Hi. I’m still working on this since I haven’t touched it in a while. I still have the critical alerts since I wanted to get to the bottom of this before acknowledging them. Traffic seems to be working fine, despite the alerts persisting.
There are 2 physical switches going to the vDS: HP ProCurve —> Flex-10 pair switch —> vDS
The ProCurve pair is trunking 3 Vlans to the Flex-10s:
2 ports in a trunk (x2, 4 total, 2 per switch)
Vlan 100 Untagged
Vlan 200 Tagged
Lan 300 Tagged
The Flex-10s configuration shows the same:
6 nics per host x 5 hosts (30 uplinks to vDS)
Vlan 100 (Native)
Vlan 200
Vlan 300
vDS:
dvUplink Group 1 (6 links x 5 hosts = 30 total)
Port Group A (Vlan ID = 0)
Port Group B (Vlan ID = 0)
Port Group C (Vlan ID = 0)
These links from the Flex-10s are all trunked to a single dvUplink group on the vDS, and then there are a few vDistributed Port Groups and each of those have no Vlan ID assigned, as mentioned (so, Vlan ID = 0)
For some reason, all 5 of the hosts appear to be configured the same but only one of them now shows no critical alerts. I don’t recall acknowledging the alerts.
I’m thinking of testing out just assigning the matching Vlan IDs to the Port Groups as recommended, but I’d like more info before I break something.
I read at the link below that if tagging is done on the physical switch, the Port Groups’ Vlan ID on the Virtual Switch should be zero, but I’m not sure if this applies here or if they mean in a situation where the vDS is connecting to an ACCESS port in a Vlan on the physical switch, or something else. Any clarification or additional help would be great, based on the detail I’ve added. Thanks.
VMware Knowledge Base
After
downloading, staging and applying patches to the first ESXi host in a
vSphere host cluster, the host, after exiting Maintenance Mode, showed 2
triggered alarms:
vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN trunked status
vSphere Distributed Switch MTU supported status
Upon
further review of vDS settings and details, selecting vDS —>
Monitor Tab —> Heath Tab, there was a warning of 10 issues (started
at 12, but apparently the out of sync issue was resolved): ‘Unsupported
VLAN’ and ‘MTU Mismatch’ for each of the 5 hosts. How do I resolve
this? We are currently running a VDS of 5.5 although the vCenter (VCSA)
and ESXi hosts are at 6.5.0. This is in a production environment and I
would need to correct this as soon as possible so I may continue with
the patching to address a critical vulnerability.
Hi. I’m still working on this since I haven’t touched it in a while. I still have the critical alerts since I wanted to get to the bottom of this before acknowledging them. Traffic seems to be working fine, despite the alerts persisting.
There are 2 physical switches going to the vDS: HP ProCurve —> Flex-10 pair switch —> vDS
The ProCurve pair is trunking 3 Vlans to the Flex-10s:
2 ports in a trunk (x2, 4 total, 2 per switch)
Vlan 100 Untagged
Vlan 200 Tagged
Lan 300 Tagged
The Flex-10s configuration shows the same:
6 nics per host x 5 hosts (30 uplinks to vDS)
Vlan 100 (Native)
Vlan 200
Vlan 300
vDS:
dvUplink Group 1 (6 links x 5 hosts = 30 total)
Port Group A (Vlan ID = 0)
Port Group B (Vlan ID = 0)
Port Group C (Vlan ID = 0)
These links from the Flex-10s are all trunked to a single dvUplink group on the vDS, and then there are a few vDistributed Port Groups and each of those have no Vlan ID assigned, as mentioned (so, Vlan ID = 0)
For some reason, all 5 of the hosts appear to be configured the same but only one of them now shows no critical alerts. I don’t recall acknowledging the alerts.
I’m thinking of testing out just assigning the matching Vlan IDs to the Port Groups as recommended, but I’d like more info before I break something.
I read at the link below that if tagging is done on the physical switch, the Port Groups’ Vlan ID on the Virtual Switch should be zero, but I’m not sure if this applies here or if they mean in a situation where the vDS is connecting to an ACCESS port in a Vlan on the physical switch, or something else. Any clarification or additional help would be great, based on the detail I’ve added. Thanks.
VMware Knowledge Base
I was doing some testing of the new vSphere 5.1 features and came across something odd with the new Distributed Switch Health Check feature with Cisco UCS.
In my lab I have 4 ESXi 5.1 hosts running on older B200 M1s with VIC M81KR adaptors.
On my ESXi service profiles I have 8 vNICs; 2 for management, 2 for vMotion 2 for IP storage and 2 for VM networking.
Each pair of vNICs has 1 in Fabric A and 1 in Fabric B
In VMware there are 3 standard vSwitches and 1 Distributed vSwitch for VM networking VLANs.
On the Distributed switch I enabled the new Health Check feature via the new vSphere Web Client.
About a minute later the following Alerts were triggered.
“vSphere Distributed Switch MTU supported status”
“vSphere Distributed Switch vlan trunked status”
The first thing I did was double check my vNICs to make sure they had the same VLANs trunked and to make sure my MTU settings were the default of 1500.
This got thinking that it must be something to do with the way UCS Fabric Interconnects handle vNICs or something to do with how End Host mode works. I then remembered the new option on the Network Control policy that controls the VLANs that vNIC MAC addresses get registered on.
I was already using a custom Network Control policy to enable CDP on ESXi vNICs.
By default the Network Control policy is set to only register vNIC MACs on the native VLAN. This is set this way to reduce the size of the MAC address tables on the Fabric Interconnects.
I changed this policy to register on all host VLANs and about a minute later the Health Check alerts cleared.
The max MAC addresses per Fabric Interconnect in UCS firmware 2.0/2.1 – http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/sw/configuration_limits/2.0/b_UCS_Configuration_Limits_2_0.html
6100s = 13800
6200s = 20000
Those are fairly high limits so I don’t think most folks would run into that limit if the Network Control policy is changed to all host vlans.
This posting is ~5 years years old. You should keep this in mind. IT is a short living business. This information might be outdated.
During the replacement of some VMware ESXi hosts at a customer, I discovered a recurrent failure of the vSphere Distributed Switch health checks. A VLAN and MTU mismatch was reported. On the physical side, the ESXi hosts were connected to two HPE 5820 switches, that were configured as an IRF stack. Inside the VMware bubble, the hosts were sharing a vSphere Distributed Switch.
The switch ports of the old ESXi hosts were configured as Hybrid ports. The switch ports of the new hosts were configured as Trunk ports, to streamline the switch and port configuration.
Some words about port types
Comware knows three different port types:
- Access
- Hybrid
- Trunk
If you were familiar with Cisco, you will know Access and Trunk ports. If you were familiar with HPE ProCurve or Alcatel-Lucent Enterprise, these two port types refer to untagged and tagged ports.
So what is a Hybrid port? A Hybrid port can belong to multiple VLANs where they can be untagged and tagged. Yes, multiple untagged VLANs on a port are possible, but the switch will need additional information to bridge the traffic into correct untagged VLANs. This additional information can be MAC addresses, IP addresses, LLDP-MED etc. Typically, hybrid ports are used for in VoIP deployments.
The benefit of a Hybrid port is, that I can put the native VLAN of a specific port, which is often referred as Port VLAN identifier (PVID), as a tagged VLAN on that port. This configuration allows, that all dvPortGroups have a VLAN tag assigned, even if the VLAN tag represents the native VLAN of a switch port.
Failing health checks
A failed health check rises a vCenter alarm. In my case, a VLAN and MTU alarm was reported. In both cases, VLAN 1 was causing the error. According to VMware, the three main causes for failed health checks are:
- Mismatched VLAN trunks between a vSphere distributed switch and physical switch
- Mismatched MTU settings between physical network adapters, distributed switches, and physical switch ports
- Mismatched virtual switch teaming policies for the physical switch port-channel settings.
Let’s take a look at the port configuration on the Comware switch:
# interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/9 port link-mode bridge description "ESX-05 NIC1" port link-type trunk port trunk permit vlan all stp edged-port enable #
As you can see, this is a normal trunk port. All VLANs will be passed to the host. This is an except from the display interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/9 output:
PVID: 1 Mdi type: auto Port link-type: trunk VLAN passing : 1(default vlan), 2-3, 5-7, 100-109 VLAN permitted: 1(default vlan), 2-4094 Trunk port encapsulation: IEEE 802.1q
The native VLAN is 1, this is the default configuration. Traffic, that is received and sent from a trunk port, is always tagged with a VLAN id of the originating VLAN – except traffic from the default (native) VLAN! This traffic is sent without a VLAN tag, and if frames were received with a VLAN tag, this frames will be dropped!
If you have a dvPortGroup for the default (native) VLAN, and this dvPortGroup is sending tagged frames, the frames will be dropped if you use a “standard” trunk port. And this is why the health check fails!
Ways to resolve this issue
In my case, the dvPortGroup was configured for VLAN 1, which is the default (native) VLAN on the switch ports.
There are two ways to solve this issue:
- Remove the VLAN tag from the dvPortGroup configuration
- Change the PVID for the trunk port
To change the PVID for a trunk port, you have to enter the following command in the interface context:
[ToR-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/9] port trunk pvid vlan 999
You have to change the PVID on all ESXi facing switch ports. You can use a non-existing VLAN ID for this.
vSphere Distributed Switch health check will switch to green for VLAN and MTU immediately.
Please note, that this is not the solution for all VLAN-related problems. You should make sure that you are not getting any side effects.
- Author
- Recent Posts
vcloudnine.de is the personal blog of Patrick Terlisten. Patrick has a strong focus on virtualization & cloud solutions, but also storage, networking, and IT infrastructure in general. He is a fan of Lean Management and agile methods, and practices continuous improvement whereever it is possible.
Feel free to follow him on Twitter and/ or leave a comment.
Сегодня создадим Distributed Switch на vCenter 6.7.
Идея распределённого коммутатора заключается в следующем — создать один коммутатор, который будет обслуживать сразу несколько гипервизоров. Вы получаете один единственный логический коммутатор, существующий сразу на всех серверах ESX(i). Распределённый — потому что он рулится из одной точки — vCenter, а распределяется на все хосты. Если vCenter выйдет из строя, то коммутатор продолжит работу. Мы просто потеряем возможность настраивать коммутатор.
Распределённый коммутатор имеет несколько больший функционал в отличие от обычного. Ключевые моменты:
- Private VLAN.
- Bi-directional Traffic Shaping.
- Network VMotion.
Ссылки
Установка vCenter 6.7
vCenter 6.7 — создаём Datacenter
vCenter 6.7 — создаём Cluster
Добавление хоста ESXi 6.0 в vCenter 6.7 c LACP через UI
vCenter 6.7 — добавляем LAG (Link Aggregation Group) в Distributed Switch
Создаём Distributed Switch
Будем считать, что вы уже знаете зачем собираетесь устанавливать Distributed Switch. Ставим.
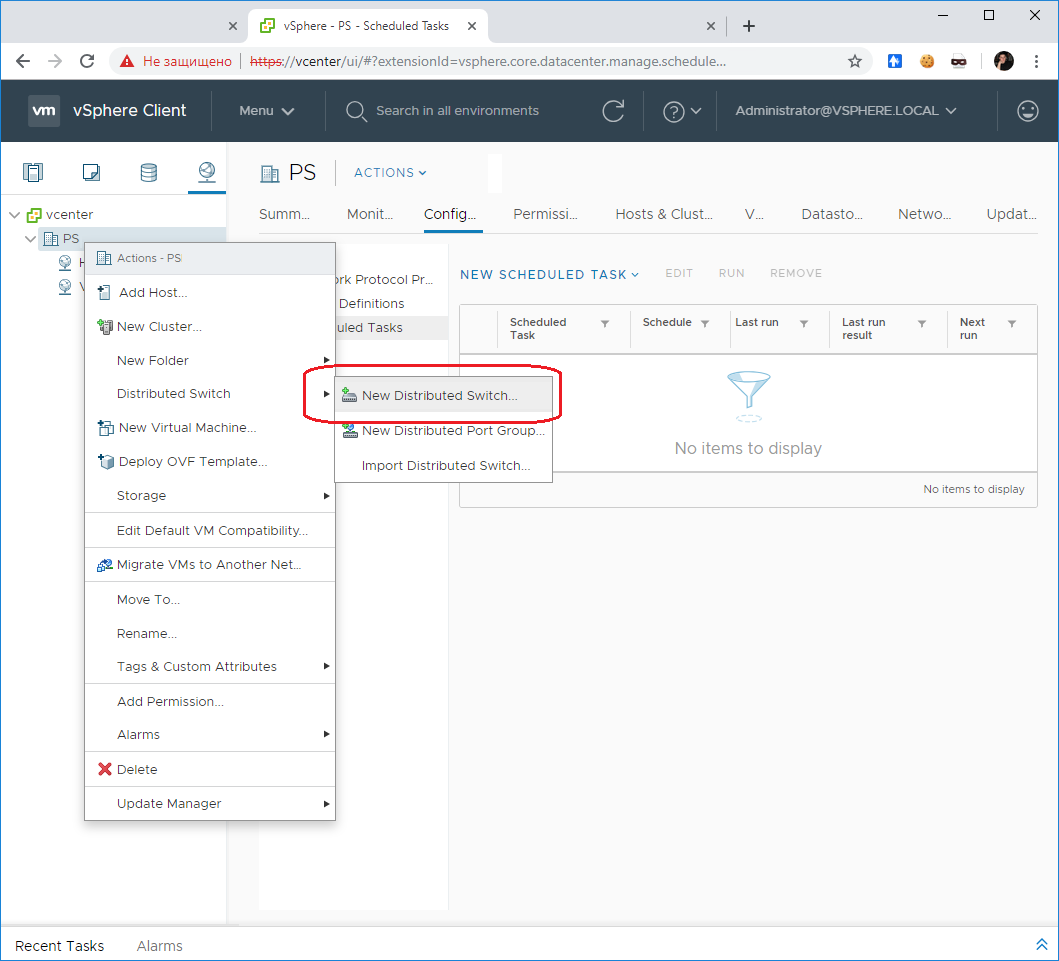
Заходим в vCenter, переходим в раздел Networking. Нажимаем правой кнопкой на выбранный кластер,выбираем Distributed Switch > New Distributed Switch.
Открывается мастер создания распределённого коммутатора. Мы на вкладке Name and location.
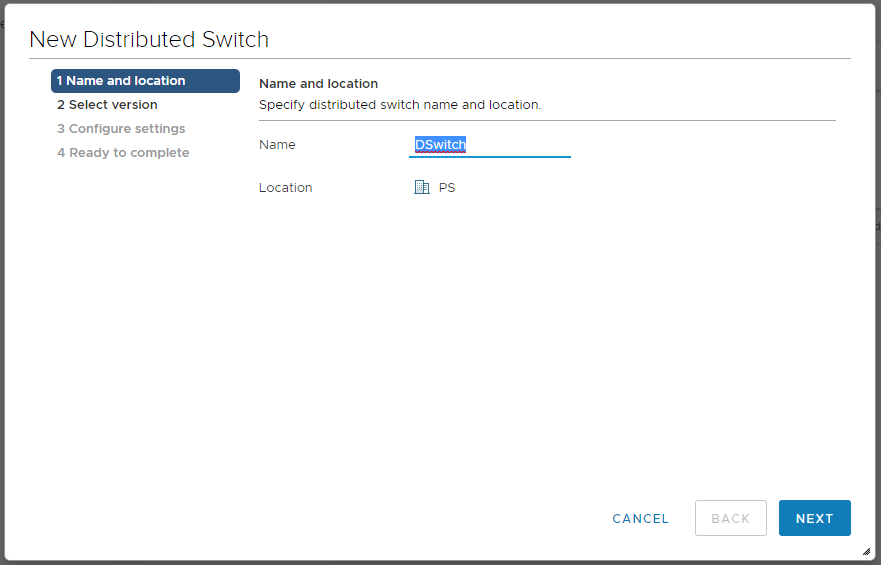
Указываем название, NEXT. Мы на вкладке Select version.
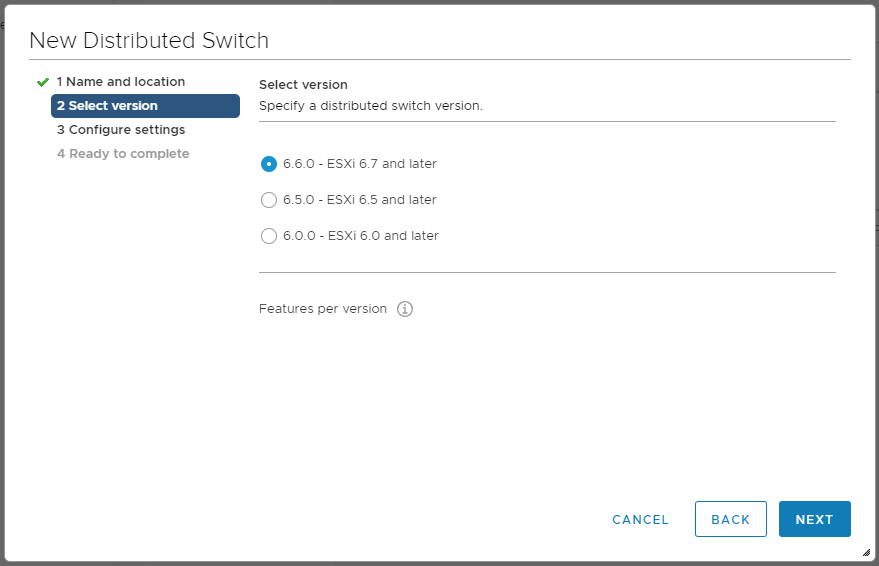
Выбираем версию коммутатора. Коммутатор 6.0 не поддерживает хосты версии 6.5. Так что я выбираю последнюю версию. NEXT. Мы на вкладке Configure settings.
