This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Ошибка: | |
| .venvScriptsactivate : Невозможно загрузить файл C:pathvenvScriptsactivate.ps1, так как выполнение сценариев отключено в этой системе. | |
| Для получения дополнительных сведений см. about_Execution_Policies по адресу http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170. | |
| строка:1 знак:1 | |
| .venvScriptsactivate | |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |
| CategoryInfo : Ошибка безопасности: (:) [], PSSecurityException | |
| FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess | |
| Решение проблемы: | |
| — Открываем терминал PowerShell от админа. | |
| — Вставляем и запускаем — Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned | |
| — На вопрос отвечаем — A |
Не работает виртуальная среда venv в VSCode на Win10.
Создаю проект, папку, пытаюсь запустить скрипт Activate.ps1, но он не работает. Работает Activate.bat, но это не помогает, и весь pip install идет не в виртуальную среду. + терминал не просит обновить pip. В чем моя ошибка? Что я не сделал или сделал, но не так?
Терминал VSCode:
Windows PowerShell
PS C:Users99622> cd .DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_server
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_server> New-Item -ItemType directory DarkBot
Каталог: C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_server
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_server> cd .DarkBot
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBot> py.exe -m venv env
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBot> cd .envScripts
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBotenvScripts> .Activate.ps1
.Activate.ps1 : Невозможно загрузить файл C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBotenvSc
riptsActivate.ps1, так как выполнение сценариев отключено в этой системе. Для получения дополнительных с
ведений см. about_Execution_Policies по адресу https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170.
строка:1 знак:1
+ .Activate.ps1
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : Ошибка безопасности: (:) [], PSSecurityException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBotenvScripts> .activate.bat
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBotenvScripts> pip list
Package Version
----------------- ----------
astroid 2.3.3
beautifulsoup4 4.9.0
bs4 0.0.1
certifi 2020.4.5.1
chardet 3.0.4
colorama 0.4.3
get 2019.4.13
idna 2.9
lazy-object-proxy 1.4.3
mccabe 0.6.1
pip 20.1
post 2019.4.13
public 2019.4.13
pylint 2.4.4
pyTelegramBotAPI 3.6.7
query-string 2019.4.13
request 2019.4.13
requests 2.23.0
setuptools 41.2.0
six 1.14.0
soupsieve 2.0
urllib3 1.25.9
wrapt 1.11.2
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBotenvScripts> pip install pyTelegramBotAPI
Requirement already satisfied: pyTelegramBotAPI in c:users99622appdatalocalprogramspythonpython38-32libsite-packages (3.6.7)
Requirement already satisfied: requests in c:users99622appdatalocalprogramspythonpython38-32libsite-packages (from pyTelegramBotAPI) (2.23.0)
Requirement already satisfied: six in c:users99622appdataroamingpythonpython38site-packages (from pyTelegramBotAPI) (1.14.0)
Requirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in c:users99622appdatalocalprogramspythonpython38-32libsite-packages (from requests->pyTelegramBotAPI) (2020.4.5.1)
Requirement already satisfied: urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 in c:users99622appdatalocalprogramspythonpython38-32libsite-packages (from requests->pyTelegramBotAPI) (1.25.9)
Requirement already satisfied: chardet<4,>=3.0.2 in c:users99622appdatalocalprogramspythonpython38-32libsite-packages (from requests->pyTelegramBotAPI) (3.0.4)
Requirement already satisfied: idna<3,>=2.5 in c:users99622appdatalocalprogramspythonpython38-32libsite-packages (from requests->pyTelegramBotAPI) (2.9)
Could not build wheels for pyTelegramBotAPI, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Could not build wheels for requests, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Could not build wheels for six, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Could not build wheels for certifi, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Could not build wheels for urllib3, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Could not build wheels for chardet, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Could not build wheels for idna, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
PS C:Users99622DocumentsPythonTG_Bot_f_serverDarkBotenvScripts>I am using VSCode and started getting the following error when launching VSCode:
You have been signed out because reading stored authentication information failed.
I checked the «Microsoft Authentication» output and see the following being logged:
[Info - 12:53:11.944] Reading sessions from secret storage...
[Info - 12:53:12.8] Got 2 stored sessions
[Trace - 12:53:12.8] Read the following stored session with scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Info - 12:53:12.8] Refreshing token for scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Trace - 12:53:12.9] Read the following stored session with scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Info - 12:53:12.9] Refreshing token for scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Error - 12:53:12.381] Refreshing token failed (for scopes: email offline_access openid profile): {"error":"invalid_grant","error_description":"AADSTS50173: The provided grant has expired due to it being revoked, a fresh auth token is needed. The user might have changed or reset their password. The grant was issued on '2022-01-18T01:28:57.1010000Z' and the TokensValidFrom date (before which tokens are not valid) for this user is '2022-03-17T00:24:27.0000000Z'.rnTrace ID: 61f7c850-e661-4df6-804d-b09ac98a4300rnCorrelation ID: 52be35ff-e99b-4b53-9dbb-2dba8582d605rnTimestamp: 2022-03-21 12:53:12Z","error_codes":[50173],"timestamp":"2022-03-21 12:53:12Z","trace_id":"61f7c850-e661-4df6-804d-b09ac98a4300","correlation_id":"52be35ff-e99b-4b53-9dbb-2dba8582d605","error_uri":"https://login.microsoftonline.com/error?code=50173"}
[Error - 12:53:12.382] Error: Refreshing token failed
[Info - 12:53:12.382] Logging out of session 'f140c6a2-c524-4206-9a98-2b24b0c5a952/3046af31-b03b-4dec-ac69-5e441c677bfa/cdcd3466-2921-45ce-b841-62e6f5e4151a'
[Info - 12:53:12.382] Session not found 'f140c6a2-c524-4206-9a98-2b24b0c5a952/3046af31-b03b-4dec-ac69-5e441c677bfa/cdcd3466-2921-45ce-b841-62e6f5e4151a'
[Info - 12:53:12.423] Setting token for scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Info - 12:53:12.423] Token refresh success for scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Info - 12:53:12.425] Getting sessions for the following scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Info - 12:53:12.425] Got 1 sessions for scopes: email offline_access openid profile
[Info - 12:53:12.425] Token available from cache (for scopes email offline_access openid profile), expires in 3756998 milliseconds
I do not recall having to log into any Microsoft environment to use VSCode, and not sure how to check or reset password to resolve this.
VSCode version:
Version: 1.65.2 (user setup)
Commit: c722ca6c7eed3d7987c0d5c3df5c45f6b15e77d1
Date: 2022-03-10T14:33:55.248Z
Electron: 13.5.2
Chromium: 91.0.4472.164
Node.js: 14.16.0
V8: 9.1.269.39-electron.0
OS: Windows_NT x64 10.0.19042
When debugging/running a web service or web application in Visual Studio Code or Visual Studio the following error will show up in the browser the first time an application is run immediately after the .NET 5 (or other) SDK is installed:
The text of the error is:
Your connection is not private
Attackers might be trying to steal your information from localhost (for example, passwords, messages, or credit cards). Learn more
NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID
The error is caused because the certificates used during running/debugging provided by the .NET 5 SDK have not been trusted on the local host. The DotNet CLI provides a command-line for trusting these certificates:
dotnet dev-certs https —trust
The command above should be run from Visual Studio Code’s Terminal window:
When the above command is invoked, the following dialog is displayed:
Click on Yes to trust the certificates. Restart the application being debugged/run in Visual Studio code and the error should disappear.
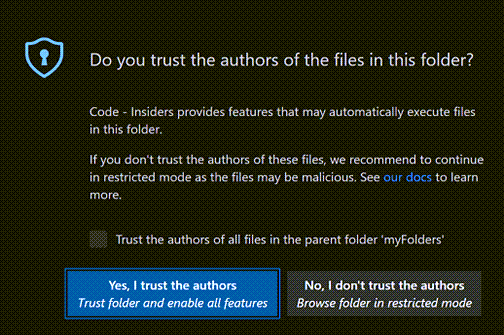
Visual Studio Code takes security seriously and wants to help you safely browse and edit code no matter the source or original authors. The Workspace Trust feature lets you decide whether code in your project folder can be executed by VS Code and extensions without your explicit approval.
Note: When in doubt, leave a folder in Restricted Mode. You can always enable trust later.
Safe code browsing
It’s great that there is so much source code available on public repositories and file shares. No matter the coding task or problem, there is probably already a good solution available somewhere. It is also great that there are so many powerful coding tools available to help you understand, debug, and optimize your code. However, using open-source code and tools does have risks, and you can leave yourself open to malicious code execution and exploits.
Workspace Trust provides an extra layer of security when working with unfamiliar code, by preventing automatic code execution of any code in your workspace if the workspace is open in «Restricted Mode».
