-
#1
hi there!
Saturday in my realm is a revision time. I’ve just woken up a bit troubled about this haunting question. What is the situation I might pose them? Are they interchangeable? I tried different configurations but I’m not sure if it makes any sense.
1. Where were you yesterday? (when I rang, when I needed you…)
2. Where did you be yesterday? ( ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ??)
cheers
-
#2
The second sentence is not possible in English. The verb to be cannot take a do support in Standard English.
-
#3
I had a sneaking suspicion that it was incorrect… I’ve never seen this form, still to be is a verb like many other.
-
#4
I would actually say the opposite :»to be» is unlike many other verbs; it is quite irregular in many ways. Nat’s comment is one of those ways.
-
#5
There are a set of verbs in English which behave a little bit differently than other verbs.
They consist of auxiliaries, modals, numerous other categories, but as a collective term we can call these raising verbs (As they would be referred to in linguistics).
One of the characteristics of raising verbs is that they don’t take do-support in questions. I won’t go into syntactic theory here but it’s best to imagine that do-support applies to nearly all verbs, but some verbs can ‘raise themselves‘ out of this area, so do-support doesn’t affect these verbs.
You can see this through some examples here:
*Did you can do it?
Could you do it?
*Did he should go?
Should he have gone?
Here question formation is done by inversion, and not do-support.
‘To be‘ always raises itself out of the way where do-support applies, and ‘to have’ does as well (when not used in its normal sense of possession). That’s why do-support isn’t used in:
Have I told you?
Were have you been?
But ‘have’ is a little bit odd in that when it is not grammatical, it behaves in a non-raising fashion:
Did you have a car?
There are also some instances of raising when it is not used grammatically, like in sentences such as «Have you any idea what you’ve done?«, but these are always alternatives to the expected non-raising forms (where do applies), like in «Do you have any idea what you’ve done?«. Anyway ‘have‘ is a bit of a rebel when it comes to being classified grammatically, but the idea is that ‘to be‘, being ‘irregular’ as Julian said, is always raising and this explains why you can’t use it with do in the way you asked.
-
#6
2. Where did you be yesterday? ( ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?
Miraculously, while being totally incorrect and unacceptable, your sentence is totally understandable
Многие студенты часто меня спрашивают – как правильно употреблять was, were и did, как правильно сказать I was или I were / they was или they were?
В этой статье вы найдете ответы на эти вопросы, предложения с was, were, did, и познакомитесь с правилом использования was, were и did в английском языке.
Что такое was и were?
Was и were – это формы прошедшего времени глагола to be (быть) – был/были.
В чем же разница?
Разница в том, что was употребляется с единственным числом (с местоимениями I, he, she, it), а were – со множественным (you, we, they):
I was – я был, he was – он был, she was – она была.
- I was there. – Я был там.
- They were happy. – Они были счастливы.
Аналогично was/were используются в вопросах:
- Was she at school? – Она была в школе?
- Were you a student? – Ты был студентом?
И в отрицательных предложениях:
- He wasn’t hungry. – Он не был голоден.
- We weren’t at the beach. – Мы не были на пляже.
В прошедшем простом времени was и were – всегда единственные глаголы в предложении.
Did – это форма прошедшего времени глагола do (делать).
В утвердительной форме он выступает только как основной глагол и имеет одинаковую форму для всех лиц.
- I did exercises. – Я делал упражнения.
- We did sport yesterday. – Мы занимались спортом вчера.
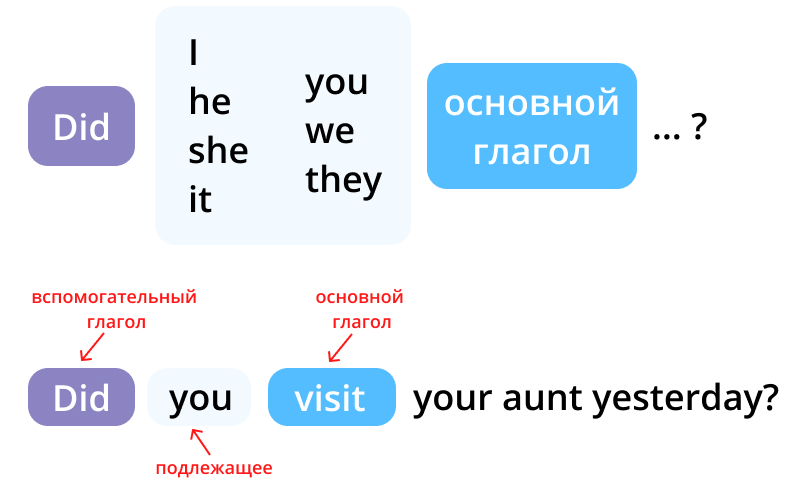
В вопросах и отрицательных предложениях в прошедшем простом времени Past Simple глагол did используется как вспомогательный (то есть он только помогает строить вопрос и отрицание, и на русский язык не переводится). Главным в предложении является основной (смысловой) глагол.
