Автор оригинала: Chris.
Вы можете столкнуться с специальными ValueError При работе с Python’s Математический модуль Отказ
ValueError: math domain error
Python поднимает эту ошибку, когда вы пытаетесь сделать то, что не математически возможно или математически определяется.
Чтобы понять эту ошибку, посмотрите на определение домен :
« Домен функции – это полный набор возможных значений независимой переменной. Грубо говоря, домен это набор всех возможных (входных) X-значений, который приводит к действительному (выводу) Y-значению. ” ( Источник )
Домен функции – это набор всех возможных входных значений. Если Python бросает ValueError: Ошибка математического домена Вы пропустили неопределенный ввод в Математика функция. Исправьте ошибку, передавая действительный вход, для которого функция может рассчитать числовой выход.
Вот несколько примеров:
Ошибка домена математики Python SQRT
Ошибка по математике домена появляется, если вы передаете отрицательный аргумент в math.sqrt () функция. Математически невозможно рассчитать квадратный корень отрицательного числа без использования сложных чисел. Python не получает это и бросает ValueError: Ошибка математического домена Отказ
Вот минимальный пример:
from math import sqrt
print(sqrt(-1))
'''
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 2, in
print(sqrt(-1))
ValueError: math domain error
'''
Вы можете исправить ошибку математической домена, используя CMATH Пакет, который позволяет создавать комплексные числа:
from cmath import sqrt print(sqrt(-1)) # 1j
Журнал ошибки домена Python Math
Ошибка математической домена для math.log () Появится функция, если вы проходите нулевое значение в него – логарифм не определен для значения 0.
Вот код на входном значении за пределами домена функции логарифма:
from math import log print(log(0))
Выходной выход – это ошибка домена математики:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in
print(log(0))
ValueError: math domain error
Вы можете исправить эту ошибку, передавая действительное входное значение в math.log () Функция:
from math import log print(log(0.000001)) # -13.815510557964274
Эта ошибка иногда может появиться, если вы пройдете очень небольшое число в IT-Python, который не может выразить все номера. Чтобы пройти значение «Близки к 0», используйте Десятичная Модуль с более высокой точностью или пройти очень маленький входной аргумент, такой как:
math.log(sys.float_info.min)
Ошибка ошибки домена математики Python ACOS
Ошибка математической домена для math.acos () Появится функция, если вы передаете значение для него, для которого он не определен-ARCCO, определяется только значениями между -1 и 1.
Вот неверный код:
import math print(math.acos(2))
Выходной выход – это ошибка домена математики:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in
print(math.acos(2))
ValueError: math domain error
Вы можете исправить эту ошибку, передавая действительное входное значение между [-1,1] в math.acos () Функция:
import math print(math.acos(0.5)) # 1.0471975511965979
Ошибка домена Math Python Asin
Ошибка математической домена для math.asin () Функция появляется, если вы передаете значение в него, для которого он не определен – Arcsin определяется только значениями между -1 и 1.
Вот ошибочный код:
import math print(math.asin(2))
Выходной выход – это ошибка домена математики:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in
print(math.asin(2))
ValueError: math domain error
Вы можете исправить эту ошибку, передавая действительное входное значение между [-1,1] в math.asin () Функция:
import math print(math.asin(0.5)) # 0.5235987755982989
Ошибка ошибки домена Python Math POW POW
Ошибка математической домена для math.pow (a, b) Функция для расчета A ** B, по-видимому, если вы передаете негативное базовое значение, и попытайтесь вычислить негативную мощность. Причина этого не определена, состоит в том, что любое отрицательное число к мощности 0,5 будет квадратным числом – и, таким образом, комплексное число. Но комплексные числа не определены по умолчанию в Python!
import math print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
Выходной выход – это ошибка домена математики:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in
print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
ValueError: math domain error
Если вам нужен комплекс номер, A B должен быть переписан в E B ln a Отказ Например:
import cmath print(cmath.exp(0.5 * cmath.log(-2))) # (8.659560562354932e-17+1.414213562373095j)
Видите ли, это сложный номер!
Ошибка numpy математический домен – np.log (x)
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Plotting y = log(x) fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set(xlim=(-5, 20), ylim=(-4, 4), title='log(x)', ylabel='y', xlabel='x') x = np.linspace(-10, 20, num=1000) y = np.log(x) plt.plot(x, y)
Это график log (x) . Не волнуйтесь, если вы не понимаете код, что важнее, является следующим точком. Вы можете видеть, что журнал (X) имеет тенденцию к отрицательной бесконечности, когда X имеет тенденцию к 0. Таким образом, математически бессмысленно рассчитать журнал отрицательного числа. Если вы попытаетесь сделать это, Python поднимает ошибку математической домена.
>>> math.log(-10) Traceback (most recent call last): File "", line 1, in ValueError: math domain error
Куда пойти отсюда?
Достаточно теории, давайте познакомимся!
Чтобы стать успешным в кодировке, вам нужно выйти туда и решать реальные проблемы для реальных людей. Вот как вы можете легко стать шестифункциональным тренером. И вот как вы польские навыки, которые вам действительно нужны на практике. В конце концов, что такое использование теории обучения, что никто никогда не нуждается?
Практические проекты – это то, как вы обостряете вашу пилу в кодировке!
Вы хотите стать мастером кода, сосредоточившись на практических кодовых проектах, которые фактически зарабатывают вам деньги и решают проблемы для людей?
Затем станьте питоном независимым разработчиком! Это лучший способ приближения к задаче улучшения ваших навыков Python – даже если вы являетесь полным новичком.
Присоединяйтесь к моему бесплатным вебинаре «Как создать свой навык высокого дохода Python» и посмотреть, как я вырос на моем кодированном бизнесе в Интернете и как вы можете, слишком от комфорта вашего собственного дома.
Присоединяйтесь к свободному вебинару сейчас!
Работая в качестве исследователя в распределенных системах, доктор Кристиан Майер нашел свою любовь к учению студентов компьютерных наук.
Чтобы помочь студентам достичь более высоких уровней успеха Python, он основал сайт программирования образования Finxter.com Отказ Он автор популярной книги программирования Python одноклассники (Nostarch 2020), Coauthor of Кофе-брейк Python Серия самооставленных книг, энтузиаста компьютерных наук, Фрилансера и владелец одного из лучших 10 крупнейших Питон блоги по всему миру.
Его страсти пишут, чтение и кодирование. Но его величайшая страсть состоит в том, чтобы служить стремлению кодер через Finxter и помогать им повысить свои навыки. Вы можете присоединиться к его бесплатной академии электронной почты здесь.
Оригинал: “https://blog.finxter.com/python-math-domain-error/”
Время чтения 3 мин.
ValueError: ошибка математического домена возникает в Python, когда вы пытаетесь сделать что-то, что математически невозможно или не определено.
Пример.
|
import math var = —1 result = math.sqrt(var) print(result) |
Выход
|
ValueError: math domain error |
Вы можете видеть, что он выдает ошибку, потому что функция math.sqrt() не определена для отрицательных чисел, и попытка найти квадратный корень из отрицательного числа приводит к ошибке ValueError: math domain.