Note: The terms «workspace» and «folder» are used widely in the VS Code UI and documentation. You can think of a «workspace» as a folder with extra metadata created and used by VS Code.
Restricted Mode
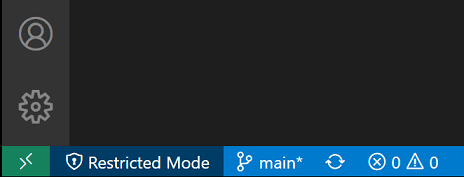
When prompted by the Workspace Trust dialog, if you choose No, I don’t trust the authors, VS Code will go into Restricted Mode to prevent code execution. The workbench will display a banner at the top with links to Manage your folder via the Workspace Trust editor, and Learn More about Workspace Trust (which takes you to back to this documentation).
You will also see a Restricted Mode badge in the Status bar.
Restricted Mode tries to prevent automatic code execution by disabling or limiting the operation of several VS Code features: tasks, debugging, workspace settings, and extensions.
To see the full list of features disabled in Restricted Mode, you can open the Workspace Trust editor via the Manage link in the banner, or by clicking the Restricted Mode badge in the Status bar.
Note: Workspace Trust can not prevent a malicious extension from executing code and ignoring Restricted Mode. You should only install and run extensions that come from a well-known publisher that you trust.
Tasks
Tasks can run scripts and tool binaries, and because task definitions are defined in the workspace .vscode folder, they are part of the committed source code for a repo, and shared to every user of that repo. Were someone to create a malicious task, it could be unknowningly run by anyone who cloned that repository.
If you try to run or even enumerate tasks (Terminal > Run Task…) while in Restricted Mode, VS Code will display a prompt to trust the folder and continue executing the task. Cancelling the dialog leaves VS Code in Restricted Mode.
Debugging
Similar to running a VS Code task, debug extensions can run debugger binaries when launching a debug session. For that reason, debugging is also disabled when a folder is open in Restricted Mode.
If you try to start a debug session (Run > Start Debugging) while in Restricted Mode, VS Code will display a prompt to trust the folder and continue launching the debugger. Cancelling the dialog leaves VS Code in Restricted Mode, and does not start the debug session.
Workspace settings
Workspace settings are stored in the .vscode folder at the root of your workspace, and are therefore shared by anyone who clones the workspace repository. Some settings contain paths to executables (for example, linter binaries), which if set to point to malicious code, could do damage. For this reason, there is a set of workspace settings that are disabled when running in Restricted Mode.
In the Workspace Trust editor, there is a link to display the workspace settings that aren’t being applied. Clicking the link brings up the Settings editor scoped by the @tag:requireTrustedWorkspace tag.
Extensions
The VS Code extensions ecosystem is incredibly rich and diverse. People have created extensions to help with just about any programming task or editor customization. Some extensions provide full programming language support (IntelliSense, debugging, code analysis), and others let you play music or
have virtual pets.
Most extensions run code on your behalf and could potentially do harm. Some extensions have settings that could cause them to act maliciously if configured to run an unexpected executable. For this reason, extensions that have not explicitly opted into Workspace Trust are disabled by default in Restricted Mode.
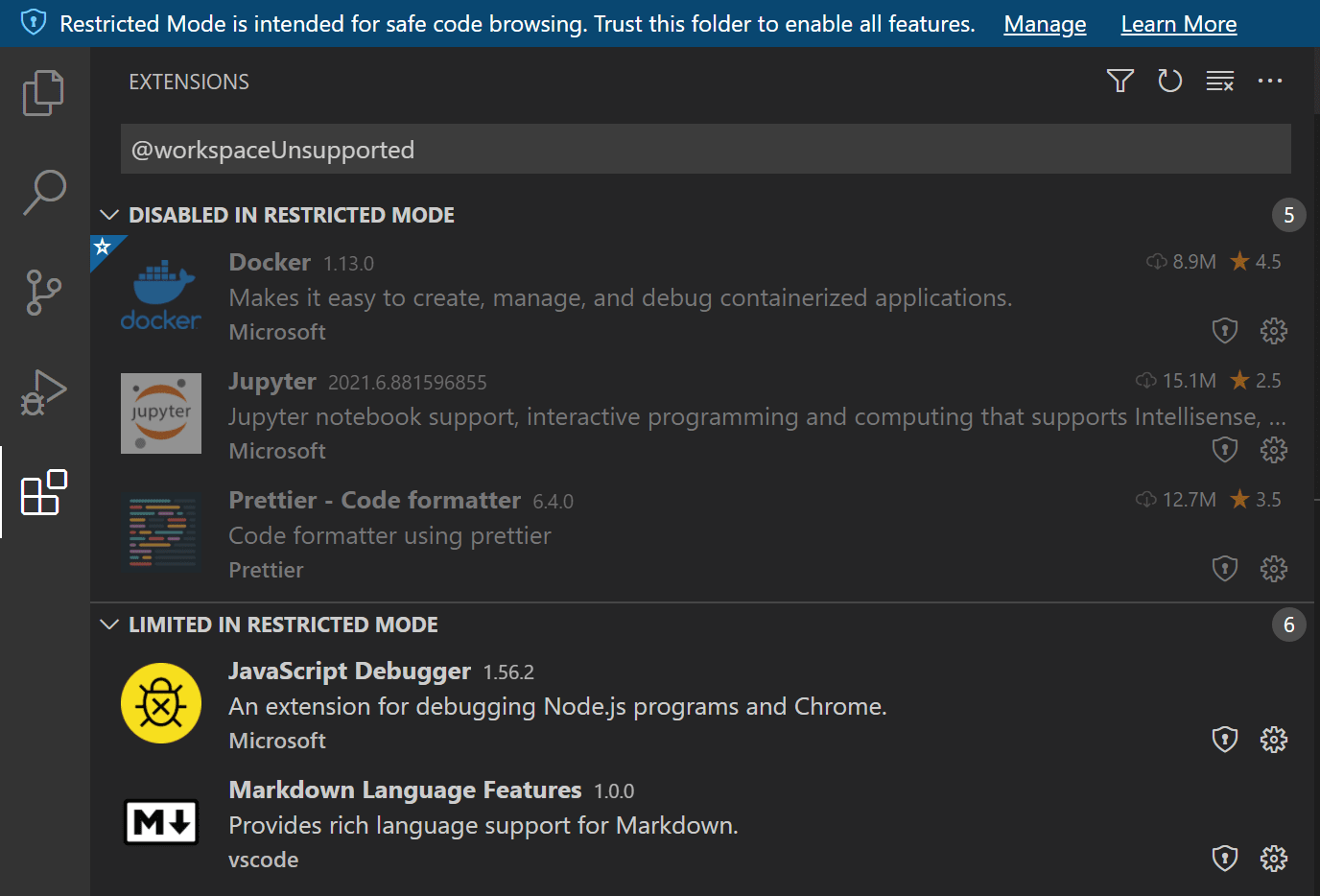
You can review an installed extension’s status by clicking the extensions are disabled or have limited functionality link in the Workspace Trust editor, which displays the Extensions view scoped with the @workspaceUnsupported filter.
Disabled in Restricted Mode
Extensions that have either not explicitly indicated that they support running in Restricted Mode are shown in the Disabled in Restricted Mode section. An extension author can also indicate that they never want to be enabled in Restricted Mode if they determine that their extension could be misused by modifications (settings or files) in a workspace.
Limited in Restricted Mode
Extension authors can also evaluate their extensions for possible security vulnerabilities and declare that they have limited support when running in Restricted Mode. This mode means the extension may disable some features or functionality to prevent a possible exploit.
Extensions can add custom text to the Extensions view Workspace Trust badge explaining the limitation when running in an untrusted folder.
For example, the VS Code built-in PHP extension limits the use of the php.validate.executablePath setting to trusted folders since overriding this setting could run a malicious program.
You can override an extension’s Workspace Trust support level using the extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces setting described in the Enabling extensions section below.
If you try to install an extension in Restricted Mode, you will be prompted to either trust the workspace or just install the extension. If the extension doesn’t support Workspace Trust, it will be installed, but be disabled or running with limited functionality.
Note: Extension authors can learn how to update their extensions to support Workspace Trust by reading the Workspace Trust Extension Guide.
Trusting a workspace
If you trust the authors and maintainers of a project, you can trust the project’s folder on your local machine. For example, it is usually safe to trust repositories from well-known GitHub organizations such as github.com/microsoft or github.com/docker.
The initial Workspace Trust prompt when you open a new folder allows you to trust that folder and its subfolders.
You can also bring up the Workspace Editor and quickly toggle a folder’s trusted state.
There are several ways to bring up the Workspace Editor dialog.