- Did you see her? – Ты видел ее?
- Did he drive the car? – Он вел машину?
- I didn’t go to school yesterday. – Я не ходил в школу вчера.
- They didn’t call last night. – Они не звонили вчера вечером.
Что использовать – DID или WAS / WERE?
В утвердительном предложении употребление этих глаголов зависит от смысла.
Did употребляется в значении “делал(а)”:
- I did it yesterday. – Я делал это вчера.
Was и were употребляются в значении “был / были”:
- I was there. – Я был там.
- They were here. – Они были здесь.
В вопросах и отрицаниях мы смотрим на то, есть ли другие глаголы в предложении. Если нет – используется was/were:
- Were you a nurse? – Ты была медсестрой?
- Was she in the office? – Она была в офисе?
Если есть основной глагол, то в вопросе и отрицании используется вспомогательный did:
- Did you read yesterday? – Ты читал вчера? (основной глагол – read)
- I didn’t sleep last night. – Я не спал прошлой ночью. (основной глагол – sleep)
Если вопрос начинается с was/were, то и краткий ответ должен содержать was/were:
- Was she sick yesterday? – Она была больной вчера?
- Yes, she was. – Да.
Если вопрос начинается с did, то и краткий ответ содержит did:
- Did you call me? – Ты звонил мне?
- No, I didn’t. – Нет.
Другие случаи употребления WAS / WERE
Was и were также употребляются в составе Past Continuous (прошедшего длительного времени).
- I was writing at 5 pm yesterday. – Я писал в 5 вечера вчера.
- We were walking when you called. – Мы гуляли, когда ты позвонил.
Past Simple Passive (пассивный залог в простом прошедшем времени)
В пассивном залоге was/were + V3/ V-ed (V3 – глагол в третьей форме) употребляется, когда мы говорим, что что-то было сделано в прошлом.
- The dinner was cooked by my cousin. – Ужин был приготовлен моей кузиной.
- The letters were written by the teacher. – Буквы были написаны учителем.
Was, Were or Did?
Выберите один правильный вариант:
Вам может быть интересно:
- Упражнения на TO BE в прошедшем времени (was/were)
- Упражнения на Past Simple с ответами
- Тест на Past Simple с ответами
- Past Simple или Past Continuous: упражнения с ответами
Официальный сайт автора данного курса лекций: https://eng-professor.ru/
Закончились такие нехитрые, а теперь начинаются уже серьезные.
193-е.
Давайте так, я вам сейчас назову грамматику, а вы дома еще раз ее посмотрите.
1. «Nina (to celebrate) her birthday yesterday – Вчера Нина отмечала свой день рождения»: «Nina celebrated…» — Past Indefinite Tense.
«Her room looked beautiful, there (to be) many flowers in it – Ее комната выглядела прекрасно, там было множество цветов»: «…, there was…». Past Indefinite
«When I (to come) in, somebody (to play) the piano, two or three pairs (to dance) – Когда я пришел кто-то игра на пианино, две или три пары танцевали»: «When I came in, somebody was playing the piano, … were dancing.».
2. «Listen! Somebody (to play) the piano – Послушайте! Кто-то играет на пианино»: «… Somebody is playing…» — Present Continuous Tense.
3. «I (to like) music very much – Я очень люблю музыку»: «I like music…» — Present Indefinite Tense.
4. «When I (to look) out of the window, it (to rain) heavily and people (to hurry) along the streets – Когда я выглянул из окна шел сильный дождь и люди спешили вдоль улиц»: «When I looked…, it was raining… people were hurrying…» — потому что всё это было, когда я глядел.
5. «What you (to do) at seven o’clock yesterday? – Что ты делал вчера в семь часов?»: «What were you doing at…?» — Past Continuous Tense.
«- I (to have) supper – Я ужинал»: «I was having supper».
6. «When I (to come) home yesterday, I (to see) that all my family (to sit) round the table – Когда я пришел вчера домой, я увидел, что вся моя семья сидит вокруг стола»: «When I came…, I saw… were sitting…».
