SMTP reply code is received when one of the servers on the way to the destination is unable to resolve the domain name of a recipient email address. Said differently : one of the servers on the way to the destination, including your server or your ISP, has a DNS problem or, possibly correctly, does not like one of the email addresses in the message’s TO, CC, and BCC fields.
The first check you should perform to resolve a 5.1.2 reply code is to check all the recipient email addresses for Examples of typical SMTP error 512 messages : “5.1.2 — Bad destination host ‘DNS Hard Error looking up domain”, |
| 5.1.3 | Address type is incorrect (most mail servers)( OR ) Relaying denied or Authentication required (a small percentage of mail servers) |
This status code (from the sender’s
mail server) is usually symptomatic, in an Exchange + Outlook environment, of the user’s Outlook Contacts having been imported from another system or PST and where some of the addresses are not defined correctly. Or, in any environment it is simply that the end-user simply did enter the email address completely wrongly, such as copying it from a website and not replacing “at” with “@”, e.g. : John.DoeatUCLA.edu (which should have been [email protected]), or [email protected]” (“, quotes, is not allowed in email addresses and is often included in error as a result of copying and pasting an email from somewhere). The user should check all the recipient addresses in the email, including those that were inserted from Contacts. |
| 5.2.3 | The Recipient’s mailbox cannot receive messages this big | This error will be received when the
total size of the message you have sent (ie: message + all of its attachments) exceeds the size limits on the Recipient’s server. Many companies implement the good practice of configuring their servers with limits on the size of emails they can receive to prevent their systems running out of space as a result of a spam attack where the spam emails contain large attachments, or as a result of valid but not very technically savvy senders sending enormous scans (through not knowing that scanning at 1200dpi rather than the usually perfectly usable and acceptable 300dpi, will create humongous attachments). Check the size of the email you sent, and, specifically, the size of the attachments you included, and consider splitting your email into smaller emails. If that does not work, check with the Recipient the maximum size of email they can receive, and if that is still prohibitive then consider FTP arrangements between you and the recipient. |
| 5.3.0 | Authentication is required( OR ) Your server has been blacklisted by the recipient’s server( OR ) The recipient’s mailbox does not exist |
|
| 5.4.1 | Recipient Address Rejected – Access denied (typically by the recipient’s antispam program / appliance) | |
| 5.5.0 | Requested actions not taken as the mailbox is unavailable.
550 is always a problem external to your own mail server. Usually it is at the recipient’s end, but it could also originate from inside your own “walls” through being caused, for example, by an appliance which scans your outgoing emails once they’ve left your server. |
|
| 5.5.1 | User not local or invalid address – Relay denied. | |
| 5.5.2 | Requested mail actions aborted – Exceeded storage allocation. or Size of the incoming message exceeds the incoming size limit. | |
| 5.5.3 | Requested action not taken – Mailbox name invalid.( OR ) You are attempting to send emails through a specific ISP’s SMTP server without authentication and without being connected to the Internet through that ISP’s service.( OR ) You are sending from an Exchange server configured to send via DNS and you do not have a public reverse DNS record pointing back to your Exchange server. |
|
| 5.5.4 | Transaction failed. Nowadays SMTP status 554 is in most cases returned when the recipient server believes your email is spam or your IP address or ISP server has been blacklisted on one or more Internet blacklists. With Yahoo, on the other hand, this usually means the email address does not exist or has been disabled.( OR ) With IBM’s Lotus Domino this is either a Domino bug or a Disk Full error |
|
| 5.7.1 | I have been told not to work with you!!! |
Collected Status Codes[edit | edit source]
| X.1.0 | Other address status |
| X.1.1 | Bad destination mailbox address |
| X.1.2 | Bad destination system address |
| X.1.3 | Bad destination mailbox address syntax |
| X.1.4 | Destination mailbox address ambiguous |
| X.1.5 | Destination mailbox address valid |
| X.1.6 | Mailbox has moved |
| X.1.7 | Bad sender’s mailbox address syntax |