When in Restricted Mode:
- Restricted Mode banner Manage link
- Restricted Mode Status bar item
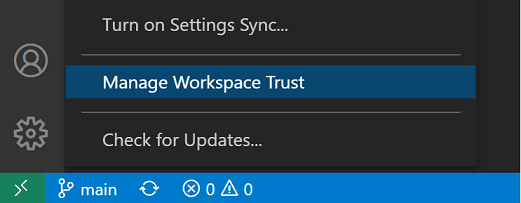
You can also at any time use:
- Workspaces: Manage Workspace Trust command from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P))
- Manage Workspace Trust from the Manage gear in the Activity bar
Selecting folders
When you trust a folder, it is added to the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list displayed in the Workspace Trust editor.
You can manually add, edit, and remove folders from this list and the active folder enabling trust is highlighted in bold.
Selecting a parent folder
When you trust a folder via the Workspace Trust editor, you have the option to trust the parent folder. This will apply trust to the parent folder and all subfolders.
This can be helpful if you have many folders with trusted content co-located under one folder.
When opening a subfolder under a trusted parent, you won’t see the usual Don’t Trust button to put you back in Restricted Mode, instead there is text mentioning that your folder is trusted due to another folder.
You can add, modify, and remove a parent folder entry from the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list.
Folder configurations
As mentioned above, you can trust a parent folder and all subfolders will be trusted. This allows you to control Workspace Trust via a repository’s location on disk.
For example, you could put all trusted repos under a «TrustedRepos» parent folder, and unfamiliar repos under another parent folder such as «ForEvaluation». You would trust the «TrustedRepos» folder, and selectively trust folders under «ForEvaluation».
├── TrustedRepos - Clone trusted repositories under this parent folder
└── ForEvaluation - Clone experimental or unfamiliar repositories under this parent folder
You also group and set trust on your repositories by grouping them under organization-base parent folders.
├── github/microsoft - Clone a specific organization's repositories under this parent folder
├── github/{myforks} - Place your forked repositories under this parent folder
└── local - Local un-published repositories
Enabling extensions
What happens if you want to use Restricted Mode but your favorite extension doesn’t support Workspace Trust? This can happen if an extension, while useful and functional, isn’t being actively maintained and hasn’t declared their Workspace Trust support. To handle this scenario, you can override the extension’s trust state with the extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces setting.
Note: Be careful overriding an extension’s Workspace Trust support. It may be that the extension author has a good reason for disabling their extension in Restricted Mode. If in doubt, reach out to the extension author or review recent changelogs to get more context.
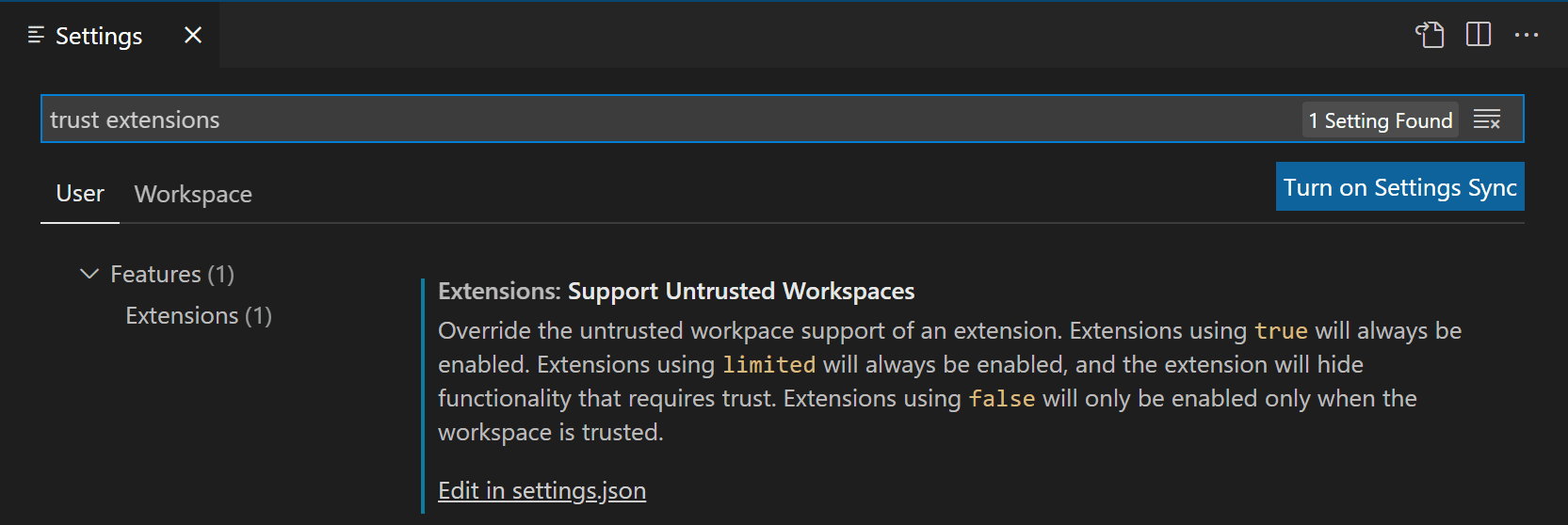
If you open the Settings editor (⌘, (Windows, Linux Ctrl+,)) and search for «trust extensions», you can find the Extensions: Support Untrusted Workspaces setting, which has an Edit in settings.json link.
Select that link and you will go to your user settings.json file with a new entry for extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces. This setting takes an object that has a list of extension IDs and their support status and version. You can select any of your installed extensions via IntelliSense suggestions.
Below you can see a settings.json entry for the Prettier extension.
"extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces": {
"esbenp.prettier-vscode": {
"supported": true,
"version": "6.4.0"
},
},
You can either enable or disable Workspace Trust support with the supported attribute. The version attribute specifies the exact extension version applicable and you can remove the version field if you want to set the state for all versions.
If you’d like to learn more about how extension authors evaluate and determine which features to limit in Restricted Mode, you can read the Workspace Trust Extension Guide.
Opening untrusted files
If you open a file that is located outside of a trusted folder, VS Code will detect that the file comes from somewhere outside the folder root and prompt you with the option to continue to open the file or open the file in a new window in Restricted Mode. Opening in Restricted Mode is the safest option and you can always reopen the file in your original VS Code window once you determine the file is trustworthy.
If you would prefer to not be prompted when opening files from outside trusted workspaces, you can set security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles to open. You can also set security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles to newWindow to always create a new window in Restricted Mode. Checking the Remember my decision for all workspaces option in the untrusted files dialog applies your choice to the security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles user setting.
Opening untrusted folders
When working with multi-root workspaces with multiple folders, if you try to add a new folder to a trusted multi-root workspace, you will be prompted to decide if you trust the files in that folder or if not, the entire workspace will switch to Restricted Mode.
Empty windows (no open folder)
By default, if you open a new VS Code window (instance) without opening a folder or workspace, VS Code runs the window with full trust. All installed extensions are enabled and you can use the empty window without restrictions.
When you open a file, you will be prompted whether you want to open an untrusted file since there is no folder to parent it.
You can switch an empty window to Restricted Mode using the Workspace Trust editor (select Manage Workspace Trust from the Manage gear button or the Command Palette) and selecting Don’t Trust. The empty window will remain in Restricted Mode for your current session but will go back to trusted if you restart or create a new window.
If you want all empty windows to be in Restricted Mode, you can set security.workspace.trust.emptyWindow to false.
Settings
Below are the available Workspace Trust settings:
security.workspace.trust.enabled— Enable Workspace Trust feature. Default is true.security.workspace.trust.startupPrompt— Whether to show the Workspace Trust dialog on startup. Default is to only show once per distinct folder or workspace.security.workspace.trust.emptyWindow— Whether to always trust an empty window (no open folder). Default is true.security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles— Controls how to handle loose files in a workspace. Default is to prompt.extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces— Override extension Workspace Trust declarations. Either true or false.security.workspace.trust.banner— Controls when the Restricted Mode banner is displayed. Default isuntilDismissed.
Command-line switch
You can disable Workspace Trust via the VS Code command line by passing --disable-workspace-trust. This switch only affects the current session.
Next steps
Learn more at:
- Workspace Trust Extension Guide — Learn how extension authors can support Workspace Trust.
- What is a VS Code «workspace»? — Find out more details about the VS Code «workspace» concept.
- GitHub Repositories extension — Work directly on a repository without cloning the source code to your local machine.
Common questions
Can I still edit my source code in Restricted Mode?
Yes, you can still browse and edit source code in Restricted Mode. Some language features may be disabled, but text editing is always supported.
Where did my installed extensions go?
In Restricted Mode, any extension that doesn’t support Workspace Trust will be disabled, and all UI elements such as Activity bar icons and commands will not be displayed.
You can override an extension’s Workspace Trust support level with the extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces setting but do so with care. Enabling extensions has more details.
Can I disable the Workspace Trust feature?