«Father (to read) a letter from my uncle who (to live) in Kiev – Отец читал письмо от моего дяди, который живет в Киеве»: «Father was reading… uncle who lived in Kiev». Хотя по-русски мы говорим «живет», а переведем на английский Past Indefinite’ом, потому что Sequence (согласование времен). Хотя глагол «жить» можно делать и Past Continuous’ом. Наше право – «жить», «учиться», «работать» можно и Past Indefinite’ом и Past Continuous’ом, но нельзя Present’ом никаким, потому что Sequence накладывает свою лапу. По-русски «который живет», он же и сейчас живет, не только вчера жил.
7. «Where you (to be) yesterday? – Где ты был вчера?»: «Where were you yesterday?».
«— I (to be) at home the whole day – Я был дома целый день»: «I was at home…». Несмотря на то, что «весь день – явный Past Continuous», но глагол be говорит, что он ему не интересен. И мы оставляем его в Past Indefinite.
«— How strange. I (to ring) you up at two o’clock, but nobody (to answer) – Как странно. Я звонил тебе в два часа, но никто не ответил»: «… I was ringing you up…., nobody answered». Вот это интересный момент, я бы поставил «Я звонил» в Past Continuous, потому что точное указание времени, а «никто не ответил» — это я бы уже взял Past Indefinite, потому что «отвечать» — это не процесс, а «звонить» — я держал трубку, набирал номер.
«— Oh, I (to be) in the garden – Я был в саду»: «Oh, I was in…».
«I (to read) your book and (not to hear) the telephone – Я читал твою книгу и не слышал телефон»: «I was reading… and did not hear…». «Слышал» вроде можно тоже рассматривать как процесс, но hear – ментальный глагол и в Past Continuous’е он не работает.
8. «What you (to do) at five o’clock yesterday? Что ты делал вчера в пять часов?»: «What were you doing..?».
«— I (to work) in the library – Я работал в библиотеке»: «I was working…» — Past Continuous.
«— I (to be) there, too, but I (not to see) you – Я тоже там был, но тебя не видел»: «I was…. Idid not see you». Хотя он имеет в виду, что он в пять же часов там был, но be и see не работают в Continuous, поэтому оба мы ставим Past Indefinite’ом.
9. «Yesterday I (to work) at my English from five till seven – Вчера я работал над моим английским с пяти до семи»: «… I was working…» — Past Continuous.
10. «It (to rain) the whole day yesterday – Вчера целый день шел дождь»: «It was raining…».
11. «Where your sister (to be) now? – Где сейчас твоя сестра?»: «Where are your sister now?» — Present Indefinite.
«— She (to be) in her room – Она в своей комнате»: «She is…» — Present Indefinite.
«She (to do) her homework – Она делает свое домашнее задание»: «She is doing…» — Present Continuous.
Помогите пожалуйста с английским, буду очень вам признательна, за ранее огромное спасибо, тем кто не пройдёт мимо….
1. This is a pen. Those ….. books.
a) is b) am c) are d) be
2. I speak English. She ….. Japanese.
a) speaking b) do speak c) speaks d) are speaking
3. I’m sorry, I ….. understand.
a) no b) not c) doesn’t d) don’t
4. “ Where ….. now?”
a) lives he b) is he living c) he is living d) he living
5. Take your coat. It ….. rain.
a)is going to b) will c) is d) has
6. “ Where ….. yesterday?” “ I was at home.”
a) you were b) you was c) you d) were you
7. “ Where ….. yesterday?” “ I didn’t go anywhere.”
a) went you b) did you went c) did you do d) was you go
8. My French is very good. I speak French …..
a) good b) bad c) well d) badly
9. Richard ….. the tickets.
a) already bought b) has already buy c) has already bought d) buy
10. Richard ….. To a girl when I saw him.
a) talk b) talking c) will talk d) was talking
11. The man ….. came yesterday is very rich.
a) he b) who c) has d) when
12. John ….. since he left school.
a) was working b) woks c) has been working d) will be working
13. “ I’m a student.” He told me that ….. A student.
a) I am b) I was c) he was d) he is
14. I’m not as clever as you. You are ….. that I am.
a) clever as b) cleverer as c) clever that d) more clever
15. “ ….. Romeo and Juliet?” “ Yes. I saw it on Wednesday.”
a) Did you seen b) Have you seen c) Will you seen d) do you seen
-
#1
hi there!
