- Печать
Страницы: [1] Вниз
Тема: Vlc ошибка сегментации. (Прочитано 1346 раз)
0 Пользователей и 1 Гость просматривают эту тему.

Николай 12
Здравствуйте!
Ребята может кто поможет.
Вылетает vlc ошибка сегментации.Понятие не имею что делать??
отчет об ошибки
(gdb) backtrace
#0 0xa527d4a3 in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/dri/r600_dri.so
#1 0xa527d283 in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/dri/r600_dri.so
#2 0x9c6f6bd5 in vdp_imp_device_create_x11 ()
from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/vdpau/libvdpau_r600.so.1
#3 0xa020658a in vdp_device_create_x11 ()
from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libvdpau.so.1
#4 0xa0d74253 in vdp_create_x11 () from /usr/lib/vlc/libvlc_vdpau.so.0
#5 0xa0d745bc in vdp_get_x11 () from /usr/lib/vlc/libvlc_vdpau.so.0
#6 0xa0d78d7f in ?? ()
from /usr/lib/vlc/plugins/vdpau/libvdpau_avcodec_plugin.so
#7 0xa0cd0863 in ?? () from /usr/lib/vlc/plugins/codec/libavcodec_plugin.so
#8 0xb743bd96 in ?? () from /usr/lib/libvlccore.so.8
#9 0xb743c2c2 in vlc_module_load () from /usr/lib/libvlccore.so.8
#10 0xa0cd08da in ?? () from /usr/lib/vlc/plugins/codec/libavcodec_plugin.so
#11 0xa0ccbec4 in ?? () from /usr/lib/vlc/plugins/codec/libavcodec_plugin.so
#12 0x9e4f5790 in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libavcodec-ffmpeg.so.56
#13 0x9e1c471a in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libavcodec-ffmpeg.so.56
#14 0x9e1c8ee8 in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libavcodec-ffmpeg.so.56
#15 0x9e17ac40 in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libavcodec-ffmpeg.so.56
#16 0x9e420f7a in ?? () from /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libavcodec-ffmpeg.so.56
#17 0xb769b295 in start_thread (arg=0xa688eb40) at pthread_create.c:333
#18 0xb75c105e in clone () at ../sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/i386/clone.S:114
(gdb) Quit

soarin
Либо обновить версию, либо отключить в настройках аппаратно декодирование видео

Николай 12
Либо обновить версию, либо отключить в настройках аппаратно декодирование видео
Не выходит

mahinist
Попробуй сбросить все настройки —
vlc --reset-config --reset-plugins-cache
и запустить vlc.

Николай 12
vlc —reset-config —reset-plugins-cache
Пробовал, ещё раз попробовал- всё ровно

mahinist
Тогда пробуй снести полностью vlc и удалить —
rm -r ~/.cache/vlс
rm -r ~/.config/vlcЗатем по новой установи .
- Печать
Страницы: [1] Вверх
|
# |
|
|
Темы: 16 Сообщения: 108 Участник с: 16 октября 2011 |
Перестал запускаться vlc. Выдает «Ошибка сегментирования (core dumped)». Делаю как указано в ВИКИ: usr/lib/vlc/vlc-cache-gen -f /usr/lib/vlc/plugins и затем переустанавливаю vlc. Проблема при этом не уходит. Пробовал устанавливать git версию vlc. Ошибка остается. Подскажите, где смотреть? |
|
Perfect_Gentleman |
# |
|
Темы: 55 Сообщения: 1039 Участник с: 29 октября 2012 |
так делал? |
|
alexandr05 |
# |
|
Темы: 16 Сообщения: 108 Участник с: 16 октября 2011 |
Да, так. |
|
Perfect_Gentleman |
# |
|
Темы: 55 Сообщения: 1039 Участник с: 29 октября 2012 |
тогда попробуй
|
|
alexandr05 |
# |
|
Темы: 16 Сообщения: 108 Участник с: 16 октября 2011 |
не помогло. |
|
Perfect_Gentleman |
# |
|
Темы: 55 Сообщения: 1039 Участник с: 29 октября 2012 |
тогда смотри на что именно выдает ошибку перед падением и гугли |
|
alexandr05 |
# |
|
Темы: 16 Сообщения: 108 Участник с: 16 октября 2011 |
Запускаю в командной строке vlc и сразу получаю ошибку, указанную в первом сообщении. |
|
Perfect_Gentleman |
# |
|
Темы: 55 Сообщения: 1039 Участник с: 29 октября 2012 |
чё-то вообще как-то сурово. pacman -S strace strace vlc перед этим удали папку с конфигом vlc, если не поможет, то вышеуказанное пробуй |
|
alexandr05 |
# |
|
Темы: 16 Сообщения: 108 Участник с: 16 октября 2011 |
Посоветовали проверить целостность дисков. Сейчас проверяю. |
|
teplovoz |
# |
|
Темы: 7 Сообщения: 1044 Участник с: 28 мая 2012 |
Так же —
|
I’m trying to build an ‘out of tree’ plugin for VLC.
