1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 |
Uses Crt; Type TInf=Record Num: Integer; FIO: String; Nomer_zachetki: String; Sredniy_bal: Integer; Gruppa: String; end; TTree=^Tree; Tree=Record Inf:TInf; Left,Right: TTree; end; {-------------------------------------------------------------------------} Procedure Tab (n: Integer); Begin GoToXY(n,WhereY); End; {Процедура установки курсора в позицию n текущей строки} {-------------------------------------------------------------------------} Procedure ShowHeader;{Отображение заголовка к данным} Begin Write('# FIO #Zachetki Sr.bal Gruppa'); WriteLn; {Переводим строку, подготавливаемся к выводу данных} End; Procedure Show(I: TInf);{Отображение данных записи} Begin Write(I.Num); {Аналогично выводу заголовков только выводим данные из записи T} Tab(5);Write(I.FIO); Tab(15);Write(I.Nomer_zachetki); Tab(25);Write(I.Sredniy_bal); Tab(35);Write(I.Gruppa); WriteLn; {Перевод строки} End; Procedure Input(Var I: TInf);{Заполнение записи путём ввода данных с клавиатуры} Begin Write(' 1. Num : ');ReadLn(I.Num); Write(' 2. FIO : ');ReadLn(I.FIO); Write(' 3. Nomer_zachetki : ');ReadLn(I.Nomer_zachetki); Write(' 4. Sredniy_bal : ');ReadLn(I.Sredniy_bal); Write(' 5. Gruppa : ');ReadLn(I.Gruppa); End; {-------------------------------------------------------------------------} Function SignKey(A,B: TInf): Boolean; Begin SignKey:=False; If A.Num<B.Num then SignKey:=True; End; Function FindKey(A,B: TInf): Boolean; Begin FindKey:=False; If A.Num=B.Num then FindKey:=True; End; Function NewSheet(X:TInf): TTree; {размещение в куче нового элемента} Var T: TTree; Begin New (T); T^.Inf:=X; T^.Right:=Nil; T^.Left:=Nil; NewSheet:=T; End; Procedure AddSheet(Var R: TTree; N: TInf);{размещение нового элемента (листа) в структуре} Begin If R<>Nil then begin If SignKey(R^.Inf,N) then begin If R^.Left=Nil then R^.Left:=NewSheet(N) else AddSheet(R^.Left,N); end else begin If R^.Right=Nil then R^.Right:=NewSheet(N) else AddSheet(R^.Right,N); end; end else begin {дерево не создано, создаем его} R:=NewSheet(N); end; End; Procedure AddTree(Var R: TTree; N: TTree);{размещение нового в структуре} Begin If R<>Nil then begin If N<>Nil then begin If SignKey(R^.Inf,N^.Inf) then begin If R^.Left=Nil then R^.Left:=N else AddTree(R^.Left,N); end else begin If R^.Right=Nil then R^.Right:=N else AddTree(R^.Right,N); end; end; end else begin {дерево не создано, пытаемся создать его} R:=N; end; End; Function Find(R: TTree; F: TInf): TTree;{Поиск элемента} Var t: Ttree; Begin t:=Nil; If R<>Nil then begin {Если дерево не пустое} If FindKey(R^.Inf,F) then begin {Проверяем значение ключевого поля} t:=R; {Если нашли нужный элемент, запоминаем его значение} end else begin {если не нашли} t:=Find(R^.Left,F); {пытаемся найти в других ветвях дерева (сначала слева)} If t=Nil