Содержание
- Как исправить ошибку математического домена
- Дополнительный пример
- Python sqrt: math domain error
- Python pow: math domain error
Как исправить ошибку математического домена
Чтобы исправить ошибку ValueError: math domain в Python, передайте допустимые входные данные, для которых функция может вычислить числовой вывод.
|
import math var = —1 if var >= 0: result = math.sqrt(var) else: print(«Error: Cannot find square root of negative number») |
Выход:
|
Error: Cannot find square root of negative number |
Вы можете видеть, что мы использовали оператор if-else, чтобы проверить, является ли число отрицательным, и если да, то мы печатаем оператор; в противном случае он найдет квадратный корень из этого числа.
Дополнительный пример
Если вы делаете журнал числа меньше или равного нулю. К сожалению, это математически не определено, поэтому функция Python log() вызывает исключение.
|
from math import log print(log(—1)) |
Выход:
|
Traceback(most recent call last): File «/Users/krunal/Desktop/code/pyt/database/app.py», line 3, in <module> print(log(—1)) ValueError: math domain error |
И мы получаем ошибку ValueError: math domain.
Всякий раз, когда вы получаете ошибку математической области по любой причине, вы пытаетесь использовать отрицательное число внутри функции журнала или нулевое значение.
Логарифмы определяют основание после получения числа и степени, в которую оно было возведено. log(0) означает, что что-то, возведенное в степень 2, равно 0.
Показатель степени никогда не может привести к 0 *, что означает, что log(0) не имеет ответа, что приводит к ошибке математической области.
Область определения функции — это набор всех возможных входных значений. Если Python выдает ошибку ValueError: math domain, вы передали неопределенный ввод в математическую функцию. В нашем случае не вычисляйте логарифм отрицательного числа или нуля; это устранит ошибку.
Существуют различные сценарии, в которых может возникнуть эта ошибка. Давайте посмотрим на некоторые из них один за другим.
Python sqrt: math domain error
Чтобы вычислить квадратный корень числа в Python, используйте метод math.sqrt(). Ошибка математической области появляется, если вы передаете отрицательный аргумент в функцию math.sqrt().
Математически невозможно вычислить квадратный корень из отрицательного числа без использования комплексных чисел.
|
from math import sqrt print(sqrt(—1)) |
Выход:
|
Traceback(most recent call last): File «/Users/krunal/Desktop/code/pyt/database/app.py», line 3, in <module> print(sqrt(—1)) ValueError: math domain error |
Квадратный корень из отрицательного числа математически невозможен. Вот почему он выдает ошибку.
Python pow: math domain error
Ошибка математической области для функции math.pow(a,b) для вычисления a**b возникает, если вы передаете в нее отрицательное базовое значение и пытаетесь вычислить отрицательную степень.
|
from math import pow print(pow(—1, 0.5)) |
Выход:
|
Traceback(most recent call last): File «/Users/krunal/Desktop/code/pyt/database/app.py», line 3, in <module> print(pow(—1, 0.5)) ValueError: math domain error |
И мы получаем ValueError.
I was just testing an example from Numerical Methods in Engineering with Python.
from numpy import zeros, array
from math import sin, log
from newtonRaphson2 import *
def f(x):
f = zeros(len(x))
f[0] = sin(x[0]) + x[1]**2 + log(x[2]) - 7.0
f[1] = 3.0*x[0] + 2.0**x[1] - x[2]**3 + 1.0
f[2] = x[0] + x[1] + x[2] -5.0
return f
x = array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0])
print(newtonRaphson2(f,x))
When I run it, it shows the following error:
File "example NR2method.py", line 8, in f
f[0] = sin(x[0]) + x[1]**2 + log(x[2]) - 7.0
ValueError: math domain error
I have narrowed it down to the log as when I remove log and add a different function, it works. I assume it is because of some sort of interference with the base, I can’t figure out how. Can anyone suggest a solution?
See also: Python math domain error using math.acos function for the equivalent problem using math.acos; python math domain error — sqrt for the equivalent problem using math.sqrt.
Karl Knechtel
61.7k11 gold badges97 silver badges147 bronze badges
asked Apr 8, 2013 at 22:58
Your code is doing a log of a number that is less than or equal to zero. That’s mathematically undefined, so Python’s log function raises an exception. Here’s an example:
>>> from math import log
>>> log(-1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#59>", line 1, in <module>
log(-1)
ValueError: math domain error
Without knowing what your newtonRaphson2 function does, I’m not sure I can guess where the invalid x[2] value is coming from, but hopefully this will lead you on the right track.
answered Apr 8, 2013 at 23:06
BlckknghtBlckknght
100k11 gold badges120 silver badges168 bronze badges
4
You may also use math.log1p.
According to the official documentation :
math.log1p(x)
Return the natural logarithm of 1+x (base e). The result
is calculated in a way which is accurate for x near zero.
You may convert back to the original value using math.expm1 which returns e raised to the power x, minus 1.
answered Feb 10, 2020 at 8:55
Catalina ChircuCatalina Chircu
1,5062 gold badges7 silver badges19 bronze badges
you are getting math domain error for either one of the reason :
either you are trying to use a negative number inside log function or a zero value.
answered Jun 23, 2020 at 16:37
We face this problem when we use log() or sqrt() from math library. In this problem “math domain error”, we are using a negative number like (-1 or another) or a zero number where we should not be use.
answered Nov 17, 2021 at 17:48
You are trying to do a logarithm of something that is not positive.
Logarithms figure out the base after being given a number and the power it was raised to. log(0) means that something raised to the power of 2 is 0. An exponent can never result in 0*, which means that log(0) has no answer, thus throwing the math domain error
*Note: 0^0 can result in 0, but can also result in 1 at the same time. This problem is heavily argued over.
answered Jul 1, 2019 at 21:54
Eric XueEric Xue
2152 silver badges11 bronze badges
In mathematics, there are certain operations that are considered to be mathematically undefined operations.
Some examples of these undefined operations are:
- The square root of a negative number (√-2).
- A divisor with a value of zero (20/0).
The «ValueError: math domain error» error in Python occurs when you carry out a math operation that falls outside the domain of the operation.
To put it simply, this error occurs in Python when you perform a math operation with mathematically undefined values.
In this article, you’ll learn how to fix the «ValueError: math domain error» error in Python.
You’ll start by learning what the keywords found in the error message mean. You’ll then see some practical code examples that raise the error and a fix for each example.
Let’s get started!
How to Fix the «ValueError: math domain error» Error in Python
A valueError is raised when a function or operation receives a parameter with an invalid value.
A domain in math is the range of all possible values a function can accept. All values that fall outside the domain are considered «undefined» by the function.
So the math domain error message simply means that you’re using a value that falls outside the accepted domain of a function.
Here are some examples:
Example #1 – Python Math Domain Error With math.sqrt
import math
print(math.sqrt(-1))
# ValueError: math domain errorIn the code above, we’re making use of the sqrt method from the math module to get the square root of a number.
We’re getting the «ValueError: math domain error» returned because -1 falls outside the range of numbers whose square root can be obtained mathematically.
Solution #1 – Python Math Domain Error With math.sqrt
To fix this error, simply use an if statement to check if the number is negative before proceeding to find the square root.