You can but it is not recommended. If you don’t want VS Code to check for Workspace Trust when opening a new folder or repository, you can set security.workspace.trust.enabled to false. VS Code will then behave as it did before the 1.57 release.
How do I untrust a folder/workspace?
Bring up Workspace Trust editor (Workspaces: Manage Workspace Trust from the Command Palette) and select the Don’t Trust button. You can also remove the folder from the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list.
Why don’t I see the «Don’t Trust» button?
If you don’t see the Don’t Trust button in the Workspace Trust dialog, the folder’s trust level may be inherited from a parent folder. Review the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list to check if a parent folder has enabled Workspace Trust.
Some workflows such as connecting to a GitHub Codespace or attaching to a running Docker container are automatically trusted since these are managed environments to which you should already have a high level of trust.
What does Workspace Trust protect against?
Many features of VS Code allow third-party tools and extensions to run automatically, such as linting or format on save, or when you do certain operations like compiling code or debugging. An unethical person could craft an innocent looking project that would run malicious code without your knowledge and harm your local machine. Workspace Trust provides an extra layer of security by trying to prevent code execution while you are evaluating the safety and integrity of unfamiliar source code.
5/3/2023
Are you unable to open or launch the Visual Studio Code application on your Windows, macOS, or Linux desktop PC? Are any changes you made not being updated in real-time?
Visual Studio Code is an incredibly popular free and open-source code editor most developers use globally. It is a powerful, highly-customizable tool that streamlines the coding procedure, making writing, debugging, and managing code easier. In addition, it is versatile and highly extensible, with the ability to cater to the needs of every developer via integrating its vast library of extensions, which makes it an ideal choice for any developer, novice or seasoned.
But just like other software Visual Studio Code is also prone to crashes due to bugs or random errors. So if you are unable to open Visual Studio Code on your PC, don’t worry. You are not alone.
In this guide, we go over nine solutions that you can try to fix your Visual Studio Code not opening.
Table of Contents
- 10 Fixes for When You Can’t Open or Launch Visual Studio Code
- 1. Restart VS Code/Your PC
- 2. Update the Graphics Driver (For Windows)
- 3. Remove the Backup of Open Files
- 4. Disable Hardware Acceleration
- 5. Disable Extensions
- 6. Run VSCode as an Administrator (For Windows)
- 7. Disable AntiVirus Temporarily
- 8. Check for Updates
- 9. Analyze Log Files
- 10. Reinstall VSCode
10 Fixes for When You Can’t Open or Launch Visual Studio Code
1. Restart VS Code/Your PC
The first step to fixing the problem is to use the decade-old technique of rebooting your system. This simple fix can resolve most issues interfering with the opening of visual studio code. Usually, other applications or background processes interfere with the normal functionality of VS Code, causing it to crash or not load properly.
Therefore sometimes it is optimal to start VSCode from scratch. To proceed with this action, save all of your previous work, then stop all your installed extensions by closing VSCode. Following that, you can relaunch the VS Code application.
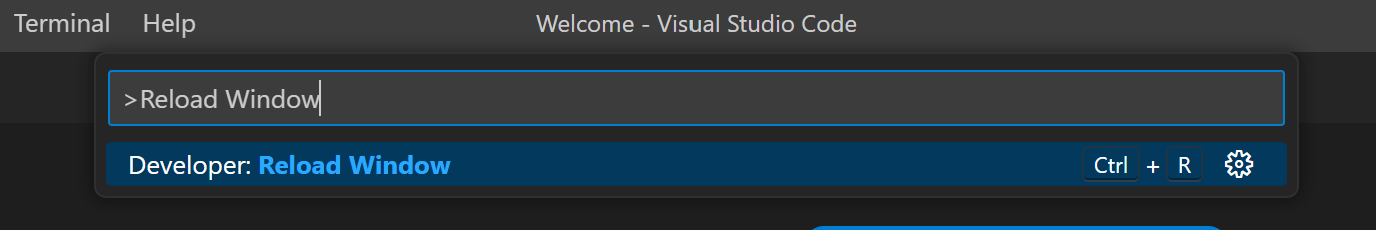
Apart from restarting Visual Studio Code by either closing the application and opening it again, you can open the command palette and enter the following command:
>Reload Window
2. Update the Graphics Driver (For Windows)
An outdated graphics driver is among the most common reasons which cause VSCode to crash. An outdated graphics driver does not permit the user to run any programming apps and usually crashes your system, especially if your program is long. Proceed by using the windows update feature to update your driver. Here’s how:
For Windows
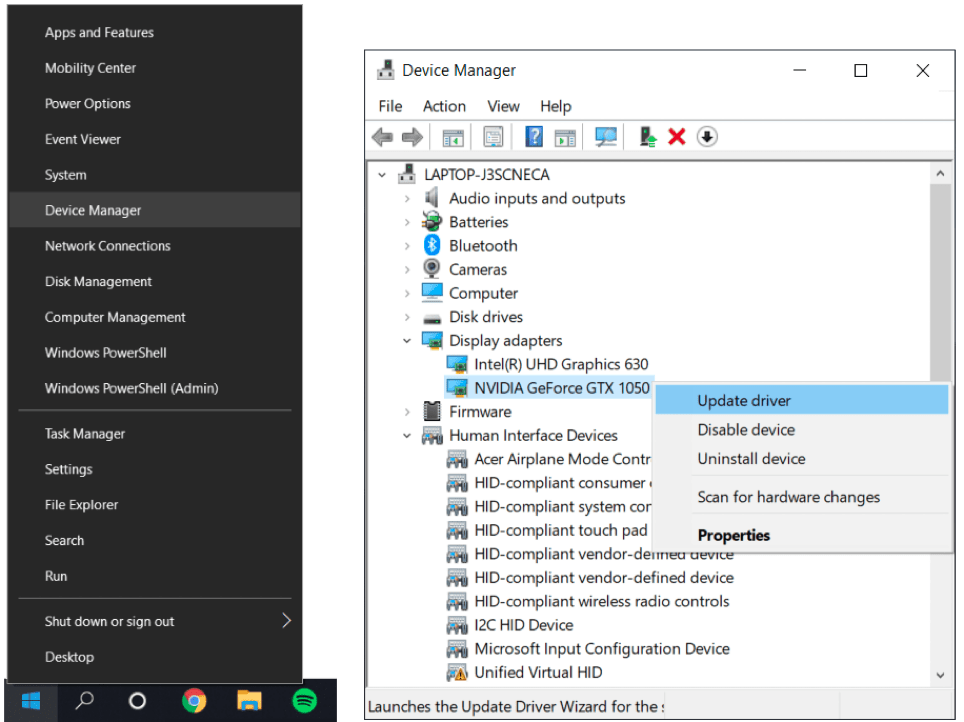
Method 1: Updating GPU Drivers through the Device Manager
The first method we recommend trying is updating through the Device Manager settings. To do this, right-click the Start menu at the bottom left and select Device Manager. Subsequently, under Display adapters, right-click the GPU drivers available, and select Update driver.
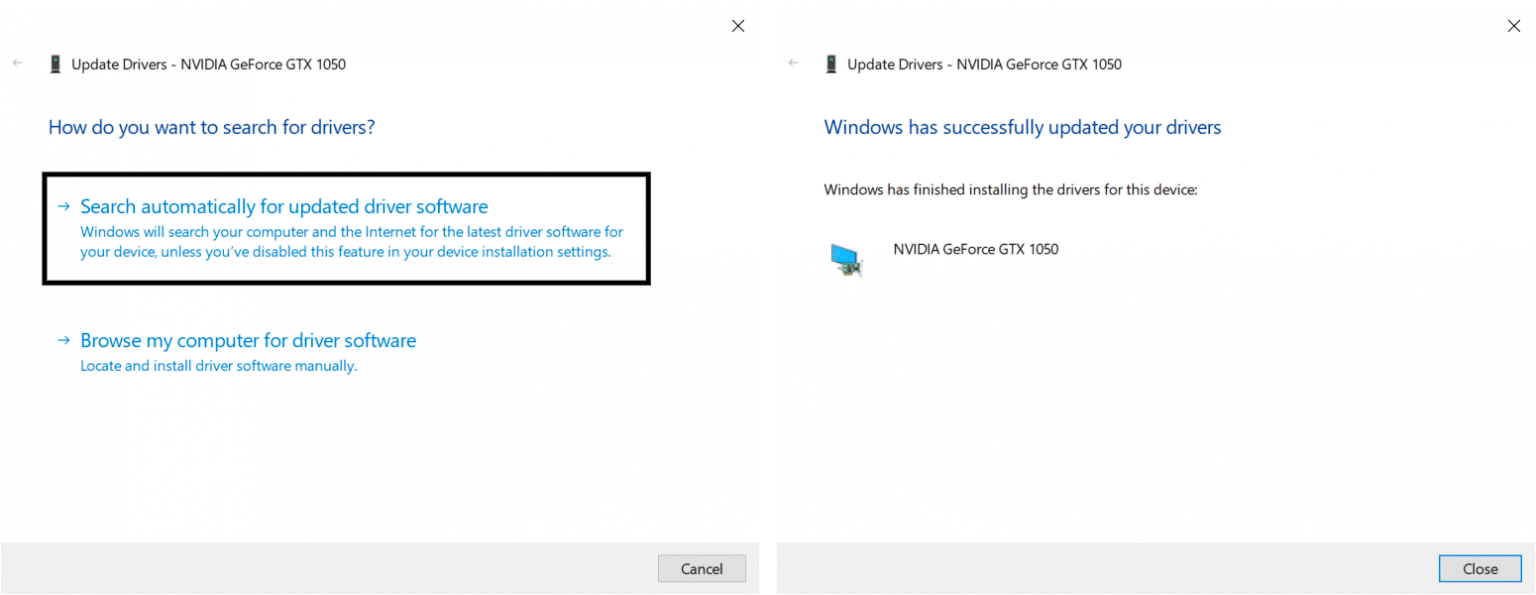
After that select, “Search automatically for updated driver software”, so your PC can begin searching online for any available updates. If there are updates available, it will immediately start downloading and installing it.