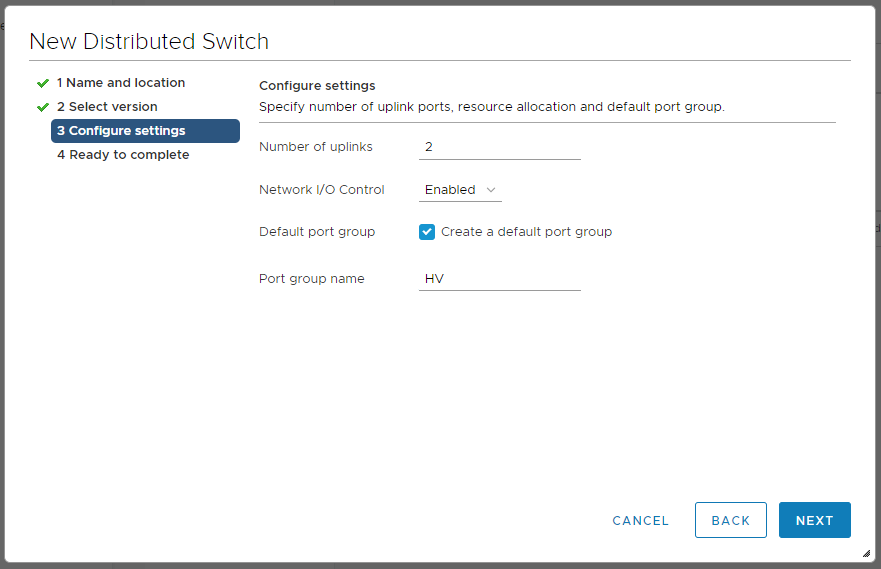
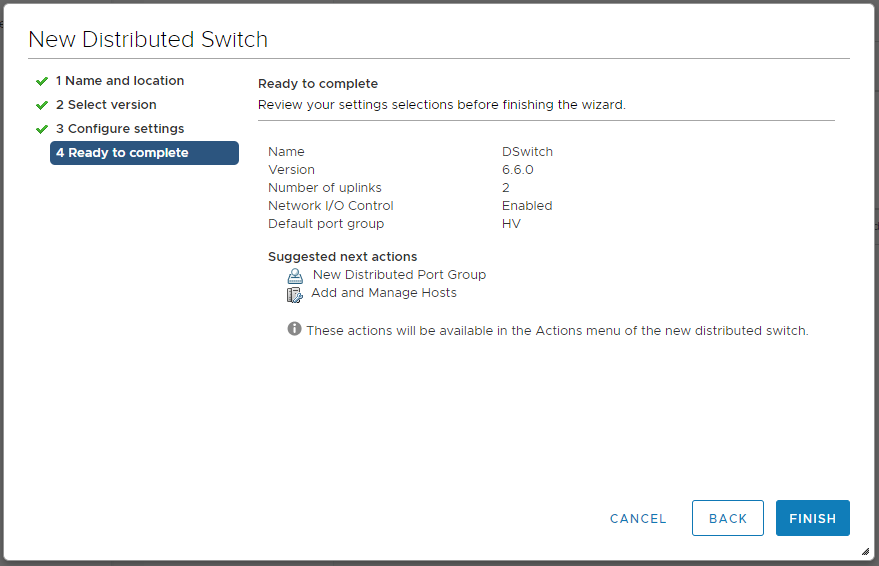
Выбираем количество аплинков. Можно включить Network I/O Control. Можно выбрать галку для создания дефолтной port group и указать её название. Я буду использовать эту группу для управления гипервизорами и vCenter, называю HV. NEXT. Мы на вкладке Ready to complete.
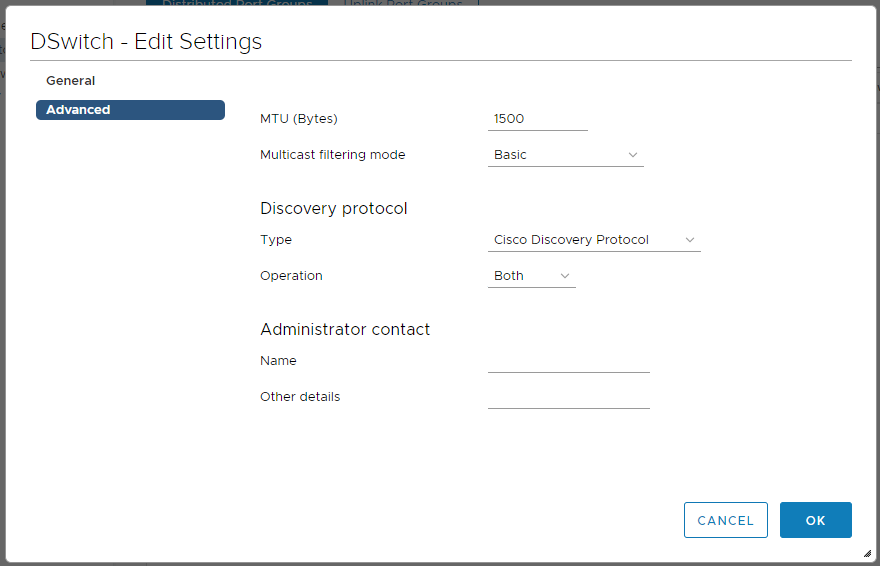
Проверяем настройки и нажимаем FINISH. Distributed Switch создан. Давайте его настроим. Нажимаем правой кнопкой на коммутатор — Settings > Edit Settings. Переключаемся в раздел Advanced. Находим блок Discovery protocol. Type — ставим в Cisco Discovery Protocol. Operations — Both.
OK.
Настройка LACP
Отдельная инструкция по настройке LACP на Distributed Switch:
vCenter 6.7 — добавляем LAG (Link Aggregation Group) в Distributed Switch
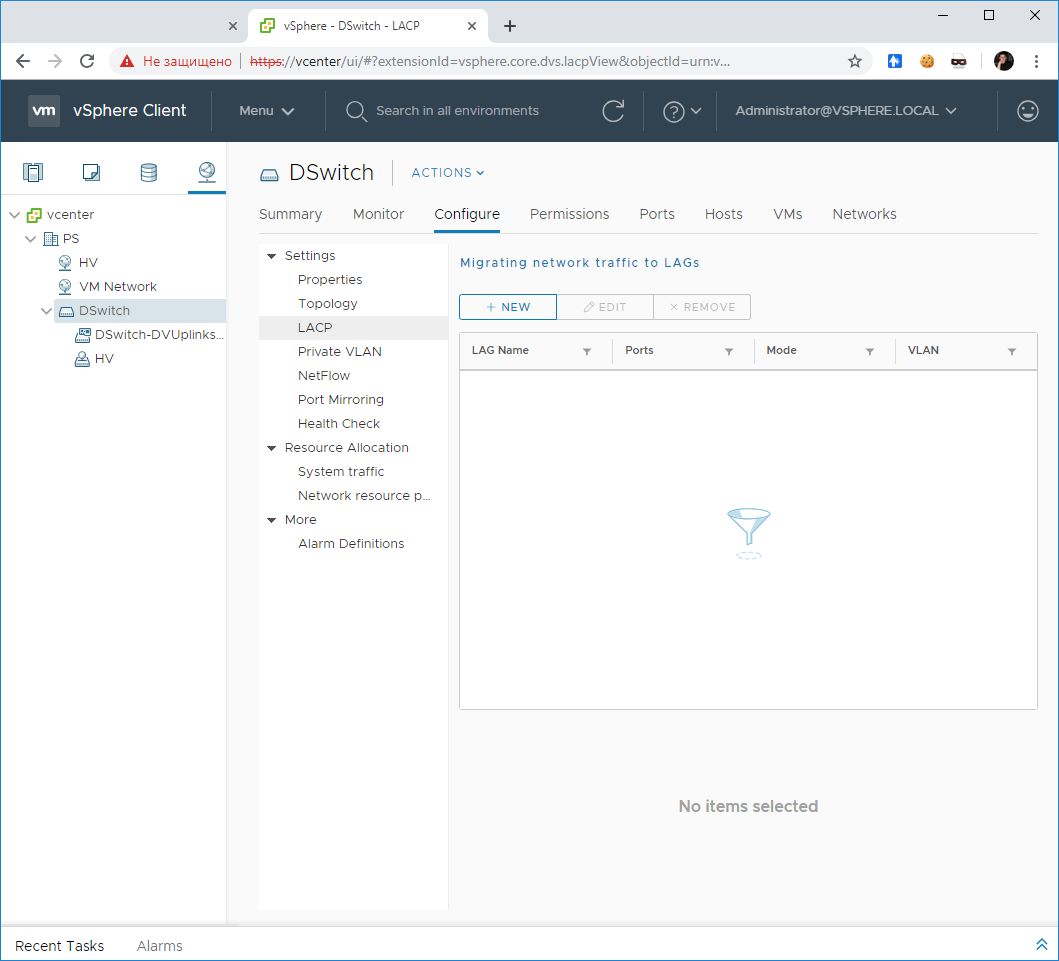
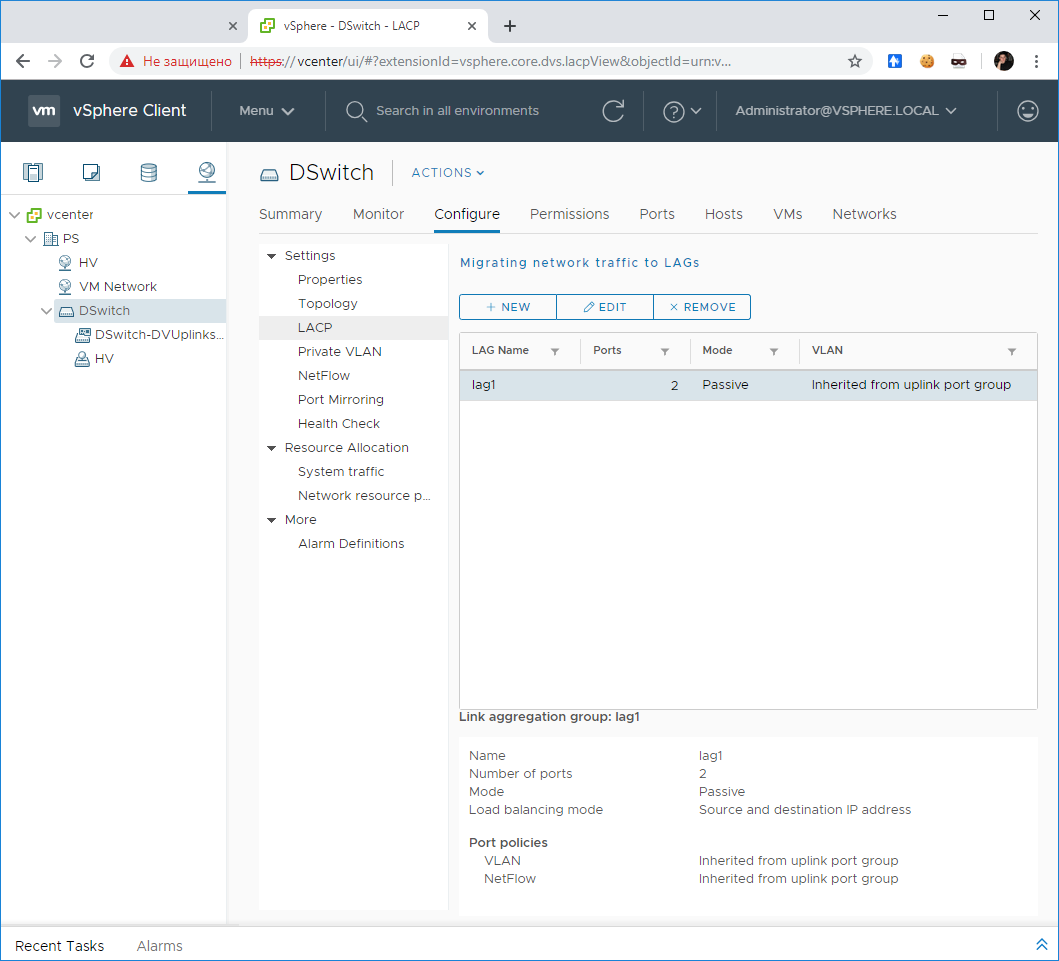
Выбираем Distributed Switch в UI. Открываем Configure > Settings > LACP.
Нажимаем кнопку +NEW. Открывается мастер создания группы LAG.
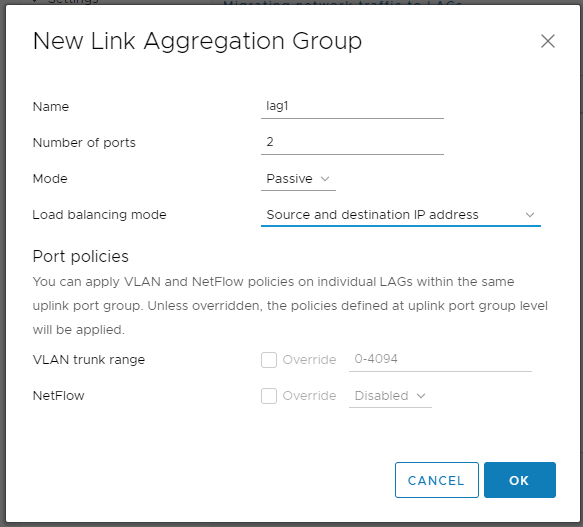
Указываем название, я оставляю по умолчанию — lag1.
В поле Number of ports указываем количество линков. В моей практики встречалось 4 гигабитных линка, 2 десятигигабитных. Всё зависит от вашей конфигурации.
Mode — Passive. Здесь могут быть варианты в разных сетях.
Load balancing mode — я ставлю Source and destination IP address. Если вы используете Cisco, то это оправдано, иначе MAC адрес сетевухи может скакать с одного интерфейса на другой.
OK.
LACP создан.
Настройка Default Port Group
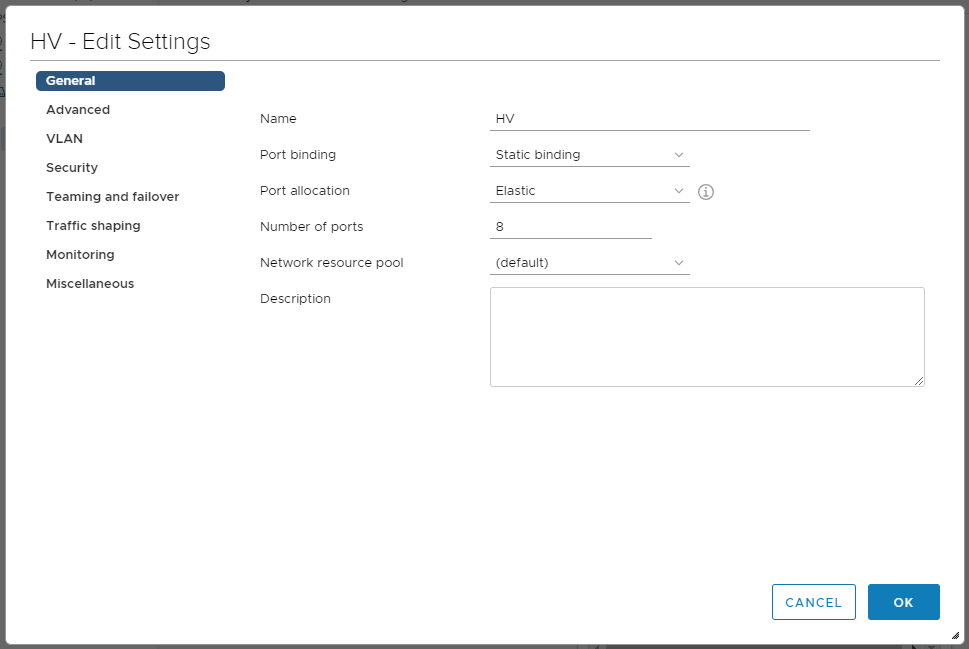
Выбираем созданную вместе с коммутатором port group, мы назвали её HV. Нажимаем правой кнопкой — Edit Settings.
Открывается мастер настройки. Мы в разделе General. Port binding ставим в Static binding. Port allocation — Elastic.
Переключаемся на раздел VLAN. Эту группу портов мы будем использовать для управления хостами, поэтому настраиваем такой же VLAN, в котором живут ESXi и vCenter.
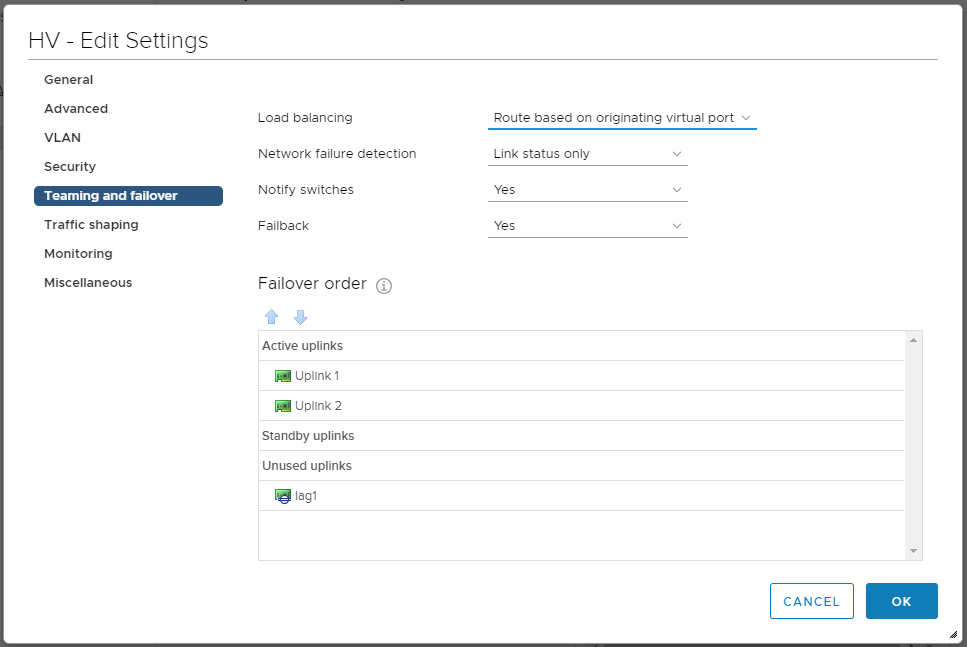
Переключаемся на раздел Teaming and failover.
По умолчанию у Port Group LACP не используется, включим. Перетаскиваем lag1 вверх, а аплинки вниз.
OK. Сохраняем. Каждый раз потом при создании новой группы портов нужно настраивать LACP для этой группы. Можно это делать прямо в процессе создания.
Добавление хоста в Distributed Switch
Добавляем хост в vCenter, если он ещё не добавлен:
Добавление хоста ESXi 6.0 в vCenter 6.7 c LACP через UI
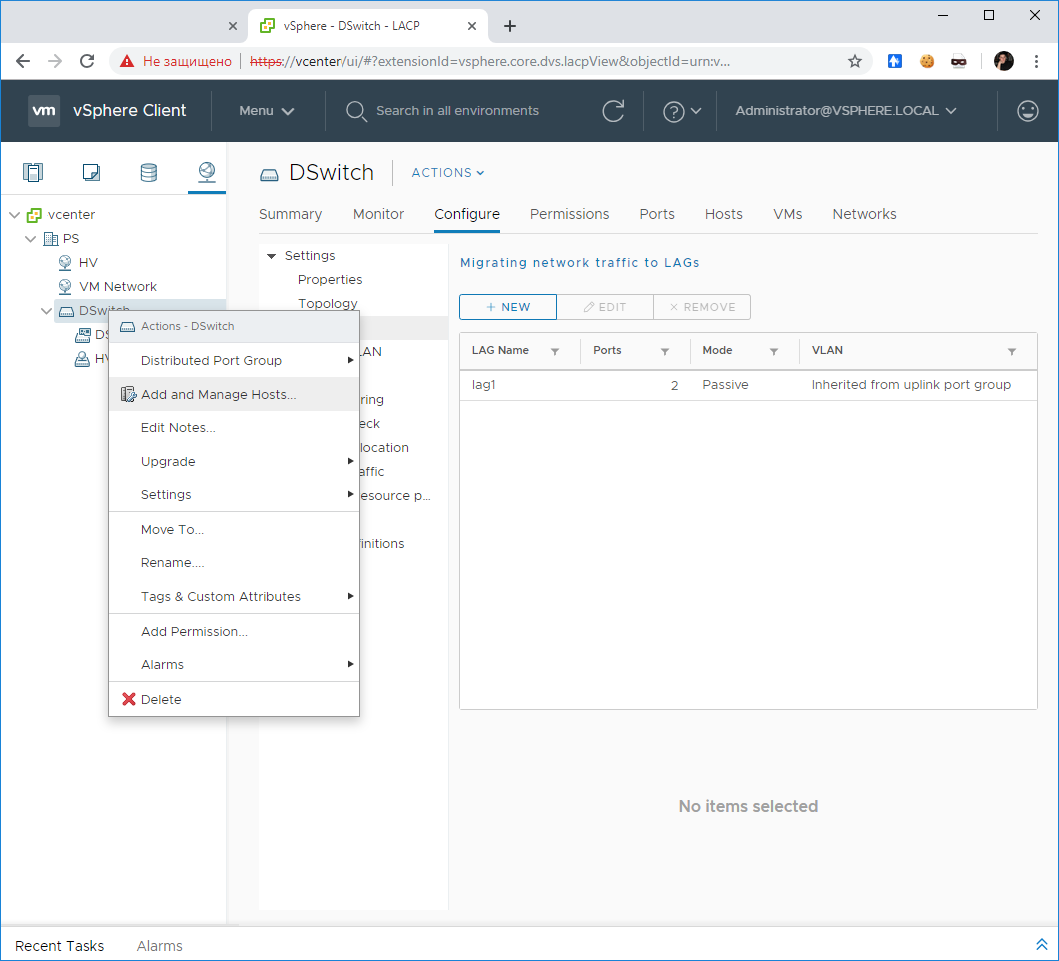
Нажимаем правой кнопкой на Distributed Switch — Add and Manage Hosts.