then t:=Find(R^.Right,F); {Потом справа, если слева ничего не нашли} end; end; Find:=t; {Результат функции - значение временной переменной t} End; Procedure ShowTree(R: TTree); {Вывод дерева на экран} Begin If R<>Nil then begin {Если ветвь не пуста} Show(R^.Inf); {выводим информацию} If R^.Left <> nil then ShowTree(R^.Left); {если слева имеется сук, выводим и его} If R^.Right <> nil then ShowTree(R^.Right);{тоже самое справа...} end; End; Function DeleteNode(R: TTree;W: TTree):TTree; Var t: TTree; Begin t:=Nil; If R<>Nil then begin {Если ветвь существует} If W<> Nil then begin If R^.Left = W then begin R^.Left:=W^.Left; t:=W^.Right; Dispose(W); end else begin t:=DeleteNode(R^.Left,W); end; If t=Nil Then {Если ничего не нашли в левой ветви, ищем в правой} If R^.Right = W then begin R^.Right:=W^.Left; t:=W^.Right; Dispose(W); end else begin t:=DeleteNode(R^.Right,W); end; end; end; DeleteNode:=t; End; Procedure DeleteTree(Var R: TTree;W: TTree); Begin If R=W then begin R:=W^.Left; AddTree(R,W^.Right); Dispose(W); end else AddTree(R,DeleteNode(R,W)); End; Procedure Done(R: TTree); {Освобождает в памяти место, занятое деревом R} begin If R<> nil then begin If R^.Left <> nil then Done(R^.Left); If R^.Right <> nil then Done (R^.Right); Dispose(R); End; End; Procedure Print(T: TTree; g: integer); {Печать дерева. G-глубина (по лекции)} Const k=6; Begin If T=nil then Writeln ('Derevo pustoe') else begin g:=g+1; If T^.Right <> nil then Print (T^.Right, g) else begin {Tab(4*(g+1));Writeln('RNil');} end; Tab(k*g); Writeln (T^.Inf.Num,' ', T^.Inf.FIO); If T^.Left <> nil then Print (T^.Left,g) else begin {Tab(4*(g+1));Writeln('LNil');} end; g:=g-1; End; End; {-------------------------------------------------------------------------} Var Root,W: TTree; I: TInf; n: Integer; {Определяем необходимые переменные} BEGIN ClrScr; {Основная программа} Randomize; Root:=Nil; {Начальные условия - пустое дерево} WriteLn('!!!!!!!!!!! Posle vvedeniya dannuh, i ih polucheniya, najmite [ENTER] !!!!!!!!!!!'); For n:=1 to 4 do begin {В цикле вводим записи (4 штук)} WriteLn('-===[Zapis: ',n,']=====---'); Input(I); AddSheet(Root,I);{Добовляем данные} end; WriteLn; WriteLn('ccedenie dannie: '); ShowHeader;ShowTree(Root); WriteLn; ReadLn; WriteLn('Otobrazenie v vide dereva:'); Print(Root,0); ReadLn; WriteLn('Vvedite danie dlya vstavki: '); Input(I);AddSheet(Root,I);{Добовляем данные} WriteLn('Rezultat vstavki novogo elementa: '); ShowHeader;ShowTree(Root); WriteLn; ReadLn; WriteLn('Otobrajenoe v vide dereva:'); Print(Root,0); ReadLn; While W=Nil do begin Write('Vvedite znachenie klucha dlya poiska i ydaleniya elementa: ');ReadLn(I.Num); W:=Find(Root,I); If W=Nil Then WriteLn('Element ne nayden. Povtorite vvod.'); end; WriteLn('Nayden element:'); ShowHeader;Show(W^.Inf); WriteLn; WriteLn('Udalyaem naydeniy element!'); DeleteTree(Root,W); WriteLn('Derevo posle ydaleniya naydenogo elementa: '); ShowHeader;ShowTree(Root); ReadLn; WriteLn('Otobrajenie v vide dereva:'); Print(Root,0); ReadLn; Done(Root); END. |