If the number is greater than or equal to zero, then the code can be executed. Otherwise, a message would be printed out to notify the user that a negative number can’t be used.
Here’s a code example:
import math
number = float(input('Enter number: '))
if number >= 0:
print(f'The square root of {number} is {math.sqrt(number)}')
else:
print('Cannot find the square root of a negative number')Example #2 – Python Math Domain Error With math.log
You use the math.log method to get the logarithm of a number. Just like the sqrt method, you can’t get the log of a negative number.
Also, you can’t get the log of the number 0. So we have to modify the condition of the if statement to check for that.
Here’s an example that raises the error:
import math
print(math.log(0))
# ValueError: math domain errorSolution #2 – Python Math Domain Error With math.log
import math
number = float(input('Enter number: '))
if number > 0:
print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}')
else:
print('Cannot find the log of 0 or a negative number')In the code above, we’re using the condition of the if statement to make sure the number inputted by the user is neither zero nor a negative number (the number must be greater than zero).
Example #3 – Python Math Domain Error With math.acos
You use the math.acos method to find the arc cosine value of a number.
The domain of the acos method is from -1 to 1, so any value that falls outside that range will raise the «ValueError: math domain error» error.
Here’s an example:
import math
print(math.acos(2))
# ValueError: math domain errorSolution #3 – Python Math Domain Error With math.acos
import math
number = float(input('Enter number: '))
if -1 <= number <= 1:
print(f'The arc cosine of {number} is {math.acos(number)}')
else:
print('Please enter a number between -1 and 1.')
Just like the solution in other examples, we’re using an if statement to make sure the number inputted by the user doesn’t exceed a certain range.
That is, any value that falls outside the range of -1 to 1 will prompt the user to input a correct value.
Summary
In this article, we talked about the «ValueError: math domain error» error in Python.
We had a look at some code examples that raised the error, and how to check for and fix them using an if statement.
Happy coding!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
The domain of a mathematical function is the set of all possible input values. If you pass an undefined input to a function from the math library, you will raise the ValueError: math domain error.
To solve this error, ensure that you use a valid input for the mathematical function you wish to use. You can put a conditional statement in your code to check if the number is valid for the function before performing the calculation.
You cannot use functions from the math library with complex numbers, such as calculating a negative number’s square root. To do such calculations, use the cmath library.
This tutorial will go through the error in detail and solve it with the help of some code examples.
Table of contents
- ValueError: math domain error
- What is a ValueError?
- Example #1: Square Root of a Negative Number
- Solution #1: Use an if statement
- Solution #2: Use cmath
- Example #2: Logarithm of Zero
- Solution
- Summary
ValueError: math domain error
What is a ValueError?
In Python, a value is the information stored within a particular object. You will encounter a ValueError in Python when you use a built-in operation or function that receives an argument with the right type but an inappropriate value.
The ValueError: math domain error occurs when you attempt to use a mathematical function with an invalid value. You will commonly see this error using the math.sqrt() and math.log() methods.
Example #1: Square Root of a Negative Number
Let’s look at an example of a program that calculates the square root of a number.
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
sqrt_number = math.sqrt(number)
print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')We import the math library to use the square root function in the above code. We collect the number from the user using the input() function. Next, we find the square root of the number and print the result to the console using an f-string. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Enter a number: -4---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
3 number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
4
----> 5 sqrt_number = math.sqrt(number)
6
7 print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')
ValueError: math domain errorWe raise the ValueError because a negative number does not have a real square root.
Solution #1: Use an if statement
To solve this error, we can check the value of the number before attempting to calculate the square root by using an if statement. Let’s look at the revised code:
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number > 0:
sqrt_number = math.sqrt(number)
print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')
else:
print('The number you input is less than zero. You cannot find the real square root of a negative number.')In the above code, we check if the user’s number is greater than zero. If it is, we calculate the number’s square root and print it to the console. Otherwise, we print a statement telling the user the number is invalid for the square root function. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Enter a number: -4
The number you input is less than zero. You cannot find the real square root of a negative number.Go to the article: Python Square Root Function for further reading on calculating the square root of a number in Python.
Solution #2: Use cmath
We can also solve the square root math domain error using the cmath library. This library provides access to mathematical functions for complex numbers. The square root of a negative number is a complex number with a real and an imaginary component. We will not raise a math domain error using the square root function from cmath on a negative number. Let’s look at the revised code:
import cmath
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
sqrt_number = cmath.sqrt(number)
print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')Let’s run the code to get the result:
Enter a number: -4
The square root of -4 is 2jExample #2: Logarithm of Zero
Let’s look at an example of a program that calculates the natural logarithm of a number. The log() method returns the natural logarithm of a number or to a specified base. The syntax of the math.log() method is:
math.log(x, base)Parameters:
- x: Required. The value to calculate the number logarithm for.
- base: Optional. The logarithmic base to use. The default is e.
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}.')We import the math library to use the natural logarithm function in the above code. We collect the number from the user using the input() function. Next, we find the natural logarithm of the number and print the result to the console using an f-string. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Enter a number: 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
3 number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
4
----> 5 print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}.')
ValueError: math domain errorWe raise the ValueError because you cannot calculate the natural logarithm of 0 or a negative number. The log(0) means that the exponent e raised to the power of a number is 0. An exponent can never result in 0, which means log(0) has no answer, resulting in the math domain error.
Solution
We can put an if statement in the code to check if the number we want to use is positive to solve this error. Let’s look at the revised code:
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number > 0:
print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}.')
else:
print(f'The number you provided is less than or equal to zero. You can only get the logarithm of positive real numbers')Now we will only calculate the natural logarithm of the number if it is greater than zero. Let’s run the code to get the result:
Enter a number: 0
The number you provided is less than or equal to zero. You can only get the logarithm of positive real numbersSummary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! ValueError: math domain error occurs when you attempt to perform a mathematical function with an invalid number. Every mathematical function has a valid domain of input values you can choose. For example, the logarithmic function accepts all positive, real numbers. To solve this error, ensure you use input from the domain of a function. You can look up the function in the math library documentation to find what values are valid and which values will raise a ValueError.
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about coding in Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!
In mathematics, there are operations which do not work on negative numbers or zero numbers. Consider the square root, for example. You cannot find the square root of a negative number. Python recognizes that not all operations work with negative or zero numbers.
Python will raise an error when you try to use a negative number on an operation that does not support one. In this guide, we’re going to talk about the cause of the ValueError: math domain error. Toward the end of the guide, we’ll walk through a solution to this issue.

Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
ValueError: math domain error
The Python ValueError: math domain error is raised when you use a number that is not supported by a mathematical operation. This error is commonly raised with the sqrt() method and the log() method.
The ValueError is a type of error that indicates you are performing a mathematical operation on a value that does not work with that operation. In the case of the “math domain error”, we are using a negative number or a zero number where we should not be.
Let’s walk through an example of the ValueError: math domain error issue in action.
An Example Scenario
We are building a program that calculates the square root of a given number. This program is designed to help students revise their knowledge of square roots.