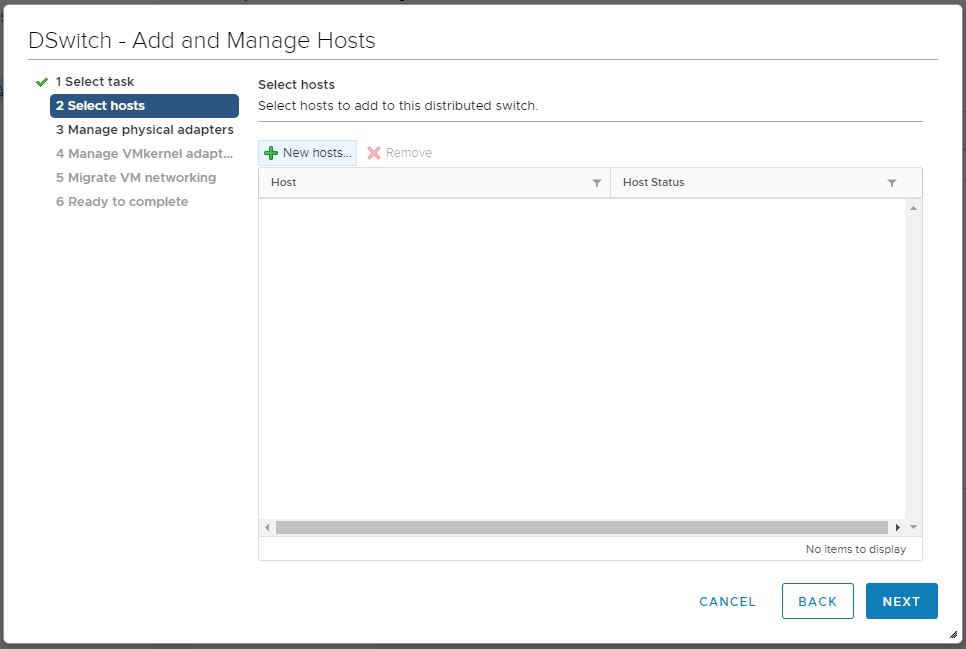
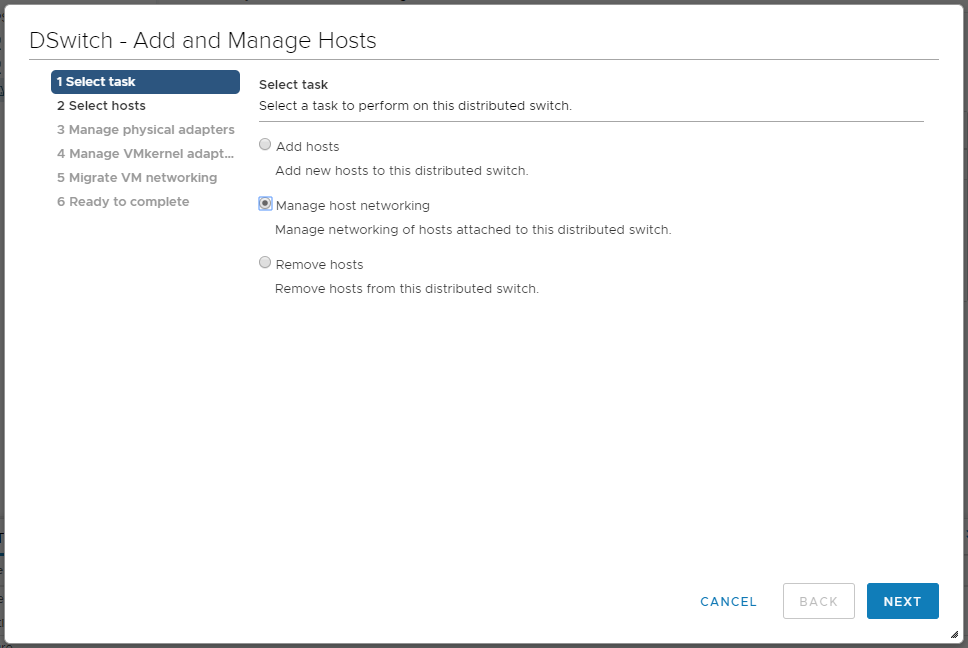
Открывается мастер. Мы попадаем в раздел Select task.
Выбираем Add hosts. NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Select hosts.
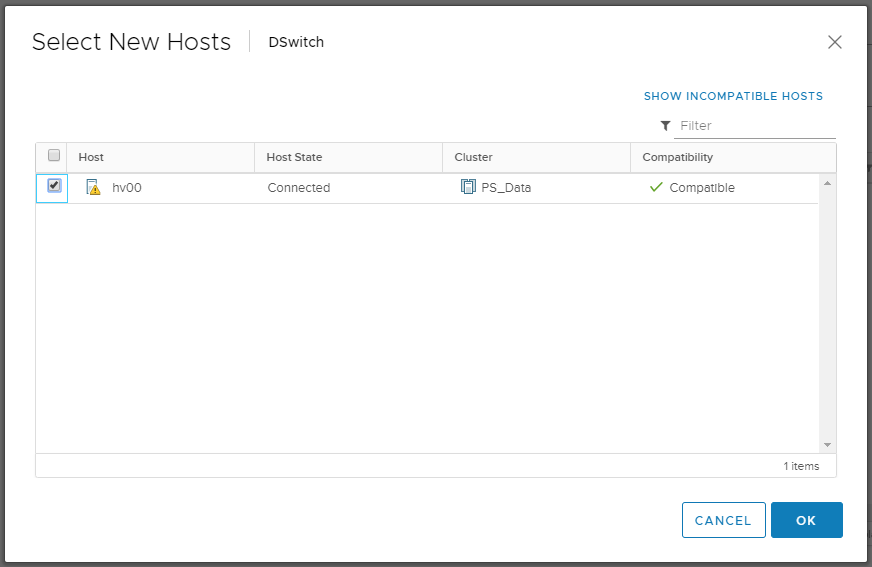
Нажимаем кнопку + New hosts. Открывается окно со списком доступных хостов. У меня пока один — hv00.
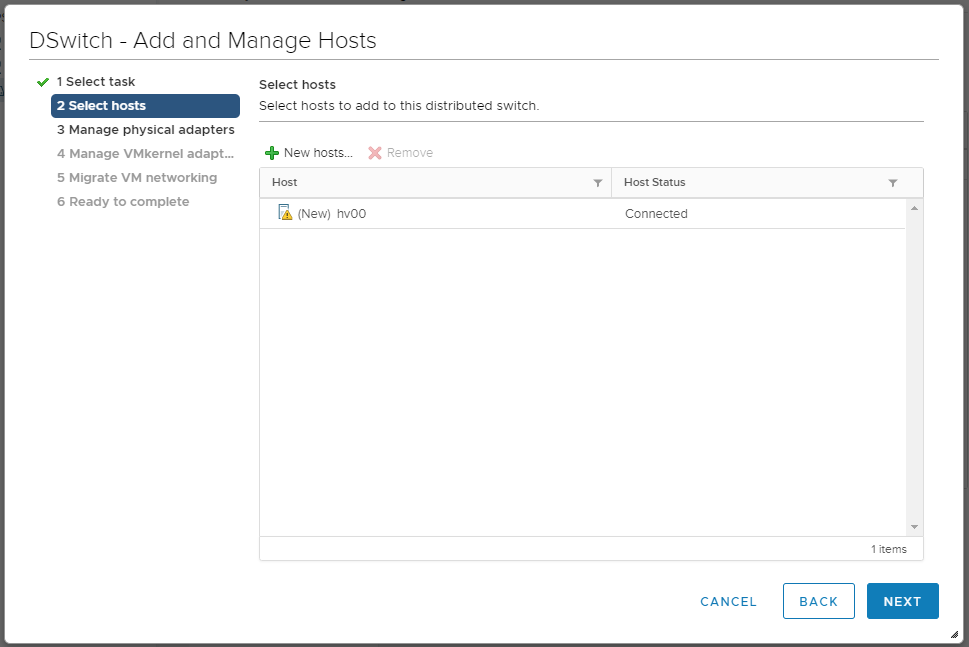
Выделяем хост галкой, OK.
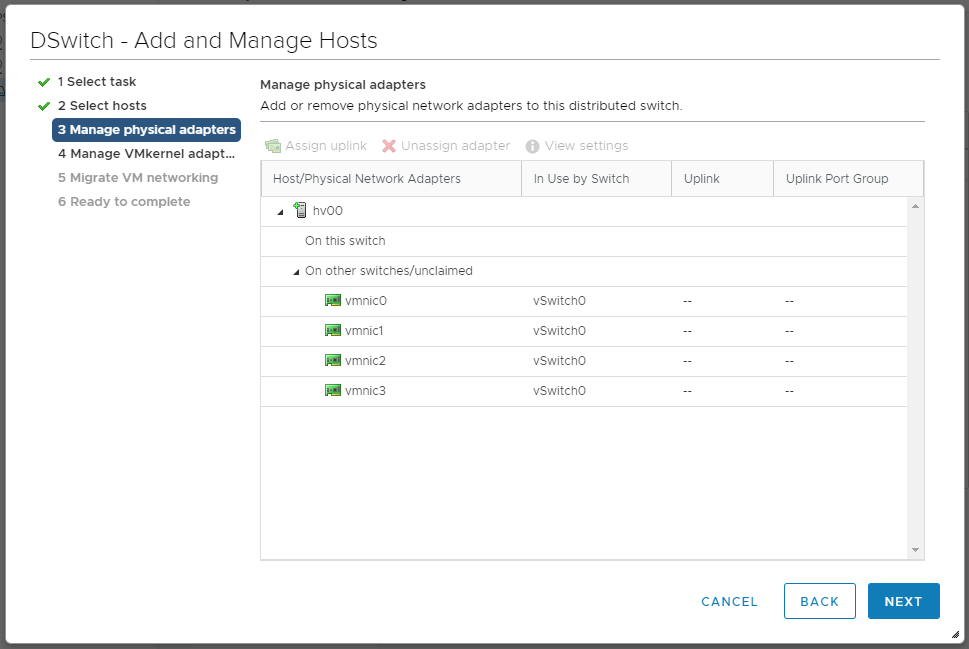
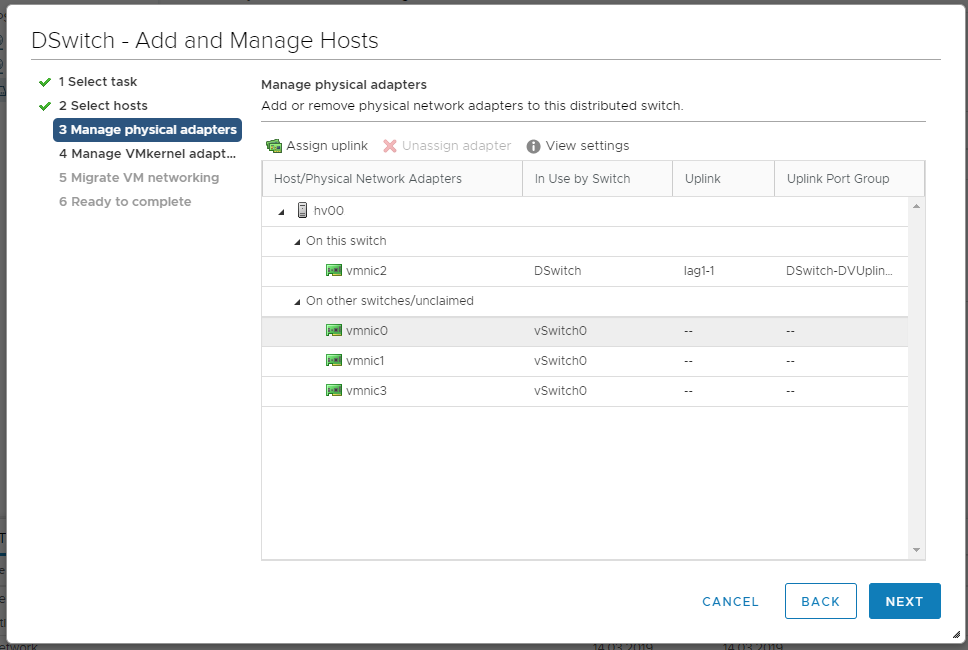
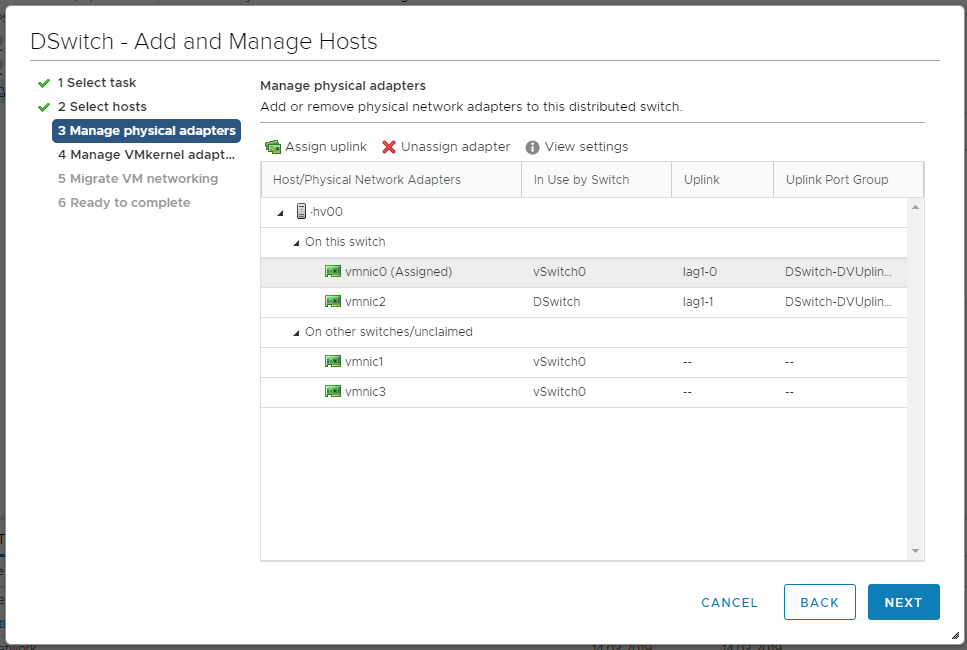
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Manage physical adapters.
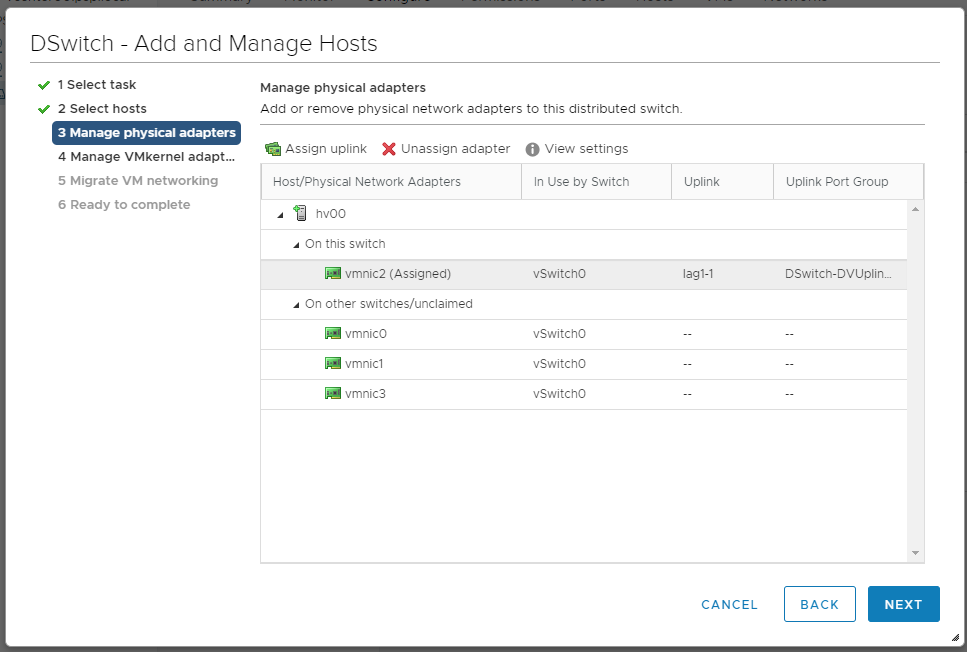
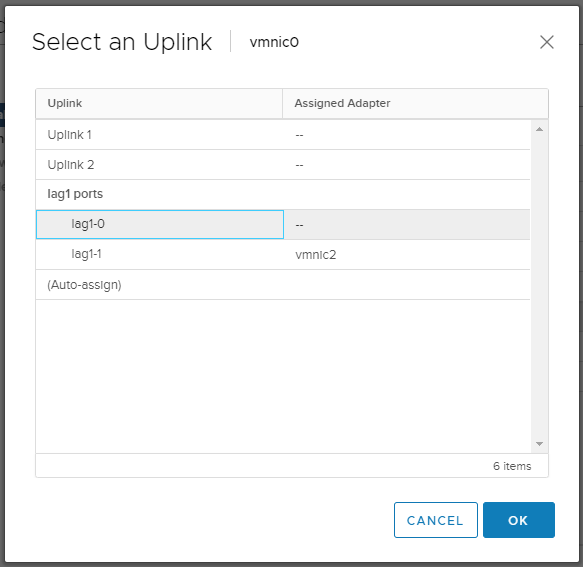
vmnic1 цепляем кнопкой Assign upling к lag1-1.