Computer Specs: Intel x64 Ubuntu 12.04
VLC Specs: VLC media player 2.0.8
To tackle this I
- cloned the VLC git repository
- added my module (just a copy of vmem with some name changes)
- added modules info to the autotools
It worked! I can see my module in VLC when I go to tools->preferences->video->output.
I want to do the same thing ‘Out of Tree’ where I build the module independent of the VLC tree and copy the generated shared object library to a place where VLC can read it and VLC detects it.
I followed the instructions on here:
VLC Out of tree compile
- I copied my ‘in tree’ module to a new directory
- Wrote a
SConstructfile to build it based off of the instructions from above as well as the instructions on http://wiki.videolan.org/Documentation:VLC_Modules_Loading/
Here is a shortened version of the module:
#define DOMAIN "vlc-nysa"
#define _(str) dgettext(DOMAIN, str)
#define N_(str) (str)
#define MODULE_STRING "nysa-video"
vlc_module_begin()
/* VLC Uses these to identify the module */
set_text_domain (DOMAIN)
set_description (N_("Nysa Video Output" ))
set_shortname (N_("Nysa Video" ))
set_category (CAT_VIDEO )
set_subcategory (SUBCAT_VIDEO_VOUT )
set_capability ("vout display", 1 )
/* Options left out for brevity */
/* Add Callbacks */
set_callbacks (Open, Close )
vlc_module_end()
/* implementation here */
Output
So people don’t have to figure out the scons syntax here is the build output:
scons: Reading SConscript files ...
scons: done reading SConscript files.
scons: Building targets ...
gcc -o src/nysa_video.os -c -std=gnu99 -Wall -Wextra -O2 -fPIC -fPIC -D__PLUGIN__ -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -D_REENTRANT -D_THREAD_SAFE -DPIC -I/usr/include/vlc -I/usr/include/vlc/plugins -Iinclude src/nysa_video.c
gcc -o build/libnysa_video_plugin.so -Wl,-no-undefined,-z,defs -shared src/nysa_video.os -L/usr/lib -L/usr/local/lib -lvlc -lvlccore
scons: `install' is up to date.
scons: done building targets.
Results
I do get a file called libnysa_video_plugin.so which I copy into /usr/lib/vlc/plugins/video_output directory
When I run VLC I get a seg fault:
VLC media player 2.0.8 Twoflower (revision 2.0.8a-0-g68cf50b)
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
dmesg | tail prints out:
[141376.468964] vlc[27609]: segfault at 88 ip 00007f06ccd6a4db sp 00007fff029a6310 error 6 in libvlccore.so.5.1.1[7f06ccce4000+db000]
Here is a link to my git repo for this project:
Nysa Video Git Repo
To build you need scons and in the base directory:
- to build:
scons - to install (installs to
/usr/lib/vlc/plugins/video_output):sudo scons install
Вот, ловите концовку…
Код: Выделить всё
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, {35401, 767856491}) = 0
rt_sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, [INT QUIT PIPE TERM], [HUP INT QUIT PIPE TERM CHLD], 8) = 0
sched_get_priority_max(SCHED_OTHER) = 0
sched_get_priority_min(SCHED_OTHER) = 0
sched_get_priority_max(SCHED_OTHER) = 0
mmap2(NULL, 528384, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS|0x20000, -1, 0) = 0xb2634000
mprotect(0xb2634000, 4096, PROT_NONE) = 0
clone(child_stack=0xb26b4494, flags=CLONE_VM|CLONE_FS|CLONE_FILES|CLONE_SIGHAND|CLONE_THREAD|CLONE_SYSVSEM|CLO
NE_SETTLS|CLONE_PARENT_SETTID|CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID, parent_tidptr=0xb26b4bd8, {entry_number:6, base_addr:0xb26b4b70, limit:1048575, seg_32bit:1, contents:0, read_exec_only:0, limit_in_pages:1, seg_not_present:0, useable:1}, child_tidptr=0xb26b4bd8) = 9497
rt_sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, [HUP INT QUIT PIPE TERM CHLD], NULL, 8) = 0
futex(0x99d59d0, FUTEX_WAIT_PRIVATE, 1, NULLQPainter::begin: Paint device returned engine == 0, type: 1