Saturday in my realm is a revision time. I’ve just woken up a bit troubled about this haunting question. What is the situation I might pose them? Are they interchangeable? I tried different configurations but I’m not sure if it makes any sense.
1. Where were you yesterday? (when I rang, when I needed you…)
2. Where did you be yesterday? ( ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ??)
cheers
-
#2
The second sentence is not possible in English. The verb to be cannot take a do support in Standard English.
-
#3
I had a sneaking suspicion that it was incorrect… I’ve never seen this form, still to be is a verb like many other.
-
#4
I would actually say the opposite :»to be» is unlike many other verbs; it is quite irregular in many ways. Nat’s comment is one of those ways.
-
#5
There are a set of verbs in English which behave a little bit differently than other verbs.
They consist of auxiliaries, modals, numerous other categories, but as a collective term we can call these raising verbs (As they would be referred to in linguistics).
One of the characteristics of raising verbs is that they don’t take do-support in questions. I won’t go into syntactic theory here but it’s best to imagine that do-support applies to nearly all verbs, but some verbs can ‘raise themselves‘ out of this area, so do-support doesn’t affect these verbs.
You can see this through some examples here:
*Did you can do it?
Could you do it?
*Did he should go?
Should he have gone?
Here question formation is done by inversion, and not do-support.
‘To be‘ always raises itself out of the way where do-support applies, and ‘to have’ does as well (when not used in its normal sense of possession). That’s why do-support isn’t used in:
Have I told you?
Were have you been?
But ‘have’ is a little bit odd in that when it is not grammatical, it behaves in a non-raising fashion:
Did you have a car?
There are also some instances of raising when it is not used grammatically, like in sentences such as «Have you any idea what you’ve done?«, but these are always alternatives to the expected non-raising forms (where do applies), like in «Do you have any idea what you’ve done?«. Anyway ‘have‘ is a bit of a rebel when it comes to being classified grammatically, but the idea is that ‘to be‘, being ‘irregular’ as Julian said, is always raising and this explains why you can’t use it with do in the way you asked.
-
#6
2. Where did you be yesterday? ( ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?
Miraculously, while being totally incorrect and unacceptable, your sentence is totally understandable
5
Correct the errors
Where did you be yesterday?
My brother dont watch horror films.
Whe I was seeing him he played football.
Прошу! ПОМОГИТЕ! Буду очень благодарен 
2 ответа:
0
0
Исправить ошибки
Где вы были вчера? Мой брат не смотрел фильмы ужасов. Я видел, как он играл в футбол.
0
0
Исправить ошибки
Где вы были вчера?
Мой брат не смотрел фильмы ужасов.
Когда я видел его, он играл в футбол.
Читайте также
Sam, Kate: 2
J. Alexander: 3
Maxim: 6
Vera: 5
Dasha: 4
NATIONAL
BUILDINGS
SECOND
MOST REAL
ASSISTANT
FAMOUS
British houses are usually built of brick. Semi-detached houses are usually in the suburbs, which are near the town centre. Terraced houses and blocks of flats are mostly in the town centre. These are often the inner city areas which have the poorest people and the highest crime. Although not always, it depends on whether it is a working class area, or a middle class area. Also the area may have changed over time from an area of rich people to an area of poor people. In such cases (for example, New Cross in London), the big Georgian and Victorian houses have been divided up into lots of flats. Where one large house would have had one family and some servants, it may now have 5-10 families. Most British people love gardens, and this is one reason why so many people prefer to live in houses rather than flats. Actually, about 80% of British people live in houses. About 67% of British people own their houses or flats. The rest are ‘renting’ i.e. living in rented accommodation.
удачи
Hello my name is Pasha. I have got a mother,father,brother and sister. we eat
apple,banana,milk and rice
2) Did Peter play golf yesterday? Yes, he did.
3) Did Peter write a letter yesterday? No, he didn’t.
4) Dod Mr and Mrs Page play golf yesterday. No, they didn’t.
5) Did Mr and Mrs Page wash the car yesterday. Yes, they did.
Грамматика
Choose the right answer.