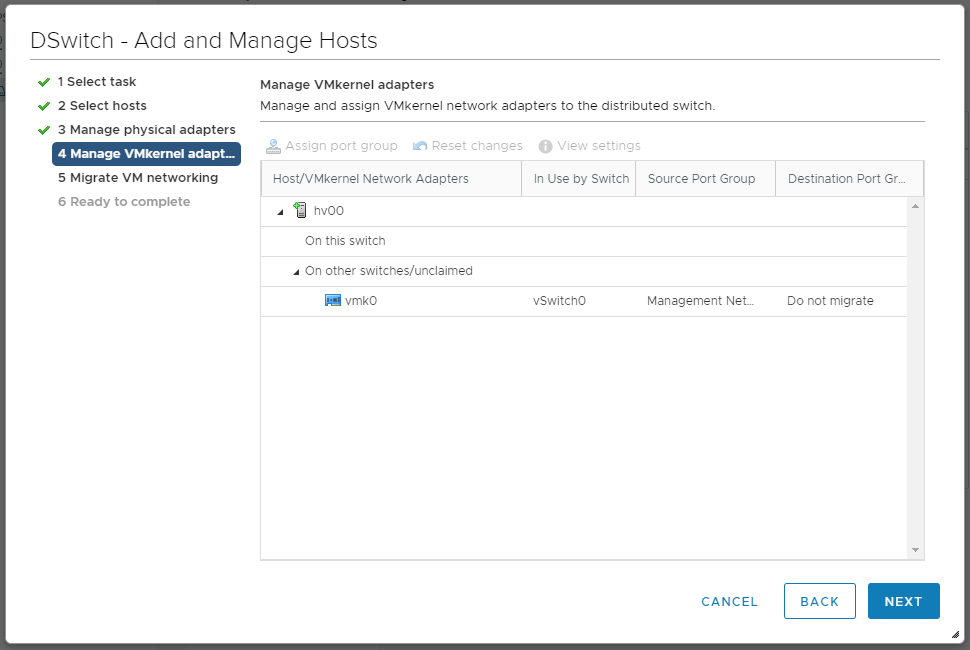
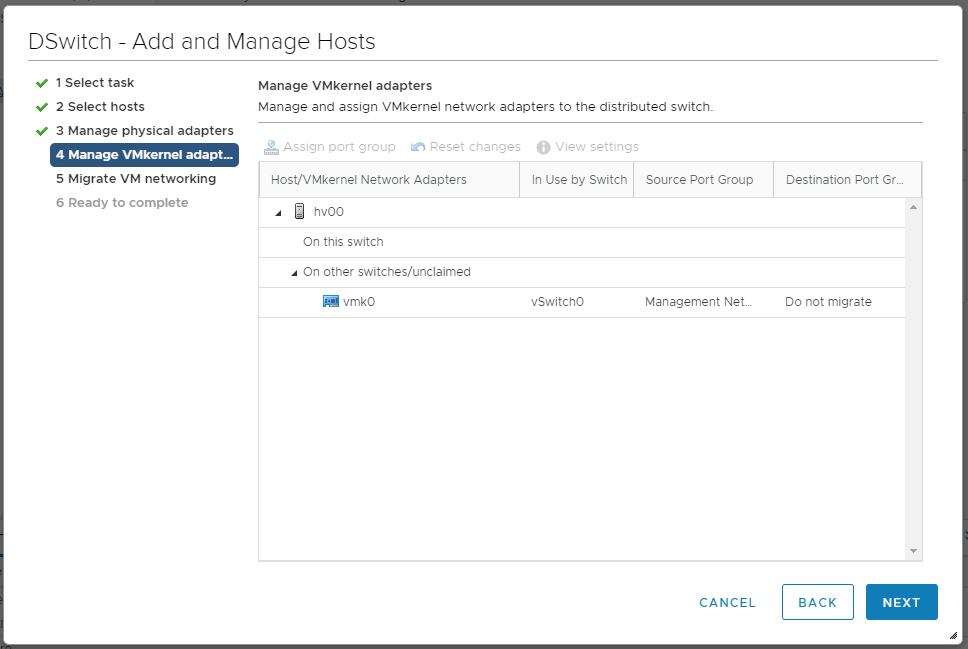
Наша задача добиться того, чтобы хост одной ногой был в старом коммутаторе, а второй — в новом. NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Manage VMkernel adapter.
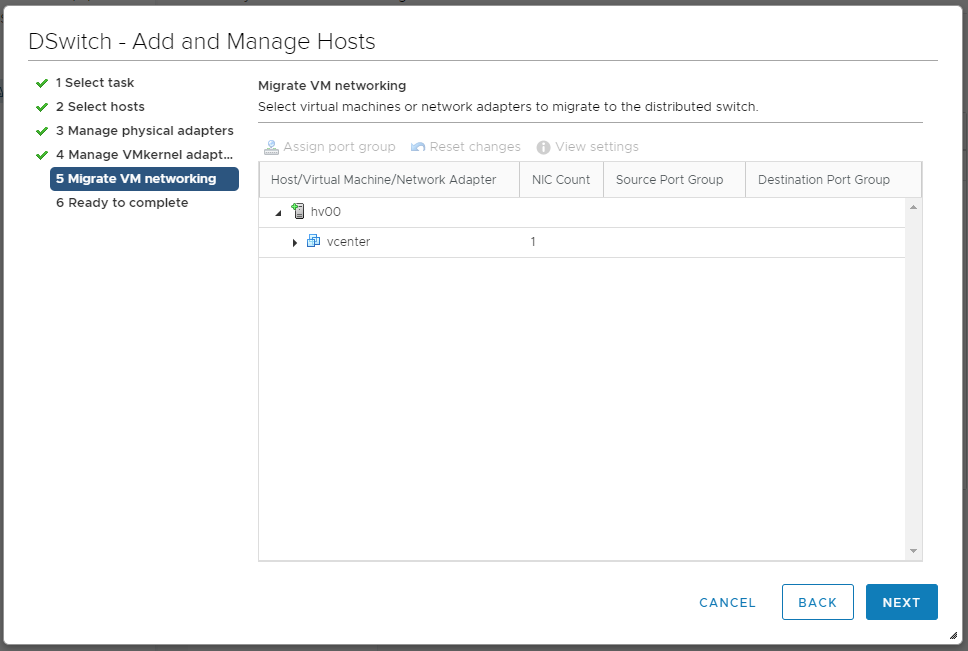
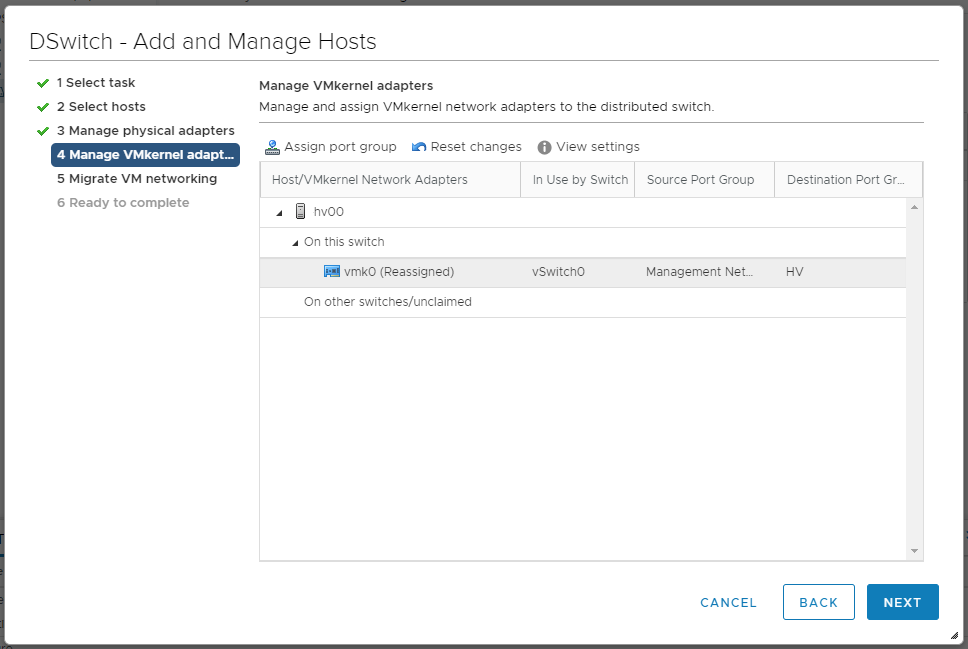
Пока ничего не меняем, пусть vmk0 будет на старом локальном коммутаторе. NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Migrate VM networking.
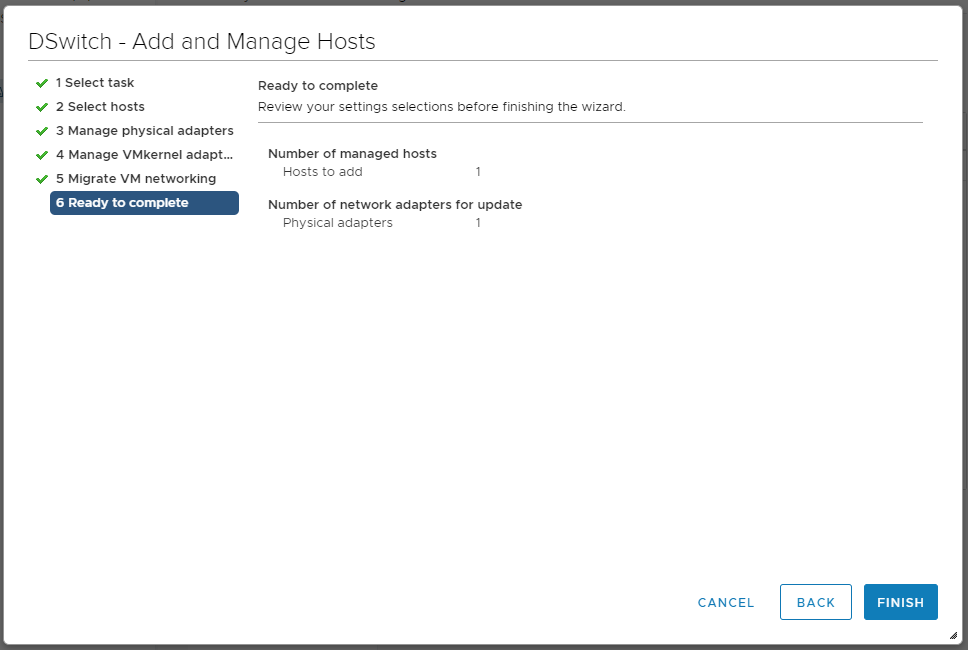
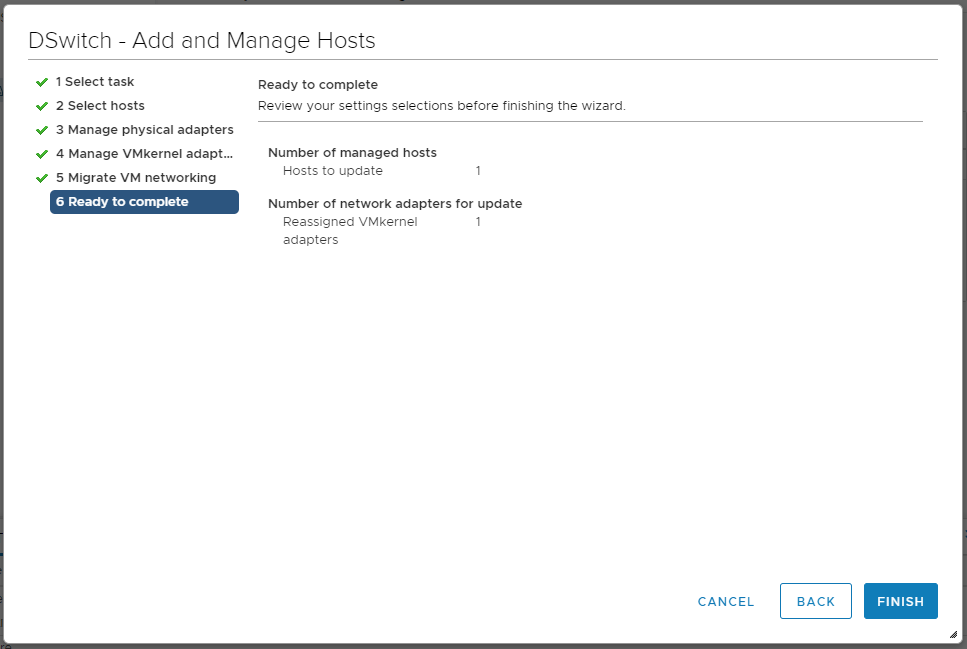
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Ready to complete.
FINISH. Ждём когда хост добавится.
Снова нажимаем правой кнопкой на Distributed Switch — Add and Manage Hosts.
Открывается мастер. Мы попадаем в раздел Select task.
Теперь выбираем пункт Manage host networking. NEXT. Доходим до раздела Manage VMkernel adapter.
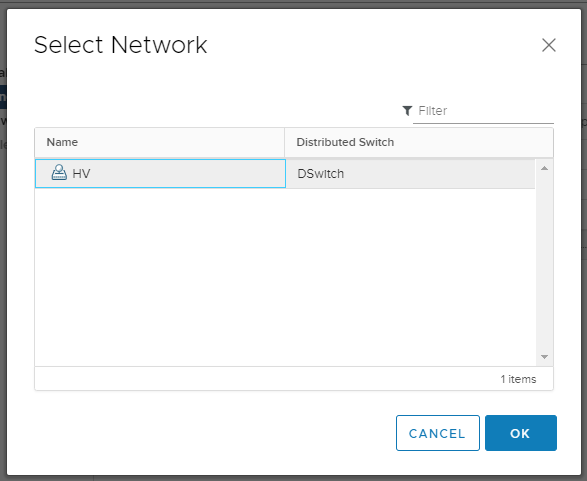
Выбираем vmk0, нажимаем Assign port group.
Выбираем наш Port Group с названием HV, который находится в управляющем VLAN. OK.
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Migrate VM networking.
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Ready to complete.
FINISH. Управление хостом должно перейти на Distributed Switch.
Снова редактируем сеть хоста.
vmnik0 привязываем к lag1-0.
OK.
NEXT. NEXT. NEXT. FINISH.
Теперь можно зайти в хост — Configure > Networking > Virtual switches и удалить локальный vSwitch0.
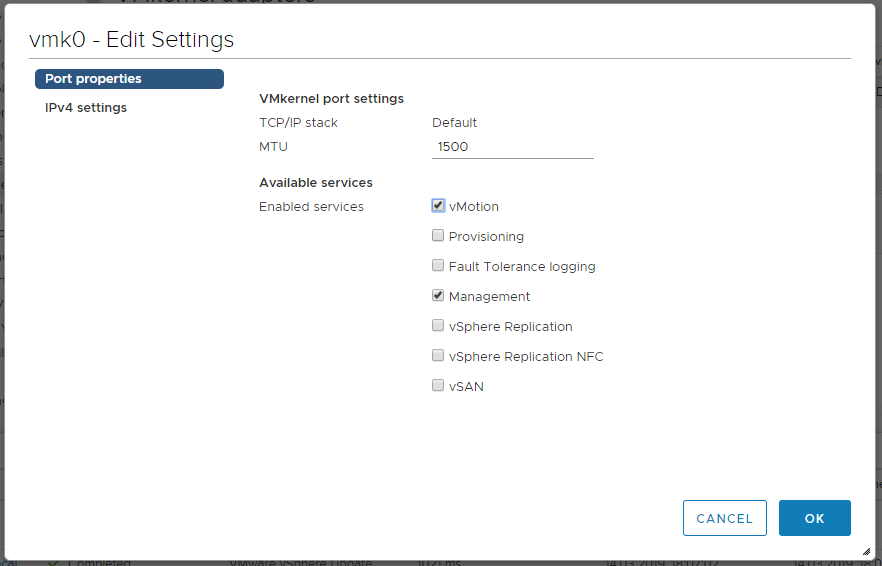
Потом заходим в хост — Configure > Networking > VMkernel adapters, выбираем vmk0, редактируем, разрешаем галкой vMotion.
OK.
Резюме
Итак, мы создали Distributed Switch, перенесли в него хосты, настроили LACP, разрешили vMotion.