| X.1.8 | Bad sender’s system address |
| X.2.0 | Other or undefined mailbox status |
| X.2.1 | Mailbox disabled, not accepting messages |
| X.2.2 | Mailbox full |
| X.2.3 | Message length exceeds administrative limit |
| X.2.4 | Mailing list expansion problem |
| X.3.0 | Other or undefined mail system status |
| X.3.1 | Mail system full |
| X.3.2 | System not accepting network messages |
| X.3.3 | System not capable of selected features |
| X.3.4 | Message too big for system |
| X.4.0 | Other or undefined network or routing status |
| X.4.1 | No answer from host |
| X.4.2 | Bad connection |
| X.4.3 | Routing server failure |
| X.4.4 | Unable to route |
| X.4.5 | Network congestion |
| X.4.6 | Routing loop detected |
| X.4.7 | Delivery time expired |
| X.5.0 | Other or undefined protocol status |
| X.5.1 | Invalid command |
| X.5.2 | Syntax error |
| X.5.3 | Too many recipients |
| X.5.4 | Invalid command arguments |
| X.5.5 | Wrong protocol version |
| X.6.0 | Other or undefined media error |
| X.6.1 | Media not supported |
| X.6.2 | Conversion required and prohibited |
| X.6.3 | Conversion required but not supported |
| X.6.4 | Conversion with loss performed |
| X.6.5 | Conversion failed |
| X.7.0 | Other or undefined security status |
| X.7.1 | Delivery not authorized, message refused |
| X.7.2 | Mailing list expansion prohibited |
| X.7.3 | Security conversion required but not possible |
| X.7.4 | Security features not supported |
| X.7.5 | Cryptographic failure |
| X.7.6 | Cryptographic algorithm not supported |
| X.7.7 | Message integrity failure |
SMTP-сервер — это программное обеспечение для отправки электронных писем, использующее SMTP протокол. Напомним, что вообще работа электронной почты обеспечивается с помощью трех протоколов: POP3 или IMAP — для получения писем, SMTP — для отправки.
Передача письма по SMTP происходит с помощью TCP-соединения. Стандартный порт для незащищенного соединения — 25. Однако многие сервисы по умолчанию его блокируют, так как именно на него обычно идет рассылка вирусного спама.
В качестве альтернативных можно прописывать в настройках порты 587 и 2525.
Для защищенного соединения по SSL используется порт 465.
Как работает SMTP-сервер
Функции почтового сервера SMTP сводятся к следующему:
- определить домен получателя письма и то, совпадает ли он с доменом отправителя;
-
определить IP-адрес сервера SMTP получателя;
-
установить соединение с ним;
-
с помощью серии запросов-ответов передать адреса отправителя и получателя, а также само письмо вместе с заголовками.
Если провести аналогию с обычной почтой, то функции SMTP-сервера можно сравнить с работой почтового отделения, которое проверяет корректность данных получателя на вашем конверте и отправляет письмо по месту назначения. Само письмо почтовое отделение не вскрывает. Сервер SMTP также не проверяет заголовки и содержимое вашего письма, а отправляет его как есть.
Виды почтовых серверов
SMTP-сервер встречается в нескольких вариантах:
- Бесплатные серверы SMTP. Идут как дополнение к бесплатным почтовым сервисам, таким как Яндекс.Почта, Gmail, Mail.ru и другим. Предназначены в основном для личного использования и не подходят для корпоративных рассылок: есть ограничения на количество отправок, высокий риск попасть под спам-фильтры и т. д.
- Сервер, предоставляемый интернет-провайдером. Этот вариант SMTP чем-то похож на использование бесплатных почтовых серверов: у вас также будут ограничения на отправку писем и, возможно, на скорость обработки очереди отправки
- SMTP от хостинга. Обычно достаточно производительный и без ограничений на отправку. Но нужно учитывать, что при массовых рассылках и низком качестве списка получателей есть большой риск попасть под спам-фильтр, причем не только того адреса, с которого ведется рассылка, но и всего домена.
- Коммерческие серверы SMTP. Предлагаются многими сервисами рассылок. Лучшее решение, если вы рассылаете множество писем, причем как транзакционных, так и рекламных. Обеспечивают быструю и надежную доставку и снижают риск попадания ваших писем в папку «Спам» у получателей.
Ответы SMTP-сервера. Коды успешной или неуспешной обработки запроса
В процессе передачи данных по SMTP ваш сервер отправляет на почтовый сервер получателя запросы, а тот высылает ответы. Ответы содержат трехзначный код, в котором зашифрован результат обработки запроса, и поясняющий текст к нему. Коды ответов могут иметь вид:
- 2xx. Такой ответ означает, что предыдущая команда была успешно выполнена.
- 3xx. Коды, начинающиеся на тройку, высылаются на промежуточном этапе передачи, когда сервер ждет остальную часть данных.
- 4xx. Это коды ошибок, которые могут носить временный характер.