ddanbe
2,724
Professional Procrastinator
Featured Poster
5 Years Ago
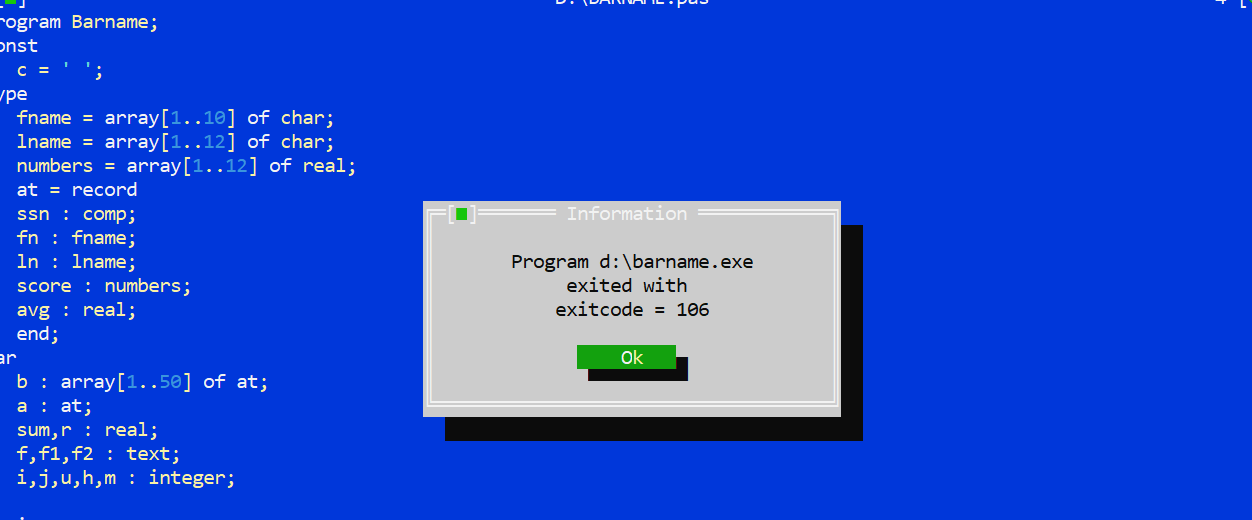
Could you tell me what error 106 means and where in your code it occurs?
Schol-R-LEA
1,446
Commie Mutant Traitor
Featured Poster
5 Years Ago
As DDanbe said, we’d need to know what ‘error 106’ meant here. However, I think we can elaborate on that to make something of a teachable moment.
First, before I address that, I will point out to you that when you post code samples here, you need to indent every line of the code by at least four spaces, or the formatting won’t be preserved. I suggest reading the docs for the Daniweb version of Markdown for a more detailed explanation.
With that out of the way, let’s get on with the show.
While it isn’t entirely clear without more context, it is safe to guess that the ‘106 error’ is a compiler error message, that is, a report of a problem in the code that indicates a fatal error — something that prevents the compiler from finishing the compilation.
It also could be a compiler warning, which indicates something that could be a mistake, but isn’t serious enough to be a showstopper — something which the compiler isn’t sure is a problem, but thinks you should look into. Or, since you didn’t say when it comes up, it could even be an error message that you get after it is compiled, when the program is running.
But the safe bet is that it is a compiler error message.
This means we’d need to know which compiler you are using. Different compilers — even for the same language — will have different error and warning messages and codes, so we’d have to know where to look the error up in order to figure it out.
There are several Pascal compilers around, the most notable being Delphi, FreePascal, and Gnu Pascal .
Now, Delphi is actually an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Object Pascal, which is a different language derived from Pascal, but the Delphi compiler will compile most Standard Pascal code as well, and is sometimes used in courses that teach Pascal (in the same way C++ compilers often double as C compilers). However, the Delphi compiler is a commercial product, so most people have shifted to using the mostly-compatible FreePascal instead.
As the name implies, FreePascal is a free, open-source compiler for Pascal and Object Pascal. It isn’t as refined as Delphi, but it is pretty close, and the limited market interest in Pascal in general means it is a lot more appealing to most people than Delphi. It is often paired with Lazarus IDE, an IDE which emulated the tools found in earlier versions of Delphi.