Appliance Management Health Alarm Appliance Management service alarm to monitor health status Low Autodeploy Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Autodeploy File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Boot Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Boot File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Cannot connect to storage Default alarm to monitor host connectivity to storage device High Cannot find vSphere HA master agent Default alarm to alert when vCenter Server has been unable to connect to a vSphere HA master agent for a prolonged period High Certificate Status Default alarm that monitors whether a certificate is getting close to its expiration date. Low Cis License Health Alarm Cis License service alarm to monitor health status Low Component Manager Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of Component Manager Service. Medium New in 6.5 Content Library Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of the VMware Content Library Service. Low Core and Inventory Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Core and Inventory File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 CPU Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere CPU Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Data Service Health Alarm Data Service service alarm to monitor health status Medium Medium Database Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the database health status. High New in 6.5 Datastore capability alarm Default alarm that is triggered when the capability status of volumes backing the datastore changes Low Datastore cluster is out of space Alarm that monitors when a datastore cluster is out of space High Datastore compliance alarm Default alarm that is triggered when the virtual disk on the datastore goes out of compliance with the object-based storage Low Datastore is in multiple datacenters Datastore in a datastore cluster is visible in more than one datacenter Low Datastore usage on disk Default alarm to monitor datastore disk usage Medium Diagnostics Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Diagnostics File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Errors occurred on the disk(s) of a vSAN host Default alarm that monitors whether there are errors on the host disk(s) in the vSAN cluster. Medium ESX Agent Manager Health Alarm ESX Agent Manager service alarm to monitor health status Low ESXi Dump Collector Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere ESXi Dump Collector File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 ESXi Host Certificate Status Alarm to indicate certificate status of an ESXi host Low Exit standby error Default alarm to monitor if a host cannot exit standby mode Low Expired host license Default alarm to monitor for expired host license or evaluation period. Medium Expired host time-limited license Default alarm to monitor for expired host time-limited license. Medium Expired vCenter Server license Default alarm to monitor for expired vCenter Server license or evaluation period. Medium Expired vCenter Server time-limited license Default alarm to monitor for expired vCenter Server time-limited license. Medium Expired vSAN license Default alarm for expired vSAN license or evaluation period. Medium Expired vSAN time-limited license Default alarm to monitor for expired vSAN time-limited license. Medium Health status changed alarm Default alarm to monitor changes to service and extension health status Medium Host Baseboard Management Controller status Monitors the status of the Baseboard Management Controller. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. Low Host battery status Default alarm to monitor batteries. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host compliance check for hyperconverged cluster configuration Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Host compliance check for hyperconverged cluster configuration’ High New in 6.7u1 Host connection and power state Default alarm to monitor host connection and power state High Host connection failure Default alarm to monitor host connection failure High Host CPU usage Default alarm to monitor host CPU usage Medium Host error Default alarm to monitor host error and warning events High Host hardware fan status Default alarm to monitor fans. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host hardware power status Default alarm to monitor power. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host hardware sensor state Default alarm to monitor sensor state change. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High New in 6.7u1 Host hardware system board status Default alarm to monitor system boards. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host hardware temperature status Default alarm to monitor temperature. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host hardware voltage Default alarm to monitor voltage. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host IP Address Conflict Alarm Default alarm to indicate that the host has taken an IP address that conflicts with another host. High New in 6.5 Host IPMI System Event Log status Monitors the fullness of the IPMI System Event Log. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. Low Host memory status Default alarm to monitor memory. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host memory usage Default alarm to monitor host memory usage Medium Host processor status Default alarm to monitor processors. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host Requires Encryption Mode Enabled Alarm Alarm to indicate that the host requires encryption mode enabled. High New in 6.7u1 Host storage status Default alarm to monitor storage. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Host virtual flash resource status Default alarm to monitor the VMware Flash Read Cache resource status on the host Low Host virtual flash resource usage Default alarm to monitor the VMware Flash Read Cache resource usage on the host Low Identity Health Alarm Identity service alarm to monitor health status Low Image Builder Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Image Builder File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Image Builder Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of Image Builder Service. Low Insufficient vSphere HA failover resources Default alarm to alert when there are insufficient cluster resources for vSphere HA to guarantee failover Low KMS Client Certificate Status This alarm indicates that the KMS client certificate is getting close to its expiration date. High New in 6.7u1 KMS Server Certificate Status This alarm indicates that the KMS server certificate is getting close to its expiration date. High New in 6.7u1 License capacity monitoring Default alarm to monitor if a license capacity is exceeded Low License error Default alarm to monitor license errors Low License inventory monitoring Default alarm to monitor if license inventory is not compliant Low License user threshold monitoring Default alarm to monitor if a user-defined license threshold is exceeded Low Log Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Log File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Memory Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Memory Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Message Bus Config Health Alarm Message Bus Config service alarm to monitor health status Medium Migration error Default alarm to monitor if a virtual machine cannot migrate, relocate, or is orphaned Low Network connectivity lost Default alarm to monitor network connectivity on a virtual switch High Network uplink redundancy degraded Default alarm to monitor network uplink redundancy degradation on a virtual switch High Network uplink redundancy lost Default alarm to monitor loss of network uplink redundancy on a virtual switch High No compatible host for Secondary VM Default alarm to monitor if no compatible hosts are available to place Secondary VM Low Object type storage alarm Default alarm that is triggered when a VASA provider raises an Object type alarm on an entity backing the datastore Medium Performance Charts Service Health Alarm Performance Charts Service alarm to monitor health status Low PostgreSQL Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of the PostgreSQL Service. High New in 6.5 PSC Service Health Alarm. Default alarm that monitors the health status of PSC Service. High New in 6.5 RBD Health Alarm RBD service alarm to monitor health status Disabled Only needed if using Autodeploy Refreshing CA certificates and CRLs for a VASA provider failed Default alarm that monitors whether the refreshing of CA certificates and CRLs for some of the VASA providers has failed. Low Registration/unregistration of a VASA vendor provider on a vSAN host fails Default alarm that monitors whether the registration or unregistration of a VASA vendor provider on a vSAN host fails. Low Registration/unregistration of third-party IO filter storage providers fails on a host Default alarm that monitors whether vCenter Server fails to register or unregister third-party IO filter storage providers on a host. Low Root Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Root File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 SEAT Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Stats, events, alarms, and tasks File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Service Control Agent Health Alarm Alarm that is triggered when the Service Control Agent is not reachable. Low Status of other host hardware objects Default alarm to monitor objects. See the host’s Hardware Status tab for more details. High Storage DRS is not supported on a host Alarm that monitors and alerts when Storage DRS is not supported on a host Low Storage DRS recommendation Alarm that monitors a Storage DRS recommendation Low The host license edition is not compatible with the vCenter Server license edition Default alarm to monitor if host license edition is not allowed Low Thin-provisioned volume capacity threshold exceeded Default alarm that is triggered when the thin provisioning threshold on the storage array is exceeded for volume(s) backing the datastore High Timed out starting Secondary VM Default alarm to monitor time-outs when starting a Secondary VM Low Unmanaged workload detected on SIOC-enabled datastore Default alarm that is triggered if an unmanaged I/O workload is detected on a SIOC-enabled datastore Low Update Manager Disk Exhaustion on vCenterServerHostname Alarm that monitors vSphere Update Manager File System Resource Exhaustion. High New in 6.7u1 Update Manager Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of Update Manager Service. Low New in 6.5 VASA Provider certificate expiration alarm Default alarm that is triggered when a VASA Provider certificate is about to expire Low VASA provider disconnected Default alarm that is triggered when a VASA provider is in a disconnected state Low vCenter HA Cluster Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health of vCenter HA Medium New in 6.5 vCenter HA Service Health Alarm. Default alarm that monitors the health status of vCenter HA Service. Medium New in 6.5 vCenter Server Health Alarm vCenter Server service alarm to monitor health status Medium vCenter Stats Monitor Service Health Alarm. Default alarm that monitors the health status of vCenter Stats Monitor Service. Low New in 6.5 VDS compliance check for hyperconverged cluster configuration Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘VDS compliance check for hyperconverged cluster configuration’ High New in 6.7u1 Virtual machine Consolidation Needed status Default alarm that is triggered when virtual machine Consolidation Needed status is set Medium Virtual machine CPU usage Default alarm to monitor virtual machine CPU usage Disabled Too many alerts Low Virtual machine error Default alarm to monitor virtual machine error and warning events Medium Virtual machine Fault Tolerance state changed Default alarm to monitor changes in the Fault Tolerance state of a virtual machine Medium Virtual Machine Fault Tolerance vLockStep interval Status Changed Default Alarm to monitor changes in the Fault Tolerance Secondary vLockStep interval Medium Virtual Machine Locked Alarm Alarm to indicate that the virtual machine is locked. Medium New in 6.7u1 Virtual machine memory usage Default alarm to monitor virtual machine memory usage Disabled Too many alerts Low Virtual Machine network adapter reservation status Default alarm to monitor changes in the reservation status of a virtual machine network adapter Medium VM storage compliance alarm Default alarm that is triggered when the virtual disk goes out of compliance with the object-based storage Low VMKernel NIC not configured correctly Default alarm for incorrectly configured VMkernel NIC Medium vMon API Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of vMon API Service. Medium New in 6.5 VMware Directory Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health of VMware Directory Service High New in 6.7u1 VMware HTTP Reverse Proxy Service Health Alarm. Default alarm that monitors the health status of HTTP Reverse Proxy Service. Medium New in 6.5 VMware vAPI Endpoint Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of the VMware vAPI Endpoint Service. Medium VMware vCenter-Services Health Alarm VMware vCenter-Services alarm to monitor health status Medium New in 6.5 VMware vSphere Authentication Proxy Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of VMware vSphere Authentication Proxy Service. Medium New in 6.5 VMware vSphere ESXi Dump Collector Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of the VMware vSphere ESXi Dump Collector Service. Low VMware vSphere Profile-Driven Storage Service Health Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of the VMware vSphere Profile-Driven Storage Service. Low vSAN hardware compatibility issues Default alarm to monitor changes for the health tests related to vSAN hardware compatibility Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Active multicast connectivity check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Active multicast connectivity check’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Advanced vSAN configuration in sync’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Advanced vSAN configuration in sync’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN Health Alarm ‘Advanced vSAN configuration supported’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Advanced vSAN configuration supported’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘After 1 additional host failure’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘After 1 additional host failure’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘All hosts contributing stats’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks if all host are contributing performance stats’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘All hosts have a vSAN vmknic configured’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘All hosts have a vSAN vmknic configured’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘All hosts have matching multicast settings’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘All hosts have matching multicast settings’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Basic (unicast) connectivity check (normal ping)’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Basic (unicast) connectivity check (normal ping)’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Cluster health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘Cluster health’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Component metadata health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Component metadata health’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Congestion’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Congestion’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Controller disk group mode is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Controller disk group mode is VMware certified’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Controller driver is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Controller driver is VMware certified’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Controller firmware is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Controller firmware is VMware certified’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Controller is VMware certified for ESXi release’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Controller is VMware certified for ESXi release’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN Health Alarm ‘Controller utility is installed on host’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Controller utility is installed on host’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘Controller with pass-through and RAID disks’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Controller with pass-through and RAID disks’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘Coredump partition size check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Coredump partition size check’ Medium New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘CPU AES-NI is disabled on hosts’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘CPU AES-NI is enabled on hosts’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Current cluster situation’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Current cluster situation’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP)’ Default alarm to monitor changes for online health check ‘Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP)’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Data health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘Data health’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘Data protection archival target accessibility check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN Data protection archival target accessibility check’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘Data protection service version check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Data protection service version check’ Medium New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Disk capacity’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Disk capacity’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Disk format version’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Disk format version’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN Health Alarm ‘Disks usage on storage controller’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Disks usage on storage controller’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘ESXi vSAN Health service installation’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘ESXi vSAN Health service installation’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm for ‘Firmware provider health’ Default alarm to monitor’Firmware provider’ config issues High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm for vMotion ‘Basic (unicast) connectivity check (normal ping)’ Default alarm for vMotion to monitor changes for the health test ‘Basic (unicast) connectivity check (normal ping)’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm for vMotion ‘MTU check (ping with large packet size)’ Default alarm for vMotion to monitor changes for the health test ‘MTU check (ping with large packet size)’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm for ‘vSAN firmware recommendation’ Default alarm to monitor recommendation from ‘vSAN firmware recommendation’ Medium New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Home object’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Home object of iSCSI target service’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Host component limit’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Host component limit’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Host component limit’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Host component limit’ Medium New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Host issues retrieving hardware info’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Host issues retrieving hardware info’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Host issues retrieving hardware info’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Host issues retrieving hardware info’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Host Maintenance Mode and Decommission State’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Host Maintenance Mode and Decommission State’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Hosts disconnected from VC’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Hosts disconnected from VC’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Hosts with connectivity issues’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Hosts with connectivity issues’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Invalid preferred fault domain on witness host’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Invalid preferred fault domain on witness host’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Invalid unicast agent’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Invalid unicast agent’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘iSCSI target service’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘iSCSI target service’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Limits health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘Limits health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Memory pools (heaps)’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Memory pools (heaps)’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Memory pools (slabs)’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Memory pools (slabs)’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘MTU check (ping with large packet size)’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘MTU check (ping with large packet size)’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Multicast assessment based on other checks’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Multicast assessment based on other checks’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Network adapter driver is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Network adapter driver is VMware certified’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Network adapter firmware is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Network adapter firmware is VMware certified’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Network adapter is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Network adapter is VMware certified’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘Network adapter is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Network adapter is VMware certified’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Network adapter is VMware certified for ESXi release’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Network adapter is VMware certified for ESXi release’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Network configuration’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Network configuration of iSCSI target service’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Network health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘Network health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Network latency check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Network latency check’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘No disk claimed on witness host’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘No disk claimed on witness host’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Online health connectivity’ Default alarm to monitor changes for online health check ‘Online health connectivity’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Operation health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Operation health’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Performance data collection’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks statistics collection of vSAN Performance Service’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Performance service status’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks status of vSAN Performance service’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Physical disk component limit health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Physical disk component limit health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Physical disk health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘Physical disk health’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Physical disk health retrieval issues’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Physical disk health retrieval issues’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN Health Alarm ‘Physical network adapter speed consistency’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Physical network adapter speed consistency’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Preferred fault domain unset’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Preferred fault domain unset’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN Health Alarm ‘RAID controller configuration’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘RAID controller configuration’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘Resync operations throttling’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Resync operations throttling’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘SCSI controller is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘SCSI controller is VMware certified’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Service runtime status’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Service runtime status of iSCSI target service’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Site Latency Health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Site Latency Health’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Software version compatibility’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Software version compatibility’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Space efficiency configuration consistency’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Space efficiency configuration consistency’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Space efficiency usage health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Space efficiency usage health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Stats DB object’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks status of vSAN Performance Service stats DB object’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Stats DB object conflicts’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks stats DB object conflicts’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Stats master election’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks stats master of vSAN Performance Service’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘Stretched cluster health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘Stretched cluster health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Time is not synchronized across hosts and VC Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Time is synchronized across hosts and VC’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Unexpected number of fault domains’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Unexpected number of fault domains’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Unicast agent configuration inconsistent’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Unicast agent configuration inconsistent’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Unicast agent not configured’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Unicast agent not configured’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Unsupported host version’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Unsupported host version’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarm ‘vCenter or hosts are not connected to Key Management Servers’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vCenter and all hosts are connected to Key Management Servers’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vCenter state is authoritative’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vCenter state is authoritative’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Verbose mode’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Checks the verbose mode status of the vSAN performance service’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN and VMFS datastores on a Dell H730 controller with the lsi_mr3 driver’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN and VMFS datastores on a Dell H730 controller with the lsi_mr3 driver’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN Build Recommendation Engine build recommendation’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘vSAN Build Recommendation Engine’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN Build Recommendation Engine Health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘vSAN Build Recommendation Engine Health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN Build Recommendation Engine Health’ configuration issues Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘vSAN Build Recommendation Engine’ configuration issues Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN CLOMD liveness’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN CLOMD liveness’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN cluster configuration consistency’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN cluster configuration consistency’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN cluster partition’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN cluster partition’ Critical Can disable if not using VSAN Critical vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN configuration for LSI-3108 based controller’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN configuration for LSI-3108 based controller» High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN data protection health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN data protection health’ Critical New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Critical vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN data protection service configuration in sync’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN data protection service configuration in sync’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN datastore usage threshold check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the data protection health test ‘vSAN datastore usage threshold check’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN disk balance’ Default alarm to monitor changes from health test ‘vSAN disk balance’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN DPD liveness’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the data protection health test ‘vSAN DPD liveness’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN extended configuration in sync’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN extended configuration in sync’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN HCL DB Auto Update’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN HCL DB Auto Update’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN HCL DB up-to-date’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN HCL DB up-to-date’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN HCL health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘vSAN HCL health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN Health Service up-to-date’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN Health Service up-to-date’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN Hosts with new patch available’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN Hosts with new patch available’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN max component size’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN max component size’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN Health Alarm ‘vSAN object data protection health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN object data protection health’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN object health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN object health’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN Performance Service health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘vSAN Performance Service health’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN release catalog up-to-date’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health group test ‘vSAN release catalog up-to-date’ Medium New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘vSAN VM health’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSAN VM health’ High Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN health alarm ‘vSphere cluster members do not match vSAN cluster members’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘vSphere cluster members match vSAN cluster members’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Witness host fault domain misconfigured’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Witness host fault domain misconfigured’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Witness host not found’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Witness host not found’ Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health alarm ‘Witness host within vCenter cluster’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the health test ‘Witness host within vCenter cluster’ Low Can disable if not using VSAN Low vSAN health alarms are suppressed vSAN health alarms are suppressed until the cluster is fully configured or this Quickstart workflow is skipped. Medium New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN Medium VSAN Health Service Alarm Default alarm that monitors the health status of VSAN Health Services. Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN health service alarm for Overall Health Summary Default alarm to monitor changes for the overall health summary Medium Can disable if not using VSAN Medium vSAN online health alarm ‘Advanced vSAN configuration supported’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Advanced vSAN configuration supported’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘Controller utility is installed on host’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Controller utility is installed on host’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘Controller with pass-through and RAID disks’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Controller with pass-through and RAID disks’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘Coredump partition size check’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Coredump partition size check’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘Disks usage on storage controller’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Disks usage on storage controller’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘Network adapter is VMware certified’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Network adapter is VMware certified’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘Physical network adapter speed consistency’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘Physical network adapter speed consistency’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘RAID controller configuration’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘RAID controller configuration’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘vCenter Server up to date’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vCenter Server up to date’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘vSAN and VMFS datastores on a Dell H730 controller with the lsi_mr3 driver’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN and VMFS datastores on a Dell H730 controller with the lsi_mr3 driver’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘vSAN configuration for LSI-3108 based controller’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN configuration for LSI-3108 based controller» High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘vSAN Hosts with new patch available’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN Hosts with new patch available’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarm ‘vSAN max component size’ Default alarm to monitor changes for the online health test ‘vSAN max component size’ High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vSAN online health alarms This alarm is from vSAN online health, please check the vSAN online health group High New in 6.7u1. Can disable if not using VSAN High vService Manager Health Alarm vService Manager service alarm to monitor health status Medium vSphere APIs for IO Filtering (VAIO) Filter Management Operations Default alarm that is triggered when vSphere APIs for IO Filtering (VAIO) operations (installing/uninstalling/upgrading filters) fail for some hosts in the cluster Low vSphere Client Health Alarm vSphere Client service alarm to monitor health status Medium vSphere Distributed Switch MTU matched status Default alarm to monitor changes in vSphere Distributed Switch MTU matched status High vSphere Distributed Switch MTU supported status Default alarm to monitor changes in vSphere Distributed Switch MTU supported status High vSphere Distributed Switch teaming matched status Default alarm to monitor changes in vSphere Distributed Switch teaming matched status High vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN trunked status Default alarm to monitor changes in vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN trunked status High vSphere HA failover in progress Default alarm to alert when vSphere HA is in the process of failing over virtual machines High vSphere HA host status Default alarm to monitor health of a host as reported by vSphere HA Medium vSphere HA virtual machine failover failed Default alarm to alert when vSphere HA failed to failover a virtual machine High vSphere HA virtual machine monitoring action Default alarm to alert when vSphere HA reset a virtual machine Medium vSphere HA virtual machine monitoring error Default alarm to alert when vSphere HA failed to reset a virtual machine Medium vSphere HA VM Component Protection could not power off a virtual machine Default alarm that is triggered when vSphere HA VM Component Protection cannot power off a virtual machine with an inaccessible datastore Low vSphere UI Health Alarm vSphere UI service alarm to monitor health status Medium New in 6.5 vSphere vCenter Host Certificate Management Mode Alarm to monitor changes in the certificate management mode of vCenter Server Low
Objective 3.4 Topics:
- Perform a vDS Health Check for Teaming, MTU, mismatches etc…
- Configure Port Groups to Properly Isolate Network Traffic
- Use Command Line Tools to Troubleshoot and Identify Configuration Issues
- Use Command Line Tools to Trouble and Identify VLAN Configurations
- Use DCUI Network Tool to Correct Network Connectivity Issues
Perform a vDS Hath Check for Teaming, MTU, Mismatches etc…
The health check support in vSphere Distributed Switch 5.1 and later helps you identify and troubleshoot configuration errors in a vSphere Distributed Switch.
vSphere runs regular health checks to examine certain settings on the distributed and physical switches to identify common errors in the networking configuration. The default interval between two health checks is 1 minute.