- 5xx. В эту категорию относятся коды критичных ошибок.
Коды ошибок SMTP, их причины и варианты исправления ситуации
Прежде всего учтите важный момент: хотя многие коды ответов стандартны, существуют и уникальные для каждого SMTP сервера коды. Их могут создавать администраторы почтовых серверов. Обычно к ним идет поясняющий текст, из него можно понять, в чем дело.
Мы же разберем самые распространенные ошибки SMTP и поясним, что делать в этих ситуациях.
Ошибка 421
Расшифровка ошибки SMTP 421 — «сервис недоступен». Причиной могут быть:
-
Блокировка трафика на 25 порту. Пропишите в настройках альтернативные порты.
-
Неправильно заданы настройки соединения. Проверьте и исправьте настройки.
-
Ваш антивирус или брандмауер блокирует соединение с сервером SMTP.
Попробуйте отключить программу защиты и отправить письмо. Если ошибка исчезла, значит дело в этом. Добавьте IP-адрес сервера в исключения антивируса или брандмауера.
- Использование VPN. Встречается достаточно редко, но все же проверьте, отправляется ли письмо, если отключить VPN. Если да, то необходимо обратиться к администраторам VPN-сервиса, чтобы устранить проблему.
-
Вы используете бесплатный сервер SMTP и при этом отправляете много писем. У таких серверов существуют лимиты на отправку в определенный промежуток времени, возможно, вы его превысили. Вам лучше использовать профессиональные платные решения.
-
Грейслистинг (серый список). Это функция защиты от спама. Работает она следующим образом: в ответ на все подозрительные письма, письма с адресов, с которых сообщение приходит впервые, сервер отправляет эту ошибку. Если на стороне отправителя — легитимный SMTP-сервер, а не спамерское ПО, то через некоторое время он отправит письмо еще раз, и уже тогда сервер получателя примет письмо. Спамеры обычно не предпринимают повторных попыток отправки. Предпринимать в этом случае обычно ничего не нужно — если вы пользуетесь надежным сервером, он сам повторит отправку и письмо будет доставлено.
Ошибка 451
Эта ошибка означает, что отправка была прервана в процессе. Возможные причины и пути решения проблемы следующие:
- На DNS-сервере неправильно прописаны параметры почтового сервера (MX записи). Например, некорректно проставлены предпочтения, если почтовых серверов для домена несколько. Перепроверьте и исправьте записи. Возможно, потребуется также посмотреть логи и файлы конфигурации.
- Превышены лимиты сервера на отправки или подключения. Проверьте, нет ли подозрительно большого количества отправляемых писем, если все нормально — увеличьте лимиты в настройках.
Ошибка 452
Означает, что либо у вас, либо у получателя закончилось место на машине, где установлен сервер, или не хватает памяти для обработки. Проверьте, есть ли в сообщении упоминание про «memory», и проверьте свою систему. Если у вас все в порядке, обратитесь к получателю.
Ошибка 550
Самый распространенный тип ошибки SMTP. В большинстве случаев возникает, если указан несуществующий email-адрес получателя. Но также возможны следующие причины:
- Не работает почтовый сервер на стороне адресата. Попробуйте отправить любое письмо на домен, за который отвечает другой почтовый сервер. Если письмо успешно отправлено — значит, проблема не у вас, нужно связаться с адресатом и объяснить ему ситуацию.
-
Неправильно настроены параметры SMTP — перепроверьте настройки.
-
Вы используете сервер провайдера, и у него установлены лимиты на отправку сообщений. Свяжитесь с провайдером, узнайте значения лимитов. При необходимости перейдите на другой тариф или используйте платный SMTP-сервер.
-
Возможно, в вашей сети вирус и с вашего адреса рассылается спам. Проверьте систему с помощью антивирусного ПО.
Ошибка 571
Это ошибка означает, что сервер SMTP получателя не принял ваше письмо. Возможные причины:
- Ваш IP-адрес заблокирован почтовым сервером адресата. Это может сделать антивирусное ПО, или файервол, или программное обеспечение для защиты от спама. Проблему нужно решать с системным администратором получателя.
-
Ваш email внесен в списки спамеров. Нужно разбираться в причине и предпринимать меры, чтобы его оттуда удалили.
-
У вашего IP нет rDNS записи. Это необходимый параметр, без него ни один почтовый сервер не примет ваше письмо. Для решения проблемы обратитесь к хостинг-провайдеру.
Истек сертификат почтового сервера
Просто обновите сертификат SMTP.