Finally, repeat the same steps for your other GPU drivers on the list as well.
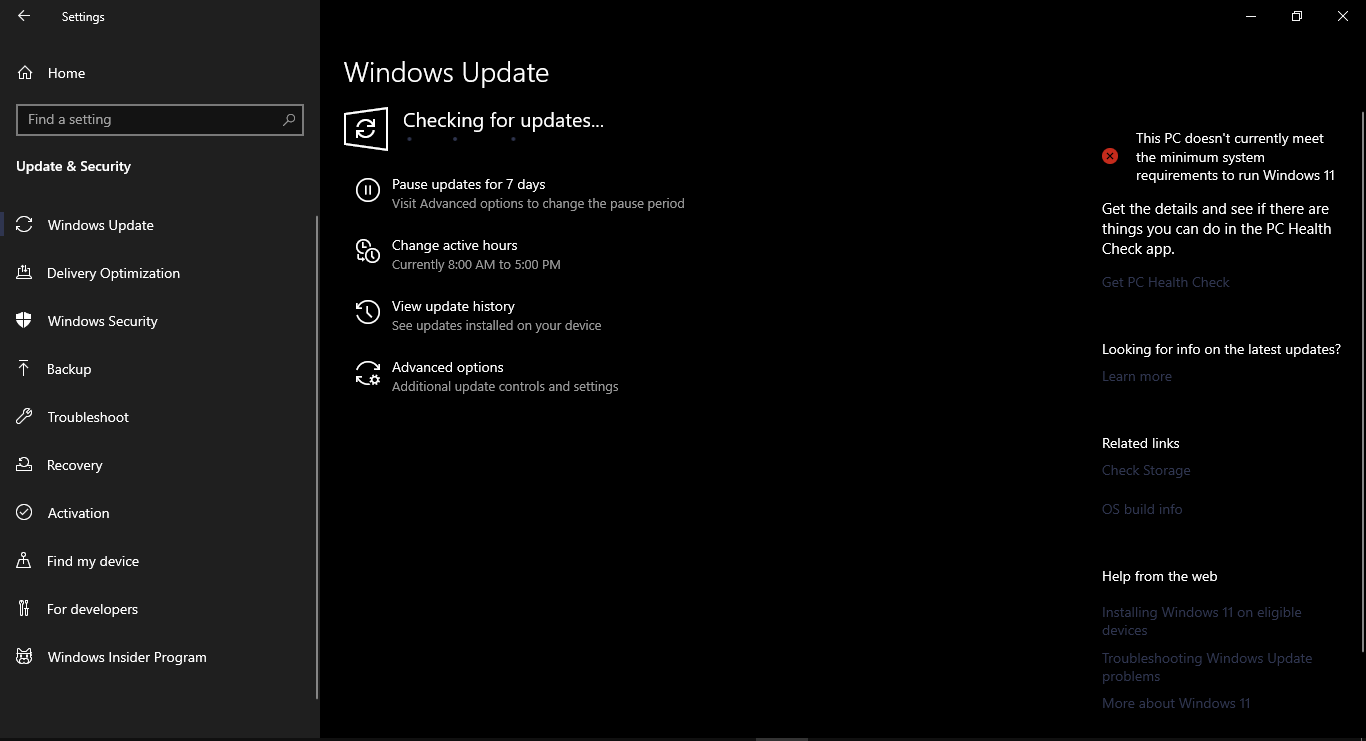
Method 2: Updating GPU Drivers through Windows Updates
- First, open the Settings app in Windows and click on Update & Security.
- Next, select Windows Update.
- After that, click on Check for updates.
- Windows will now search for updates, including updates for your graphics driver. If an update is available, click on the Download and install button to install it.
To manually search for GPU driver updates, you’ll need to find the GPU model for your PC through the System Information. After that, head over to the official site of your GPU manufacturer to search for updates for your specific GPU model. The following are links to the GPU driver download pages, which you can visit according to your GPU model.
- NVIDIA
- AMD
- INTEL
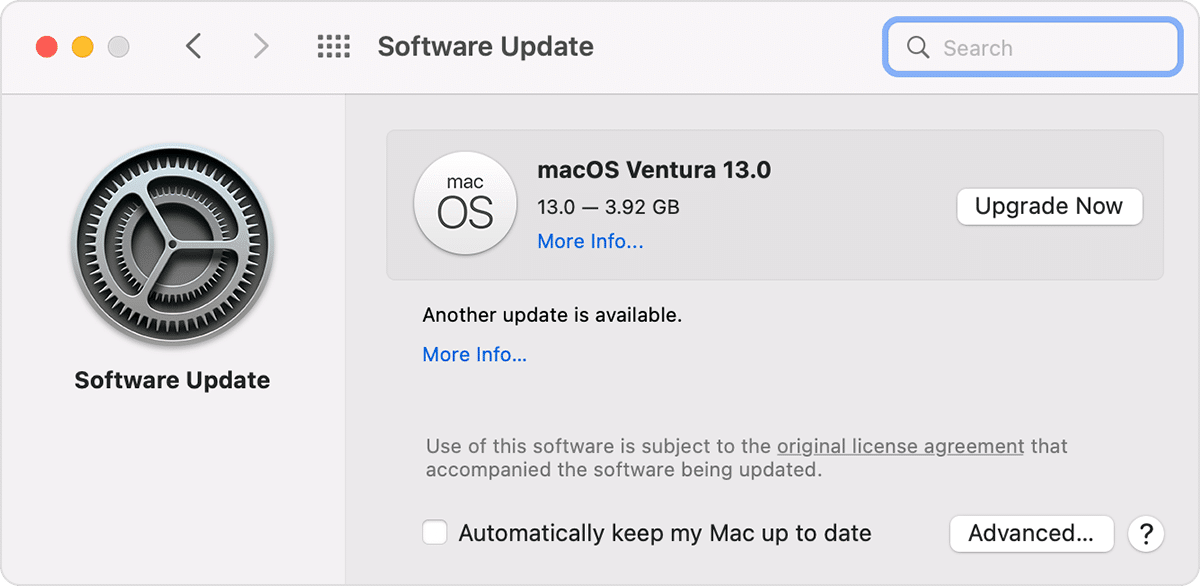
For macOS
There is no native way to update the graphic drivers on macOS. However, one can check and install pending software updates on their macOS device that may include updates for various components, by going to System settings, General, and Software Update.
After updating your graphics driver, reopen VSCode and see if the issue resolves.