Gnu Pascal is a part of the Gnu Compiler Collection, being a front-end for the same code generators used by gcc and g++. It isn’t as commonly used as FreePascal, for a variety of reasons, but it is there. It is sometimes used with the Dev-Pascal IDE, but like with all GNU packages, it is really aimed at being used with a general-purpose programmer’s editor such as vim or EMACS.
So, we will need to know which compiler gives an ‘error 106’ message in order to figure this out. Presumably, you know what compiler — or at least what IDE — you are using, so that’s what you would need to tell us.
It would also help if you could tell us the error message itself, and if possible, what part of the code it is pointing to. If you could copy and paste the error message (or make a screen shot of it, though getting the text would be preferable), it should give us a better idea of what it is trying to tell you.
Doing a search on the error message would make sense too, but without knowing the compiler, it might be of limited use. So, Let Me Google That For You, and see what it gives us.
/me reads search results OK, it seems to be a FreePascal ‘invalid numeric format’ error. Oh, it could be some ancient version of Turbo Pascal with a ‘string expression expected’ error, but honestly, if your professor has you using an MS-DOS compiler from thirty years ago, the only solution is to get the other students together, walk out of the course en masse, and complain to the Dean of the university about the incompetent who is teaching the class.
That’s about as much as we really can say, without more information. We could make some guesses, but that’s all they would be, so it would be better if we refrain from that.
Hopefully, this post has taught you a few important lessons about doing the necessary research on your own before asking for help, and providing enough information when you do ask for help. Good luck with that, because no one here is going to give you this much hand-holding ever again.
Edited
5 Years Ago
by Schol-R-LEA because:
clarification re: GCC
rproffitt
2,424
«Nothing to see here.»
Moderator
5 Years Ago
106 Invalid numeric format
Since we don’t know what you typed in response to each question it appears your code is what we call fragile. Blows up when you input a numeric but answer with a character.
1 Year Ago
what is this error?
please answer soon!
Schol-R-LEA
1,446
Commie Mutant Traitor
Featured Poster
1 Year Ago
As Rproffitt said, please make your own new threads rather than resurrecting long-dead ones.
As for the error code, that was explained in detail earlier in this thread: it indicates that you tried to read a number from a file, and got something other than a number, as defined here. The likely solution is to add a check for an end-of-file in the loop, using the function eof().
Though from the screenshot, you might be using Turbo Pascal, where the error indicates a malformed string. The correct solution to this is Don’t Use Turbo Pascal.
Edited
1 Year Ago
by Schol-R-LEA
Ошибка в работе новичка
Модератор: Модераторы
Ошибка в работе новичка
program Sum_1mas;
var
a:array [1..10] of integer:
i, s : integer;
begin
writeln(‘ Введите 10 чисел ‘ );
for i:=1 to 10 do readln(a[i]);
s:=0;
for i:1 to 10 do s:=s+a[i];
writeln(‘исходный массив’);
for i:=1 to 10 write(a[i], ‘ ‘);
writeln(‘ответ’);
writeln(s);
readln;
end.
Программа компилируется . Я ввожу числа 12+12 ит.д Нажимаю Enter и выходит ошибка Runtime error 106 $0040146B
$00407641
- TatarinChita
- незнакомец
- Сообщения: 2
- Зарегистрирован: 04.12.2010 13:15:15
Re: Ошибка в работе новичка
Odyssey » 04.12.2010 20:38:04
Ваш код рассчитан на ввод не «12+12+…», а на 12 (ввод) 12 (ввод) … и так десять чисел.
P.S. К сведению, ошибка 106 означает «Неправильный формат числа». Потому что «12+12» не является числом. Все коды ошибок и их значения написаны тут (правда, на английском):
http://www.freepascal.org/docs-html/user/userap4.html
- Odyssey
- энтузиаст
- Сообщения: 580
- Зарегистрирован: 29.11.2007 17:32:24
Вернуться в Обучение Free Pascal
Кто сейчас на конференции
Сейчас этот форум просматривают: нет зарегистрированных пользователей и гости: 4
I’m still fairly new to Pascal and I’m getting these errors and I’m not sure why. Some help would be greatly appreciated.