Let’s write a program that calculates the square root of a given number. We will start by importing the math library that we need to calculate a square root:
Next, we’re going to collect a number from the user:
number = input("Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: ")
We prompt the user to try finding the answer themselves, as our program is designed to help people check their answers. Next, we’re going to find the square root of the value the user inserts:
answer = math.sqrt(int(number))
We convert the value of “number”, which stores the number whose square root the user wants to find, into an integer. This is necessary because the input() method, which we used to collect the aforementioned number, returns a string. We cannot find the square root of a string value.
Finally, let’s print the answer to the console:
print("The square root of {} is {}.".format(number, answer))
We use a format() statement to add numbers to our string. Our string will show:
"The square root of [Number user inserted] is [The square root our program calculated]"
Let’s test our program with a negative number:
Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: -16 Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 5, in <module> answer = math.sqrt(int(number)) ValueError: math domain error
We inserted the value -16 into our program. Our code returned an error.
Let’s fix this error.
The Solution
To fix this error, we need to prompt the user that you cannot calculate the square root of a negative number before we execute the math.sqrt() function.
Let’s revise our code to make this happen:
import math
number = input("Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: ")
if int(number) >= 0:
answer = math.sqrt(int(number))
print("The square root of {} is {}.".format(number, answer))
else:
print("You cannot find the square root of a number less than 0.")
We use an if statement to check if the number the user inserts into the program is equal to or greater than zero. If the number meets this criterion, the contents of the if statement run. Otherwise, the else statement executes, presenting us with a message that we have inserted an invalid number.
Let’s run our program again. Our program returns:
Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: -16 You cannot find the square root of a number less than 0.
Our code works successfully.
Conclusion
The ValueError: math domain error is raised when you perform a mathematical function on a negative or zero number which cannot be computed. To solve this error, make sure you are using a valid number for the mathematical function you are using.
If you want to learn more about coding in Python, check out our How to Learn Python guide. This guide contains a number of learning resources, courses, and books designed for people who are learning the Python programming language.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- ⚠️What Is a Math Domain Error in Python?
- ➥ Fixing “ValueError: math domain error”-sqrt
- 💡 Solution 1: Using “cmath” Module
- 💡 Solution 2: Use Exception Handling
- ➥ “ValueError: math domain error” Examples
- ✰ Scenario 1: Math Domain Error While Using pow()
- ✰ Scenario 2: Python Math Domain Error While Using log()
- ✰ Scenario 3: Math Domain Error While Using asin()
- 📖 Exercise: Fixing Math Domain Error While Using Acos()
- Conclusion
Introduction
So, you sit down, grab a cup of coffee and start programming in Python. Then out of nowhere, this stupid python error shows up: ValueError: math domain error. 😞
Sometimes it may seem annoying, but once you take time to understand what Math domain error actually is, you will solve the problem without any hassle.
To fix this error, you must understand – what is meant by the domain of a function?
Let’s use an example to understand “the domain of a function.”
Given equation: y= √(x+4)
- y = dependent variable
- x = independent variable
The domain of the function above is x≥−4. Here x can’t be less than −4 because other values won’t yield a real output.
❖ Thus, the domain of a function is a set of all possible values of the independent variable (‘x’) that yield a real/valid output for the dependent variable (‘y’).
If you have done something that is mathematically undefined (not possible mathematically), then Python throws ValueError: math domain error.
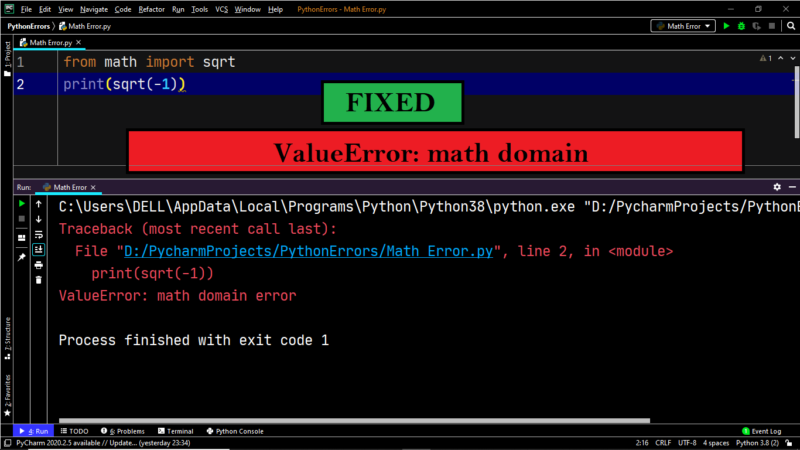
➥ Fixing “ValueError: math domain error”-sqrt
Example:
|
from math import * print(sqrt(—5)) |
Output:
|
Traceback (most recent call last): File «D:/PycharmProjects/PythonErrors/Math Error.py», line 2, in <module> print(sqrt(—5)) ValueError: math domain error |
Explanation:
Calculating the square root of a negative number is outside the scope of Python, and it throws a ValueError.
Now, let’s dive into the solutions to fix our problem!
💡 Solution 1: Using “cmath” Module
When you calculate the square root of a negative number in mathematics, you get an imaginary number. The module that allows Python to compute the square root of negative numbers and generate imaginary numbers as output is known as cmath.
Solution:
|
from cmath import sqrt print(sqrt(—5)) |
Output:
2.23606797749979j
💡 Solution 2: Use Exception Handling
If you want to eliminate the error and you are not bothered about imaginary outputs, then you can use try-except blocks. Thus, whenever Python comes across the ValueError: math domain error it is handled by the except block.
Solution:
|
from math import * x = int(input(‘Enter an integer: ‘)) try: print(sqrt(x)) except ValueError: print(«Cannot Compute Negative Square roots!») |
Output:
Enter an integer: -5
Cannot Compute Negative Square roots!
Let us have a look at some other scenarios that lead to the occurrence of the math domain error and the procedure to avoid this error.
➥ “ValueError: math domain error” Examples
✰ Scenario 1: Math Domain Error While Using pow()
Cause of Error: If you try to calculate a negative base value raised to a fractional power, it will lead to the occurrence of ValueError: math domain error.
Example:
|
import math e = —1.7 print(math.pow(—3, e)) |
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “D:/PycharmProjects/PythonErrors/Math Error.py”, line 3, in
print(math.pow(-3, e))
ValueError: math domain error
Solution: Use the cmath module to solve this problem.
- Note:
- Xy = ey ln x
Using the above property, the error can be avoided as follows:
|
from cmath import exp,log e = —1.7 print(exp(e * log(—3))) |
Output:
(0.0908055832509843+0.12498316306449488j)
✰ Scenario 2: Python Math Domain Error While Using log()
Consider the following example if you are working on Python 2.x:
|
import math print(2/3*math.log(2/3,2)) |
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “main.py”, line 2, in
print(2/3*math.log(2/3,2))
ValueError: math domain error
Explanation: In Python 2.x, 2/3 evaluates to 0 since division floors by default. Therefore you’re attempting a log 0, hence the error. Python 3, on the other hand, does floating-point division by default.