QPainter::begin: Paint device returned engine == 0, type: 1
QPainter::begin: Paint device returned engine == 0, type: 1
<unfinished ...>
+++ killed by SIGSEGV +++А вот попробовал запустить другой видео-файл:
Код: Выделить всё
mmap2(NULL, 528384, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS|0x20000, -1, 0) = 0xb256b000
mprotect(0xb256b000, 4096, PROT_NONE) = 0
clone(child_stack=0xb25eb494, flags=CLONE_VM|CLONE_FS|CLONE_FILES|CLONE_SIGHAND|CLONE_THREAD|CLONE_SYSVSEM|CLO
NE_SETTLS|CLONE_PARENT_SETTID|CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID, parent_tidptr=0xb25ebbd8, {entry_number:6, base_addr:0xb25ebb70, limit:1048575, seg_32bit:1, contents:0, read_exec_only:0, limit_in_pages:1, seg_not_present:0, useable:1}, child_tidptr=0xb25ebbd8) = 9518
rt_sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, [HUP INT QUIT PIPE TERM CHLD], NULL, 8) = 0
futex(0x893b9d0, FUTEX_WAIT_PRIVATE, 1, NULL[0x8c5d078] a52 decoder: A/52 channels:6 samplerate:48000 bitrate:384000
No accelerated IMDCT transform found
QPainter::begin: Paint device returned engine == 0, type: 1
QPainter::begin: Paint device returned engine == 0, type: 1
<unfinished ...>
+++ killed by SIGSEGV +++Linux unixboy-pc 2.6.30-ARCH #1 SMP PREEMPT Mon Jul 20 11:20:32 UTC 2009 i686 Intel® Celeron® CPU 1.70GHz GenuineIntel GNU/Linux
Не всегда программы в Linux запускаются как положено. Иногда, в силу разных причин программа вместо нормальной работы выдает ошибку. Но нам не нужна ошибка, нам нужна программа, вернее, та функция, которую она должна выполнять. Сегодня мы поговорим об одной из самых серьезных и непонятных ошибок. Это ошибка сегментации Ubuntu. Если такая ошибка происходит только один раз, то на нее можно не обращать внимания, но если это регулярное явление нужно что-то делать.
Конечно, случается эта проблема не только в Ubuntu, а во всех Linux дистрибутивах, поэтому наша инструкция будет актуальна для них тоже. Но сосредоточимся мы в основном на Ubuntu. Рассмотрим что такое ошибка сегментирования linux, почему она возникает, а также как с этим бороться и что делать.
Что такое ошибка сегментации?
Ошибка сегментации, Segmentation fault, или Segfault, или SIGSEGV в Ubuntu и других Unix подобных дистрибутивах, означает ошибку работы с памятью. Когда вы получаете эту ошибку, это значит, что срабатывает системный механизм защиты памяти, потому что программа попыталась получить доступ или записать данные в ту часть памяти, к которой у нее нет прав обращаться.
Чтобы понять почему так происходит, давайте рассмотрим как устроена работа с памятью в Linux, я попытаюсь все упростить, но приблизительно так оно и работает.
Допустим, в вашей системе есть 6 Гигабайт оперативной памяти, каждой программе нужно выделить определенную область, куда будет записана она сама, ее данные и новые данные, которые она будет создавать. Чтобы дать возможность каждой из запущенных программ использовать все шесть гигабайт памяти был придуман механизм виртуального адресного пространства. Создается виртуальное пространство очень большого размера, а из него уже выделяется по 6 Гб для каждой программы. Если интересно, это адресное пространство можно найти в файле /proc/kcore, только не вздумайте никуда его копировать.
Выделенное адресное пространство для программы называется сегментом. Как только программа попытается записать или прочитать данные не из своего сегмента, ядро отправит ей сигнал SIGSEGV и программа завершится с нашей ошибкой. Более того, каждый сегмент поделен на секции, в некоторые из них запись невозможна, другие нельзя выполнять, если программа и тут попытается сделать что-то запрещенное, мы опять получим ошибку сегментации Ubuntu.