Runtime error 106 at $004015DFF
$004015DF
$004016D2
$004016FD
$004078D1
This is my code if you guys want to take a look.
program BasicReadWrite;
type
ArrayOfPersons = record
name: String;
age: String;
end;
procedure WriteLinesToFile(var myFile: TextFile);
begin
WriteLn(myFile, 5);
WriteLn(myFile, 'Fred Smith');
WriteLn(myFile, 28);
WriteLn(myFile, 'Jill Jones');
WriteLn(myFile, 54);
WriteLn(myFile, 'John Doe');
WriteLn(myFile, 15);
WriteLn(myFile, 'Samantha Pritchard');
WriteLn(myFile, 19);
WriteLn(myFile, 'Hans Fredrickson');
WriteLn(myFile, 77);
end;
procedure PrintRecordsToTerminal(personArray: ArrayOfPersons; count:
Integer);
begin
WriteLn('Person name: ', personArray.name);
WriteLn('Age: ', personArray.age);
end;
procedure ReadLinesFromFile(var myFile: TextFile);
var
p: ArrayOfPersons;
number: Integer;
begin
number := 0;
while number <= 19 do
begin
ReadLn(myFile, number);
ReadLn(myFile, p.name[number]);
ReadLn(myFile, p.age);
number := number + 1;
end;
end;
I wrote this program and I just can’t figure out what is wrong with it.
The SkaitytiDuomenis (read values) procedure takes two arrays as arguments so it can read coordinates from a text file and store them in the arrays, but the problem is it doesn’t really read it. There is something wrong with the assign() part, but I can’t figure it out for the life of me. Anyone who helps will be greatly appreciated, as this is a state exam I’m trying to prepare for.
program Uzduotis1;
type
masyvas = array[1..50] of integer;
{*************************Kintamieji************************}
var
Duomenys, Rezultatai :text;
x, y :masyvas; {koordinates (x;y) }
UzsakymuSk, {uzsakymu skaicius}
DienosKm, {dienos kilometrazo limitas}
NuvaziuotiKm, {nuvaziuotu kilometru suma}
LikeKlientai, {neaptarnautu klientu skaicius}
UzsakymoNr {atliekamo uzsakymo numeris}
:integer;
{*************************Proceduros************************}
procedure SkaitytiDuomenis(var a,b:masyvas);
var i:integer;
begin
for i:=1 to UzsakymuSk do
readln(Duomenys, a[i], b[i]);
end;
procedure IsvestiRezultatus;
begin
rewrite(Rezultatai);
write(LikeKlientai,' ',NuvaziuotiKm);
close(Rezultatai)
end;
{************************Funkcijos**************************}
function atstumas(a,b :integer) :integer;
begin
atstumas := (abs(a) + abs(b)) * 2;
end;
{********************Pagrindine programa********************}
begin
assign(Duomenys,'C:DuomenysU1.txt');
assign(Rezultatai,'C:DuomenysU1rez.txt');
reset(Duomenys);
readln(Duomenys,UzsakymuSk,DienosKm);
SkaitytiDuomenis(x,y);
NuvaziuotiKm := 0;
LikeKlientai := UzsakymuSk;
UzsakymoNr := 1;
while ((UzsakymoNr<UzsakymuSk) and (NuvaziuotiKm<DienosKm)) do
begin
NuvaziuotiKm := NuvaziuotiKm + atstumas(x[UzsakymoNr],y[UzsakymoNr]);
LikeKlientai := LikeKlientai - 1;
UzsakymoNr := UzsakymoNr + 1
end;
IsvestiRezultatus;
end.
This is the input file:
14 30
2 3
3 –1
-2 –4
–3 0
-2 4
0 2
5 -4
1 2
4 -3
2 1
-5 -5
-1 0
0 5
2 5