Solution:
To Avoid the error try this instead:
from __future__ import division, which gives you Python 3 division behaviour in Python 2.7.
|
from __future__ import division import math print(2/3*math.log(2/3,2)) # Output: -0.389975000481 |
✰ Scenario 3: Math Domain Error While Using asin()
Example:
|
import math k = 5 print(«asin(«,k,«) is = «, math.asin(k)) |
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “D:/PycharmProjects/PythonErrors/rough.py”, line 4, in
print(“asin(“,k,”) is = “, math.asin(k))
ValueError: math domain error
Explanation: math.asin() method only accepts numbers between the range of -1 to 1. If you provide a number beyond of this range, it returns a ValueError – “ValueError: math domain error“, and if you provide anything else other than a number, it returns error TypeError – “TypeError: a float is required“.
Solution: You can avoid this error by passing a valid input number to the function that lies within the range of -1 and 1.
|
import math k = 0.25 print(«asin(«,k,«) is = «, math.asin(k)) #OUTPUT: asin( 0.25 ) is = 0.25268025514207865 |
📖 Exercise: Fixing Math Domain Error While Using Acos()
Note: When you pass a value to math.acos() which does not lie within the range of -1 and 1, it raises a math domain error.
Fix the following code:
|
import math print(math.acos(10)) |
Answer:
Conclusion
I hope this article helped you. Please subscribe and stay tuned for more exciting articles in the future. Happy learning! 📚
You may encounter a special ValueError when working with Python’s math module.
ValueError: math domain error
Python raises this error when you try to do something that is not mathematically possible or mathematically defined.
To understand this error, have a look at the definition of the domain:
“The domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable. Roughly speaking, the domain is the set of all possible (input) x-values which result in a valid (output) y-value.” (source)
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values. If Python throws the ValueError: math domain error, you’ve passed an undefined input into the math function. Fix the error by passing a valid input for which the function is able to calculate a numerical output.
Here are a few examples:
The math domain error appears if you pass a negative argument into the math.sqrt() function. It’s mathematically impossible to calculate the square root of a negative number without using complex numbers. Python doesn’t get that and throws a ValueError: math domain error.
Here’s a minimal example:
from math import sqrt
print(sqrt(-1))
'''
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 2, in <module>
print(sqrt(-1))
ValueError: math domain error
'''
You can fix the math domain error by using the cmath package that allows the creation of complex numbers:
from cmath import sqrt print(sqrt(-1)) # 1j
Python Math Domain Error Log
The math domain error for the math.log() function appears if you pass a zero value into it—the logarithm is not defined for value 0.
Here’s the code on an input value outside the domain of the logarithm function:
from math import log print(log(0))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(log(0))
ValueError: math domain error
You can fix this error by passing a valid input value into the math.log() function:
from math import log print(log(0.000001)) # -13.815510557964274
This error can sometimes appear if you pass a very small number into it—Python’s float type cannot express all numbers. To pass a value “close to 0”, use the Decimal module with higher precision, or pass a very small input argument such as:
math.log(sys.float_info.min)
Python Math Domain Error Acos
The math domain error for the math.acos() function appears if you pass a value into it for which it is not defined—arccos is only defined for values between -1 and 1.
Here’s the wrong code:
import math print(math.acos(2))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(math.acos(2))
ValueError: math domain error
You can fix this error by passing a valid input value between [-1,1] into the math.acos() function:
import math print(math.acos(0.5)) # 1.0471975511965979
Python Math Domain Error Asin
The math domain error for the math.asin() function appears if you pass a value into it for which it is not defined—arcsin is only defined for values between -1 and 1.
Here’s the erroneous code:
import math print(math.asin(2))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(math.asin(2))
ValueError: math domain error
You can fix this error by passing a valid input value between [-1,1] into the math.asin() function:
import math print(math.asin(0.5)) # 0.5235987755982989
Python Math Domain Error Pow
The math domain error for the math.pow(a,b) function to calculate a**b appears if you pass a negative base value into it and try to calculate a negative power of it. The reason it is not defined is that any negative number to the power of 0.5 would be the square number—and thus, a complex number. But complex numbers are not defined by default in Python!
import math print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
ValueError: math domain error
If you need a complex number, ab must be rewritten into eb ln a. For example:
import cmath print(cmath.exp(0.5 * cmath.log(-2))) # (8.659560562354932e-17+1.414213562373095j)
You see, it’s a complex number!
NumPy Math Domain Error — np.log(x)
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Plotting y = log(x) fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set(xlim=(-5, 20), ylim=(-4, 4), title='log(x)', ylabel='y', xlabel='x') x = np.linspace(-10, 20, num=1000) y = np.log(x) plt.plot(x, y)
This is the graph of log(x). Don’t worry if you don’t understand the code, what’s more important is the following point. You can see that log(x) tends to negative infinity as x tends to 0. Thus, it is mathematically meaningless to calculate the log of a negative number. If you try to do so, Python raises a math domain error.
>>> math.log(-10) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: math domain error
Where to Go From Here?
Enough theory. Let’s get some practice!
Coders get paid six figures and more because they can solve problems more effectively using machine intelligence and automation.
To become more successful in coding, solve more real problems for real people. That’s how you polish the skills you really need in practice. After all, what’s the use of learning theory that nobody ever needs?
You build high-value coding skills by working on practical coding projects!
Do you want to stop learning with toy projects and focus on practical code projects that earn you money and solve real problems for people?
🚀 If your answer is YES!, consider becoming a Python freelance developer! It’s the best way of approaching the task of improving your Python skills—even if you are a complete beginner.
If you just want to learn about the freelancing opportunity, feel free to watch my free webinar “How to Build Your High-Income Skill Python” and learn how I grew my coding business online and how you can, too—from the comfort of your own home.
Join the free webinar now!
While working as a researcher in distributed systems, Dr. Christian Mayer found his love for teaching computer science students.
To help students reach higher levels of Python success, he founded the programming education website Finxter.com that has taught exponential skills to millions of coders worldwide. He’s the author of the best-selling programming books Python One-Liners (NoStarch 2020), The Art of Clean Code (NoStarch 2022), and The Book of Dash (NoStarch 2022). Chris also coauthored the Coffee Break Python series of self-published books. He’s a computer science enthusiast, freelancer, and owner of one of the top 10 largest Python blogs worldwide.
His passions are writing, reading, and coding. But his greatest passion is to serve aspiring coders through Finxter and help them to boost their skills. You can join his free email academy here.
Если вы занимаетесь разработкой на языке Python, вероятно, вам знаком сбой «Math domain error». Эта ошибка возникает, когда происходит математическая операция, которая не может быть выполнена из-за арифметических ограничений в Python.
Поскольку она может привести к сбою приложения или даже к потере данных, знание причин возникновения «Math domain error» и методов ее устранения является важным навыком для любого Python-разработчика.
В данной статье мы разберем, какие операции могут привести к возникновению ошибки «Math domain error», как ее обработать и как предотвратить ее появление в будущем.
Понимание ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
Содержание
- 1 Понимание ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
- 1.1 Что означает ошибка «Math domain error» в Python?
- 1.2 Как исправить ошибку «Math domain error» в Python?