Почему возникает ошибка сегментации?
И зачем бы это порядочной программе лезть, куда ей не положено? Да в принципе, незачем. Это происходит из-за ошибки при написании программ или несовместимых версиях библиотек и ПО. Часто эта ошибка встречается в программах на Си или C++. В этом языке программисты могут вручную работать с памятью, а язык со своей стороны не контролирует, чтобы они это делали правильно, поэтому одно неверное обращение к памяти может обрушить программу.
Почему может возникать эта ошибка при несовместимости библиотек? По той же причине — неверному обращению к памяти. Представим, что у нас есть библиотека linux (набор функций), в которой есть функция, которая выполняет определенную задачу. Для работы нашей функции нужны данные, поэтому при вызове ей нужно передать строку. Наша старая версия библиотеки ожидает, что длина строки будет до 256 символов. Но программа была обновлена формат записи поменялся, и теперь она передает библиотеке строку размером 512 символов. Если обновить программу, но оставить старую версию библиотеки, то при передаче такой строки 256 символов запишутся нормально в подготовленное место, а вот вторые 256 перезапишут данные программы, и возможно, попытаются выйти за пределы сегмента, тогда и будет ошибка сегментирования linux.
Что делать если возникла ошибка сегментирования?
Если вы думаете, что это ошибка в программе, то вам остается только отправить отчет об ошибке разработчикам. Но вы все-таки еще можете попытаться что-то сделать.
Например, если падает с ошибкой сегментации неизвестная программа, то мы можем решить что это вина разработчиков, но если с такой ошибкой падает chrome или firefox при запуске возникает вопрос, может мы делаем что-то не так? Ведь это уже хорошо протестированные программы.
Первое, что нужно сделать — это обновить систему до самой последней версии, возможно, был баг и его уже исправили, а может у вас установлены старые версии библиотек и обновление решит проблему. В Ubuntu это делается так:
sudo apt update
sudo apt full-upgrade
Если это не помогло, нужно обнулить настройки программы до значений по умолчанию, возможно, удалить кэш. Настройки программ в Linux обычно содержатся в домашней папке, скрытых подкаталогах с именем программы. Также, настройки и кэш могут содержаться в каталогах ~/.config и ~/.cache. Просто удалите папки программы и попробуйте снова ее запустить. Если и это не помогло, вы можете попробовать полностью удалить программу, а потом снова ее установить, возможно, какие-нибудь зависимости были повреждены:
sudo apt remove пакет_программы
sudo apt autoremove
sudo apt install пакет_программы
Если есть возможность, попробуйте установить программу из другого источника, например, не из PPA, а более старую версию, из официальных репозиториев.
Когда вы все это выполнили, скорее всего, проблема не в вашем дистрибутиве, а в самой программе. Нужно отправлять отчет разработчикам. В Ubuntu это можно сделать с помощью программы apport-bug. Обычно Ubuntu предлагает это сделать сразу, после того как программа завершилась с ошибкой сегментирования. Если же ошибка сегментирования Ubuntu встречается не в системной программе, то вам придется самим искать разработчиков и вручную описывать что произошло.
Чтобы помочь разработчикам решить проблему, недостаточно отправить им только сообщение что вы поймали Segmentation Fault, нужно подробно описать проблему, действия, которые вы выполняли перед этим, так чтобы разработчик мог их воспроизвести. Также, желательно прикрепить к отчету последние функции, которые вызывала программа (стек вызовов функций), это может очень сильно помочь разработчикам.
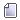
Рассмотрим, как его получить. Это не так уж сложно. Сначала запустите вашу программу, затем узнайте ее PID с помощью команды:
pgrep программа
Дальше запускаем отладчик gdb:
sudo gdb -q
Подключаемся к программе:
(gdb) attach ваш_pid
После подключения программа станет на паузу, продолжаем ее выполнение командой:
(gdb) continue
Затем вам осталось только вызвать ошибку:
И набрать команду, которая выведет стек последних вызовов:
(gdb) backtrace
Вывод этой команды и нужно отправлять разработчикам. Чтобы отключиться от программы и выйти наберите:
(gdb) detach
(gdb) quit
Дальше остается отправить отчет и ждать исправления ошибки. Если вы не уверены, что ошибка в программе, можете поспрашивать на форумах. Когда у вас есть стек вызовов, уже можно попытаться, если не понять в чем проблема, то попытаться узнать, не сталкивался ли с подобной проблемой еще кто-то.