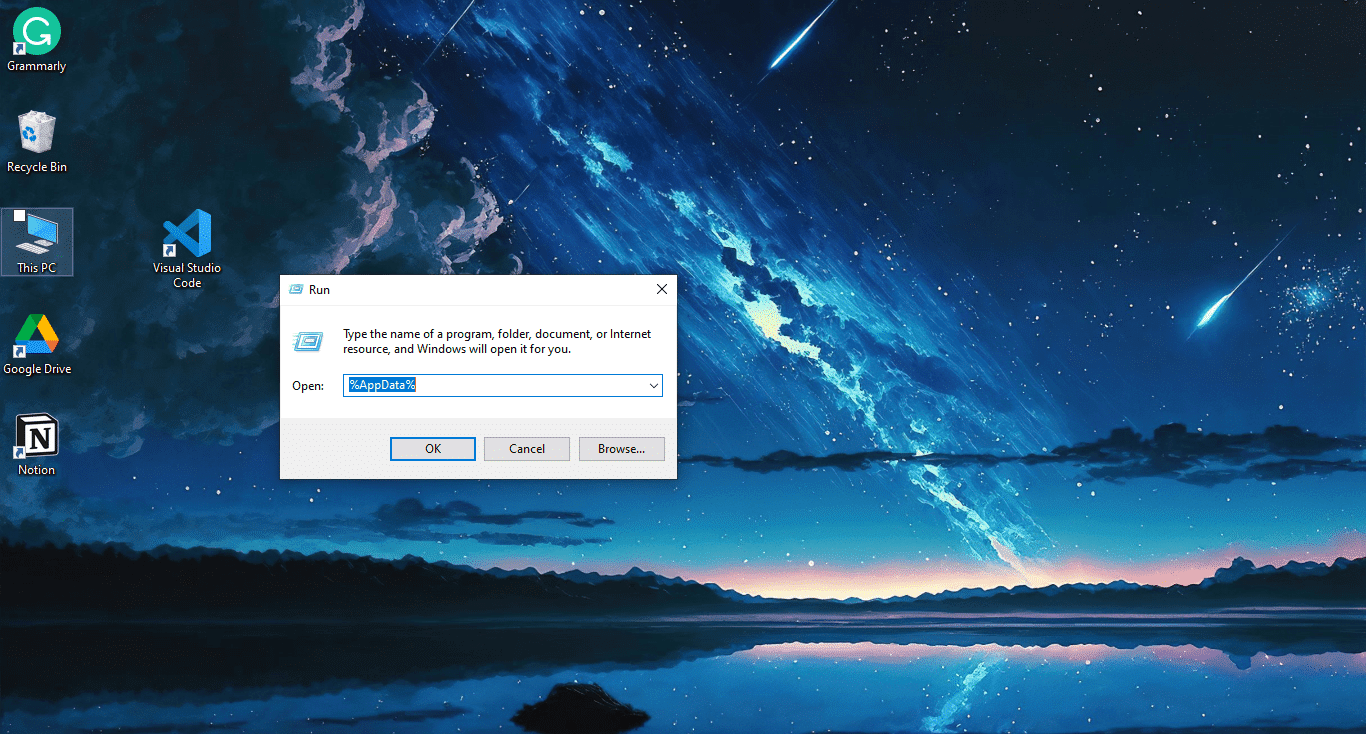
3. Remove the Backup of Open Files
If your VSCode stops or freezes abruptly and then crashes, you must delete some files. Removing the backup of open files helps to free up space on your system which ensures that VS Code runs smoothly and efficiently without crashing.
To begin with this fix, launch Run, paste “%AppData%” and click the “OK” button.
Next, navigate to the “Code > Backup” directory and delete the only folder within it. Afterward, restart VSCode to see if the issue persists.
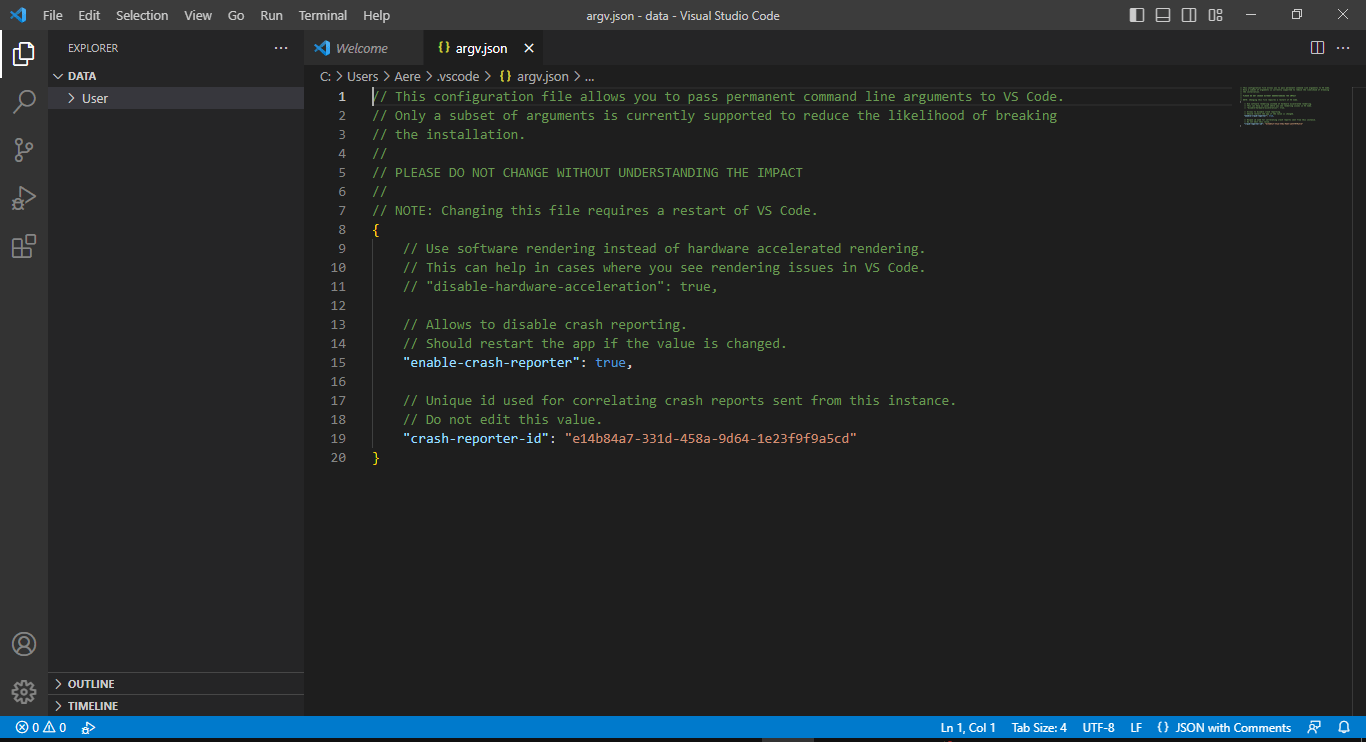
4. Disable Hardware Acceleration
If the issue persists, then you can try disabling GPU Hardware Acceleration. This forces VSCode to use Software rendering, resulting in a much more stable and smooth experience. To do so, follow the steps given below.
- Launch Visual Studio Code on Your Device
- Press Ctrl+Shift+P to bring up the command palette
- Type out the following phrase “Preferences: Configure Runtime Arguments” in the Command Palette and then hit Enter.
- Afterward, add the command
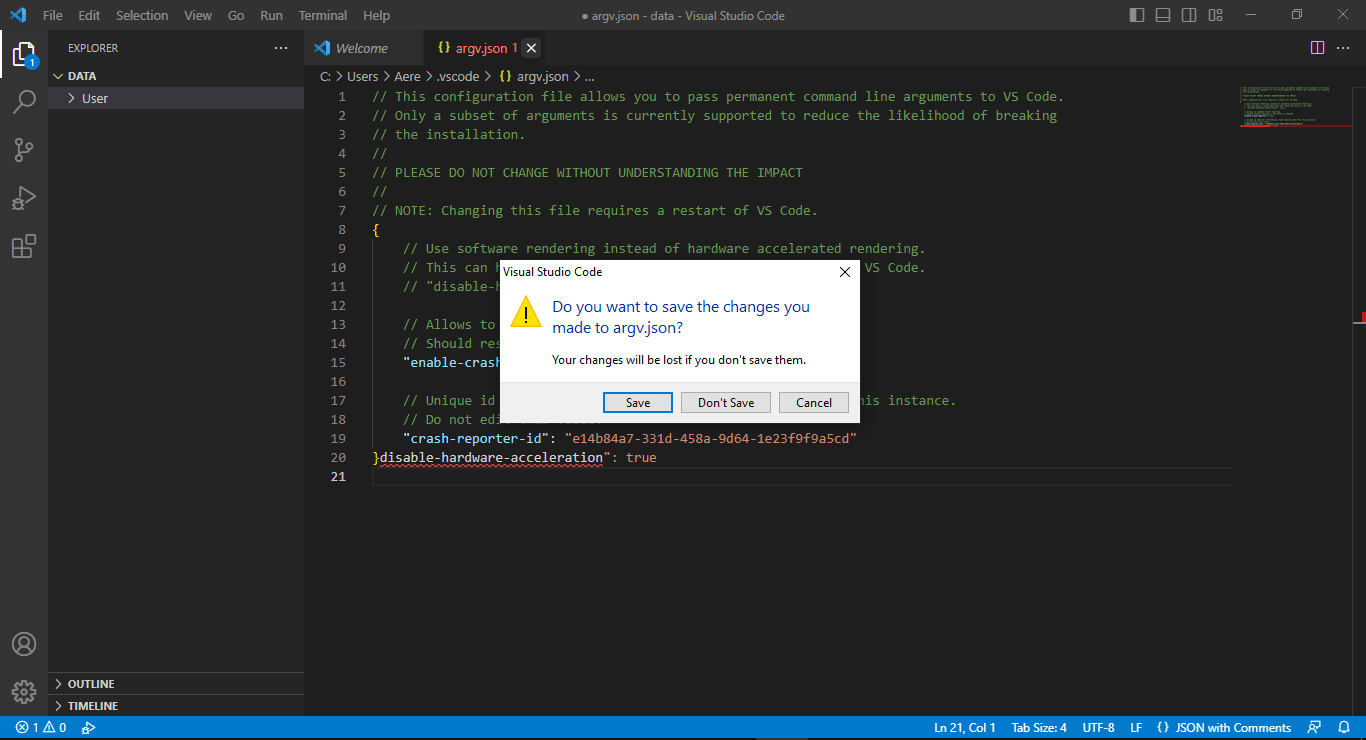
"disable-hardware-acceleration": true, to the file that appears. - Make sure to save changes by pressing Ctrl+S.