- 2 Причины возникновения ошибки «Math domain error»
- 3 Варианты решения проблемы «Math domain error»
- 4 Способ 1: Проверка на входные данные, вызывающие ошибку
- 5 Способ 2: Использование функции math.isnan()
- 6 Способ 3: Использование функций numpy.isnan() и numpy.isinf()
- 7 Использование функций np.nan и np.inf в библиотеке NumPy для исправления ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
- 8 Использование библиотеки mpmath в Python
- 9 Кейсы использования ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
- 10 Особенности работы с ошибкой «Math domain error» в Python
- 11 Итоги и выводы по исследованию ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
- 12 Вопрос-ответ:
-
- 12.0.1 Что такое ошибка «Math domain error» в Python?
- 12.0.2 Каковы причины возникновения ошибки «Math domain error» в Python?
- 12.0.3 Как исправить ошибку «Math domain error» в Python?
- 12.0.4 Может ли ошибка «Math domain error» повлиять на работу программы в целом?
- 12.0.5 Как можно предотвратить возникновение ошибки «Math domain error» в Python?
-
Что означает ошибка «Math domain error» в Python?
Ошибка «Math domain error» возникает в Python, когда происходит попытка выполнить математическую операцию, которая приводит к неопределенному или недопустимому результату. Это может произойти, например, в случае деления на ноль, вычисления корня из отрицательного числа, или при выполнении других математических операций с недопустимыми значениями.
Как исправить ошибку «Math domain error» в Python?
Чтобы исправить ошибку «Math domain error» в Python, необходимо проверить входные данные, которые используются для выполнения математической операции. Если данные содержат недопустимые значения, то необходимо произвести коррекцию перед выполнением операции. Например, если используется функция sqrt() для вычисления квадратного корня из числа, то необходимо проверить, что это число неотрицательное.
Еще одним способом предотвращения ошибки «Math domain error» может быть использование функций, которые специально разработаны для работы с недопустимыми значениями, например, функция np.nan_to_num() из библиотеки NumPy, которая может заменить NaN (Not a Number) и Inf (Infinity) значения на определенные числа.
Таким образом, важно быть внимательным при работе с математическими операциями в Python, проверять входные данные и использовать специальные функции для работы с недопустимыми значениями, чтобы избежать возникновения ошибки «Math domain error».
Причины возникновения ошибки «Math domain error»
В Python ошибка «Math domain error» может возникнуть при использовании математических функций с некорректными аргументами. Так, например, при попытке взятия квадратного корня из отрицательного числа или натурального логарифма от нуля. Также ошибка может возникать при попытке вычисления значения функций на бесконечности или неопределенности.
Другой причиной возникновения ошибки может быть неправильная операция с числами, например, деление на ноль или возведение числа в отрицательную степень.
Также стоит учитывать, что ошибка может быть связана с особенностями компьютерной арифметики, например, при округлении чисел.
Варианты решения проблемы «Math domain error»
Разбейте проблему на подзадачи. Сначала стоит выделить место возникновения «Math domain error», а уже затем искать решение для конкретного случая. Это позволит сократить время на поиск причины ошибки и упростить ее исправление.
Проверьте входные данные. Возможно, ошибка связана с некорректными данными, которые не соответствуют допустимому диапазону для математических операций. Попробуйте отследить и устранить такие ошибки перед расчетами.
Используйте специальные функции. В Python есть множество математических функций, которые могут обрабатывать данные, вызывающие ошибку «Math domain error». Например, функция math.isnan() позволяет определить, является ли значение NaN (Not a Number), а функция math.isinf() — бесконечным. Также можно использовать функцию math.fabs() для нахождения абсолютного значения числа.
Проверьте наличие библиотек и модулей. Некоторые математические функции могут не быть доступны, если соответствующая библиотека или модуль не были импортированы. Убедитесь, что необходимые библиотеки и модули импортированы и доступны для использования.
Сверьтесь со стандартами. Возможно, проблема связана с несоответствием используемых математических функций стандартам IEEE 754 для чисел с плавающей точкой. В этом случае может помочь использование альтернативных функций, которые соответствуют стандартам.
Способ 1: Проверка на входные данные, вызывающие ошибку
Ошибка «Math domain error» в Python возникает, когда в математических функциях используется недопустимое значение или аргумент. Обычно это происходит при делении на ноль, вычислении квадратного корня из отрицательного числа или логарифма из неположительного числа.
Для исправления этой ошибки необходимо проверить входные данные на корректность. Например, если вы используете функцию для вычисления квадратного корня, проверьте, что число, из которого вы хотите извлечь корень, больше или равно нулю.
Если вы не можете предугадать, какие значения пользователь будет вводить, то можно предварительно провести проверки на входные данные. Например, используйте конструкцию try-except для обработки исключений, которые могут возникнуть при некорректном вводе данных. В таком случае код не будет прерываться и будет продолжать выполняться, а вы сможете сообщить пользователю о некорректном вводе данных.
Пример:
| Код | Описание |
|---|---|
x = input("Введите число: ") |
Запрос у пользователя ввода числа. |
try: |
Конструкция для обработки исключения, если введенное число некорректно. |
y = math.sqrt(float(x)) |
Использование функции sqrt() для вычисления квадратного корня. |
except ValueError: |
Обработка исключения ValueError, если введенное число не может быть преобразовано в число с плавающей точкой или меньше нуля. |
print("Некорректное значение") |
Вывод сообщения об ошибке. |
Способ 2: Использование функции math.isnan()
Если ошибка «Math domain error» возникает из-за попытки выполнения математических операций с нечисловыми значениями, то для ее исправления можно использовать функцию math.isnan(). Данная функция позволяет проверить, является ли переданное ей значение «Not a Number» (NaN).
Для использования функции необходимо импортировать модуль math:
import math Далее, можно использовать функцию math.isnan() для проверки каждого значения, передаваемого в математическую операцию:
x = float(input("Введите число: "))
if math.isnan(x):
print("Ошибка! Введено нечисловое значение.")
else:
print(math.sqrt(x)) В данном примере функция math.isnan() используется для проверки числа, введенного пользователем. Если введенное значение является «Not a Number», то программа выводит сообщение об ошибке. В противном случае, программа вычисляет квадратный корень из введенного числа.
Способ 3: Использование функций numpy.isnan() и numpy.isinf()
Для более точной обработки математических операций в Python, можно использовать библиотеку numpy. С помощью функции numpy.isnan() можно проверить, является ли значение NaN (не число), а функция numpy.isinf() позволяет проверить бесконечно ли значение.
Применение этих функций в коде поможет избежать ошибки «Math domain error», связанной с неопределенными значениями, такими как деление на ноль или взятие корня из отрицательного числа. Если при использовании функций numpy.isnan() и numpy.isinf() обнаружатся неопределенные значения, можно заменить их на другие значения, либо исключить из расчетов.
Например, при вычислении функции, содержащей корень, можно применить следующий код:
| Исходный код | Исправленный код |
|---|---|
|
x = -1 y = math.sqrt(x) |
x = -1 if numpy.isinf(x) or numpy.isnan(x): y = 0 else: y = math.sqrt(x) |
Такой подход позволяет учесть возможные ошибки в данных и обеспечить более точные результаты.