Выводы
Теперь у вас есть приблизительный план действий, что нужно делать, когда появляется ошибка сегментирования сделан дамп памяти ubuntu. Если вы знаете другие способы решить эту проблему, напишите в комментариях!
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Содержание:
- Handling
- Overview
- Causes
- Что такое ошибка сегментации?
- Additional Information
- Examples
- Writing to read-only memory
- Null pointer dereference
- Stack overflow
Handling
The default action for a segmentation fault or bus error is abnormal termination of the process that triggered it. A core file may be generated to aid debugging, and other platform-dependent actions may also be performed. For example, Linux systems using the grsecurity patch may log SIGSEGV signals in order to monitor for possible intrusion attempts using buffer overflows.
On some systems, like Linux and Windows, it is possible for the program itself to handle a segmentation fault.. Depending on the architecture and operating system, the running program can not only handle the event but may extract some information about its state like getting a stack trace, processor register values, the line of the source code when it was triggered, memory address that was invalidly accessed and whether the action was a read or a write.
Although a segmentation fault generally means that the program has a bug that needs fixing, it is also possible to intentionally cause such failure for the purposes of testing, debugging and also to emulate platforms were direct access to memory is needed. On the latter case, the system must be able to allow the program to run even after the fault occurs. In this case, when the system allows, it is possible to handle the event and increment the processor program counter to «jump» over the failing instruction to continue the execution.
Overview
Example of human generated signal
A null pointer dereference on Windows 8
A segmentation fault occurs when a program attempts to access a memory location that it is not allowed to access, or attempts to access a memory location in a way that is not allowed (for example, attempting to write to a read-only location, or to overwrite part of the operating system).
The term «segmentation» has various uses in computing; in the context of «segmentation fault», a term used since the 1950s, it refers to the address space of a program.[citation needed] With memory protection, only the program’s own address space is readable, and of this, only the stack and the read/write portion of the data segment of a program are writable, while read-only data and the code segment are not writable. Thus attempting to read outside of the program’s address space, or writing to a read-only segment of the address space, results in a segmentation fault, hence the name.
On systems using hardware memory segmentation to provide virtual memory, a segmentation fault occurs when the hardware detects an attempt to refer to a non-existent segment, or to refer to a location outside the bounds of a segment, or to refer to a location in a fashion not allowed by the permissions granted for that segment. On systems using only paging, an invalid page fault generally leads to a segmentation fault, and segmentation faults and page faults are both faults raised by the virtual memory management system. Segmentation faults can also occur independently of page faults: illegal access to a valid page is a segmentation fault, but not an invalid page fault, and segmentation faults can occur in the middle of a page (hence no page fault), for example in a buffer overflow that stays within a page but illegally overwrites memory.
At the hardware level, the fault is initially raised by the memory management unit (MMU) on illegal access (if the referenced memory exists), as part of its memory protection feature, or an invalid page fault (if the referenced memory does not exist). If the problem is not an invalid logical address but instead an invalid physical address, a bus error is raised instead, though these are not always distinguished.
At the operating system level, this fault is caught and a signal is passed on to the offending process, activating the process’s handler for that signal. Different operating systems have different signal names to indicate that a segmentation fault has occurred. On Unix-like operating systems, a signal called SIGSEGV (abbreviated from segmentation violation) is sent to the offending process. On Microsoft Windows, the offending process receives a STATUS_ACCESS_VIOLATION exception.
Causes
The conditions under which segmentation violations occur and how they manifest themselves are specific to hardware and the operating system: different hardware raises different faults for given conditions, and different operating systems convert these to different signals that are passed on to processes. The proximate cause is a memory access violation, while the underlying cause is generally a software bug of some sort. Determining the root cause – debugging the bug – can be simple in some cases, where the program will consistently cause a segmentation fault (e.g., dereferencing a null pointer), while in other cases the bug can be difficult to reproduce and depend on memory allocation on each run (e.g., dereferencing a dangling pointer).