Checks:
- VLAN trunk ranges on dVS match that on the physical switch
- MTU settings on vDS and physical switch match
- Teaming policy on port groups match that of the port-channel on the physical switch
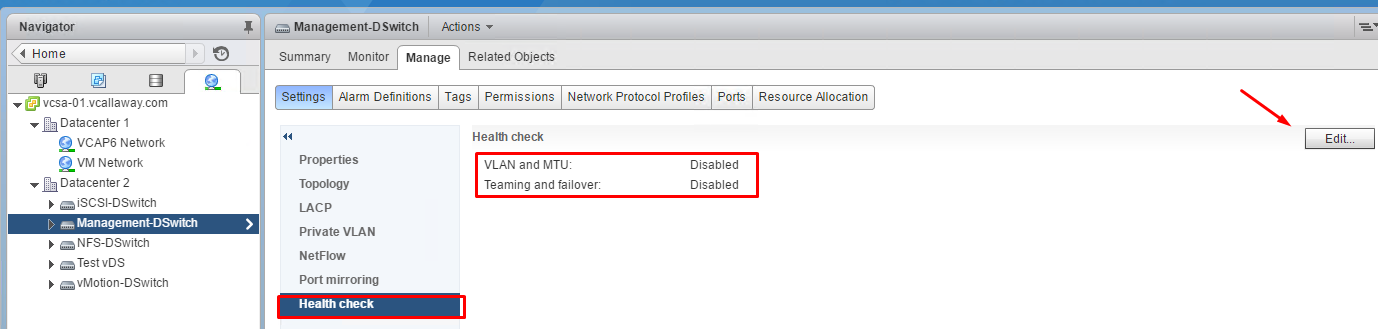
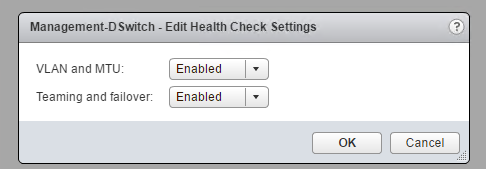
Enable/Disable Health Check on the Distributed Switch
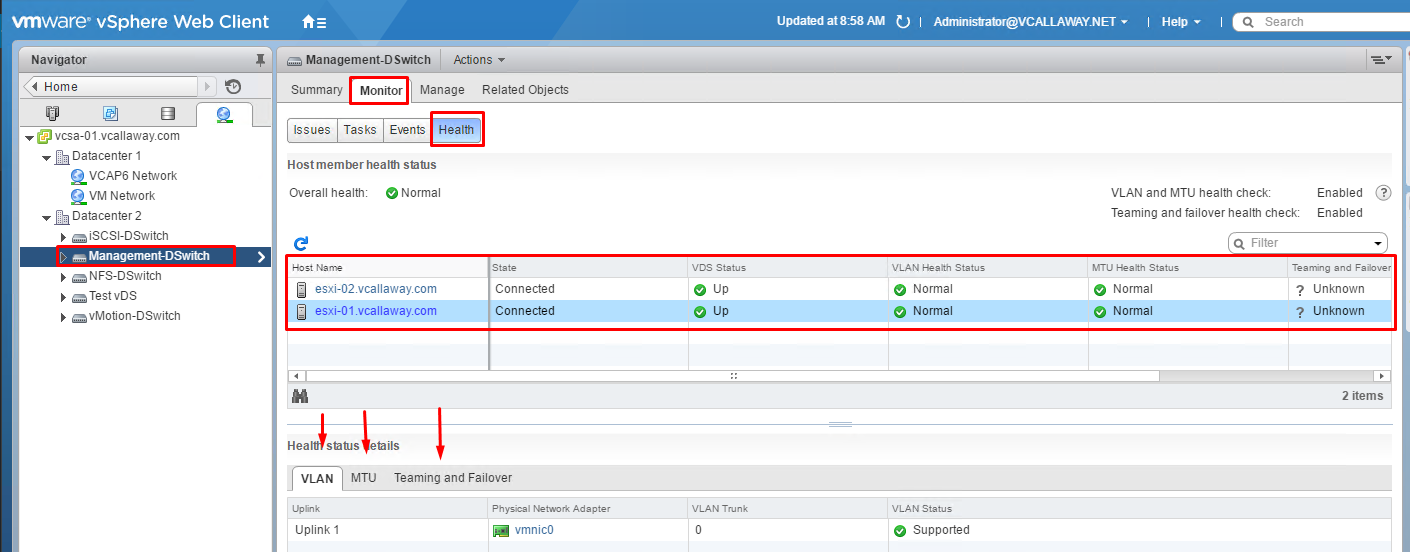
View Distributed Health Status
My teaming and Failover shows as unknown since the vDS’s aren’t connected to a physical switch, since this is a nested environment.
Use Command Line Tools to Troubleshoot and Identify Configuration Issues
Linux commands for retrieving networking information are not included in the ESXi Shell. You can instead use ESXCLI commands
On ESXi 5.0 and later, ifconfig information is the information for the VMkernel NIC that attaches to the Management Network port group.
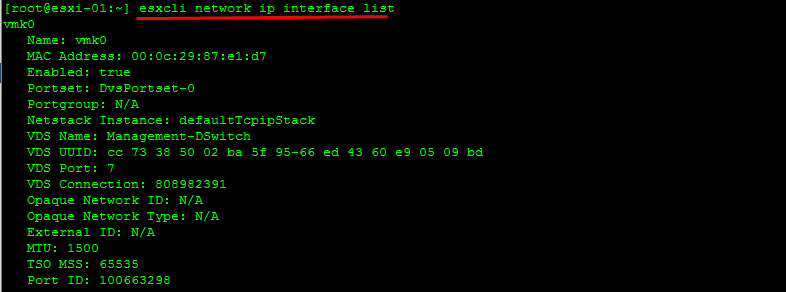
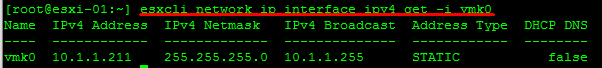
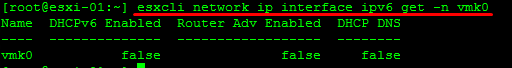
Retrieve Network Information
Information on our vmkernels
IP information on a specific vmkernel
Information on a IP 6 on a vmkernel
Information on IP 6 addresses.
Retrieve Information about DNS
Information on the search domain
Information on the DNS servers used
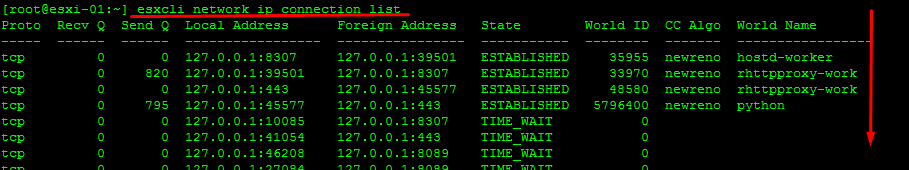
Information on the connections
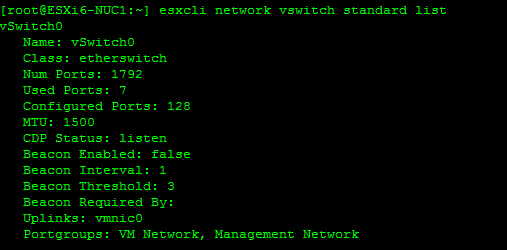
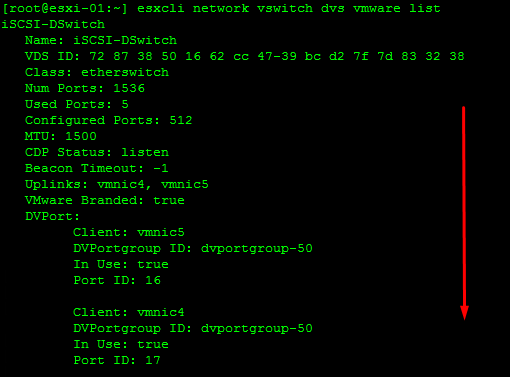
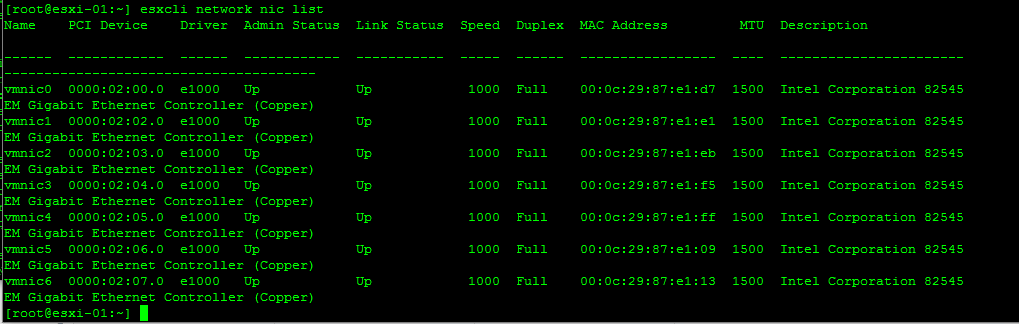
Retrieve Information on the vSwitch Configuration and VMkernel interfaces
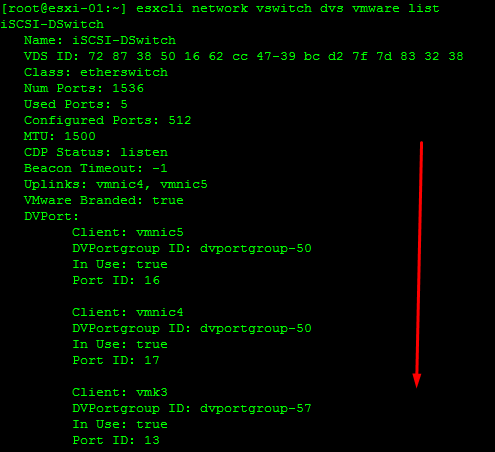
Add/Remove Network Cards (vmnics) to/from a Standard Switch
esxcli network vswitch standard uplink remove –uplink-name=vmnic –vswitch-name=vSwitch # unlink an uplink
esxcli network vswitch standard uplink add –uplink-name=vmnic –vswitch-name=vSwitch # add an uplink
Add/Remove Network Cards (vmnics) to/from a Distributed Switch
esxcfg-vswitch -Q vmnic -V dvPort_ID_of_vmnic dvSwitch # unlink/remove a vDS uplink
esxcfg-vswitch -P vmnic -V unused_dvPort_ID dvSwitch # add a vDS uplink
Remove an Existing VMkernel port on vDS
esxcli network ip interface remove –interface-name=vmkX
Note: The vmk interface number used for management can be determined by running the esxcli network ip interface list command.
Create new Standard Switch and Port Group
esxcli network vswitch standard add –vswitch-name=vSwitch
esxcli network vswitch standard portgroup add –portgroup-name=portgroup –vswitch-name=vSwitch
Create VMkernel port and Attach it to a Port Group
esxcli network ip interface add –interface-name=vmkX –portgroup-name=portgroup
esxcli network ip interface ipv4 set –interface-name=vmkX –ipv4=ipaddress –netmask=netmask –type=static
To set a VLAN ID we can run the following command:
esxcli network vswitch standard portgroup set -p portgroup –vlan-id VLAN
We might need to restart the management agents if network connectivity is not working. services.sh restart
Use Command Line Tools to Troubleshoot and Identify VLAN Configurations
Setting the Port Group VLAN ID
A VLAN ID restricts port group traffic to a logical Ethernet segment within the physical network.
- Set the VLAN ID to 4095 to allow a port group to reach port groups located on other VLAN.
- Set the VLAN ID to 0 to disable the VLAN for this port group.
Allow port groups to reach port groups located on other VLANs
esxcli <conn_options> network vswitch standard portgroup set -p <pg_name> –vlan-id 4095
Disable VLAN for Port Group
esxcli <conn_options> network vswitch standard portgroup set –vlan-id 0 -p <pg_name>
Host Networking Rollbacks
Host networking rollbacks occur when an invalid change is made to the networking configuration for the connection with vCenter Server.
Below is a list of changes that could trigger a rollback:
- Updating speed/duplex of a physical NIC
- Updating DNS/Routing settings
- Updating teaming/failover policies
- Updating traffic shaping policies for management traffic
- Updating VLANs for management traffic
- Updating MTU of management adapters
- Changing UP settings of management VMkernel adapters
- Removing management VMkernel network adapters from a standard or vDS switch
- Removing a physical NIC of a standard/vDS switch from management VMkernel
- Migrating the management VMkernel adapter from standard to vDS switch
If a network disconnects for any of these reasons, the task fails and the host reverts to the last valid configuration.
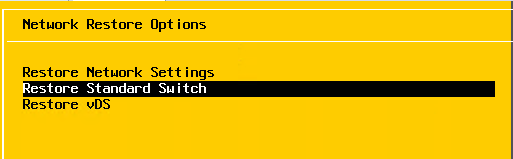
Restoring the Standard Switch
From the DCUI.
The same can be done for the distributed switch if the management network is affected by am adverse change.
Мне приходится вести довольно обширную переписку. Угадайте по какой теме
Слово “приходится” не означает, что я недоволен – мне нравится такое положение вещей.
Может быть, не всегда есть возможность ответить развернуто, а иногда ответ я и не знаю, но без внимания я не оставляю ни одного письма.
Что меня радует, иногда обращающиеся ко мне специалисты склонны и делиться знаниями. Вот как раз такой случай:
Настройка VLAN на vSphere Distributed Switch и блейд-свитче HP GbE2c Layer 2/3.
Давайте рассмотрим задачу организации сети с несколькими vlan на распределенном свитче.
Когда и кому это может понадобиться?
Представим себе следующий классический вариант – сервер с 2-мя сетевыми адаптерами. Один физический адаптер необходимо зарезервировать под служебные нужды VMWare, такие как Service Console и VMkernel. На базе же второго адаптера мы можем создать только один виртуальный свитч для проброса сети для виртуальных машин. А что делать, если виртуальным машинам необходимо пробросить как минимум две изолированных сети, а то и 3-4.
Ну или другой вариант – пусть мы озаботились заранее и купили сервер с четырьмя сетевыми интерфейсам. Но при постройке среды виртуализации сделали все правильно и один физический адаптер отвели под ServiceConsole, а другой под VMkernel Port. Остается два адаптера для проброса сетей виртуальным машинам. В большинстве случаев этого достаточно. Но вот появляется срочная задача прокинуть еще одну изолированную сеть в виртуальную среду.
Что делать? Пожалуй, самый очевидный и простой вариант – купить сетевую карту и на ее базе создать очередной виртуальный свитч. Но бывают ситуации, когда нет времени на долгий процесс закупки, или нет слотов в сервере под дополнительную сетевую карту и т.п. Вот тут на помощь нам приходят vlan. Именно настройка vlan на виртуальном и физическом свитче позволит вам через один физический интерфейс прокинуть несколько разных сетей виртуальным машинам.
Рассмотрим конкретную практическую задачу.
Есть хост ESX(блейд-лезвие), с четырьмя сетевыми интерфейсам подключенный в блейд-свитч HP GbE2c Layer 2/3. Один интерфейс ESX хоста, как описывалось выше, отведен под Service Console, а второй VMkernel Port для vMotion. Двум оставшимся интерфейсам соответствуют два распределенных свитча Distributed Switch 1&2, позволяющие вывести две группы виртуальных машины в две изолированных сети. Появляется третья группа виртуальных машин, которым необходима третья изолированная сеть. Решено настроить vlan`ы на одном из двух существующих распределенных свитчей.
Дополнительная сеть – это дополнительный трафик. После мониторинга становится понятно, что виртуальный свитч Distributed Switch2 менее нагружен и легко перенесет добавочный трафик, поэтому через него будут проброшены две сети. Distributed Switch 1 конфигурироваться не будет.
*При использовании большого количества vlan, рекомендую мониторить текущую и планировать будущую нагрузку. Можно пробросить несколько сетей с малой нагрузкой через один виртуальный свитч, а второй оставить под сеть с основным трафиком. Если же виртуальные машины генерируют примерно одинаковый трафик в каждую сеть, то следует размазывать нагрузку и конфигурировать по несколько vlan на каждый виртуальный свитч. Всегда помним, что каждый виртуальный свитч опирается на физический интерфейс с ограниченной пропускной способностью.
Теперь о прикладной задаче. При пробросе трех сетей для виртуальных машин это выглядит так:
Настройка очень проста. Каждая группа портов виртуального распределенного свитча, соответствующая отдельной изолированной сети, должна находиться в отдельном vlan`е. Порты-аплинки между свитчами, должны быть сконфигурированы как tagged порты (т.е. могут пропускать через себя трафик разных vlan`ов).
Для распределенного коммутатора Distributed Switch 2 необходимо сделать следующие настройки:
1. Создаем 2-е группы портов на одном распределенном коммутаторе.
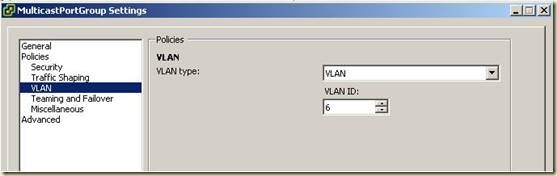
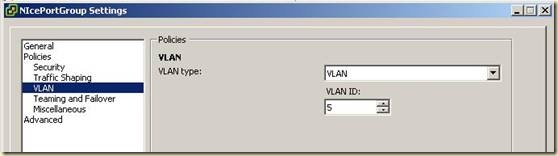
2. В настройках 1-й группы портов в пункте VLAN указать VLAN Type = VLAN и задать VLAN ID (для текущего примера VID=6).
3. В настройках 2-й группы портов в пункте VLAN указать VLAN Type = VLAN и задать VLAN ID (для текущего примера VID=5).
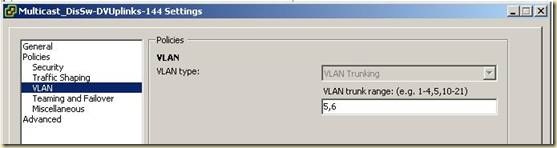
4. В настройках Uplink-группы в пункте VLAN указать VLAN Type = VLAN Trunking. В поле VLAN trunk range указать VLAN ID, для vlan, созданных выше.
На этом вся конфигурации виртуальной среды завершена. Остается настроить физический блейд-свитч.
Ниже приведена настройка для свитча HP GbE2c Layer 2/3. Хосты ESX подключены к внутренним портам 1,2,9,10. Порт 21, 23 внешние аплинки в разные сети.
Включаем тегирование и задаем default vlan внутренних портов.
/cfg/port 1
tag e
pvid 5
/cfg/port 2
tag e
pvid 5
/cfg/port 9
tag e
pvid 5
/cfg/port 10
tag e
pvid 5
Создаем Vlan, включаем их, задаем имя и порты
/cfg/l2/vlan 5
ena
name “…”
def 1 2 9 10 21
/cfg/l2/vlan 6
Ena
name “…”
def 1 2 9 10 23
На этом настройка закончена.
thx Kirill Shusherin.
Выполняем настройку групп агрегации каналов (Link Aggregation Groups) с использованием LACP на распределённом коммутаторе vSphere (vSphere Distributed Switch)
В данной статье мы рассмотрим пример настройки агрегации для VMware vSAN.
Агрегация каналов позволяет объединять несколько сетевых подключений параллельно для увеличения пропускной способности и обеспечения избыточности. Когда группирование сетевых адаптеров настроено с помощью LACP, происходит распределение нагрузки сети vSAN по нескольким аплинкам. Однако это происходит на сетевом уровне, а не через vSAN.
Ознакомиться с общей информацией об агрегировании каналов можно в одной из моих статей про Агрегирование каналов Cisco
В то время как объединение каналов является очень свободным термином, для целей этой статьи основное внимание будет уделяться протоколу управления объединением каналов или LACP. В то время как IEEE имеет свой собственный стандарт LACP 802.3ad, некоторые производители разработали проприетарные типы LACP. Например, PAgP (протокол агрегации портов) похож на LAG, но является собственностью Cisco. Таким образом, руководство поставщика имеет решающее значение, и следует всегда придерживаться лучших практик поставщиков.