- Now restart VSCode to see if the fix has resolved the issue.
5. Disable Extensions
While VSCode extensions can enhance the program’s functionality, they can become a nuisance, sometimes causing VSCode to crash or not load properly. If you recently added a new extension to your VSCode or updated an existing one, consider disabling it.
Begin by disabling all extensions and then reopening VSCode. If it opens successfully, without crashing, then it is highly likely that one of the existing extensions is the problem.
The technique is to enable your extensions individually to identify the potential problematic extension. After identification of the problematic extension, disable or remove it from VSCode.
Follow the steps below to execute this fix:
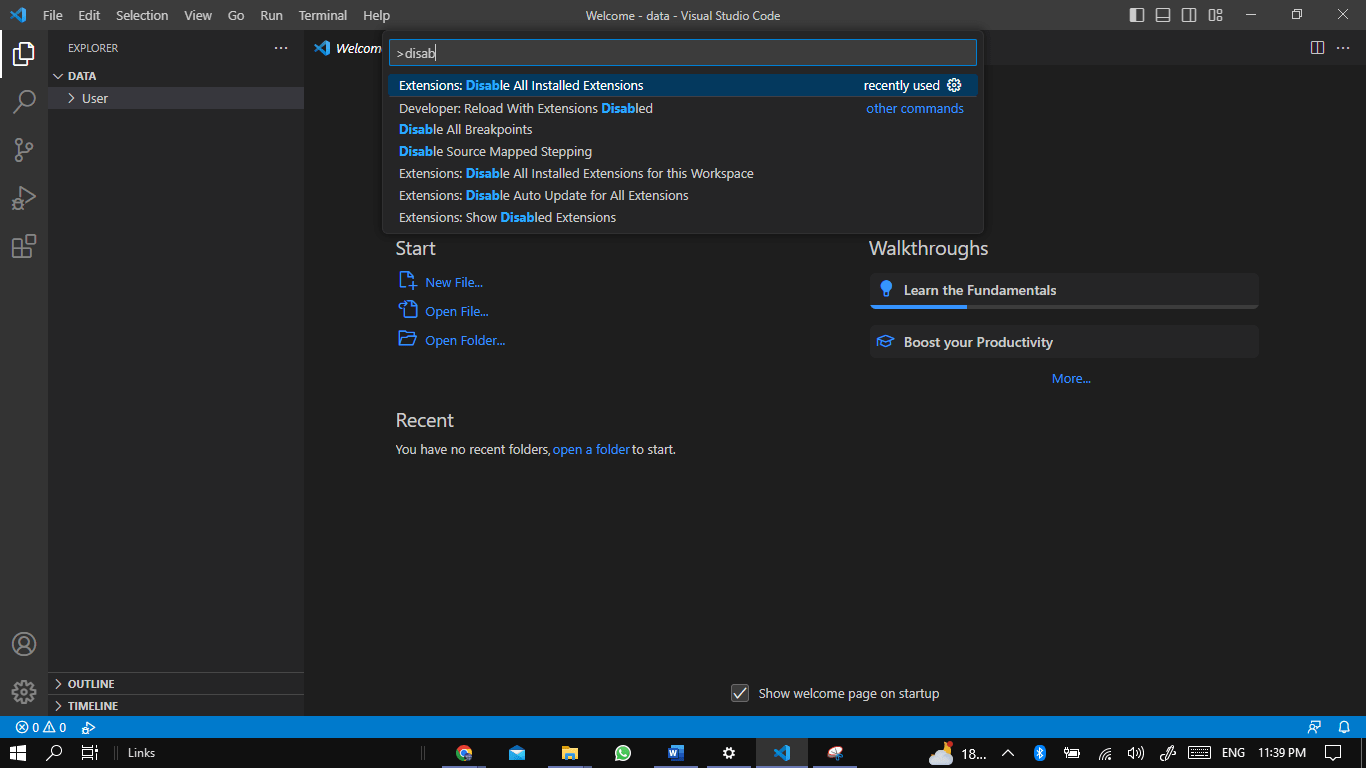
Disabling All Extensions
- Open VS Code.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + P (Windows/Linux) or Cmd + Shift + P (macOS) to pull up the Command Palette.
- Type in “Disable All Installed Extensions” and select the command from the list that appears.
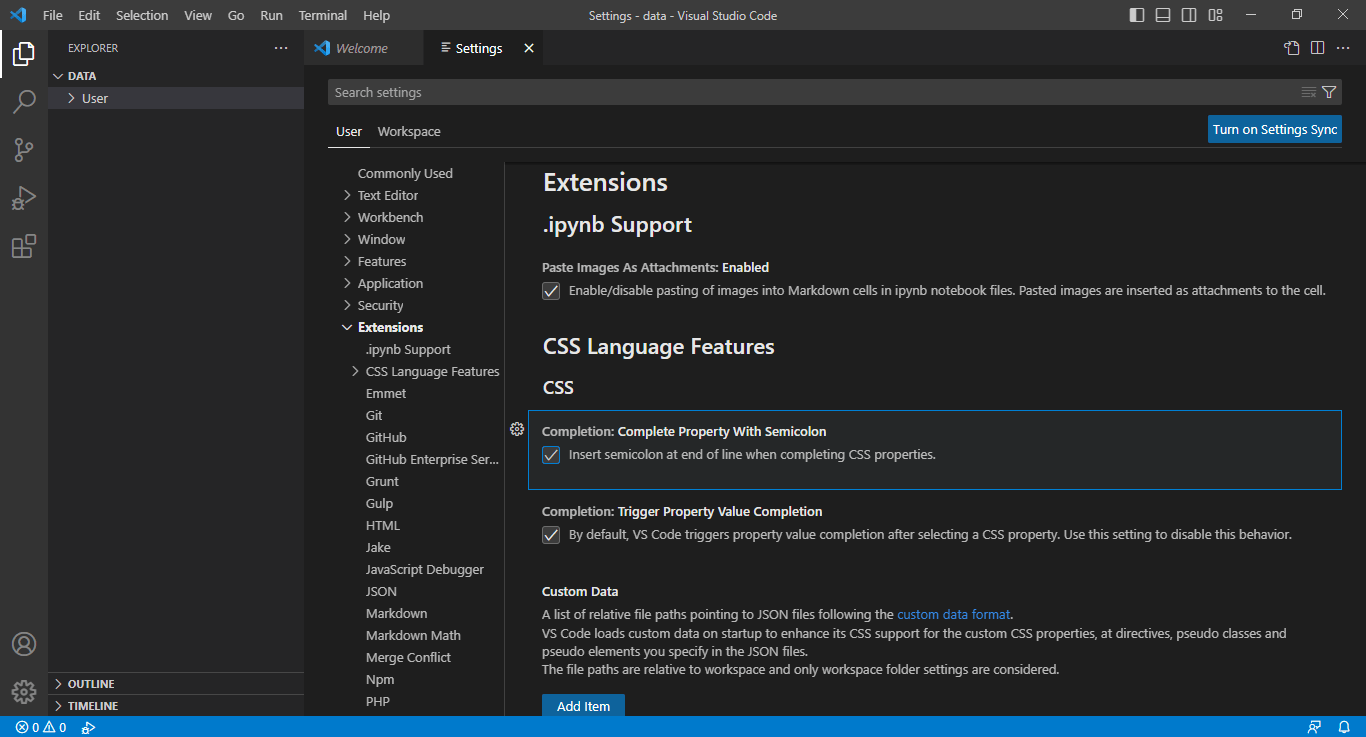
Disabling Extensions Individually
- Start VS Code.
- Click on “File” in the top menu bar.
- After selecting “Preferences,” select “Settings.”
- Choose “Extensions.”
- A list of the installed extensions will be displayed. Choose the gear icon next to the extension you wish to disable by finding it.
- Then choose “Disable.”
- Now the extension will be turned off.