1. Where ___ yesterday? — I was at home.
a) you were b) you was c) were you d) did you
2. Where ______ yesterday? I didn’t go anywhere.
a) went you b) did you went c) did you go d)was you go
3. Why not go to the National Gallery? I ______ there yesterday.
a)go b) went c)gone d) have gone
4. I _______ to the USA .
a) have never been b) been have never c) have never d) never been
5.73rd
a) seventy-third b) seventy-three c) seventy-threeth d) seventy-thirty
6. Your homework is even worse __ mine!
a) then b) than c) as d) of
7. Your English…. getting better. Try to do more exercises.
a) do b) is not c) is d) are
8 . It…. dark at 8 o’clock in the evening.
a) are b) is c) am d) be
9. Show___ the plan of your article.
a) they b) them c) their d) themselves
10. Was there … lecture on physics yesterday?
a) some b) any c) no d) not any
11. Will you be there ___Sunday?
a) at b) in c) on d) of
12. June is___than May in our region.
a) hot b) the hottest c) hotter d) hottest
13. Who is ___ popular engineer in our country?
a) more b) most c) much d) the most
14. My results in the test are ___of all.
a) good b) better c) best d) the best
15. Do you like him___there?
a) coming b) came c) to come d) come
16. Tea will be ready when you_____ home.
a) gets b) get c) will get d) shall get
17. She will come to tea if you______ her .
a)asks b) ask c) asked d) will ask
18. She didn’t open the door because she _____ a rest.
a)having b) has c) was having d) had
19. My house is at ___.
a) end of street b) end of the street c) the end of the street d) the end of street
20. I saw Lucy and Steve this morning. They ___ at the bus stop.
a) waiting b) waited c) were waiting d) was waiting
21. I ___television yesterday.
a) didn’t watch b) didn’t watched c) don’t watched d) don’t watch
22.When I go abroad I prefer to go _____ plane.
a) in b)by c) with the d) by the
23. Do you want him___there?
a)coming b) came c) to come d) come
Добавить свой ответ
Ответы на вопрос
1) were you
2)did you go
3)went
4)have never been
5)seventy third
6)than
7)is not
8)is
9)them
10)any
1. Where were you (c) yesterday? I was at home.
2. Where did you go (c) yesterday? I didn’t go anywhere.
3. Why not go to the National Gallery? I went (b) there yesterday.
4. I have never been (a) to the USA.
5. 73rd—seventy-third (a) (правда, тут должно быть понятно, так как там rd на конце, но ладно)
6. Your homework is even worse than mine! (главное—не перепутать then & than: then значит потом/тогда, а than для сравнения)
P.S. Извиняюсь, список вопросов не пролистала. Сейчас все будет.
Новые вопросы
bobot
14.04.200913.03.2015
Рубрика Разное Коммент.
Where did you be yesterday?
Where were you yesterday?
Вопросительные предложения в Past Indefinite образуются, по правилу, с помощью глагола to do в прошедшем времени и инфинитива знаменательного глагола (без частицы to). Например: Where did Mary go yesterday?
Но, чувствую копчиком, правильно второе предложение (Where were you yesterday?), а не первое… Помогите, please 
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
BraveRobot нашел еще статьи на эту тему:
- Эволюция нашей планеты: миллиард лет за 40 секунд. И посмотрите на красивые фото природы Земли и ее обитателей!
- Польский язык: мифы и реальность
- Не бойтесь, а просто помогите лежащему стрижу улететь!
- Китаец выложил 25 iPhone X в форме сердца и сделал предложение своей девушке
- Для чего нужны дырки в сыре
- Чтобы мужчина быстрее сделал предложение руки и сердца
- С чего следует начинать интернет-бизнес
- Хочешь быть богатой — будь ей! 5 законов привлечения денег
- Защищаем свои гаджеты пленкой!
- Как работает магнитный парашют: неодимовый магнит и медная труба
Похожее
Многие студенты часто меня спрашивают – как правильно употреблять was, were и did, как правильно сказать I was или I were / they was или they were?
В этой статье вы найдете ответы на эти вопросы, предложения с was, were, did, и познакомитесь с правилом использования was, were и did в английском языке.
Что такое was и were?
Was и were – это формы прошедшего времени глагола to be (быть) – был/были.
В чем же разница?
Разница в том, что was употребляется с единственным числом (с местоимениями I, he, she, it), а were – со множественным (you, we, they):
I was – я был, he was – он был, she was – она была.
- I was there. – Я был там.
- They were happy. – Они были счастливы.
Аналогично was/were используются в вопросах:
- Was she at school? – Она была в школе?
- Were you a student? – Ты был студентом?
И в отрицательных предложениях:
- He wasn’t hungry. – Он не был голоден.
- We weren’t at the beach. – Мы не были на пляже.
В прошедшем простом времени was и were – всегда единственные глаголы в предложении.