Использование функций np.nan и np.inf в библиотеке NumPy для исправления ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
Если в вашем коде возникает ошибка «Math domain error», то одним из способов ее исправления может быть использование функций np.nan и np.inf, доступных в библиотеке NumPy. np.nan означает «not a number» (не число) и может использоваться для представления отсутствующей или неопределенной информации в массивах NumPy. Когда np.nan включен в математические операции, результатом будет np.nan.
np.inf, с другой стороны, означает бесконечность и может быть использован для представления очень больших или очень маленьких значений. Когда np.inf включен в математические операции, результатом будет np.inf. Однако, когда np.inf включен в операции деления или умножения, результатом может быть np.nan.
Чтобы использовать эти функции для исправления ошибки «Math domain error», вам необходимо определить, где в вашем коде происходит деление на ноль или возведение в отрицательную степень. Затем замените такие операции на использование np.nan и np.inf в соответствии с логикой вашего кода.
Пример использования np.nan:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([0, 0, 0])
result = np.divide(a, b, out=np.full_like(a, np.nan), where=b!=0)
Пример использования np.inf:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([0, 0, 0])
result = np.divide(a, b, out=np.full_like(a, np.inf), where=b==0)
В целом, использование функций np.nan и np.inf для представления отсутствующей или неопределенной информации может помочь избежать ошибки «Math domain error» в вашем коде.
Использование библиотеки mpmath в Python
Библиотека mpmath — это библиотека высокой точности для выполнения математических операций в Python. Она может использоваться в тех случаях, когда стандартные математические функции в Python дают ошибку Math domain error.
Чтобы начать использовать библиотеку mpmath, ее нужно установить с помощью команды pip install mpmath в терминале. После успешной установки можно использовать ее функции и методы.
Например, если нужно выполнить операцию sin(x) с высокой точностью, в коде нужно импортировать функцию sin из mpmath:
from mpmath import sin
После чего можно вызывать функцию sin с необходимым аргументом:
x = sin(1.5)
Если нужно выполнить другую математическую операцию, можно обратиться к документации по библиотеке mpmath для выбора нужной функции или метода.
В результате использования библиотеки mpmath в Python, можно выполнить математические операции с высокой точностью и без ошибки Math domain error.
Кейсы использования ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
Ошибка «Math domain error» возникает в Python, когда выполняется математическая операция, результат которой не является допустимым значением в математике. Это может произойти, например, при попытке извлечения квадратного корня из отрицательного числа. Помимо этого, причины ошибки «Math domain error» могут быть связаны с переполнением переменной, делением на ноль и т.д.
Часто данная ошибка используется для обработки исключительных ситуаций, связанных с математическими вычислениями. Например, при разработке алгоритмов машинного обучения, инженеры часто сталкиваются с необходимостью обработки некорректных данных. В таких случаях ошибка «Math domain error» может быть использована для выявления некорректных значений и проведения дополнительных проверок перед вычислением.
Кроме того, ошибка «Math domain error» может быть использована для определения границ функции. Например, для определения области определения функции можно использовать следующий код:
import math
def my_function(x):
if x < 0 or x > 1:
raise ValueError ("Math domain error")
return math.sqrt(x)
В данном примере функция будет работать только при x от 0 до 1, т.к. при других значениях аргумента будет возникать ошибка «Math domain error». Такой подход позволяет сократить время вычислений, т.к. программа не будет пытаться вычислить значение функции в некорректной области определения.
Особенности работы с ошибкой «Math domain error» в Python
Ошибка «Math domain error» возникает в Python, когда выполняются математические операции с недопустимыми значениями, например, когда пытаются извлечь квадратный корень из отрицательного числа или вычислить логарифм от нуля.
Чтобы исправить эту ошибку, нужно убедиться, что аргументы функций математических операций находятся в допустимом диапазоне. Для этого можно использовать условные операторы, которые проверяют значения перед выполнением операции.
Кроме того, в Python есть специальные функции, которые позволяют избежать ошибки «Math domain error». Например, функция math.isnan() проверяет, является ли аргумент нечисловым (NaN), а функция math.isinf() проверяет, является ли аргумент бесконечностью.
- Обработка ошибок «Math domain error» имеет важное значение для обеспечения корректной работы программы и предотвращения ее аварийного завершения.
- Необходимо внимательно проверять аргументы функций математических операций и использовать специальные функции, чтобы избежать возникновения ошибки.
- Если ошибка все же произошла, то нужно анализировать код и данные, которые привели к ее возникновению, и внести соответствующие изменения в программу.
Итоги и выводы по исследованию ошибки «Math domain error» в Python
Ошибки «Math domain error» в Python могут возникать при выполнении математических операций, в которых используются значения, выходящие за допустимый диапазон. Эта ошибка может привести к остановке программы и необходимости ее исправления.
Для решения проблемы могут быть использованы несколько способов. Например, можно использовать проверку на допустимость значений перед выполнением операций и предусмотреть обработку ошибок исключений. Также можно использовать функции, которые возвращают значение NaN (Not a Number) при попытке выполнить операцию с недопустимым значением.
Важно отметить, что использование функций, которые возвращают NaN, может привести к возникновению других ошибок при продолжении выполнения программы. Поэтому, при использовании таких функций, необходимо предусмотреть дополнительные проверки на допустимость значений перед их использованием.
В целом, решение проблемы «Math domain error» в Python требует тщательного анализа кода и предусмотрительного подхода при написании программы. Необходимо следить за допустимыми значениями при выполнении математических операций и предусматривать обработку возможных ошибок.
ValueError: math domain error
While working with mathematical functions in Python, you might come across an error called «ValueError math domain error«. This error is usually encountered when you are trying to solve quadratic equations or finding out the square root of a negative number.
You can avoid this error by providing the correct values to the math functions. Avoiding the use of negative values will be ideal.
Let us look at some examples where the error might be encountered.
Example 1: Square Root of Negative Number
We can calculate the square root of a number in python by importing the sqrt method from the math module. But what if a user entered a negative number?
Will it throw an error or will we get the desired output? let’s understand it with a few examples.
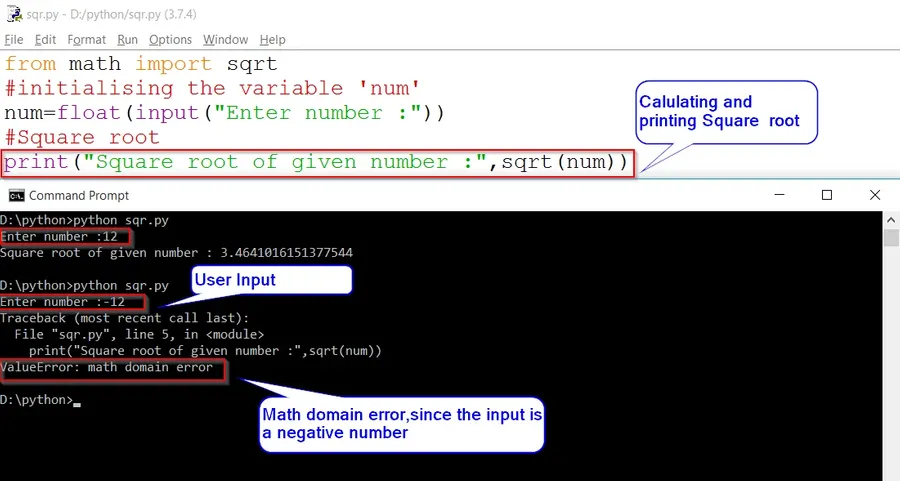
from math import sqrt
# Initialising the variable 'num'
num=float(input("Enter number :"))
#Square root of num
print("Square root of given number :",sqrt(num))Output:
Enter number :12
Square root of given number : 3.4641016151377544
Enter number :-12
File "sqr.py", line 5, in <module>
print("Square root of given number :",sqrt(num))
ValueError: math domain errorIf num less then 0 or negative number then this code throws a math domain error as mentioned above.