The following are some typical causes of a segmentation fault:
- Attempting to access a nonexistent memory address (outside process’s address space)
- Attempting to access memory the program does not have rights to (such as kernel structures in process context)
- Attempting to write read-only memory (such as code segment)
These in turn are often caused by programming errors that result in invalid memory access:
- Dereferencing a null pointer, which usually points to an address that’s not part of the process’s address space
- Dereferencing or assigning to an uninitialized pointer (wild pointer, which points to a random memory address)
- Dereferencing or assigning to a freed pointer (dangling pointer, which points to memory that has been freed/deallocated/deleted)
- A buffer overflow
- A stack overflow
- Attempting to execute a program that does not compile correctly. (Some compilers will output an executable file despite the presence of compile-time errors.)
In C code, segmentation faults most often occur because of errors in pointer use, particularly in C dynamic memory allocation. Dereferencing a null pointer will always result in a segmentation fault, but wild pointers and dangling pointers point to memory that may or may not exist, and may or may not be readable or writable, and thus can result in transient bugs. For example:
char *p1 = NULL; // Null pointer
char *p2; // Wild pointer: not initialized at all.
char *p3 = malloc(10 * sizeof(char)); // Initialized pointer to allocated memory
// (assuming malloc did not fail)
free(p3); // p3 is now a dangling pointer, as memory has been freed
Now, dereferencing any of these variables could cause a segmentation fault: dereferencing the null pointer generally will cause a segfault, while reading from the wild pointer may instead result in random data but no segfault, and reading from the dangling pointer may result in valid data for a while, and then random data as it is overwritten.
Что такое ошибка сегментации?
Ошибка сегментации, Segmentation fault, или Segfault, или SIGSEGV в Ubuntu и других Unix подобных дистрибутивах, означает ошибку работы с памятью. Когда вы получаете эту ошибку, это значит, что срабатывает системный механизм защиты памяти, потому что программа попыталась получить доступ или записать данные в ту часть памяти, к которой у нее нет прав обращаться.
Чтобы понять почему так происходит, давайте рассмотрим как устроена работа с памятью в Linux, я попытаюсь все упростить, но приблизительно так оно и работает.
Допустим, в вашей системе есть 6 Гигабайт оперативной памяти, каждой программе нужно выделить определенную область, куда будет записана она сама, ее данные и новые данные, которые она будет создавать. Чтобы дать возможность каждой из запущенных программ использовать все шесть гигабайт памяти был придуман механизм виртуального адресного пространства. Создается виртуальное пространство очень большого размера, а из него уже выделяется по 6 Гб для каждой программы. Если интересно, это адресное пространство можно найти в файле /proc/kcore, только не вздумайте никуда его копировать.
Выделенное адресное пространство для программы называется сегментом. Как только программа попытается записать или прочитать данные не из своего сегмента, ядро отправит ей сигнал SIGSEGV и программа завершится с нашей ошибкой. Более того, каждый сегмент поделен на секции, в некоторые из них запись невозможна, другие нельзя выполнять, если программа и тут попытается сделать что-то запрещенное, мы опять получим ошибку сегментации Ubuntu.
Additional Information
BackgroundModern general purpose hardware includes a «memory management unit» (or MMU). This hardware feature is used by operating systems like Linux to implement memory protection, i.e. to prevent different processes from accessing or modifying each other’s memory (except in a strictly controlled fashion through specific APIs). This simplifies troubleshooting and increases resilience as processes are carefully contained and separated from one another.A «segmentation violation» signal is sent to a process of which the memory management unit detected an attempt to use a memory address that does not belong to it.Common cause: programming errorIf a process tries to access memory through a pointer which has not been properly initialised, or which is pointing to memory that has previously been deallocated, this will likely result in a segfault. In this case, the segfault is occurring with a specific process or binary, possibly under a specific set of circumstances.To deal with this type of segfault, begin by applying all relevant service packs and maintenance updates. Next, if the problem is still reproducible with current code, try to capture an application core dump for analysis. Details for this are found in TID 3054866 — How to obtain application core dumps.If the problematic binary is shipped by Novell as part of the product, open a service request with Novell Technical services, supplying
- a description of the circumstances under which the core dump was generated,
- a supportconfig -v report for the affected system (supportconfig home page), and
- the core dump file itself, if smaller than 50 MB. If it is larger, wait for the service request to be assigned to an engineer and then work with the engineer to transfer it.