Правила употребления DID
Did – это форма прошедшего времени глагола do (делать).
В утвердительной форме он выступает только как основной глагол и имеет одинаковую форму для всех лиц.
- I did exercises. – Я делал упражнения.
- We did sport yesterday. – Мы занимались спортом вчера.
В вопросах и отрицательных предложениях в прошедшем простом времени Past Simple глагол did используется как вспомогательный (то есть он только помогает строить вопрос и отрицание, и на русский язык не переводится). Главным в предложении является основной (смысловой) глагол.
- Did you see her? – Ты видел ее?
- Did he drive the car? – Он вел машину?
- I didn’t go to school yesterday. – Я не ходил в школу вчера.
- They didn’t call last night. – Они не звонили вчера вечером.
Вам может быть интересно:
- Вспомогательные глаголы в английском языке
Что использовать – DID или WAS / WERE?
В утвердительном предложении употребление этих глаголов зависит от смысла.
Did употребляется в значении “делал(а)”:
- I did it yesterday. – Я делал это вчера.
Was и were употребляются в значении “был / были”:
- I was there. – Я был там.
- They were here. – Они были здесь.
В вопросах и отрицаниях мы смотрим на то, есть ли другие глаголы в предложении. Если нет – используется was/were:
- Were you a nurse? – Ты была медсестрой?
- Was she in the office? – Она была в офисе?
Если есть основной глагол, то в вопросе и отрицании используется вспомогательный did:
- Did you read yesterday? – Ты читал вчера? (основной глагол – read)
- I didn’t sleep last night. – Я не спал прошлой ночью. (основной глагол – sleep)
Если вопрос начинается с was/were, то и краткий ответ должен содержать was/were:
- Was she sick yesterday? – Она была больной вчера?
- Yes, she was. – Да.
Если вопрос начинается с did, то и краткий ответ содержит did:
- Did you call me? – Ты звонил мне?
- No, I didn’t. – Нет.
Другие случаи употребления WAS / WERE
Was и were также употребляются в составе Past Continuous (прошедшего длительного времени).
- I was writing at 5 pm yesterday. – Я писал в 5 вечера вчера.
- We were walking when you called. – Мы гуляли, когда ты позвонил.
Past Simple Passive (пассивный залог в простом прошедшем времени)
В пассивном залоге was/were + V3/ V-ed (V3 – глагол в третьей форме) употребляется, когда мы говорим, что что-то было сделано в прошлом.
- The dinner was cooked by my cousin. – Ужин был приготовлен моей кузиной.
- The letters were written by the teacher. – Буквы были написаны учителем.
Was, Were or Did?
Выберите один правильный вариант:
Вам может быть интересно:
- Упражнения на TO BE в прошедшем времени (was/were)
- Упражнения на Past Simple с ответами
- Тест на Past Simple с ответами
- Past Simple или Past Continuous: упражнения с ответами
Помогите пожалуйста с английским, буду очень вам признательна, за ранее огромное спасибо, тем кто не пройдёт мимо….
1. This is a pen. Those ….. books.
a) is b) am c) are d) be
2. I speak English. She ….. Japanese.
a) speaking b) do speak c) speaks d) are speaking
3. I’m sorry, I ….. understand.
a) no b) not c) doesn’t d) don’t
4. “ Where ….. now?”
a) lives he b) is he living c) he is living d) he living
5. Take your coat. It ….. rain.
a)is going to b) will c) is d) has
6. “ Where ….. yesterday?” “ I was at home.”
a) you were b) you was c) you d) were you
7. “ Where ….. yesterday?” “ I didn’t go anywhere.”
a) went you b) did you went c) did you do d) was you go
8. My French is very good. I speak French …..
a) good b) bad c) well d) badly
9. Richard ….. the tickets.
a) already bought b) has already buy c) has already bought d) buy
10. Richard ….. To a girl when I saw him.
a) talk b) talking c) will talk d) was talking
11. The man ….. came yesterday is very rich.
a) he b) who c) has d) when
12. John ….. since he left school.
a) was working b) woks c) has been working d) will be working
13. “ I’m a student.” He told me that ….. A student.
a) I am b) I was c) he was d) he is
14. I’m not as clever as you. You are ….. that I am.
a) clever as b) cleverer as c) clever that d) more clever
15. “ ….. Romeo and Juliet?” “ Yes. I saw it on Wednesday.”
a) Did you seen b) Have you seen c) Will you seen d) do you seen