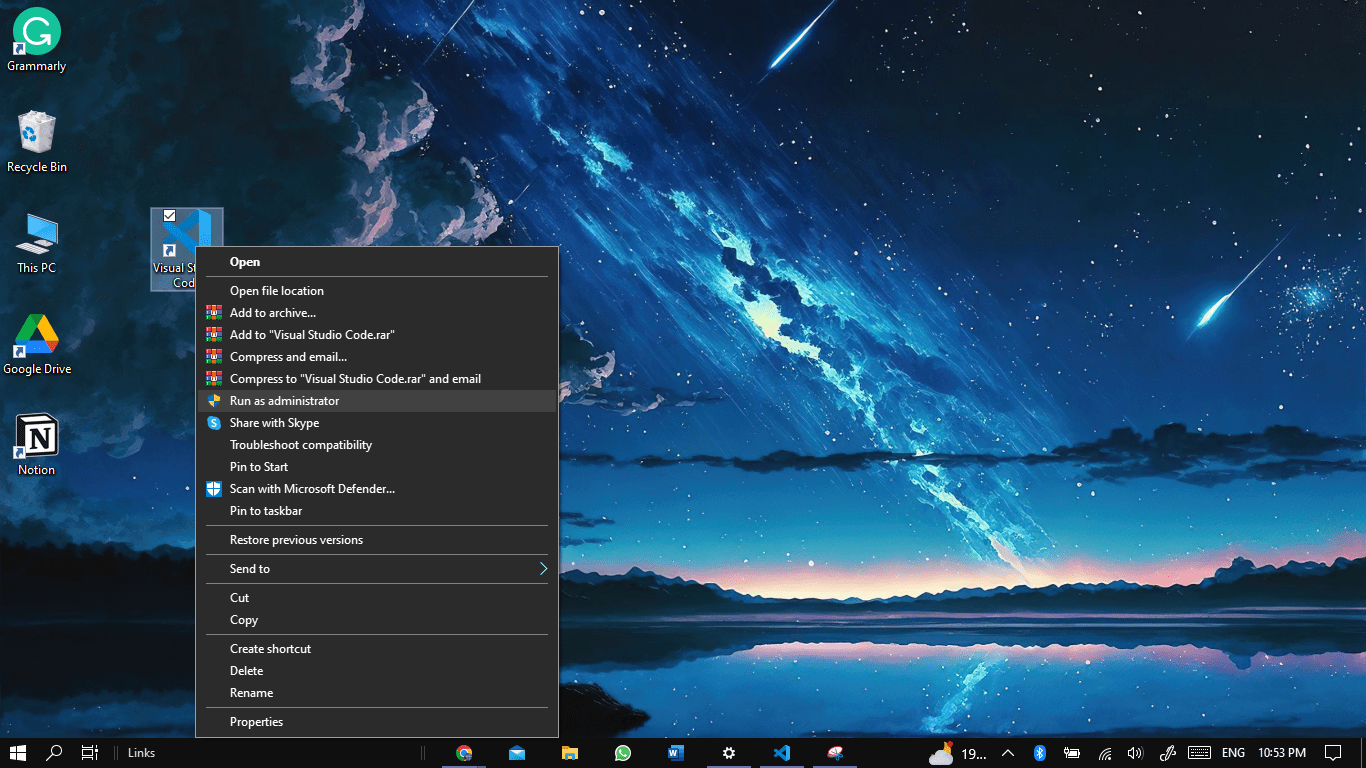
6. Run VSCode as an Administrator (For Windows)
Sometimes VSCode crashes or fails to open after you’ve installed a new Windows update due to permission issues. Therefore if you are running VSCode on a Windows device, try running the software as an administrator.
- Begin by right-clicking on the Visual Studio Code shortcut and selecting Run as Administrator.
- If VSCode runs smoothly, you need to modify the permissions for your user account.
7. Disable AntiVirus Temporarily
Sometimes VSCode fails to open due to an Antivirus that interferes with its operation. First, try temporarily disabling your antivirus software to see if VSCode opens successfully. If this fix works, then make sure to add VSCode to your antivirus software’s whitelist to prevent it from being blocked in the future.
8. Check for Updates
Usually, outdated versions of VSCode can cause issues resulting in premature closure or crashing of software. Check for updates by clicking on the gear icon in the lower-left corner of the screen and selecting “Check for Updates.”
If an update is available, then download and install it. This will fix any bugs that were present in the previous version.
If you encounter issues with updating your Visual Studio Code application, you can check out our other comprehensive guide for resolving such issues here.
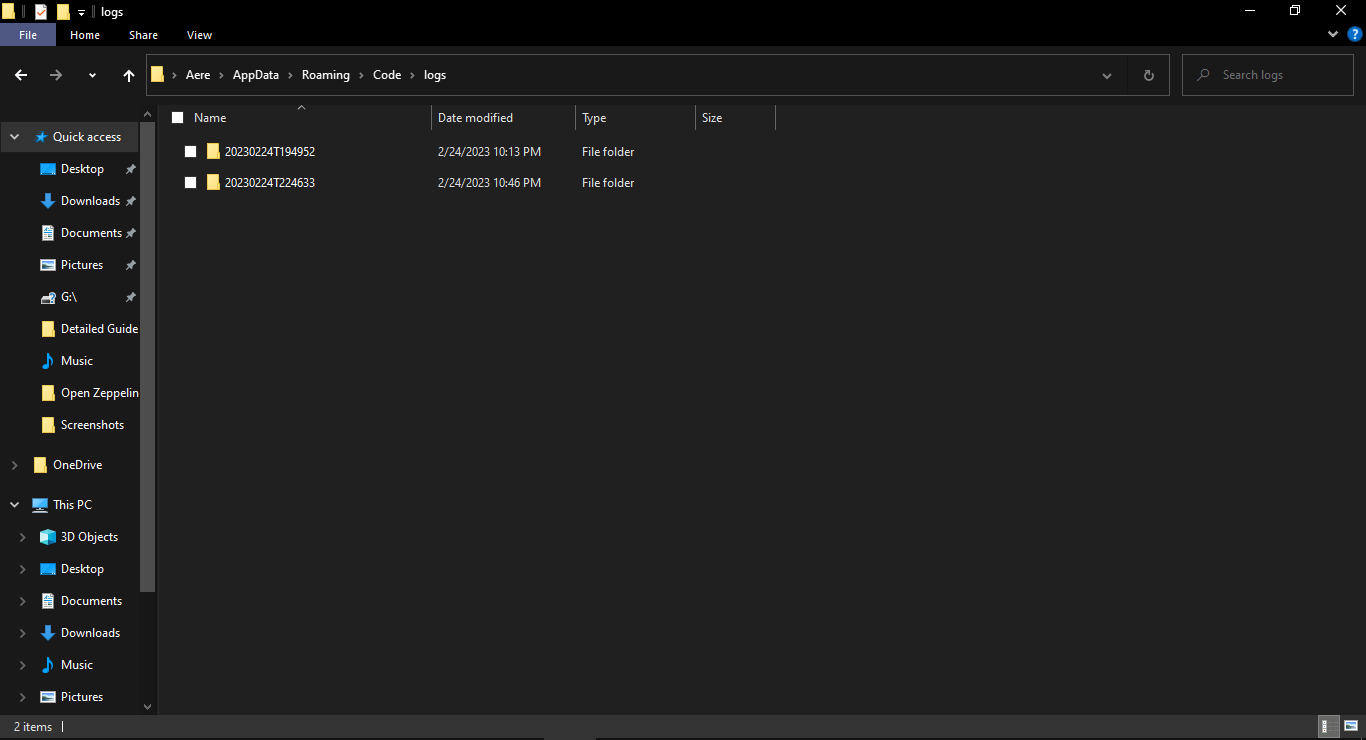
9. Analyze Log Files
VSCode creates log files that may contain useful information about why it is not running. Navigate to %APPDATA%Codelogs (on Windows) or ~/.config/Code/logs (on Linux/macOS) to view the log files.
10. Reinstall VSCode
If you are still facing problems and none of the fixes mentioned before seem to work, then the issue is likely due to a corrupted VSCode file. Therefore you should try reinstalling VSCode on your device.
To fix the issue, you should Uninstall Visual Studio Code and then redownload and reinstall the software to see if the issue persists.
For steps to uninstall and reinstall the Visual Studio Code application on your desktop (Windows, macOS, Linux), you can refer to our complete guide on that here.
Conclusion
All the solutions described above will help you troubleshoot your problems as to why you can’t open Visual Studio Code. We are optimistic that these fixes will eliminate your problem quickly and enable you to run VSCode smoothly.
Lastly, let us know in the comments:
- Did any of the solutions work for you?
- Is there a solution that you would like to add to the list?
- Were you also unable to fix issues with your VSCode?
Feel free to share this article with your fellow developers!