If the problematic binary was supplied by a third party, contact that party’s support department for assistance.Common cause: mismatched binary and librariesSegfaults can occur with processes that combine binaries and shared libraries which aren’t (fully) compatible. This can occur, for instance, when a library is updated in a way that changes the library’s ABI (application binary interface), but the library’s internal version number is not updated to reflect this. A binary that was built against an older version of the library may start to segfault when loaded against the newer version.This case may be difficult to recognise, and there is no step list for dealing with it. When this case is suspected, some things to consider are:
- Checking the system for file corruption (e.g. using the rpm-verify.txt file in a supportconfig -v report)
- Checking the system’s settings that relate to shared libraries, like the /etc/ld.so.conf and /etc/ld.so.conf.d/* configuration files and the LD_LIBRARY_PATH and LD_PRELOAD environment variables.
- Using the objdump tool to check the binary for a built-in library search path override (RPATH).
Common cause: hardware or hardware configuration issueWhen segfaults are occurring frequently, or with different processes or without a clear pattern to them, this can indicate that a system’s hardware (memory subsystem) is problematic, or that low-level system configuration settings are inappropriate. Please refer to TID 3301593 — Linux system hangs or is unstable for more information on how to handle this situation.
+ Upgrading to Open Enterprise Server 2 SP1 Linux
+ Open Enterprise Server 2 SP1 Migration Strategies
Examples
Segmentation fault on an EMV keypad
Writing to read-only memory
Writing to read-only memory raises a segmentation fault. At the level of code errors, this occurs when the program writes to part of its own code segment or the read-only portion of the data segment, as these are loaded by the OS into read-only memory.
Here is an example of ANSI C code that will generally cause a segmentation fault on platforms with memory protection. It attempts to modify a string literal, which is undefined behavior according to the ANSI C standard. Most compilers will not catch this at compile time, and instead compile this to executable code that will crash:
int main(void)
{
char *s = "hello world";
*s = 'H';
}
When the program containing this code is compiled, the string «hello world» is placed in the rodata section of the program executable file: the read-only section of the data segment. When loaded, the operating system places it with other strings and constant data in a read-only segment of memory. When executed, a variable, s, is set to point to the string’s location, and an attempt is made to write an H character through the variable into the memory, causing a segmentation fault. Compiling such a program with a compiler that does not check for the assignment of read-only locations at compile time, and running it on a Unix-like operating system produces the following runtime error:
$ gcc segfault.c -g -o segfault $ ./segfault Segmentation fault
Backtrace of the core file from GDB:
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault. 0x1c0005c2 in main () at segfault.c6 6 *s = 'H';
This code can be corrected by using an array instead of a character pointer, as this allocates memory on stack and initializes it to the value of the string literal:
char s[] = "hello world"; s = 'H'; // equivalently, *s = 'H';
Even though string literals should not be modified (this has undefined behavior in the C standard), in C they are of type, so there is no implicit conversion in the original code (which points a at that array), while in C++ they are of type, and thus there is an implicit conversion, so compilers will generally catch this particular error.
Null pointer dereference
In C and C-like languages, null pointers are used to mean «pointer to no object» and as an error indicator, and dereferencing a null pointer (a read or write through a null pointer) is a very common program error. The C standard does not say that the null pointer is the same as the pointer to memory address 0, though that may be the case in practice. Most operating systems map the null pointer’s address such that accessing it causes a segmentation fault. This behavior is not guaranteed by the C standard. Dereferencing a null pointer is undefined behavior in C, and a conforming implementation is allowed to assume that any pointer that is dereferenced is not null.
int *ptr = NULL;
printf("%d", *ptr);
This sample code creates a null pointer, and then tries to access its value (read the value). Doing so causes a segmentation fault at runtime on many operating systems.
Dereferencing a null pointer and then assigning to it (writing a value to a non-existent target) also usually causes a segmentation fault:
int *ptr = NULL; *ptr = 1;
The following code includes a null pointer dereference, but when compiled will often not result in a segmentation fault, as the value is unused and thus the dereference will often be optimized away by dead code elimination:
int *ptr = NULL; *ptr;
Stack overflow
Another example is recursion without a base case:
int main(void)
{
main();
return ;
}
which causes the stack to overflow which results in a segmentation fault. Infinite recursion may not necessarily result in a stack overflow depending on the language, optimizations performed by the compiler and the exact structure of a code. In this case, the behavior of unreachable code (the return statement) is undefined, so the compiler can eliminate it and use a tail call optimization that might result in no stack usage. Other optimizations could include translating the recursion into iteration, which given the structure of the example function would result in the program running forever, while probably not overflowing its stack.