Solution:
We can either handle the ValueError by raising an exception or by importing sqrt method from cmath library lets discuss both of them.
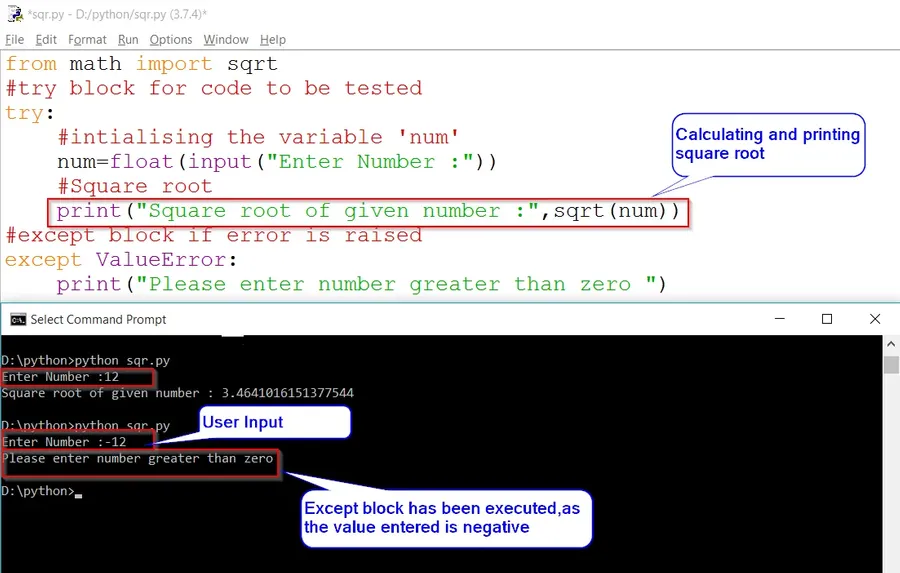
Method 1: Using Try and Except Block for Handling the Error.
from math import sqrt
#try block for code to be tested
try:
#intialising the variable 'num'
num=float(input("Enter Number :"))
#Square root
print("Square root of given number :",sqrt(num))
#except block if error is raised
except ValueError:
print("Please enter a number greater than zero ")OUTPUT :
Enter Number : 12
Square root of given number : 3.4641016151377544
Enter Number : -12
Please enter a number greater than zeroIn the above code, when we enter a positive value we will get the desired output. But, when we will enter a negative value it’ll throw an error i.e «ValueError: math domain error«.
And to handle the ValueError we use try and except block.
The try block includes the code to be tested.
The Except block handles the error by displaying the desired message. Which in this case is «Please enter the number greater than zero«.
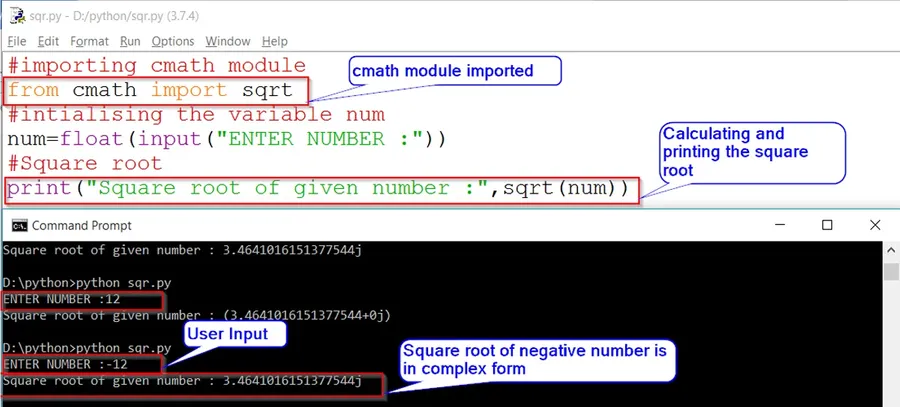
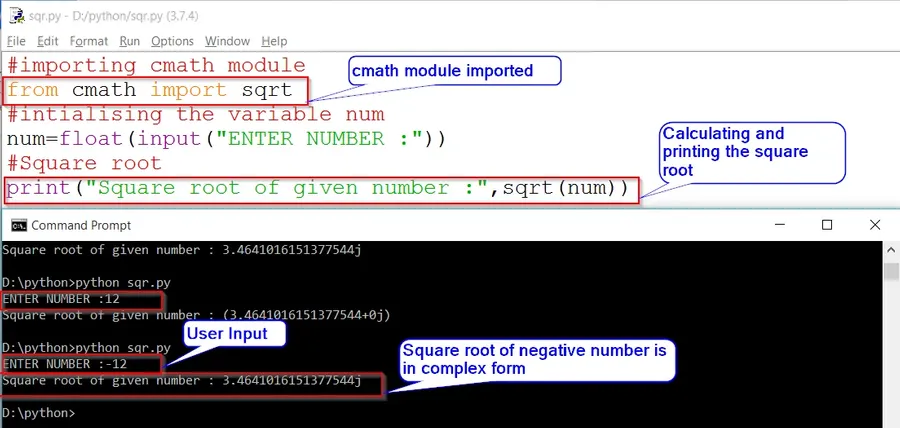
Method2: Importing Sqrt From «cmath» Which Will Return Square Root of Negative Number in Complex/Imaginary Form.
# Importing cmath module
from cmath import sqrt
# Input from user
num=float(input("Enter Number: "))
#Square root
print("Square root of given number : ", sqrt(num))OUTPUT:
Enter Number : 12
Square root of given number : (3.4641016151377544+0j)
Enter Number : -12
Square root of given number : 3.4641016151377544jIn Method 1 we did not get the result instead we raised an exception. But what if we want the square root of a negative index in complex form.
To solve this issue import «sqrt» from cmath module. Which shows the result in complex/imaginary form as in mathematics.
When we import the cmath module the result which we will get will be in the complex form as shown in the output of «Method 2«.
Example 2: Log of a Negative Number
#importing log from math module
from math import log
#Intialising the variable 'num'
num= float(input("Enter Number :"))
#Natural logarithm of num
print("Natural logarithm of provided number :",log(num))OUTPUT:
Enter Number :12
Natural logarithm of provided number : 2.4849066497880004
Enter Number :-12
File "sqr.py", line 6, in <module>
print("Natural logarithm of provided number :",log(num))
ValueError: math domain errorIn the above code, When we try to find the log of the positive value we get the desired output. But when we try to find the log of the negative index it throws an error «ValueError: math domain error«.
This is because the negative of the log is not defined in python.

![ValueError: math domain error [Solved Python Error]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2023/02/python-math-domain-error.png)