Основным выводом при реализации LACP является то, что он использует отраслевой стандарт и реализован с использованием port-channel. Там может быть много алгоритмов хеширования. Политика группы портов vSwitch и конфигурация канала порта (хэш) должны совпадать и соответствовать.
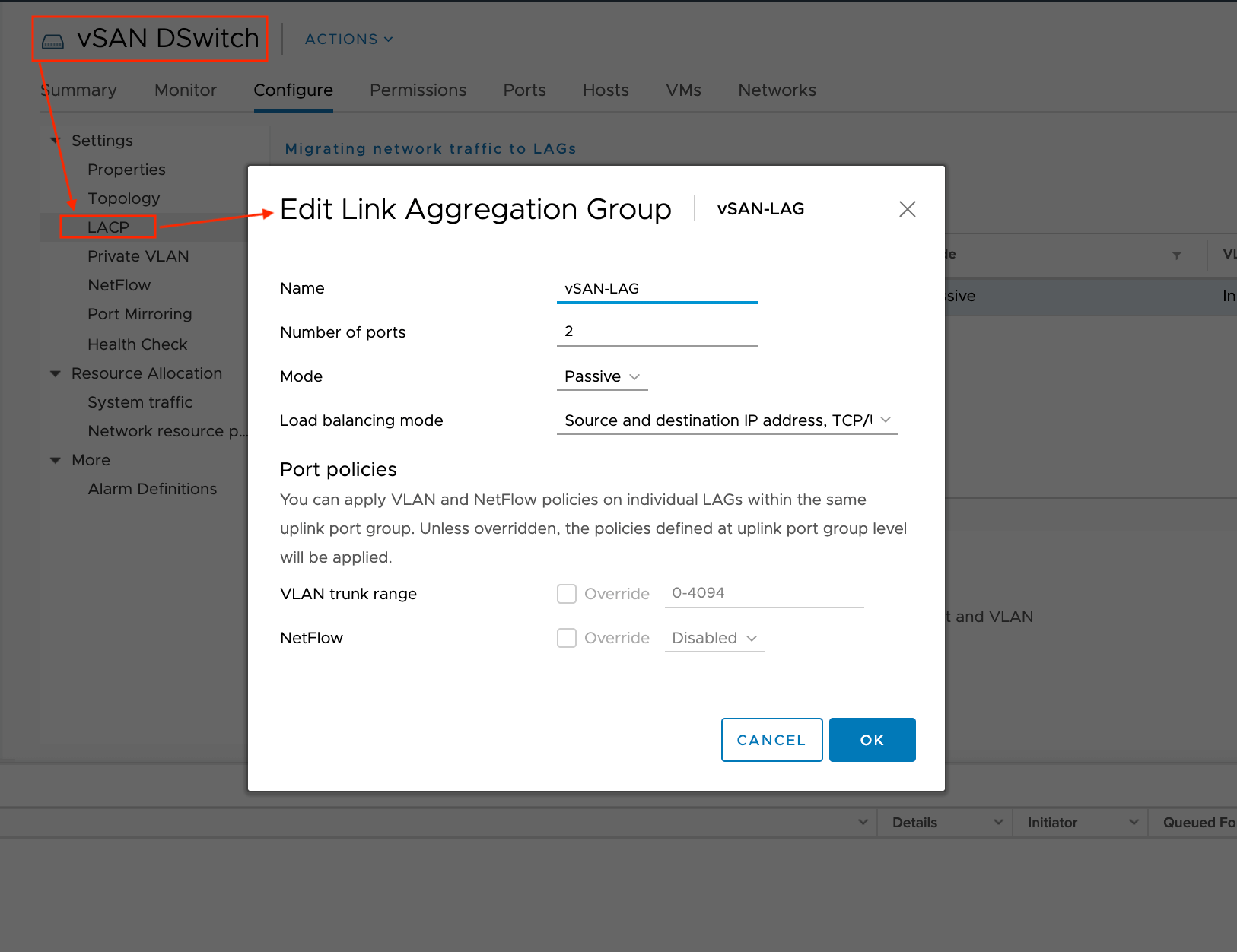
Добавляем LAG
Переходим в наш распределённый коммутатор и создаём новую группу агрегации. Указываем имя, количество портов агрегации, режим работы, а так же режим балансировки.
Активный режим (Active) — устройства немедленно отправляют сообщения LACP, когда порт подходит. Конечные устройства с включенным LACP отправляют/получают кадры, называемые сообщениями LACP, друг другу для согласования создания LAG.
Пассивный режим (Passive) — переводит порт в состояние пассивного согласования, в котором порт отвечает только на полученные сообщения LACP, но не инициирует согласование.
Обратите внимание, что если хост и коммутатор находятся в пассивном режиме, LAG не будет инициализирован, так как нет активной части, которая инициировала бы соединение.
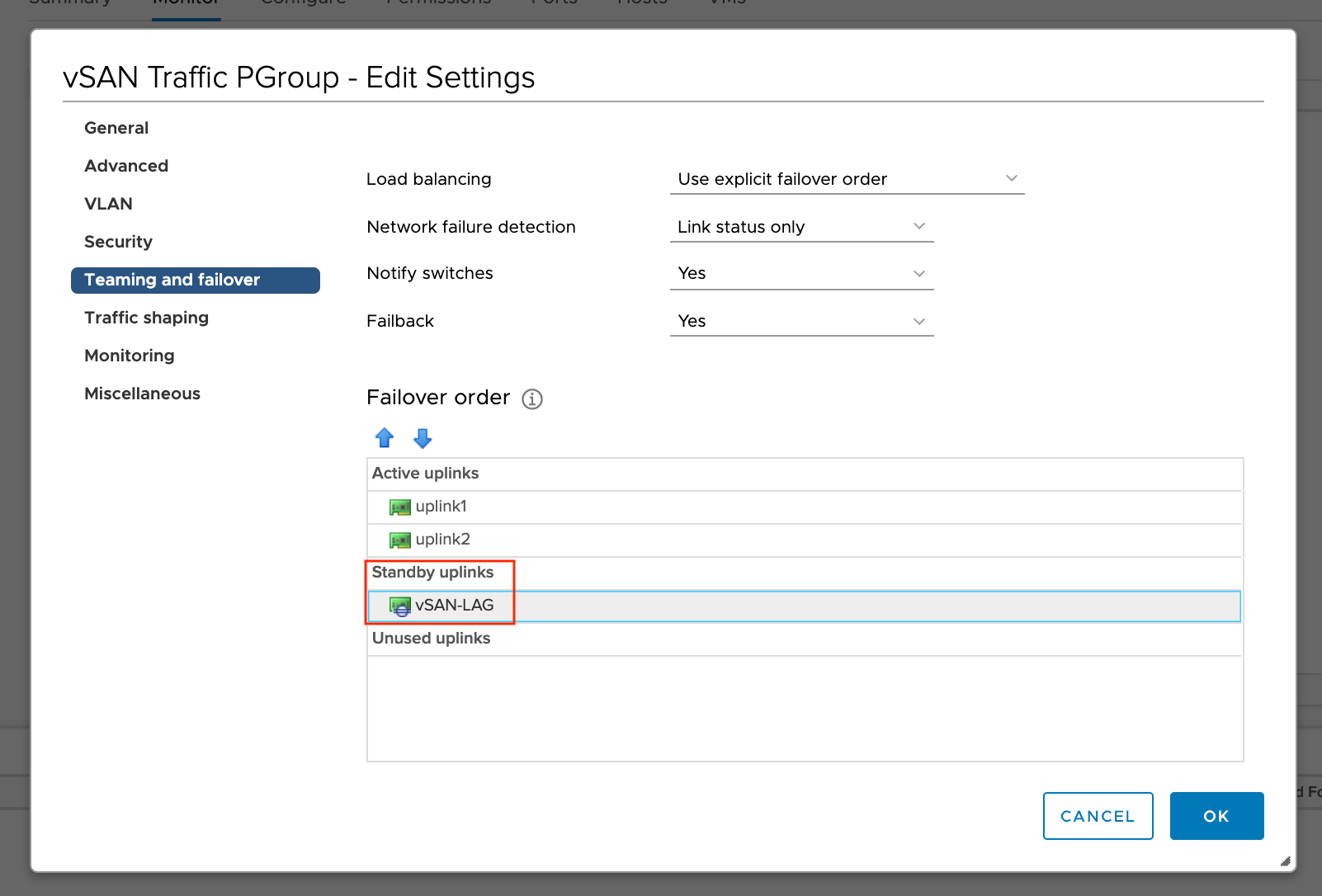
Назначаем LAG для PortGroup
Назначаем созданную группу агрегации необходимой порт группе и переводим LAG в режим ожидания (Standby).
При подтверждение изменений появится предупреждающее окно, о том, что использование комбинации активных аплинков и LAG в режиме ожидания поддерживается только для переноса физических адаптеров между LAG и автономными аплинками. Нажимаем ОК.
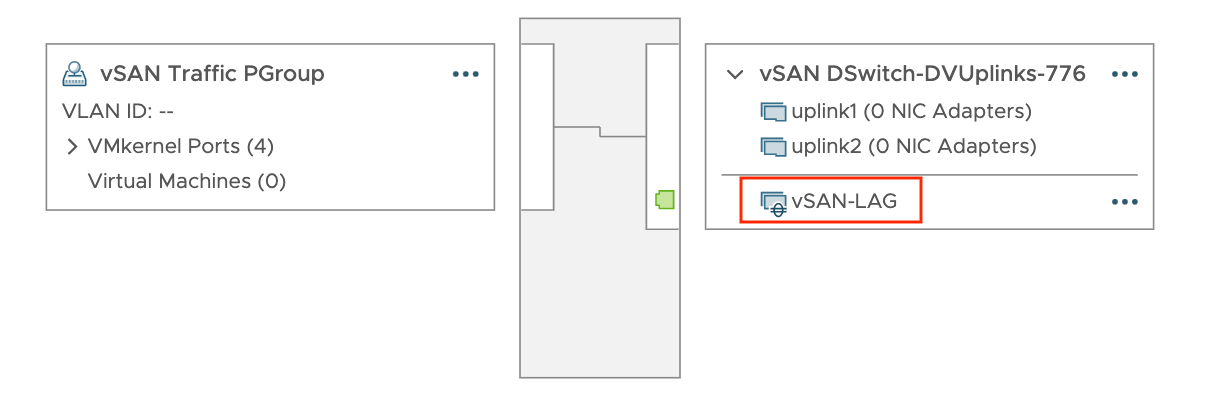
Проверяем, что LAG добавился.
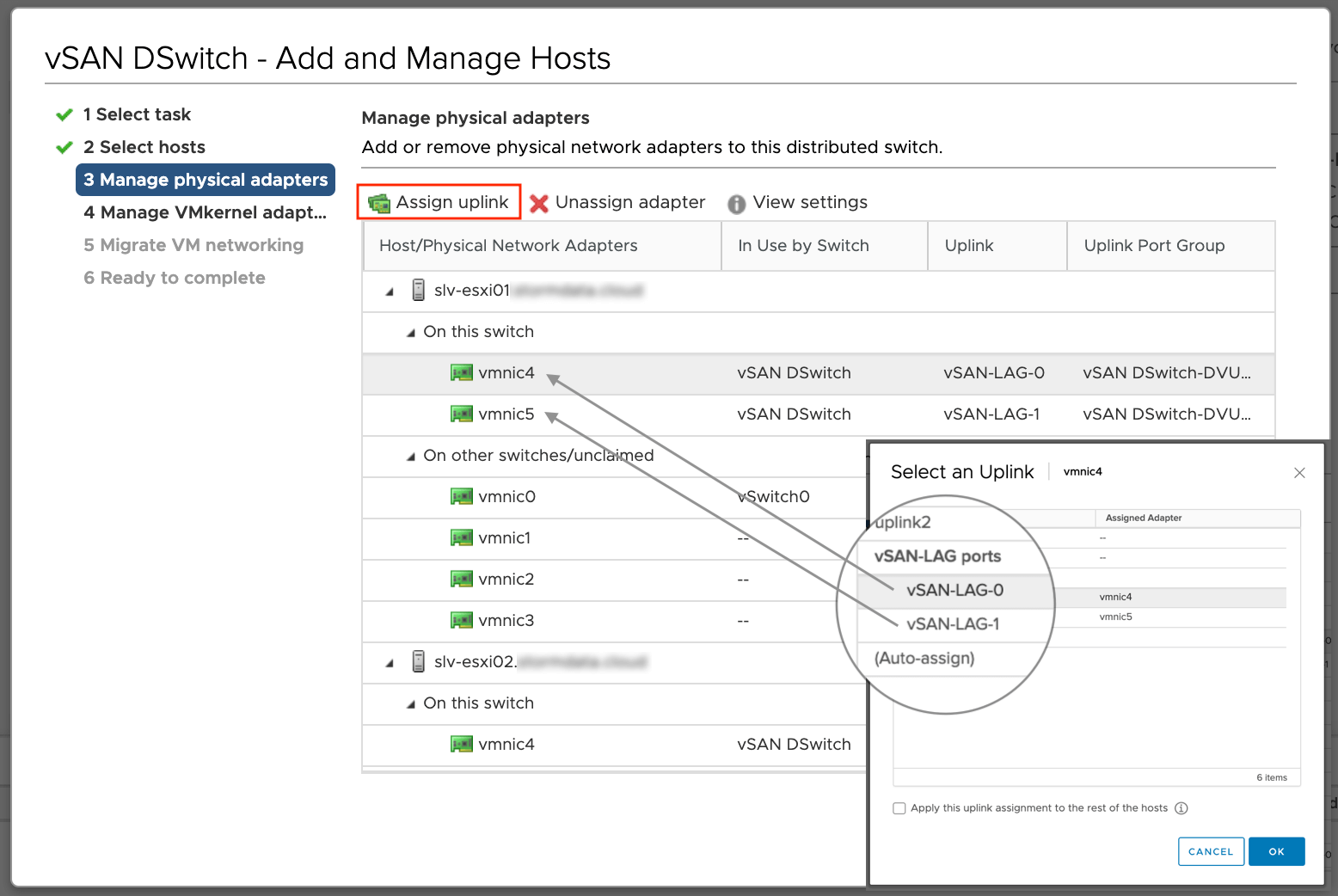
Настраиваем адаптеры на хостах
Переходим в меню “Добавление и редактирование хостов” нашего распределённого коммутатора, выбираем пункт “Редактирование хостов”, добавляем хосты, которые подключены к данному distributed switch.
Назначаем LAG-порты к соответствующим vmnic. По аналогии назначаем порты для других хостов.
Создаём PortChannel на Cisco
Тема конфигурации PortChannel затронута в одной из моих статей по настройке объединения портов (bonding) Cisco IOS и CentOS LACP
Рассмотрим пример нашего тестового стенда:
4900m(config)
4900m(config-if-rang)
4900m(config-if-rang)
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2
4900m(config-if-range)
interface Port-channel2
description slv-esxi01[vSAN-LAG]
switchport
switchport access vlan 2
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast trunk
spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1
description slv-esxi01[vSAN-LAG]_Uplink1
switchport access vlan 2
switchport mode access
channel-group 2 mode active
spanning-tree portfast trunk
spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/2
description slv-esxi01[vSAN-LAG]_Uplink2
switchport access vlan 2
switchport mode access
channel-group 2 mode active
spanning-tree portfast trunk
spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
Проверьте какой алгоритм балансировки используется на физическом коммутаторе.
4900m
port-channel load-balance src-dst-ip
Проверяем состояние PortChannel.
C4900m
Flags: D - down P - bundled in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
M - not in use, minimum links not met
u - unsuitable for bundling
w - waiting to be aggregated
d - default port
Number of channel-groups in use: 4
Number of aggregators: 4
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------
2 Po2(SU) LACP Te1/1(P) Te1/2(P)
3 Po3(SU) LACP Te1/3(P) Te1/4(P)
4 Po4(SU) LACP Te1/5(P) Te1/6(P)
5 Po5(SU) LACP Te1/7(P) Te1/8(P)
Переводим LAG в активный режим
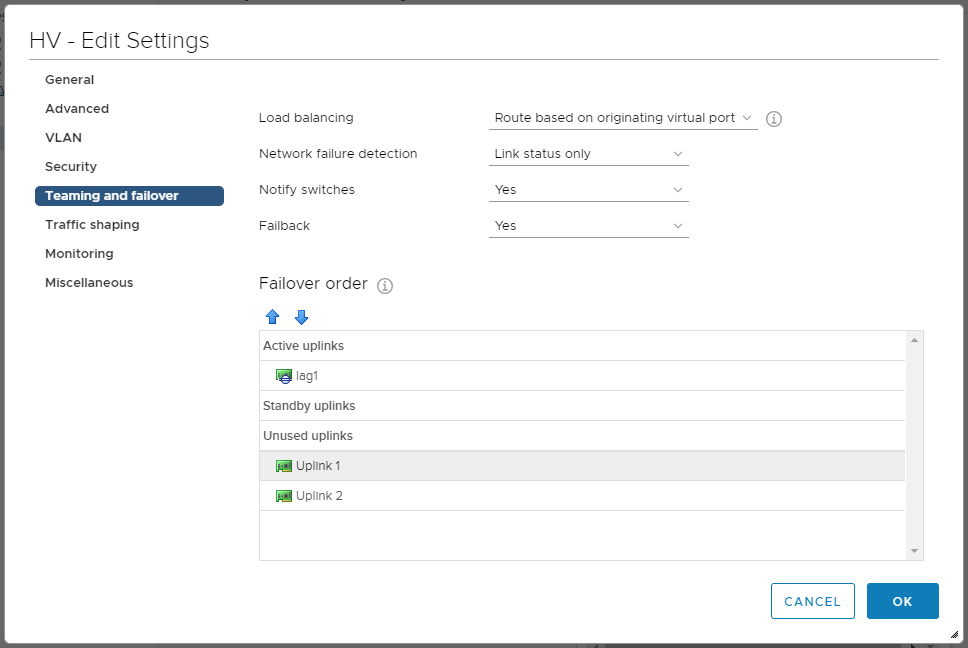
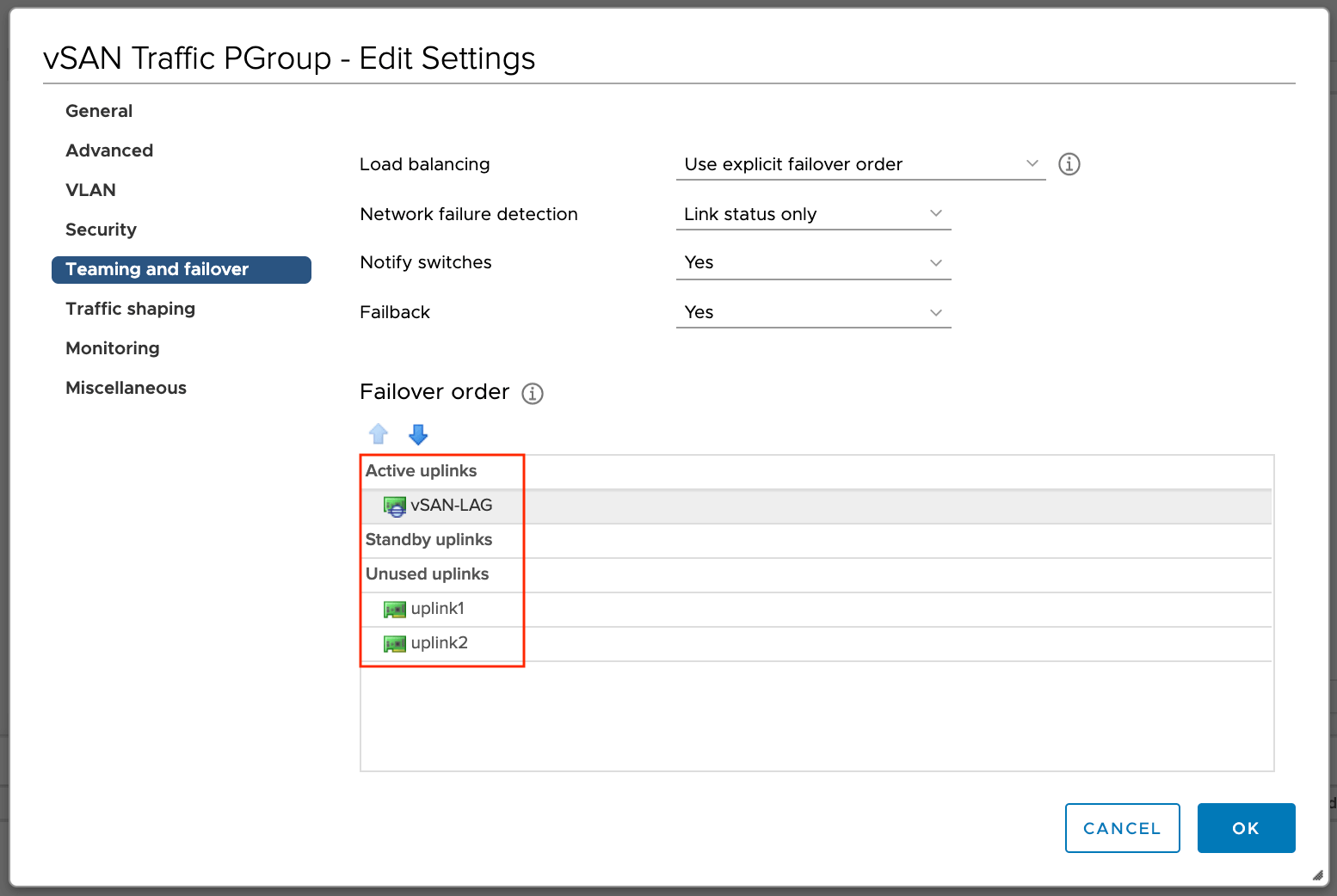
Возвращаемся к настройкам нашего распределённого коммутатора, переходим в настройки порт группы и переводим LAG в режим Active, а автономные аплинки — в раздел неиспользуемых.
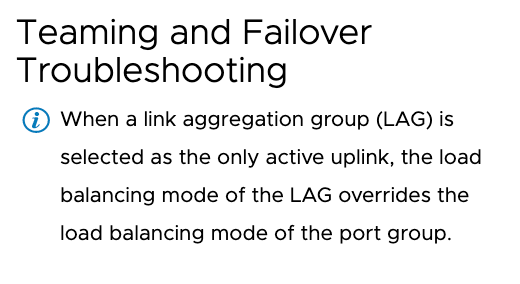
Обратите внимание, что когда LAG выбран, как основной аплинк, режим балансировки порт группы наследуется от режима балансировки, указанного в LAG, о чём нас дополнительно информируют.
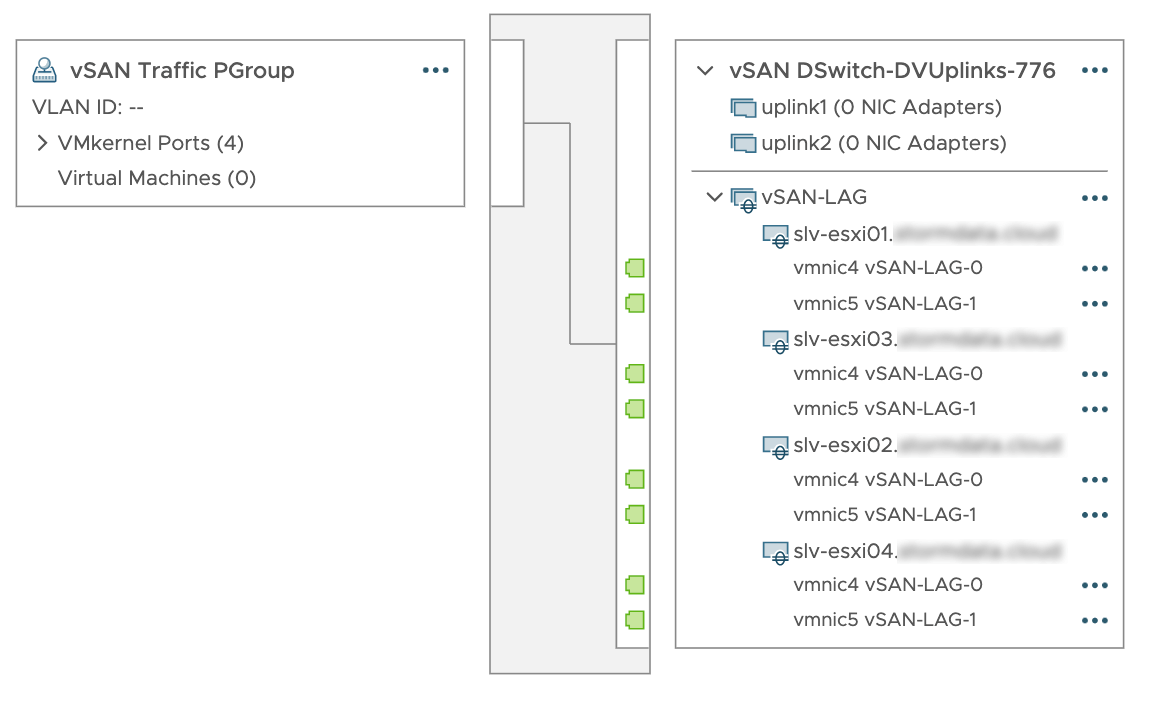
Ещё раз проверяем топологию сети.
Особое внимание хочу уделить тому факту, что данная настройка не увеличивает пропускную способность, а выполняет роль отказоустойчивости и балансировки нагрузки.
Источники:
LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
VMware® vSAN Network Design
I was doing some testing of the new vSphere 5.1 features and came across something odd with the new Distributed Switch Health Check feature with Cisco UCS.
In my lab I have 4 ESXi 5.1 hosts running on older B200 M1s with VIC M81KR adaptors.
On my ESXi service profiles I have 8 vNICs; 2 for management, 2 for vMotion 2 for IP storage and 2 for VM networking.
Each pair of vNICs has 1 in Fabric A and 1 in Fabric B
In VMware there are 3 standard vSwitches and 1 Distributed vSwitch for VM networking VLANs.
On the Distributed switch I enabled the new Health Check feature via the new vSphere Web Client.
About a minute later the following Alerts were triggered.
“vSphere Distributed Switch MTU supported status”
“vSphere Distributed Switch vlan trunked status”
The first thing I did was double check my vNICs to make sure they had the same VLANs trunked and to make sure my MTU settings were the default of 1500.
This got thinking that it must be something to do with the way UCS Fabric Interconnects handle vNICs or something to do with how End Host mode works. I then remembered the new option on the Network Control policy that controls the VLANs that vNIC MAC addresses get registered on.
I was already using a custom Network Control policy to enable CDP on ESXi vNICs.
By default the Network Control policy is set to only register vNIC MACs on the native VLAN. This is set this way to reduce the size of the MAC address tables on the Fabric Interconnects.
I changed this policy to register on all host VLANs and about a minute later the Health Check alerts cleared.
The max MAC addresses per Fabric Interconnect in UCS firmware 2.0/2.1 – http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/sw/configuration_limits/2.0/b_UCS_Configuration_Limits_2_0.html
6100s = 13800
6200s = 20000
Those are fairly high limits so I don’t think most folks would run into that limit if the Network Control policy is changed to all host vlans.
This posting is ~5 years years old. You should keep this in mind. IT is a short living business. This information might be outdated.
During the replacement of some VMware ESXi hosts at a customer, I discovered a recurrent failure of the vSphere Distributed Switch health checks. A VLAN and MTU mismatch was reported. On the physical side, the ESXi hosts were connected to two HPE 5820 switches, that were configured as an IRF stack. Inside the VMware bubble, the hosts were sharing a vSphere Distributed Switch.
The switch ports of the old ESXi hosts were configured as Hybrid ports. The switch ports of the new hosts were configured as Trunk ports, to streamline the switch and port configuration.
Some words about port types
Comware knows three different port types:
- Access
- Hybrid
- Trunk
If you were familiar with Cisco, you will know Access and Trunk ports. If you were familiar with HPE ProCurve or Alcatel-Lucent Enterprise, these two port types refer to untagged and tagged ports.
So what is a Hybrid port? A Hybrid port can belong to multiple VLANs where they can be untagged and tagged. Yes, multiple untagged VLANs on a port are possible, but the switch will need additional information to bridge the traffic into correct untagged VLANs. This additional information can be MAC addresses, IP addresses, LLDP-MED etc. Typically, hybrid ports are used for in VoIP deployments.
The benefit of a Hybrid port is, that I can put the native VLAN of a specific port, which is often referred as Port VLAN identifier (PVID), as a tagged VLAN on that port. This configuration allows, that all dvPortGroups have a VLAN tag assigned, even if the VLAN tag represents the native VLAN of a switch port.
Failing health checks
A failed health check rises a vCenter alarm. In my case, a VLAN and MTU alarm was reported. In both cases, VLAN 1 was causing the error. According to VMware, the three main causes for failed health checks are:
- Mismatched VLAN trunks between a vSphere distributed switch and physical switch
- Mismatched MTU settings between physical network adapters, distributed switches, and physical switch ports
- Mismatched virtual switch teaming policies for the physical switch port-channel settings.
Let’s take a look at the port configuration on the Comware switch:
# interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/9 port link-mode bridge description "ESX-05 NIC1" port link-type trunk port trunk permit vlan all stp edged-port enable #
As you can see, this is a normal trunk port. All VLANs will be passed to the host. This is an except from the display interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/9 output:
PVID: 1 Mdi type: auto Port link-type: trunk VLAN passing : 1(default vlan), 2-3, 5-7, 100-109 VLAN permitted: 1(default vlan), 2-4094 Trunk port encapsulation: IEEE 802.1q
The native VLAN is 1, this is the default configuration. Traffic, that is received and sent from a trunk port, is always tagged with a VLAN id of the originating VLAN – except traffic from the default (native) VLAN! This traffic is sent without a VLAN tag, and if frames were received with a VLAN tag, this frames will be dropped!
If you have a dvPortGroup for the default (native) VLAN, and this dvPortGroup is sending tagged frames, the frames will be dropped if you use a “standard” trunk port. And this is why the health check fails!
Ways to resolve this issue
In my case, the dvPortGroup was configured for VLAN 1, which is the default (native) VLAN on the switch ports.
There are two ways to solve this issue:
- Remove the VLAN tag from the dvPortGroup configuration
- Change the PVID for the trunk port
To change the PVID for a trunk port, you have to enter the following command in the interface context:
[ToR-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/9] port trunk pvid vlan 999
You have to change the PVID on all ESXi facing switch ports. You can use a non-existing VLAN ID for this.
vSphere Distributed Switch health check will switch to green for VLAN and MTU immediately.
Please note, that this is not the solution for all VLAN-related problems. You should make sure that you are not getting any side effects.
- Author
- Recent Posts
vcloudnine.de is the personal blog of Patrick Terlisten. Patrick has a strong focus on virtualization & cloud solutions, but also storage, networking, and IT infrastructure in general. He is a fan of Lean Management and agile methods, and practices continuous improvement whereever it is possible.
Feel free to follow him on Twitter and/ or leave a comment.
Go to vmware
VLAN trunking not working with distributed switch
ok so we are running 5.5 with the vdswitch running in 5.5 mode. We have 4 DvUplinks attached, with a single portgroup and 1 VLAN per portgroup, and it works perfectly fine as expected.
What I am trying to do is, have 1 single portgroup for all vlans that way I don’t have to make like 20 or so portgroups (1 per VLAN). I have set this up, but soon as i switch the portgroup VLAN settings over to VLAN Trunking and add the VLAN or let it use all VLANs my guest networking breaks until I set it back to a single VLAN per portgroup.
I have verified that the switchports on the physical switch are trunked and with dot1q.
Is this even possible?
Default alarm to monitor changes in vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN trunked status
english: Default alarm to monitor changes in vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN trunked status
german: Standardalarm zum Überwachen von Änderungen im VLAN-Trunk-Status des vSphere Distributed Switch
french: Alarme par défaut pour contrôler les modifications de l’état de liaison VLAN vSphere Distributed Switch.
spanish: Alarme par défaut pour contrôler les modifications de l’état de liaison VLAN vSphere Distributed Switch.
korean: vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN 트렁킹 상태의 변경 내용을 모니터링하는 기본 경보입니다.
simplified chinese: 监控 vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN 中继状态的更改的默认警报
traditional chinese: 监控 vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN 中继状态的更改的默认警报
japanese: vSphere Distributed Switch VLAN のトランキング ステータスでの変化を監視するデフォルト アラーム
Display all Alarms
This website uses cookies to give you the best online experience. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Accept
Сегодня создадим Distributed Switch на vCenter 6.7.
Идея распределённого коммутатора заключается в следующем — создать один коммутатор, который будет обслуживать сразу несколько гипервизоров. Вы получаете один единственный логический коммутатор, существующий сразу на всех серверах ESX(i). Распределённый — потому что он рулится из одной точки — vCenter, а распределяется на все хосты. Если vCenter выйдет из строя, то коммутатор продолжит работу. Мы просто потеряем возможность настраивать коммутатор.
Распределённый коммутатор имеет несколько больший функционал в отличие от обычного. Ключевые моменты:
- Private VLAN.
- Bi-directional Traffic Shaping.
- Network VMotion.
Ссылки
Установка vCenter 6.7
vCenter 6.7 — создаём Datacenter
vCenter 6.7 — создаём Cluster
Добавление хоста ESXi 6.0 в vCenter 6.7 c LACP через UI
vCenter 6.7 — добавляем LAG (Link Aggregation Group) в Distributed Switch
Создаём Distributed Switch
Будем считать, что вы уже знаете зачем собираетесь устанавливать Distributed Switch. Ставим.
Заходим в vCenter, переходим в раздел Networking. Нажимаем правой кнопкой на выбранный кластер,выбираем Distributed Switch > New Distributed Switch.
Открывается мастер создания распределённого коммутатора. Мы на вкладке Name and location.
Указываем название, NEXT. Мы на вкладке Select version.
Выбираем версию коммутатора. Коммутатор 6.0 не поддерживает хосты версии 6.5. Так что я выбираю последнюю версию. NEXT. Мы на вкладке Configure settings.
Выбираем количество аплинков. Можно включить Network I/O Control. Можно выбрать галку для создания дефолтной port group и указать её название. Я буду использовать эту группу для управления гипервизорами и vCenter, называю HV. NEXT. Мы на вкладке Ready to complete.
Проверяем настройки и нажимаем FINISH. Distributed Switch создан. Давайте его настроим. Нажимаем правой кнопкой на коммутатор — Settings > Edit Settings. Переключаемся в раздел Advanced. Находим блок Discovery protocol. Type — ставим в Cisco Discovery Protocol. Operations — Both.
OK.
Настройка LACP
Отдельная инструкция по настройке LACP на Distributed Switch:
vCenter 6.7 — добавляем LAG (Link Aggregation Group) в Distributed Switch
Выбираем Distributed Switch в UI. Открываем Configure > Settings > LACP.
Нажимаем кнопку +NEW. Открывается мастер создания группы LAG.
Указываем название, я оставляю по умолчанию — lag1.
В поле Number of ports указываем количество линков. В моей практики встречалось 4 гигабитных линка, 2 десятигигабитных. Всё зависит от вашей конфигурации.
Mode — Passive. Здесь могут быть варианты в разных сетях.
Load balancing mode — я ставлю Source and destination IP address. Если вы используете Cisco, то это оправдано, иначе MAC адрес сетевухи может скакать с одного интерфейса на другой.
OK.
LACP создан.
Настройка Default Port Group
Выбираем созданную вместе с коммутатором port group, мы назвали её HV. Нажимаем правой кнопкой — Edit Settings.
Открывается мастер настройки. Мы в разделе General. Port binding ставим в Static binding. Port allocation — Elastic.
Переключаемся на раздел VLAN. Эту группу портов мы будем использовать для управления хостами, поэтому настраиваем такой же VLAN, в котором живут ESXi и vCenter.
Переключаемся на раздел Teaming and failover.
По умолчанию у Port Group LACP не используется, включим. Перетаскиваем lag1 вверх, а аплинки вниз.
OK. Сохраняем. Каждый раз потом при создании новой группы портов нужно настраивать LACP для этой группы. Можно это делать прямо в процессе создания.
Добавление хоста в Distributed Switch
Добавляем хост в vCenter, если он ещё не добавлен:
Добавление хоста ESXi 6.0 в vCenter 6.7 c LACP через UI
Нажимаем правой кнопкой на Distributed Switch — Add and Manage Hosts.
Открывается мастер. Мы попадаем в раздел Select task.
Выбираем Add hosts. NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Select hosts.
Нажимаем кнопку + New hosts. Открывается окно со списком доступных хостов. У меня пока один — hv00.
Выделяем хост галкой, OK.
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Manage physical adapters.
vmnic1 цепляем кнопкой Assign upling к lag1-1.
Наша задача добиться того, чтобы хост одной ногой был в старом коммутаторе, а второй — в новом. NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Manage VMkernel adapter.
Пока ничего не меняем, пусть vmk0 будет на старом локальном коммутаторе. NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Migrate VM networking.
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Ready to complete.
FINISH. Ждём когда хост добавится.
Снова нажимаем правой кнопкой на Distributed Switch — Add and Manage Hosts.
Открывается мастер. Мы попадаем в раздел Select task.
Теперь выбираем пункт Manage host networking. NEXT. Доходим до раздела Manage VMkernel adapter.
Выбираем vmk0, нажимаем Assign port group.
Выбираем наш Port Group с названием HV, который находится в управляющем VLAN. OK.
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Migrate VM networking.
NEXT. Мы попадаем в раздел Ready to complete.
FINISH. Управление хостом должно перейти на Distributed Switch.
Снова редактируем сеть хоста.
vmnik0 привязываем к lag1-0.
OK.
NEXT. NEXT. NEXT. FINISH.
Теперь можно зайти в хост — Configure > Networking > Virtual switches и удалить локальный vSwitch0.
Потом заходим в хост — Configure > Networking > VMkernel adapters, выбираем vmk0, редактируем, разрешаем галкой vMotion.
OK.
Резюме
Итак, мы создали Distributed Switch, перенесли в него хосты, настроили LACP, разрешили vMotion.